Duty Cycle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one
 A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Period (punctuation)
* Era, a length or span of time
*Menstruation, commonly referred to as a "period"
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (o ...
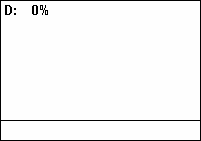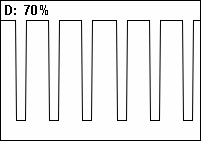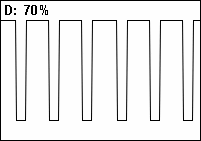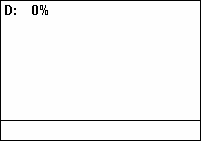
in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a formula, a duty cycle (%) may be expressed as:
:
Equally, a duty cycle (ratio) may be expressed as:
:
where is the duty cycle, is the pulse width (pulse active time), and is the total period of the signal. Thus, a 60% duty cycle means the signal is on 60% of the time and off 40% of the time. The "on time" for a 60% duty cycle could be a fraction of a second, a day, or even a week, depending on the length of the period.
Duty cycles can be used to describe the percent time of an active signal in an electrical device such as the power switch in a switching power supply
A switched-mode power supply (SMPS), also called switching-mode power supply, switch-mode power supply, switched power supply, or simply switcher, is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical powe ...
or the firing of action potentials
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell rapidly rises and falls. ...
by a living system such as a neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
.
Some publications use as the symbol for duty cycle.
As a ratio, duty cycle is unitless and may be given as decimal fraction and percentage alike.
An alternative term in use is duty factor.
Applications
Electrical and electronics
Inelectronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield ...
, duty cycle is the percentage of the ratio of pulse duration, or pulse width (PW) to the total period (T) of the waveform. It is generally used to represent time duration of a pulse when it is high (1). In digital electronics
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. It deals with the relationship between Binary number, binary inputs and outputs by passing electrical s ...
, signals are used in rectangular waveform which are represented by logic 1 and logic 0. Logic 1 stands for presence of an electric pulse and 0 for absence of an electric pulse. For example, a signal (10101010) has 50% duty cycle, because the pulse remains high for 1/2 of the period and low for 1/2 of the period. Similarly, for pulse (10001000) the duty cycle will be 25% because the pulse remains high only for 1/4 of the period and remains low for 3/4 of the period.
Electric motors
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate Laplace force i ...
typically use a duty cycle of less than 100%. For example, if a motor runs for one out of 100 seconds (or 1/100 of the time), its duty cycle is 1/100, or 1%.
Pulse-width modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), also known as pulse-duration modulation (PDM) or pulse-length modulation (PLM), is any method of representing a signal as a rectangular wave with a varying duty cycle (and for some methods also a varying peri ...
(PWM) is used in a variety of electronic situations, such as power delivery and voltage regulation.
In electronic music, music synthesizers
A synthesizer (also synthesiser or synth) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis and ...
vary the duty cycle of their audio-frequency oscillators to obtain a subtle effect on the tone color
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or musical tone, tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musica ...
s. This technique is known as pulse-width modulation.
In the printer / copier industry, the duty cycle specification refers to the rated throughput (that is, printed pages) of a device per month.
In a welding power supply
A welding power supply is a device that provides or modulates an electric current to perform arc welding.- - There are multiple arc welding processes ranging from Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) to inert shielding gas like Gas metal arc weldin ...
, the maximum duty cycle is defined as the percentage of time in a 10-minute period that it can be operated continuously before overheating.
Biological systems
The concept of duty cycles is also used to describe the activity of neurons andmuscle fibers
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are a ...
. In neural circuits for example, a duty cycle specifically refers to the proportion of a cycle period in which a neuron remains active.
Generation
One way to generate fairly accuratesquare wave Square wave may refer to:
*Square wave (waveform)
A square wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform, non-sinusoidal periodic waveform in which the amplitude alternates at a steady frequency between fixed minimum and maximum values, with the same ...
signals with 1/''n'' duty factor, where ''n'' is an integer, is to vary the duty cycle until the ''n''th-harmonic
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st har ...
is significantly suppressed. For audio-band signals, this can even be done "by ear"; for example, a −40 dB reduction in the 3rd harmonic corresponds to setting the duty factor to 1/3 with a precision of 1% and −60 dB reduction corresponds to a precision of 0.1%.
Mark–space ratio
Mark–space ratio, or mark-to-space ratio, is another term for the same concept, to describe the temporal relationship between two alternating periods of a waveform. However, whereas the duty cycle relates the duration of one period to the duration of the entire cycle, the mark–space ratio relates the durations of the two individual periods: : where and are the durations of the two alternating periods.References
{{Reflist Electrical engineering Mechanical engineering Timing in electronic circuits Articles containing video clips