The history of the Netherlands extends back before the founding of the modern
Kingdom of the Netherlands
The Kingdom of the Netherlands (, ;, , ), commonly known simply as the Netherlands, is a sovereign state consisting of a collection of constituent territories united under the monarch of the Netherlands, who functions as head of state. The re ...
in 1815 after the defeat of Napoleon. For thousands of years, people have been living together around the river deltas of this section of the
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
coast. Records begin with the four centuries during which the region formed a militarized border zone of the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
. As the
Western Roman Empire
In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. ...
collapsed and the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
began, three dominant
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of ...
coalesced in the area –
Frisians
The Frisians () are an ethnic group indigenous to the German Bight, coastal regions of the Netherlands, north-western Germany and southern Denmark. They inhabit an area known as Frisia and are concentrated in the Dutch provinces of Friesland an ...
in the north and coastal areas,
Low Saxons in the northeast, and the
Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
to the south. By 800, the Frankish
Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty ( ; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charles Martel and his grandson Charlemagne, descendants of the Arnulfing and Pippinid c ...
dynasty had once again integrated the area into an empire covering a large part of Western Europe. The region was part of the duchy of
Lower Lotharingia
The Duchy of Lower Lotharingia, also called Northern Lotharingia, Lower Lorraine or Northern Lorraine (and also referred to as '' Lothier'' or '' Lottier'' within the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, but neither the empire nor the duchy were governed in a centralized manner. For several centuries, medieval lordships such as
Brabant,
Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former provinces of the Netherlands, province on the western coast of the Netherland ...
,
Zeeland
Zeeland (; ), historically known in English by the Endonym and exonym, exonym Zealand, is the westernmost and least populous province of the Netherlands. The province, located in the southwest of the country, borders North Brabant to the east ...
,
Friesland
Friesland ( ; ; official ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia (), named after the Frisians, is a Provinces of the Netherlands, province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen (p ...
,
Guelders
The Duchy of Guelders (; ; ) is a historical duchy, previously county, of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the Low Countries.
Geography
The duchy was named after the town of Geldern (''Gelder'') in present-day Germany. Though the present pr ...
and others held a changing patchwork of territories.
By 1433, the
Duke of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy () was a title used by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, from its establishment in 843 to its annexation by the Crown lands of France, French crown in 1477, and later by members of the House of Habsburg, including Holy Roman E ...
had assumed control over most of Lower Lotharingia, creating the
Burgundian Netherlands
The Burgundian Netherlands were those parts of the Low Countries ruled by the Dukes of Burgundy during the Burgundian Age between 1384 and 1482. Within their Burgundian State, which itself belonged partly to the Holy Roman Empire and partly t ...
. This included what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and a part of France. When their heirs the Catholic kings of Spain took measures against Protestantism, the subsequent
Dutch revolt
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt (; 1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Reformation, centralisation, exc ...
led to the splitting in 1581 of the Netherlands into southern and northern parts. The southern "
Spanish Netherlands
The Spanish Netherlands (; ; ; ) (historically in Spanish: , the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the Habsburg Netherlands ruled by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556 to 1714. They were a collection of States of t ...
" corresponds approximately to modern Belgium and Luxembourg, and the northern
"United Provinces" (or "Dutch Republic)", which spoke Dutch and was predominantly Protestant, was the predecessor of the modern Netherlands.
In the
Dutch Golden Age
The Dutch Golden Age ( ) was a period in the history of the Netherlands which roughly lasted from 1588, when the Dutch Republic was established, to 1672, when the '' Rampjaar'' occurred. During this period, Dutch trade, scientific development ...
, which had its zenith around 1667, there was a flowering of trade, industry, and the
sciences
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
. The Dutch Republic practiced
religious toleration
Religious tolerance or religious toleration may signify "no more than forbearance and the permission given by the adherents of a dominant religion for other religions to exist, even though the latter are looked on with disapproval as inferior, ...
and Amsterdam attracted
Portuguese Jews
Spanish and Portuguese Jews, also called Western Sephardim, Iberian Jews, or Peninsular Jews, are a distinctive sub-group of Sephardic Jews who are largely descended from Jews who lived as New Christians in the Iberian Peninsula during the fe ...
, many of whom were merchants, that practiced their religion and engaged in economic activity. A worldwide
Dutch empire
The Dutch colonial empire () comprised overseas territories and trading posts under some form of Dutch control from the early 17th to late 20th centuries, including those initially administered by Dutch chartered companies—primarily the Du ...
developed in Asia and the Americas. The
Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States Ge ...
became one of the earliest and most important of national mercantile companies of the time, based on invasion, colonialism, and extraction of outside resources, but not religious evangelization. During the eighteenth century, the power, wealth and influence of the Netherlands declined. A series of wars with the more powerful
British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
and
French neighbours weakened it. The English seized the North American colony of
New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam (, ) was a 17th-century Dutch Empire, Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''Factory (trading post), fac ...
, and renamed it "
New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
". There was growing unrest and
conflict between the
Orangists and the
Patriots
A patriot is a person with the quality of patriotism.
Patriot(s) or The Patriot(s) may also refer to:
Political and military groups United States
* Patriot (American Revolution), those who supported the cause of independence in the American R ...
. The French Revolution spilled over after 1789, and a pro-French
Batavian Republic
The Batavian Republic (; ) was the Succession of states, successor state to the Dutch Republic, Republic of the Seven United Netherlands. It was proclaimed on 19 January 1795 after the Batavian Revolution and ended on 5 June 1806, with the acce ...
was established in 1795–1806. Napoleon made it a satellite state, the
Kingdom of Holland
The Kingdom of Holland ( (contemporary), (modern); ) was the successor state of the Batavian Republic. It was created by Napoleon Bonaparte in March 1806 in order to strengthen control over the Netherlands by replacing the republican governmen ...
(1806–1810), and later simply a French imperial province.
After the defeat of Napoleon in 1813–1815, an expanded "
United Kingdom of the Netherlands
The United Kingdom of the Netherlands is the unofficial name given to the Kingdom of the Netherlands as it existed from 1815 to 1839. The United Netherlands was created in the aftermath of the Napoleonic Wars through the fusion of territories t ...
" was created with the
House of Orange
The House of Orange-Nassau (, ), also known as the House of Orange because of the prestige of the princely title of Orange, also referred to as the Fourth House of Orange in comparison with the other noble houses that held the Principality of O ...
as monarchs, also ruling Belgium and Luxembourg. After the King imposed unpopular Protestant reforms on Belgium,
it left the kingdom in 1830 and new borders were agreed in 1839. After an initially conservative period, following the introduction of the 1848 constitution, the country became a
parliamentary democracy
A parliamentary system, or parliamentary democracy, is a form of government where the head of government (chief executive) derives their democratic legitimacy from their ability to command the support ("confidence") of a majority of the legisl ...
with a
constitutional monarch
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. ...
. Modern-day Luxembourg became officially independent of the Netherlands in 1839, but a personal union remained until 1890. Since 1890, it is ruled by another branch of the same dynasty.
The Netherlands was neutral during the
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, but during the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, it was invaded and occupied by
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
. The Nazis, including many collaborators, rounded up and killed almost all of the country's Jewish population. When the Dutch resistance increased, the Nazis cut off food supplies to much of the country, causing severe starvation in 1944–1945. In 1942, the Dutch East Indies were conquered by Japan, but prior to this the Dutch destroyed the oil wells for which Japan was desperate.
Indonesia proclaimed its independence from the Netherlands in 1945, followed by
Suriname
Suriname, officially the Republic of Suriname, is a country in northern South America, also considered as part of the Caribbean and the West Indies. It is a developing country with a Human Development Index, high level of human development; i ...
in 1975. The post-war years saw rapid economic recovery (helped by the American
Marshall Plan
The Marshall Plan (officially the European Recovery Program, ERP) was an American initiative enacted in 1948 to provide foreign aid to Western Europe. The United States transferred $13.3 billion (equivalent to $ in ) in economic recovery pr ...
), followed by the introduction of a
welfare state
A welfare state is a form of government in which the State (polity), state (or a well-established network of social institutions) protects and promotes the economic and social well-being of its citizens, based upon the principles of equal oppor ...
during an era of peace and prosperity. The Netherlands formed a new economic alliance with Belgium and Luxembourg, the
Benelux
The Benelux Union (; ; ; ) or Benelux is a politico-economic union, alliance and formal international intergovernmental cooperation of three neighbouring states in Western Europe: Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg. The name is a portma ...
, and all three became founding members of the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
and
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
. In recent decades, the Dutch economy has been closely linked to that of Germany and is highly prosperous. The four countries adopted the
euro
The euro (currency symbol, symbol: euro sign, €; ISO 4217, currency code: EUR) is the official currency of 20 of the Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union. This group of states is officially known as the ...
on 1 January 2002, along with eight other EU member states.
Prehistory (before 57 BC)

During the last ice age, the Netherlands had a
tundra
In physical geography, a tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. There are three regions and associated types of tundra: #Arctic, Arctic, Alpine tundra, Alpine, and #Antarctic ...
climate with scarce vegetation, and the inhabitants survived as hunter-gatherers. The
Swifterbant culture The Swifterbant culture was a Subneolithic archaeological culture in the Netherlands, dated between 5300 BC and 3400 BC. Like the Ertebølle culture, the settlements were concentrated near water, in this case creeks, riverdunes and bogs along post ...
, appearing around 5600 BC
[Louwe Kooijmans, L.P.,]
Trijntje van de Betuweroute, Jachtkampen uit de Steentijd te Hardinxveld-Giessendam
, 1998, ''Spiegel Historiael'' 33, pp. 423–428 were
hunter gatherers strongly linked to rivers and open water and related to the southern Scandinavian
Ertebølle culture.

Agriculture also arrived in areas near the Netherlands somewhere around 5000 BC with the
Linear Pottery culture
The Linear Pottery culture (LBK) is a major archaeological horizon of the European Neolithic period, flourishing . Derived from the German ''Linearbandkeramik'', it is also known as the Linear Band Ware, Linear Ware, Linear Ceramics or Incis ...
, who were central European farmers with Mediterranean ancestry. Their farms were restricted to southern
Limburg and only temporarily established. However, there is some evidence that the coastal Swifterband people took up pottery and animal husbandry in the rest of the country. Local groups made the switch to animal husbandry sometime between 4800 BC and 4500 BC.
[Leendert Louwe Kooijmans, "It is becoming increasingly clear that the agricultural transformation of prehistoric communities was a purely indigenous process that took place very gradually." Louwe Kooijmans, L.P.,]
Trijntje van de Betuweroute, Jachtkampen uit de Steentijd te Hardinxveld-Giessendam
, 1998, ''Spiegel Historiael'' 33, pp. 423–428[Raemakers, Daan.]
De spiegel van Swifterbant
, University of Groningen, 2006. By about 4000 BC the
Funnelbeaker culture
The Funnel(-neck-)beaker culture, in short TRB or TBK (, ; ; ), was an archaeological culture in north-central Europe.
It developed as a technological merger of local neolithic and mesolithic techno-complexes between the lower Elbe and middle V ...
brought farming permanently into the region. This culture extended from Denmark through northern Germany into the northern Netherlands. The
Vlaardingen culture
Vlaardingen Culture was an archaeological culture on the border of the middle and late Neolithic era in what is now the coastal region in the west of the Netherlands. In 1958, archeologists found objects in Vlaardingen, a city near Rotterdam, w ...
continued the hunter-gatherer tradition in coastal areas.
By around 2950 BCE, there was a transition from the Funnelbeaker farming culture to the
Corded Ware culture which extended across much of northern and central Europe. The expansion of this culture is believed to have involved the movement of people from the direction of Ukraine, bringing
Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
and
Copper Age
The Chalcolithic ( ) (also called the Copper Age and Eneolithic) was an archaeological period characterized by the increasing use of smelted copper. It followed the Neolithic and preceded the Bronze Age. It occurred at different periods in dif ...
technology. The earliest bronze tools were in the
Wageningen horde, found in the grave of a
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
metalworker. The
Elp culture
The Elp culture (c. 1800—800 BCE) is a Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age archaeological culture of the Netherlands having earthenware pottery of low quality known as "Kümmerkeramik" (also "Grobkeramik") as a marker. The initial phase is characteri ...
in the north and the
Hilversum culture
The Hilversum culture is a prehistoric material culture found in middle Bronze Age in the region of the southern Netherlands and northern Belgium. It has been associated with the Wessex culture from the same period in southern England, and is one ...
in the south developed during the Bronze Age, with the latter having cultural ties with Britain.
The
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
brought a measure of prosperity to the people living in the area of the present-day Netherlands with iron ore available throughout the country.
Smiths travelled from small settlement to settlement with
bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
and iron, fabricating tools on demand, including axes, knives, pins, arrowheads and swords. The
Vorstengraf large burial mound contained a number of objects, including a curved iron sword. Leading up to the arrival of the Romans, the probably Germanic
Harpstedt culture rose in the north
[Mallory, J.P., ''In Search of the Indo-Europeans: Language, Archaeology and Myth'', London: Thames & Hudson, 1989, p. 87.] possibly migrating from Scandinavia due to climatic deterioration which had separated
[de Vries, Jan W., Roland Willemyns and Peter Burger, ''Het verhaal van een taal'', Amsterdam: Prometheus, 2003, pp. 12, 21–27] into a northern group that would later become
early Frisians and early
Saxons
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
and a southern group that extended into the Rhine which eventually developed into the Salian Franks,
while further to the south were peoples influenced by the
Hallstatt culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western Europe, Western and Central European archaeological culture of the Late Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe (Hallst ...
who eventually assimilated into the Celtic
La Tène culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a Iron Age Europe, European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman Republic, Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age ...
with some mixture between the two. This is consistent with
Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war. He ...
's account of the Rhine forming the boundary between Celtic and Germanic tribes. Some scholars have speculated that a separate ethnic identity with its own language that was neither Germanic nor Celtic, formed a
Nordwestblock
The Nordwestblock (German language, German, "Northwest Block") is a hypothetical Northwestern European cultural region that some scholars propose as a prehistoric culture in the present-day Netherlands, Belgium, far-northern France, and Northern ...
stretching from the
Somme __NOTOC__
Somme or The Somme may refer to: Places
*Somme (department), a department of France
* Somme, Queensland, Australia
* Canal de la Somme, a canal in France
*Somme (river), a river in France
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Somme'' (book), ...
to the
Weser
The Weser () is a river of Lower Saxony in north-west Germany. It begins at Hannoversch Münden through the confluence of the Werra and Fulda. It passes through the Hanseatic city of Bremen. Its mouth is further north against the ports o ...
[Lendering, Jona]
"Germania Inferior"
, Livius.org. Retrieved 6 October 2011. and survived until the Roman period before being absorbed by their Celtic and Germanic neighbours.
Roman era (57 BC – 410 AD)

During his
Gallic Wars
The Gallic Wars were waged between 58 and 50 BC by the Roman general Julius Caesar against the peoples of Gaul (present-day France, Belgium, and Switzerland). Gauls, Gallic, Germanic peoples, Germanic, and Celtic Britons, Brittonic trib ...
,
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil wa ...
conquered all of
Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
for Rome, and this included the Netherlands south of the
Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
. He also wrote about his experiences in his ''
Commentarii de Bello Gallico
''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' (; ), also ''Bellum Gallicum'' (), is Julius Caesar's first-hand account of the Gallic Wars, written as a third-person narrative. In it, Caesar describes the battles and intrigues that took place in the nine yea ...
'', which is the first surviving written account of the region. Caesar mentioned the
Menapii
The Menapii were a Belgic tribe dwelling near the North Sea, around present-day Cassel, during the Iron Age and the Roman period.
History
The Menapii were persistent opponents of Julius Caesar's conquest of Gaul, resisting until 54 BC. They ...
living in the river delta, and the
Eburones
The Eburones ( Greek: ) were a Gaulish- Germanic tribe dwelling in the northeast of Gaul, who lived north of the Ardennes in the region near what is now the southern Netherlands, eastern Belgium and the German Rhineland, in the period immediately ...
to their southeast towards what is now Limburg. He called the land between the Rhine and
Waal
WAAL (99.1 FM broadcasting, FM; "The Whale") is a commercial radio, commercial radio station licensed to Binghamton, New York. It airs a classic rock radio format and is owned by Townsquare Media. WAAL is the oldest FM radio station continuou ...
"the island of the Batavi" (''insula batavorum''). He portrayed the Rhine as a natural boundary between the
Gauls
The Gauls (; , ''Galátai'') were a group of Celts, Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age Europe, Iron Age and the Roman Gaul, Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). Th ...
and
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of ...
on the other side but he understood that peoples such as the Eburones had a kinship with their neighbours over the river. Later Roman authors such as
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' ( ...
and
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
describe the region north of the Rhine being inhabited by the
Frisii
The Frisii were an ancient tribe, who were neighbours of the Roman empire in the low-lying coastal region between the Rhine and the Ems (river), Ems rivers, in what what is now the northern Netherlands. They are not mentioned in Roman records af ...
,
Chamavi
The Chamavi were a Germanic people of Roman imperial times who lived just north of the Roman border () along the Rhine river delta in what is now the Netherlands, and perhaps stretching into what is now Germany.
In the Roman records of the th ...
and
Tubantes. Within the delta lived the
Cananefates
The Cananefates, or Canninefates, Caninefates, or Canenefatae, meaning 'boat masters' – or less likely, 'leek masters' – were a Germanic tribe, who lived in the Rhine delta, in western Batavia (later Betuwe), in the Roman province of ''Germ ...
,
Batavians
The Batavi were an ancient Germanic tribe that lived around the modern Dutch Rhine delta in the area that the Romans called Batavia, from the second half of the first century BC to the third century AD. The name is also applied to several mil ...
,
Sturii,
Marsacii
The Marsaci or Marsacii were a tribe in Roman imperial times, who lived within the area of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, under Roman domination. (The river Meuse is the Maas in Dutch, and this name is also often used in English. In Latin sourc ...
, and
Frisiavones
The Frisiavones (also Frisaevones or Frisaebones) were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people living near the northern border of Gallia Belgica during the early first millennium AD. Little is known about them, but they appear to have resided in the ar ...
. The
Texuandri,
Baetasii
The Baetasii (or Betasii) were a Germanic tribal grouping within the Roman province of Germania Inferior (which later became Germania Secunda). Their exact location is still unknown, although two proposals are, first, that it might be the source o ...
and
Tungri
The Tungri (or Tongri, or Tungrians) were a tribe, or group of tribes, who lived in the Belgic part of Gaul, during the times of the Roman Empire. Within the Roman Empire, their territory was called the '' Civitas Tungrorum''. They were described ...
lived south of the delta.
The 450 years of Roman rule profoundly changed the region that would later become the Netherlands. The Rhine was a militarized border, frequently destabilized by violent incursions, and Rome recruited soldiers on both sides of it. The tribes of the region were esteemed soldiers in the empire, often serving in the
Roman cavalry
Roman cavalry (Latin: ''equites Romani'') refers to the horse-mounted forces of the Roman army throughout the regal, republican, and imperial eras.
In the regal era, the Roman cavalry was a group of 300 soldiers called ''celeres'', tasked wi ...
. The frontier culture was influenced by Roman, Germanic, and Gaulish elements, and trade flourished after Rome's conquest of Gaul. There were still grievances against Roman rule, including the taking of young Batavians as
slaves
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
. This led to the
Batavian rebellion
The Revolt of the Batavi took place in the Roman province of Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") between AD 69 and 70. It was an uprising against the Roman Empire started by the Batavi (Germanic tribe), Batavi, a small but militarily powerful G ...
under
Gaius Julius Civilis
Gaius Julius Civilis (AD 25 – ) was the leader of the Batavian rebellion against the Romans in 69 AD. His Roman naming conventions, nomen shows that he (or one of his male ancestors) was made a Roman citizen (and thus, the tribe a Roman vassal) ...
in 69 AD, which resulted in the burning of several Roman
Castellum
A ''castellum'' in Latin is usually:
* a small Roman fortlet or tower,C. Julius Caesar, Gallic War; 2,30 a diminutive of (' military camp'), often used as a watchtower or signal station like on Hadrian's Wall. It is distinct from a , which ...
and the desertion of sections of the northern Roman army. In April 70 AD, legions led by
Quintus Petillius Cerialis
Quintus Petillius Cerialis Caesius Rufus ( AD 30 — after AD 83), otherwise known as Quintus Petillius Cerialis, was a Roman general and administrator who served in Britain during Boudica's rebellion and went on to participate in the civil wars ...
defeated the rebels.
The Batavians were considered the "true" forefathers of the Dutch by 17th and 18th-century writers, inspiring the naming of colonial Jakarta as "
Batavia" in 1619 and the
Batavian Republic
The Batavian Republic (; ) was the Succession of states, successor state to the Dutch Republic, Republic of the Seven United Netherlands. It was proclaimed on 19 January 1795 after the Batavian Revolution and ended on 5 June 1806, with the acce ...
of 1795. The term "Batavian" is occasionally used to describe the Dutch today, similar to how "Gallic" describes the French.
[Beyen, Marnix, "A Tribal Trinity: the Rise and Fall of the Franks, the Frisians and the Saxons in the Historical Consciousness of the Netherlands since 1850" in ''European History Quarterly'' 2000 30(4):493–532. Fulltext: EBSCO] A
Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages, a group of Low Germanic languages also commonly referred to as "Frankish" varieties
* Francia, a post-Roman ...
identity emerged in the
lower
Lower may refer to:
* ''Lower'' (album), 2025 album by Benjamin Booker
*Lower (surname)
*Lower Township, New Jersey
*Lower Receiver (firearms)
*Lower Wick
Lower Wick is a small hamlet located in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It is sit ...
and
middle
Middle or The Middle may refer to:
* Centre (geometry), the point equally distant from the outer limits.
Places
* Middle (sheading), a subdivision of the Isle of Man
* Middle Bay (disambiguation)
* Middle Brook (disambiguation)
* Middle Creek ...
Rhine valley during the first half of the 3rd century, forming a confederation of smaller
Germanic groups
[Previté-Orton, Charles, ''The Shorter Cambridge Medieval History'', vol. I, pp. 51–52, 151] including the descendants of the Batavian rebels. The Frisii probably
disappeared from the northern Netherlands with the last reference to them in c. 296, likely due to
resettlement to other areas of Roman control
and coastal flooding.
Early Middle Ages (411–1000)
Frisians

As climatic conditions improved, there was another mass migration of
Germanic peoples into the area from the east. This is known as the "
Migration Period
The Migration Period ( 300 to 600 AD), also known as the Barbarian Invasions, was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories ...
" (''Volksverhuizingen''). The northern Netherlands received an influx of new migrants and settlers, mostly
Saxons
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
, but also
Angles
Angles most commonly refers to:
*Angles (tribe), a Germanic-speaking people that took their name from the Angeln cultural region in Germany
*Angle, a geometric figure formed by two rays meeting at a common point
Angles may also refer to:
Places ...
and
Jutes
The Jutes ( ) were one of the Germanic people, Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the end of Roman rule in Britain, departure of the Roman Britain, Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic na ...
. Many of these migrants did not stay in the northern Netherlands but moved on to England and are known today as the
Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
. The newcomers who stayed in the northern Netherlands would eventually be referred to as "Frisians", although they were not descended from the ancient
Frisii
The Frisii were an ancient tribe, who were neighbours of the Roman empire in the low-lying coastal region between the Rhine and the Ems (river), Ems rivers, in what what is now the northern Netherlands. They are not mentioned in Roman records af ...
. These new Frisians settled in the northern Netherlands and would become the ancestors of the modern
Frisians
The Frisians () are an ethnic group indigenous to the German Bight, coastal regions of the Netherlands, north-western Germany and southern Denmark. They inhabit an area known as Frisia and are concentrated in the Dutch provinces of Friesland an ...
. (Because the early Frisians and Anglo-Saxons were formed from largely identical tribal confederacies, their respective languages were very similar.
Old Frisian
Old Frisian was a West Germanic language spoken between the late 13th century and the end of 16th century. It is the common ancestor of all the modern Frisian languages except for the North Frisian language#Insular North Frisian, Insular North ...
is the most closely related language to
Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
and the modern Frisian dialects are in turn the closest related languages to contemporary English.) By the end of the 6th century, the Frisian territory in the northern Netherlands had expanded west to the
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
coast and, by the 7th century, south to
Dorestad
Dorestad (''Dorestat, Duristat'') was an early medieval emporium, located in the present-day province of Utrecht in the Netherlands, close to the modern-day town of Wijk bij Duurstede.
It flourished during the 8th to early 9th centuries, as a ...
. During this period most of the northern Netherlands was known as
Frisia
Frisia () is a Cross-border region, cross-border Cultural area, cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Stretching along the Wadden Sea, it encompasses the north of the Netherlands and parts of northwestern Germany. Wider definitions of "Frisia" ...
. This extended Frisian territory is sometimes referred to as ''
Frisia Magna'' (or
Greater Frisia).

In the 7th and 8th centuries, the
Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages, a group of Low Germanic languages also commonly referred to as "Frankish" varieties
* Francia, a post-Roman ...
chronologies mention this area as the
kingdom of the Frisians. This kingdom comprised the coastal provinces of the Netherlands and the German North Sea coast. During this time, the Frisian language was spoken along the entire southern North Sea coast. The 7th-century
Frisian Kingdom
The Frisian Kingdom (; ) is a modern name for the post-Roman Frisian realm in Western Europe in the period when it was at its largest (650–734). This dominion was ruled by kings and emerged in the mid-7th century and probably ended with the ...
(650–734) under King
Aldegisel and King
Redbad Radbod, Radbot, Ratbod, Ratpot, Redbod, Redbad, Radboud, Rapoto, or sometimes just Boddo, is a Germanic masculine first name that may refer to:
*Radbod of Frisia, leader of the Frisians (died 719)
*Radbod (prefect) (833–854), Frankish prefect
*Ra ...
, had its centre of power in
Utrecht
Utrecht ( ; ; ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city of the Netherlands, as well as the capital and the most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of Utrecht (province), Utrecht. The ...
.
Dorestad was the largest settlement (
emporia) in northwestern Europe. It had grown around a former Roman fortress. It was a large, flourishing trading place, three kilometers long and situated where the rivers
Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
and
Lek diverge southeast of
Utrecht
Utrecht ( ; ; ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city of the Netherlands, as well as the capital and the most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of Utrecht (province), Utrecht. The ...
near the modern town of
Wijk bij Duurstede
Wijk bij Duurstede () is a Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality and a city in the central Netherlands.
Population centres
*Cothen
*Langbroek
*Wijk bij Duurstede
Topography
''Dutch Topographic map of the municipality of Wijk bij Du ...
.
Although inland, it was a North Sea trading centre that primarily handled goods from the Middle
Rhineland
The Rhineland ( ; ; ; ) is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly Middle Rhine, its middle section. It is the main industrial heartland of Germany because of its many factories, and it has historic ties to the Holy ...
.
Wine was among the major products traded at Dorestad, likely from vineyards south of
Mainz
Mainz (; #Names and etymology, see below) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, and with around 223,000 inhabitants, it is List of cities in Germany by population, Germany's 35th-largest city. It lies in ...
.
It was also widely known because of its
mint
Mint or The Mint may refer to:
Plants
* Lamiaceae, the mint family
** ''Mentha'', the genus of plants commonly known as "mint"
Coins and collectibles
* Mint (facility), a facility for manufacturing coins
* Mint condition, a state of like-new ...
. Between 600 and around 719 Dorestad was often fought over between the Frisians and the Franks.
Franks

After
Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
government in the area collapsed, the
Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
expanded their territories until there were numerous small Frankish kingdoms, especially at
Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
,
Tournai
Tournai ( , ; ; ; , sometimes Anglicisation (linguistics), anglicised in older sources as "Tournay") is a city and Municipalities in Belgium, municipality of Wallonia located in the Hainaut Province, Province of Hainaut, Belgium. It lies by ...
,
Le Mans
Le Mans (; ) is a Communes of France, city in Northwestern France on the Sarthe (river), Sarthe River where it meets the Huisne. Traditionally the capital of the Provinces of France, province of Maine (province), Maine, it is now the capital of ...
and
Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; ; ), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Escaut river.
A sub-pref ...
.
[Milis, L.J.R., "A Long Beginning: The Low Countries Through the Tenth Century" in J.C.H. Blom & E. Lamberts ''History of the Low Countries'', pp. 6–18, Berghahn Books, 1999. .] The kings of Tournai eventually came to subdue the other Frankish kings. By the 490s,
Clovis I
Clovis (; reconstructed Old Frankish, Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first List of Frankish kings, king of the Franks to unite all of the Franks under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a ...
had conquered and united all the Frankish territories to the west of the
Meuse
The Meuse or Maas is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a total length of .
History
From 1301, the upper ...
, including those in the southern Netherlands. He continued his conquests into
Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
.
After the death of
Clovis I
Clovis (; reconstructed Old Frankish, Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first List of Frankish kings, king of the Franks to unite all of the Franks under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a ...
in 511, his four sons partitioned his kingdom amongst themselves, with
Theuderic I
__NOTOC__
Theuderic I ( 487 – 534) was the Merovingian king of Metz, Rheims, or Austrasia—as it is variously called—from 511 to 534.
He was the son of Clovis I and one of his earlier wives or concubines (possibly a Franco-Rhenish Pr ...
receiving the lands that were to become Austrasia (including the southern Netherlands). A line of kings descended from Theuderic ruled
Austrasia
Austrasia was the northeastern kingdom within the core of the Francia, Frankish Empire during the Early Middle Ages, centring on the Meuse, Middle Rhine and the Moselle rivers. It included the original Frankish-ruled territories within what had ...
until 555, when it was united with the other Frankish kingdoms of
Chlothar I
Chlothar I, sometime called "the Old" (French: le Vieux), (died December 561) also anglicised as Clotaire from the original French version, was a king of the Franks of the Merovingian dynasty and one of the four sons of Clovis I.
With his eldes ...
, who inherited all the Frankish realms by 558. He redivided the Frankish territory amongst his four sons, but the four kingdoms coalesced into three on the death of
Charibert I
Charibert I (; ; 517 – December 567) was the Merovingian King of Paris, the second-eldest son of Chlothar I and his first wife Ingund. His elder brother Gunthar died sometime before their father's death. He shared in the partition of the Fran ...
in 567. Austrasia (including the southern Netherlands) was given to
Sigebert I
Sigebert I ( 535 – 575) was a Frankish king of Austrasia from the death of his father in 561 to his own death. He was the third surviving son out of four of Clotaire I and Ingund. His reign found him mostly occupied with a successful civil ...
. The southern Netherlands remained the northern part of
Austrasia
Austrasia was the northeastern kingdom within the core of the Francia, Frankish Empire during the Early Middle Ages, centring on the Meuse, Middle Rhine and the Moselle rivers. It included the original Frankish-ruled territories within what had ...
until the rise of the
Carolingians
The Carolingian dynasty ( ; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charles Martel and his grandson Charlemagne, descendants of the Arnulfing and Pippinid ...
.
The Franks who expanded south into
Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
settled there and eventually adopted the
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Colloquial, Popular, Spoken or Vernacular Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. ''Vulgar Latin'' a ...
of the local population.
However, a Germanic language was spoken as a second tongue by public officials in western
Austrasia
Austrasia was the northeastern kingdom within the core of the Francia, Frankish Empire during the Early Middle Ages, centring on the Meuse, Middle Rhine and the Moselle rivers. It included the original Frankish-ruled territories within what had ...
and
Neustria
Neustria was the western part of the Kingdom of the Franks during the Early Middle Ages, in contrast to the eastern Frankish kingdom, Austrasia. It initially included land between the Loire and the Silva Carbonaria, in the north of present-day ...
as late as the 850s. It completely disappeared as a spoken language from these regions during the 10th century. During this expansion to the south, many Frankish people remained in the north (i.e. southern Netherlands, Flanders and a small part of northern France). A widening cultural divide grew between the Franks remaining in the north and the rulers far to the south in what is now France.
Salian Franks continued to reside in their original homeland and the area directly to the south and to speak their original language,
Old Frankish
Frankish ( reconstructed endonym: *), also known as Old Franconian or Old Frankish, was the West Germanic language spoken by the Franks from the 5th to 10th centuries.
Franks under king Chlodio settled in Roman Gaul in the 5th century. O ...
, which by the 9th century had evolved into
Old Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch ( Modern Dutch: ') or Old Low Franconian (Modern Dutch: ') is the set of dialects that evolved from Frankish spoken in the Low Countries during the Early Middle Ages, from around the 6th Page 55: "''Uit de zesde eeu ...
.
A Dutch-French language boundary came into existence (but this was originally south of where it is today).
In the Maas and Rhine areas of the Netherlands, the Franks had political and trading centres, especially at
Nijmegen
Nijmegen ( , ; Nijmeegs: ) is the largest city in the Dutch province of Gelderland and the ninth largest of the Netherlands as a whole. Located on the Waal River close to the German border, Nijmegen is one of the oldest cities in the ...
and
Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; ; ; ) is a city and a Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital city, capital and largest city of the province of Limburg (Netherlands), Limburg. Maastricht is loca ...
.
These Franks remained in contact with the Frisians to the north, especially in places like
Dorestad
Dorestad (''Dorestat, Duristat'') was an early medieval emporium, located in the present-day province of Utrecht in the Netherlands, close to the modern-day town of Wijk bij Duurstede.
It flourished during the 8th to early 9th centuries, as a ...
and
Utrecht
Utrecht ( ; ; ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city of the Netherlands, as well as the capital and the most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of Utrecht (province), Utrecht. The ...
.
Doubts over archaeological divisions

In the 19th century, Dutch historians believed that the Franks, Frisians, and Saxons had populated and inhabited the Low Countries, but this theory fell out of favour in the 20th century.
Due to the scarcity of written sources, knowledge of this period depends to a large degree on the interpretation of archaeological data. The traditional view of a clear-cut division between Frisians in the north and coast,
Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
in the south and
Saxons
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
in the east has proven historically problematic. Archeological evidence suggests dramatically different models for different regions, with demographic continuity for some parts of the country and depopulation and possible replacement in other parts, notably the coastal areas of Frisia and Holland.
Emergence of the Dutch language
The language from which
Old Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch ( Modern Dutch: ') or Old Low Franconian (Modern Dutch: ') is the set of dialects that evolved from Frankish spoken in the Low Countries during the Early Middle Ages, from around the 6th Page 55: "''Uit de zesde eeu ...
arose is unknown with certainty, but it is thought to be the language spoken by the
Salian Franks
The Salian Franks, or Salians, sometimes referred to using the Latin word or , were a Frankish people who lived in what was is now the Netherlands in the fourth century. They are only mentioned under this name in historical records relating to ...
. Even though the Franks are traditionally categorized as
Weser–Rhine Germanic, Dutch has a number of
Ingvaeonic
North Sea Germanic, also known as Ingvaeonic ( ), is a subgrouping of West Germanic languages that consists of Old Frisian, Old English, and Old Saxon, and their descendants. These languages share a number of commonalities, such as a single pl ...
characteristics and is classified by modern linguists as an Ingvaeonic language. Dutch also has a number of
Old Saxon
Old Saxon (), also known as Old Low German (), was a Germanic language and the earliest recorded form of Low German (spoken nowadays in Northern Germany, the northeastern Netherlands, southern Denmark, the Americas and parts of Eastern Eur ...
characteristics. There was a close relationship between Old Dutch, Old Saxon,
Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
and
Old Frisian
Old Frisian was a West Germanic language spoken between the late 13th century and the end of 16th century. It is the common ancestor of all the modern Frisian languages except for the North Frisian language#Insular North Frisian, Insular North ...
. Because texts written in the language spoken by the Franks are almost non-existent, and Old Dutch texts scarce and fragmentary, not much is known about the development of Old Dutch. Old Dutch made the transition to
Middle Dutch
Middle Dutch is a collective name for a number of closely related West Germanic dialects whose ancestor was Old Dutch. It was spoken and written between 1150 and 1500. Until the advent of Modern Dutch after 1500 or , there was no overarching sta ...
around 1150.
Christianization
The Christianity that arrived in the Netherlands with the Romans appears not to have died out completely (in
Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; ; ; ) is a city and a Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital city, capital and largest city of the province of Limburg (Netherlands), Limburg. Maastricht is loca ...
, at least) after the withdrawal of the Romans in about 411.
The
Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
became Christians after their king
Clovis I
Clovis (; reconstructed Old Frankish, Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first List of Frankish kings, king of the Franks to unite all of the Franks under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a ...
converted to Catholicism, an event which is traditionally set in 496. Christianity was introduced in the north after the conquest of
Friesland
Friesland ( ; ; official ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia (), named after the Frisians, is a Provinces of the Netherlands, province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen (p ...
by the Franks. The
Saxons
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
in the east were converted before the conquest of
Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
, and became Frankish allies.
Hiberno-Scottish and
Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
missionaries, particularly
Willibrord
Willibrord (; 658 – 7 November AD 739) was an Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon monk, bishop, and missionary. He became the first Diocese of Utrecht (695–1580), Bishop of Utrecht in what is now the Netherlands, dying at Echternach in Luxembourg, and ...
,
Wulfram and
Boniface
Boniface, OSB (born Wynfreth; 675 –5 June 754) was an English Benedictine monk and leading figure in the Anglo-Saxon mission to the Germanic parts of Francia during the eighth century. He organised significant foundations of the church i ...
, played an important role in converting the Frankish and Frisian peoples to Christianity by the 8th century. Boniface was martyred by the Frisians in
Dokkum
Dokkum is a Dutch fortified city in the municipality of Noardeast-Fryslân in the province of Friesland. It has 12,669 inhabitants (February 8, 2020). The fortifications of Dokkum are well preserved and are known as the ''bolwerken'' (bulwarks) ...
(754).
Frankish dominance and incorporation into the Holy Roman Empire

In the early 8th century the Frisians came increasingly into conflict with the
Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
to the south, resulting in a
series of wars in which the
Frankish Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lomba ...
eventually subjugated Frisia. In 734, at the
Battle of the Boarn
The Battle of the Boarn (; ) or Battle by Jirnsum was an 8th century battle between the Franks and the Frisians near the mouth of the river Boarn in what is now Jirnsum in the Dutch province of Friesland.
Battle
In 734 a Frankish army comm ...
, the Frisians in the Netherlands were defeated by the Franks, who thereby conquered the area west of the
Lauwers
The Lauwers () is a river in the Netherlands. It forms part of the border between the provinces of Friesland and Groningen. From the 730s to Widukind's defeat in 785, it was part of the border of the Frankish Empire.
The former Lauwerszee an ...
. The Franks then conquered the area east of the Lauwers in 785 when
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
defeated
Widukind
Widukind, also known as Wittekind and Wittikund, was a leader of the Saxons and the chief opponent of the Frankish king Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 777 to 785. Charlemagne ultimately prevailed, organized Saxony as a Frankish provinc ...
.
The linguistic descendants of the Franks, the modern
Dutch -speakers of the
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
and
Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
, seem to have broken with the
endonym
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate them ...
"Frank" around the 9th century. By this time Frankish identity had changed from an ethnic identity to a national identity, becoming localized and confined to the modern ''
Franconia
Franconia ( ; ; ) is a geographical region of Germany, characterised by its culture and East Franconian dialect (). Franconia is made up of the three (governmental districts) of Lower Franconia, Lower, Middle Franconia, Middle and Upper Franco ...
'' and principally to the French province of ''
Île-de-France
The Île-de-France (; ; ) is the most populous of the eighteen regions of France, with an official estimated population of 12,271,794 residents on 1 January 2023. Centered on the capital Paris, it is located in the north-central part of the cou ...
''.
Although the people no longer referred to themselves as "Franks", the Netherlands was still part of the Frankish empire of Charlemagne. Indeed, because of the Austrasian origins of the Carolingians in the area between the Rhine and the Maas, the cities of Aachen, Maastricht, Liège and Nijmegen were at the heart of Carolingian culture.
Charlemagne maintained his ''palatium'' in
Nijmegen
Nijmegen ( , ; Nijmeegs: ) is the largest city in the Dutch province of Gelderland and the ninth largest of the Netherlands as a whole. Located on the Waal River close to the German border, Nijmegen is one of the oldest cities in the ...
at least four times.
The
Carolingian empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Franks, Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as List of Frankish kings, kings of the Franks since ...
would eventually include France, Germany, northern Italy and much of Western Europe. In 843, the Frankish empire was divided into three parts, giving rise to
West Francia
In medieval historiography, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () constitutes the initial stage of the Kingdom of France and extends from the year 843, from the Treaty of Verdun, to 987, the beginning of the Capet ...
in the west,
East Francia
East Francia (Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire created in 843 and ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was established through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the for ...
in the east, and
Middle Francia
Middle Francia () was a short-lived Frankish kingdom which was created in 843 by the Treaty of Verdun after an intermittent civil war between the grandsons of Charlemagne resulted in division of the united empire. Middle Francia was allocated ...
in the centre. Most of what is today the Netherlands became part of Middle Francia; Flanders became part of West Francia. This division was an important factor in the historical distinction between Flanders and the other Dutch-speaking areas.
Middle Francia () was an ephemeral
Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages, a group of Low Germanic languages also commonly referred to as "Frankish" varieties
* Francia, a post-Roman ...
kingdom that had no historical or ethnic identity to bind its varied peoples. It was created by the
Treaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun (; ), agreed to on 10 August 843, ended the Carolingian civil war and divided the Carolingian Empire between Lothair I, Louis the German, Louis II and Charles the Bald, Charles II, the surviving sons of the emperor Louis the ...
in 843, which divided the Carolingian Empire among the sons of
Louis the Pious
Louis the Pious (; ; ; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and Holy Roman Emperor, co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aquitaine from 781. As the only ...
. Situated between the realms of East and West Francia, Middle Francia comprised the Frankish territory between the rivers Rhine and
Scheldt
The Scheldt ( ; ; ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of Netherlands, the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corresponding to Old Englis ...
, the
Frisia
Frisia () is a Cross-border region, cross-border Cultural area, cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Stretching along the Wadden Sea, it encompasses the north of the Netherlands and parts of northwestern Germany. Wider definitions of "Frisia" ...
n coast of the
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
, the former
Kingdom of Burgundy
Kingdom of Burgundy was a name given to various successive Monarchy, kingdoms centered in the historical region of Burgundy during the Middle Ages. The heartland of historical Burgundy correlates with the border area between France and Switze ...
(except for a western portion, later known as
''Bourgogne''),
Provence
Provence is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which stretches from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the France–Italy border, Italian border to the east; it is bordered by the Mediterrane ...
and the
Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
.
Middle Francia fell to
Lothair I
Lothair I (9th. C. Frankish: ''Ludher'' and Medieval Latin: ''Lodharius''; Dutch and Medieval Latin: ''Lotharius''; German: ''Lothar''; French: ''Lothaire''; Italian: ''Lotario''; 795 – 29 September 855) was a 9th-century emperor of the ...
, the eldest son and successor of
Louis the Pious
Louis the Pious (; ; ; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and Holy Roman Emperor, co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aquitaine from 781. As the only ...
, after an intermittent civil war with his younger brothers
Louis the German
Louis the German (German language, German: ''Ludwig der Deutsche''; c. 806/810 – 28 August 876), also known as Louis II of Germany (German language, German: ''Ludwig II. von Deutschland''), was the first king of East Francia, and ruled from 8 ...
and
Charles the Bald
Charles the Bald (; 13 June 823 – 6 October 877), also known as CharlesII, was a 9th-century king of West Francia (843–877), King of Italy (875–877) and emperor of the Carolingian Empire (875–877). After a series of civil wars during t ...
. In acknowledgement of Lothair's
Imperial title, Middle Francia contained the imperial cities of
Aachen
Aachen is the List of cities in North Rhine-Westphalia by population, 13th-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, 27th-largest city of Germany, with around 261,000 inhabitants.
Aachen is locat ...
, the residence of Charlemagne, as well as Rome. In 855, on his deathbed at
Prüm Abbey
Prüm Abbey is a former Order of Saint Benedict, Benedictine abbey in Prüm, now in the diocese of Trier (Germany), founded by the Franks, Frankish widow Bertrada of Prüm, Bertrada the elder and her son Caribert of Laon, Charibert, Count of Laon, ...
, Emperor Lothair I again partitioned his realm amongst his sons. Most of the lands north of the
Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
, including the Netherlands, passed to
Lothair II
Lothair II (835 – 8 August 869) was a Carolingian king and ruler of northern parts of Middle Francia, that came to be known as Lotharingia, reigning there from 855 until his death in 869. He also ruled over Burgundy, holding from 855 just th ...
and consecutively were named
Lotharingia
Lotharingia was a historical region and an early medieval polity that existed during the late Carolingian and early Ottonian era, from the middle of the 9th to the middle of the 10th century. It was established in 855 by the Treaty of Prüm, a ...
. After Lothair II died in 869, Lotharingia was partitioned by his uncles Louis the German and Charles the Bald in the
Treaty of Meerssen
The Treaty of Mersen or Meerssen, concluded on 8 August 870, was a treaty to partition the realm of Lothair II, known as Lotharingia, by his uncles Louis the German of East Francia and Charles the Bald of West Francia, the two surviving sons of ...
in 870. Although some of the Netherlands had come under Viking control, in 870 it technically became part of East Francia, which became the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
in 962.
Viking raids
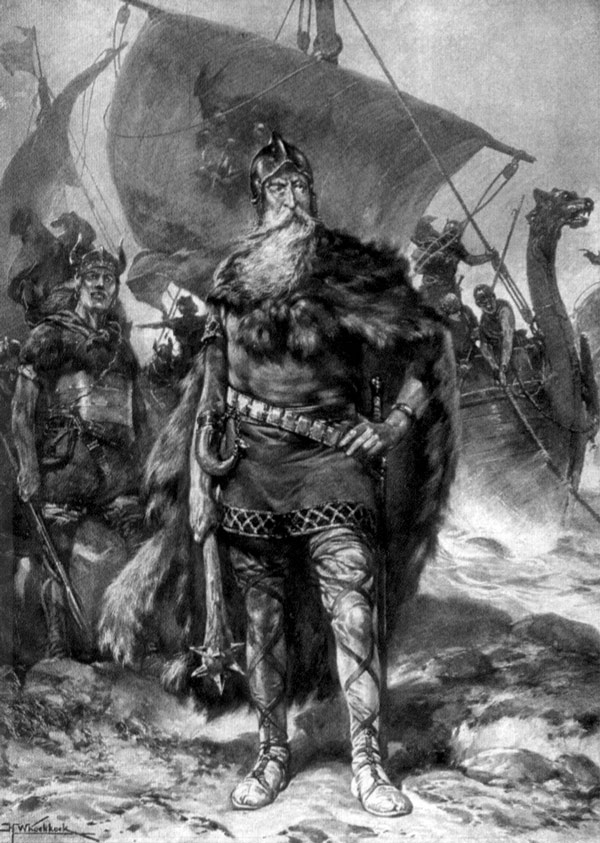

In the 9th and 10th centuries, the Vikings raided the largely defenceless Frisian and
Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages, a group of Low Germanic languages also commonly referred to as "Frankish" varieties
* Francia, a post-Roman ...
towns lying on the coast and along the rivers of the
Low Countries
The Low Countries (; ), historically also known as the Netherlands (), is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower Drainage basin, basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting today of the three modern "Bene ...
. Although Vikings never settled in large numbers in those areas, they did set up long-term bases and were even acknowledged as lords in a few cases. In Dutch and Frisian historical tradition, the trading centre of
Dorestad
Dorestad (''Dorestat, Duristat'') was an early medieval emporium, located in the present-day province of Utrecht in the Netherlands, close to the modern-day town of Wijk bij Duurstede.
It flourished during the 8th to early 9th centuries, as a ...
declined after Viking raids from 834 to 863; however, since no convincing Viking archaeological evidence has been found at the site (as of 2007), doubts about this have grown in recent years.
One of the most important Viking families in the Low Countries was that of
Rorik of Dorestad
Rorik (, ; ; – ) was a Danish Viking, who ruled over parts of Friesland between 841 and 873, conquering Dorestad and Utrecht in 850. Rorik swore allegiance to Louis the German in 873. He was born in Denmark around 800. He died at some point ...
(based in
Wieringen
Wieringen () is located in the province of North Holland in the Netherlands. Now a part of the municipality of Hollands Kroon, it was a separate municipality before 2012. Its name first appeared in 8th and 9th century records. By 1200 it was an i ...
) and his brother the "younger Harald" (based in
Walcheren
Walcheren () is a region and former island in the Dutch province of Zeeland at the mouth of the Scheldt estuary. It lies between the Eastern Scheldt in the north and the Western Scheldt in the south and is roughly the shape of a rhombus. The two ...
), both thought to be nephews of
Harald Klak
Harald 'Klak' Halfdansson (c. 785 – c. 852) was a king in Jutland (and possibly other parts of Denmark) around 812–814 and again from 819–827."Carolingian Chronicles: Royal Frankish Annals and Nithard's Histories" (1970), translation by Bernh ...
. Around 850,
Lothair I
Lothair I (9th. C. Frankish: ''Ludher'' and Medieval Latin: ''Lodharius''; Dutch and Medieval Latin: ''Lotharius''; German: ''Lothar''; French: ''Lothaire''; Italian: ''Lotario''; 795 – 29 September 855) was a 9th-century emperor of the ...
acknowledged Rorik as ruler of most of Friesland. And again in 870, Rorik was received by
Charles the Bald
Charles the Bald (; 13 June 823 – 6 October 877), also known as CharlesII, was a 9th-century king of West Francia (843–877), King of Italy (875–877) and emperor of the Carolingian Empire (875–877). After a series of civil wars during t ...
in
Nijmegen
Nijmegen ( , ; Nijmeegs: ) is the largest city in the Dutch province of Gelderland and the ninth largest of the Netherlands as a whole. Located on the Waal River close to the German border, Nijmegen is one of the oldest cities in the ...
, to whom he became a vassal. Viking raids continued during that period. Harald's son Rodulf and his men were killed by the people of
Oostergo
Eastergoa (also Ostergau, Ostergo, or Oostergo) was one of the Seven Sealands and one of the three ''gau (territory), Gaue'' within what is today the province of Friesland in the Netherlands.
Area
On its west side Eastergoa was bordered by ...
in 873. Rorik died sometime before 882.
Buried Viking treasures consisting mainly of silver have been found in the Low Countries. Two such treasures have been found in Wieringen. A large treasure found in Wieringen in 1996 dates from around 850 and is thought perhaps to have been connected to Rorik. The burial of such a valuable treasure is seen as an indication that there was a permanent settlement in Wieringen.
Around 879, Godfrid arrived in Frisian lands as the head of a large force that terrorised the Low Countries. Using
Ghent
Ghent ( ; ; historically known as ''Gaunt'' in English) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the Provinces of Belgium, province ...
as his base, they ravaged Ghent,
Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; ; ; ) is a city and a Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital city, capital and largest city of the province of Limburg (Netherlands), Limburg. Maastricht is loca ...
,
Liège
Liège ( ; ; ; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and Municipalities in Belgium, municipality of Wallonia, and the capital of the Liège Province, province of Liège, Belgium. The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east o ...
,
Stavelot
Stavelot (; ; ) is a town and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Liège, Belgium.
The municipality consists of the following districts: Francorchamps and Stavelot.
It is best known as the home of Spa-Francorchamps Circuit a ...
,
Prüm
Prüm () is a town in the Westeifel (Rhineland-Palatinate), Germany. Formerly a district capital, today it is the administrative seat of the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' ("collective municipality") Prüm (Verbandsgemeinde), Prüm.
Geography
Prüm lies o ...
,
Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
, and
Koblenz
Koblenz ( , , ; Moselle Franconian language, Moselle Franconian: ''Kowelenz'') is a German city on the banks of the Rhine (Middle Rhine) and the Moselle, a multinational tributary.
Koblenz was established as a Roman Empire, Roman military p ...
. Controlling most of Frisia between 882 and his death in 885, Godfrid became known to history as
Godfrid, Duke of Frisia. His lordship over Frisia was acknowledged by
Charles the Fat
Charles the Fat (839 – 13 January 888) was the emperor of the Carolingian Empire from 881 to 887. A member of the Carolingian dynasty, Charles was the youngest son of Louis the German and Hemma, and a great-grandson of Charlemagne. He was t ...
, to whom he became a vassal. Godfried was assassinated in 885, after which
Gerolf of Holland assumed lordship and Viking rule of Frisia came to an end.
Viking raids of the Low Countries continued for over a century. Remains of Viking attacks dating from 880 to 890 have been found in
Zutphen
Zutphen () is a city and municipality located in the province of Gelderland, Netherlands. It lies some northeast of Arnhem, on the eastern bank of the river IJssel at the point where it is joined by the Berkel. First mentioned in the 11th centur ...
and
Deventer
Deventer (; Sallaans dialect, Sallands: ) is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Salland historical region of the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of Overijssel, ...
. In 920, King
Henry
Henry may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Henry (given name), including lists of people and fictional characters
* Henry (surname)
* Henry, a stage name of François-Louis Henry (1786–1855), French baritone
Arts and entertainmen ...
of Germany liberated
Utrecht
Utrecht ( ; ; ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city of the Netherlands, as well as the capital and the most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of Utrecht (province), Utrecht. The ...
. According to a number of chronicles, the last attacks took place in the first decade of the 11th century and were directed at
Tiel
Tiel () is a Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality and a town in the middle of the Netherlands. The town is enclosed by the Waal (river), Waal river and the Linge river to the South and the North, and the Amsterdam-Rhine Canal to the Eas ...
and/or
Utrecht
Utrecht ( ; ; ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city of the Netherlands, as well as the capital and the most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of Utrecht (province), Utrecht. The ...
.
These Viking raids occurred about the same time that French and German lords were fighting for supremacy over the middle empire that included the Netherlands, so their sway over this area was weak. Resistance to the Vikings, if any, came from local nobles, who gained in stature as a result.
High and Late Middle Ages (1000–1433)
Part of the Holy Roman Empire
The German kings and emperors ruled the Netherlands in the 10th and 11th century, with the assistance of the
Dukes of Lotharingia, and the bishops of Utrecht and Liège. Germany was called the Holy Roman Empire after the coronation of
King Otto the Great as emperor. The Dutch city of
Nijmegen
Nijmegen ( , ; Nijmeegs: ) is the largest city in the Dutch province of Gelderland and the ninth largest of the Netherlands as a whole. Located on the Waal River close to the German border, Nijmegen is one of the oldest cities in the ...
used to be the spot of an important domain of the German emperors. Several German emperors were born and died there, including for example
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
empress
Theophanu
Theophanu Skleraina (; also ''Theophania'', ''Theophana'', ''Theophane'' or ''Theophano''; Medieval Greek ; AD 955 15 June 991) was empress of the Holy Roman Empire by marriage to Emperor Otto II, and regent of the Empire during the minority ...
, who died in Nijmegen. Utrecht was also an important city and trading port at the time.
Political disunity

The Holy Roman Empire was not able to maintain political unity. In addition to the growing independence of the towns, local rulers turned their counties and duchies into private kingdoms and felt little sense of obligation to the emperor who reigned over large parts of the nation in name only. Large parts of what now comprise the Netherlands were governed by the Count of Holland, the Duke of
Gelre
The Duchy of Guelders (; ; ) is a historical duchy, previously county, of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the Low Countries.
Geography
The duchy was named after the town of Geldern (''Gelder'') in present-day Germany. Though the present pro ...
, the Duke of Brabant and the Bishop of Utrecht.
Friesland
Friesland ( ; ; official ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia (), named after the Frisians, is a Provinces of the Netherlands, province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen (p ...
and
Groningen
Groningen ( , ; ; or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen (province), Groningen province in the Netherlands. Dubbed the "capital of the north", Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of ...
in the north maintained their independence and were governed by the lower nobility.
The various feudal states were in a state of almost continual war.
Gelre
The Duchy of Guelders (; ; ) is a historical duchy, previously county, of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the Low Countries.
Geography
The duchy was named after the town of Geldern (''Gelder'') in present-day Germany. Though the present pro ...
and Holland fought for control of
Utrecht
Utrecht ( ; ; ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city of the Netherlands, as well as the capital and the most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of Utrecht (province), Utrecht. The ...
. Utrecht, whose bishop had in 1000 ruled over half of what is today the Netherlands, was marginalised as it experienced continuing difficulty in electing new bishops. At the same time, the dynasties of neighbouring states were more stable. Groningen,
Drenthe
Drenthe () is a province of the Netherlands located in the northeastern part of the country. It is bordered by Overijssel to the south, Friesland to the west, Groningen to the north, and the German state of Lower Saxony to the east. As of Jan ...
and most of Gelre, which used to be part of Utrecht, became independent. Brabant tried to conquer its neighbours, but was not successful. Holland also tried to assert itself in Zeeland and Friesland, but its attempts failed.
The Frisians
The language and culture of most of the people who lived in the area that is now Holland were originally
Frisia
Frisia () is a Cross-border region, cross-border Cultural area, cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Stretching along the Wadden Sea, it encompasses the north of the Netherlands and parts of northwestern Germany. Wider definitions of "Frisia" ...
n. The sparsely populated area was known as "West Friesland" (''Westfriesland''). A common theory states that Frankish migration from either Flanders, Utrecht or both displaced the Frisians in Holland, however no evidence has been found in support of this theory and more recent studies have suggested that Frisians from the mouth of the Rhine adopted the Franconian language, feudal system and religion,
spreading this new 'Hollandic' identity northward over the centuries (the part of North Holland situated north of
Alkmaar
Alkmaar () is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Netherlands, located in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of North Holland. Alkmaar is well known fo ...
is still colloquially known as West Friesland).
The rest of
Friesland
Friesland ( ; ; official ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia (), named after the Frisians, is a Provinces of the Netherlands, province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen (p ...
in the north continued to maintain its independence during this time. It had its own institutions (collectively called the "
Frisian freedom") and resented the imposition of the feudal system and the patriciate found in other European towns. They regarded themselves as allies of Switzerland. The Frisian battle cry was "better dead than a slave". They later lost their independence when they were defeated in 1498 by the German
Landsknecht
The (singular: , ), also rendered as Landsknechts or Lansquenets, were German mercenaries used in pike and shot formations during the early modern period. Consisting predominantly of pikemen and supporting foot soldiers, their front line was ...
mercenaries of
Duke Albrecht of Saxony-Meissen.
The rise of Holland

The center of power in these emerging independent territories was in the
County of Holland
The County of Holland was a Imperial State, state of the Holy Roman Empire from its inception until 1433. From 1433 onward it was part of the Burgundian Netherlands, from 1482 part of the Habsburg Netherlands and from 1581 onward the leading pro ...
. Originally granted as a fief to the Danish chieftain
Rorik in return for loyalty to the emperor in 862, the region of
Kennemara (the region around modern
Haarlem
Haarlem (; predecessor of ''Harlem'' in English language, English) is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Netherlands. It is the capital of the Provinces of the Nether ...
) rapidly grew under Rorik's descendants in size and importance. By the early 11th century,
Dirk III, Count of Holland
Dirk III (also called ''Dirik'' or ''Theodoric'') was the count with jurisdiction over what would become the county of Holland, often referred to in this period as "West Frisia", from 993 to 27 May 1039. Until 1005, this was under regency of his ...
was levying tolls on the Meuse estuary and was able to resist military intervention from his overlord, the Duke of Lower Lorraine.
In 1083, the name "Holland" first appears in a deed referring to a region corresponding more or less to the current province of South Holland and the southern half of what is now North Holland. Holland's influence continued to grow over the next two centuries. The
counts of Holland
The counts of Holland ruled over the County of Holland in the Low Countries between the 10th and the 16th century.
The Frisian origins
While the Frisian kingdom had comprised most of the present day Netherlands, the later province of Friesland ...
conquered most of
Zeeland
Zeeland (; ), historically known in English by the Endonym and exonym, exonym Zealand, is the westernmost and least populous province of the Netherlands. The province, located in the southwest of the country, borders North Brabant to the east ...
but it was not until 1289 that Count
Floris V
Floris V (24 June 1254 – 27 June 1296) reigned as Count of Holland and Zeeland from 1256 until 1296. His life was documented in detail in the Rijmkroniek by Melis Stoke, his chronicler. He is credited with a mostly peaceful reign, modern ...
was able to subjugate the Frisians in West Friesland (that is, the northern half of North Holland).
Expansion and growth
Around 1000 C.E. there were several agricultural developments (described sometimes as an agricultural revolution) that resulted in an increase in production, especially food production. The economy started to develop at a fast pace, and the higher productivity allowed workers to farm more land or to become tradesmen.
Draining of low-lying swampy areas and flood control was expanded significantly after 1200 CE. Before that, towns were built north of the major rivers, Utrecht, Kampen, Deventer, Zwolle, Nijmegen, and Zutphen, but with the expansion of dikes and drainage, cultivable land was created and population expanded. In this period, Holland expanded relative to the other regions. From the thirteenth century onwards, the necessity of controlling water in this northern was a given, transforming the physical environment, but also requiring institutions and cooperation between areas for water management. Drainage boards (''heemraadschappen'') were established and the "dike count", took on responsibilities not only for water management issues, but also fiscal, policing, and judicial functions. By the end of the thirteenth century, Holland emerged in the dominant position of the northern region.
The southern Low Countries remained highly populous and developed and was among the most highly urbanized areas in Europe. Because of the east–west flow of the Low Countries' large rivers, they were a military and political barrier between north and south. The southern Low Countries could not exert influence over the north. This division meant that the counts of Holland became politically important in the north. Holland extended its political power over Zeeland.
Guilds
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular territory. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradespeople belonging to a professional association. They so ...
were established and markets developed as production exceeded local needs. Also, the introduction of currency made trading a much easier affair than it had been before. Existing towns grew and new towns sprang into existence around
monasteries
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone ( hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which m ...
and
castles
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars usually consider a ''castle'' to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble. This i ...
, and a mercantile middle class began to develop in these urban areas. Commerce and town development increased as the population grew.
The
Crusade
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding t ...
s were popular in the Low Countries and drew many to fight in the
Holy Land
The term "Holy Land" is used to collectively denote areas of the Southern Levant that hold great significance in the Abrahamic religions, primarily because of their association with people and events featured in the Bible. It is traditionall ...
. At home, there was relative peace. Viking pillaging had stopped. Both the Crusades and the relative peace at home contributed to trade and the growth in commerce.
Cities arose and flourished, especially in
Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
and
Brabant. As the cities grew in wealth and power, they started to buy certain privileges for themselves from the
sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title that can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to ...
, including
city rights
Town privileges or borough rights were important features of European towns during most of the second millennium. The city law customary in Central Europe probably dates back to Italian models, which in turn were oriented towards the tradition ...
, the right to self-government and the right to pass laws. In practice, this meant that the wealthiest cities became quasi-independent republics in their own right. Two of the most important cities were
Bruges
Bruges ( , ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the province of West Flanders, in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is in the northwest of the country, and is the sixth most populous city in the country.
The area of the whole city amoun ...
and
Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after ...
(in
Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
) which would later develop into some of the most important cities and ports in Europe.
Hook and Cod Wars
The
Hook and Cod Wars
The Hook and Cod wars (; sometimes semi-anglicised as the wars of the Hoecks and the Cabbeljaws) comprise a series of wars and battles in the County of Holland between 1350 and 1490. Most of these wars were fought over who should hold the title ...
() were a series of wars and battles in the
County of Holland
The County of Holland was a Imperial State, state of the Holy Roman Empire from its inception until 1433. From 1433 onward it was part of the Burgundian Netherlands, from 1482 part of the Habsburg Netherlands and from 1581 onward the leading pro ...
between 1350 and 1490. Most of these wars were fought over the title of
count of Holland
The counts of Holland ruled over the County of Holland in the Low Countries between the 10th and the 16th century.
The Frisian origins
While the Frisian kingdom had comprised most of the present day Netherlands, the later province of Friesland ...
, but some have argued that the underlying reason was because of the power struggle of the traders in the cities against the ruling nobility.
The Cod faction generally consisted of the more progressive cities of
Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former provinces of the Netherlands, province on the western coast of the Netherland ...
. The Hook faction consisted for a large part of the conservative noblemen. Some of the main figures in this multi-generational conflict were
William IV
William IV (William Henry; 21 August 1765 – 20 June 1837) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from 26 June 1830 until his death in 1837. The third son of George III, William succeeded hi ...
,
Margaret
Margaret is a feminine given name, which means "pearl". It is of Latin origin, via Ancient Greek and ultimately from Iranian languages, Old Iranian. It has been an English language, English name since the 11th century, and remained popular thro ...
,
William V William V may refer to:
* William V, Duke of Aquitaine (969–1030)
* William V of Montpellier (1075–1121)
* William V, Marquess of Montferrat (1191)
* William V, Count of Nevers (before 11751181)
* William V, Duke of Jülich (1299–1361)
* Will ...
,
William VI, Count of Holland and Hainaut,
John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second E ...
and
Philip the Good
Philip III the Good (; ; 31 July 1396 – 15 June 1467) ruled as Duke of Burgundy from 1419 until his death in 1467. He was a member of a cadet line of the Valois dynasty, to which all 15th-century kings of France belonged. During his reign, ...
,
Duke of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy () was a title used by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, from its establishment in 843 to its annexation by the Crown lands of France, French crown in 1477, and later by members of the House of Habsburg, including Holy Roman E ...
. But perhaps the most well known is
Jacqueline, Countess of Hainaut
Jacqueline (; ; ; 15 July 1401 – 8 October 1436), of the House of Wittelsbach, was a noblewoman who ruled the counties of Holland, Zeeland and Hainaut in the Low Countries from 1417 to 1433. She was also Dauphine of France for a short time ...
.
The conquest of the county of Holland by the Duke
Philip the Good
Philip III the Good (; ; 31 July 1396 – 15 June 1467) ruled as Duke of Burgundy from 1419 until his death in 1467. He was a member of a cadet line of the Valois dynasty, to which all 15th-century kings of France belonged. During his reign, ...
of Burgundy was an odd affair. Leading noblemen in Holland invited the duke to conquer Holland, even though he had no historical claim to it. Some historians say that the ruling class in Holland wanted Holland to integrate with the
Flemish
Flemish may refer to:
* Flemish, adjective for Flanders, Belgium
* Flemish region, one of the three regions of Belgium
*Flemish Community, one of the three constitutionally defined language communities of Belgium
* Flemish dialects, a Dutch dialec ...
economic system and adopt Flemish legal institutions. Europe had been wracked by many civil wars in the 14th and 15th centuries, while Flanders had grown rich and enjoyed peace.
Burgundian and Habsburg period (1433–1567)
Burgundian period
Most of what is now the Netherlands and Belgium was eventually united by the
Duke of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy () was a title used by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, from its establishment in 843 to its annexation by the Crown lands of France, French crown in 1477, and later by members of the House of Habsburg, including Holy Roman E ...
,
Phillip the Good (1396–1467). Before the Burgundian union, the Dutch identified themselves by the town they lived in, their local duchy or county or as subjects of the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
. These collections of fiefs were ruled under the personal union of the
House of Valois-Burgundy
The House of Valois-Burgundy (, ), or the Younger House of Burgundy, was a noble Kingdom of France, French family deriving from the royal House of Valois. (It is distinct from the Capetian House of Burgundy, descendants of King Robert II of France ...
.
Trade in the region developed rapidly, especially in the areas of shipping and transport. The new rulers defended Dutch trading interests. Amsterdam grew and in the 15th century became the primary trading port in Europe for grain from the Baltic region. Amsterdam distributed grain to the major cities of Belgium, Northern France and England. This trade was vital to the people of the region as they could no longer produce enough grain to feed themselves. Land drainage had caused the peat of the former
wetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
s to reduce to a level that was too low for drainage to be maintained.
Habsburg rule from Spain
Charles V Charles V may refer to:
Kings and Emperors
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
Others
* Charles V, Duke ...
(1500–1558) was born and raised in the
Flemish
Flemish may refer to:
* Flemish, adjective for Flanders, Belgium
* Flemish region, one of the three regions of Belgium
*Flemish Community, one of the three constitutionally defined language communities of Belgium
* Flemish dialects, a Dutch dialec ...
city of
Ghent
Ghent ( ; ; historically known as ''Gaunt'' in English) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the Provinces of Belgium, province ...
; he spoke French. Charles extended the Burgundian territory with the annexation of
Tournai
Tournai ( , ; ; ; , sometimes Anglicisation (linguistics), anglicised in older sources as "Tournay") is a city and Municipalities in Belgium, municipality of Wallonia located in the Hainaut Province, Province of Hainaut, Belgium. It lies by ...
, Artois,
Utrecht
Utrecht ( ; ; ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city of the Netherlands, as well as the capital and the most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of Utrecht (province), Utrecht. The ...
,
Groningen
Groningen ( , ; ; or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen (province), Groningen province in the Netherlands. Dubbed the "capital of the north", Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of ...
and
Guelders
The Duchy of Guelders (; ; ) is a historical duchy, previously county, of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the Low Countries.
Geography
The duchy was named after the town of Geldern (''Gelder'') in present-day Germany. Though the present pr ...
to create the
Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the France, French Departments of Franc ...
. The towns of the region had already been unified by Charles's Burgundian ancestors, but were nominally fiefs of either France or the Holy Roman Empire. When he was a minor, his aunt
Margaret
Margaret is a feminine given name, which means "pearl". It is of Latin origin, via Ancient Greek and ultimately from Iranian languages, Old Iranian. It has been an English language, English name since the 11th century, and remained popular thro ...
acted as regent until 1515. France relinquished its ancient claim on
Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
in 1528.

From 1515 to 1523, Charles's government in the Netherlands had to contend with the rebellion of
Frisian peasants (led by
Pier Gerlofs Donia and
Wijard Jelckama).
Gelre
The Duchy of Guelders (; ; ) is a historical duchy, previously county, of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the Low Countries.
Geography
The duchy was named after the town of Geldern (''Gelder'') in present-day Germany. Though the present pro ...
attempted to build up its own state in northeast Netherlands and northwest Germany. Lacking funds in the 16th century, Gelre had soldiers provide for themselves by pillaging enemy lands. These soldiers were a great menace to the
Habsburg Netherlands
Habsburg Netherlands were the parts of the Low Countries that were ruled by sovereigns of the Holy Roman Empire's House of Habsburg. This rule began in 1482 and ended for the Northern Netherlands in 1581 and for the Southern Netherlands in 1797. ...
, as when they pillaged
The Hague
The Hague ( ) is the capital city of the South Holland province of the Netherlands. With a population of over half a million, it is the third-largest city in the Netherlands. Situated on the west coast facing the North Sea, The Hague is the c ...
.
The dukes of Burgundy over the years through astute marriages, purchases and wars, had taken control of the Seventeen Provinces that made up the Low Countries. They are now the Netherlands in the north, the
Southern Netherlands
The Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, were the parts of the Low Countries belonging to the Holy Roman Empire which were at first largely controlled by Habsburg Spain (Spanish Netherlands, 1556–1714) and later by the ...
(now Belgium) in the south, and Luxemburg in the southeast. Known as the "Burgundian Circle", these lands came under the control of the Habsburg family.
Charles became the ruler in 1506, but in 1515 he left the territory to become king of Spain and later Holy Roman Emperor. Charles turned over control to regents (his close relatives), and in practice the rule over the Low Countries were exercised by the Spaniards under his authority. The provinces each had their own governments and courts, controlled by the local nobility, and their own traditions and rights ("liberties") dating back centuries. Likewise the numerous cities had their own legal rights and local governments, usually controlled by the merchants. On top of this the Spanish had imposed a somewhat centralized government, the Estates General of the Netherlands, with its own officials and courts. The Spanish officials sent by Charles ignored traditions and the Dutch nobility as well as local officials, inciting an anti-Spanish sense of nationalism which led to the
Dutch Revolt
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt (; 1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Reformation, centralisation, exc ...
. With the emergence of the Protestant Reformation, Charles—now the Emperor—was determined to crush Protestantism. Unrest began in the south, centered in the large rich metropolis of Antwerp. The Netherlands was an especially rich unit of the Spanish realm, especially after the
Treaty of Cateau-Cambrésis
The Treaty of Cateau-Cambrésis in April 1559 ended the Italian Wars (1494–1559). It consisted of two separate treaties, one between England and France on 2 April, and another between France and Spain on 3 April. Although he was not a signatory ...
of 1559; it ended four decades of warfare between France and Spain and allowed Spain to reposition its army.
[Albert Guerard, ''France, A Modern History'', (1959), pp. 134–136.]
In 1548, Charles granted the Netherlands status as an entity in which many of the laws of the Holy Roman Empire became obsolete. The "Transaction of Augsburg" created the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire, which comprised the Netherlands and Franche-Comté. A year later the
Pragmatic Sanction of 1549
The Pragmatic Sanction of 1549 was an edict, promulgated by Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, reorganising the Seventeen Provinces of the present-day Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg into one indivisible territory, while retaining existing custom ...
stated that the Seventeen Provinces could only be passed on to his heirs as a composite entity.
The Reformation

During the 16th century, the
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the papacy and ...
rapidly gained ground in northern Europe, especially in its
Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
and
Calvinist
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Protestantism, Continenta ...
forms. Dutch
Protestants
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
, after initial repression, were tolerated by local authorities. By the 1560s, the Protestant community had become a significant influence in the Netherlands, although it clearly formed a minority then. In a society dependent on trade, freedom and tolerance were considered essential. Nevertheless, the Catholic rulers Charles V, and later
Philip II, made it their mission to defeat Protestantism, which was considered a heresy by the Catholic Church and a threat to the stability of the whole hierarchical political system. On the other hand, the intensely moralistic Dutch Protestants insisted their Biblical theology, sincere piety and humble lifestyle was morally superior to the luxurious habits and superficial religiosity of the ecclesiastical nobility. The rulers' harsh punitive measures led to increasing grievances in the Netherlands, where the local governments had embarked on a course of peaceful coexistence. In the second half of the century, the situation escalated. Philip sent troops to crush the rebellion and make the Netherlands once more a Catholic region.
In the first wave of the Reformation,
Lutheranism
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
won over the elites in Antwerp and the South. The Spanish successfully suppressed it there, and Lutheranism only flourished in east Friesland.
The second wave of the Reformation, came in the form of
Anabaptism
Anabaptism (from Neo-Latin , from the Greek language, Greek : 're-' and 'baptism'; , earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re-baptizers"), considering it biased. ...
, that was popular among ordinary farmers in
Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former provinces of the Netherlands, province on the western coast of the Netherland ...
and
Friesland
Friesland ( ; ; official ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia (), named after the Frisians, is a Provinces of the Netherlands, province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen (p ...
. Anabaptists were socially very radical and equalitarian; they believed that the apocalypse was very near. They refused to live the old way, and began new communities, creating considerable chaos. A prominent Dutch Anabaptist was
Menno Simons
Menno Simons (; ; 1496 – 31 January 1561) was a Roman Catholic priest from the Friesland region of the Low Countries who was excommunicated from the Catholic Church and became an influential Anabaptist religious leader. Simons was a contempor ...
, who initiated the
Mennonite
Mennonites are a group of Anabaptism, Anabaptist Christianity, Christian communities tracing their roots to the epoch of the Radical Reformation. The name ''Mennonites'' is derived from the cleric Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland, part of ...
church. The movement was allowed in the north, but never grew to a large scale.
The third wave of the Reformation, that ultimately proved to be permanent, was
Calvinism
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Christian, Presbyteri ...
. It arrived in the Netherlands in the 1540s, attracting both the elite and the common population, especially in
Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
. The Catholic Spanish responded with harsh persecution and introduced the
Inquisition of the Netherlands. Calvinists rebelled. First there was the
iconoclasm
Iconoclasm ()From . ''Iconoclasm'' may also be considered as a back-formation from ''iconoclast'' (Greek: εἰκοκλάστης). The corresponding Greek word for iconoclasm is εἰκονοκλασία, ''eikonoklasia''. is the social belie ...
in 1566, which was the systematic destruction of statues of saints and other Catholic devotional depictions in churches. In 1566,
William the Silent
William the Silent or William the Taciturn (; 24 April 153310 July 1584), more commonly known in the Netherlands as William of Orange (), was the leader of the Dutch revolt against the Spanish Habsburg Netherlands, Habsburgs that set off the ...
, a Calvinist, started the
Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt (; 1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish Empire, Spanish government. The Origins of the Eighty Years' War, causes of the w ...
to liberate all Dutch of whatever religion from Catholic Spain. Blum says, "His patience, tolerance, determination, concern for his people, and belief in government by consent held the Dutch together and kept alive their spirit of revolt." The provinces of
Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former provinces of the Netherlands, province on the western coast of the Netherland ...
and
Zeeland
Zeeland (; ), historically known in English by the Endonym and exonym, exonym Zealand, is the westernmost and least populous province of the Netherlands. The province, located in the southwest of the country, borders North Brabant to the east ...
, being mainly Calvinist by 1572, submitted to the rule of William. The other states remained almost entirely Catholic.
Prelude to war
The Netherlands was a valuable part of the Spanish Empire, especially after the Treaty of Cateau-Cambresis of 1559. This treaty ended a forty-year period of warfare between France and Spain conducted in Italy from 1521 to 1559.
The Treaty of Cateau-Cambresis was somewhat of a watershed—not only for the battleground that Italy had been, but also for northern Europe. Spain had been keeping troops in the Netherlands to be ready to attack France from the north as well as from the south.
With the settlement of so many major issues between France and Spain by the Treaty of Cateau-Cambresis, there was no longer any reason to keep Spanish troops in the Netherlands. Thus, the people of the Netherlands could get on with their peacetime pursuits. As they did so they found that there was a great deal of demand for their products. Fishing had long been an important part of the economy of the Netherlands. However, now the fishing of herring alone came to occupy 2,000 boats operating out of Dutch ports. Spain, still the Dutch trader's best customer, was buying fifty large ships full of furniture and household utensils from Flanders merchants. Additionally, Dutch woolen goods were desired everywhere. The Netherlands bought and processed enough Spanish wool to sell four million florins of wool products through merchants in Bruges. So strong was the Dutch appetite for raw wool at this time that they bought nearly as much English wool as they did Spanish wool. Total commerce with England alone amounted to 24 million florins. Much of the export going to England resulted in pure profit to the Dutch because the exported items were of their own manufacture. The Netherlands was just starting to enter its "Golden Age." Brabant and Flanders were the richest and most flourishing parts of the Dutch Republic at the time.
[Claflin, W. Harold, ed. ''History of Nations: Holland and Belgium'', (New York: P.F. Collier & Son, 1907), pp. 72–74, 103–105] The Netherlands was one of the richest places in the world. The population reached 3 million in 1560, with 25 cities of 10,000 people or more, by far the largest urban presence in Europe; with the trading and financial center of Antwerp being especially important (population 100,000). Spain could not afford to lose this rich land, nor allow it to fall from Catholic control. Thus came 80 years of warfare.
A devout Catholic, Philip was appalled by the success of the
Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
in the
Low Countries
The Low Countries (; ), historically also known as the Netherlands (), is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower Drainage basin, basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting today of the three modern "Bene ...
, which had led to an increasing number of
Calvinists
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Christian, Presbyterian, ...
. His attempts to enforce religious persecution of the Protestants, and his centralization of government, law enforcement, and taxes, made him unpopular and led to a
revolt
Rebellion is an uprising that resists and is organized against one's government. A rebel is a person who engages in a rebellion. A rebel group is a consciously coordinated group that seeks to gain political control over an entire state or a ...
.
Fernando Alvarez de Toledo, Duke of Alba, was sent with a Spanish Army to punish the unruly Dutch in 1567.
[John Lathrop Motley, ''The Rise of the Dutch Republic'' (Harper & Bros.: New York, 1855) pp. 106–115, 121, 122, 207, 213]
The only opposition the Duke of Alba faced in his march across the Netherlands were the nobles,
Lamoral, Count of Egmont
Lamoral, Count of Egmont, Prince of Gavere (18 November 1522 – 5 June 1568) was a general and statesman in the Habsburg Netherlands, Spanish Netherlands just before the start of the Eighty Years' War, whose execution helped spark the national up ...
;
Philippe de Montmorency, Count of Horn and others. With the approach of Alba and the Spanish army,
William the Silent
William the Silent or William the Taciturn (; 24 April 153310 July 1584), more commonly known in the Netherlands as William of Orange (), was the leader of the Dutch revolt against the Spanish Habsburg Netherlands, Habsburgs that set off the ...
of Orange fled to Germany with his three brothers and his whole family on 11 April 1567. The Duke of Alba sought to meet and negotiate with the nobles that now faced him with armies. However, when the nobles arrived in Brussels they were all arrested and Egmont and Horn were executed.
Alba then revoked all the prior treaties that Margaret, the
Duchess of Parma
Consorts of Parma House of Farnese, 1545–1731
House of Bourbon-Anjou, 1731–1735
:None
House of Habsburg, 1735–1748
House of Bourbon-Parma, 1748–1802
House of Habsburg, 1814–1847
House of Bourbon-Parma, 1847–1859
...
had signed with the Protestants of the Netherlands and instituted the Inquisition to enforce the decrees of the
Council of Trent
The Council of Trent (), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation at the time, it has been described as the "most ...
.
The Eighty Years' War (1568–1648)


The Dutch War for Independence from Spain is frequently called the Eighty Years' War (1568–1648). The first fifty years (1568 through 1618) were a war solely between Catholic Spain and the Protestant rebels of the Netherlands. It was a military conflict with integral religious elements. During the last thirty years (1618–1648) the conflict between Spain and the Netherlands was submerged in the general European War that became known as the
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
. The seven rebellious provinces of the Netherlands were eventually united by the
Union of Utrecht
The Union of Utrecht () was an alliance based on an agreement concluded on 23 January 1579 between a number of Habsburg Netherlands, Dutch provinces and cities, to reach a joint commitment against the king, Philip II of Spain. By joining forces ...
in 1579 and formed the
Republic of the Seven United Netherlands
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherland ...
(also known as the "United Provinces"). The
Act of Abjuration or ''Plakkaat van Verlatinghe'' was signed on 26 July 1581, and was the formal
declaration of independence
A declaration of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the territory of another state or failed state, or are breaka ...
of the northern
Low Countries
The Low Countries (; ), historically also known as the Netherlands (), is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower Drainage basin, basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting today of the three modern "Bene ...
from the Spanish king.
Religious toleration
Religious tolerance or religious toleration may signify "no more than forbearance and the permission given by the adherents of a dominant religion for other religions to exist, even though the latter are looked on with disapproval as inferior, ...
was a key element of Protestant ideology.
William of Orange (1533–1584), the founder of the Dutch royal family, led the Dutch during the first part of the war. The very first years were a success for the Spanish troops. However, the Dutch countered subsequent sieges in
Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former provinces of the Netherlands, province on the western coast of the Netherland ...
. In November and December 1572, all the citizens of
Zutphen
Zutphen () is a city and municipality located in the province of Gelderland, Netherlands. It lies some northeast of Arnhem, on the eastern bank of the river IJssel at the point where it is joined by the Berkel. First mentioned in the 11th centur ...
and
Naarden
Naarden () is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and former List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Gooi region in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of North Holland, Netherlands. It has been part ...
were slaughtered by the Spanish. From 11 December that year the city of
Haarlem
Haarlem (; predecessor of ''Harlem'' in English language, English) is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Netherlands. It is the capital of the Provinces of the Nether ...
was besieged, holding out for seven months until 13 July 1573.
Oudewater was conquered by the Spanish on 7 August 1575, and most of its inhabitants were killed. Maastricht was besieged, sacked and destroyed twice in succession (in 1576 and 1579) by the Spanish.
In a war largely of sieges rather than battles,
Governor-General Alexander Farnese proved his mettle. His strategy was to offer generous terms for the surrender of a city: there would be no more massacres or looting; historic urban privileges were retained; there was a full pardon and amnesty; return to the Catholic Church would be gradual. Conservative Catholics in the south and east supported the Spanish. Farnese recaptured
Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after ...
and nearly all of what became Belgium. Most of the Dutch-speaking territory in the Netherlands was taken from Spain, but not in
Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
, which to this day remains part of
Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
. Flanders was the most radical anti-Spanish territory. Many Flemish fled to Holland, among them half of the population of Antwerp, 3/4 of Bruges and Ghent and the entire population of Nieuwpoort, Dunkerque and countryside. His successful campaign gave the Catholics control of the lower half of the Low Countries, and was part of the
Catholic Counter-Reformation.
The war dragged on for another half century, but the main fighting was over. The
Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy Roman Empire ...
, signed in 1648, confirmed the independence of the United Provinces from Spain. The Dutch people started to develop a national identity, beginning in the 15th century, but they officially remained a part of the Holy Roman Empire until 1648. National identity was mainly formed by the province people came from. Holland was the most important province by far.
The Catholics in the Netherlands were an outlawed minority that had been suppressed by the Calvinists. After 1572, however, they made a striking comeback (also as part of the Catholic Counter-Reformation), setting up seminaries, reforming their Church, and sending missionaries into Protestant districts. Laity often took the lead; the Calvinist government often arrested or harassed priests who seemed too effective. Catholic numbers stabilized at about a third of the population in the Netherlands; they were strongest in the southeast.
Golden Age

The ''Dutch Golden Age'' was a period which roughly lasted from 1588, when the
Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands ...
was established, to 1672, when the ''
Rampjaar
In Dutch history, the year 1672 is referred to as the (; Disaster Year). In May 1672, following the outbreak of the Franco-Dutch War and its peripheral conflict the Third Anglo-Dutch War, France, supported by Münster and Cologne, invaded a ...
'' occurred. During this period, Dutch
trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
Traders generally negotiate through a medium of cr ...
,
scientific developments,
art
Art is a diverse range of cultural activity centered around ''works'' utilizing creative or imaginative talents, which are expected to evoke a worthwhile experience, generally through an expression of emotional power, conceptual ideas, tec ...
and
overseas colonisation was among the most prominent in Europe. The first half of the period spanned from the beginning of the
Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt (; 1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish Empire, Spanish government. The Origins of the Eighty Years' War, causes of the w ...
until its conclusion in 1648, with the second half lasting until the outbreak of the
Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, 1672 to 1678, was primarily fought by Kingdom of France, France and the Dutch Republic, with both sides backed at different times by a variety of allies. Related conflicts include the 1672 to 1674 Third Anglo-Dutch War and ...
. During the period, Dutch colonialists, many of them affiliated with the
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
and
West India Company, established trading posts and colonies in the
Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
,
Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost region of Africa. No definition is agreed upon, but some groupings include the United Nations geoscheme for Africa, United Nations geoscheme, the intergovernmental Southern African Development Community, and ...
and
Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
, protected by the powerful
Dutch States Navy
The Dutch States Navy (, ) was the navy of the Dutch Republic from 1588 to 1795. Coming into existence during the Eighty Years' War, the States Navy played a major role in expanding and protecting the Dutch colonial empire, in addition to partici ...
. The Dutch dominated the
triangular trade
Triangular trade or triangle trade is trade between three ports or regions. Triangular trade usually evolves when a region has export commodities that are not required in the region from which its major imports come. It has been used to offset ...
and
Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in Africa, enslaved African people to the Americas. European slave ships regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Pass ...
.
Dutch culture
Dutch culture may refer to:
* used more narrowly, the Culture of the Netherlands
* used more widely, the culture of Dutch-speaking Europe, including:
**Dutch architecture
**Dutch literature
** Dutch music
** Dutch festivities
**Dutch folklore
Se ...
experienced a renaissance. However, by the end of the 17th century, conflicts with neighbouring powers as well as a declining economic influence led to waning of Dutch power. The process by which the Dutch Republic became one of the foremost maritime and economic powers of the world during the era has been referred to as the "Dutch Miracle" by historian
K. W. Swart. The term "Dutch Golden Age" has been controversial in the 21st century due to the extensive Dutch involvement in
slavery
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
and
colonialism
Colonialism is the control of another territory, natural resources and people by a foreign group. Colonizers control the political and tribal power of the colonised territory. While frequently an Imperialism, imperialist project, colonialism c ...
during the period, and it has been deprecated by several museums in the
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
, including the
Amsterdam Museum
The Amsterdam Museum, known until 2010 as the Amsterdam Historical Museum, is an Amsterdam-based museum dedicated to the city's past and present. Due to the renovation of its main location, the museum is temporarily located in the Amstelhof on the ...
.
Dutch Empire
The Dutch in the Americas
The Dutch West India Company was a
chartered company
A chartered company is an association with investors or shareholders that is Incorporation (business), incorporated and granted rights (often Monopoly, exclusive rights) by royal charter (or similar instrument of government) for the purpose of ...
(known as the "GWC") of Dutch merchants. On 2 June 1621, it was granted a
charter
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the ...
for a trade monopoly in the
West Indies
The West Indies is an island subregion of the Americas, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island country, island countries and 19 dependent territory, dependencies in thr ...
(meaning the Caribbean) by the
Republic of the Seven United Netherlands
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherland ...
and given jurisdiction over the
African slave trade
Slavery has historically been widespread in Africa. Systems of servitude and slavery were once commonplace in parts of Africa, as they were in much of the rest of the ancient and medieval world. When the trans-Saharan slave trade, Red Sea s ...
, Brazil, the Caribbean, and North America. Its area of operations stretched from West Africa to the Americas, and the Pacific islands. The company became instrumental in the
Dutch colonization of the Americas
The Netherlands began its colonization of the Americas with the establishment of trading posts and plantations, which preceded the much wider known colonization activities of the Dutch in Asia. While the first Dutch fort in Asia was built in 16 ...
. The first forts and settlements in
Guyana
Guyana, officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern coast of South America, part of the historic British West Indies. entry "Guyana" Georgetown, Guyana, Georgetown is the capital of Guyana and is also the co ...
and on the
Amazon River date from the 1590s. Actual colonization, with Dutch settling in the new lands, was not as common as with England and France. Many of the Dutch settlements were lost or abandoned by the end of that century, but the Netherlands managed to retain possession of
Suriname
Suriname, officially the Republic of Suriname, is a country in northern South America, also considered as part of the Caribbean and the West Indies. It is a developing country with a Human Development Index, high level of human development; i ...
and a number of Dutch Caribbean islands.
The colony was a private business venture to exploit the
fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal ecosystem, boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals h ...
in beaver pelts. New Netherland was slowly settled during its first decades, partially as a result of policy mismanagement by the
Dutch West India Company
The Dutch West India Company () was a Dutch chartered company that was founded in 1621 and went defunct in 1792. Among its founders were Reynier Pauw, Willem Usselincx (1567–1647), and Jessé de Forest (1576–1624). On 3 June 1621, it was gra ...
(WIC), and conflicts with Native Americans. During the 1650s, the colony experienced dramatic growth and became a major port for trade in the
Atlantic World, tolerating a highly diverse ethnic mix. The surrender of
Fort Amsterdam
Fort Amsterdam, (later, Fort George among other names) was a fortification on the southern tip of Manhattan Island at the confluence of the Hudson River, Hudson and East River, East rivers in what is now New York City. The fort and the island ...
to the British control in 1664 was formalized in 1667, contributing to the
Second Anglo–Dutch War. In 1673 the Dutch re-took the area, but later relinquished it under the 5 April 1674
Treaty of Westminster ending the
Third Anglo-Dutch War
The Third Anglo-Dutch War, began on 27 March 1672, and concluded on 19 February 1674. A naval conflict between the Dutch Republic and England, in alliance with France, it is considered a related conflict of the wider 1672 to 1678 Franco-Dutch W ...
.
Descendants of the original settlers played a prominent role in the history of the United States, as typified by the Roosevelt and Vanderbilt families. The Hudson Valley still boasts a Dutch heritage. The concepts of civil liberties and
pluralism
Pluralism in general denotes a diversity of views or stands, rather than a single approach or method.
Pluralism or pluralist may refer more specifically to:
Politics and law
* Pluralism (political philosophy), the acknowledgement of a diversi ...
introduced in the province became mainstays of American political and social life.
Slave trade
Although slavery was illegal inside the Netherlands it flourished in the Dutch Empire, and helped support the economy. In 1619 The Netherlands took the lead in building large-scale
slave trading between Africa and Virginia, by 1650 becoming the pre-eminent slave trading country in Europe. It was overtaken by Britain around 1700. Historians agree that in all the Dutch shipped about 550,000 African slaves across the Atlantic, about 75,000 of whom died on board before reaching their destinations. From 1596 to 1829, the Dutch traders sold 250,000 slaves in the Dutch Guianas, 142,000 in the Dutch Caribbean islands, and 28,000 in Dutch Brazil. In addition, tens of thousands of slaves, mostly from India and some from Africa, were carried to the Dutch East Indies and slaves from the East Indies to Africa and the West Indies.
The Dutch in Asia: The Dutch East India Company


The Dutch East India Company (also called the VOC) emerged in 1602, when the government gave it a monopoly to trade with Asia, mainly to
Mughal India
The Mughal Empire was an early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of pre ...
. It had many world firsts—the first
multinational corporation
A multinational corporation (MNC; also called a multinational enterprise (MNE), transnational enterprise (TNE), transnational corporation (TNC), international corporation, or stateless corporation, is a corporate organization that owns and cont ...
, the first company to issue stock, and the first
megacorporation
Megacorporation, mega-corporation, or megacorp, a term originally coined by Alfred Eichner in his book ''The Megacorp and Oligopoly: Micro Foundations of Macro Dynamics'' but popularized by William Gibson,
derives from the combination of the pre ...
, possessing quasi-governmental powers, including the ability to wage war, negotiate treaties, coin money, and establish colonial settlements.
England and France soon copied its model but could not match its record. Between 1602 and 1796 the VOC sent almost a million Europeans to work in the Asia trade on 4,785 ships. It returned over 2.5 million tons of Asian trade goods. The VOC enjoyed huge profits from its spice monopoly through most of the 17th century. The VOC was active chiefly in the
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies (; ), was a Dutch Empire, Dutch colony with territory mostly comprising the modern state of Indonesia, which Proclamation of Indonesian Independence, declared independence on 17 Au ...
, now
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
, where its base was
Batavia (now
Jakarta
Jakarta (; , Betawi language, Betawi: ''Jakartè''), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta (; ''DKI Jakarta'') and formerly known as Batavia, Dutch East Indies, Batavia until 1949, is the capital and largest city of Indonesia and ...
), which remained an important trading concern and paid an 18% annual dividend for almost 200 years; colonized parts of
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
between
1624–1662 and 1664–1667 and was the only western trading post in Japan,
Dejima
or Deshima, in the 17th century also called , was an artificial island off Nagasaki, Japan, that served as a trading post for the Portuguese (1570–1639) and subsequently the Dutch (1641–1858). For 220 years, it was the central con ...
.
During the period of
Proto-industrialization
Proto-industrialization is the regional development, alongside commercial agriculture, of rural handicraft production for external markets.
Cottage industries in parts of Europe between the 16th and 19th centuries had long been a niche topic of ...
, the empire received 50% of textile and 80% of silk imports from the Mughal Empire, chiefly from its most developed region known as the
Bengal Subah
The Bengal Subah (Bengali language, Bengali: সুবাহ বাংলা, ), also referred to as Mughal Bengal and Bengal State (after 1717), was one of the puppet states and the largest subah, subdivision of The Mughal India, Mughal Emp ...
.
Om Prakash
Om Prakash Chibber (19 December 1919 – 21 February 1998) was an Indian film actor. He was born in Jammu and was a well known character actor of Bollywood, Hindi Cinema. His most well-known movies are Mere Hamdam Mere Dost (1968 film), ''Mere ...
,
Empire, Mughal
, ''History of World Trade Since 1450'', edited by John J. McCusker, vol. 1, Macmillan Reference USA, 2006, pp. 237–240, ''World History in Context''. Retrieved 3 August 2017
By the 17th century, the Dutch East India Company established their base in parts of Ceylon (modern-day Sri Lanka). Afterward, they established ports in
Dutch occupied Malabar, leading to
Dutch settlements and trading posts in India. However, their expansion into India was halted, after their defeat in the
Battle of Colachel
The Battle of Colachel (or The Battle of Kolachel) was fought on
between the Indian kingdom of Travancore and the Dutch East India Company. During the Travancore-Dutch War, King Marthanda Varma's (1729–1758) forces defeated the Dutch East ...
by the
Kingdom of Travancore
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , , "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star.
Computer scientists and mathematicians often vocalize it as st ...
, during the
Travancore-Dutch War. The Dutch never recovered from the defeat and no longer posed a large colonial threat to India.
Eventually, the 18th century saw the Dutch East India Company weighted down by corruption, and the VOC eventually went bankrupt in 1800. Its possessions were taken over by the government and turned into the
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies (; ), was a Dutch Empire, Dutch colony with territory mostly comprising the modern state of Indonesia, which Proclamation of Indonesian Independence, declared independence on 17 Au ...
.
The Dutch in Africa
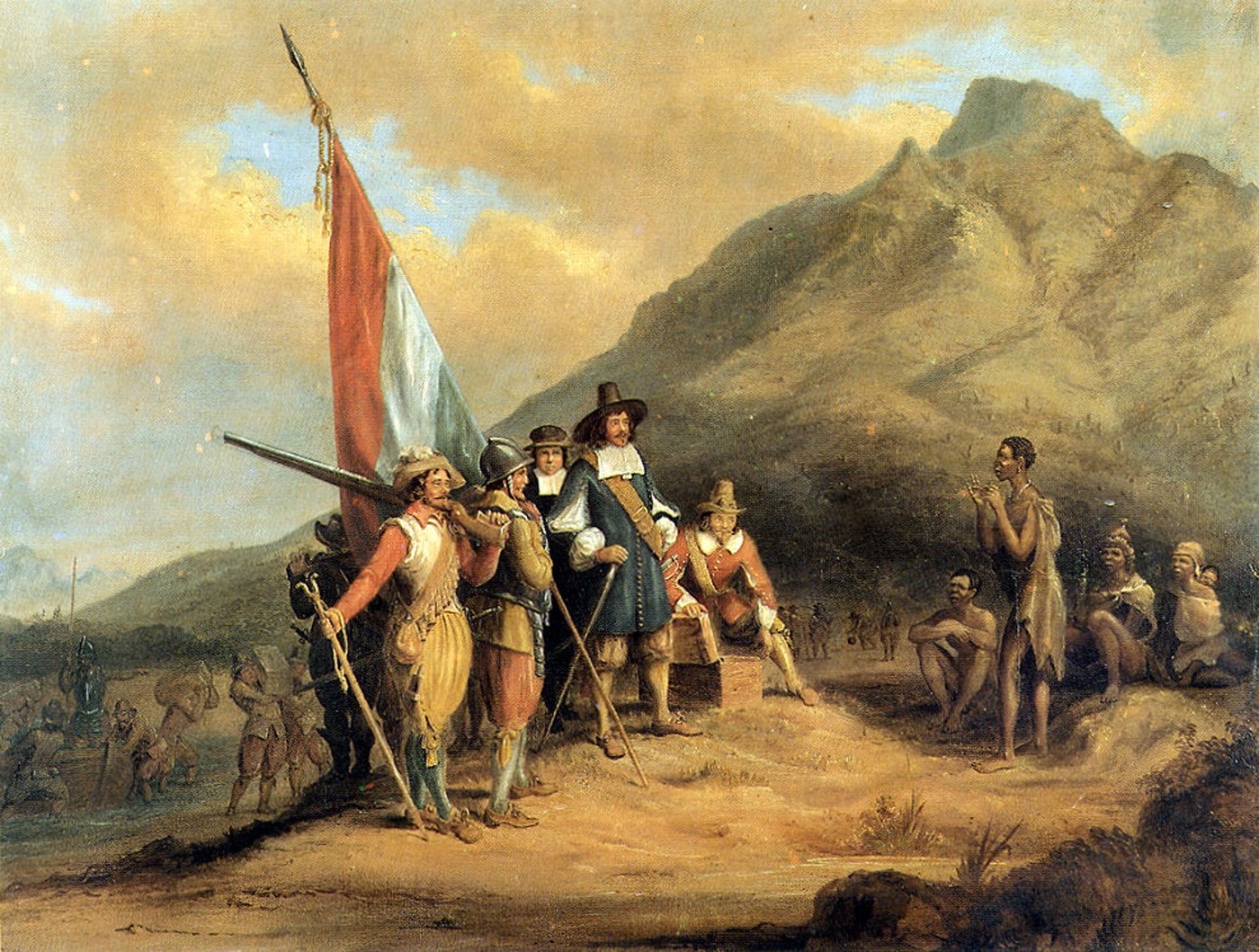

In 1647, a Dutch vessel was wrecked in the present-day
Table Bay
Table Bay (Afrikaans: ''Tafelbaai'') is a natural bay on the Atlantic Ocean overlooked by Cape Town and is at the northern end of the Cape Peninsula, which stretches south to the Cape of Good Hope. It was named because it is dominated by the fl ...
at
Cape Town
Cape Town is the legislature, legislative capital city, capital of South Africa. It is the country's oldest city and the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. Cape Town is the country's List of municipalities in South Africa, second-largest ...
. The marooned crew, the first Europeans to attempt settlement in the area, built a
fort
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from La ...
and stayed for a year until they were rescued. Shortly thereafter, the
Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States Ge ...
(in the Dutch of the day: ''Vereenigde Oostindische Compagnie'', or VOC) decided to establish a permanent settlement. The VOC, one of the major European trading houses sailing the
spice route
The spice trade involved historical civilizations in Asia, Northeast Africa and Europe. Spices, such as cinnamon, cassia, cardamom, ginger, pepper, nutmeg, star anise, clove, and turmeric, were known and used in antiquity and traded in the Eas ...
to East Asia, had no intention of colonizing the area, instead wanting only to establish a secure base camp where passing ships could shelter, and where hungry sailors could stock up on fresh supplies of meat, fruit, and vegetables. To this end, a small VOC expedition under the command of
Jan van Riebeeck
Johan Anthoniszoon "Jan" van Riebeeck (21 April 1619 – 18 January 1677) was a Dutch navigator, ambassador and colonial administrator of the Dutch East India Company.
Life
Early life
Jan van Riebeeck was born in Culemborg on 21 April ...
reached
Table Bay
Table Bay (Afrikaans: ''Tafelbaai'') is a natural bay on the Atlantic Ocean overlooked by Cape Town and is at the northern end of the Cape Peninsula, which stretches south to the Cape of Good Hope. It was named because it is dominated by the fl ...
on 6 April 1652.
To remedy a labour shortage, the VOC released a small number of VOC employees from their contracts and permitted them to establish farms with which they would supply the VOC settlement from their harvests. This arrangement proved highly successful, producing abundant supplies of fruit, vegetables, wheat, and wine; they also later raised livestock. The small initial group of "free burghers", as these farmers were known, steadily increased in number and began to expand their farms further north and east.
The majority of burghers had Dutch ancestry and belonged to the
Calvinist Reformed Church of the Netherlands, but there were also numerous Germans as well as some Scandinavians. In 1688 the Dutch and the Germans were joined by French
Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
, also Calvinists, who were fleeing religious persecution in France under
King Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the longest of any monar ...
. The
Huguenots in South Africa
Many people of European heritage in South Africa are descended from Huguenots. Most of these originally settled in the Dutch Cape Colony, but were subsequently absorbed into the Afrikaners, Afrikaner and Afrikaans-speaking population due to r ...
were absorbed into the Dutch population but they played a prominent role in South Africa's history.
From the beginning, the VOC used the cape as a place to supply ships travelling between the Netherlands and the Dutch East Indies. There was a close association between the cape and these Dutch possessions in the far east. Van Riebeeck and the VOC began to import large numbers of slaves, primarily from
Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
and Indonesia. These slaves often married Dutch settlers, and their descendants became known as the
Cape Coloureds
Cape Coloureds () are a South African group of Coloured people who are from the Cape region in South Africa which consists of the Western Cape, Northern Cape and the Eastern Cape. Their ancestry comes from the interracial mixing between the ...
and the
Cape Malays
Cape Malays (, in Arabic script) also known as Cape Muslims or Malays, are a Muslim community or ethnic group in South Africa. They are the descendants of enslaved and free Muslims from different parts of the world, specifically Indonesia (a ...
.
During the 18th century, the Dutch settlement in the area of the cape grew and prospered. By the late 1700s, the
Cape Colony
The Cape Colony (), also known as the Cape of Good Hope, was a British Empire, British colony in present-day South Africa named after the Cape of Good Hope. It existed from 1795 to 1802, and again from 1806 to 1910, when it united with three ...
was one of the best developed European settlements outside Europe or the Americas.
[Smith, Adam (1776)]
Wealth of Nations
, Penn State Electronic Classics Edition, republished 2005, p. 516 The two bases of the Cape Colony's economy for almost the entirety of its history were shipping and agriculture. Its strategic position meant that almost every ship sailing between Europe and Asia stopped off at the colony's capital
Cape Town
Cape Town is the legislature, legislative capital city, capital of South Africa. It is the country's oldest city and the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. Cape Town is the country's List of municipalities in South Africa, second-largest ...
. The supplying of these ships with fresh provisions, fruit, and
wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented fruit. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the fruit and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Wine is most often made f ...
provided a very large market for the surplus produce of the colony.
Some free burghers continued to expand into the rugged hinterlands of the north and east, many began to take up a semi-nomadic
pastoralist lifestyle, in some ways not far removed from that of the
Khoikhoi
Khoikhoi (Help:IPA/English, /ˈkɔɪkɔɪ/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''KOY-koy'') (or Khoekhoe in Namibian orthography) are the traditionally Nomad, nomadic pastoralist Indigenous peoples, indigenous population of South Africa. They ...
they had displaced. In addition to its herds, a family might have a wagon, a tent, a Bible, and a few guns. As they became more settled, they would build a mud-walled cottage, frequently located, by choice, days of travel from the nearest European settlement. These were the first of the
Trekboer
The Trekboers ( ) were nomadic pastoralists descended from mostly Dutch colonists on the frontiers of the Dutch Cape Colony in Southern Africa. The Trekboers began migrating into the interior from the areas surrounding what is now Cape Town, su ...
s (Wandering Farmers, later shortened to
Boer
Boers ( ; ; ) are the descendants of the proto Afrikaans-speaking Free Burghers of the eastern Cape frontier in Southern Africa during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries. From 1652 to 1795, the Dutch East India Company controlled the Dutch ...
s), completely independent of official controls, extraordinarily self-sufficient, and isolated from the government and the main settlement in
Cape Town
Cape Town is the legislature, legislative capital city, capital of South Africa. It is the country's oldest city and the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. Cape Town is the country's List of municipalities in South Africa, second-largest ...
.
 Dutch
Dutch was the official language, but a dialect had formed that was quite distinct from Dutch. The
Afrikaans
Afrikaans is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language spoken in South Africa, Namibia and to a lesser extent Botswana, Zambia, Zimbabwe and also Argentina where there is a group in Sarmiento, Chubut, Sarmiento that speaks the Pat ...
language originated mainly from 17th-century Dutch dialects.
This Dutch dialect sometimes referred to as the "kitchen language" (''kombuistaal''), would eventually in the late 19th century be recognised as a distinct language called
Afrikaans
Afrikaans is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language spoken in South Africa, Namibia and to a lesser extent Botswana, Zambia, Zimbabwe and also Argentina where there is a group in Sarmiento, Chubut, Sarmiento that speaks the Pat ...
and replace Dutch as the official language of the
Afrikaners
Afrikaners () are a Southern African ethnic group descended from predominantly Dutch people, Dutch Settler colonialism, settlers who first arrived at the Cape of Good Hope in Free Burghers in the Dutch Cape Colony, 1652.Entry: Cape Colony. '' ...
.
As the 18th century drew to a close, Dutch mercantile power began to fade and the
British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
moved in to fill the vacuum. They seized the Cape Colony in 1795 to prevent it from falling into French hands, then briefly relinquished it back to the Dutch (1803), before definitively conquering it in 1806. British sovereignty of the area was recognised at the
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
in 1815. By the time the Dutch colony was seized by the British in 1806, it had grown into an established settlement with 25,000 slaves, 20,000 white colonists, 15,000
Khoisan
Khoisan ( ) or () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for the various Indigenous peoples of Africa, indigenous peoples of Southern Africa who traditionally speak non-Bantu languages, combining the Khoekhoen and the San people, Sān peo ...
, and 1,000 freed black slaves. Outside Cape Town and the immediate hinterland, isolated black and white
pastoralists
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as "livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands (pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The anima ...
populated the country.
Dutch interest in South Africa was based chiefly on the strategically located VOC port. Yet in the 17th and 18th centuries the Dutch created the foundation of the modern state of South Africa. The Dutch legacy in South Africa is evident everywhere, but particularly in the Afrikaner people and the Afrikaans language.
Dutch Republic: Regents and Stadholders (1649–1784)

The ''United Provinces of the Netherlands'', commonly referred to in
historiography
Historiography is the study of the methods used by historians in developing history as an academic discipline. By extension, the term ":wikt:historiography, historiography" is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiog ...
as the ''Dutch Republic'', was a
confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a political union of sovereign states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
of provinces that existed from 1579 until the
Batavian Revolution
The Batavian Revolution () was a time of political, social and cultural turmoil at the end of the 18th century that marked the end of the Dutch Republic and saw the proclamation of the Batavian Republic.
The initial period, from about 1780 to ...
in 1795. It was the first independent Dutch state. The republic was established after seven Dutch provinces revolted against
Spanish rule, declaring their independence in 1581. As the Netherlands was a republic, it was largely governed by an aristocracy of city-merchants called the
regents
In a monarchy, a regent () is a person appointed to govern a state because the actual monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge their powers and duties, or the throne is vacant and a new monarch has not yet been dete ...
, rather than by a king. Every city and province had its own government and laws, and a large degree of autonomy. After attempts to find a competent sovereign proved unsuccessful, it was decided that sovereignty would be vested in the various provincial Estates, the governing bodies of the provinces. The
Estates-General, with its representatives from all the provinces, would decide on matters important to the Republic as a whole. Each province was led by an official known as the for, nl,
stadtholder
In the Low Countries, a stadtholder ( ) was a steward, first appointed as a medieval official and ultimately functioning as a national leader. The ''stadtholder'' was the replacement of the duke or count of a province during the Burgundian and ...
, steward; this office was nominally open to anyone, but most provinces appointed a member of the
House of Orange
The House of Orange-Nassau (, ), also known as the House of Orange because of the prestige of the princely title of Orange, also referred to as the Fourth House of Orange in comparison with the other noble houses that held the Principality of O ...
. The position gradually became hereditary, with the
Prince of Orange
Prince of Orange (or Princess of Orange if the holder is female) is a title associated with the sovereign Principality of Orange, in what is now southern France and subsequently held by the stadtholders of, and then the heirs apparent of ...
simultaneously holding most or all of the stadtholderships, making him effectively the
head of state
A head of state is the public persona of a sovereign state.#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 "he head of state
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (letter), the fifth letter of the Semitic abjads
* He (pronoun), a pronoun in Modern English
* He (kana), one of the Japanese kana (へ in hiragana and ヘ in katakana)
* Ge (Cyrillic), a Cyrillic letter cal ...
being an embodiment of the State itself or representative of its international persona." The name given to the office of head of sta ...
. This created tension between political factions: the
Orangists favoured a powerful stadtholder, while the Republicans favoured a strong States General. The Republicans forced two
Stadtholderless Periods, 1650–1672 and 1702–1747, with the latter causing
national instability and the end of
Great Power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power ...
status. In the
Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy Roman Empire ...
(1648) the republic gained approximately 20% more territory, located outside the member provinces, which was ruled directly by the States General as
Generality Lands
The Generality Lands, Lands of the Generality or Common Lands () were about one-fifth of the territories of the United Provinces of the Netherlands, that were directly governed by the States-General. Unlike the seven provinces of Holland, Zeel ...
.
Although the state was small and had only around 1.5 million inhabitants, it controlled a worldwide network of seafaring
trade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over land or water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a singl ...
s. Through its trading companies, the
Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States Ge ...
(VOC) and the
Dutch West India Company
The Dutch West India Company () was a Dutch chartered company that was founded in 1621 and went defunct in 1792. Among its founders were Reynier Pauw, Willem Usselincx (1567–1647), and Jessé de Forest (1576–1624). On 3 June 1621, it was gra ...
(GWC), it established an empire. These companies were based on the English model and the success of England's joint-stock enterprises and trading guilds.
The income from this trade allowed the Dutch Republic to compete militarily against much larger countries. It amassed a huge fleet of 2,000 ships, initially larger than the fleets of England and France combined. Major conflicts were fought in the Eighty Years' War against Spain, the Dutch–Portuguese War (1602–1663), four Anglo-Dutch Wars, the
Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, 1672 to 1678, was primarily fought by Kingdom of France, France and the Dutch Republic, with both sides backed at different times by a variety of allies. Related conflicts include the 1672 to 1674 Third Anglo-Dutch War and ...
(1672–1678), War of the Grand Alliance (1688–1697), the War of the Spanish Succession (1702–1713), the War of Austrian Succession (1744–1748), and the War of the First Coalition (1792–1795) against the Kingdom of France.
The republic was more tolerant of different religions and ideas than contemporary states, allowing freedom of thought to its residents. Artists flourished under this regime, including painters such as Rembrandt. So did scientists, such as Hugo Grotius, Christiaan Huygens and Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. Dutch trade, science, armed forces, and art were among the most acclaimed in the world during much of the 17th century, a period which became known as the Dutch Golden Age.
The economy, based on Amsterdam's role as the center of world trade, was strong in the 17th century. In 1670 the Dutch merchant marine totalled 568,000 tons of shipping—about half the European total. The province of Holland was highly commercial and dominated the country. Its nobility was small and closed and had little influence, for it was numerically small, politically weak, and formed a strictly closed caste. Most land in the province of Holland was commercialized for cash crops and was owned by urban capitalists, not nobles; there were few links between Holland's nobility and the merchants. By 1650 the burgher families which had grown wealthy through commerce and become influential in government controlled the province of Holland, and to a large extent shaped national policies. The other six provinces were more rural and traditional in life style, had an active nobility, and played a small role in commerce and national politics. Instead they concentrated on their flood protections and land reclamation projects.
Economic decline led to a period of political instability known as the Patriottentijd (1780–1787).
This unrest was temporarily suppressed by a Prussian invasion of Holland, Prussian invasion in support of the stadtholder. The French Revolution and subsequent War of the First Coalition reignited these tensions. Following military defeat by France, the stadtholder was expelled in the
Batavian Revolution
The Batavian Revolution () was a time of political, social and cultural turmoil at the end of the 18th century that marked the end of the Dutch Republic and saw the proclamation of the Batavian Republic.
The initial period, from about 1780 to ...
of 1795, ending the Dutch Republic, which was succeeded by the
Batavian Republic
The Batavian Republic (; ) was the Succession of states, successor state to the Dutch Republic, Republic of the Seven United Netherlands. It was proclaimed on 19 January 1795 after the Batavian Revolution and ended on 5 June 1806, with the acce ...
.
Batavian Republic (1795–1806)
The French Revolution was popular, and numerous underground clubs were promoting it when in January 1795 the Low Countries theatre of the War of the First Coalition, French army invaded. The underground rose up, overthrew the municipal and provincial governments, and proclaimed the
Batavian Republic
The Batavian Republic (; ) was the Succession of states, successor state to the Dutch Republic, Republic of the Seven United Netherlands. It was proclaimed on 19 January 1795 after the Batavian Revolution and ended on 5 June 1806, with the acce ...
() Batavian Revolution in Amsterdam, in Amsterdam. Stadtholder William V fled to England and the States General dissolved itself. The new government was virtually a puppet of France. The Batavian Republic enjoyed widespread support and sent soldiers to fight in the French armies. The 1799 Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland was repulsed by Batavian–French forces. Nevertheless, Napoleon replaced it because the regime of Grand Pensionary Rutger Jan Schimmelpenninck (1805–1806) was insufficiently docile.
The confederal structure of the old Dutch Republic was permanently replaced by a unitary state. The 1798 constitution had a genuinely democratic character, though a coup d'état of 1801 put an authoritarian regime in power. Ministerial government was introduced for the first time in Dutch history and many of the current government departments date their history back to this period.
The exiled stadholder Kew Letters, handed over the Dutch colonies in "safekeeping" to Great Britain and ordered the colonial governors to comply. This permanently ended the colonial Dutch empire in Guyana, Ceylon and the Cape Colony. The Dutch East Indies was returned to the Netherlands under the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814.
Kingdom of Holland to William I (1806–1815)
In 1806 Napoleon transformed the Netherlands (along with a small part of what is now Germany) into the
Kingdom of Holland
The Kingdom of Holland ( (contemporary), (modern); ) was the successor state of the Batavian Republic. It was created by Napoleon Bonaparte in March 1806 in order to strengthen control over the Netherlands by replacing the republican governmen ...
, putting his brother Louis Bonaparte (1778–1846), on the throne. The new king was unpopular, but he was willing to cross his brother for the benefit of his new kingdom. Napoleon forced his abdication in 1810 and Incorporation (Netherlands), incorporated the Netherlands directly into the First French Empire, French empire, imposing economic controls and conscription of all young men as soldiers.

When the French retreated from the northern provinces in 1813, a Triumvirate of 1813, Triumvirate took over at the helm of a Sovereign Principality of the United Netherlands, provisional government. Although most members of the provisional government had been among the men who had driven out William V 18 years earlier, the leaders of the provisional government knew that any new regime would have to be headed by his son, William I of the Netherlands, William Frederick. They also knew that it would be better in the long term if the Dutch people themselves installed the prince, rather than have him imposed on the country by the anti-French alliance. Accordingly, the Triumvirate called William Frederick back on 30 November and offered him the crown. He refused, but instead proclaimed himself "Sovereign Principality of the United Netherlands, hereditary sovereign prince" on 6 December.
The Great Powers had Eight Articles of London, secretly agreed to merge the northern Netherlands with the more populated Austrian Netherlands and the smaller Prince-Bishopric of Liège into a single constitutional monarchy. Having a stronger country on France's northern border was considered (especially by Alexander I of Russia, Tsar Alexander) to be an important part of the strategy to keep France's power in check. In 1814, William Frederick gained sovereignty over the Austrian Netherlands and Liège as well. Thus, William Frederick had fulfilled his family's three-century quest to unite the Low Countries under a single rule.
On 15 March 1815; with the encouragement of the powers gathered at the
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
, William Frederick raised the Netherlands to the status of a kingdom and proclaimed himself William I of the Netherlands, King William I. This was made official later in 1815, when the Low Countries were formally recognized as the
United Kingdom of the Netherlands
The United Kingdom of the Netherlands is the unofficial name given to the Kingdom of the Netherlands as it existed from 1815 to 1839. The United Netherlands was created in the aftermath of the Napoleonic Wars through the fusion of territories t ...
. The crown was made a hereditary office of the House of Orange-Nassau.
United Kingdom of the Netherlands (1815–1839)

William I of the Netherlands, William I became king and also became the hereditary Grand Duke of Luxembourg, that was part of the Netherlands but at the same time part of the German Confederation. The newly created country had two capitals: Amsterdam and Brussels. The new nation had two equal parts. The north (Netherlands proper) had 2 million people. They spoke chiefly Dutch but were divided religiously between a Protestant majority and a large Catholic minority. The south (which would be known as "Belgium" after 1830) had a population of 3.4 million people. Nearly all were Catholic, but it was divided between French-speaking Walloons and Dutch-speaking Flemings. The upper and middle classes in the south were mostly French-speaking. About 60,000 Belgians were eligible to vote, compared to about 80,000 Dutchmen. Officially Amsterdam was the capital, but in a compromise the government met alternately in Brussels and The Hague.
Adolphe Quetelet (1796–1874), the great Belgian statistician, calculated that the new nation was significantly better off than other states. Mortality was low, the food supply was good, education was good, public awareness was high and the charity rate was the highest in the world. The best years were in the mid-1820s.
The quality of schooling was dismal, however. According to Schama, about 1800 the local school teacher was the "humble auxiliary of the local priest. Despised by his co-villagers and forced to subsist on the gleanings of the peasants, he combined drumming the catechism into the heads of his unruly charges with the duties of winding the town clock, ringing the church bells or digging its graves. His principal use to the community was to keep its boys out of mischief when there was no labour for them in the fields, or setting the destitute orphans of the town to the 'useful arts' of picking tow or spinning crude flax. As one would expect, standards in such an occupation were dismal." But in 1806 the Dutch, led by Adriaan van den Ende, energetically set out to modernise education, focusing on a new system for advanced training of teachers with an elaborate system of inspectors, training courses, teacher examinations and teaching societies. By 1826, although much smaller than France, the Dutch national government was spending 12 times more than Paris on education.
Constitutional monarchy
William I, who reigned from 1815 to 1840, had great constitutional power. An enlightened despot, he accepted the modernizing transformations of the previous 25 years, including equality of all before the law. However, he resurrected the Estates of the realm, estates as a political class and elevated a large number of people to the nobility. Voting rights were still limited, and only the nobility were eligible for seats in the upper house. The old provinces were reestablished in name only. The government was now fundamentally unitary, and all authority flowed from the center.
William I was a Calvinist and unsympathetic to the religious culture and practices of the Catholic majority. He promulgated the "Fundamental Law of Holland", with some modifications. This entirely overthrew the old order of things in the southern Netherlands: it abolished the privileges of the Catholic Church, and guaranteed equal protection to every religious creed and the enjoyment of the same civil and political rights to every subject of the king. It reflected the spirit of the French Revolution and in so doing did not please the Catholic bishops in the south, who had detested the Revolution.
William I actively promoted economic modernization. The first 15 years of the Kingdom showed progress and prosperity, as industrialization proceeded rapidly in the south, where the Industrial Revolution allowed entrepreneurs and labor to combine in a new textile industry, powered by local coal mines. There was little industry in the northern provinces, but most overseas colonies were restored, and highly profitable trade resumed after a 25-year hiatus. Economic liberalism combined with moderate monarchical authoritarianism accelerated the adaptation of the Netherlands to the new conditions of the 19th century. The country prospered until a crisis arose in relations with the southern provinces.
Belgium breaks away
William was determined to create a united people, even though the north and south had drifted far apart in the past three centuries. Protestants were the largest denomination in the North (population 2 million), but formed a quarter of the population in the overwhelmingly Catholic South (population 3.5 million). Nevertheless, Protestants dominated William's government and army. The Catholics did not consider themselves an integral part of the United Netherlands, preferring instead to identify with mediaeval Dutch culture. Other factors that contributed to this feeling were economic (the South was industrialising, the North had always been a merchants' nation) and linguistic (French was spoken in Wallonia and a large part of the bourgeoisie in Flemish cities).
After having been dominant for centuries, the French-speaking elite in the Southern Netherlands now felt like second-class citizens.
In the Catholic South, William's policies were unpopular. The French-speaking Walloons strenuously rejected his attempt to make Dutch the universal language of government, while the population of
Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
was divided. Flemings in the south spoke a Dutch dialect ("Flemish") and welcomed the encouragement of Dutch with a revival of literature and popular culture. Other Flemings, notably the educated bourgeoisie, preferred to speak French. Although Catholics possessed legal equality, they resented their subordination to a government that was fundamentally Protestant in spirit and membership after having been the state church for centuries in the north. Few Catholics held high office in state or army. Furthermore, political liberals in the south complained about the king's authoritarian methods. All southerners complained of underrepresentation in the national legislature. Although the south was industrializing and was more prosperous than the north the accumulated grievances allowed the multiple opposition forces to coalesce.
The outbreak of July Revolution, revolution in France in 1830 was a signal for action, at first on behalf of autonomy for Belgium, as the southern provinces were now called, and later on behalf of total independence. William dithered and his half-hearted efforts to reconquer Belgium were thwarted both by the efforts of the Belgians themselves and by the diplomatic opposition of the great powers.
At the London Conference of 1830, the chief powers of Europe ordered (in November 1830) an armistice between the Dutch and the Belgians. The first draft for a treaty of separation of Belgium and the Netherlands was rejected by the Belgians. A second draft (June 1831) was rejected by William I, who resumed hostilities. Franco-British intervention forced William to withdraw Dutch forces from Belgium late in 1831, and in 1833 an armistice of indefinite duration was concluded. Belgium was effectively independent but William's attempts to recover Luxembourg and Limburg led to renewed tension. The London Conference of 1838–1839 prepared the final Dutch-Belgian Treaty of London (1839), separation treaty of 1839. It divided Luxembourg and Limburg between the Dutch and Belgian crowns. The Kingdom of the Netherlands thereafter was made up of the 11 northern provinces.
Democratic and Industrial Development (1840–1900)

The Netherlands did not industrialize as rapidly as Belgium after 1830, but it was prosperous enough. Griffiths argues that certain government policies facilitated the emergence of a national economy in the 19th century. They included the abolition of internal tariffs and guilds, a unified coinage system, modern methods of tax collection, standardized weights and measures, and the building of many roads, canals, and railroads. However, compared to Belgium, which was leading in industrialization on the Continent, the Netherlands moved slowly. Possible explanations for this difference are the higher costs due to geography and high wages, and the emphasis of entrepreneurs on trade rather than industry.
For example, in the Dutch coastal provinces agricultural productivity was relatively high. Hence, industrial growth arrived relatively late – after 1860 – because incentives to move to labour-intensive industry were quite weak.
However, the provinces of North Brabant and Overijssel did industrialize, and they became the most economically advanced areas of the country.
As in the rest of Europe, the 19th century saw the gradual transformation of the Netherlands into a modern middle-class industrial society. The number of people employed in agriculture decreased, while the country made a strong effort to revive its stake in the highly competitive shipping and trade business. The Netherlands lagged behind Belgium until the late 19th century in industrialization, and caught up around 1920. Major industries included textiles and (later) the great Philips industrial conglomerate. Rotterdam became a major shipping and manufacturing center. Poverty slowly declined as begging largely disappeared along with steadily improving working conditions for the population.
1848 Constitutional reform and liberalism
In 1840 William I abdicated in favor of his son, William II of the Netherlands, William II, who attempted to carry on the policies of his father in the face of a powerful liberal movement. In 1848 Revolutions of 1848, unrest broke out all over Europe. Although there were no major events in the Netherlands, these foreign developments persuaded King William II of the Netherlands, William II to agree to liberal and democratic reform. That same year Johan Rudolf Thorbecke, a prominent liberal, was asked by the king to draft a constitution that would turn the Netherlands into a constitutional monarchy. The new constitution was proclaimed on 3 November 1848. It severely limited the king's powers (making the government accountable only to an elected parliament), and it protected civil liberties. The new liberal constitution, which put the government under the control of the States General, was accepted by the legislature in 1848. The relationship between monarch, government and parliament has remained essentially unchanged ever since. In fact, the current Constitution of the Netherlands is the 1848 Constitution, albeit with amendments.
William II was succeeded by William III of the Netherlands, William III in 1849. The new king reluctantly chose Thorbecke to head the new government, which introduced several liberal measures, notably the extension of suffrage. However, Thorbecke's government soon fell, when Protestants rioted against the Vatican's reestablishment of the Catholic episcopate, in abeyance since the 16th century. A conservative government was formed, but it did not undo the liberal measures, and the Catholics were finally given equality after two centuries of subordination. Dutch political history from the middle of the 19th century until the
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
was fundamentally one of the extension of liberal reforms in government, the reorganization and modernization of the Dutch economy, and the rise of trade unionism and socialism as working-class movements independent of traditional liberalism. The growth in prosperity was enormous, as real per capita GNP soared from 106 guilders in 1804 to 403 in 1913.
Religion and pillarisation

Religion was a contentious issue with repeated struggles over the relations of church and state in the field of education. In 1816, the government took full control of the Dutch Reformed Church (). In 1857, all religious instruction was ended in public schools, but the various churches set up their own schools, and even universities. Dissident members broke away from the Dutch Reformed Church in the Secession of 1834. They were harassed by the government under an onerous Napoleonic law prohibiting gatherings of more than 20 members without a permit. After the harassment ended in the 1850s, a number of these dissidents eventually created the Christian Reformed Church in 1869; thousands migrated to Michigan, Illinois, and Iowa in the United States. By 1900, the dissidents represented about 10% of the population, compared to 45% of the population who were in the Dutch Reformed Church, which continued to be the only church to receive state money.
At mid-century, most Dutch belonged either to the Dutch Reformed Church or dissenter groups that separated from it (around 55%), or the Roman Catholic Church (35% to 40%), together with smaller Protestant (for example,
Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
) and Jewish groups. A large and powerful sector of nominal Protestants were in fact secular liberals seeking to minimize religious influence. In reaction a novel alliance developed with Catholics and devout Calvinists joining against secular liberals. The Catholics, who had been loosely allied with the liberals in earlier decades, turned against them on the issue of state support, which the liberals insisted should be granted only to public schools, and joined with Protestant political parties in demanding equal state support to schools maintained by religious groups.
The Netherlands remained one of the most tolerant countries in Europe towards religious belief, although conservative Protestants objected to the liberalization of the Dutch Reformed Church during the 19th century and faced opposition from the government when they tried to establish separate communities (Catholics and other non-Protestants were left unmolested by Dutch authorities). Some moved to the United States as a consequence, but as the century drew to a close, religious persecution had totally ceased.

Dutch social and political life became divided by fairly clear-cut internal borders that were emerging as the society pillarized into three separate parts based on religion. The economy was not affected. One of the people most responsible for designing pillarization was Abraham Kuyper (1837–1920), a leading politician, neo-Calvinist theologian, and journalist. Kuyper established orthodox Calvinist organizations, and also provided a theoretical framework by developing such concepts as "sphere-sovereignty" that celebrated Dutch society as a society of organized minorities. ''Verzuiling'' ("pillarization" or "pluralism") after 1850 became the solution to the danger of internal conflict. Everyone was part of one (and only one) pillar (''zuil'') based chiefly on religion (Protestant, Catholic, secular). The secular pillar eventually split into a socialist/working class pillar and a liberal (pro-business) secular pillar. Each pillar built a full set of its own social organizations, including churches (for the religious pillars), political parties, schools, universities, labor unions, sport clubs, boy scout unions and other youth clubs, and newspapers. The members of different ''zuilen'' lived in close proximity in cities and villages, spoke the same language, and did business with one another, but seldom interacted informally and rarely intermarried. In politics Kuyper formed the Anti-Revolutionary Party (ARP) in 1879, and headed it until 1905.
Pillarization was officially recognized in the Pacification of 1917, whereby socialists and liberals achieved their goal of universal male suffrage and the religious parties were guaranteed equal funding of all schools. In 1930 radio was organized so that each pillar had full control of its own network. When television began in the late 1940s the pillars divided up time equally on the one station. In politics and civic affairs leaders of the pillar organizations cooperated and they acknowledged the right of the other pillars, so public life generally ran smoothly.
Flourishing of art, culture and science
The late 19th century saw a cultural revival. The Hague School brought a revival of realist painting, 1860–1890. The world-famous Dutch painter was Vincent van Gogh, but he spent most of his career in France. Literature, music, architecture and science also flourished. A representative leader of science was Johannes Diderik van der Waals (1837–1923), a working class youth who taught himself physics, earned a PhD at the nation's leading school Leiden University, and in 1910 won the Nobel Prize for his discoveries in thermodynamics. Hendrik Lorentz (1853–1928) and his student Pieter Zeeman (1865–1943) shared the 1902 Nobel Prize in physics. Other notable scientists included biologist Hugo de Vries (1848–1935), who rediscovered Mendelian genetics.
1900 to present
From 1900 to 1940, the Netherlands experienced significant population growth. This era included significant colonial expansion, particularly in the
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies (; ), was a Dutch Empire, Dutch colony with territory mostly comprising the modern state of Indonesia, which Proclamation of Indonesian Independence, declared independence on 17 Au ...
, coupled with the challenges posed by World War I and the Great Depression. Although the Netherlands maintained neutrality during World War I, its strategic geographic location and colonial resources had profound implications for its economic and political stability. The period saw the rise of socialism and labor unrest, which were partly driven by industrialization and the shifting dynamics of Dutch society. A half-hearted socialist revolution attempt during the Red Week (Netherlands), Red Week in November 1918 failed.
World War II marked a devastating period for the Netherlands, which suffered under German occupation from 1940 until liberation in 1945. The war's impact was severe, with the Rotterdam Blitz causing extensive destruction and loss of life. Dutch resistance was significant, though the nation also faced collaboration from within. Post-war, the Netherlands underwent a painful process of recovery and retribution against collaborators. The immediate post-war years were focused on rebuilding and economic stabilization, facilitated by U.S. aid through the
Marshall Plan
The Marshall Plan (officially the European Recovery Program, ERP) was an American initiative enacted in 1948 to provide foreign aid to Western Europe. The United States transferred $13.3 billion (equivalent to $ in ) in economic recovery pr ...
, which helped to revive the Dutch economy and infrastructure.
The post-war period saw significant changes in the
Dutch empire
The Dutch colonial empire () comprised overseas territories and trading posts under some form of Dutch control from the early 17th to late 20th centuries, including those initially administered by Dutch chartered companies—primarily the Du ...
, with Indonesia proclaiming independence in 1945, leading to a violent and tumultuous decolonization process completed in 1949. This era brought about substantial social change within the Netherlands, including the establishment of a welfare state in the subsequent decades. Economic prosperity in the 1960s and 1970s led to social liberalization, culminating in progressive policies on immigration, drugs, and euthanasia. The Netherlands also became a founding member of key international institutions, including the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
, reflecting its deepening commitment to international cooperation.
Historians
* Julia Adams, economic and social history
* Petrus Johannes Blok, survey
* Hans Blom (historian), J. C. H. Blom, survey
* M. R. Boxell, political history
* Pieter Geyl, Dutch revolt; historiography
* Johan Huizinga (1872–1945), cultural history
* Jonathan Israel, Dutch Republic, Age of Enlightenment, Baruch Spinoza
* Loe de Jong, Louis De Jong, World War II
* John Lothrop Motley, American historian of the Dutch Revolt
* Jan Romein (1893–1962), theoretical and world history
* Jan de Vries (historian), Jan de Vries, economic history
Historiography
The American John Lothrop Motley was the first foreign historian to write a major history of the Dutch Republic. In 3500 pages he crafted a literary masterpiece that was translated into numerous languages; his dramatic story reached a wide audience in the 19th century. Motley relied heavily on Dutch scholarship and immersed himself in the sources. His style no longer attracts readers, and scholars have moved away from his simplistic dichotomies of good versus evil, Dutch versus Spanish, Catholic versus Protestant, freedom versus authoritarianism. His theory of causation overemphasized ethnicity as an unchanging characteristic, exaggerated the importance of William of Orange, and gave undue importance to the issue of religious tolerance.
The pioneering Dutch cultural historian Johan Huizinga, author of ''The Autumn of the Middle Ages'' (1919) (the English translation was called ''The Waning of the Middle Ages'') and ''Homo Ludens: A Study of the Play Element in Culture'' (1935), which expanded the field of cultural history and influenced the historical anthropology of younger historians of the French Annales School. He was influenced by art history and advised historians to trace "patterns of culture" by studying "themes, figures, motifs, symbols, styles and sentiments".
The "polder model" continues to strongly influence historians as well as Dutch political discussion. The polder model stressed the need for finding consensus and discouraged furious debate and angry dissent in both academia and politics – in contrast to the highly developed, intense debates in Germany.
The H-Net list ''H-Low-Countries'' is published free by email and is edited by scholars. Its occasional messages serve an international community with diverse methodological approaches, archival experiences, teaching styles, and intellectual traditions, promotes discussion relevant to the region and to the different national histories in particular, with an emphasis on the Netherlands. H-Low-Countries publishes conference announcements, questions and discussions; reviews of books, journals, and articles; and tables of contents of journals on the history of the Low Countries (in both Dutch and English). After World War II both research-oriented and teaching-oriented historians have been rethinking their interpretive approaches to Dutch history, balancing traditional memories and modern scholarship. In terms of popular history, there has been an effort to ensure greater historical accuracy in museums and historic tourist sites.
Once heralded as the leading event of modern Dutch history, the
Dutch Revolt
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt (; 1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Reformation, centralisation, exc ...
lasted from 1568 to 1648, and historians have worked to interpret it for even longer. In 2007, Laura Cruz explained the major debates among scholars regarding the Dutch bid for independence from Spanish rule. While agreeing that the intellectual milieus of late 19th and 20th centuries affected historians' interpretations, Cruz argued that writings about the revolt trace changing perceptions of the role played by small countries in the history of Europe. In recent decades grand theory has fallen out of favor among most scholars, who emphasize the particular over the general. Dutch and Belgian historiography since 1945 no longer says the revolt was the culmination of an inevitable process leading to independence and freedom. Instead scholars have put the political and economic details of the towns and provinces under the microscope, while agreeing on the weaknesses of attempts at centralization by the Habsburg rulers. The most influential new studies have been rooted in demographic and economic history, though scholars continue to debate the relationship between economics and politics. The religious dimension has been viewed in terms of mentalities, exposing the minority position of Calvinism, while the international aspects have been studied more seriously by foreign historians than by the Dutch themselves.
Pieter Geyl was the leading historian of the Dutch Revolt, and an influential professor at the University of London (1919–1935) and at the State University of Utrecht (1936–1958). He wrote a six-volume history of the Dutch-speaking peoples. The Nazis imprisoned him in World War II. In his political views, Geyl adopted the views of the 17th-century Dutch Louvestein faction, led by Johan van Oldenbarneveldt and Johan de Witt. It stood for liberty, toleration, and national interests in contrast to the Orange stadholders who sought to promote their own self-interest. According to Geyl, the Dutch Republic reached the peak of its powers during the 17th century. He was also a staunch nationalist and suggested that Flanders could split off from Belgium and join the Netherlands. Later he decried what he called radical nationalism and stressed more the vitality of Western Civilization. Geyl was highly critical of the World history (field), world history approach of Arnold J. Toynbee.
Jan Romein created a "theoretical history" in an attempt to reestablish the relevance of history to public life in the 1930s at a time of immense political uncertainty and cultural crisis, when Romein thought that history had become too inward-looking and isolated from other disciplines. Romein, a Marxist, wanted history to contribute to social improvement. At the same time, influenced by the successes of theoretical physics and his study of Oswald Spengler, Arnold J. Toynbee, Frederick John Teggart, and others, he spurred on the development of theoretical history in the Netherlands, to the point where it became a subject in its own right at the university level after the war. Romein used the term integral history as a substitute for cultural history and focused his attention on the period around the turn of the century. He concluded that a serious crisis occurred in European civilization in 1900 because of the rise of anti-Semitism, extreme nationalism, discontent with the parliamentary system, depersonalization of the state, and the rejection of positivism. European civilization waned as the result of this crisis which was accompanied by the rise of the United States, the Americanization of the world, and the emergence of Asia. His interpretation is reminiscent of that of his mentor Johan Huizinga and was criticized by his colleague Pieter Geyl.
[; ]
See also
* Canon of the Netherlands
* Culture of the Netherlands
* Demographics of the Netherlands
* Dutch diaspora
*
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies (; ), was a Dutch Empire, Dutch colony with territory mostly comprising the modern state of Indonesia, which Proclamation of Indonesian Independence, declared independence on 17 Au ...
* Economy of the Netherlands
* Geography of the European Netherlands
* History of religion in the Netherlands
* List of prime ministers of the Netherlands
* List of monarchs of the Netherlands
* Politics of the Netherlands
* Provinces of the Netherlands
* Netherlands in World War II
Notes
Sources
*
* Kennedy, James C. ''A Concise History of The Netherlands''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 2017.
* , Detailed survey
Further reading
* Abbenhuis, Maartje. ''The art of staying neutral: the Netherlands in the First World War, 1914-1918'' (Amsterdam University Press, 2006
online
* Bieleman, Jan. ''Five centuries of farming: a short history of Dutch agriculture 1500-2000'' (BRILL, 2023
online
* Blok, Petrus Johannes. ''History of the People of the Netherlands'' (Putnam's, 1912
online
* C't Hart, Marjolein, Joost Jonker, and Jan Luiten van Zanden, eds. ''A financial history of the Netherlands'' (Cambridge University Press, 1997)
* Kennedy, James C. ''A Concise History of The Netherlands''. (Cambridge University Press 2017
online* Meijer, Reinder. ''Literature of the low countries: a short history of Dutch literature in the Netherlands and Belgium'' (Springer Science & Business Media, 2012
online
* Van Zanden, Jan L. ''The economic history of the Netherlands 1914-1995: A small open economy in the 'long' twentieth century'' (Routledge, 2005).
* Wielenga, Friso. ''A history of the Netherlands: From the sixteenth century to the present day'' (Bloomsbury, 2024).
* Wintle, Michael. ''An economic and social history of the Netherlands, 1800–1920: demographic, economic and social transition'' (Cambridge University Press, 2000).
External links
''Dutch Crossing: Journal of Low Countries Studies'' a scholarly journal
History of Netherlands: Primary DocumentsNetherlands Geographic Information System (1812–1997)
{{European history by country
History of the Netherlands,
Articles which contain graphical timelines
 By 1433, the
By 1433, the  During the last ice age, the Netherlands had a
During the last ice age, the Netherlands had a  Agriculture also arrived in areas near the Netherlands somewhere around 5000 BC with the
Agriculture also arrived in areas near the Netherlands somewhere around 5000 BC with the  During his
During his  In the 7th and 8th centuries, the
In the 7th and 8th centuries, the  After
After  In the 19th century, Dutch historians believed that the Franks, Frisians, and Saxons had populated and inhabited the Low Countries, but this theory fell out of favour in the 20th century. Due to the scarcity of written sources, knowledge of this period depends to a large degree on the interpretation of archaeological data. The traditional view of a clear-cut division between Frisians in the north and coast,
In the 19th century, Dutch historians believed that the Franks, Frisians, and Saxons had populated and inhabited the Low Countries, but this theory fell out of favour in the 20th century. Due to the scarcity of written sources, knowledge of this period depends to a large degree on the interpretation of archaeological data. The traditional view of a clear-cut division between Frisians in the north and coast,  In the early 8th century the Frisians came increasingly into conflict with the
In the early 8th century the Frisians came increasingly into conflict with the  In the 9th and 10th centuries, the Vikings raided the largely defenceless Frisian and
In the 9th and 10th centuries, the Vikings raided the largely defenceless Frisian and  The center of power in these emerging independent territories was in the
The center of power in these emerging independent territories was in the  From 1515 to 1523, Charles's government in the Netherlands had to contend with the rebellion of Frisian peasants (led by Pier Gerlofs Donia and Wijard Jelckama).
From 1515 to 1523, Charles's government in the Netherlands had to contend with the rebellion of Frisian peasants (led by Pier Gerlofs Donia and Wijard Jelckama).  During the 16th century, the
During the 16th century, the 
 The Dutch War for Independence from Spain is frequently called the Eighty Years' War (1568–1648). The first fifty years (1568 through 1618) were a war solely between Catholic Spain and the Protestant rebels of the Netherlands. It was a military conflict with integral religious elements. During the last thirty years (1618–1648) the conflict between Spain and the Netherlands was submerged in the general European War that became known as the
The Dutch War for Independence from Spain is frequently called the Eighty Years' War (1568–1648). The first fifty years (1568 through 1618) were a war solely between Catholic Spain and the Protestant rebels of the Netherlands. It was a military conflict with integral religious elements. During the last thirty years (1618–1648) the conflict between Spain and the Netherlands was submerged in the general European War that became known as the  The ''Dutch Golden Age'' was a period which roughly lasted from 1588, when the
The ''Dutch Golden Age'' was a period which roughly lasted from 1588, when the 
 The Dutch East India Company (also called the VOC) emerged in 1602, when the government gave it a monopoly to trade with Asia, mainly to
The Dutch East India Company (also called the VOC) emerged in 1602, when the government gave it a monopoly to trade with Asia, mainly to  In 1647, a Dutch vessel was wrecked in the present-day
In 1647, a Dutch vessel was wrecked in the present-day  Dutch was the official language, but a dialect had formed that was quite distinct from Dutch. The
Dutch was the official language, but a dialect had formed that was quite distinct from Dutch. The  The ''United Provinces of the Netherlands'', commonly referred to in
The ''United Provinces of the Netherlands'', commonly referred to in  When the French retreated from the northern provinces in 1813, a Triumvirate of 1813, Triumvirate took over at the helm of a Sovereign Principality of the United Netherlands, provisional government. Although most members of the provisional government had been among the men who had driven out William V 18 years earlier, the leaders of the provisional government knew that any new regime would have to be headed by his son, William I of the Netherlands, William Frederick. They also knew that it would be better in the long term if the Dutch people themselves installed the prince, rather than have him imposed on the country by the anti-French alliance. Accordingly, the Triumvirate called William Frederick back on 30 November and offered him the crown. He refused, but instead proclaimed himself "Sovereign Principality of the United Netherlands, hereditary sovereign prince" on 6 December.
The Great Powers had Eight Articles of London, secretly agreed to merge the northern Netherlands with the more populated Austrian Netherlands and the smaller Prince-Bishopric of Liège into a single constitutional monarchy. Having a stronger country on France's northern border was considered (especially by Alexander I of Russia, Tsar Alexander) to be an important part of the strategy to keep France's power in check. In 1814, William Frederick gained sovereignty over the Austrian Netherlands and Liège as well. Thus, William Frederick had fulfilled his family's three-century quest to unite the Low Countries under a single rule.
On 15 March 1815; with the encouragement of the powers gathered at the
When the French retreated from the northern provinces in 1813, a Triumvirate of 1813, Triumvirate took over at the helm of a Sovereign Principality of the United Netherlands, provisional government. Although most members of the provisional government had been among the men who had driven out William V 18 years earlier, the leaders of the provisional government knew that any new regime would have to be headed by his son, William I of the Netherlands, William Frederick. They also knew that it would be better in the long term if the Dutch people themselves installed the prince, rather than have him imposed on the country by the anti-French alliance. Accordingly, the Triumvirate called William Frederick back on 30 November and offered him the crown. He refused, but instead proclaimed himself "Sovereign Principality of the United Netherlands, hereditary sovereign prince" on 6 December.
The Great Powers had Eight Articles of London, secretly agreed to merge the northern Netherlands with the more populated Austrian Netherlands and the smaller Prince-Bishopric of Liège into a single constitutional monarchy. Having a stronger country on France's northern border was considered (especially by Alexander I of Russia, Tsar Alexander) to be an important part of the strategy to keep France's power in check. In 1814, William Frederick gained sovereignty over the Austrian Netherlands and Liège as well. Thus, William Frederick had fulfilled his family's three-century quest to unite the Low Countries under a single rule.
On 15 March 1815; with the encouragement of the powers gathered at the  William I of the Netherlands, William I became king and also became the hereditary Grand Duke of Luxembourg, that was part of the Netherlands but at the same time part of the German Confederation. The newly created country had two capitals: Amsterdam and Brussels. The new nation had two equal parts. The north (Netherlands proper) had 2 million people. They spoke chiefly Dutch but were divided religiously between a Protestant majority and a large Catholic minority. The south (which would be known as "Belgium" after 1830) had a population of 3.4 million people. Nearly all were Catholic, but it was divided between French-speaking Walloons and Dutch-speaking Flemings. The upper and middle classes in the south were mostly French-speaking. About 60,000 Belgians were eligible to vote, compared to about 80,000 Dutchmen. Officially Amsterdam was the capital, but in a compromise the government met alternately in Brussels and The Hague.
Adolphe Quetelet (1796–1874), the great Belgian statistician, calculated that the new nation was significantly better off than other states. Mortality was low, the food supply was good, education was good, public awareness was high and the charity rate was the highest in the world. The best years were in the mid-1820s.
The quality of schooling was dismal, however. According to Schama, about 1800 the local school teacher was the "humble auxiliary of the local priest. Despised by his co-villagers and forced to subsist on the gleanings of the peasants, he combined drumming the catechism into the heads of his unruly charges with the duties of winding the town clock, ringing the church bells or digging its graves. His principal use to the community was to keep its boys out of mischief when there was no labour for them in the fields, or setting the destitute orphans of the town to the 'useful arts' of picking tow or spinning crude flax. As one would expect, standards in such an occupation were dismal." But in 1806 the Dutch, led by Adriaan van den Ende, energetically set out to modernise education, focusing on a new system for advanced training of teachers with an elaborate system of inspectors, training courses, teacher examinations and teaching societies. By 1826, although much smaller than France, the Dutch national government was spending 12 times more than Paris on education.
William I of the Netherlands, William I became king and also became the hereditary Grand Duke of Luxembourg, that was part of the Netherlands but at the same time part of the German Confederation. The newly created country had two capitals: Amsterdam and Brussels. The new nation had two equal parts. The north (Netherlands proper) had 2 million people. They spoke chiefly Dutch but were divided religiously between a Protestant majority and a large Catholic minority. The south (which would be known as "Belgium" after 1830) had a population of 3.4 million people. Nearly all were Catholic, but it was divided between French-speaking Walloons and Dutch-speaking Flemings. The upper and middle classes in the south were mostly French-speaking. About 60,000 Belgians were eligible to vote, compared to about 80,000 Dutchmen. Officially Amsterdam was the capital, but in a compromise the government met alternately in Brussels and The Hague.
Adolphe Quetelet (1796–1874), the great Belgian statistician, calculated that the new nation was significantly better off than other states. Mortality was low, the food supply was good, education was good, public awareness was high and the charity rate was the highest in the world. The best years were in the mid-1820s.
The quality of schooling was dismal, however. According to Schama, about 1800 the local school teacher was the "humble auxiliary of the local priest. Despised by his co-villagers and forced to subsist on the gleanings of the peasants, he combined drumming the catechism into the heads of his unruly charges with the duties of winding the town clock, ringing the church bells or digging its graves. His principal use to the community was to keep its boys out of mischief when there was no labour for them in the fields, or setting the destitute orphans of the town to the 'useful arts' of picking tow or spinning crude flax. As one would expect, standards in such an occupation were dismal." But in 1806 the Dutch, led by Adriaan van den Ende, energetically set out to modernise education, focusing on a new system for advanced training of teachers with an elaborate system of inspectors, training courses, teacher examinations and teaching societies. By 1826, although much smaller than France, the Dutch national government was spending 12 times more than Paris on education.
 The Netherlands did not industrialize as rapidly as Belgium after 1830, but it was prosperous enough. Griffiths argues that certain government policies facilitated the emergence of a national economy in the 19th century. They included the abolition of internal tariffs and guilds, a unified coinage system, modern methods of tax collection, standardized weights and measures, and the building of many roads, canals, and railroads. However, compared to Belgium, which was leading in industrialization on the Continent, the Netherlands moved slowly. Possible explanations for this difference are the higher costs due to geography and high wages, and the emphasis of entrepreneurs on trade rather than industry.
For example, in the Dutch coastal provinces agricultural productivity was relatively high. Hence, industrial growth arrived relatively late – after 1860 – because incentives to move to labour-intensive industry were quite weak.
However, the provinces of North Brabant and Overijssel did industrialize, and they became the most economically advanced areas of the country.
As in the rest of Europe, the 19th century saw the gradual transformation of the Netherlands into a modern middle-class industrial society. The number of people employed in agriculture decreased, while the country made a strong effort to revive its stake in the highly competitive shipping and trade business. The Netherlands lagged behind Belgium until the late 19th century in industrialization, and caught up around 1920. Major industries included textiles and (later) the great Philips industrial conglomerate. Rotterdam became a major shipping and manufacturing center. Poverty slowly declined as begging largely disappeared along with steadily improving working conditions for the population.
The Netherlands did not industrialize as rapidly as Belgium after 1830, but it was prosperous enough. Griffiths argues that certain government policies facilitated the emergence of a national economy in the 19th century. They included the abolition of internal tariffs and guilds, a unified coinage system, modern methods of tax collection, standardized weights and measures, and the building of many roads, canals, and railroads. However, compared to Belgium, which was leading in industrialization on the Continent, the Netherlands moved slowly. Possible explanations for this difference are the higher costs due to geography and high wages, and the emphasis of entrepreneurs on trade rather than industry.
For example, in the Dutch coastal provinces agricultural productivity was relatively high. Hence, industrial growth arrived relatively late – after 1860 – because incentives to move to labour-intensive industry were quite weak.
However, the provinces of North Brabant and Overijssel did industrialize, and they became the most economically advanced areas of the country.
As in the rest of Europe, the 19th century saw the gradual transformation of the Netherlands into a modern middle-class industrial society. The number of people employed in agriculture decreased, while the country made a strong effort to revive its stake in the highly competitive shipping and trade business. The Netherlands lagged behind Belgium until the late 19th century in industrialization, and caught up around 1920. Major industries included textiles and (later) the great Philips industrial conglomerate. Rotterdam became a major shipping and manufacturing center. Poverty slowly declined as begging largely disappeared along with steadily improving working conditions for the population.
 Dutch social and political life became divided by fairly clear-cut internal borders that were emerging as the society pillarized into three separate parts based on religion. The economy was not affected. One of the people most responsible for designing pillarization was Abraham Kuyper (1837–1920), a leading politician, neo-Calvinist theologian, and journalist. Kuyper established orthodox Calvinist organizations, and also provided a theoretical framework by developing such concepts as "sphere-sovereignty" that celebrated Dutch society as a society of organized minorities. ''Verzuiling'' ("pillarization" or "pluralism") after 1850 became the solution to the danger of internal conflict. Everyone was part of one (and only one) pillar (''zuil'') based chiefly on religion (Protestant, Catholic, secular). The secular pillar eventually split into a socialist/working class pillar and a liberal (pro-business) secular pillar. Each pillar built a full set of its own social organizations, including churches (for the religious pillars), political parties, schools, universities, labor unions, sport clubs, boy scout unions and other youth clubs, and newspapers. The members of different ''zuilen'' lived in close proximity in cities and villages, spoke the same language, and did business with one another, but seldom interacted informally and rarely intermarried. In politics Kuyper formed the Anti-Revolutionary Party (ARP) in 1879, and headed it until 1905.
Pillarization was officially recognized in the Pacification of 1917, whereby socialists and liberals achieved their goal of universal male suffrage and the religious parties were guaranteed equal funding of all schools. In 1930 radio was organized so that each pillar had full control of its own network. When television began in the late 1940s the pillars divided up time equally on the one station. In politics and civic affairs leaders of the pillar organizations cooperated and they acknowledged the right of the other pillars, so public life generally ran smoothly.
Dutch social and political life became divided by fairly clear-cut internal borders that were emerging as the society pillarized into three separate parts based on religion. The economy was not affected. One of the people most responsible for designing pillarization was Abraham Kuyper (1837–1920), a leading politician, neo-Calvinist theologian, and journalist. Kuyper established orthodox Calvinist organizations, and also provided a theoretical framework by developing such concepts as "sphere-sovereignty" that celebrated Dutch society as a society of organized minorities. ''Verzuiling'' ("pillarization" or "pluralism") after 1850 became the solution to the danger of internal conflict. Everyone was part of one (and only one) pillar (''zuil'') based chiefly on religion (Protestant, Catholic, secular). The secular pillar eventually split into a socialist/working class pillar and a liberal (pro-business) secular pillar. Each pillar built a full set of its own social organizations, including churches (for the religious pillars), political parties, schools, universities, labor unions, sport clubs, boy scout unions and other youth clubs, and newspapers. The members of different ''zuilen'' lived in close proximity in cities and villages, spoke the same language, and did business with one another, but seldom interacted informally and rarely intermarried. In politics Kuyper formed the Anti-Revolutionary Party (ARP) in 1879, and headed it until 1905.
Pillarization was officially recognized in the Pacification of 1917, whereby socialists and liberals achieved their goal of universal male suffrage and the religious parties were guaranteed equal funding of all schools. In 1930 radio was organized so that each pillar had full control of its own network. When television began in the late 1940s the pillars divided up time equally on the one station. In politics and civic affairs leaders of the pillar organizations cooperated and they acknowledged the right of the other pillars, so public life generally ran smoothly.
 From 1900 to 1940, the Netherlands experienced significant population growth. This era included significant colonial expansion, particularly in the
From 1900 to 1940, the Netherlands experienced significant population growth. This era included significant colonial expansion, particularly in the