Early Modern France on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The
 In the mid 15th century, France was significantly smaller than it is today, and numerous border provinces (such as Roussillon, Cerdagne,
In the mid 15th century, France was significantly smaller than it is today, and numerous border provinces (such as Roussillon, Cerdagne, 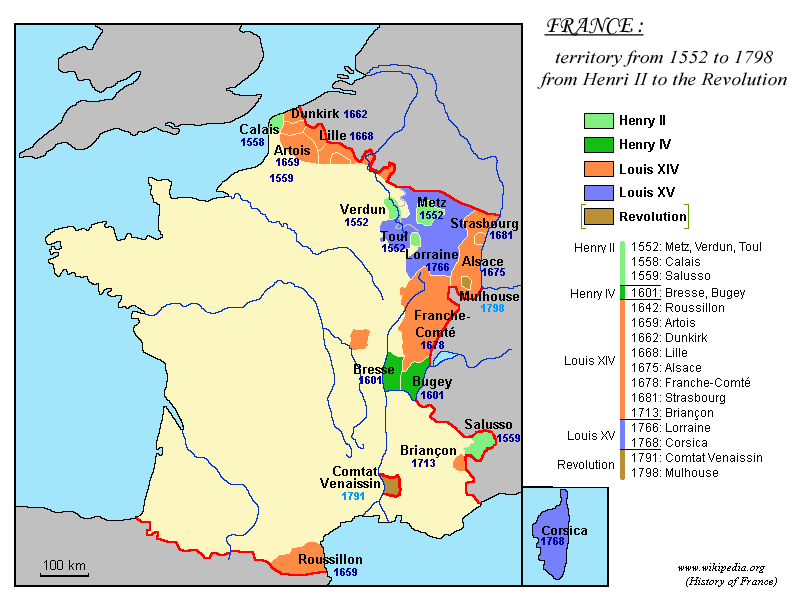 French acquisitions from 1461 to 1789:
* Under Louis XI –
French acquisitions from 1461 to 1789:
* Under Louis XI –

Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from th ...
in the early modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
, from the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
() to the Revolution
In political science, a revolution (, 'a turn around') is a rapid, fundamental transformation of a society's class, state, ethnic or religious structures. According to sociologist Jack Goldstone, all revolutions contain "a common set of elements ...
(1789–1804), was a monarchy ruled by the House of Bourbon
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a dynasty that originated in the Kingdom of France as a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Kingdom of Navarre, Navarre in the 16th century. A br ...
(a Capetian cadet branch). This corresponds to the so-called ''Ancien Régime
''Ancien'' may refer to
* the French word for " ancient, old"
** Société des anciens textes français
* the French for "former, senior"
** Virelai ancien
** Ancien Régime
** Ancien Régime in France
{{disambig ...
'' ("old rule"). The territory of France during this period increased until it included essentially the extent of the modern country, and it also included the territories of the first French colonial empire overseas.
The period is dominated by the figure of the "Sun King", Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
(his reign of 1643–1715 being one of the longest in history), who managed to eliminate the remnants of medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was a combination of legal, economic, military, cultural, and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe from the 9th to 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of struc ...
and established a centralized state under an absolute monarch, a system that would endure until the French Revolution and beyond.
Geography
Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a French port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Calais is the largest city in Pas-de-Calais. The population of the city proper is 67,544; that of the urban area is 144,6 ...
, Béarn, Navarre, County of Foix, Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
, Artois, Lorraine, Alsace
Alsace (, ; ) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in the Grand Est administrative region of northeastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine, next to Germany and Switzerland. In January 2021, it had a population of 1,9 ...
, Trois-Évêchés, Franche-Comté, Savoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
, Bresse, Bugey, Gex, Nice
Nice ( ; ) is a city in and the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative city limits, with a population of nearly one millionProvence
Provence is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which stretches from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the France–Italy border, Italian border to the east; it is bordered by the Mediterrane ...
, Corsica and Brittany
Brittany ( ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the north-west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica in Roman Gaul. It became an Kingdom of Brittany, independent kingdom and then a Duch ...
) were autonomous or foreign-held (as by the Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from the late 9th century, when it was unified from various Heptarchy, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to f ...
); there were also foreign enclaves, like the Comtat Venaissin
The (; ; 'County of Venaissin'), often called the for short, was a part of the Papal States from 1274 to 1791, in what is now the region of Southern France.
The region was an enclave within the Kingdom of France, comprising the area aroun ...
. In addition, certain provinces within France were ostensibly personal fiefdoms of noble families (like the Bourbonnais
The Bourbonnais (; Occitan language, Occitan: ''Borbonés'') was a Provinces of France, historic province in the centre of France that corresponds to the modern ''département in France, département'' of Allier, along with part of the ''dépar ...
, Marche
Marche ( ; ), in English sometimes referred to as the Marches ( ) from the Italian name of the region (Le Marche), is one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. The region is located in the Central Italy, central area of the country, ...
, Forez
Forez (; ) is a Provinces of France, former province of France, corresponding approximately to the central part of the modern Loire (department), Loire ''département in France, département'' and a part of the Haute-Loire and Puy-de-Dôme ''dépa ...
and Auvergne provinces held by the House of Bourbon
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a dynasty that originated in the Kingdom of France as a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Kingdom of Navarre, Navarre in the 16th century. A br ...
until the provinces were forcibly integrated into the royal domaine in 1527 after the fall of Charles III, Duke of Bourbon).
The late 15th, 16th and 17th centuries would see France undergo a massive territorial expansion and an attempt to better integrate its provinces into an administrative whole. During this period, France expanded to nearly its modern territorial extent through the acquisition of Picardy
Picardy (; Picard language, Picard and , , ) is a historical and cultural territory and a former regions of France, administrative region located in northern France. The first mentions of this province date back to the Middle Ages: it gained it ...
, Burgundy
Burgundy ( ; ; Burgundian: ''Bregogne'') is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. ...
, Anjou, Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
, Provence
Provence is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which stretches from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the France–Italy border, Italian border to the east; it is bordered by the Mediterrane ...
, Brittany
Brittany ( ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the north-west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica in Roman Gaul. It became an Kingdom of Brittany, independent kingdom and then a Duch ...
, Franche-Comté, French Flanders, Navarre, Roussillon, the Duchy of Lorraine
The Duchy of Lorraine was a principality of the Holy Roman Empire which existed from the 10th century until 1766 when it was annexed by the kingdom of France. It gave its name to the larger present-day region of Lorraine in northeastern France ...
, Alsace
Alsace (, ; ) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in the Grand Est administrative region of northeastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine, next to Germany and Switzerland. In January 2021, it had a population of 1,9 ...
and Corsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
.
 French acquisitions from 1461 to 1789:
* Under Louis XI –
French acquisitions from 1461 to 1789:
* Under Louis XI – Provence
Provence is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which stretches from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the France–Italy border, Italian border to the east; it is bordered by the Mediterrane ...
(1482), Dauphiné
The Dauphiné ( , , ; or ; or ), formerly known in English as Dauphiny, is a former province in southeastern France, whose area roughly corresponded to that of the present departments of Isère, Drôme and Hautes-Alpes. The Dauphiné was ...
(1461, under French control since 1349)
* Under Henry II – Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a French port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Calais is the largest city in Pas-de-Calais. The population of the city proper is 67,544; that of the urban area is 144,6 ...
, Trois-Évêchés (1552)
* Under Henry IV – County of Foix (1607)
* Under Louis XIII – Béarn and Navarre (1620, under French control since 1589 as part of Henry IV's possessions)
* Under Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
** Treaty of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two Peace treaty, peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy R ...
(1648) – Alsace
Alsace (, ; ) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in the Grand Est administrative region of northeastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine, next to Germany and Switzerland. In January 2021, it had a population of 1,9 ...
** Treaty of the Pyrenees (1659) – Artois, Northern Catalonia
Northern Catalonia, North Catalonia or French Catalonia is the Catalan language, Catalan-speaking and cultural territory ceded to France by Spain through the signing of the Treaty of the Pyrenees in 1659 in exchange for France's effective renu ...
( Roussillon, Cerdagne)
** Treaty of Nijmegen (1678–79) – Franche-Comté, Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
* Under Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached maturity (then defi ...
– Lorraine (1766), Corsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
(1768)
Only the Duchy of Savoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
, the city of Nice
Nice ( ; ) is a city in and the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative city limits, with a population of nearly one millionAvignon
Avignon (, , ; or , ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Vaucluse department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of southeastern France. Located on the left bank of the river Rhône, the Communes of France, commune had a ...
) and foreign possessions would be acquired later. (For a map of historic French provinces, see Provinces of France
Under the Ancien Régime, the Kingdom of France was subdivided in multiple different ways (judicial, military, ecclesiastical, etc.) into several administrative units, until the National Constituent Assembly adopted a more uniform division into ...
). France also embarked on exploration, colonisation, and mercantile exchanges with the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
(New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
, Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
, Martinique
Martinique ( ; or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the eastern Caribbean Sea. It was previously known as Iguanacaera which translates to iguana island in Carib language, Kariʼn ...
, Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre Island, Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Guadeloupe, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galant ...
, Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican ...
, French Guiana
French Guiana, or Guyane in French, is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France located on the northern coast of South America in the Guianas and the West Indies. Bordered by Suriname to the west ...
), India (Pondicherry
Pondicherry, officially known as Puducherry, is the Capital city, capital and most populous city of the Puducherry (union territory), Union Territory of Puducherry in India. The city is in the Puducherry district on the southeast coast of Indi ...
), the Indian Ocean (Réunion
Réunion (; ; ; known as before 1848) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France. Part of the Mascarene Islands, it is located approximately east of the isl ...
), the Far East, and a few African trading posts.
Although Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
was the capital of France, the later Valois kings largely abandoned the city as their primary residence, preferring instead various châteaux of the Loire Valley and Parisian countryside. Henry IV made Paris his primary residence (promoting a major building boom in private mansions), but Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
once again withdrew from the city in the last decades of his reign and Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; ) is a former royal residence commissioned by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, in the Yvelines, Yvelines Department of Île-de-France, Île-de-France region in Franc ...
became the primary seat of the French monarchy for much of the following century.
The administrative and legal system in France in this period is generally called the Ancien Régime
''Ancien'' may refer to
* the French word for " ancient, old"
** Société des anciens textes français
* the French for "former, senior"
** Virelai ancien
** Ancien Régime
** Ancien Régime in France
{{disambig ...
.
Demography
TheBlack Death
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the list of epidemics, most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. ...
had killed an estimated one-third of the population of France from its appearance in 1348. The concurrent Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy ...
slowed recovery. It would be the early 16th century before the population recovered to mid-14th-century levels.
With an estimated population of 11 million in 1400, 20 million in the 17th century, and 28 million in 1789, until 1795 France was the most populated country in Europe (even twice the size of Britain or the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands ...
) and the third most populous country in the world, behind only China and India.
These demographic changes also led to a massive increase in urban populations, although on the whole France remained a profoundly rural country. Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
was one of the most populated cities in Europe (estimated at 400,000 inhabitants in 1550; 650,000 at the end of the 18th century). Other major French cities include Lyon
Lyon (Franco-Provençal: ''Liyon'') is a city in France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of the French Alps, southeast of Paris, north of Marseille, southwest of Geneva, Switzerland, north ...
, Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine, in northwestern France. It is in the prefecture of Regions of France, region of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the Departments of France, department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one ...
, Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( ; ; Gascon language, Gascon ; ) is a city on the river Garonne in the Gironde Departments of France, department, southwestern France. A port city, it is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the Prefectures in F ...
, Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
, and Marseille
Marseille (; ; see #Name, below) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Departments of France, department of Bouches-du-Rhône and of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region. Situated in the ...
.
These centuries saw several periods of epidemics and crop failures due to wars and climatic change. (Historians speak of the period 1550–1850 as the " Little Ice Age".) Between 1693 and 1694, France lost 6% of its population. In the extremely harsh winter of 1709, France lost 3.5% of its population. In the past 300 years, no period has been so proportionally deadly for the French, both World Wars included.
Language
Linguistically, the differences in France were extreme. Before the Renaissance, the language spoken in the north of France was a collection of different dialects called Oïl languages whereas the written and administrative language remainedLatin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
. By the 16th century, there had developed a standardised form of French (called Middle French
Middle French () is a historical division of the French language that covers the period from the mid-14th to the early 17th centuries. It is a period of transition during which:
* the French language became clearly distinguished from the other co ...
) which would be the basis of the standardised "modern" French of the 17th and 18th century which in turn became the lingua franca of the European continent. (In 1539, with the Ordinance of Villers-Cotterêts, Francis I of France
Francis I (; ; 12 September 1494 – 31 March 1547) was King of France from 1515 until his death in 1547. He was the son of Charles, Count of Angoulême, and Louise of Savoy. He succeeded his first cousin once removed and father-in-law Louis&nbs ...
made French alone the language for legal and juridical acts.) Nevertheless, in 1790, only half of the population spoke or understood standard French.
The southern half of the country continued to speak Occitan language
Occitan (; ), also known by its native speakers as (; ), sometimes also referred to as Provençal, is a Romance language spoken in Southern France, Monaco, Italy's Occitan Valleys, as well as Spain's Val d'Aran in Catalonia; collectively, ...
s (such as Provençal), and other inhabitants spoke Breton, Catalan, Basque
Basque may refer to:
* Basques, an ethnic group of Spain and France
* Basque language, their language
Places
* Basque Country (greater region), the homeland of the Basque people with parts in both Spain and France
* Basque Country (autonomous co ...
, Dutch ( West Flemish), and Franco-Provençal
Franco-Provençal (also Francoprovençal, Patois or Arpitan) is a Gallo-Romance languages, Gallo-Romance language that originated and is spoken in eastern France, western Switzerland, and northwestern Italy.
Franco-Provençal has several di ...
. In the north of France, regional dialects of the various langues d'oïl
The ''langues d'oïl'' are a dialect continuum that includes standard French and its closest relatives historically spoken in the northern half of France, southern Belgium, and the Channel Islands. They belong to the larger category of Gallo- ...
continued to be spoken in rural communities. During the French revolution, the teaching of French was promoted in all the schools. The French used would be that of the legal system, which differed from the French spoken in the courts of France before the revolution. Like the orators during the French revolution, the pronunciation of every syllable would become the new language.
France would not become a linguistically unified country until the end of the 19th century.
Administrative structures
The Ancien Régime, the French term rendered in English as "Old Rule", "Old Kingdom", or simply "Old Regime", refers primarily to the aristocratic,social
Social organisms, including human(s), live collectively in interacting populations. This interaction is considered social whether they are aware of it or not, and whether the exchange is voluntary or not.
Etymology
The word "social" derives fro ...
and political
Politics () is the set of activities that are associated with decision-making, making decisions in social group, groups, or other forms of power (social and political), power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of Social sta ...
system established in France from (roughly) the 15th century to the 18th century under the late Valois and Bourbon dynasties. The administrative and social structures of the Ancien Régime were the result of years of state-building, legislative acts (like the Ordinance of Villers-Cotterêts), internal conflicts and civil wars, but they remained a confusing patchwork of local privilege and historic differences until the French Revolution took place in a radical time suppression of administrative incoherence.
Economy
Culture
Political history
Background
The Peace of Etaples (1492) marks, for some, the beginning of the early modern period in France. After theHundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy ...
(1337–1453), France supported the Lancastrian side in The Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses, known at the time and in following centuries as the Civil Wars, were a series of armed confrontations, machinations, battles and campaigns fought over control of the English throne from 1455 to 1487. The conflict was f ...
. France and England signed the Treaty of Picquigny in 1475 — the official end date of the Hundred Years' War. In 1492 and 1493, after supporting the victorious House of Tudor in the Battle of Bosworth Field
The Battle of Bosworth or Bosworth Field ( ) was the last significant battle of the Wars of the Roses, the civil war between the houses of House of Lancaster, Lancaster and House of York, York that extended across England in the latter half ...
, Charles VIII of France signed three additional treaties with Henry VII of England
Henry VII (28 January 1457 – 21 April 1509), also known as Henry Tudor, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from his seizure of the crown on 22 August 1485 until his death in 1509. He was the first monarch of the House of Tudor.
Henr ...
, Maximilian I of Habsburg, and Ferdinand II of Aragon
Ferdinand II, also known as Ferdinand I, Ferdinand III, and Ferdinand V (10 March 1452 – 23 January 1516), called Ferdinand the Catholic, was King of Aragon from 1479 until his death in 1516. As the husband and co-ruler of Queen Isabella I of ...
respectively at Étaples (1492), Senlis (1493) and in Barcelona
Barcelona ( ; ; ) is a city on the northeastern coast of Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second-most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
(1493). As the 15th century drew to a close, French kings could take confidence in the fact that England had been mostly driven from their territory and so they could now embark on an expansionist foreign policy. The invasion of Italy by Charles VIII in 1494 began 62 years of war with the Habsburgs (the Italian Wars
The Italian Wars were a series of conflicts fought between 1494 and 1559, mostly in the Italian Peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and Mediterranean Sea. The primary belligerents were the House of Valois, Valois kings o ...
).
Foreign relations
Wars
Despite the beginnings of rapid demographic and economic recovery after theBlack Death
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the list of epidemics, most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. ...
of the 14th century, the gains of the previous half-century were to be jeopardised by a further protracted series of conflicts, the Italian Wars
The Italian Wars were a series of conflicts fought between 1494 and 1559, mostly in the Italian Peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and Mediterranean Sea. The primary belligerents were the House of Valois, Valois kings o ...
(1494–1559), where French efforts to gain dominance ended in the increased power of the Habsburg Holy Roman Emperors of Germany.
In 1445, the first steps were made towards fashioning a regular army out of the poorly disciplined mercenary bands that French kings traditionally relied on. The medieval division of society into "those who fought (nobility), those who prayed (clergy), and those who worked (everyone else)" still held strong and warfare was considered a domain of the nobles. Charles VIII marched into Italy with a core force consisting of noble horsemen and non-noble foot soldiers, but in time the role of the latter grew stronger so that by the middle of the 16th century, France had a standing army of 5000 cavalry and 30,000 infantry. The military was reorganized from a system of legions recruited by province (Norman legion, Gascon legion, etc.) to regiments, an arrangement which persisted into the next century. However, the nobility and troops were often disloyal to the king, if not outright rebellious, and it took another army reform by Louis XIV to finally transform the French army into an obedient force.

Ludovico Sforza
Ludovico Maria Sforza (; 27 July 1452 – 27 May 1508), also known as Ludovico il Moro (; 'the Moor'), and called the "arbiter of Italy" by historian Francesco Guicciardini,
, the Duke of Milan, seeking an ally against the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
, encouraged Charles VIII of France to invade Italy, using the Angevin claim to the throne of Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
, then under Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and ; ) is an autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces of Spain, ...
ese control, as a pretext. When Ferdinand I of Naples died in 1494, Charles invaded the peninsula. For several months, French forces moved through Italy virtually unopposed, since the '' condottieri'' armies of the Italian city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world throughout history, including cities such as Rome, ...
s were unable to resist them. Their sack of Naples finally provoked a reaction, however, and the League of Venice was formed against them. Italian troops defeated the French at the Battle of Fornovo, forcing Charles to withdraw to France. Ludovico, having betrayed the French at Fornovo, retained his throne until 1499, when Charles's successor, Louis XII of France, invaded Lombardy
The Lombardy Region (; ) is an administrative regions of Italy, region of Italy that covers ; it is located in northern Italy and has a population of about 10 million people, constituting more than one-sixth of Italy's population. Lombardy is ...
and seized Milan
Milan ( , , ; ) is a city in northern Italy, regional capital of Lombardy, the largest city in Italy by urban area and the List of cities in Italy, second-most-populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of nea ...
.
In 1500, Louis XII, having reached an agreement with Ferdinand II of Aragon
Ferdinand II, also known as Ferdinand I, Ferdinand III, and Ferdinand V (10 March 1452 – 23 January 1516), called Ferdinand the Catholic, was King of Aragon from 1479 until his death in 1516. As the husband and co-ruler of Queen Isabella I of ...
to divide Naples, marched south from Milan. By 1502, combined French and Aragonese forces had seized control of the Kingdom; disagreements about the terms of the partition led to a war between Louis and Ferdinand. By 1503, Louis, having been defeated at the Battle of Cerignola and Battle of Garigliano, was forced to withdraw from Naples, which was left under the control of the Spanish viceroy, Ramón de Cardona. French forces under Gaston de Foix inflicted an overwhelming defeat on a Spanish army at the Battle of Ravenna in 1512, but Foix was killed during the battle, and the French were forced to withdraw from Italy by an invasion of Milan by the Swiss, who reinstated Maximilian Sforza to the ducal throne. The Holy League, left victorious, fell apart over the subject of dividing the spoils, and in 1513 Venice allied with France, agreeing to partition Lombardy between them.
Louis mounted another invasion of Milan, but was defeated at the Battle of Novara, which was quickly followed by a series of Holy League victories at La Motta, Guinegate, and Flodden, in which the French, Venetian, and Scottish forces were decisively defeated. However, the death of Pope Julius left the League without effective leadership, and when Louis' successor, Francis I, defeated the Swiss at Marignano in 1515, the League collapsed, and by the treaties of Noyon and Brussels, surrendered to France and Venice the entirety of northern Italy.
The elevation of Charles of Spain to Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans (disambiguation), Emperor of the Romans (; ) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period (; ), was the ruler and h ...
, a position that Francis had desired, led to a collapse of relations between France and the Habsburgs. In 1519, a Spanish invasion of Navarre, nominally a French fief, provided Francis with a pretext for starting a general war; French forces flooded into Italy and began a campaign to drive Charles from Naples. The French were outmatched, however, by the fully developed Spanish tercio tactics, and suffered a series of crippling defeats at Bicocca and Sesia against Spanish troops under Fernando d'Avalos. With Milan itself threatened, Francis personally led a French army into Lombardy in 1525, only to be defeated and captured at the Battle of Pavia
The Battle of Pavia, fought on the morning of 24 February 1525, was the decisive engagement of the Italian War of 1521–1526 between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg Empire of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V, Holy Roman Empero ...
; imprisoned in Madrid
Madrid ( ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in Spain, most populous municipality of Spain. It has almost 3.5 million inhabitants and a Madrid metropolitan area, metropolitan area population of approximately 7 million. It i ...
, Francis was forced to agree to extensive concessions over his Italian territories in the "Treaty of Madrid" (1526).
The inconclusive third war between Charles and Francis began with the death of Francesco II Sforza, the duke of Milan
Milan ( , , ; ) is a city in northern Italy, regional capital of Lombardy, the largest city in Italy by urban area and the List of cities in Italy, second-most-populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of nea ...
. When Charles' son Philip
Philip, also Phillip, is a male name derived from the Macedonian Old Koine language, Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominen ...
inherited the duchy, Francis invaded Italy, capturing Turin
Turin ( , ; ; , then ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital from 1861 to 1865. The city is main ...
, but failed to take Milan. In response, Charles invaded Provence
Provence is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which stretches from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the France–Italy border, Italian border to the east; it is bordered by the Mediterrane ...
, advancing to Aix-en-Provence
Aix-en-Provence, or simply Aix, is a List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, city and Communes of France, commune in southern France, about north of Marseille. A former capital of Provence, it is the Subprefectures in France, s ...
, but withdrew to Spain rather than attacking the heavily fortified Avignon
Avignon (, , ; or , ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Vaucluse department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of southeastern France. Located on the left bank of the river Rhône, the Communes of France, commune had a ...
. The Truce of Nice ended the war, leaving Turin in French hands but effecting no significant change in the map of Italy. Francis, allying himself with Suleiman I of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, launched a final invasion of Italy. A Franco-Ottoman fleet captured the city of Nice
Nice ( ; ) is a city in and the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative city limits, with a population of nearly one millionBattle of Ceresole in 1544, but the French failed to penetrate further into Lombardy. Charles and
 France's pacification under Henry IV laid much of the ground for the beginnings of France's rise to European hegemony. One of the most admired French kings, Henry was fatally stabbed by a Catholic fanatic in 1610 as war with Spain threatened. Troubles gradually developed during the regency headed by his queen Marie de Medici. France was expansive during all but the end of the 17th century: the French began trading in
France's pacification under Henry IV laid much of the ground for the beginnings of France's rise to European hegemony. One of the most admired French kings, Henry was fatally stabbed by a Catholic fanatic in 1610 as war with Spain threatened. Troubles gradually developed during the regency headed by his queen Marie de Medici. France was expansive during all but the end of the 17th century: the French began trading in  French culture was part of French hegemony. In the early part of the century French painters had to go to Rome to shed their provinciality (
French culture was part of French hegemony. In the early part of the century French painters had to go to Rome to shed their provinciality (
 Valois (1328–1498)
* Louis XI
* Charles VIII
''After Charles VIII the Affable, the last king in the direct Valois line, three other branches of the House of Capet reigned in France until the fall of the
Valois (1328–1498)
* Louis XI
* Charles VIII
''After Charles VIII the Affable, the last king in the direct Valois line, three other branches of the House of Capet reigned in France until the fall of the
French Pamphlet collection
documents significant events and periods in French history throughout the 17th–20th centuries, at the University of Maryland Libraries {{DEFAULTSORT:Early Modern France States and territories established in 1492
Henry VIII of England
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
then proceeded to invade northern France, seizing Boulogne and Soissons. A lack of cooperation between the Spanish and English armies, coupled with increasingly aggressive Ottoman attacks, led Charles to abandon these conquests, restoring the status quo once again.
In 1547, Henry II of France, who had succeeded Francis to the throne, declared war against Charles with the intent of recapturing Italy and ensuring French, rather than Habsburg, domination of European affairs. An early offensive against Lorraine was successful, but the attempted French invasion of Tuscany
Tuscany ( ; ) is a Regions of Italy, region in central Italy with an area of about and a population of 3,660,834 inhabitants as of 2025. The capital city is Florence.
Tuscany is known for its landscapes, history, artistic legacy, and its in ...
in 1553 was defeated at the Battle of Marciano. Charles's abdication in 1556 split the Habsburg empire between Philip II of Spain
Philip II (21 May 152713 September 1598), sometimes known in Spain as Philip the Prudent (), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from 1580, and King of Naples and List of Sicilian monarchs, Sicily from 1554 until his death in 1598. He ...
and Ferdinand I, and shifted the focus of the war to Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
, where Philip, in conjunction with Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy, defeated the French at St. Quentin. England's entry into the war later that year led to the French capture of Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a French port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Calais is the largest city in Pas-de-Calais. The population of the city proper is 67,544; that of the urban area is 144,6 ...
, England's last possession on the French mainland, and French armies plundered Spanish possessions in the Low Countries
The Low Countries (; ), historically also known as the Netherlands (), is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower Drainage basin, basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting today of the three modern "Bene ...
; but Henry was nonetheless forced to accept the Peace of Cateau-Cambrésis, in which he renounced any further claims to Italy.
The Wars of Religion
Barely were the Italian Wars over, when France was plunged into a domestic crisis with far-reaching consequences. Despite the conclusion of a Concordat between France and the Papacy (1516), granting the crown unrivalled power in senior ecclesiastical appointments, France was deeply affected by theProtestant Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the papacy and ...
's attempt to break the unity of Roman Catholic Europe. A growing urban-based Protestant minority (later dubbed ''Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
'') faced ever harsher repression under the rule of Francis I's son King Henry II. After Henry II's unfortunate death in a joust, the country was ruled by his widow Catherine de' Medici
Catherine de' Medici (, ; , ; 13 April 1519 – 5 January 1589) was an Italian Republic of Florence, Florentine noblewoman of the Medici family and Queen of France from 1547 to 1559 by marriage to Henry II of France, King Henry II. Sh ...
and her sons Francis II, Charles IX and Henry III. Renewed Catholic reaction headed by the powerful dukes of Guise culminated in a massacre of Huguenots (1562), starting the first of the French Wars of Religion
The French Wars of Religion were a series of civil wars between French Catholic Church, Catholics and Protestantism, Protestants (called Huguenots) from 1562 to 1598. Between two and four million people died from violence, famine or disease di ...
, during which English, German, and Spanish forces intervened on the side of rival Protestant and Catholic forces. Opposed to absolute monarchy, the Huguenots Monarchomachs theorized during this time the right of rebellion and the legitimacy of tyrannicide
Tyrannicide is the killing or assassination of a tyrant or unjust ruler, purportedly for the common good, and usually by one of the tyrant's subjects. Tyrannicide was legally permitted and encouraged in Classical Athens. Often, the term "tyrant ...
.
The Wars of Religion culminated in the War of the Three Henrys in which Henry III assassinated Henry de Guise, leader of the Spanish-backed Catholic league, and the king was murdered in return. After the assassination of both Henry of Guise (1588) and Henry III (1589), the conflict was ended by the accession of the Protestant king of Navarre as Henry IV (first king of the Bourbon dynasty) and his subsequent abandonment of Protestantism (Expedient of 1592) effective in 1593, his acceptance by most of the Catholic establishment (1594) and by the Pope (1595), and his issue of the toleration decree known as the Edict of Nantes
The Edict of Nantes () was an edict signed in April 1598 by Henry IV of France, King Henry IV and granted the minority Calvinism, Calvinist Protestants of France, also known as Huguenots, substantial rights in the nation, which was predominantl ...
(1598), which guaranteed freedom of private worship and civil equality.
France in the 17th and 18th centuries
 France's pacification under Henry IV laid much of the ground for the beginnings of France's rise to European hegemony. One of the most admired French kings, Henry was fatally stabbed by a Catholic fanatic in 1610 as war with Spain threatened. Troubles gradually developed during the regency headed by his queen Marie de Medici. France was expansive during all but the end of the 17th century: the French began trading in
France's pacification under Henry IV laid much of the ground for the beginnings of France's rise to European hegemony. One of the most admired French kings, Henry was fatally stabbed by a Catholic fanatic in 1610 as war with Spain threatened. Troubles gradually developed during the regency headed by his queen Marie de Medici. France was expansive during all but the end of the 17th century: the French began trading in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
and Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
, founded Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
and penetrated the North American Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
and Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
, established plantation economies in the West Indies
The West Indies is an island subregion of the Americas, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island country, island countries and 19 dependent territory, dependencies in thr ...
and extended their trade contacts in the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
and enlarged their merchant marine.
Henry IV's son Louis XIII and his minister (1624–1642) Cardinal Richelieu
Armand Jean du Plessis, 1st Duke of Richelieu (9 September 1585 – 4 December 1642), commonly known as Cardinal Richelieu, was a Catholic Church in France, French Catholic prelate and statesman who had an outsized influence in civil and religi ...
, elaborated a policy against Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
and the German emperor during the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
(1618–1648) which had broken out among the lands of Germany's Holy Roman Empire. An English-backed Huguenot rebellion (1625–1628) defeated, France intervened directly (1635) in the wider European conflict following her ally (Protestant) Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
's failure to build upon initial success.
After the death of both king and cardinal, the Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy Roman Empire ...
(1648) secured universal acceptance of Germany's political and religious fragmentation, but the Regency of Anne of Austria
Anne of Austria (; ; born Ana María Mauricia; 22 September 1601 – 20 January 1666) was Queen of France from 1615 to 1643 by marriage to King Louis XIII. She was also Queen of Navarre until the kingdom's annexation into the French crown ...
and her minister Cardinal Mazarin experienced a civil uprising known as the Fronde (1648–1653) which expanded into a Franco-Spanish War (1653–1659). The Treaty of the Pyrenees (1659) formalised France's seizure (1642) of the Spanish territory of Roussillon after the crushing of the ephemeral Catalan Republic and ushered a short period of peace.
For most of the reign of Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
(1643–1715), France was the dominant power in Europe, aided by the diplomacy of Richelieu's successor (1642–1661) Cardinal Mazarin and the economic policies (1661–1683) of Colbert. Colbert's attempts to promote economic growth and the creation of new industries were not a great success, and France did not undergo any sort of industrial revolution during Louis XIV's reign. Indeed, much of the French countryside during this period remained poor and overpopulated. The resistance of peasants to adopt the potato, according to some monarchist apologists, and other new agricultural innovations while continuing to rely on cereal crops led to repeated catastrophic famines long after they had ceased in the rest of Western Europe. Prior to Louis XIV's reign, French soldiers frequently went into battle barefoot and with no weapons. On the other hand, France's high birthrate until the 18th century proved beneficial to its rulers since it meant the country could field larger armies than its neighbors. In fact, the king's foreign policy, as well as his lavish court and construction projects, left the country in enormous debt. The Palace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; ) is a former royal residence commissioned by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, in the Yvelines, Yvelines Department of Île-de-France, Île-de-France region in Franc ...
was criticized as overly extravagant even while it was still under construction, but dozens of imitations were built across Europe. Renewed war (the War of Devolution
The War of Devolution took place from May 1667 to May 1668. In the course of the war, Kingdom of France, France occupied large parts of the Spanish Netherlands and County of Burgundy, Franche-Comté, both then provinces of the Holy Roman Empire ...
1667–1668 and the Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, 1672 to 1678, was primarily fought by Kingdom of France, France and the Dutch Republic, with both sides backed at different times by a variety of allies. Related conflicts include the 1672 to 1674 Third Anglo-Dutch War and ...
1672–1678) brought further territorial gains ( Artois and western Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
and the free county of Burgundy, left to the Empire in 1482), but at the cost of the increasingly concerted opposition of rival powers.
 French culture was part of French hegemony. In the early part of the century French painters had to go to Rome to shed their provinciality (
French culture was part of French hegemony. In the early part of the century French painters had to go to Rome to shed their provinciality (Nicolas Poussin
Nicolas Poussin (, , ; June 1594 – 19 November 1665) was a French painter who was a leading painter of the classical French Baroque style, although he spent most of his working life in Rome. Most of his works were on religious and mythologic ...
, Claude Lorrain), but Simon Vouet brought home the taste for a classicized baroque that would characterise the French Baroque, epitomised in the Académie de peinture et de sculpture, in the painting of Charles Le Brun
Charles Le Brun (; baptised 24 February 1619 – 12 February 1690) was a French Painting, painter, Physiognomy, physiognomist, Aesthetics, art theorist, and a director of several art schools of his time. He served as a court painter to Louis XIV, ...
and the sculpture of François Girardon. With the Palais du Luxembourg, the Château de Maisons
The Château de Maisons (now Château de Maisons-Laffitte ), designed by François Mansart from 1630 to 1651, is a prime example of French Baroque architecture and a reference point in the history of French architecture. The château is located in ...
and Vaux-le-Vicomte
The Château de Vaux-le-Vicomte () or simply Vaux-le-Vicomte is a Baroque French château located in Maincy, near Melun, southeast of Paris in the Seine-et-Marne Departments of France, department of Île-de-France.
Built between 1658 and 1661 ...
, French classical architecture was admired abroad even before the creation of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; ) is a former royal residence commissioned by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, in the Yvelines, Yvelines Department of Île-de-France, Île-de-France region in Franc ...
or Perrault's Louvre colonnade. Parisian salon culture set standards of discriminating taste from the 1630s, and with Pascal, Descartes, Bayle, Corneille, Racine and Molière
Jean-Baptiste Poquelin (; 15 January 1622 (baptised) – 17 February 1673), known by his stage name Molière (, ; ), was a French playwright, actor, and poet, widely regarded as one of the great writers in the French language and world liter ...
, France became the cultural center of Europe. In an effort to prevent the nobility from revolting and challenging his authority, Louis implemented an extremely elaborate system of court etiquette with the idea that learning it would occupy most of the nobles' time and they could not plan rebellion. By the start of the 18th century, the nobility in France had been effectively neutered and would never again have more power than the crown. Also, Louis willingly granted titles of nobility to those who had performed distinguished service to the state so that it did not become a closed caste and it was possible for commoners to rise through the social ranks. The king sought to impose total religious uniformity on the country, repealing the Edict of Nantes in 1685. The infamous practice of dragonnades
The ''Dragonnades'' was a policy implemented by Louis XIV in 1681 to force French Protestants known as Huguenots to convert to Catholicism. It involved the billeting of dragoons of the French Royal Army in Huguenot households, with the so ...
was adopted, whereby rough soldiers were quartered in the homes of Protestant families and allowed to have their way with them. Scores of Protestants fled France, costing the country a great many intellectuals, artisans, and other valuable people. Persecution extended to unorthodox Catholics like the Jansenists, a group that denied free will and had already been condemned by the popes. Louis was no theologian and understood little of the complex doctrines of Jansenism, satisfying himself with the fact that they threatened the unity of the state. In this, he garnered the friendship of the papacy, which had previously been hostile to France because of its policy of putting all church property in the country under the jurisdiction of the state rather than of Rome.
Cardinal Mazarin oversaw the creation of a French navy that rivaled England's, expanding it from 25 ships to almost 200. The size of the army was also considerably increased.
Starting in the 1670s, Louis XIV established the so-called Chambers of Reunion, courts in which judges would determine whether certain Habsburg territories belonged rightfully to France. The king was relying on the somewhat vague wording in the Treaty of Westphalia, while also dredging up older French claims, some dating back to medieval times. Through this, he concluded that the strategically important imperial city of Strassburg
Strasbourg ( , ; ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est Regions of France, region of Geography of France, eastern France, in the historic region of Alsace. It is the prefecture of the Bas-Rhin Departmen ...
should have gone to France in 1648. In September 1681, French troops occupied the city, which was at once strongly fortified. As the imperial armies were then busy fighting the Ottoman Empire, they could not do anything about this for a number of years. The basic aim of Louis' foreign policy was to give France more easily defensible borders, and to eliminate weak spots (Strassburg had often been used by the Habsburgs as a gateway into France).
Following the Whig establishment on the English and Scottish thrones by the Dutch prince William of Orange in 1688, the anti-French " Grand Alliance" of 1689 was established. With the Turks now in retreat, the emperor Leopold could turn his attention to France. The ensuing War of the Grand Alliance lasted from 1688 to 1697. France's resources were stretched to the breaking point by the cost of fielding an army of over 300,000 men and two naval squadrons. Famine in 1692–1693 killed up to two million people. The exhaustion of the powers brought the fighting to an end in 1697, by which time the French were in control of the Spanish Netherlands and Catalonia. However, Louis gave back his conquests and gained only Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican ...
. The French people, feeling that their sacrifices in the war had been for nothing, never forgave him.
The Battle of La Hougue (1692) was the decisive naval battle in the war and confirmed the durable dominance of the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
of England.
In November 1700, the severely ill Spanish king Charles II died, ending the Habsburg line in that country. Louis had long waited for this moment, and now planned to put a Bourbon relative, Philip, Duke of Anjou, on the throne. Essentially, Spain was to become an obedient satellite of France, ruled by a king who would carry out orders from Versailles. Realizing how this would upset the balance of power, the other European rulers were outraged. However, most of the alternatives were equally undesirable. For example, putting another Habsburg on the throne would end up recreating the empire of Charles V, which would also grossly upset the power balance. After nine years of exhausting war, the last thing Louis wanted was another conflict. However, the rest of Europe would not stand for his ambitions in Spain, and so the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish E ...
began, a mere three years after the War of the Grand Alliance.
The disasters of the war (accompanied by another famine) were so great that France was on the verge of collapse by 1709. In desperation, the king appealed to the French people to save their country, and in doing so gained thousands of new army recruits. Afterwards, his general Marshal Villars managed to drive back the allied forces. In 1714, the war ended with the treaties of Utrecht and Rastadt. France did not lose any territory, and there was no discussion of returning Flanders or Alsace to the Habsburgs. While the Duke of Anjou was accepted as King Philip V of Spain, this was done under the condition that the French and Spanish thrones never be united. Finally, France agreed to stop supporting Jacobite pretenders to the English throne. Just after the war ended, Louis died, having ruled France for 72 years.
While often considered a tyrant and a warmonger (especially in England), Louis XIV was not in any way a despot in the 20th-century sense. The traditional customs and institutions of France limited his power and in any case, communications were poor and no national police force existed.
Overall, the discontent and revolts of 16th- and 17th-century France did not approach the conditions that led to 1789. Events such as the Frondes were a naïve, unrevolutionary discontent and the people did not challenge the right of the king to govern nor did they question the Church.
The reign (1715–1774) of Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached maturity (then defi ...
saw an initial return to peace and prosperity under the regency (1715–1723) of Philip II, Duke of Orléans, whose policies were largely continued (1726–1743) by Cardinal Fleury, prime minister in all but name. The exhaustion of Europe after two major wars resulted in a long period of peace, only interrupted by minor conflicts like the War of the Polish Succession from 1733 to 1735. Large-scale warfare resumed with the War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession was a European conflict fought between 1740 and 1748, primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italian Peninsula, Italy, the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. Related conflicts include King Ge ...
(1740–1748). But alliance with the traditional Habsburg enemy (the " Diplomatic Revolution" of 1756) against the rising power of Britain and Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
led to costly failure in the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
(1756–1763) and the loss of France's North American colonies.
On the whole, the 18th century saw growing discontent with the monarchy and the established order. Louis XV was a highly unpopular king for his sexual excesses, overall weakness, and for losing Canada to the British. A strong ruler like Louis XIV could enhance the position of the monarchy, while Louis XV weakened it. The writings of the philosophers such as Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778), known by his ''Pen name, nom de plume'' Voltaire (, ; ), was a French Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment writer, philosopher (''philosophe''), satirist, and historian. Famous for his wit ...
were a clear sign of discontent, but the king chose to ignore them. He died of smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
in 1774, and the French people shed few tears at his passing. While France had not yet experienced the industrial revolution that was beginning in England, the rising middle class of the cities felt increasingly frustrated with a system and rulers that seemed silly, frivolous, aloof, and antiquated, even if true feudalism no longer existed in France.
Anti-establishment ideas fermented in 18th-century France in part due to the country's relative egalitarianism. While less liberal than England during the same period, the French monarchy never approached the absolutism of the eastern rulers in Vienna, Berlin, St. Petersburg, and Constantinople in part because the country's traditional development as a decentralized, feudal society acted as a restraint on the power of the king. Different social classes in France each had their own unique set of privileges so that no one class could completely dominate the others.
Upon Louis XV's death, his grandson Louis XVI
Louis XVI (Louis-Auguste; ; 23 August 1754 – 21 January 1793) was the last king of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. The son of Louis, Dauphin of France (1729–1765), Louis, Dauphin of France (son and heir- ...
became king. Initially popular, he too came to be widely detested by the 1780s. Again a weak ruler, he was married to an Austrian archduchess, Marie Antoinette
Marie Antoinette (; ; Maria Antonia Josefa Johanna; 2 November 1755 – 16 October 1793) was the last List of French royal consorts, queen of France before the French Revolution and the establishment of the French First Republic. She was the ...
, whose naïvety and cloistered/alienated Versailles life permitted ignorance of the true extravagance and wasteful use of borrowed money (Marie Antoinette was significantly more frugal than her predecessors). French intervention in the US War of Independence was also very expensive.
With the country deeply in debt, Louis XVI
Louis XVI (Louis-Auguste; ; 23 August 1754 – 21 January 1793) was the last king of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. The son of Louis, Dauphin of France (1729–1765), Louis, Dauphin of France (son and heir- ...
permitted the radical reforms of Turgot and Malesherbes, but noble disaffection led to Turgot's dismissal and Malesherbes' resignation in 1776. They were replaced by Jacques Necker. Necker had resigned in 1781 to be replaced by Calonne and Brienne, before being restored in 1788. A harsh winter that year led to widespread food shortages, and by then France was a powder keg ready to explode.
On the eve of the French Revolution of 1789, France was in a profound institutional and financial crisis, but the ideas of the Enlightenment had begun to permeate the educated classes of society.
On 1792 September 21 the French monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, reigns as head of state for the rest of their life, or until abdication. The extent of the authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutio ...
was effectively abolished by the proclamation of the French First Republic
In the history of France, the First Republic (), sometimes referred to in historiography as Revolutionary France, and officially the French Republic (), was founded on 21 September 1792 during the French Revolution. The First Republic lasted un ...
.
Monarchs
Ancien Régime
''Ancien'' may refer to
* the French word for " ancient, old"
** Société des anciens textes français
* the French for "former, senior"
** Virelai ancien
** Ancien Régime
** Ancien Régime in France
{{disambig ...
in 1792:''
Valois-Orléans (1498–1515)
* Louis XII
Valois-Angoulême (1515–1589)
* Francis I
* Henry II and Catherine de' Medici
Catherine de' Medici (, ; , ; 13 April 1519 – 5 January 1589) was an Italian Republic of Florence, Florentine noblewoman of the Medici family and Queen of France from 1547 to 1559 by marriage to Henry II of France, King Henry II. Sh ...
* Francis II
* Charles IX
* Henry III
House of Bourbon
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a dynasty that originated in the Kingdom of France as a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Kingdom of Navarre, Navarre in the 16th century. A br ...
(1589–1792)
* Henry IV
* the Regency of Marie de Medici
* Louis XIII and his minister Cardinal Richelieu
Armand Jean du Plessis, 1st Duke of Richelieu (9 September 1585 – 4 December 1642), commonly known as Cardinal Richelieu, was a Catholic Church in France, French Catholic prelate and statesman who had an outsized influence in civil and religi ...
* the Regency of Anne of Austria
Anne of Austria (; ; born Ana María Mauricia; 22 September 1601 – 20 January 1666) was Queen of France from 1615 to 1643 by marriage to King Louis XIII. She was also Queen of Navarre until the kingdom's annexation into the French crown ...
and her minister Cardinal Mazarin
* Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
* the Régence of Philip II of Orleans
* Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached maturity (then defi ...
* Louis XVI
Louis XVI (Louis-Auguste; ; 23 August 1754 – 21 January 1793) was the last king of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. The son of Louis, Dauphin of France (1729–1765), Louis, Dauphin of France (son and heir- ...
Social history
France in the Ancien Régime covered a territory of around , and supported 22 million people in 1700. At least 96% of the population were peasants. France had the largest population in Europe, with European Russia second at 20 million. Britain had nearly six million, Spain had eight million, and the Austrian Habsburgs had around eight million. France's lead slowly faded after 1700, as other countries grew faster.Rural society
In the 17th century rich peasants who had ties to the market economy provided much of the capital investment necessary for agricultural growth, and frequently moved from village to village (or town). Geographic mobility, directly tied to the market and the need for investment capital, was the main path to social mobility. The "stable" core of French society, town guilds people and village laboureurs, included cases of staggering social and geographic continuity, but even this core required regular renewal. Accepting the existence of these two societies, the constant tension between them, and extensive geographic and social mobility tied to a market economy holds the key to a clearer understanding of the evolution of the social structure, economy, and even political system of early modern France. Collins (1991) argues that the Annales School paradigm underestimated the role of the market economy; failed to explain the nature of capital investment in the rural economy; and grossly exaggerated social stability.Women and families
Very few women held any power—some queens did, as did the heads of Catholic convents. In the Enlightenment, the writings of philosopherJean-Jacques Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (, ; ; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Republic of Geneva, Genevan philosopher (''philosophes, philosophe''), writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment through ...
gave a political program for reform of the Ancien Régime, founded on a reform of domestic mores. Rousseau's conception of the relations between private and public spheres is more unified than that found in modern sociology. Rousseau argued that the domestic role of women is a structural precondition for a "modern" society. Within early modern society, women of urban artisanal classes participated in a range of public activities and also shared work settings with men (even though they were generally disadvantaged in terms of tasks, wages and access to property.)
Salic law prohibited women from rule; however, the laws for the case of a regency, when the king was too young to govern by himself, brought the queen into the center of power. The queen could assure the passage of power from one king to another—from her late husband to her young son—while simultaneously assuring the continuity of the dynasty.
Education for girls
Educational aspirations were on the rise and were becoming increasingly institutionalized in order to supply the church and state with the functionaries to serve as their future administrators. Girls were schooled too, but not to assume political responsibility. Girls were ineligible for leadership positions and were generally considered to have an inferior intellect to their brothers. France had many small local schools where working-class children—both boys and girls—learned to read, the better "to know, love and serve God". The sons and daughters of the noble and bourgeois elites, however, were given quite distinct educations: boys were sent to upper school, perhaps a university, while their sisters (if they were lucky enough to leave the house) were sent for finishing at a convent. The Enlightenment challenged this model, but no real alternative presented itself for female education. Only through education at home were knowledgeable women formed, usually to the sole end of dazzling their salons.Stepfamilies
A large proportion of children lived in broken homes or in blended families and had to cope with the presence of half-siblings and stepsiblings in the same residence. Brothers and sisters were often separated during the guardianship period and some of them were raised in different places for most of their childhood. Half-siblings and stepsiblings lived together for rather short periods of time because of their difference in age, their birth rank, or their gender. The lives of the children were closely linked to the administration of their heritage: when both their mothers and fathers were dead, another relative took charge of the guardianship and often removed the children from a stepparent's home, thus separating half-siblings. The experience of step-motherhood was surrounded by negative stereotypes; the Cinderella story and many other jokes and stories made the second wife an object of ridicule. Language, theater, popular sayings, the position of the Church, and the writings of jurists all made stepmother a difficult identity to take up. However, the importance of male remarriage suggests that reconstitution of family units was a necessity and that individuals resisted negative perceptions circulating through their communities. Widowers did not hesitate to take a second wife, and they usually found quite soon a partner willing to become a stepmother. For these women, being a stepmother was not necessarily the experience of a lifetime or what defined their identity. Their experience depended greatly on factors such as the length of the union, changing family configuration, and financial dispositions taken by their husbands. By a policy adopted at the beginning of the 16th century, adulterous women during the ancien régime were sentenced to a lifetime in a convent unless pardoned by their husbands and were rarely allowed to remarry even if widowed.Religion
Prior to the French Revolution, theCatholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
was the official state religion of the Kingdom of France. France was traditionally considered the Church's eldest daughter (French: ''Fille aînée de l'Église''), and the King of France
France was ruled by monarchs from the establishment of the kingdom of West Francia in 843 until the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, with several interruptions.
Classical French historiography usually regards Clovis I, king of the Fra ...
always maintained close links to the Pope. However, the French monarchy maintained a significant degree of autonomy, namely through its policy of " Gallicanism", whereby the king selected bishops rather than the papacy.
During the Protestant Reformation of the mid 16th century, France developed a large and influential Protestant population, primarily of Reformed confession; after French theologian and pastor John Calvin
John Calvin (; ; ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French Christian theology, theologian, pastor and Protestant Reformers, reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system of C ...
introduced the Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
in France, the number of French Protestants (Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
) steadily swelled to 10 percent of the population, or roughly 1.8 million people. The ensuring French Wars of Religion
The French Wars of Religion were a series of civil wars between French Catholic Church, Catholics and Protestantism, Protestants (called Huguenots) from 1562 to 1598. Between two and four million people died from violence, famine or disease di ...
, and particularly the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre, decimated the Huguenot community;Hans J. Hillerbrand, ''Encyclopedia of Protestantism: 4-volume Set'', paragraphs "France" and "Huguenots"The Huguenot Population of France, 1600-1685: The Demographic Fate and Customs of a Religious Minority by Philip Benedict; American Philosophical Society, 1991 - 164 Protestants declined to seven to eight percent of the kingdom's population by the end of the 16th century. The Edict of Nantes
The Edict of Nantes () was an edict signed in April 1598 by Henry IV of France, King Henry IV and granted the minority Calvinism, Calvinist Protestants of France, also known as Huguenots, substantial rights in the nation, which was predominantl ...
brought decades of respite until its revocation in the late 17th century by Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
. The resulting exodus of Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
from the Kingdom of France created a brain drain, as many of them had occupied important places in society.''Encyclopædia Britannica'', 11th ed, Frank Puaux, "Huguenot"
French exploration and colonies
*Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (), also known as the Age of Exploration, was part of the early modern period and overlapped with the Age of Sail. It was a period from approximately the 15th to the 17th century, during which Seamanship, seafarers fro ...
* French colonization of the Americas
* French colonial empires
Literature
* French Renaissance literature * French literature of the 17th century * French literature of the 18th centuryArt
*French Renaissance
The French Renaissance was the cultural and artistic movement in France between the 15th and early 17th centuries. The period is associated with the pan-European Renaissance, a word first used by the French historian Jules Michelet to define ...
* French Baroque and Classicism
* French Rococo and Neoclassicism
See also
*French Enlightenment
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band) ...
* Paris in the 17th century
* Paris in the 18th century
Notes
References
Works cited
* * * , academic biographyFurther reading
General
* Behrens, C.B.A. ''Ancien Régime'' (1989) * Bluche, François. ''L'Ancien régime: Institutions et société'' Collection: Livre de poche. Paris: Fallois, 1993. * * Doyle, William, ed. ''The Oxford Handbook of the Ancien Régime'' (2012) * Doyle, William, ed. ''Old Regime France: 1648–1788'' (2001) * Holt, Mack P. ''Renaissance and Reformation France: 1500–1648'' (2002) * * Jouanna, Arlette and Philippe Hamon, Dominique Biloghi, Guy Thiec. ''La France de la Renaissance; Histoire et dictionnaire'' Collection: Bouquins. Paris: Laffont, 2001. * Jouanna, Arlette and Jacqueline Boucher, Dominique Biloghi, Guy Thiec. ''Histoire et dictionnaire des Guerres de religion'' Collection: Bouquins. Paris: Laffont, 1998. * Le Roy Ladurie, Emmanuel. ''The Ancien Régime: A History of France 1610–1774'' (1999), political survey * Viguerie, Jean de. ''Histoire et dictionnaire du temps des Lumières 1715–1789'' Collection: Bouquins. Paris: Laffont, 1995.Political and military
* Baker, Keith, ed. ''The Political Culture of the Old Regime'' (1987), articles by leading historians * Black, Jeremy. ''From Louis XIV to Napoleon: The Fate of a Great Power'' (1999) * * Collins, James B. ''The State in Early Modern France'' (2009) * Knecht, R.J. ''The Rise and Fall of Renaissance France''. (1996). * Lynn, John A. ''The Wars of Louis XIV, 1667–1714'' (1999) * * Perkins, James Breck. ''France under Louis XV'' (2 vol 1897) * Potter, David. ''A History of France, 1460–1560: The Emergence of a Nation-State'' (1995) * Tocqueville, Alexis de. ''Ancien Régime and the French Revolution'' (1856; 2008 edition)Society and culture
* Beik, William. ''A Social and Cultural History of Early Modern France'' (2009) * * Farr, James Richard. ''The Work of France: Labor and Culture in Early Modern Times, 1350–1800'' (2008) * * Goubert, Pierre. ''Louis XIV and Twenty Million Frenchmen'' (1972), social history from Annales School * Goubert, Pierre. ''The French Peasantry in the Seventeenth Century'' (1986) * * McManners, John. ''Church and Society in Eighteenth-Century France.'' Vol. 1: ''The Clerical Establishment and Its Social Ramifications''; Vol. 2: ''The Religion of the People and the Politics of Religion''(1999) * Van Kley, Dale. ''The Religious Origins of the French Revolution: From Calvin to the Civil Constitution, 1560–1791'' (1996) * Ward, W.R. ''Christianity under the Ancien Régime, 1648–1789'' (1999).External links
French Pamphlet collection
documents significant events and periods in French history throughout the 17th–20th centuries, at the University of Maryland Libraries {{DEFAULTSORT:Early Modern France States and territories established in 1492
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
States and territories disestablished in 1791