Dynastic union on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A dynastic union is a type of union in which different states are governed beneath the same
 The
The
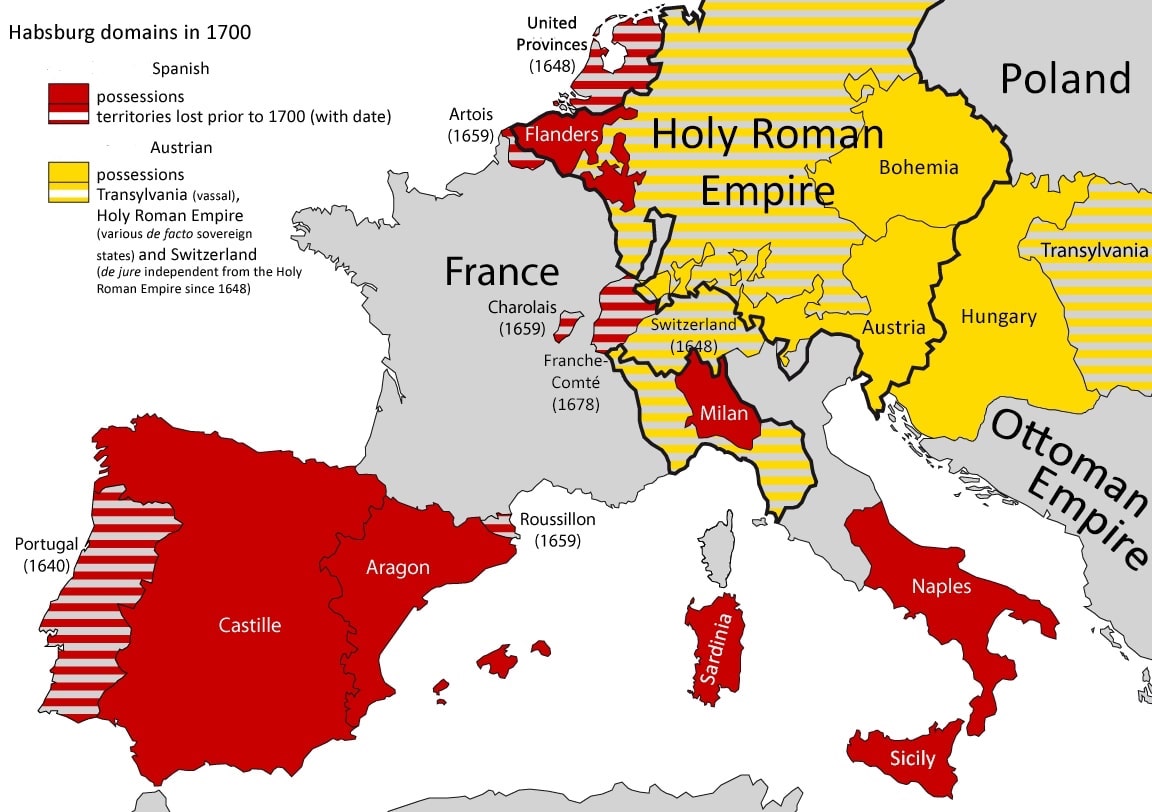 At the end of the reign of
At the end of the reign of
dynasty
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family, usually in the context of a monarchy, monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A dynasty may also be referred to as a "house", "family" or "clan", among others.
H ...
, with their boundaries, their laws, and their interests remaining distinct from each other.
It is a form of association looser than a personal union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent in ...
, when several states share the same monarch, and a real union
Real union is a union of two or more states, which share some state institutions in contrast to personal unions; however, they are not as unified as states in a political union. It is a development from personal union and has historically been ...
, when they have common institutions in addition to the same monarch.
Historical examples
Marriage
Iberia
Marriage of Count of Barcelona Raymond Berengar IV of Barcelona and future Queen of Aragon Petronila of Aragon in 1137 that formed theCrown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon (, ) ;, ; ; . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of Barcelona (later Principality of Catalonia) and ended as a consequence of the War of the Sp ...
.
Marriage of Isabella I of Castile
Isabella I (; 22 April 1451 – 26 November 1504), also called Isabella the Catholic (Spanish: ''Isabel la Católica''), was Queen of Castile and List of Leonese monarchs, León from 1474 until her death in 1504. She was also Queen of Aragon ...
and Ferdinand II of Aragon
Ferdinand II, also known as Ferdinand I, Ferdinand III, and Ferdinand V (10 March 1452 – 23 January 1516), called Ferdinand the Catholic, was King of Aragon from 1479 until his death in 1516. As the husband and co-ruler of Queen Isabella I of ...
in 1469 that laid the foundations for the kingdom of Spain. They did not ascend to their respective thrones until 1474 and 1479 respectively.
Lithuania and Poland
Marriage of Jogaila and QueenJadwiga of Poland
Jadwiga (; 1373 or 137417 July 1399), also known as Hedwig (from German) and in , was the first woman to be crowned as monarch of the Kingdom of Poland. She reigned from 16 October 1384 until her death. Born in Buda, she was the youngest daught ...
on 1385, generally called the Union of Krewo
In a strict sense, the Union of Krewo or Act of Krėva (also spelled Union of Krevo, Act of Kreva; ; ) comprised a set of prenuptial promises made at Kreva Castle on 14 August 1385 by Jogaila, Grand Duke of Lithuania, in regard to his prospectiv ...
. That union laid the foundations for the eventual formation of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
.
Scotland and France
Norman or French culture first gained a foothold in Scotland during theDavidian Revolution
The Davidian Revolution is a name given by many scholars to the changes which took place in the Kingdom of Scotland during the reign of David I (1124–1153). These included his foundation of burghs, implementation of the ideals of Gregoria ...
, when King David I introduced Continental-style reforms throughout all aspects of Scottish life: social, religious, economic and administrative. He also invited immigrant French and Anglo-French peoples to Scotland. This effectively created a Franco-Scottish aristocracy, with ties to the French aristocracy as well as many to the Franco-English aristocracy. From the Wars of Scottish Independence, as common enemies of England and its ruling House of Plantagenet
The House of Plantagenet (Help:IPA/English, /plænˈtædʒənət/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''plan-TAJ-ə-nət'') was a royal house which originated from the Medieval France, French county of Anjou. The name Plantagenet is used by mo ...
, Scotland and France started to enjoy a close diplomatic relationship, the Auld Alliance, from 1295 to 1560. From the Late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the Periodization, period of History of Europe, European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period ( ...
and into the Early Modern Period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
Scotland and its burgh
A burgh ( ) is an Autonomy, autonomous municipal corporation in Scotland, usually a city, town, or toun in Scots language, Scots. This type of administrative division existed from the 12th century, when David I of Scotland, King David I created ...
s also benefited from close economic and trading links with France in addition to its links to the Low Countries, Scandinavia and the Baltic.
The prospect of dynastic union came in the 15th and 16th centuries, when Margaret
Margaret is a feminine given name, which means "pearl". It is of Latin origin, via Ancient Greek and ultimately from Iranian languages, Old Iranian. It has been an English language, English name since the 11th century, and remained popular thro ...
, eldest daughter of James I of Scotland
James I (late July 1394 – 21 February 1437) was List of Scottish monarchs, King of Scots from 1406 until his assassination in 1437. The youngest of three sons, he was born in Dunfermline Abbey to King Robert III of Scotland, Robert III and ...
, married the future Louis XI of France
Louis XI (3 July 1423 – 30 August 1483), called "Louis the Prudent" (), was King of France from 1461 to 1483. He succeeded his father, Charles VII. Louis entered into open rebellion against his father in a short-lived revolt known as the ...
. James V of Scotland
James V (10 April 1512 – 14 December 1542) was List of Scottish monarchs, King of Scotland from 9 September 1513 until his death in 1542. He was crowned on 21 September 1513 at the age of seventeen months. James was the son of King James IV a ...
married two French brides in succession. His infant daughter, Mary I
Mary I (18 February 1516 – 17 November 1558), also known as Mary Tudor, was Queen of England and Ireland from July 1553 and Queen of Spain as the wife of King Philip II from January 1556 until her death in 1558. She made vigorous a ...
, succeeded him on his death in 1542. For many years thereafter the country was ruled under a regency led by her French mother, Mary of Guise
Mary of Guise (; 22 November 1515 – 11 June 1560), also called Mary of Lorraine, was List of Scottish royal consorts, Queen of Scotland from 1538 until 1542, as the second wife of King James V. She was a French people, French noblewoman of the ...
, who succeeded in marrying her daughter to the future Francis II of France
Francis II (; 19 January 1544 – 5 December 1560) was List of French monarchs, King of France from 1559 to 1560. He was also List of Scottish consorts, King of Scotland as the husband of Mary, Queen of Scots, from 1558 until his death in ...
. The young couple were king and queen of France and Scotland from 1559 until Francis died in 1560. Mary returned to a Scotland heaving with political revolt and religious revolution, which made a continuation of the alliance impossible.
Cordial economic and cultural relations did continue however, although throughout the 17th century, the Scottish establishment became increasingly Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a historically Reformed Protestant tradition named for its form of church government by representative assemblies of elders, known as "presbyters". Though other Reformed churches are structurally similar, the word ''Pr ...
, often belligerent to Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, a facet which was somewhat at odds with Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
's aggressively Catholic foreign and domestic policy. The relationship was further weakened by the Union of the Crowns
The Union of the Crowns (; ) was the accession of James VI of Scotland to the throne of the Kingdom of England as James I and the practical unification of some functions (such as overseas diplomacy) of the two separate realms under a single ...
in 1603, which meant from then on that although still independent, executive power in the Scottish government, the Crown, was shared with the Kingdom of England and Scottish foreign policy came into line more with that of England than with France. France would later support the Catholic Stuart pretenders.
Shared Dynasty
Iberia
With the assassination of Sancho IV,Navarre
Navarre ( ; ; ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre, is a landlocked foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, bordering the Basque Autonomous Community, La Rioja, and Aragon in Spain and New Aquitaine in France. ...
was invaded by his cousins Alfonso VI of Castile and Sancho V Ramirez of Aragon, and the latter was made king in 1076, which led to more than half a century (1076–1134) of Aragonese control. They were members of the Jiménez dynasty which ruled over all Christian kingdoms 1037–1126 in Spain.
Crown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon (, ) ;, ; ; . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of Barcelona (later Principality of Catalonia) and ended as a consequence of the War of the Sp ...
was a composite monarchy
A composite monarchy (or composite state) is a historical category, introduced by H. G. Koenigsberger in 1975 and popularised by Sir John H. Elliott, that describes early modern states consisting of several countries under one ruler, sometimes ...
but some of its states were given to relatives. For example king James II of the Kingdom of Majorca
The Kingdom of Majorca (, ; ; ; ) was an insular realm off the east coast of modern day Spain, which included the islands of Mallorca, Menorca, Ibiza and Formentera. The islands were conquered from the Almohad Caliphate by James I of Aragon, ...
was the brother of Peter III of Aragon, whose son Frederick III became king of Trinacria (Sicily) and Frederick's son Manfred became Duke of Athens
The Duchy of Athens (Greek language, Greek: Δουκᾶτον Ἀθηνῶν, ''Doukaton Athinon''; Catalan language, Catalan: ''Ducat d'Atenes'') was one of the Crusader states set up in Greece after the conquest of the Byzantine Empire during ...
and Neopatria.
A dynastic union existed between Spain (the union between the Crowns of Castile and Aragon) and Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
(1580–1640), generally called the Iberian Union
The Iberian Union is a historiographical term used to describe the period in which the Habsburg Spain, Monarchy of Spain under Habsburg dynasty, until then the personal union of the crowns of Crown of Castile, Castile and Crown of Aragon, Aragon ...
by modern historians, under the Philippine Dynasty
The Philippine dynasty (), also known as the House of Habsburg in Portugal, was the third royal house of Portugal. It was named after the three Habsburg Spanish kings, all named Philip (; , ), who ruled Portugal between 1581 and 1640 under th ...
.
Habsburg
 At the end of the reign of
At the end of the reign of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles V (24 February 1500 – 21 September 1558) was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain (as Charles I) from 1516 to 1556, and Lord of the Netherlands as titular Duke of Burgundy (as Charles II) ...
, he split his empire into a Spanish and Austrian line who remained closely allied and famously heavily intermarried. A similar situation appeared in Northern Italy
Northern Italy (, , ) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. The Italian National Institute of Statistics defines the region as encompassing the four Northwest Italy, northwestern Regions of Italy, regions of Piedmo ...
, Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany (; ) was an Italian monarchy located in Central Italy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1860, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In the 19th century the population ...
(1737–1860), the Duchy of Modena and Reggio
The Duchy of Modena and Reggio (; ; ) was an Italian state created in 1452 located in Northern Italy, Northwestern Italy, in the present day region of Emilia-Romagna. It was ruled since its establishment by the noble House of Este, and from 1814 ...
(1814–1859), the Duchy of Parma and Piacenza (1815–1847) and the Duchy of Massa and Carrara (1829–1836) were all ruled by cadet branches of the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
dynasty and became increasingly dependent from the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
.
Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus', also known as Kyivan Rus,.
* was the first East Slavs, East Slavic state and later an amalgam of principalities in Eastern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical At ...
was officially ruled by a grand prince but was de facto an amalgamation of different principalities ruled by the Rurik dynasty
The Rurik dynasty, also known as the Rurikid or Riurikid dynasty, as well as simply Rurikids or Riurikids, was a noble lineage allegedly founded by the Varangian prince Rurik, who, according to tradition, established himself at Novgorod in the ...
.
Capet
=Frankish Greece
= Many Latin states or titles in Greece were held by different branches of the Capetian dynasty. They were Latin Emperors (who were officially the overlords of all states) since 1216, Kings of Albania (since 1271), (titular) Kings of Thessalonica (since 1266 Burgundian claim or 1274 Angevin claim) and Prince of Achaea since 1316. Additionally, they were related and overlapped with theKings of Naples
The following is a list of rulers of the Kingdom of Naples, from its first separation from the Kingdom of Sicily to its merger with the same into the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies.
Kingdom of Naples (1282–1501)
House of Anjou
In 1382, the Kin ...
, with Charles III of Naples being Prince of Achaea, King of Naples and even King of Hungary
The King of Hungary () was the Monarchy, ruling head of state of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1000 (or 1001) to 1918. The style of title "Apostolic King of Hungary" (''Magyarország apostoli királya'') was endorsed by Pope Clement XIII in 1758 ...
and Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
at once.
=France and Navarre
=Philip IV of France
Philip IV (April–June 1268 – 29 November 1314), called Philip the Fair (), was King of France from 1285 to 1314. Jure uxoris, By virtue of his marriage with Joan I of Navarre, he was also King of Navarre and Count of Champagne as Philip&n ...
became ''jure uxoris
''Jure uxoris'' (a Latin phrase meaning "by right of (his) wife"), citing . describes a title of nobility used by a man because his wife holds the office or title '' suo jure'' ("in her own right"). Similarly, the husband of an heiress could beco ...
'' king of Navarre in 1284 through his marriage with Joan I of Navarre and Navarre remained in a personal union with France until the death Charles IV of France
Charles IV (18/19 June 1294 – 1 February 1328), called the Fair (''le Bel'') in France and the Bald (''el Calvo'') in Navarre, was the last king of the direct line of the House of Capet, List of French monarchs, King of France and List of Nav ...
. Then the likewise Capetian Évreux
Évreux () is a commune in and the capital of the department of Eure, in the French region of Normandy.
History Antiquity
In late Antiquity, the town, attested in the fourth century AD, was named '' Mediolanum Aulercorum'', "the central town ...
took the throne until the death of Blanche I of Navarre
Blanche I (, ; 6 July 1387 – 1 April 1441) was Queen of Navarre from the death of her father, King Charles III, in 1425 until her own death. She had been Queen of Sicily from 1402 to 1409 by marriage to King Martin I, serving as regent of Si ...
in 1441.
With Antoine of Navarre
Antoine (, , 22 April 1518 – 17 November 1562), sometimes called Antoine of Bourbon, was King of Navarre from 1555 until his death in 1562 as the husband and co-ruler of Queen Jeanne III. He was the first monarch of the House of Bourbon, of whi ...
the House of Bourbon
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a dynasty that originated in the Kingdom of France as a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Kingdom of Navarre, Navarre in the 16th century. A br ...
gained control over Lower Navarre
Lower Navarre (; Gascon/Bearnese: ''Navarra Baisha''; ; ) is a traditional region of the present-day French '' département'' of Pyrénées-Atlantiques. It corresponds to the northernmost ''region'' of the Kingdom of Navarre during the Middle A ...
in 1555 through a marriage Joan III of Navarre. Following Salic law
The Salic law ( or ; ), also called the was the ancient Frankish Civil law (legal system), civil law code compiled around AD 500 by Clovis I, Clovis, the first Frankish King. The name may refer to the Salii, or "Salian Franks", but this is deba ...
, Henry III, King of Navarre, a member of the House of Bourbon, succeeded to the French throne in 1589 upon the extinction of the male line of the House of Valois
The Capetian House of Valois ( , also , ) was a cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty. They succeeded the House of Capet (or "Direct Capetians") to the List of French monarchs, French throne, and were the royal house of France from 1328 to 1589. ...
. Both houses were cadet branches of the Capetian dynasty, the ruling house of the kingdom of France since 987.
United Kingdom and Hanover
Thepersonal union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent in ...
between the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was the union of the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland into one sovereign state, established by the Acts of Union 1800, Acts of Union in 1801. It continued in this form until ...
and the Kingdom of Hanover
The Kingdom of Hanover () was established in October 1814 by the Congress of Vienna, with the restoration of George III to his Hanoverian territories after the Napoleonic Wars, Napoleonic era. It succeeded the former Electorate of Hanover, and j ...
, jointly ruled by the head of the House of Hanover
The House of Hanover ( ) is a European royal house with roots tracing back to the 17th century. Its members, known as Hanoverians, ruled Hanover, Great Britain, Ireland, and the British Empire at various times during the 17th to 20th centurie ...
since 1707, ended with the death of William IV
William IV (William Henry; 21 August 1765 – 20 June 1837) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from 26 June 1830 until his death in 1837. The third son of George III, William succeeded hi ...
in 1837, and was replaced with a dynastic union: due to the different laws of succession, he was succeeded by two members of the dynasty, in the United Kingdom by his niece Victoria, the daughter of his late next brother Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn
Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn (Edward Augustus; 2 November 1767 – 23 January 1820) was the fourth son and fifth child of King George III and Queen Charlotte. His only child, Queen Victoria, Victoria, became Queen of the United Ki ...
, and in Hanover by his second next brother Ernest Augustus.
King Ernest Augustus hoped that his son and heir, the future George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until Death and state funeral of George V, his death in 1936.
George w ...
, could marry Queen Victoria, his first cousin, which, provided they had had a son and joint heir, would have reunited the two countries in a personal union; however, this did not happen. The dynastic union lasted until the annexation of Hanover by Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
in 1866.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Dynastic Union Monarchy - Political union