|
Louis The Child
Louis the Child (893 – 20/24 September 911), sometimes called Louis III or Louis IV, was the king of East Francia from 899 until his death and was also recognized as king of Lotharingia after 900. He was the last East Frankish ruler of the Carolingian dynasty. He succeeded his father, Arnulf, in East Francia and his elder illegitimate half-brother Zwentibold in Lotharingia. Louis became king when he was six and reigned until his death aged 17 or 18. During his reign the country was ravaged by Magyar raids. Life Louis was born in September or October 893 in Altötting, Duchy of Bavaria. He was the only legitimate son of king Arnulf of Carinthia and his wife, Ota, a member of the Conradine dynasty. He had at least two brothers: his elder, illegitimate brother Zwentibold, who ruled Lotharingia, and another brother named Ratold, who briefly ruled the Kingdom of Italy. East Francia Louis was crowned in Forchheim on 4 February 900. This is the earliest East Frankish royal co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Sword
The Imperial Sword (, ) is one of the four most important parts of the Imperial Regalia (''Reichskleinodien'') of the Holy Roman Empire. During a coronation, it was given to the emperor along with the Imperial Crown of the Holy Roman Empire, Imperial Crown (''Reichskrone''), Imperial Sceptre (''Reichszepter''), and the Imperial Globus cruciger, Orb (''Reichsapfel''). All four parts of the Imperial Regalia are displayed in the Imperial Treasury, Vienna, Imperial Treasury at the Hofburg Palace in Vienna, Austria.Kunsthistorisches 1991, p. 170. It is also known as ''Mauritiusschwert'', or the sword of Saint Maurice. History The Imperial Sword was made for Emperor Otto IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Otto IV in the twelfth century, possibly for his coronation as King of the Romans in 1198. Its predecessor, the sword of Otto III, is also preserved, in the Essen Abbey treasury. The first known explicit mention of the sword dates to 1315, in a letter of a lady-in-waiting of Elisabeth of Aragon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
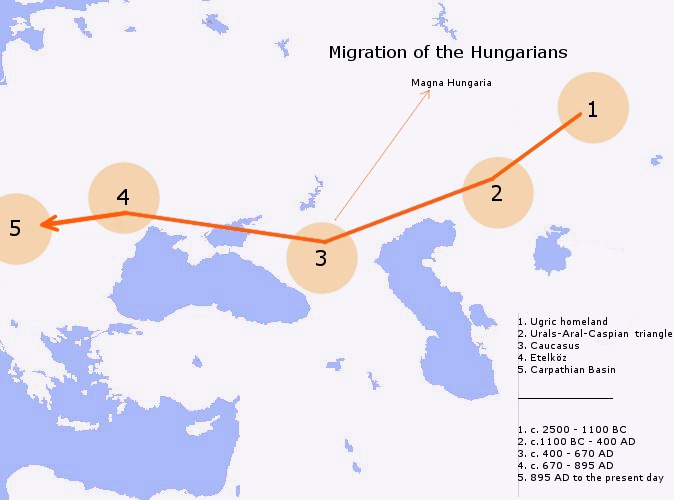
Magyars
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common culture, language and history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ugric branch of the Uralic language family, alongside the Khanty and Mansi languages. There are an estimated 14.5 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia, and Austria. In addition, significant groups of people with Hungarian ancestry live in various other parts of the world, most of them in the United States, Canada, Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Chile, Brazil, Australia, and Argentina, and therefore constitute the Hungarian diaspo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Invasions Of Europe
The Hungarian invasions of Europe (, ) occurred in the 9th and 10th centuries, during the period of transition in the history of Europe of the Early Middle Ages, when the territory of the former Carolingian Empire was threatened by invasion by the Magyars (Hungarians) from the east, the Viking expansion from the north, and the Early Muslim conquests, Arabs from the south.Barbara H. Rosenwein, A short history of the Middle Ages, University of Toronto Press, 2009, p. 15/ref> The Hungarians took possession of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin (corresponding to the later Kingdom of Hungary) in a pre-planned manner, with a long period of settlement between 862–895, and launched a number of campaigns both westward into former Francia and southward into the Byzantine Empire. The westward raids were stopped only with the Magyar defeat at the Battle of Lechfeld (955), Battle of Lechfeld in 955, which led to the revival of the Holy Roman Empire in 962, producing a new political order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Lotharingia
The kings and dukes of Lorraine have held different posts under different governments over different regions, since its creation as the kingdom of Lotharingia by the Treaty of Prüm, in 855. The first rulers of the newly established region were kings of the Franks. The Latin construction "Lotharingia" evolved over time into "Lorraine" in French, "Lotharingen" in Dutch and "Lothringen" in German. After the Carolingian kingdom was absorbed into its neighbouring realms in the late ninth century, dukes were appointed over the territory. In the mid-tenth century, the duchy was divided into Lower Lorraine and Upper Lorraine, the first evolving into the historical Low Countries, the second became known as the Duchy of Lorraine and existed well into the modern era. Kings of Lotharingia *Lothair II (855–869) Charles the Bald claimed Lotharingia on Lothair's death and was crowned king in Metz, but his brother Louis the German opposed his claim and in 870 the Treaty of Mersen divided Loth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gebhard, Duke Of Lorraine
Gebhard of Lahngau ( 860/868 – 22 June 910), of the Conradine dynasty, son of Odo (aka Udo, died 879), count of Lahngau, and Judith, was himself count of Wetterau (909–910) and Rheingau (897–906) and then duke of Lotharingia (Lorraine). In 903, Louis the Child, king of Germany, gave him the government of Lotharingia with the title of duke (''Kebehart dux regni quod a multis Hlotharii dicitur''). Gebhard died in battle against the Magyars, somewhere by Augsburg. With his wife Ida, he had two children: * Herman (died 949), duke of Swabia The Dukes of Swabia were the rulers of the Duchy of Swabia during the Middle Ages. Swabia was one of the five stem duchy, stem duchies of the medieval German kingdom, and its dukes were thus among the most powerful magnates of Germany. The most no ... * Odo (died 949), count of Wetterau (from 914), Lahngau (from 918), and Rheingau (from 917), married Cunigunda, daughter of Herbert I of Vermandois Ancestry References Sources * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radbod Of Trier
Radbod (or Ratbod) (died 915) was the Archbishop of Trier from 883 until his death. Under the last Carolingians he obtained a great deal of benefits and converted the archdiocese of Trier into one of the most powerful institutions in Germany. In 898, Radbod received complete immunity from all taxes for the entire episcopal territory from Zwentibold. He obtained from Louis the Child the district and city of Trier, as well as the right to have a mint and impose customs duties. From Charles the Simple he gained the right of free election for his diocese of Trier. In this way the secular possessions of the bishops of Trier, which had sprung from the valuable donations of the Merovingian The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from around the middle of the 5th century until Pepin the Short in 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the ..., were raised to a secular principality. Sources ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raffelstetten Customs Regulations
Raffelstetten customs regulations (Latin: ''Inquisitio de theloneis Raffelstettensis'', literally: "Inquiry of the Raffelstetten Tolls") is a rare example of a legal regulation of customs in Early Medieval Europe, the text of which has been preserved until modern times. The regulation is only known from a single copy, a manuscript dated to the 1250s, which was preserved in a church at Passau. The critical edition of the manuscript was published in the ''Monumenta Germaniae Historica'' in 1897 by Alfred Boretius and Victor Krause. The incipit reads: "Noverit omnium fidelium orthodoxorum...". Contents and examination Overview The text has been given the scholarly name ''Inquisitio de theloneis Raffelstettensis'' after Raffelstetten (called ''Raffoltestetun'' in the text), a toll-bar on the Danube, a few kilometres downstream (southeast) from Linz (nowadays part of the town of Asten in Upper Austria). The regulation has been dated to somewhere 903 and 905/906. At the time, Raff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Franconia
The Duchy of Franconia () was one of the five stem duchies of East Francia and the medieval Kingdom of Germany emerging in the early 10th century. The word Franconia, first used in a Latin charter of 1053, was applied like the words Francia, France, and '' Franken'', to a portion of the land occupied by the Franks. Geography It stretched along the valley of the River Main from its confluence with the Upper Rhine up to the Bavarian March of the Nordgau, in the areas of the present-day Bavarian region of Franconia, the adjacent southern parts of the Free State of Thuringia, northern Baden-Württemberg (i.e. Rhine-Neckar and Heilbronn-Franken) and Hesse. It also included several '' Gaue'' on the left bank of the Rhine around the cities of Mainz, Speyer and Worms comprising present-day Rhenish Hesse and the Palatinate region. Located in the centre of what was to become the German kingdom about 919, it bordered the stem Duchy of Saxony in the north, Austrasian Lorraine (Upper a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babenberger
The House of Babenberg was a noble dynasty of Austrian Dukes and Margraves. Descending from the Popponids and originally from Bamberg in the Duchy of Franconia (present-day Bavaria), the Babenbergs ruled the imperial Margraviate of Austria from its creation in 976 AD until its elevation to a duchy in 1156, and from then until the extinction of the line in 1246, whereafter they were succeeded by the House of Habsburg. Origin Elder and Younger Houses of Babenberg The Babenberg family can be broken down into two distinct groups; # The Elder or Franconian House of Babenberg. Their name refers to Babenburg Castle, the present site of Bamberg Cathedral. They also called '' Popponids'' after their progenitor Count Poppo of Grapfeld (d. 839–41). They were related to the Frankish Robertian dynasty and ancestors of the Franconian Counts of Henneberg and the House of Schweinfurt. # The Younger or Austrian House of Babenberg, or simply the House of Babenberg, are the descendants of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conradine
The Conradines or Conradiner were a dynasty of Franconian counts and dukes in the 8th to 11th Century, named after Duke Conrad the Elder and his son King Conrad I of Germany. History The family is first mentioned in 832, with Count Gebhard in the lower Lahn region. His sons are mentioned in 861 as ''propinqui'' (close relatives) of Adalard the Seneschal, who had served Louis the Pious. But the clan's rise to prominence began with Oda, wife of Emperor Arnulf of Carinthia, who was a member of the family. In view of his family relationship with Oda, Conrad the Elder was frequently referred to as nepos (nephew, grandson, descendant) of the Emperor. He and his brothers apparently were in fact Arnulf's closest relatives, and he relied heavily on their support in his feud with the counts of Babenberg. Arnulf rewarded them by helping them gain territories, beyond their original realm in Hesse, in Thuringia and the Frankish regions along the Main river. After Arnulf's death, the Conra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon III (bishop Of Constance)
Solomon III (died 919) was the Bishop of Constance from 890 to his death. In 885, the Emperor Charles III made him archchancellor of the Empire, for Konstanz was then the greatest diocese in Swabia, which had been Charles' original kingdom and was still his home most of the time. As well as bishop, he was also abbot of Reichenau Island, Reichenau and Abbey of St. Gall, Saint Gall, immensely powerful abbeys in Swabia. Solomon founded a church in honour of Magnus of Füssen, Saint Magnus at Saint Gall. Solomon was a warlike prelate, originally an ally of both King Louis the Child and Count Palatine Erchanger in the wars for the Swabian dukedom against the Burchards. He was influential in the execution of Burchard I, Duke of Swabia, Burchard I in 911, but he left his alliance with Erchanger when the latter allied with King Conrad I of Germany, Conrad I. Erchanger even imprisoned Solomon in 914. Conrad, however, supported the bishop and freed him. Conrad later had Erchanger beheaded. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatto I
Hatto I (c. 850 – 15 May 913) was Archbishop of Mainz (Mayence) from 891 until his death. Family and early life Hatto belonged to a Swabian family, and was probably educated at the monastery of Reichenau, of which he became abbot in 888. He was also abbot of Ellwangen Abbey. Counsellor of Arnulf of Carinthia Hatto soon became known to the German king, Arnulf, who appointed him archbishop of Mainz in 891, and he became such a trustworthy and loyal counsellor that he was popularly called the heart of the king. He presided over the important synod at Tribur in 895 and accompanied the king to Italy in 894 and 895, where he was received with great favor by Pope Formosus. In 899, when Arnulf died, Hatto became regent of the Empire and guardian of the young king, Louis the Child, whose authority he compelled Zwentibold, duke of Lorraine, an illegitimate son of Arnulf, to recognize. Execution of Adalbert of Babenberg During these years Hatto did not neglect his own interests, for in 89 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |