duplicating machines on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Duplicating machines were the predecessors of modern document-reproduction technology. They have now been replaced by digital duplicators, scanners,
 In document duplication (as opposed to
In document duplication (as opposed to
 In the late 1880s, adoption of improvements in office systems for filing unbound documents increased the demand for copying machines that made unbound copies of letters, as opposed to copies in bound books. In 1886, Schlicht & Field of Rochester, N.Y., introduced the Rapid Roller Damp-Leaf Copier, a roller copier, which used pressure supplied by rollers to copy letters onto a roll of dampened paper. After copies were pressed onto the paper, the paper entered the cabinet under the copier, where it dried on a large roller. An attachment was used to cut dried copies off the roll.
Copies could be made more quickly with a roller copier than with a letter copying press. It was claimed that nearly 100 papers could be copied in two minutes with a roller copier. Roller copiers competed with carbon paper technology. It was claimed that a roller copier could make a half dozen copies of a typewritten letter if the letter was run through the copier several times. It could make a dozen copies if the letter was written with a pen and good copying ink.
The Process Letter Machine Co. of Muncie, Indiana, offered the New Rotary Copying Press, a loose-leaf copier, in 1902. This machine was similar to roller copiers but copied onto loose-leaf paper.
In the late 1880s, adoption of improvements in office systems for filing unbound documents increased the demand for copying machines that made unbound copies of letters, as opposed to copies in bound books. In 1886, Schlicht & Field of Rochester, N.Y., introduced the Rapid Roller Damp-Leaf Copier, a roller copier, which used pressure supplied by rollers to copy letters onto a roll of dampened paper. After copies were pressed onto the paper, the paper entered the cabinet under the copier, where it dried on a large roller. An attachment was used to cut dried copies off the roll.
Copies could be made more quickly with a roller copier than with a letter copying press. It was claimed that nearly 100 papers could be copied in two minutes with a roller copier. Roller copiers competed with carbon paper technology. It was claimed that a roller copier could make a half dozen copies of a typewritten letter if the letter was run through the copier several times. It could make a dozen copies if the letter was written with a pen and good copying ink.
The Process Letter Machine Co. of Muncie, Indiana, offered the New Rotary Copying Press, a loose-leaf copier, in 1902. This machine was similar to roller copiers but copied onto loose-leaf paper.
Antique Copying Machines
In-depth look at a ditto master sheet
{{DEFAULTSORT:Duplicating Machines Office equipment Printing devices Printing technology Machines Copying
laser printer
Laser printing is an electrostatic digital printing process. It produces high-quality text and graphics (and moderate-quality photographs) by repeatedly passing a laser beam back and forth over a Electric charge, negatively charged cylinder call ...
s, and photocopier
A photocopier (also called copier or copy machine, and formerly Xerox machine, the generic trademark) is a machine that makes copies of documents and other visual images onto paper or plastic film quickly and cheaply. Most modern photocopiers ...
s, but for many years they were the primary means of reproducing documents for limited-run distribution. The duplicator was pioneered by Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison (February11, 1847October18, 1931) was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These inventions, ...
and David Gestetner, with Gestetner
The Gestetner is a type of duplicating machine named after its inventor, David Gestetner (1854–1939). During the 20th century, the term ''Gestetner'' was used as a verb—as in ''Gestetnering''. The Gestetner company established its base in Lo ...
dominating the market up until the late 1990s.
Like the typewriter
A typewriter is a Machine, mechanical or electromechanical machine for typing characters. Typically, a typewriter has an array of Button (control), keys, and each one causes a different single character to be produced on paper by striking an i ...
, these machines were products of the second phase of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
which started near the end of the 19th century (also called the Second Industrial Revolution
The Second Industrial Revolution, also known as the Technological Revolution, was a phase of rapid Discovery (observation), scientific discovery, standardisation, mass production and industrialisation from the late 19th century into the early ...
). This second phase brought to mass markets technologies like the small electric motors and the products of industrial chemistry without which the duplicating machines would not have been economical. By bringing greatly increased quantities of paperwork to daily life, the duplicating machine and the typewriter
A typewriter is a Machine, mechanical or electromechanical machine for typing characters. Typically, a typewriter has an array of Button (control), keys, and each one causes a different single character to be produced on paper by striking an i ...
gradually changed the forms of the office desk
A desk or bureau is a piece of furniture with a flat table (furniture), table-style work surface used in a school, office, home or the like for academic, professional or domestic activities such as reading (activity), reading, writing, or using ...
and transformed the nature of office
An office is a space where the employees of an organization perform Business administration, administrative Work (human activity), work in order to support and realize the various goals of the organization. The word "office" may also denote a po ...
work.
They were often used in school
A school is the educational institution (and, in the case of in-person learning, the Educational architecture, building) designed to provide learning environments for the teaching of students, usually under the direction of teachers. Most co ...
s, churches, and small organizations, where revolutionarily economical copying was in demand for the production of newsletters and worksheets. Self-publishers also used these machines to produce fanzine
A fanzine (blend word, blend of ''fan (person), fan'' and ''magazine'' or ''zine'') is a non-professional and non-official publication produced by enthusiasts of a particular cultural phenomenon (such as a literary or musical genre) for the pleas ...
s.
A few alternatives to hand copying were invented between the mid-17th century and the late 18th century, but none were widely adopted for business use.
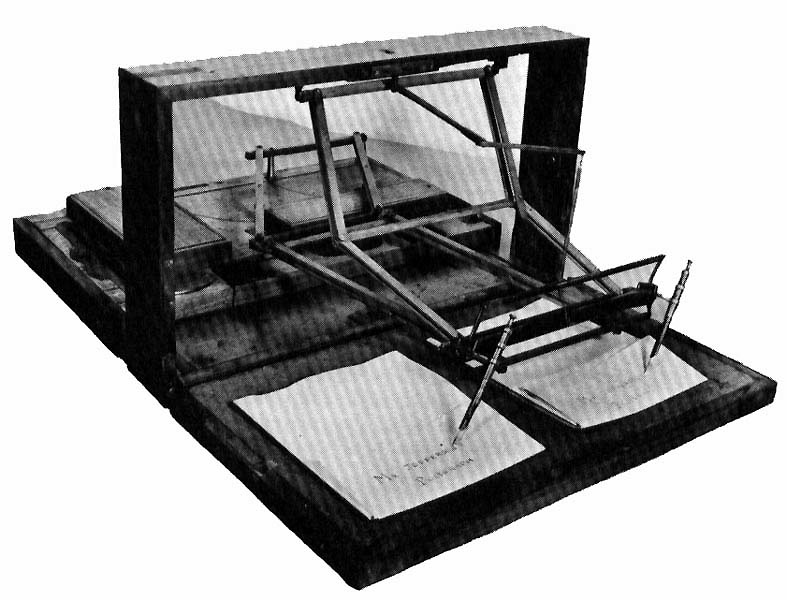
Polygraphs
 In document duplication (as opposed to
In document duplication (as opposed to law enforcement
Law enforcement is the activity of some members of the government or other social institutions who act in an organized manner to enforce the law by investigating, deterring, rehabilitating, or punishing people who violate the rules and norms gove ...
and such), a polygraph
A polygraph, often incorrectly referred to as a lie detector test, is a pseudoscientific device or procedure that measures and records several physiological indicators such as blood pressure, pulse, respiration, and skin conductivity while a ...
is a mechanical device that moves a second pen parallel to one held by a writer, enabling the writer to make a duplicate of a document as it is written. Polygraphs appeared in the 17th century but did not become popular until 1800. John Isaac Hawkins and Charles Willson Peale
Charles Willson Peale (April 15, 1741 – February 22, 1827) was an American painter, military officer, scientist, and naturalist.
In 1775, inspired by the American Revolution, Peale moved from his native Maryland to Philadelphia, where he set ...
patented a polygraph in the US in 1803, and beginning in 1804 Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
collaborated with them in working on improvements in the machine. He used a polygraph for the rest of his life. However, polygraphs were not practical for most office purposes and were never widely used in businesses. Hawkins & Peale lost money producing polygraphs. The problem was their "inherent instability, and constant need for repair and adjustment."
Letter copying presses
In 1780James Watt
James Watt (; 30 January 1736 (19 January 1736 OS) – 25 August 1819) was a Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved on Thomas Newcomen's 1712 Newcomen steam engine with his Watt steam engine in 1776, which was f ...
obtained a patent for letter copying presses, which James Watt & Co. produced beginning in that year. Letter copying presses were used by the early 1780s by the likes of Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin (April 17, 1790) was an American polymath: a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher and Political philosophy, political philosopher.#britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the m ...
, George Washington
George Washington (, 1799) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the first president of the United States, serving from 1789 to 1797. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led Patriot (American Revoluti ...
, Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish ( ; 10 October 1731 – 24 February 1810) was an English experimental and theoretical chemist and physicist. He is noted for his discovery of hydrogen, which he termed "inflammable air". He described the density of inflammable a ...
, and Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
. In 1785, Jefferson was using both stationary and portable presses made by James Watt & Co.
Using letter copying presses, copies could be made up to twenty-four hours after a letter was written, though copies made within a few hours were best. A copying clerk would begin by counting the number of master letters to be written during the next few hours and by preparing the copying book. Suppose the clerk wanted to copy 20 one-page letters. In that case, he would insert a sheet of oiled paper into the copying book in front of the first tissue on which he wanted to make a copy of a letter. He would then turn 20 sheets of tissue paper and insert a second oiled paper. To dampen the tissue paper, the clerk used a brush or copying paper damper. The damper had a reservoir for water that wet a cloth, and the clerk wiped the cloth over the tissues on which copies were to be made. As an alternative method of dampening the tissue paper, in 1860 Cutter, Tower & Co., Boston, advertised Lynch's patent paper moistener.
Then letters were written with special copying ink which was not blotted. The copying clerk arranged the portion of the letter book to be used in the following sequence starting from the front: a sheet of oiled paper, then a sheet of letter book tissue, then a letter placed face up against the back of the tissue on which the copy was to be made, then another oiled paper, etc.
Prior to the introduction of inks made with aniline dyes in 1856, the quality of copies made on letter copying presses was limited by the properties of the available copying inks. Some documents that were to be copied with copying presses were written with copying pencils rather than copying ink. The cores of copying pencils, which appear to have been introduced in the 1870s, were made from a mixture of graphite
Graphite () is a Crystallinity, crystalline allotrope (form) of the element carbon. It consists of many stacked Layered materials, layers of graphene, typically in excess of hundreds of layers. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable ...
, clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
, and aniline dye.
By the late 1870s, an improved method for moistening pages in copying books had been invented, and by the late 1880s it had been widely adopted. Rather than using a brush or damper to wet the tissues, the clerk inserted a thin moist cloth or pad between each oil paper and the following tissue.
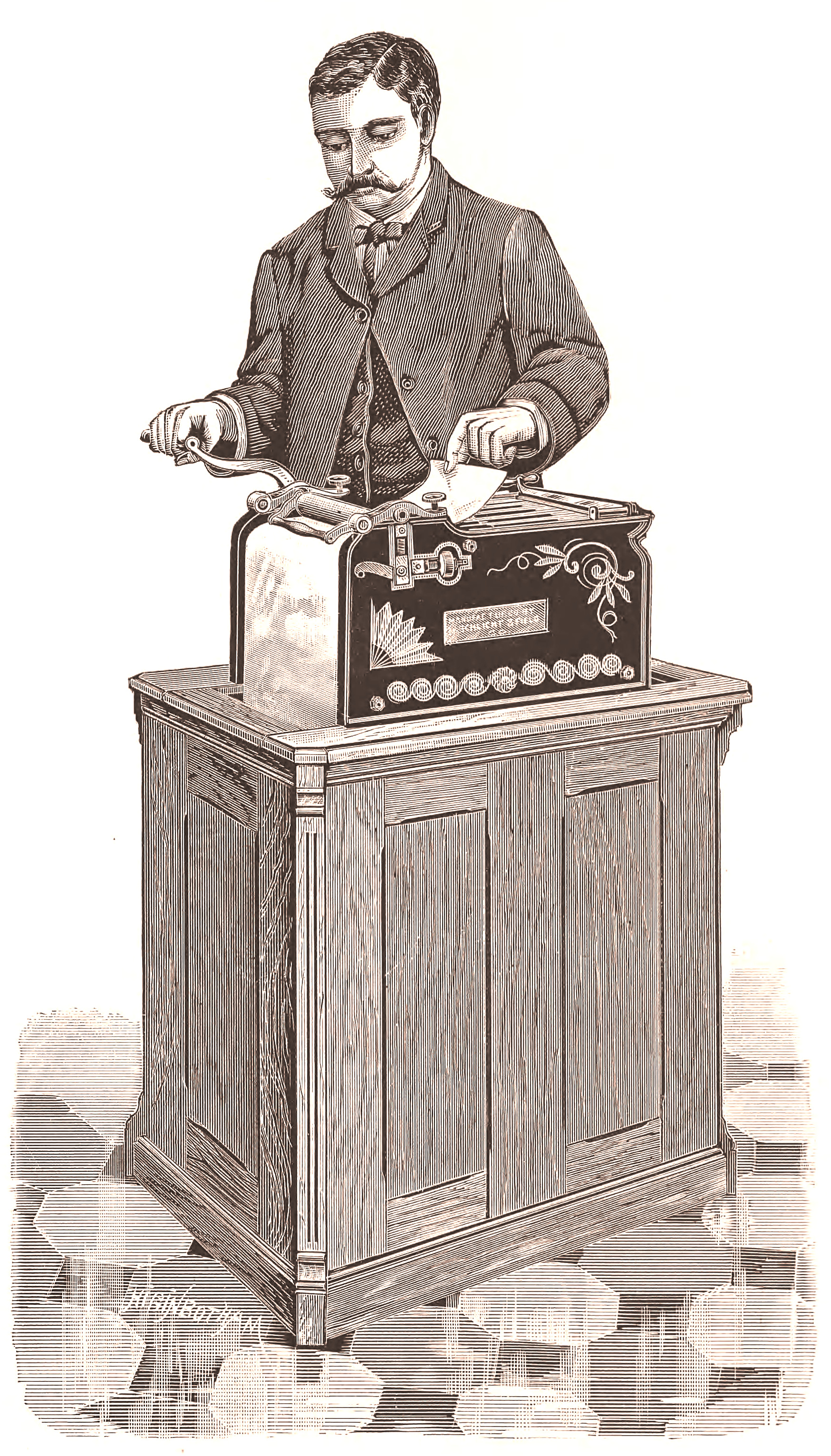
 In the late 1880s, adoption of improvements in office systems for filing unbound documents increased the demand for copying machines that made unbound copies of letters, as opposed to copies in bound books. In 1886, Schlicht & Field of Rochester, N.Y., introduced the Rapid Roller Damp-Leaf Copier, a roller copier, which used pressure supplied by rollers to copy letters onto a roll of dampened paper. After copies were pressed onto the paper, the paper entered the cabinet under the copier, where it dried on a large roller. An attachment was used to cut dried copies off the roll.
Copies could be made more quickly with a roller copier than with a letter copying press. It was claimed that nearly 100 papers could be copied in two minutes with a roller copier. Roller copiers competed with carbon paper technology. It was claimed that a roller copier could make a half dozen copies of a typewritten letter if the letter was run through the copier several times. It could make a dozen copies if the letter was written with a pen and good copying ink.
The Process Letter Machine Co. of Muncie, Indiana, offered the New Rotary Copying Press, a loose-leaf copier, in 1902. This machine was similar to roller copiers but copied onto loose-leaf paper.
In the late 1880s, adoption of improvements in office systems for filing unbound documents increased the demand for copying machines that made unbound copies of letters, as opposed to copies in bound books. In 1886, Schlicht & Field of Rochester, N.Y., introduced the Rapid Roller Damp-Leaf Copier, a roller copier, which used pressure supplied by rollers to copy letters onto a roll of dampened paper. After copies were pressed onto the paper, the paper entered the cabinet under the copier, where it dried on a large roller. An attachment was used to cut dried copies off the roll.
Copies could be made more quickly with a roller copier than with a letter copying press. It was claimed that nearly 100 papers could be copied in two minutes with a roller copier. Roller copiers competed with carbon paper technology. It was claimed that a roller copier could make a half dozen copies of a typewritten letter if the letter was run through the copier several times. It could make a dozen copies if the letter was written with a pen and good copying ink.
The Process Letter Machine Co. of Muncie, Indiana, offered the New Rotary Copying Press, a loose-leaf copier, in 1902. This machine was similar to roller copiers but copied onto loose-leaf paper.
Hectographs
Thehectograph
The hectograph, gelatin duplicator or jellygraph is a printing process that involves transfer of an original, prepared with special inks, to a pan of gelatin or a gelatin pad pulled tight on a metal frame.
While the original use of the technol ...
introduced in 1876 or shortly before, was a technology in which a dye-impregnated master copy, not unlike a spirit master, was laid on top of a cake pan full of firm gelatin. After the dye soaked into the gelatin, sheets of paper could be laid on top of the gelatin to transfer the image. This was good for 50 copies at most. Hectography was slow and clunky, but it could inspire great intrepidity in its users.
While good-quality, reasonably rapid copies from a hectograph require fairly specific materials (Aniline dye is the most effective), passable copies can be produced from a bewildering array of improvised materials on makeshift equipment. Practically speaking, any dye that soaks into the gelatin and can then be drawn out by the available paper will work. This meant that improvised hectography assumed the role of reproducing nearly every sort of censored material from subversive literature to pornography.
Mimeographs
Themimeograph
A mimeograph machine (often abbreviated to mimeo, sometimes called a stencil duplicator or stencil machine) is a low-cost duplicating machine that works by forcing ink through a stencil onto paper. The process is called mimeography, and a co ...
invented by Albert Blake Dick
Albert Blake Dick (April 16, 1856 – August 15, 1934) was a businessman who founded the A. B. Dick Company, a major American copier manufacturer and office supply company of the 20th Century. He coined the word "mimeograph".
Dick attended scho ...
in 1884 used heavy waxed-paper "stencils" that a pen or a typewriter could cut through. The stencil was wrapped around the drum of the (manual or electrical) machine, which forced ink out through the cut marks on the stencil. The paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, Textile, rags, poaceae, grasses, Feces#Other uses, herbivore dung, or other vegetable sources in water. Once the water is dra ...
had a surface texture (like bond paper), and the ink was black and odorless. A person could use special knives to cut stencils by hand, but handwriting was impractical, because any closed loop letterform would cut a hole and thus print as a black blob. The technology was soon refined to control this problem, also allowing the use of typewriter
A typewriter is a Machine, mechanical or electromechanical machine for typing characters. Typically, a typewriter has an array of Button (control), keys, and each one causes a different single character to be produced on paper by striking an i ...
s to prepare mimeograph masters. If the user put the stencil on the drum wrong-side-out, the copies came out mirror-imaged.
Spirit duplicators
Thespirit duplicator
A spirit duplicator (also Rexograph and Ditto machine in North America, Banda machine and Fordigraph machine in the U.K. and Australia) is a printing method invented in 1923 by Wilhelm Ritzerfeld, which was used for most of the 20th century. Th ...
invented in 1923 and sold by Ditto, Inc., used two-ply "spirit masters" or "ditto masters". The top sheet could be typed, drawn, or written upon. The second sheet was coated with a layer of colored wax. The pressure of writing or typing on the top sheet transferred colored wax to its back side, producing a mirror image of the desired marks. (This acted like a reverse of carbon paper.) The wax-supply sheet was then removed and discarded, and the other sheet (containing the images) was fastened onto the drum of the (manual or electrical) machine, with the waxed (back, or reverse-image) side out.
The usual wax color was aniline
Aniline (From , meaning ' indigo shrub', and ''-ine'' indicating a derived substance) is an organic compound with the formula . Consisting of a phenyl group () attached to an amino group (), aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an in ...
purple, a cheap, moderately durable pigment that provided good contrast, though other colors were also available. Unlike mimeo, ditto had the useful ability to print multiple colors in a single pass, which made it popular with cartoonists. Spirit duplicators were incapable of double-sided printing, since the saturation of the paper with solvent inherent to the process would destroy a previously printed image. One well-made spirit master could at most print about 500 copies, far fewer than a mimeograph stencil could manage. To produce further copies, an entirely new master would have to be reconstructed in the same way as the original master.
Notoriously, images would gradually fade with exposure to light, limiting their usability for permanent labels and signage. Copies made by spirit duplicators now pose a serious challenge to archivist
An archivist is an information professional who assesses, collects, organizes, preserves, maintains control over, and provides access to records and archives determined to have long-term value. The records maintained by an archivist can cons ...
s responsible for document textual and artistic preservation.
Comparison of mimeographs and spirit duplicators
Spirit duplicators and mimeograph machines were competing and complementary technologies during the first half of the 20th century. Mimeography was in general a more forgiving technology, and still survives in various forms into the 21st century. Spirit duplicators required much finer operating tolerances and careful adjustments to operate correctly. Overall print quality of spirit duplicators was frequently poor, though a capable operator could overcome this with careful adjustment of feed rate, pressure, and solvent volume. During their heyday, tabletop duplicators of both sorts were the inexpensive and convenient alternatives to conventional typesetting and offset or letterpress printing. They were well suited for the short runs used for school worksheets, church newsletters, and apazines. Even the least technically minded teachers, professors, clergy, and self-publishers could make use of them. The machines owed most of their popularity to this relative ease of use, and in some cases, to their lack of a requirement for an external power source. Mimeograph machines predated the spirit duplicator, had a lower cost per impression, superior print quality, finer resolution, and if properly adjusted could be used for multi-pass and double-sided printing. Also, mimeographed images were as durable as the paper they were printed on, and didn't bleach to illegibility if exposed to sunlight, the way that spirit duplicator pages did. A good mimeograph master could produce many more copies than the best spirit master. As with spirit masters, mimeograph stencils could be saved and reused for later print jobs. There are still mimeography enthusiasts in the United States and Canada, and mimeograph technology is still in everyday use in theThird World
The term Third World arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact. The United States, Canada, Taiwan, Japan, South Korea, the Southern Cone, NATO, Western European countries and oth ...
, since many low-cost mimeograph machines do not require electricity to operate.
Offset duplicators
In the United States, an offset press with a sheet size smaller than is classified as a duplicator. In Europe, the distinction is made between presses that have cylinder bearings, and duplicators, which do not. Duplicators were manufactured byHeidelberg
Heidelberg (; ; ) is the List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, fifth-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Baden-Württemberg, and with a population of about 163,000, of which roughly a quarter consists of studen ...
(T-offset), American Type Founders
American Type Founders (ATF) Co. was a business trust created in 1892 by the merger of 23 type foundries, representing about 85 percent of all type manufactured in the United States at the time. De Vinne, Theodore Low, ''The Practice of Typogr ...
(Chief and Davidson lines), A.B. Dick Company, and Addressograph-Mulitilith.
Digital duplicators
In 1986, the RISO Kagaku Corporation introduced the digital duplicator. It uses the basic mimeograph technology but improves on it, in that the operator does not have to create the stencil directly. The stencil, called a master, is made by use of a scanner and thermal print head. A used master is automatically removed and placed in a disposal box, as a new one is created. This way the operator should not have to touch the used master material that is coated in ink. There are also cost advantages over a copier at higher volume. For smaller print runs, the main cost is in the master material. This ranges between 40 – 80 cents per master depending on the manufacturer. When spread over 20 or more copies, the cost per copy (2 to 4 cents) is close to photocopiers. But for every additional copy, the average cost decreases. At 100 prints, the master cost per copy was only 0.4–0.8 cents per copy, and the cost of the paper printed upon will start to dominate. A master is capable of making 4000–5000 prints, and then a new master easily be made if needed for further copies. Other manufacturers have adapted the technology including: * Riso Kagaku Corporation *Gestetner
The Gestetner is a type of duplicating machine named after its inventor, David Gestetner (1854–1939). During the 20th century, the term ''Gestetner'' was used as a verb—as in ''Gestetnering''. The Gestetner company established its base in Lo ...
* Ricoh
is a Japanese multinational imaging and electronics company. It was founded by the now-defunct commercial division of the Institute of Physical and Chemical Research (Riken) known as the ''Riken Concern'', on 6 February 1936 as . Ricoh's hea ...
* Duplo
How digital duplicators work
Like the mimeo machine, digital duplicators have a stencil (called a master), ink, and drum—but the process is all automated. # The original is placed on a flat bed scanner or fed through a sheet feed scanner, depending on the model. # When the start button is pressed, the image is scanned into memory by reflecting light off the original and into a CCD. # The image is burned onto the master material that is coated or laminated on one side, in a series of small holes by the thermal print head. # As the new master is burning it is stored while the old master is removed. # There is a clamp plate on the drum that opens by motor. The drum turns and the old master material is fed into the disposal rollers and into the disposal box. # The new master is fed into the clamp which closes, then the drum is turned, pulling the master onto the drum. # The outside of the drum is covered in screens and the inside is coated in ink. The screens make sure the ink flow is regulated. # The paper is fed to the drum, and the ink only comes through the master material where there are holes. # A pressure roller presses the paper to the drum and transfers the ink to the paper to form the image. # The paper then exits the machine into an exit tray. The ink is still wet.See also
*List of duplicating processes
This is a partial list of text and image duplicating processes used in business and government from the Industrial Revolution forward. Some are mechanical and some are chemical. There is naturally some overlap with printing processes and photogra ...
* Risograph
* Thermofax
Thermo-Fax (very often Thermo fax) is 3M's trademarked name for a photocopying technology which was introduced in 1950. It was a form of thermographic printing and an example of a dry silver process. It was a significant advance as no chemicals ...
* Cyclostyle
* Gestetner
The Gestetner is a type of duplicating machine named after its inventor, David Gestetner (1854–1939). During the 20th century, the term ''Gestetner'' was used as a verb—as in ''Gestetnering''. The Gestetner company established its base in Lo ...
References
* * M P Doss, ''Information Processing Equipment'' (New York, 1955) * * W B Proudfoot, ''The Origin of Stencil Duplicating'' (London, 1972)Notes
External links
Antique Copying Machines
In-depth look at a ditto master sheet
{{DEFAULTSORT:Duplicating Machines Office equipment Printing devices Printing technology Machines Copying