|
Carbon Paper
Carbon paper (originally carbonic paper) consists of sheets of paper that create one or more copies simultaneously with the creation of an original document when inscribed by a typewriter or ballpoint pen. The email term cc which means "carbon copy" is derived from this use of carbon paper. History In 1801, Pellegrino Turri, an Italian inventor, invented carbon paper to provide the ink for his mechanical typing machine, one of the first typewriters. Ralph Wedgwood obtained the first patent for carbon paper in 1806. Carbon paper in its original form was paper coated on one side with a layer of a loosely bound dry ink or pigmented coating, bound with wax. The manufacture of carbon paper was formerly the largest consumer of montan wax. In 1954 the Columbia Ribbon & Carbon Manufacturing Company filed a patent for what became known in the trade as solvent carbon paper: the coating was changed from wax-based to polymer-based. The manufacturing process changed from a hot-melt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
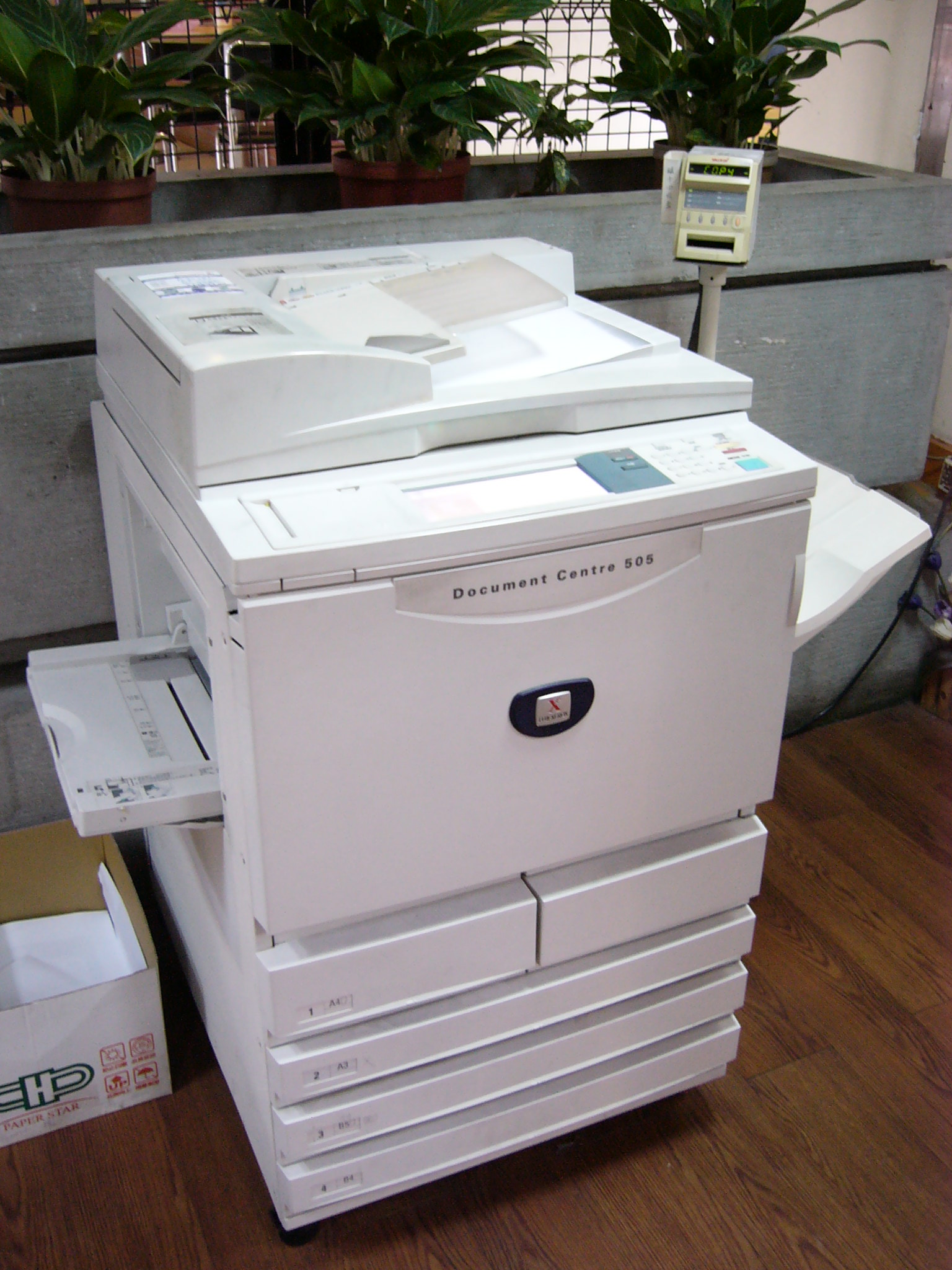
Photocopying
A photocopier (also called copier or copy machine, and formerly Xerox machine, the generic trademark) is a machine that makes copies of documents and other visual images onto paper or plastic film quickly and cheaply. Most modern photocopiers use a technology called '' xerography'', a dry process that uses electrostatic charges on a light-sensitive photoreceptor to first attract and then transfer toner particles (a powder) onto paper in the form of an image. The toner is then fused onto the paper using heat, pressure, or a combination of both. Copiers can also use other technologies, such as inkjet, but xerography is standard for office copying. Commercial xerographic office photocopying gradually replaced copies made by verifax, photostat, carbon paper, mimeograph machines, and other duplicating machines. Photocopying is widely used in the business, education, and government sectors. While there have been predictions that photocopiers will eventually become obsole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Copy
Before the development of photographic copiers, a carbon copy was the under-copy of a typed or written document placed over carbon paper and the under-copy sheet itself (not to be confused with the carbon print family of photographic reproduction processes). When copies of business letters were so produced, it was customary to use the acronym "CC" or "cc" before a colon and below the writer's signature to inform the principal recipient that carbon copies had been made and distributed to the parties listed after the colon. With the advent of word processors and e-mail, "cc" is used as a merely formal indication of the distribution of letters to secondary recipients. Process A sheet of carbon paper is placed between two or more sheets of paper. The pressure applied by the writing implement (pen, pencil, typewriter or impact printer) to the top sheet causes pigment from the carbon paper to reproduce the similar mark on the copy sheet(s). More than one copy can be made by stac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
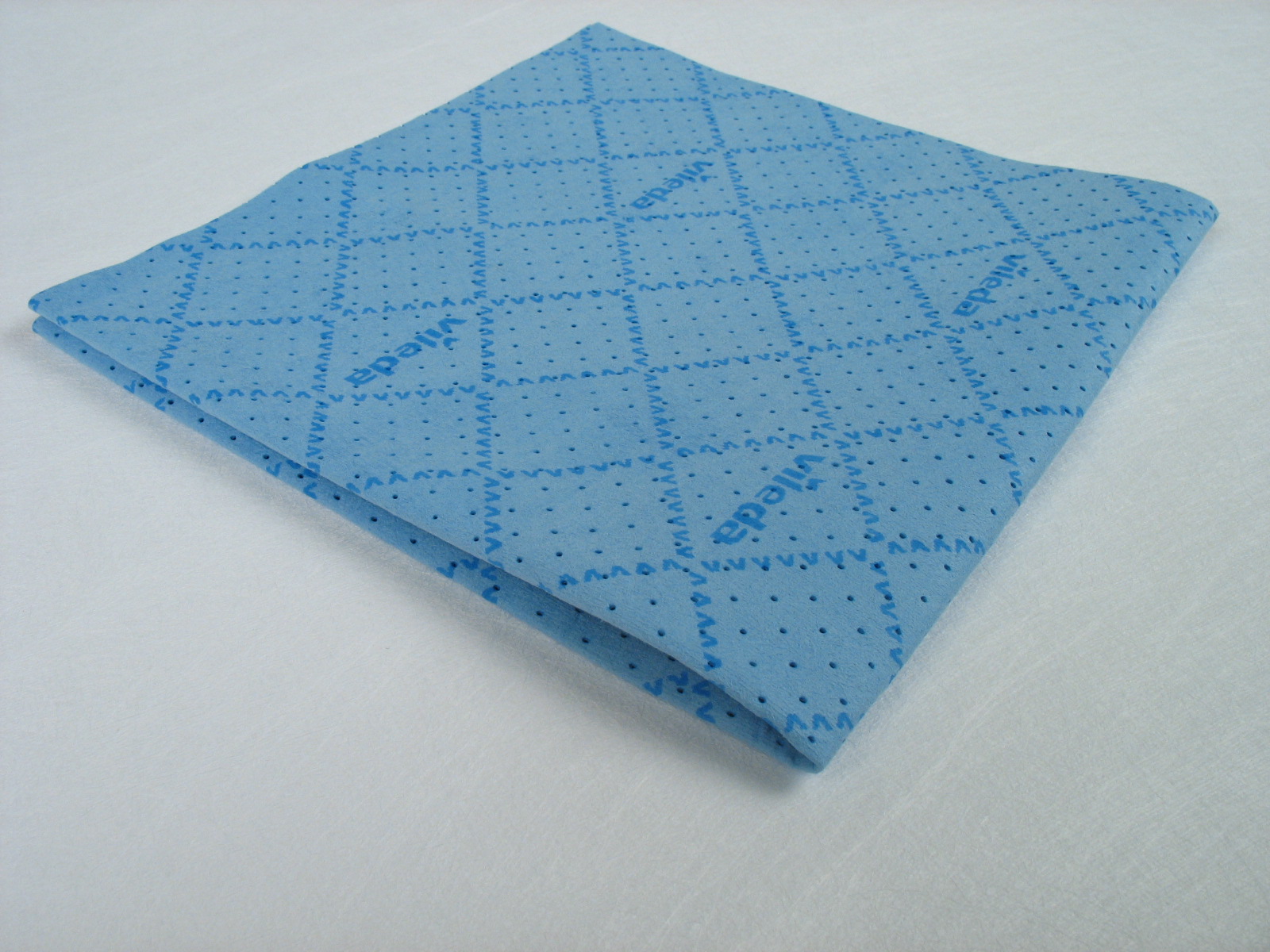
Microfiber
Microfiber (microfibre in British English) is synthetic fibre finer than one Denier (unit), denier or decitex/thread, having a diameter of less than ten micrometre, micrometers. The most common types of microfiber are made variously of polyesters; polyamides (e.g., nylon, Kevlar, Nomex); and combinations of polyester, polyamide, and polypropylene. Microfiber is used to make mats, knits, and weaves, for apparel, upholstery, industrial filters, and cleaning products. The shape, size, and combinations of synthetic fibers are chosen for specific characteristics, including softness, toughness, absorption, water repellence, electrostatics, and filtering ability. They are commonly used for cleaning scratch prone surfaces such as Display device, displays, glass, and Lens, lenses. Microfiber cloth makes use of van der Waals force to remove dirt without scratches. History Production of ultra-fine fibers (finer than 0.7 Denier (unit), denier) dates to the late 1950s, using melt-blown s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most battery (electricity), batteries in requiring a continuous source of fuel and oxygen (usually from air) to sustain the chemical reaction, whereas in a battery the chemical energy usually comes from substances that are already present in the battery. Fuel cells can produce electricity continuously for as long as fuel and oxygen are supplied. The first fuel cells were invented by Sir William Robert Grove, William Grove in 1838. The first commercial use of fuel cells came almost a century later following the invention of the hydrogen–oxygen fuel cell by Francis Thomas Bacon in 1932. The alkaline fuel cell, also known as the Bacon fuel cell after its inventor, has been used in NASA space programs since the mid-1960s to generate power for sate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stained Glass
Stained glass refers to coloured glass as a material or art and architectural works created from it. Although it is traditionally made in flat panels and used as windows, the creations of modern stained glass artists also include three-dimensional structures and sculpture. Modern vernacular usage has often extended the term "stained glass" to include domestic leadlight, lead light and ''objet d'art, objets d'art'' created from glasswork, for example in the famous lamps of Louis Comfort Tiffany. As a material ''stained glass'' is glass that has been coloured by adding Salt (chemistry), metallic salts during its manufacture. It may then be further decorated in various ways. The coloured glass may be crafted into a stained-glass window, say, in which small pieces of glass are arranged to form patterns or pictures, held together (traditionally) by strips of lead, called cames or calms, and supported by a rigid frame. Painted details and yellow-coloured Silver staining, silver stain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mail Art
Mail art, also known as postal art and correspondence art, is an artistic movement centered on sending small-scale works through the mail, postal service. It developed out of what eventually became Ray Johnson's New York Correspondence School and the Fluxus movements of the 1960s. It has since developed into a global, ongoing movement. Characteristics Media commonly used in mail art include postcards, paper, a collage of found or recycled images and objects, rubber stamps, artist-created stamps (called artistamps), and paint, but can also include music, sound art, poetry, or anything that can be put in an envelope and sent via post. Mail art is considered art once it is dispatched. Mail artists regularly call for thematic or topical mail art for use in (often unjuried) exhibition. Mail artists appreciate interconnection with other artists. The art form promotes an egalitarian way of creating that frequently circumvents official art distribution and approval systems such as the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Floss
''Mental Floss'' (stylized as ''mental_floss'') is an American online magazine and digital, print, and e-commerce media company focused on millennials. It is owned by Minute Media, an international digital media publisher based in London, England, with an associated research and development center in Tel Aviv, Israel. It is based in New York City, United States. mentalfloss.com, which presents facts, puzzles, and trivia with a humorous tone, draws 20.5 million unique users a month. Its YouTube channel produces three weekly series and has 1.3 million subscribers. In October 2015, ''Mental Floss'' teamed with the National Geographic Channel for its first televised special, ''Brain Surgery Live with'' mental_floss, the first brain surgery ever broadcast live. Launched in Birmingham, Alabama in 2001, the company has additional offices in Midtown Manhattan. The publication was included in ''Inc.'' magazine's list of the 5,000 fastest growing private companies. Before it became a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Postal Service
The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or simply the Postal Service, is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States, United States federal government responsible for providing mail, postal service in the United States, its insular areas and Compact of Free Association, associated states. It is one of a few government agencies Postal Clause, explicitly authorized by the Constitution of the United States. As of March 29, 2024, the USPS has 525,377 career employees and nearly 114,623 pre-career employees. The USPS has a monopoly on traditional Letter (message), letter delivery within the U.S. and operates under a Universal service, universal service obligation (USO), both of which are defined across a broad set of legal mandates, which obligate it to provide uniform price and quality across the entirety of its service area. The Post ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Money Orders
A money order is a directive to pay a pre-specified amount of money from prepaid funds, making it a more trusted method of payment than a cheque. History Systems similar to modern money orders can be traced back centuries. Paper documents known as "flying cash" were used in China from the 800s, while the Hawala practice of informal financial remittances through a widespread system of brokers can be traced to India in the 1300s and remains common in parts of Asia and Africa. The modern western money order system was established by a private firm in Great Britain in 1762, though due to high costs was not very successful. Around 1836 it was sold to another private firm which lowered the fees, significantly increasing the popularity and usage of the system. The Post Office (United Kingdom), Post Office noted the success and profitability, and it took over the system in 1838. Fees were further reduced and usage increased further, making the money order system reasonably profitable. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheque
A cheque (or check in American English) is a document that orders a bank, building society, or credit union, to pay a specific amount of money from a person's account to the person in whose name the cheque has been issued. The person writing the cheque, known as the ''drawer'', has a transaction banking account (often called a current, cheque, chequing, checking, or share draft account) where the money is held. The drawer writes various details including the monetary amount, date, and a payee on the cheque, and signs it, ordering their bank, known as the ''drawee'', to pay the amount of money stated to the payee. Although forms of cheques have been in use since ancient times and at least since the 9th century, they became a highly popular non-cash method for making payments during the 20th century and usage of cheques peaked. By the second half of the 20th century, as cheque processing became automated, billions of cheques were issued annually; these volumes peaked in or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fine (penalty)
A fine or mulct (the latter synonym typically used in Civil law (common law), civil law) is a penalty of money that a court of law or other authority decides has to be paid as punishment for a crime or other Offense (law), offense. The amount of a fine can be determined case by case, but it is often announced in advance. The most usual use of the term is for financial punishments for the commission of crimes, especially minor crimes, or as the settlement (law), settlement of a Claim (legal), claim. One typical example of a fine is money paid for violations of traffic laws. In English law, English common law, relatively Standard scale, small fines are used either in place of or alongside community service orders for low-level criminal offences. More considerable fines are also given independently or alongside shorter prison sentences when the judge or magistrate considers a large amount of retribution is necessary, but there is unlikely to be a significant danger to the public. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |