Domus Augustana on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Domus Augustana is the modern name given to the central residential part of the vast Roman
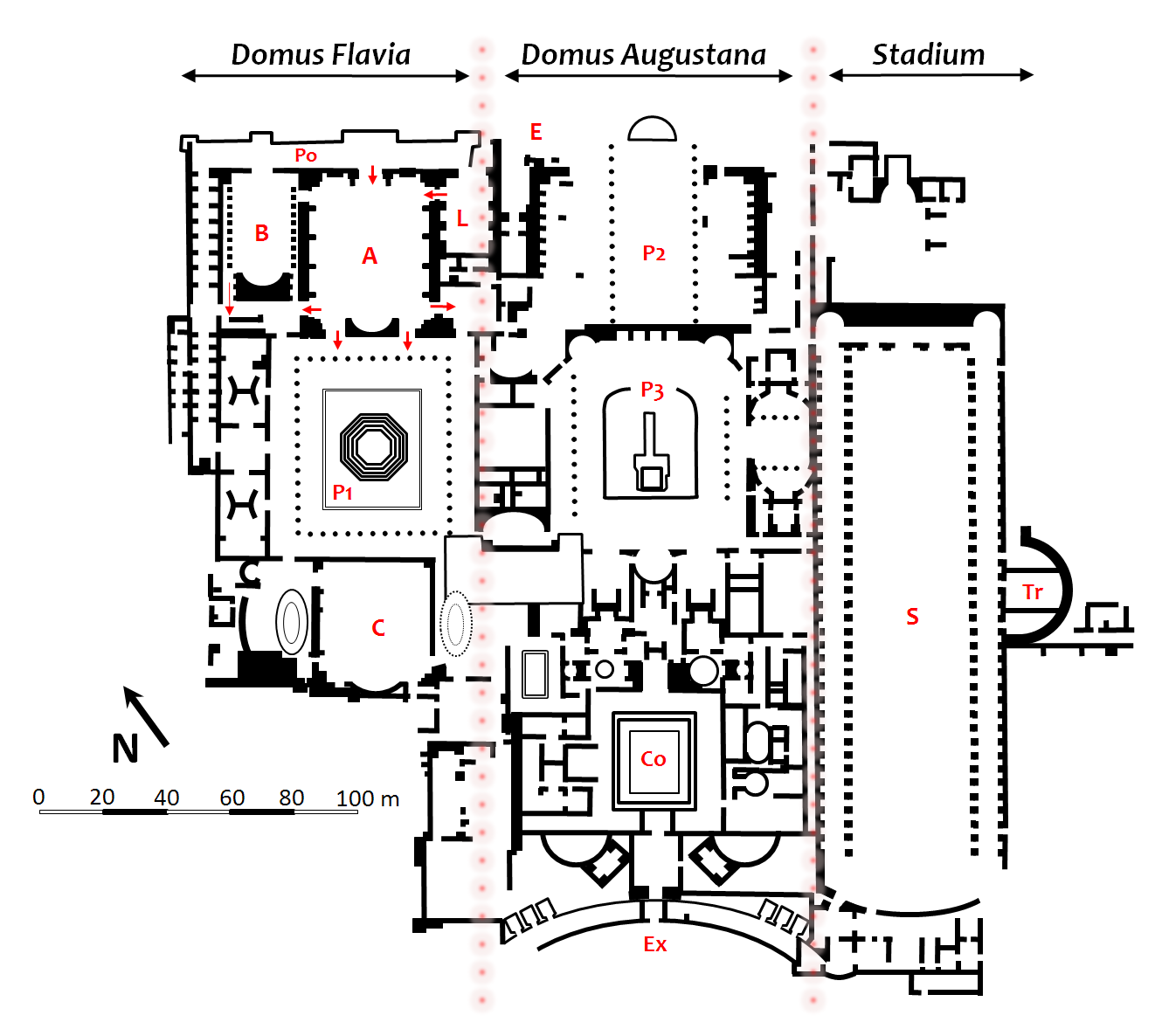 The central section of the palace (labelled "Domus Augustana" in the diagram) consists of at least four main parts: the "2nd Peristyle" to the northeast, the central "3rd Peristyle", the courtyard complex and the
The central section of the palace (labelled "Domus Augustana" in the diagram) consists of at least four main parts: the "2nd Peristyle" to the northeast, the central "3rd Peristyle", the courtyard complex and the
File:Palatino - panoramio (22).jpg, Buildings along NE side of "courtyard" garden
File:Domus augustana - temple de minerve.jpg, "3rd Peristyle" garden looking south
File:Domus Augustana.JPG, "Courtyard" garden of the Domus Augustana looking west
File:Palatine Hill Rome.jpg, 2nd Peristyle garden looking south
Palace of Domitian
The Palace of Domitian was built as Roman emperor Domitian's official residence in 81–87 AD and was used as such by subsequent emperors. Its remains sit atop and dominate Palatine Hill in Rome, alongside other palaces.
The Palace is a massive ...
(92 AD) on the Palatine Hill
The Palatine Hill (; Classical Latin: ''Palatium''; Neo-Latin: ''Collis/Mons Palatinus''; ), which relative to the seven hills of Rome is the centremost, is one of the most ancient parts of the city; it has been called "the first nucleus of the ...
. In antiquity the name may have applied to the whole of the palace.
Its name is not directly related to the emperor Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
(r. 27 BC – AD 14) and should not be confused with the nearby Domus Augusti, but probably refers to the later Roman meaning of ''Augustus'' as "emperor".
Layout
 The central section of the palace (labelled "Domus Augustana" in the diagram) consists of at least four main parts: the "2nd Peristyle" to the northeast, the central "3rd Peristyle", the courtyard complex and the
The central section of the palace (labelled "Domus Augustana" in the diagram) consists of at least four main parts: the "2nd Peristyle" to the northeast, the central "3rd Peristyle", the courtyard complex and the exedra
An exedra (: exedras or exedrae) is a semicircular architecture, architectural recess or platform, sometimes crowned by a semi-dome, and either set into a building's façade or free-standing. The original Greek word ''ἐξέδρα'' ('a seat ou ...
on the southwest. The Domus Augustana is built on two levels, the upper northern one consisting of the two peristyle
In ancient Ancient Greek architecture, Greek and Ancient Roman architecture, Roman architecture, a peristyle (; ) is a continuous porch formed by a row of columns surrounding the perimeter of a building or a courtyard. ''Tetrastoön'' () is a rare ...
s to the north on the same level and closely linked to the Domus Flavia, the public wing of the palace, and therefore probably having public functions. The southern section was built a little later and some details suggest that it was not Rabirius who directed the work.
The 2nd Peristyle garden is partly exposed but little is known of its architecture.
The 3rd Peristyle was filled almost completely with a huge pool as wide as that of the Domus Flavia and included a seascape perhaps of Greek mythology on an island connected to the side via a bridge with several arches, and with sculptures in the water. Other sources suggest a temple was built on the island, namely a temple of Minerva
Minerva (; ; ) is the Roman goddess of wisdom, justice, law, victory, and the sponsor of arts, trade, and strategy. She is also a goddess of warfare, though with a focus on strategic warfare, rather than the violence of gods such as Mars. Be ...
.Archaeological Guide to Rome, Adriano La Regina, 2005, Electa, p 65 The elaborate rooms surrounding the peristyle alternated between open and closed spaces, suited to public use and perhaps several social groups. On its southwest side the walls stand to a considerable height (after partial reconstruction in the 1930s) with several rooms around a semicircular hall.
The courtyard complex was reserved for the private quarters of the emperor and was built around another peristyle garden surrounded by a colonnade on two levels, the upper containing complex sets of rooms and the lower, 10 m below ground level, consisting of a pool with an unusual design of islands consisting of four ''peltas'', typical moon-shaped shields of the Amazons
The Amazons (Ancient Greek: ', singular '; in Latin ', ') were a people in Greek mythology, portrayed in a number of ancient epic poems and legends, such as the Labours of Hercules, Labours of Heracles, the ''Argonautica'' and the ''Iliad''. ...
, all surfaces being originally faced with marble.
On the southwest side of this complex is the great exedra, a long curving arcaded gallery linking two wings, overlooking the Circus Maximus
The Circus Maximus (Latin for "largest circus"; Italian language, Italian: ''Circo Massimo'') is an ancient Roman chariot racing, chariot-racing stadium and mass entertainment venue in Rome, Italy. In the valley between the Aventine Hill, Avent ...
to the southwest allowing the emperor to watch the races. It may have had an ornamental façade, perhaps added by Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier ...
when the seats of the circus were carried up thus far(Gnomon, 1927, p. 593 Verlag C.H.Beck). From this curved terrace a large arched opening, visible in drawings of the sixteenth century (Heemskerck II; Wyngaerde) led into the courtyard complex.
Gallery
See also
*List of ancient monuments in Rome
This is a list of ancient monuments from Roman Republic, Republican and Roman Empire, Imperial periods in the city of Rome, Italy.
Amphitheaters
* Amphitheater of Caligula
* Amphitheatrum Castrense
* Amphitheater of Nero
* Amphitheater of Stati ...
References
Other sources
* * A Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome, Samuel Ball Platner (as completed and revised by Thomas Ashby):Oxford University Press, 1929External links
* * {{Authority control Palatine Hill Ancient palaces in Rome