Ducal Saxony on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Duchy of Saxony () was originally the area settled by the
 The Saxon
The Saxon
 In 1142, King Conrad III of Germany granted the ducal title to the Welf scion Henry the Lion (as Duke Henry III). Henry gradually extended his rule over northeastern Germany, leading crusades against the pagan Wends. During his reign, Henry massively supported to the development of the cities in his dominion, such as Braunschweig, Brunswick, Lüneburg and Lübeck, a policy ultimately contributing to the movement of the House of Welf from its homelands in southern Germany to the north.
In 1152, Henry supported his cousin Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick III of Swabia, to be elected King of Germany (as Frederick I Barbarossa), likely under the promise of granting the Duchy of Bavaria back to Henry. Henry's dominion now covered more than two thirds of Germany, from the Alps to the North Sea and the Baltic Sea, making him one of the mightiest rulers in central Europe, and thus also a potential threat for other German princes and even Barbarossa.
In 1142, King Conrad III of Germany granted the ducal title to the Welf scion Henry the Lion (as Duke Henry III). Henry gradually extended his rule over northeastern Germany, leading crusades against the pagan Wends. During his reign, Henry massively supported to the development of the cities in his dominion, such as Braunschweig, Brunswick, Lüneburg and Lübeck, a policy ultimately contributing to the movement of the House of Welf from its homelands in southern Germany to the north.
In 1152, Henry supported his cousin Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick III of Swabia, to be elected King of Germany (as Frederick I Barbarossa), likely under the promise of granting the Duchy of Bavaria back to Henry. Henry's dominion now covered more than two thirds of Germany, from the Alps to the North Sea and the Baltic Sea, making him one of the mightiest rulers in central Europe, and thus also a potential threat for other German princes and even Barbarossa.
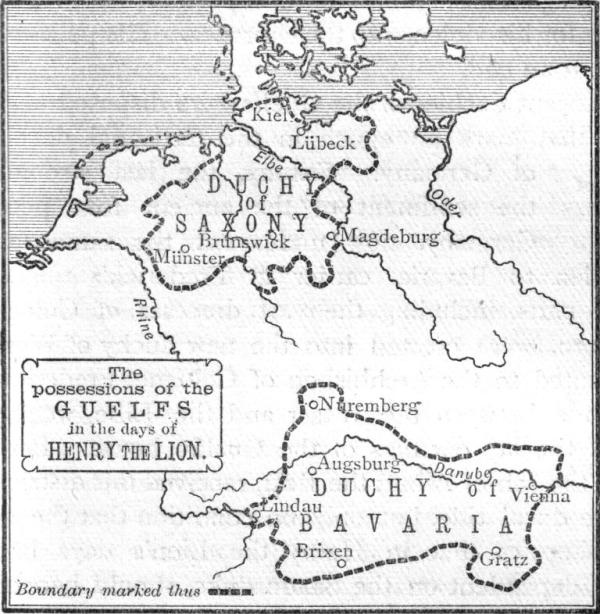 To expand his rule, Henry continued to claim titles of lesser families, who left no legitimate heir. This policy caused unrest among many Saxon nobles and other German princes, first and foremost his father's old enemy, Albrecht the Bear. During Barbarossa's fourth Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor#First Italian Campaign, Italian campaign in 1166, a league of German Nobles declared war on Henry. The war continued until 1170, despite several attempts of the Emperor to mediate. Ultimately, Henry's position remained unchallenged, due to Barbarossa's favourable rule.
In 1168, Henry married Matilda of England, Duchess of Saxony, Matilda Plantagenêt, the daughter of Henry II of England and Eleanor of Aquitaine and sister of Richard Lionheart.
The following years led to an estrangement between Barbarossa and Henry. Henry ceased to support the Emperor's Italy campaigns, which were all proven unsuccessful, as massively as he used to, and instead focused on his own possessions. In 1175 Barbarossa again asked for support against the Lombard League, which Henry is said to have refused bluntly, even though Barbarossa kneeled before him. Records of this event were not written until several years later, and sources are contradictory, depending on whom the author favoured. Nevertheless, lacking the support of the Saxons the following Battle of Legnano was a complete failure for the Emperor.
When the majority of the realm's princes had returned from Italy, Henry's refusal was instantly exploited to weaken his position. Views differ, whether Barbarossa initiated Henry's downfall or if it was orchestrated by the princes first and foremost.
Between 1175 and 1181, Henry was charged with several accusations, such as violating the ''honour of the realm'' (honor imperii), breach of the peace, and treason. If he were to follow the summons to the Hoftag, Henry would've acknowledge the charges as rightful, and therefore refused all summons. In 1181, he was ultimately stripped of his titles. Unwilling to give up without a fight, Henry already had dealt the first blow in 1180 against the city of Goslar, which he had coveted for several years already. During the following war, Henry's domestic policy and the treatment of his vassals proved fatal, and his power quickly crumbled.
In 1182, Henry the Lion ultimately went into exile, joining the court of his father-in-law, Henry II of England. Following the death of his wife and also of the Emperor, the latter while participating in the Third Crusade, Henry returned to Brunswick in 1189 and briefly tried to regain the lost lands. After several setbacks, Henry made peace with Barbarossa's son and heir, King Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor.
The ancient
To expand his rule, Henry continued to claim titles of lesser families, who left no legitimate heir. This policy caused unrest among many Saxon nobles and other German princes, first and foremost his father's old enemy, Albrecht the Bear. During Barbarossa's fourth Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor#First Italian Campaign, Italian campaign in 1166, a league of German Nobles declared war on Henry. The war continued until 1170, despite several attempts of the Emperor to mediate. Ultimately, Henry's position remained unchallenged, due to Barbarossa's favourable rule.
In 1168, Henry married Matilda of England, Duchess of Saxony, Matilda Plantagenêt, the daughter of Henry II of England and Eleanor of Aquitaine and sister of Richard Lionheart.
The following years led to an estrangement between Barbarossa and Henry. Henry ceased to support the Emperor's Italy campaigns, which were all proven unsuccessful, as massively as he used to, and instead focused on his own possessions. In 1175 Barbarossa again asked for support against the Lombard League, which Henry is said to have refused bluntly, even though Barbarossa kneeled before him. Records of this event were not written until several years later, and sources are contradictory, depending on whom the author favoured. Nevertheless, lacking the support of the Saxons the following Battle of Legnano was a complete failure for the Emperor.
When the majority of the realm's princes had returned from Italy, Henry's refusal was instantly exploited to weaken his position. Views differ, whether Barbarossa initiated Henry's downfall or if it was orchestrated by the princes first and foremost.
Between 1175 and 1181, Henry was charged with several accusations, such as violating the ''honour of the realm'' (honor imperii), breach of the peace, and treason. If he were to follow the summons to the Hoftag, Henry would've acknowledge the charges as rightful, and therefore refused all summons. In 1181, he was ultimately stripped of his titles. Unwilling to give up without a fight, Henry already had dealt the first blow in 1180 against the city of Goslar, which he had coveted for several years already. During the following war, Henry's domestic policy and the treatment of his vassals proved fatal, and his power quickly crumbled.
In 1182, Henry the Lion ultimately went into exile, joining the court of his father-in-law, Henry II of England. Following the death of his wife and also of the Emperor, the latter while participating in the Third Crusade, Henry returned to Brunswick in 1189 and briefly tried to regain the lost lands. After several setbacks, Henry made peace with Barbarossa's son and heir, King Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor.
The ancient
 Duchy of Westphalia
*
Duchy of Westphalia
*  County of Bentheim
*
County of Bentheim
*  County of Mark
*
County of Mark
*  Prince-Bishopric of Münster
* Prince-Bishopric of Osnabrück
* County of Ravensberg
*
Prince-Bishopric of Münster
* Prince-Bishopric of Osnabrück
* County of Ravensberg
*  County of Tecklenburg
County of Tecklenburg
 Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen
* Abbacy of Corvey
* County of Delmenhorst
*
Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen
* Abbacy of Corvey
* County of Delmenhorst
*  County of Diepholz
* County of Everstein
*
County of Diepholz
* County of Everstein
*  County of Hoya
*
County of Hoya
*  Principality of Lippe, Lordship of Lippe, an allodial possession within the Duchy of Saxony until 1180, gaining disputed imperial immediacy
*
Principality of Lippe, Lordship of Lippe, an allodial possession within the Duchy of Saxony until 1180, gaining disputed imperial immediacy
*  Prince-Bishopric of Minden
*
Prince-Bishopric of Minden
*  County of Oldenburg
*
County of Oldenburg
*  Prince-Bishopric of Paderborn
*
Prince-Bishopric of Paderborn
*  Prince-Bishopric of Verden
*
Prince-Bishopric of Verden
*  County of Waldeck
County of Waldeck
 County of Blankenburg, until 1180 a Saxon fief, then a fief of the Prince-Bishopric of Halberstadt
* County of Brunswick, later the
County of Blankenburg, until 1180 a Saxon fief, then a fief of the Prince-Bishopric of Halberstadt
* County of Brunswick, later the  Abbacy of Gandersheim
*
Abbacy of Gandersheim
*  Prince-Bishopric of Halberstadt
*
Prince-Bishopric of Halberstadt
*  Prince-Bishopric of Hildesheim
* County of Hohenstein, seated in Hohenstein, Thuringia, Hohenstein
*
Prince-Bishopric of Hildesheim
* County of Hohenstein, seated in Hohenstein, Thuringia, Hohenstein
*  Archbishopric of Magdeburg, Prince-Archbishopric of Magdeburg
*
Archbishopric of Magdeburg, Prince-Archbishopric of Magdeburg
*  County of Mansfeld
*
County of Mansfeld
*  Abbacy of Quedlinburg
*
Abbacy of Quedlinburg
*  County of Wernigerode
*
County of Wernigerode
*  St. Ludger's Abbey, Abbey of St. Ludger
*
St. Ludger's Abbey, Abbey of St. Ludger
*  Werden Abbey
Werden Abbey
 Holstein, County of Holstein
* Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck
*
Holstein, County of Holstein
* Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck
*  Prince-Bishopric of Ratzeburg
*
Prince-Bishopric of Ratzeburg
*  Bishopric of Schwerin, Prince-Bishopric of Schwerin
Bishopric of Schwerin, Prince-Bishopric of Schwerin
Saxons
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
in the late Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start o ...
, when they were subdued by Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
during the Saxon Wars
The Saxon Wars were the campaigns and insurrections of the thirty-three years from 772, when Charlemagne first entered Saxony with the intent to conquer, to 804, when the last rebellion of tribesmen was defeated. In all, 18 campaigns were fou ...
from 772 CE and incorporated into the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Franks, Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as List of Frankish kings, kings of the Franks since ...
(Francia
The Kingdom of the Franks (), also known as the Frankish Kingdom, or just Francia, was the largest History of the Roman Empire, post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks, Frankish Merovingian dynasty, Merovingi ...
) by 804. Upon the 843 Treaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun (; ), agreed to on 10 August 843, ended the Carolingian civil war and divided the Carolingian Empire between Lothair I, Louis the German, Louis II and Charles the Bald, Charles II, the surviving sons of the emperor Louis the ...
, Saxony was one of the five German stem duchies
A stem duchy (, from '' Stamm'', meaning "tribe", in reference to the Franks, Saxons, Bavarians and Swabians) was a constituent duchy of the Kingdom of Germany at the time of the extinction of the Carolingian dynasty (death of Louis the Child in ...
of East Francia
East Francia (Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire created in 843 and ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was established through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the for ...
; Duke Henry the Fowler
Henry the Fowler ( or '; ; – 2 July 936) was the duke of Saxony from 912 and the king of East Francia from 919 until his death in 936. As the first non- Frankish king of East Francia, he established the Ottonian dynasty of kings and emper ...
was elected German king
This is a list of monarchs who ruled over East Francia, and the Kingdom of Germany (), from Treaty of Verdun, the division of the Francia, Frankish Empire in 843 and Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, the collapse of the Holy Roman Empire in ...
in 919.
Upon the deposition of the Welf duke Henry the Lion
Henry the Lion (; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195), also known as Henry III, Duke of Saxony (ruled 1142-1180) and Henry XII, Duke of Bavaria (ruled 1156-1180), was a member of the Welf dynasty.
Henry was one of the most powerful German princes of ...
in 1180, the ducal title fell to the House of Ascania
The House of Ascania () was a dynasty of German rulers. It is also known as the House of Anhalt, which refers to its longest-held possession, Principality of Anhalt, Anhalt.
The Ascanians are named after Ascania (or Ascaria) Castle, known as ' ...
, while numerous territories split from Saxony, such as the Principality of Anhalt
The Principality of Anhalt () was a Imperial State, State of the Holy Roman Empire, located in Central Germany (cultural area), Central Germany, in what is today part of the federal state of Saxony-Anhalt.
Under the rule of the House of Ascania, ...
in 1218 and the Welf Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg
The Duchy of Brunswick and Lüneburg (), commonly known as the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg or Brunswick-Lüneburg, was an imperial principality of the Holy Roman Empire in the territory of present day Lower Saxony.
In 1235, Otto I, Duke of ...
in 1235. In 1296, the remaining lands were divided between the Ascanian dukes of Saxe-Lauenburg
The Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg (, ), was a ''reichsfrei'' duchy that existed from 1296 to 1803 and again from 1814 to 1876 in the extreme southeast region of what is now Schleswig-Holstein. Its territorial centre was in the modern district of Herz ...
and Saxe-Wittenberg
The Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg () was a medieval duchy of the Holy Roman Empire centered at Wittenberg, which emerged after the dissolution of the stem duchy of Saxony. The Ascanian dukes prevailed in obtaining the Saxon electoral dignity until ...
, the latter obtaining the title of Electors of Saxony by the Golden Bull of 1356
The Golden Bull of 1356 (, , , , ) was a decree issued by the Imperial Diet at Nuremberg and Metz ( Diet of Metz, 1356/57) headed by the Emperor Charles IV which fixed, for a period of more than four hundred years, important aspects of the con ...
.
Geography
 The Saxon
The Saxon stem duchy
A stem duchy (, from '':wikt:Stamm, Stamm'', meaning "tribe", in reference to the Franks, Saxons, Baiuvarii, Bavarians and Alemanni, Swabians) was a constituent duchy of the Kingdom of Germany at the time of the extinction of the Carolingian dyna ...
covered the greater part of present-day Northern Germany
Northern Germany (, ) is a linguistic, geographic, socio-cultural and historic region in the northern part of Germany which includes the coastal states of Schleswig-Holstein, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Lower Saxony and the two city-states Hambur ...
, including the modern German states
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
() of Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony is a States of Germany, German state (') in Northern Germany, northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ' of the Germany, Federal Re ...
and Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt ( ; ) is a States of Germany, state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.17 million inhabitants, making it the List of German states ...
up to the Elbe
The Elbe ( ; ; or ''Elv''; Upper Sorbian, Upper and , ) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Republic), then Ge ...
and Saale
The Saale (), also known as the Saxon Saale ( ) and Thuringian Saale (), is a river in Germany and a left-bank tributary of the Elbe. It is not to be confused with the smaller Fränkische Saale, Franconian Saale, a right-bank tributary of the M ...
rivers in the east, the city-states of Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (, ), is the capital of the States of Germany, German state of the Bremen (state), Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (), a two-city-state consisting of the c ...
and Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th-lar ...
, the Westphalia
Westphalia (; ; ) is a region of northwestern Germany and one of the three historic parts of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has an area of and 7.9 million inhabitants.
The territory of the region is almost identical with the h ...
n part of North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia or North-Rhine/Westphalia, commonly shortened to NRW, is a States of Germany, state () in Old states of Germany, Western Germany. With more than 18 million inhabitants, it is the List of German states by population, most ...
, and the Holstein
Holstein (; ; ; ; ) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider (river), Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost States of Germany, state of Germany.
Holstein once existed as the German County of Holstein (; 8 ...
region ( Nordalbingia) of Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; ; ; ; ; occasionally in English ''Sleswick-Holsatia'') is the Northern Germany, northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical Duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of S ...
. In the late 12th century, Duke Henry the Lion
Henry the Lion (; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195), also known as Henry III, Duke of Saxony (ruled 1142-1180) and Henry XII, Duke of Bavaria (ruled 1156-1180), was a member of the Welf dynasty.
Henry was one of the most powerful German princes of ...
also occupied the adjacent area of Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schwerin, Neubrandenburg, Wismar and Güstrow. ...
(the former Billung March
The Billung March () or March of the Billungs () was a frontier region of the far northeastern Duchy of Saxony in the 10th century. It was named after the family which held it, the House of Billung.
The march reached from the Elbe River to the ...
).
The Saxons were one of the most robust groups in the late tribal culture of the times, and eventually bequeathed their tribe's name to a variety of more and more modern geopolitical territories, such as Old Saxony
Old Saxony was the homeland of the Saxons who fought the Frankish empire during the Early Middle Ages, until they conquered it and converted it into a Carolingian stem duchy in the 8th century, the Duchy of Saxony. Contemporary authors such a ...
(), Upper Saxony, the Electorate
Electorate may refer to:
* The people who are eligible to vote in an election, especially their number e.g. the term ''size of (the) electorate''
* The dominion of a prince-elector in the Holy Roman Empire until 1806
* An electoral district
...
, the Prussian Province of Saxony
The Province of Saxony (), also known as Prussian Saxony (), was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1944. Its capital was Magdeburg.
It was formed by the merger of various territories ceded ...
(in present-day Saxony-Anhalt), and the Kingdom of Saxony
The Kingdom of Saxony () was a German monarchy in Central Europe between 1806 and 1918, the successor of the Electorate of Saxony. It joined the Confederation of the Rhine after the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, later joining the German ...
, the latter corresponding with the German Free State of Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
, which bears the name today, despite its territory not having been part of the medieval duchy (see map on the right).
History
Older stem duchy
According to the '' Res gestae saxonicae'' by tenth century chroniclerWidukind of Corvey
Widukind of Corvey (c. 925after 973; , in italian ''Vitichindo Sacco di Corvey'', in Latin VVITICHINDI SAXO) was a medieval Saxon chronicler. His three-volume '' Res gestae Saxonicae sive annalium libri tres'' is an important chronicle of 10th-cen ...
, the Saxons had arrived from Britannia
The image of Britannia () is the national personification of United Kingdom, Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used by the Romans in classical antiquity, the Latin was the name variously appli ...
at the coast of Land Hadeln in the Elbe-Weser Triangle, called by the Merovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from around the middle of the 5th century until Pepin the Short in 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the ...
rulers of Francia to support the conquest of Thuringian
Thuringian is an East Central German dialect group spoken in much of the modern German Free State of Thuringia north of the Rennsteig ridge, southwestern Saxony-Anhalt and adjacent territories of Hesse and Bavaria. It is close to Upper Saxon s ...
kingdom, a seeming reversal of the English origin myth where Saxon tribes from the region, under the leadership of legendary brothers Hengist and Horsa
Hengist (, ) and Horsa are legendary Germanic peoples, Germanic brothers who according to later English legends and ethnogenesis theories led the Angles (tribe), Angles, Saxons and Jutes, the progenitor groups of modern English people, in thei ...
, invade post-Roman Britannia (see Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain
The settlement of Great Britain by Germanic peoples from continental Europe led to the development of an Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon cultural identity and a shared Germanic language—Old English—whose closest known relative is Old Frisian, s ...
).
The Royal Frankish Annals
The ''Royal Frankish Annals'' (Latin: ''Annales regni Francorum''), also called the ''Annales Laurissenses maiores'' ('Greater Lorsch Annals'), are a series of annals composed in Latin in Carolingian Francia, recording year-by-year the state of ...
mention a 743 Frankish campaign led by the Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty ( ; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charles Martel and his grandson Charlemagne, descendants of the Arnulfing and Pippinid c ...
Mayor of the Palace Carloman against the Saxons, followed by a second expedition together with his brother Pepin the Short
the Short (; ; ; – 24 September 768), was King of the Franks from 751 until his death in 768. He was the first Carolingian dynasty, Carolingian to become king.
Pepin was the son of the Frankish prince Charles Martel and his wife Rotrude of H ...
the next year. In 747 their rebellious brother Grifo allied with Saxon tribes and temporarily conquered the stem duchy of Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
. Pepin, Frankish king from 750, again invaded Saxony and subdued several Westphalian tribes until 758.
In 772, Pepin's son Charlemagne started the final conquest of the Saxon lands. Though his ongoing campaigns were successful, he had to deal with the fragmentation of the Saxon territories in Westphalian, Eastphalia
Eastphalia ( �stˈfaːlən Eastphalian: ''Oostfalen'') is a historical region in northern Germany, encompassing the eastern '' Gaue'' (shires) of the historic stem duchy of Saxony, roughly confined by the River Leine in the west and the Elbe a ...
n, Angrian, and Nordalbingian tribes, demanding the conclusion of specific peace agreements with single tribes, which soon were to be broken by other clans. The Saxons devastated the Frankish stronghold at Eresburg
The Eresburg is the largest, well-known (Old) Saxon refuge castle (''Volksburg'') and was located in the area of the present German village of Obermarsberg in the borough of Marsberg in the county of Hochsauerlandkreis. It was a hill castle ...
; their leader (''Herzog
(; feminine ; masculine plural ; feminine plural ) is a German hereditary title held by one who rules a territorial duchy, exercises feudal authority over an estate called a duchy, or possesses a right by law or tradition to be referred to ...
'') Widukind
Widukind, also known as Wittekind and Wittikund, was a leader of the Saxons and the chief opponent of the Frankish king Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 777 to 785. Charlemagne ultimately prevailed, organized Saxony as a Frankish provinc ...
refused to appear at the 777 diet at Paderborn
Paderborn (; Westphalian language, Westphalian: ''Patterbuorn'', also ''Paterboärn'') is a city in eastern North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, capital of the Paderborn (district), Paderborn district. The name of the city derives from the river Pade ...
, retired to Nordalbingia and afterwards led several uprisings against the occupants, avenged by Charlemagne at the Massacre of Verden
The Massacre of Verden was an event during the Saxon Wars where the Franks, Frankish king Charlemagne ordered the death of 4,500 Saxons in October 782. Charlemagne claimed suzerainty over Saxony and in 772 destroyed the Irminsul, an important obj ...
in 782. Widukind allegedly had to pledge allegiance in 785, having himself baptised and becoming a Frankish count. Saxon uprisings continued until 804, when the whole stem duchy had been incorporated into the Carolingian Empire.
Afterwards, Saxony was ruled by Carolingian officials, e.g. Wala of Corbie (d. 836), a grandson of Charles Martel
Charles Martel (; – 22 October 741), ''Martel'' being a sobriquet in Old French for "The Hammer", was a Franks, Frankish political and military leader who, as Duke and Prince of the Franks and Mayor of the Palace, was the de facto ruler of ...
and cousin of the emperor, who in 811 fixed the Treaty of Heiligen
The Treaty of Heiligen was a treaty of peace between the Danish King Hemming and the Frankish Emperor Charlemagne. It is attested in the ''Royal Frankish Annals'' for the year 811.
The previous King of the Danes, Godofrid, had held a conferenc ...
with King Hemming of Denmark
Hemming I (died 812) was a king in Denmark from 810 until his death. He was the successor of King Gudfred, his uncle.
Family
Hemming I is mentioned in the Royal Frankish Annals as son to an unnamed brother of Gudfred. Though ''Gesta Hammabu ...
, defining the northern border of the Empire along the Eider
The eiders () are large seaducks in the genus ''Somateria''. The three extant species all breed in the cooler latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere.
The down feathers of eider ducks and some other ducks and geese are used to fill pillows and qu ...
River. Among the installed dukes were already nobles of Saxon descent, like Wala's successor Count Ekbert, husband of Saint Ida of Herzfeld, a close relative of Charlemagne.
Younger stem duchy
Ida of Herzfeld may have been an ancestor of the Saxon count Liudolf (d. 866), who married Oda ofBillung
The House of Billung was a dynasty of Saxon noblemen in the 9th through 12th centuries.
The first known member of the house was Count Wichmann, mentioned as a Billung in 811. Oda, the wife of Count Liudolf, oldest known member of the Liudol ...
and ruled over a large territory along the Leine
The Leine (; Old Saxon ''Lagina'') is a river in Thuringia and Lower Saxony, Germany. It is a left tributary of the Aller and the Weser and is long.
The river's source is located close to the town of Leinefelde in Thuringia. About downriver ...
river in Eastphalia, where he and Bishop Altfrid of Hildesheim
Hildesheim (; or ; ) is a city in Lower Saxony, in north-central Germany with 101,693 inhabitants. It is in the district of Hildesheim (district), Hildesheim, about southeast of Hanover on the banks of the Innerste River, a small tributary of t ...
founded Gandersheim Abbey
Gandersheim Abbey () is a former house of secular canonesses ( Frauenstift) in the present town of Bad Gandersheim in Lower Saxony, Germany. It was founded in 852 by Count Liudolf of Saxony and his wife, Oda, progenitors of the Liudolfing or Ot ...
in 852. Liudolf became the progenitor of the Saxon ducal, royal and imperial Ottonian dynasty
The Ottonian dynasty () was a Saxons, Saxon dynasty of German monarchs (919–1024), named after three of its kings and Holy Roman emperors, especially Otto the Great. It is also known as the Saxon dynasty after the family's origin in the German ...
; nevertheless his descendance, especially his affiliation with late Duke Widukind, has not been conclusively established.
Subdued only a few decades earlier, the Saxons rose to one of the leading tribes in East Francia
East Francia (Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire created in 843 and ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was established through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the for ...
; it is however uncertain if the Ottonians already held the ducal title in the ninth century. Liudolf's elder son Bruno
Bruno may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Bruno (name), including lists of people and fictional characters with either the given name or surname
* Bruno, Duke of Saxony (died 880)
* Bruno the Great (925–965), Archbishop of Cologn ...
(Brun), progenitor of the Brunswick cadet branch of the Brunonen, was killed in a battle with invading Viking
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
s under Godfrid in 880. He was succeeded by his younger brother Otto the Illustrious (d. 912), mentioned as ''dux'' in the contemporary annals of Hersfeld Abbey
Hersfeld Abbey was an important Benedictine imperial abbey in the town of Bad Hersfeld in Hesse (formerly in Hesse-Nassau), Germany, at the confluence of the rivers Geisa, Haune and Fulda. The ruins are now a medieval festival venue.
History ...
, which, however, seems to have been denied by the Frankish rulers. His position was strong enough to wed Hedwiga of the Babenberg
The House of Babenberg was a noble dynasty of Austrian Dukes and Margraves. Descending from the Popponids and originally from Bamberg in the Duchy of Franconia (present-day Bavaria), the Babenbergs ruled the imperial Margraviate of Austria fr ...
, daughter of mighty Duke Henry of Franconia
Henry (died 28 August 886) was the leading military commander of the last years of the Carolingian Empire. He was commander-in-chief under Kings Louis the Younger and Charles the Fat. His early career was mostly restricted to East Francia, his home ...
, ''princeps militiae'' of King Charles the Fat
Charles the Fat (839 – 13 January 888) was the emperor of the Carolingian Empire from 881 to 887. A member of the Carolingian dynasty, Charles was the youngest son of Louis the German and Hemma, and a great-grandson of Charlemagne. He was t ...
. As all of Hedwiga's brothers were killed in the Franconian Babenberg feud with the rivalling Conradines
The Conradines or Conradiner were a dynasty of Franconian counts and dukes in the 8th to 11th Century, named after Duke Conrad, Duke of Thuringia, Conrad the Elder and his son King Conrad I of Germany.
History
The family is first mentioned in 8 ...
, Otto was able to adopt the strong position of his father-in-law and to evolve the united Saxon duchy under his rule.
In 911, the East Frankish Carolingian dynasty went extinct with the death of King Louis the Child
Louis the Child (893 – 20/24 September 911), sometimes called Louis III or Louis IV, was the king of East Francia from 899 until his death and was also recognized as king of Lotharingia after 900. He was the last East Frankish ruler of the Car ...
, whereafter the dukes of Saxony, Swabia
Swabia ; , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of Swabia, one of ...
and Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
met at Forchheim
Forchheim () is a Town#Germany, town in Upper Franconia () in northern Bavaria, and also the seat of the administrative Forchheim (district), district of Forchheim. Forchheim is a former royal city, and is sometimes called the Gateway to the Fr ...
to elect the Conradine duke Conrad I of Franconia king. One year later, Otto's son Henry the Fowler
Henry the Fowler ( or '; ; – 2 July 936) was the duke of Saxony from 912 and the king of East Francia from 919 until his death in 936. As the first non- Frankish king of East Francia, he established the Ottonian dynasty of kings and emper ...
succeeded his father as Duke of Saxony. According to the medieval chronicler Widukind of Corvey
Widukind of Corvey (c. 925after 973; , in italian ''Vitichindo Sacco di Corvey'', in Latin VVITICHINDI SAXO) was a medieval Saxon chronicler. His three-volume '' Res gestae Saxonicae sive annalium libri tres'' is an important chronicle of 10th-cen ...
, King Conrad designated Henry his heir, thereby denying the succession of his own brother Eberhard of Franconia
Eberhard (c. 885 – 2 October 939), a member of the Conradines, Conradine dynasty, was Duchy of Franconia, Duke of Franconia, succeeding his elder brother, King Conrad I of Germany, Conrad I, in December 918. From 926 to 928, he also acted as ru ...
, and in 919 the Saxon duke was elected King of East Francia by the assembled Saxon and Franconian princes at Fritzlar
Fritzlar () is a small town (pop. 15,000) in the Schwalm-Eder-Kreis, Schwalm-Eder district in northern Hesse, Germany, north of Frankfurt, with a storied history.
The town has a medieval center ringed by a wall with numerous watch towers. high ...
. Henry was able to integrate the Swabian, Bavarian and Lotharingian duchies into the imperial federation, vital to handle the continuous attacks by Hungarian forces, whereby the Saxon troops about 928/929 occupied large territories in the east settled by Polabian Slavs
Polabian Slavs, also known as Elbe Slavs
and more broadly as Wends, is a collective term applied to a number of Lechites, Lechitic (West Slavs, West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Germany. The ...
. Henry's eastern campaigns to Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
and Meissen
Meissen ( ), is a town of approximately 30,000 about northwest of Dresden and 75 km (46 mi) west of Bautzen on both banks of the Elbe river in the Free State of Saxony, in eastern Germany. Meissen is the home of Meissen porcelain, th ...
, the establishment of Saxon marches
In medieval Europe, a march or mark was, in broad terms, any kind of borderland, as opposed to a state's "heartland". More specifically, a march was a border between realms or a neutral buffer zone under joint control of two states in which diffe ...
as well as the surrender of Duke Wenceslaus of Bohemia marked the beginning of the German eastward expansion ().
House of Billung
* 936: Upon Henry's death atMemleben
Memleben is a village and part of the Kaiserpfalz, Saxony-Anhalt, Kaiserpfalz municipality of the Burgenlandkreis district, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is known for former Memleben Abbey, the site of a medieval ''Kaiserpfalz''.
Geography
It is l ...
, his son Otto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), known as Otto the Great ( ) or Otto of Saxony ( ), was East Francia, East Frankish (Kingdom of Germany, German) king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the eldest son o ...
succeeded him. According to Widukind, he was crowned king at Aachen Cathedral
Aachen Cathedral () is a Catholic Church, Catholic church in Aachen, Germany and the cathedral of the Diocese of Aachen.
One of the oldest cathedral buildings in Europe, it was constructed as the royal chapel of the Palace of Aachen of Holy Rom ...
, with the other Stem duchy, German Dukes Gilbert, Duke of Lorraine, Gilbert of Lorraine, Eberhard of Franconia
Eberhard (c. 885 – 2 October 939), a member of the Conradines, Conradine dynasty, was Duchy of Franconia, Duke of Franconia, succeeding his elder brother, King Conrad I of Germany, Conrad I, in December 918. From 926 to 928, he also acted as ru ...
, Arnulf, Duke of Bavaria, Arnulf of Bavaria and Herman I, Duke of Swabia, Herman of Swabia paying homage to him. He appoints Hermann Billung as ''princeps militiae'' or "Markgraf" in the Billung March
The Billung March () or March of the Billungs () was a frontier region of the far northeastern Duchy of Saxony in the 10th century. It was named after the family which held it, the House of Billung.
The march reached from the Elbe River to the ...
with orders to subdue the Slavic Lutici beyond the Elbe River.
* 961: Otto I leaves for Italy and his lieutenant margrave Hermann Billung becomes the administrator of Saxony. Before his death he was in all but name the duke of Saxony.
* 973: Hermann Billung dies in Quedlinburg and shortly after Otto I dies in Memleben
Memleben is a village and part of the Kaiserpfalz, Saxony-Anhalt, Kaiserpfalz municipality of the Burgenlandkreis district, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is known for former Memleben Abbey, the site of a medieval ''Kaiserpfalz''.
Geography
It is l ...
. Otto II becomes emperor and he make Hermann's son Bernard I, Duke of Saxony, Bernhard I the first duke of Saxony of the Billung
The House of Billung was a dynasty of Saxon noblemen in the 9th through 12th centuries.
The first known member of the house was Count Wichmann, mentioned as a Billung in 811. Oda, the wife of Count Liudolf, oldest known member of the Liudol ...
House.
* 983: Danish uprising in Hedeby. Slavic peoples, Slavonian uprising in Northalbingia.
* 1011: Duke Bernard I, Duke of Saxony, Bernhard I Billung dies; his son Bernard II, Duke of Saxony, Bernhard II becomes duke.
* 1042: Ordulf, Duke of Saxony, Ordulf Billung, son of Bernhard II, marries Wulfhild of Norway, Wulfhild, the half-sister of King Magnus I of Norway, Magnus of Denmark and Norway. Danes (Germanic tribe), Danes and Saxons fight against the Wends.
* 1059: Ordulf Billung becomes duke after the death of his father.
* 1072: Magnus, Duke of Saxony, Magnus Billung becomes duke.
* 1106: Duke Magnus dies without heir, ending the Billung dynasty. The Billung territory becomes part of the Welf and Ascanian countries. Lothar II, Holy Roman Emperor, Lothar of Supplinburg becomes duke of Saxony.
* 1112: Otto of Ballenstedt created duke by Emperor Henry V.
* 1115: Victory of Lothar of Supplinburg in the battle of Welfesholz over King Henry V.
* 1125: Lothar of Supplinburg elected as German king and crowned emperor.
* 1137 Death of Lothar. The Welf Henry the Proud, duke of Bavaria since 1126, had been appointed Lothar's successor (who died without a male heir) as duke of Saxony. However, as he was not officially invested and it would make him far too powerful, his claim is not recognized by his rivals.
* 1138: Henry loses the election for king of the Germans against Conrad III of Germany, Conrad of Hohenstaufen. Insisting to hold both duchies, Bavaria and Saxonia, a claim Conrad opposes, Henry refuses an oath of allegiance and is consequently stripped of all his titles. The Duchy of Saxony is granted to the Ascanian Albert the Bear.
* 1139: Due to his marriage to Lothar's only daughter Gertrude of Supplingenburg, Henry still holds substantial lands within the Duchy of Saxony. Henry fiercely resists Albert's attempts to take possession of Saxony. Preparing an attack on the Duchy of Bavaria, Henry dies unexpectedly.
* 1141: Albert the Bear renounces the Duchy of Saxony and the title (as well as the Duchy of Bavaria) is granted to Henry X's adolescent son Henry the Lion
Henry the Lion (; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195), also known as Henry III, Duke of Saxony (ruled 1142-1180) and Henry XII, Duke of Bavaria (ruled 1156-1180), was a member of the Welf dynasty.
Henry was one of the most powerful German princes of ...
.
Henry the Lion
 In 1142, King Conrad III of Germany granted the ducal title to the Welf scion Henry the Lion (as Duke Henry III). Henry gradually extended his rule over northeastern Germany, leading crusades against the pagan Wends. During his reign, Henry massively supported to the development of the cities in his dominion, such as Braunschweig, Brunswick, Lüneburg and Lübeck, a policy ultimately contributing to the movement of the House of Welf from its homelands in southern Germany to the north.
In 1152, Henry supported his cousin Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick III of Swabia, to be elected King of Germany (as Frederick I Barbarossa), likely under the promise of granting the Duchy of Bavaria back to Henry. Henry's dominion now covered more than two thirds of Germany, from the Alps to the North Sea and the Baltic Sea, making him one of the mightiest rulers in central Europe, and thus also a potential threat for other German princes and even Barbarossa.
In 1142, King Conrad III of Germany granted the ducal title to the Welf scion Henry the Lion (as Duke Henry III). Henry gradually extended his rule over northeastern Germany, leading crusades against the pagan Wends. During his reign, Henry massively supported to the development of the cities in his dominion, such as Braunschweig, Brunswick, Lüneburg and Lübeck, a policy ultimately contributing to the movement of the House of Welf from its homelands in southern Germany to the north.
In 1152, Henry supported his cousin Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick III of Swabia, to be elected King of Germany (as Frederick I Barbarossa), likely under the promise of granting the Duchy of Bavaria back to Henry. Henry's dominion now covered more than two thirds of Germany, from the Alps to the North Sea and the Baltic Sea, making him one of the mightiest rulers in central Europe, and thus also a potential threat for other German princes and even Barbarossa.
 To expand his rule, Henry continued to claim titles of lesser families, who left no legitimate heir. This policy caused unrest among many Saxon nobles and other German princes, first and foremost his father's old enemy, Albrecht the Bear. During Barbarossa's fourth Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor#First Italian Campaign, Italian campaign in 1166, a league of German Nobles declared war on Henry. The war continued until 1170, despite several attempts of the Emperor to mediate. Ultimately, Henry's position remained unchallenged, due to Barbarossa's favourable rule.
In 1168, Henry married Matilda of England, Duchess of Saxony, Matilda Plantagenêt, the daughter of Henry II of England and Eleanor of Aquitaine and sister of Richard Lionheart.
The following years led to an estrangement between Barbarossa and Henry. Henry ceased to support the Emperor's Italy campaigns, which were all proven unsuccessful, as massively as he used to, and instead focused on his own possessions. In 1175 Barbarossa again asked for support against the Lombard League, which Henry is said to have refused bluntly, even though Barbarossa kneeled before him. Records of this event were not written until several years later, and sources are contradictory, depending on whom the author favoured. Nevertheless, lacking the support of the Saxons the following Battle of Legnano was a complete failure for the Emperor.
When the majority of the realm's princes had returned from Italy, Henry's refusal was instantly exploited to weaken his position. Views differ, whether Barbarossa initiated Henry's downfall or if it was orchestrated by the princes first and foremost.
Between 1175 and 1181, Henry was charged with several accusations, such as violating the ''honour of the realm'' (honor imperii), breach of the peace, and treason. If he were to follow the summons to the Hoftag, Henry would've acknowledge the charges as rightful, and therefore refused all summons. In 1181, he was ultimately stripped of his titles. Unwilling to give up without a fight, Henry already had dealt the first blow in 1180 against the city of Goslar, which he had coveted for several years already. During the following war, Henry's domestic policy and the treatment of his vassals proved fatal, and his power quickly crumbled.
In 1182, Henry the Lion ultimately went into exile, joining the court of his father-in-law, Henry II of England. Following the death of his wife and also of the Emperor, the latter while participating in the Third Crusade, Henry returned to Brunswick in 1189 and briefly tried to regain the lost lands. After several setbacks, Henry made peace with Barbarossa's son and heir, King Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor.
The ancient
To expand his rule, Henry continued to claim titles of lesser families, who left no legitimate heir. This policy caused unrest among many Saxon nobles and other German princes, first and foremost his father's old enemy, Albrecht the Bear. During Barbarossa's fourth Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor#First Italian Campaign, Italian campaign in 1166, a league of German Nobles declared war on Henry. The war continued until 1170, despite several attempts of the Emperor to mediate. Ultimately, Henry's position remained unchallenged, due to Barbarossa's favourable rule.
In 1168, Henry married Matilda of England, Duchess of Saxony, Matilda Plantagenêt, the daughter of Henry II of England and Eleanor of Aquitaine and sister of Richard Lionheart.
The following years led to an estrangement between Barbarossa and Henry. Henry ceased to support the Emperor's Italy campaigns, which were all proven unsuccessful, as massively as he used to, and instead focused on his own possessions. In 1175 Barbarossa again asked for support against the Lombard League, which Henry is said to have refused bluntly, even though Barbarossa kneeled before him. Records of this event were not written until several years later, and sources are contradictory, depending on whom the author favoured. Nevertheless, lacking the support of the Saxons the following Battle of Legnano was a complete failure for the Emperor.
When the majority of the realm's princes had returned from Italy, Henry's refusal was instantly exploited to weaken his position. Views differ, whether Barbarossa initiated Henry's downfall or if it was orchestrated by the princes first and foremost.
Between 1175 and 1181, Henry was charged with several accusations, such as violating the ''honour of the realm'' (honor imperii), breach of the peace, and treason. If he were to follow the summons to the Hoftag, Henry would've acknowledge the charges as rightful, and therefore refused all summons. In 1181, he was ultimately stripped of his titles. Unwilling to give up without a fight, Henry already had dealt the first blow in 1180 against the city of Goslar, which he had coveted for several years already. During the following war, Henry's domestic policy and the treatment of his vassals proved fatal, and his power quickly crumbled.
In 1182, Henry the Lion ultimately went into exile, joining the court of his father-in-law, Henry II of England. Following the death of his wife and also of the Emperor, the latter while participating in the Third Crusade, Henry returned to Brunswick in 1189 and briefly tried to regain the lost lands. After several setbacks, Henry made peace with Barbarossa's son and heir, King Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor.
The ancient stem duchy
A stem duchy (, from '':wikt:Stamm, Stamm'', meaning "tribe", in reference to the Franks, Saxons, Baiuvarii, Bavarians and Alemanni, Swabians) was a constituent duchy of the Kingdom of Germany at the time of the extinction of the Carolingian dyna ...
of Saxony was partitioned in some dozens of territories of imperial immediacy by Barbarossa, and ceased to exist. The western part was split amongst several minor counties and bishoprics, as well as the newly formed Duchy of Westphalia. In the east, the Ascanians, the Welf's old rivals, finally gained a severely belittled Duchy of Saxony, occupying only the easternmost, comparably small, territories along the river Elbe
The Elbe ( ; ; or ''Elv''; Upper Sorbian, Upper and , ) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Republic), then Ge ...
around Lauenburg/Elbe, Lauenburg upon Elbe and around Wittenberg, Wittenberg upon Elbe. Limiting the lands the Ascanians gained along with the ducal title to these eastern territories caused the migration of the name Saxony from north-western Germany to the location of the modern Free State of Saxony.
The deposed ducal House of Welf could maintain its allodium, allodial possessions, which did not remain as part of the Duchy of Saxony after the enfeoffment of the Ascanians. The Welf possessions were elevated to the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg
The Duchy of Brunswick and Lüneburg (), commonly known as the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg or Brunswick-Lüneburg, was an imperial principality of the Holy Roman Empire in the territory of present day Lower Saxony.
In 1235, Otto I, Duke of ...
(also Brunswick and Lunenburg) in 1235. This duchy continued to use the old Saxon coat-of-arms showing the Saxon Steed in Argent (heraldry), argent on Gules (heraldry), gules, while the Ascanians adopted for the ''younger Duchy of Saxony'' their family colours, a Barry (heraldry)#Barry, Paly, Bendy, barry of ten, in Sable (heraldry), sable and Or (heraldry), or, covered by a crancelin of rhombs bendwise in Vert (heraldry), vert, symbolising the Saxon dukedom.
House of Ascania
In 1269, 1272, and 1282 the co-ruling brothers John I, Duke of Saxony, John I and Albert II, Duke of Saxony, Albert II gradually divided their governing competences within the then three territorially unconnected Saxon areas (Hadeln, Lauenburg, and Wittenberg), thus preparing a partition. After John I had resigned in 1282 in favour of his three minor sons Eric I of Saxe-Lauenburg, Eric I, John II of Saxe-Lauenburg, John II and Albert III of Saxe-Lauenburg, Albert III, followed by his death three years later, the three brothers and their uncle Albert II continued the joint rule in Saxony. In 1288, Albert II applied to Rudolf I of Germany, King Rudolph I for the enfeoffment of his son and heir Rudolf I, Duke of Saxe-Wittenberg, Duke Rudolph I with the Palatinate of Saxony, which ensued a long-lasting dispute with the eager clan of the House of Wettin. When the County of Brehna was reverted to the Empire after the extinction of its comital family, the king enfeoffed Duke Rudolph. In 1290, Albert II gained the County of Brehna and in 1295 the County of Gommern for Saxony. King Wenceslaus II of Bohemia succeeded in bringing Albert II in favour of electing Adolf, King of the Romans, Adolf of Germany, as new emperor (Albert II signed an elector pact on 29 November 1291 that he would vote the same as Wenceslaus). On April 27, 1292, Albert II, with his nephews still minor, wielded the Saxon prince-elector, electoral vote, electing Adolf of Germany. The last document mentioning the joint government of Albert II with his nephews as Saxon fellow dukes dates back to 1295. The definite partitioning of the Duchy of Saxony intoSaxe-Lauenburg
The Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg (, ), was a ''reichsfrei'' duchy that existed from 1296 to 1803 and again from 1814 to 1876 in the extreme southeast region of what is now Schleswig-Holstein. Its territorial centre was in the modern district of Herz ...
(), jointly ruled by the brothers Albert III, Eric I and John II, and Saxe-Wittenberg (), ruled by Albert II, took place before September 20, 1296. The Vierlande, Sadelbande (Land of Lauenburg), the Land of Ratzeburg, the Land of Darzing (today's Amt Neuhaus), and the Land of Hadeln are all mentioned as the separate territory of the brothers.Cordula Bornefeld, "Die Herzöge von Sachsen-Lauenburg", in: ''Die Fürsten des Landes: Herzöge und Grafen von Schleswig, Holstein und Lauenburg'' [De slevigske hertuger; German], Carsten Porskrog Rasmussen (ed.) on behalf of the Gesellschaft für Schleswig-Holsteinische Geschichte, Neumünster: Wachholtz, 2008, pp. 373-389, here p. 375. Albert II received Saxe-Wittenberg around the eponymous city and Belzig. Albert II thus became the founder of the Ascanian line of Saxe-Wittenberg.
Members of the Welf cadet branch House of Hanover later became prince-electors of the Electorate of Hanover, Hanover (as of 1692/1708), kings of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland (both 1714), the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom (1801), and the Kingdom of Hanover, Hanover (1814).
Territories seceded from Saxony after 1180
A number of seceded territories even gained imperial immediacy, while others only changed their liege lord on the occasion. The following list includes states that existed in the territory of the former stem duchy in addition to the two legal successors of the stem duchy, the Ascanian Duchy of Saxony formed in 1296 centered around Wittenberg and Lauenburg, as well as the Duchy of Westphalia, held by the Electorate of Cologne, Archbishops of Cologne, that already split off in 1180.Westphalia
*Angria
* Prince-Bishopric of Minden
*
Prince-Bishopric of Minden
*  Prince-Bishopric of Paderborn
*
Prince-Bishopric of Paderborn
*  Prince-Bishopric of Verden
*
Prince-Bishopric of Verden
* Eastphalia
*Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg
The Duchy of Brunswick and Lüneburg (), commonly known as the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg or Brunswick-Lüneburg, was an imperial principality of the Holy Roman Empire in the territory of present day Lower Saxony.
In 1235, Otto I, Duke of ...
(1235), the Welf allodial possessions
*  Prince-Bishopric of Halberstadt
*
Prince-Bishopric of Halberstadt
*  Prince-Bishopric of Hildesheim
* County of Hohenstein, seated in Hohenstein, Thuringia, Hohenstein
*
Prince-Bishopric of Hildesheim
* County of Hohenstein, seated in Hohenstein, Thuringia, Hohenstein
*  Archbishopric of Magdeburg, Prince-Archbishopric of Magdeburg
*
Archbishopric of Magdeburg, Prince-Archbishopric of Magdeburg
* Nordalbingia
* Bishopric of Schwerin, Prince-Bishopric of Schwerin
Bishopric of Schwerin, Prince-Bishopric of Schwerin
Dukes of Saxony
See also
* Saxony (disambiguation) * History of SaxonyNotes
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Saxony, Duchy of Duchy of Saxony, Culture of Saxony History of Schleswig-Holstein Former states and territories of North Rhine-Westphalia Former states and territories of Saxony-Anhalt Establishments in the Carolingian Empire Carolingian Empire 804 establishments Duchies of the Holy Roman Empire States and territories disestablished in the 1290s