DrGeo on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
GNU Dr. Geo is an interactive geometry software that allows its users to design & manipulate interactive geometric sketches, including dynamic models of
 A script is a
A script is a  From the script, the arguments model are reached with the messages #arg1, #arg2, etc. The arguments view are reached with the messages #costume1, #costume2, etc.
The computation of the script is done in its #compute method. For example, to calculate the square of a number, la méthode
From the script, the arguments model are reached with the messages #arg1, #arg2, etc. The arguments view are reached with the messages #costume1, #costume2, etc.
The computation of the script is done in its #compute method. For example, to calculate the square of a number, la méthode
compute
"returns the square of a number"
^ self arg1 valueItem squared
creates a numeric object, whose value is the square of its first and unique argument of type number object. Whenever the first number is changed, the script returned value changes too.
 Dr. Geo Smalltalk sketches are sketches entirely defined in the Smalltalk language. This is not about constructing a sketch with the Dr. Geo graphical interface, but about describing a sketch with the Smalltalk language. A programming interface with an easy and light syntax is provided.
Dr. Geo Smalltalk sketches are sketches entirely defined in the Smalltalk language. This is not about constructing a sketch with the Dr. Geo graphical interface, but about describing a sketch with the Smalltalk language. A programming interface with an easy and light syntax is provided.
, triangle c ,
c := DrGeoSketch new.
triangle := [:s1 :s2 :s3 :n ,
c segment: s1 to: s2; segment: s2 to: s3; segment: s3 to: s1.
n > 0 ifTrue: [
triangle
value: s1
value: (c middleOf: s1 and: s2) hide
value: (c middleOf: s1 and: s3) hide
value: n-1.
triangle
value: (c middleOf: s1 and: s2) hide
value: s2
value: (c middleOf: s2 and: s3) hide
value: n-1.
triangle
value: (c middleOf: s1 and: s3) hide
value: (c middleOf: s2 and: s3) hide
value: s3
value: n-1.
triangle value: 0@3 value: 4@ -3 value: -4@ -3 value: 3.
(c point: 0@3) show
, canvas shape alfa fibo a b m s,
canvas := DrGeoSketch new.
alfa := (canvas freeValue: -90 degreesToRadians) hide.
shape := [:c :o :f, , e p ,
e := (canvas rotate: o center: c angle: alfa) hide.
(canvas arcCenter: c from: o to: e) large.
p := canvas translate: e vector: (canvas vector: c to: o) hide.
(canvas polygon: ) name: f.
e].
fibo := [ ].
fibo := [ :f :o :c :k , , e f1 f2 f3 c2,
"f1: term Fn-1, f2: term Fn, o & c: origin and center of spiral arm
e: extremity of the spiral arm"
f1 := f first.
f2 := f second.
f3 := f1 + f2.
e := shape value: c value: o value: f3.
c2 := (canvas scale: c center: e factor: f3 / f2) hide.
k > 0 ifTrue: fibo value: value: e value: c2 value: k - 1 .
a := canvas point: 1@0.
b := canvas point: -1 @0.
m := (canvas middleOf: a and: b) hide.
s := shape value: m value: a value: 1.
shape value: m value: s value: 1.
fibo value: value: b value: a value: 10

, sketch f df xn ptA ptB,
sketch := DrGeoSketch new axesOn.
xn := 2.
f := x cos + x
"Derivate number"
df := (f value: x + 1e-8) - (f value: x) * 1e8
sketch plot: f from: -20 to: 20.
ptA := (sketch point: xn@0) large; name: 'Drag me'.
5 timesRepeat: pt point x @ (f value: pt point x)
parent: ptA.
ptB hide.
(sketch segment: ptA to: ptB) dotted forwardArrow .
ptA := sketch point:
"> x ,
x := pt point x.
x - ( (f value: x) / (df value: x) ) @ 0 parent: ptB.
ptA hide.
(sketch segment: ptB to: ptA) dotted forwardArrow
ESUG Innovation Technology Awards
(Amsterdam, 2008)
(Paris, 2000)
Physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
. It is free software (source code, translations, icons and installer are released under GNU GPL
The GNU General Public Licenses (GNU GPL or simply GPL) are a series of widely used free software licenses, or ''copyleft'' licenses, that guarantee end users the freedom to run, study, share, or modify the software. The GPL was the first ...
license), created by Hilaire Fernandes, it is part of the GNU
GNU ( ) is an extensive collection of free software (394 packages ), which can be used as an operating system or can be used in parts with other operating systems. The use of the completed GNU tools led to the family of operating systems popu ...
project.
It runs over a Morphic graphic system (which means that it runs on Linux, Mac OS, Windows, Android). Dr. Geo was initially developed in C++ with Scheme
Scheme or schemer may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''The Scheme'', a BBC Scotland documentary TV series
* The Scheme (band), an English pop band
* ''The Scheme'', an action role-playing video game for the PC-8801, made by Quest Corporation
* ...
scripting, then in various versions of Smalltalk
Smalltalk is a purely object oriented programming language (OOP) that was originally created in the 1970s for educational use, specifically for constructionist learning, but later found use in business. It was created at Xerox PARC by Learni ...
with Squeak
Squeak is an object-oriented, class-based, and reflective programming language. It was derived from Smalltalk-80 by a group that included some of Smalltalk-80's original developers, initially at Apple Computer, then at Walt Disney Imaginee ...
, Etoys_(programming_language)
Etoys is a child-friendly computer environment and object-oriented prototype-based programming language for use in education.
Etoys is a media-rich authoring environment with a scripted object model for many different objects that runs on di ...
for One Laptop per Child Pharo
Pharo is a Cross-platform software, cross-platform implementation of the classic Smalltalk-80 programming language and runtime system. It is based on the OpenSmalltalk virtual machine (VM) named Cog, which evaluates a dynamic, Reflective progr ...
then Cuis-Smalltalk.
Objects
Dr. Geo manipulates different kinds of objects such as points, lines, circles, vector, values, geometric transformations, scripts.Points
Dr. Geo has several kinds of points: a free point, which can be moved with the mouse (but may be attached to a curve) and a point given by its coordinates. Points can also be created as theintersection
In mathematics, the intersection of two or more objects is another object consisting of everything that is contained in all of the objects simultaneously. For example, in Euclidean geometry, when two lines in a plane are not parallel, their ...
of 2 curves or as the midpoint
In geometry, the midpoint is the middle point of a line segment. It is equidistant from both endpoints, and it is the centroid both of the segment and of the endpoints. It bisects the segment.
Formula
The midpoint of a segment in ''n''-dim ...
of a segment.
Lines
Dr. Geo is equipped with the classic line, ray, segment andvector
Vector most often refers to:
* Euclidean vector, a quantity with a magnitude and a direction
* Disease vector, an agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen into another living organism
Vector may also refer to:
Mathematics a ...
.
Other curvilinear objects include circles (defined by 2 points, a center and segment or a radius), arcs (defined by three points or center and angle), polygons (regular or not, defined by end points), and loci.
Transformations
Besides the parallel and perpendicular line through a point. Dr. Geo can apply to a point or a line one of these transformations: # reflexion # symmetry # translation # rotation #homothety
In mathematics, a homothety (or homothecy, or homogeneous dilation) is a transformation of an affine space determined by a point called its ''center'' and a nonzero number called its ''ratio'', which sends point to a point by the rule,
: \o ...
Macro-construction
Dr. Geo comes with macro-construction: a way to teach Dr. Geo new constructions. It allows to add new objects to Dr. Geo: new transformations likecircle inversion
In geometry, inversive geometry is the study of ''inversion'', a transformation of the Euclidean plane that maps circles or lines to other circles or lines and that preserves the angles between crossing curves. Many difficult problems in geometry ...
, tedious constructions involving a lot of intermediate objects or constructions involving script (also named macro-script).
When some objects, called ''final'' depend on other objects, called ''initial'', it is possible to create a complex construction deducing the final objects from the user-given initial objects. This is a macro-construction, a graph of interdependent objects.
Programming
Access to user programming is at the essence of Dr. Geo: from the software, the user can directly read, study, modify and redistribute modified version of Dr. Geo. Additionally, scripting embedded in sketch is proposed. Dr. Geo source code isSmalltalk
Smalltalk is a purely object oriented programming language (OOP) that was originally created in the 1970s for educational use, specifically for constructionist learning, but later found use in business. It was created at Xerox PARC by Learni ...
. It is also the language used for user programming: to extend Dr. Geo with arbitrary computing operations (Smalltalk script) and to define a geometric sketch entirely with programming instructions (Smalltalk sketch).
Dr. Geo is shipped with its source code and the developer tools. Therefore its code can be edited and recompiled from Dr. Geo while it is functioning. This design, inherited from Smalltalk, makes easy to test new ideas and new designs.
Smalltalk script
 A script is a
A script is a first class object
In a given programming language design, a first-class citizen is an entity which supports all the operations generally available to other entities. These operations typically include being passed as an argument, returned from a function, and assi ...
defined along Dr. Geo code. It comes with zero, one or several arguments, from types selected when defining the script. When an instance of a script is plugged in a canvas, the user first selects its arguments in the canvas with mouse clicks, then the position in the canvas of the script output. The script is updated at each canvas computation. Scripts can be used in cascade, with one as the argument of another one.
Script are designed to be used in two different ways:
# To output an object (i.e. a numeric value) and to show its result in the canvas. This result can be used when building subsequent objects (geometric or script).
# To access objects in the canvas: model (MathItem) or their view (Costume) for arbitrary uses and modifications. For example to modify the color of an object given the result to a computation.
 From the script, the arguments model are reached with the messages #arg1, #arg2, etc. The arguments view are reached with the messages #costume1, #costume2, etc.
The computation of the script is done in its #compute method. For example, to calculate the square of a number, la méthode
From the script, the arguments model are reached with the messages #arg1, #arg2, etc. The arguments view are reached with the messages #costume1, #costume2, etc.
The computation of the script is done in its #compute method. For example, to calculate the square of a number, la méthode
Smalltalk sketch
 Dr. Geo Smalltalk sketches are sketches entirely defined in the Smalltalk language. This is not about constructing a sketch with the Dr. Geo graphical interface, but about describing a sketch with the Smalltalk language. A programming interface with an easy and light syntax is provided.
Dr. Geo Smalltalk sketches are sketches entirely defined in the Smalltalk language. This is not about constructing a sketch with the Dr. Geo graphical interface, but about describing a sketch with the Smalltalk language. A programming interface with an easy and light syntax is provided.
Smalltalk
Smalltalk is a purely object oriented programming language (OOP) that was originally created in the 1970s for educational use, specifically for constructionist learning, but later found use in business. It was created at Xerox PARC by Learni ...
itself is a high level language, carefully crafted iteratively for about 10 years at Palo Alto Research Center. When a sketch is described with Smalltalk code, all the features of the language are used: object oriented programming
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of '' objects''. Objects can contain data (called fields, attributes or properties) and have actions they can perform (called procedures or methods and impleme ...
, variable, collection
Collection or Collections may refer to:
Computing
* Collection (abstract data type), the abstract concept of collections in computer science
* Collection (linking), the act of linkage editing in computing
* Garbage collection (computing), autom ...
, iterator
In computer programming, an iterator is an object that progressively provides access to each item of a collection, in order.
A collection may provide multiple iterators via its interface that provide items in different orders, such as forwards ...
, randomness
In common usage, randomness is the apparent or actual lack of definite pattern or predictability in information. A random sequence of events, symbols or steps often has no order and does not follow an intelligible pattern or combination. ...
to get a slightly different sketch at each execution.
A Smalltalk sketch is edited and tested with the ''Smalltalk sketch editor''. Such sketch can be debugged and executed step-by-step. Its code is saved, as any source code, to an external text file encoded with UTF-8
UTF-8 is a character encoding standard used for electronic communication. Defined by the Unicode Standard, the name is derived from ''Unicode Transformation Format 8-bit''. Almost every webpage is transmitted as UTF-8.
UTF-8 supports all 1,112,0 ...
, to support native language.
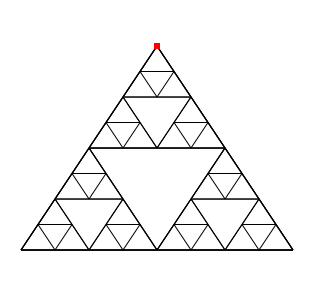
Sierpinski triangle
Here is how to program a Sierpinski triangle recursively. Its red external summit is mobile.
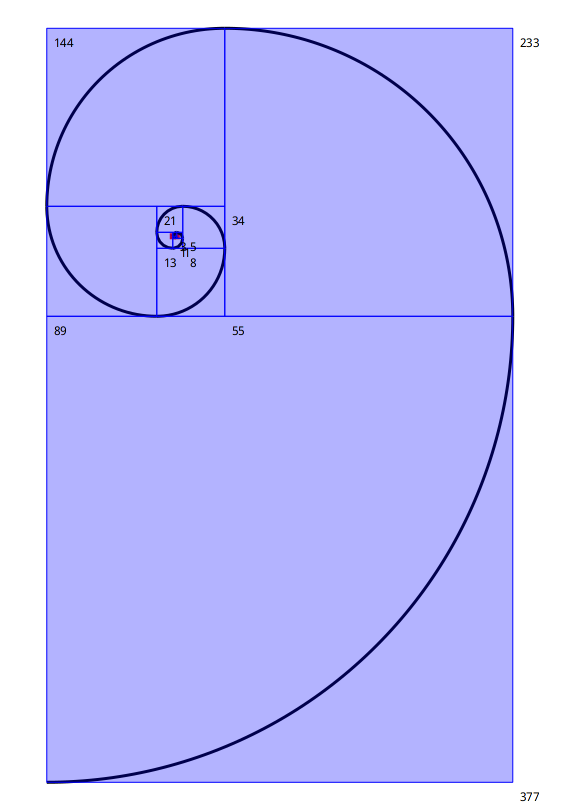
Fibonacci spiral
A Fibonacci_sequence, Fibonacci spiral programmed with geometric transformations (rotation, translation and homothety). The points ''a'' and ''b'' of the resulting interactive sketch are mobile.
Newton-Raphson algorithm
Smalltalk sktech can be used to design interactive sketch illustrating a numerical analysis method. Here the Newton-Raphson algorithm in a 5 steps iteration.
Locale languages
Smalltalk sketch can be coded in native languages, currently in French and Spanish. More native languages can be added.Awards
ESUG Innovation Technology Awards
(Amsterdam, 2008)
(Paris, 2000)
See also
*Compass-and-straightedge construction
In geometry, straightedge-and-compass construction – also known as ruler-and-compass construction, Euclidean construction, or classical construction – is the construction of lengths, angles, and other geometric figures using only an ideali ...
* Interactive geometry software
Interactive geometry software (IGS) or dynamic geometry environments (DGEs) are computer programs which allow one to create and then manipulate geometric constructions, primarily in plane geometry. In most IGS, one starts construction by putting a ...
References
{{Reflist Educational software for Linux Free educational software Free interactive geometry software GNU Project software Software using the GNU General Public License