Drip Pan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
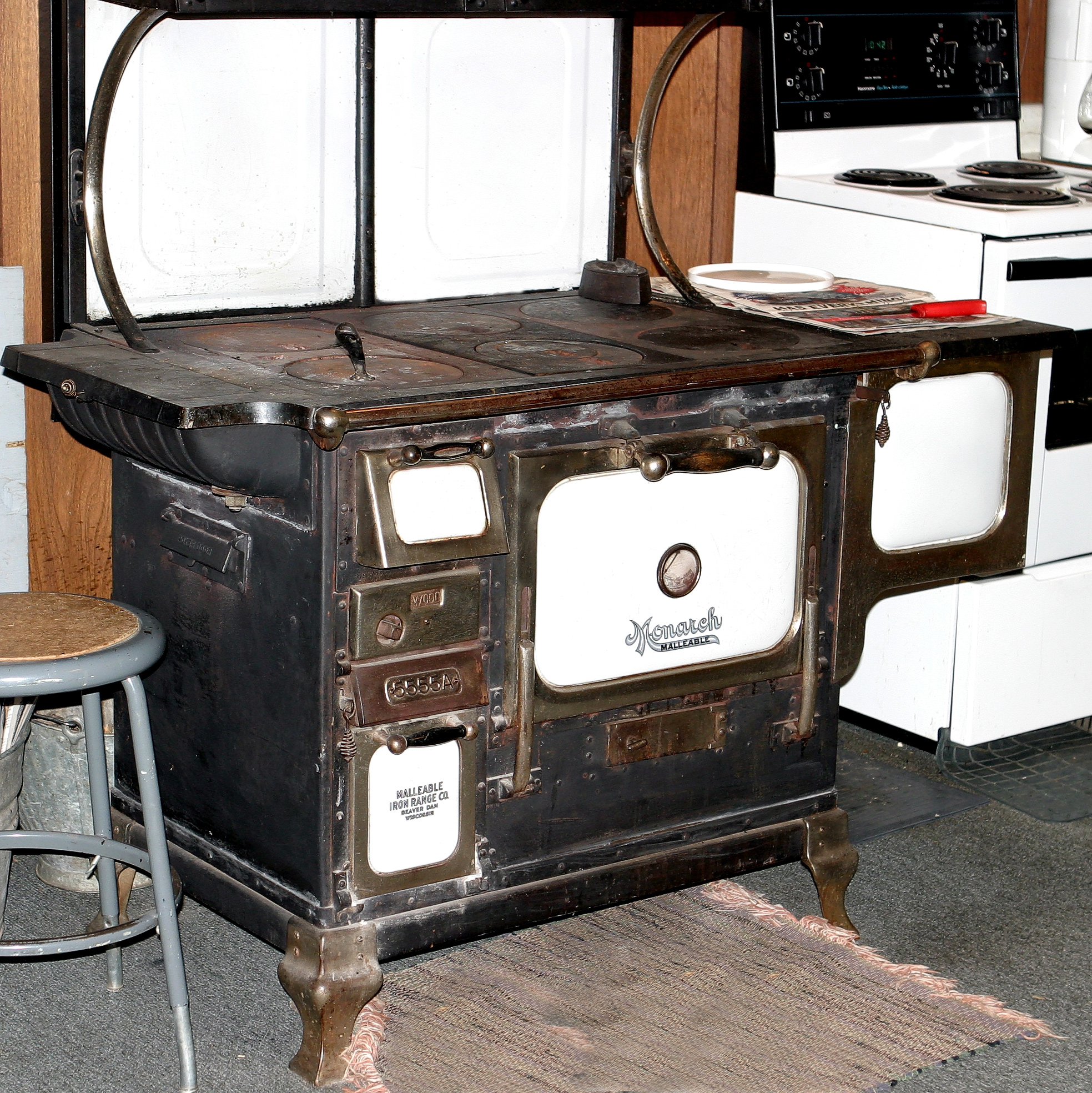 A kitchen stove, often called simply a
A kitchen stove, often called simply a

 Early
Early
Rumford fire2.jpg, Section of Rumford fireplace, invented by Sir
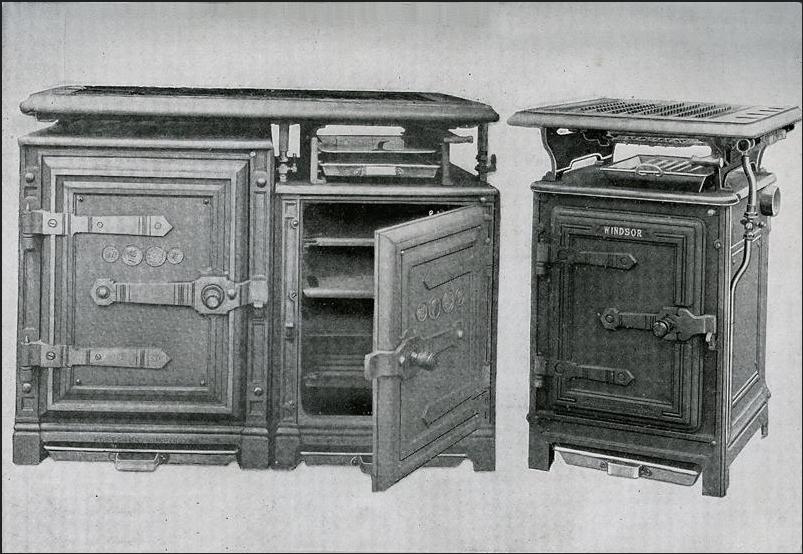 A major improvement in fuel technology came with the advent of
A major improvement in fuel technology came with the advent of
 Once electric power was widely and economically available, electric stoves became a popular alternative to fuel-burning appliances. One of the earliest such devices was patented by Canadian inventor Thomas Ahearn in 1892. Ahearn and Warren Y. Soper were owners of Ottawa's Chaudiere Electric Light and Power Company. The electric stove was showcased at the Chicago World's Fair in 1893, where an electrified model kitchen was shown.
Unlike the gas stove, the electrical stove was slow to catch on, partly due to the unfamiliar technology, and the need for cities and towns to be electrified. Early electric stoves were unsatisfactory due to the cost of electricity (compared with wood, coal, or city gas), limited power available from the electrical supply company, poor temperature regulation, and short life of heating elements. The invention of
Once electric power was widely and economically available, electric stoves became a popular alternative to fuel-burning appliances. One of the earliest such devices was patented by Canadian inventor Thomas Ahearn in 1892. Ahearn and Warren Y. Soper were owners of Ottawa's Chaudiere Electric Light and Power Company. The electric stove was showcased at the Chicago World's Fair in 1893, where an electrified model kitchen was shown.
Unlike the gas stove, the electrical stove was slow to catch on, partly due to the unfamiliar technology, and the need for cities and towns to be electrified. Early electric stoves were unsatisfactory due to the cost of electricity (compared with wood, coal, or city gas), limited power available from the electrical supply company, poor temperature regulation, and short life of heating elements. The invention of
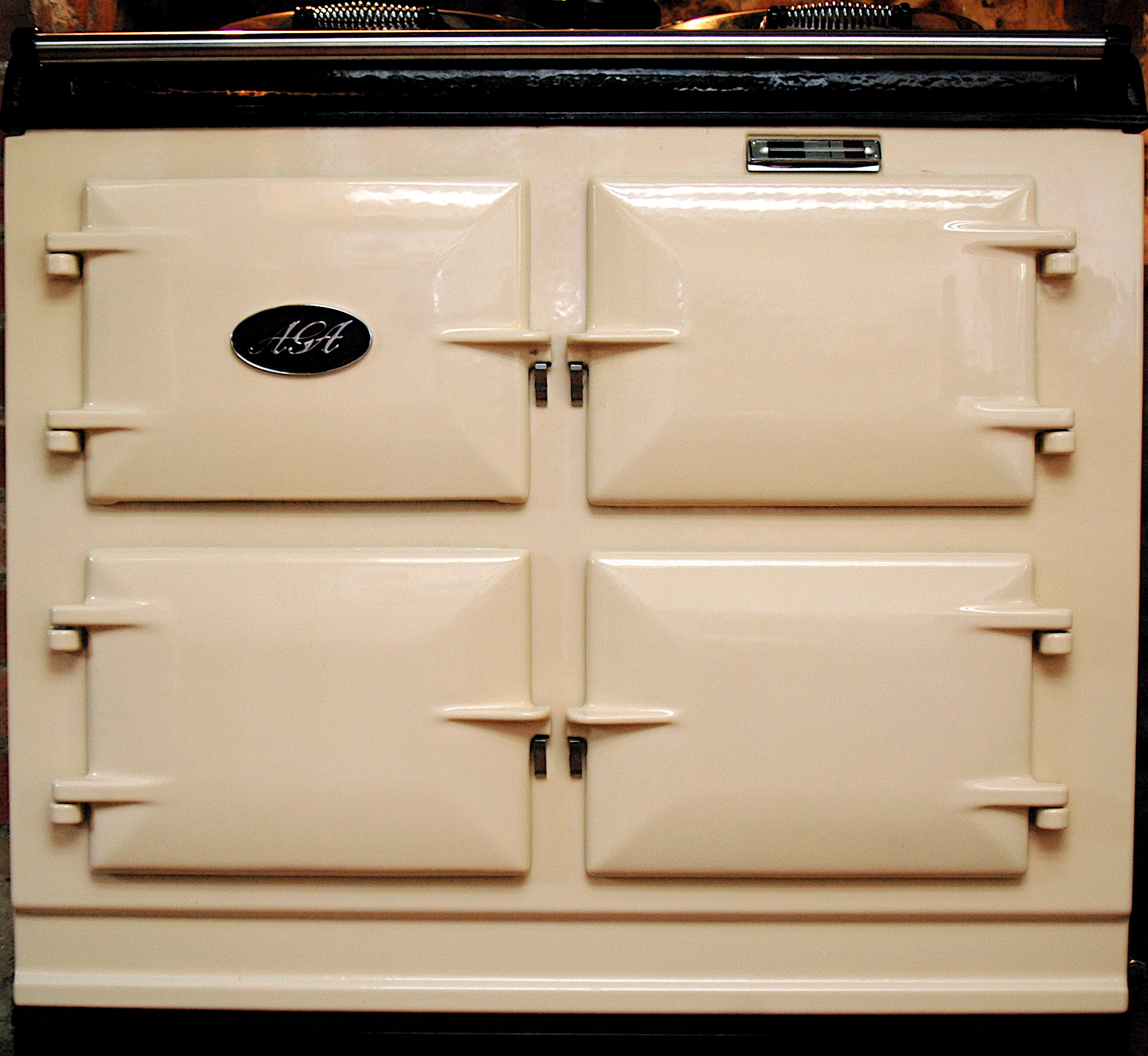 A high-end gas stove called the
A high-end gas stove called the
 A kitchen stove, often called simply a
A kitchen stove, often called simply a stove
A stove or range is a device that generates heat inside or on top of the device, for - local heating or cooking. Stoves can be powered with many fuels, such as natural gas, electricity, gasoline, wood, and coal.
Due to concerns about air pollu ...
or a cooker
Cooker may refer to several types of cooking appliances and devices used for cooking foods.
Types
* AGA cooker – a heat storage stove and cooker, which works on the principle that a heavy frame made from cast iron components can absorb heat ...
, is a kitchen appliance
A home appliance, also referred to as a domestic appliance, an electric appliance or a household appliance, is a machine which assists in household functions such as cooking, cleaning and food preservation.
The domestic application attached to ...
designed for the purpose of cooking
Cooking, also known as cookery or professionally as the culinary arts, is the art, science and craft of using heat to make food more palatable, digestible, nutritious, or Food safety, safe. Cooking techniques and ingredients vary widely, from ...
food. Kitchen stoves rely on the application of direct heat for the cooking process and may also contain an oven
upA double oven
A ceramic oven
An oven is a tool that is used to expose materials to a hot environment. Ovens contain a hollow chamber and provide a means of heating the chamber in a controlled way. In use since antiquity, they have been use ...
, used for baking
Baking is a method of preparing food that uses dry heat, typically in an oven, but it can also be done in hot ashes, or on hot Baking stone, stones. Bread is the most commonly baked item, but many other types of food can also be baked. Heat is ...
. "Cookstoves" (also called "cooking stoves" or "wood stoves") are heated by burning wood or charcoal; "gas stoves" are heated by gas; and "electric stoves" by electricity. A stove with a built-in cooktop
A cooktop (American English), stovetop (Canadian and American English) or hob (British English), is a device commonly used for cooking that is commonly found in kitchens and used to apply heat to the base of cookware, pans or pots. Cooktops are o ...
is also called a range.
In the industrialized world, as stove
A stove or range is a device that generates heat inside or on top of the device, for - local heating or cooking. Stoves can be powered with many fuels, such as natural gas, electricity, gasoline, wood, and coal.
Due to concerns about air pollu ...
s replaced open fires and brazier
A brazier () is a container used to burn charcoal or other solid fuel for cooking, heating or rituals. It often takes the form of a metal box or bowl with feet, but in some places it is made of terracotta. Its elevation helps circulate air, feed ...
s as a source of more efficient and reliable heating, models were developed that could also be used for cooking, and these came to be known as ''kitchen
A kitchen is a room (architecture), room or part of a room used for cooking and food preparation in a dwelling or in a commercial establishment. A modern middle-class residential kitchen is typically equipped with a Kitchen stove, stove, a sink ...
stoves''.Montagne, Prosper ''New Larousse Gastronomique'' Hamlin Publishing Group 1977 268,901 Quoting Eugène Viollet-le-Duc
Eugène Emmanuel Viollet-le-Duc (; 27 January 181417 September 1879) was a French architect and author, famous for his restoration of the most prominent medieval landmarks in France. His major restoration projects included Notre-Dame de Paris, ...
on cooking in the Middle Ages: "The division of stoves into several compartments as in our day was seldom seen. The dishes were cooked on the fire itself, and these fierce fires did not allow for dishes which required constant stirring, or to be made in frying pans". When homes began to be heated with central heating
A central heating system provides warmth to a number of spaces within a building from one main source of heat.
A central heating system has a Furnace (central heating), furnace that converts fuel or electricity to heat through processes. The he ...
systems, there was less need for an appliance that served as both heat source and cooker and stand-alone cookers replaced them. ''Cooker'' and ''stove'' are often used interchangeably.
The fuel-burning stove is the most basic design of a kitchen stove. As of 2012, it was found that "Nearly half of the people in the world (mainly in the developing world
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreeme ...
), burn biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how ...
(wood, charcoal, crop residues, and dung) and coal in rudimentary cookstoves or open fires to cook their food." More fuel-efficient and environmentally sound
Environment friendly processes, or environmental-friendly processes (also referred to as eco-friendly, nature-friendly, and green), are sustainability and marketing terms referring to goods and services, laws, guidelines and policies that cl ...
biomass cookstoves are being developed for use there.
Natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
and electric
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
stoves are the most common today in western countries. Electricity may reduce environmental impact if generated from non-fossil sources. The choice between the two is mostly a matter of personal preference and availability of utilities
A public utility company (usually just utility) is an organization that maintains the infrastructure for a public service (often also providing a service using that infrastructure). Public utilities are subject to forms of public control and r ...
. Bottled gas
Bottled gas is a term used for substances which are gaseous at standard temperature and pressure (STP) and have been compressed and stored in carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, or composite containers known as gas cylinders.
Gas state ...
ranges are used where utilities are unavailable.
Modern kitchen stoves often have a "stovetop" or "cooktop
A cooktop (American English), stovetop (Canadian and American English) or hob (British English), is a device commonly used for cooking that is commonly found in kitchens and used to apply heat to the base of cookware, pans or pots. Cooktops are o ...
" in American English; known as the " hob" in British English as well as an oven. A "drop-in range" is a combination stovetop-and-oven unit that installs in a kitchen's lower cabinets flush with the countertop. Most modern stoves come in a unit with built-in extractor hood
A kitchen hood, exhaust hood, hood fan, extractor hood, or range hood is a device containing a mechanical fan that hangs above the stove or cooktop in the kitchen. It removes airborne grease, combustion products, fumes, smoke, heat, and steam fr ...
s. Today's major brands offer both gas and electric stoves, and many also offer dual-fuel ranges combining a gas stovetop and an electric oven.
History
Early kitchen stoves

clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
stoves that enclosed the fire completely were known from the Chinese Qin dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ) was the first Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China. It is named for its progenitor state of Qin, a fief of the confederal Zhou dynasty (256 BC). Beginning in 230 BC, the Qin under King Ying Zheng enga ...
(221 BC – 206/207 BC), and a similar design known as ''kamado
A is a traditional Japanese wood- or charcoal-fueled cook stove.
Etymology and history
The precursor of the Kamado was introduced to Japan by Yayoi immigrants from the Korean peninsula during the Kofun period.Farrispp. 83–87./ref> The ...
'' (かまど) appeared in the Kofun period
The is an era in the history of Japan from about 300 to 538 AD (the date of the introduction of Buddhism), following the Yayoi period. The Kofun and the subsequent Asuka periods are sometimes collectively called the Yamato period. This period is ...
(3rd–6th century) in Japan. These stoves were fired by wood or charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, ca ...
through a hole in the front. In both designs, pots were placed over or hung into holes at the top of the knee-high construction. In the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
, references to similar stoves and cooking ranges where the fire was lit from below are recorded as early as the 2nd-century AD, constructed of clay and either made portable or attached to the ground. Raised ''kamados'' were developed in Japan during the Edo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
(1603–1867).
Prior to the 18th century in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, people cooked over open fires fueled by wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin t ...
. In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, waist-high brick-and-mortar hearths and the first chimney
A chimney is an architectural ventilation structure made of masonry, clay or metal that isolates hot toxic exhaust gases or smoke produced by a boiler, stove, furnace, incinerator, or fireplace from human living areas. Chimneys are typical ...
s appeared, so that cooks no longer had to kneel or sit to tend to foods on the fire. The fire was built on top of the construction; the cooking done mainly in cauldron
A cauldron (or caldron) is a large cookware and bakeware, pot (kettle) for cooking or boiling over an open fire, with a lid and frequently with an arc-shaped hanger and/or integral handles or feet. There is a rich history of cauldron lore in r ...
s hung above the fire or placed on trivet
A trivet is an object placed between a serving dish, bowl, pot, or pan and a dining table, usually to protect the table from heat damage. The word ''trivet'' refers to three feet, but the term is sometimes used in British English to refer to t ...
s. The heat was regulated by placing the cauldron higher or lower above the fire.
Open fire systems had three significant disadvantages that prompted an evolutionary series of improvements from the 16th century onwards: it was dangerous, it produced much smoke, and the heat efficiency was poor. Attempts were made to enclose the fire to make better use of the heat that is generated and thus reduce the wood consumption. An early step was the ''fire chamber'': the fire was enclosed on three sides by brick-and-mortar walls and covered by an iron plate. This technique also caused a change in the kitchenware used for cooking, for it required flat-bottomed pots instead of cauldrons. The first design that completely enclosed the fire was the 1735 ''Castrol stove'', built by the Walloon- Bavarian architect
An architect is a person who plans, designs, and oversees the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to provide services in connection with the design of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the buildings that h ...
François de Cuvilliés
François de Cuvilliés, sometimes referred to as ''the Elder'' (23 October 1695, Soignies, Hainaut14 April 1768, Munich), was a Bavarian decorative designer and architect born in the Spanish Netherlands. He was instrumental in bringing the Roco ...
. This stove was a masonry construction with several fire holes covered by perforated iron plates and was also known as a ''stew stove''. Near the end of the 18th century, the design was refined by hanging the pots in holes through the top iron plate, thus improving heat efficiency even more.
Origins of the modern kitchen range
The modern kitchen range was invented by SirBenjamin Thompson
Colonel (United Kingdom), Colonel Sir Benjamin Thompson, Count Rumford, Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS (26 March 175321 August 1814), was an American-born British military officer, scientist and inventor. Born in Woburn, Massachusetts, he sup ...
, Count Rumford in the 1790s. As an active scientist and prolific inventor, he put the study of heat onto a scientific basis and developed improvements for chimneys, fireplaces and industrial furnaces, which led to his invention of the kitchen range.
His Rumford fireplace
A Rumford fireplace, sometimes known as a Rumford stove, is a tall, shallow fireplace designed by Sir Benjamin Thompson, Count Rumford, an Anglo-American physicist best known for his investigations of heat. Its shallow, angled sides are designed ...
created a sensation in London when he introduced the idea of restricting the chimney
A chimney is an architectural ventilation structure made of masonry, clay or metal that isolates hot toxic exhaust gases or smoke produced by a boiler, stove, furnace, incinerator, or fireplace from human living areas. Chimneys are typical ...
opening to increase the updraught. This was a much more efficient way to heat a room than earlier fireplaces. He and his workers modified fireplaces by inserting bricks into the hearth to make the side walls angled, and added a choke to the chimney to increase the speed of air going up the flue. The effect was to produce a streamlined air flow, so all the smoke would go up into the chimney rather than lingering and entering the room. It also had the effect of increasing the efficiency of the fire, and gave extra control of the rate of combustion of the fuel, whether wood or coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
. Many fashionable London houses were modified to his instructions, and became free of smoke.
Following on from this success, Thompson designed a kitchen range made of brick, with a cylindrical oven and holes in the top for the insertion of pots. When not needed, the opening could be covered over leaving the fire to smolder gently. This kitchen range was much more fuel efficient than the prevailing open hearth method and to a great degree safer. His range was widely adopted in large cooking establishments, including at the soup kitchen
A soup kitchen, food kitchen, or meal center is a place where food is offered to Hunger, hungry and homeless people, usually for no price, cost, or sometimes at a below-market price (such as coin Donation, donations). Frequently located in Low i ...
s that Thompson built in Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
. However, it was too big and unwieldy to make much of an impact on domestic cooking.
The first half of the nineteenth century witnessed a steady improvement in stove design. Cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
stoves replaced those made of masonry and their size shrank to allow them to be incorporated into the domestic kitchen. By the 1850s, the modern kitchen, equipped with a cooking range, was a fixture of middle-class homes. In 1850 Mary Evard invented the Reliance Cook Stove, which was divided in two with one half for dry baking and the other half for moist. Patents issued to Mary Evard are and on April 7, 1868. She demonstrated this stove with her husband at the St. Louis World's Fair
The Louisiana Purchase Exposition, informally known as the St. Louis World's Fair, was an international exposition held in St. Louis, Missouri, United States, from April 30 to December 1, 1904. Local, state, and federal funds totaling $15 mill ...
.
In 1867 Elizabeth Hawks of New York invented and received for a baking attachment for stoves, intended to spread heat thoroughly throughout loaves while keeping the top crust tender, which she called an "Auxiliary Air-chamber for Stoves." This was so successful that she sold two thousand within months of its release.
Stoves of that era commonly burned charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, ca ...
as well as wood. These stoves had flat tops and the heat was concentrated on one side of the stove top so that cooks could cook things at different temperatures based on where the pot or pan was located. This was called the "piano" system. After coal was replaced with gas, French chefs continued to prefer the smooth cooking surface and so the majority of French gas stoves had flat metal surfaces over the gas burners, which continues to be known as the "French style" today.
Benjamin Thompson
Colonel (United Kingdom), Colonel Sir Benjamin Thompson, Count Rumford, Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS (26 March 175321 August 1814), was an American-born British military officer, scientist and inventor. Born in Woburn, Massachusetts, he sup ...
Noć muzeja 2015, Čakovec - stari štednjak iz 19.st.jpg, A 19th-century stove made in Budapest
Budapest is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns of Hungary, most populous city of Hungary. It is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, tenth-largest city in the European Union by popul ...
exhibited in the Međimurje County Museum
The Međimurje County Museum in Čakovec, the seat of Međimurje County, Croatia, is located in the Zrinski Castle inner palace, the biggest medieval fortification in the county, close to the centre of the town and its main square.
History
The ...
, Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
Fred Verity catalogue page 212 (4).JPG, British-style Kitchen range
A kitchen stove, often called simply a stove or a cooker, is a kitchen appliance designed for the purpose of cooking food. Kitchen stoves rely on the application of direct heat for the cooking process and may also contain an oven, used for bak ...
by Fred Verity & Sons, 1890s
Gas stove
 A major improvement in fuel technology came with the advent of
A major improvement in fuel technology came with the advent of gas
Gas is a state of matter that has neither a fixed volume nor a fixed shape and is a compressible fluid. A ''pure gas'' is made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon) or molecules of either a single type of atom ( elements such as ...
. The first gas stoves were developed as early as the 1820s, but these remained isolated experiments. James Sharp patented a gas stove in Northampton, England
Northampton ( ) is a town and civil parish in Northamptonshire, England. It is the county town of Northamptonshire and the administrative centre of the Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority of West Northamptonshire. The town is sit ...
, in 1826 and opened a gas stove factory in 1836. His invention was marketed by the firm Smith & Philips from 1828. An important figure in the early acceptance of this new technology, was Alexis Soyer
Alexis Benoît Soyer (4 February 1810 – 5 August 1858) was a French chef, writer and inventor, who made his reputation in Victorian England.
Born in north-east France, Soyer trained as a chef in Paris, and quickly built a career that was bro ...
, the renowned chef at the Reform Club
The Reform Club is a private members' club, owned and controlled by its members, on the south side of Pall Mall, London, Pall Mall in central London, England. As with all of London's original gentlemen's clubs, it had an all-male membership for ...
in London. From 1841, he converted his kitchen to consume piped gas, arguing that gas was cheaper overall because the supply could be turned off when the stove was not in use.
A gas stove was shown at The Great Exhibition
The Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations, also known as the Great Exhibition or the Crystal Palace Exhibition (in reference to the temporary structure in which it was held), was an international exhibition that took ...
in London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
in 1851, but it was only in the 1880s that the technology became a commercial success in England. By that stage a large and reliable network for gas pipeline transport
A pipeline is a system of Pipe (fluid conveyance), pipes for long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas, typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than of pipeline in 120 countries ...
had spread over much of the country, making gas relatively cheap and efficient for domestic use. Gas stoves only became widespread on the European Continent
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the eas ...
and in the United States in the early 20th century.
Electric stove
 Once electric power was widely and economically available, electric stoves became a popular alternative to fuel-burning appliances. One of the earliest such devices was patented by Canadian inventor Thomas Ahearn in 1892. Ahearn and Warren Y. Soper were owners of Ottawa's Chaudiere Electric Light and Power Company. The electric stove was showcased at the Chicago World's Fair in 1893, where an electrified model kitchen was shown.
Unlike the gas stove, the electrical stove was slow to catch on, partly due to the unfamiliar technology, and the need for cities and towns to be electrified. Early electric stoves were unsatisfactory due to the cost of electricity (compared with wood, coal, or city gas), limited power available from the electrical supply company, poor temperature regulation, and short life of heating elements. The invention of
Once electric power was widely and economically available, electric stoves became a popular alternative to fuel-burning appliances. One of the earliest such devices was patented by Canadian inventor Thomas Ahearn in 1892. Ahearn and Warren Y. Soper were owners of Ottawa's Chaudiere Electric Light and Power Company. The electric stove was showcased at the Chicago World's Fair in 1893, where an electrified model kitchen was shown.
Unlike the gas stove, the electrical stove was slow to catch on, partly due to the unfamiliar technology, and the need for cities and towns to be electrified. Early electric stoves were unsatisfactory due to the cost of electricity (compared with wood, coal, or city gas), limited power available from the electrical supply company, poor temperature regulation, and short life of heating elements. The invention of nichrome
Nichrome (also known as NiCr, nickel-chromium or chromium-nickel) is a family of alloys of nickel and chromium (and occasionally iron) commonly used as resistance wire, heating elements in devices like toasters, electrical kettles and space he ...
alloy for resistance wires improved the cost and durability of heating elements.Ed Sobey
Ed, ed or ED may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Ed'' (film), a 1996 film starring Matt LeBlanc
* Ed (''Fullmetal Alchemist'') or Edward Elric, a character in ''Fullmetal Alchemist'' media
* ''Ed'' (TV series), a TV series that ran fro ...
, ''The Way Kitchens Work'', Chicago Review Press, 2010 , page viii
The first practical design was patented by the Australian David Curle Smith in 1905. His device adopted (following the design of gas stoves) what later became the configuration for most electric stoves: an oven surmounted by a hotplate with a grill tray between them. Curle Smith's stove did not have a thermostat; heat was controlled by the number of the appliance's nine elements that were switched on.Introduction by H. A. Willis, ''Thermo-Electrical Cooking Made Easy'', Hesperian Press, 2011, p. 24
The first electric stoves used heating element
A heating element is a device used for conversion of electric energy into heat, consisting of a heating resistor and accessories. Heat is generated by the passage of electric current through a resistor through a process known as Joule heating. He ...
s made of high-resistance metal to produce heat. The stovetop (range) surface had one or more circular heating elements, insulated with compressed magnesia and sheathed in a spiral metal tube. Heating elements for the oven are of similar construction but an elongated loop to distribute heat. Elements were made as plug-in consumer-replaceable parts and could also be easily removed for cleaning. Temperature of cooking elements was regulated by adjusting a bimetal thermostat control switch, which switched power on and off to control the average heating effect of the elements.
Other technologies
 A high-end gas stove called the
A high-end gas stove called the AGA cooker
The Aga Range Cooker is a Swedish range Kitchen stove, cooker. Invented and initially produced in Sweden, since 1957 most production has been located in the UK. In 2015, the British AGA Cooker manufacturing company, AGA Rangemaster Group, was a ...
was invented in 1922 by Swedish Nobel prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; ; ) are awards administered by the Nobel Foundation and granted in accordance with the principle of "for the greatest benefit to humankind". The prizes were first awarded in 1901, marking the fifth anniversary of Alfred N ...
winner Gustaf Dalén
Nils Gustaf Dalén (; 30 November 1869 – 9 December 1937) was a Swedish engineer and inventor who received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1912 "for his invention of Sun valve, automatic regulators for use in conjunction with gas accumulators fo ...
. As a heat storage stove
A stove or range is a device that generates heat inside or on top of the device, for - local heating or cooking. Stoves can be powered with many fuels, such as natural gas, electricity, gasoline, wood, and coal.
Due to concerns about air pollu ...
, it worked on the principle that a heavy frame made from cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
components can absorb heat from a relatively low-intensity but continuously burning source, and the accumulated heat can then be used when needed for cooking.
Dalén took his design to Britain in 1929, where it was first manufactured under licence in the early 1930s. The cast iron components were first cast at the Coalbrookdale
Coalbrookdale is a town in the Ironbridge Gorge and the Telford and Wrekin borough of Shropshire, England, containing a settlement of great significance in the history of iron ore smelting. It lies within the civil parish called The Gorge, Shro ...
foundry in the 1940s, where they are still made today by the Aga Rangemaster Group
AGA Rangemaster Limited is a British manufacturer of range cookers, kitchen appliances, and interior furnishings owned by Middleby Corporation in September 2015 after it received a takeover approach from Whirlpool. It employs just over 2,500 p ...
. Its popularity in certain parts of English society (owners of medium to large country houses
300px, Oxfordshire.html" ;"title="Blenheim Palace - Oxfordshire">Blenheim Palace - Oxfordshire
An English country house is a large house or mansion in the English countryside. Such houses were often owned by individuals who also owned a To ...
) led to the coining of the term " Aga saga" in the 1990s, referring to a genre of fiction set amongst stereotypical upper-middle-class society.
Microwave oven
A microwave oven, or simply microwave, is an electric oven that heats and cooks food by exposing it to electromagnetic radiation in the microwave frequency range. This induces Dipole#Molecular dipoles, polar molecules in the food to rotate and ...
s were developed in the 1940s, and use microwave radiation
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz an ...
to directly heat the water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
held inside food.
Cooktop
A cooktop or hob is a cooking appliance that heats the bottoms of pans or pots; it does not have an enclosed oven as used for baking or roasting. Cooktops may be heated by gas or electricity and may also have exhaust systems.Flattop grill
A flattop grill is a cooking appliance that resembles a griddle but performs differently because the heating element is circular rather than straight (side to side). This heating technology creates an extremely hot and even cooking surface, as ...
s are also being installed into kitchen counters and islands, which do double-duty as a direct cooking surface as well as a platform for heating pots and pans. A hot plate
A hot plate or hotplate is a heated flat surface on a stove or electric cooker on which food may be cooked, either built into an electric cooker or kitchen stove, or portable, plugged into an electric outlet.
Hot plates can also be used as a h ...
is a similar device, which is mobile and can be used as an appropriate technology
Appropriate technology is a movement (and its manifestations) encompassing technology, technological choice and application that is small-scale, affordable by its users, labor-intensive, efficient energy use, energy-efficient, environmentally sust ...
.
See also
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Gas Range Stoves OvensStove
A stove or range is a device that generates heat inside or on top of the device, for - local heating or cooking. Stoves can be powered with many fuels, such as natural gas, electricity, gasoline, wood, and coal.
Due to concerns about air pollu ...