|
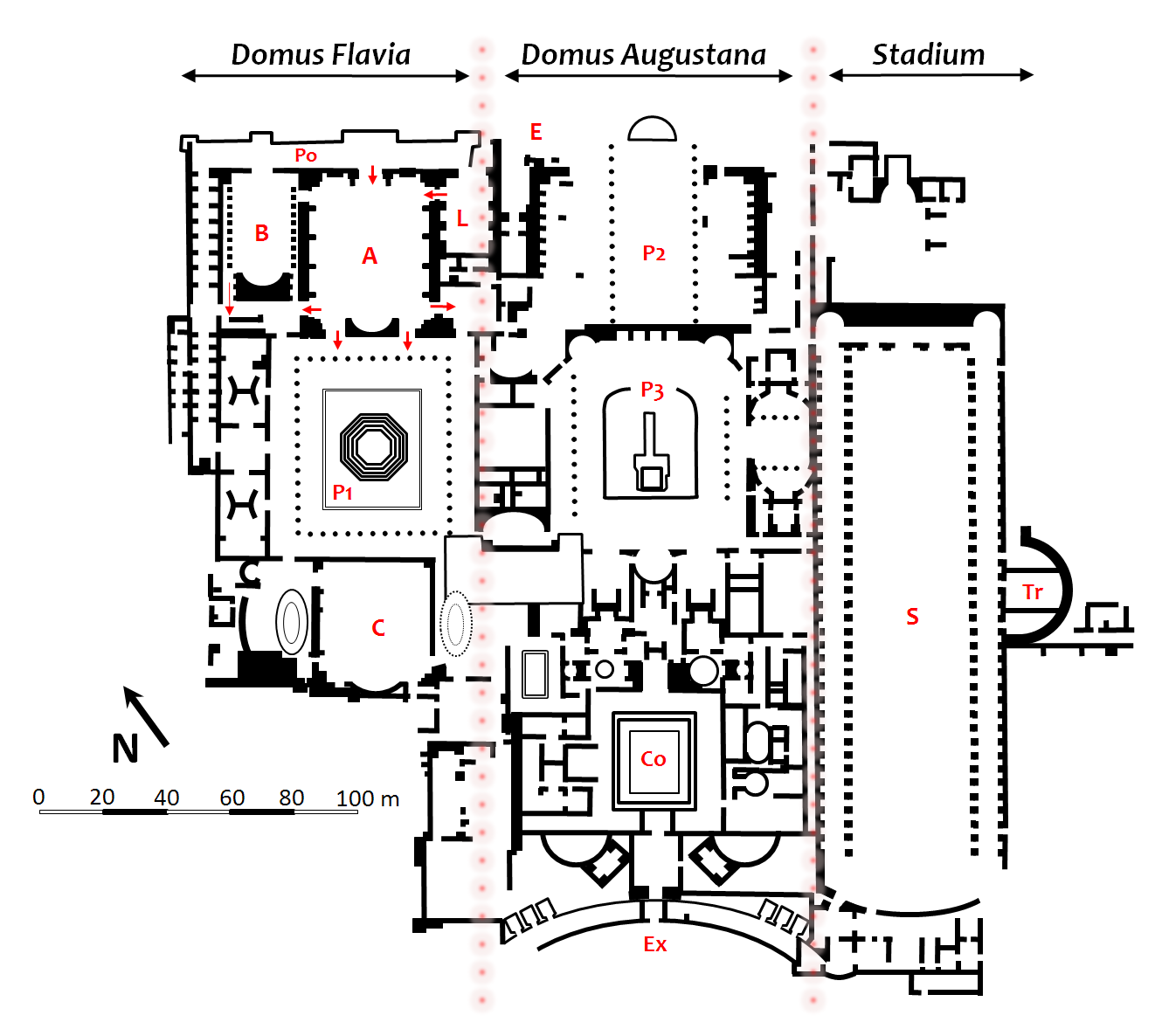
Palace Of Domitian
The Palace of Domitian was built as Roman emperor Domitian's official residence in 81–87 AD and was used as such by subsequent emperors. Its remains sit atop and dominate Palatine Hill in Rome, alongside other palaces. The Palace is a massive structure separated today into three areas. In the past, these partitions allowed business and political matters to have separation from private life while their close proximity allowed them to be conducted in parallel if required. The modern names used for these areas are: * the Domus Flavia * the Domus Augustana * the garden or "stadium". Not all of the palace can be seen as portions lie under more recent buildings, much like a significant portion of the remains of Ancient Rome. The palace was one of Domitian's many architectural projects including renovation of the Circus Maximus, renovation of the Pantheon, and three temples deifying his family members: the temple of Vespasian and Titus, the '' Porticus Diuorum'', and the Temple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domitian
Domitian ( ; ; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was Roman emperor from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Flavian dynasty. Described as "a ruthless but efficient autocrat", his authoritarian style of ruling put him at sharp odds with the Roman Senate, Senate, whose powers he drastically curtailed. Domitian had a minor and largely ceremonial role during the reigns of his father and brother. After the death of his brother, Domitian was declared emperor by the Praetorian Guard. His 15-year reign was the longest since Tiberius. As emperor, Domitian strengthened the economy by revaluing the Roman currency, Roman coinage, expanded the border defenses of the empire, and initiated a massive building program to restore the damaged city of Rome. Significant wars were fought in Britain, where his general Gnaeus Julius Agricola, Agricola made significant gains in his attempt to conquer Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Of The Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire, also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome, was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast territory was divided among several successor polities. The Roman Empire lost the strengths that had allowed it to exercise effective control over its Western provinces; modern historians posit factors including the effectiveness and numbers of the army, the health and numbers of the Roman population, the strength of the economy, the competence of the emperors, the internal struggles for power, the religious changes of the period, and the efficiency of the civil administration. Increasing pressure from invading peoples outside Roman culture also contributed greatly to the collapse. Climatic changes and both endemic and epidemic disease drove many of these immediate factors. The reasons for the collapse are major subjects of the hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honorius (emperor)
Honorius (; 9 September 384 – 15 August 423) was Roman emperor from 393 to 423. He was the younger son of emperor Theodosius I and his first wife Aelia Flaccilla. After the death of Theodosius in 395, Honorius, under the regency of Stilicho, ruled the western half of the empire while his brother Arcadius ruled the eastern half. His reign over the Western Roman Empire was notably precarious and chaotic. In 410, Sack of Rome (410), Rome was sacked for the first time since the Battle of the Allia almost 800 years prior. Family Honorius was born to Emperor Theodosius I and Empress Aelia Flaccilla on 9 September 384 in Constantinople. He was the brother of Arcadius and Pulcheria (daughter of Theodosius I), Pulcheria. In 386, his mother died, and in 387, Theodosius married Galla (wife of Theodosius I), Galla who had taken a temporary refuge in Thessaloniki with her family, including her brother Valentinian II and mother Justina (empress), Justina, away from usurper Magnus Maximus. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severan
The Severan dynasty, sometimes called the Septimian dynasty, ruled the Roman Empire between 193 and 235. It was founded by the emperor Septimius Severus () and Julia Domna, his wife, when Septimius emerged victorious from civil war of 193 - 197, which began with the Year of the Five Emperors. Their two sons, Caracalla () and Geta (), ruled briefly after the death of Septimius. In 217 - 218 there was a short interruption of dynasty's control over the empire by reigns of Macrinus () and his son Diadumenian () before Julia Domna's relatives assumed power by raising her two grandnephews, Elagabalus () and Severus Alexander (), in succession to the imperial office. The dynasty's women, Julia Domna, the mother of Caracalla and Geta, and her sister, Julia Maesa, the mother of Julia Soaemias and Julia Mamaea, mothers of Elagabalus and Severus Alexander respectively, were all powerful '' augustae''. They were also instrumental in securing imperial positions for their male relatives. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrian
Hadrian ( ; ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. Hadrian was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic peoples, Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, Aelia ''gens'', the ''Aeli Hadriani'', came from the town of Atri, Abruzzo, Hadria in eastern Italy. He was a member of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. Early in his political career, Hadrian married Vibia Sabina, grandniece of the ruling emperor, Trajan, and his second cousin once removed. The marriage and Hadrian's later succession as emperor were probably promoted by Trajan's wife Pompeia Plotina. Soon after his own succession, Hadrian had four leading senators unlawfully put to death, probably because they seemed to threaten the security of his reign; this earned him the senate's lifelong enmity. He earned further disapproval by abandoning Trajan's expansionist policies and territorial gains in Mesopotamia (Roman province), Mesopotamia, Assyria ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belvedere (structure)
A belvedere or belvidere ( ; from ) is an architectural structure sited to take advantage of a fine or scenic view. The term has been used both for rooms in the upper part of a building or structures on the roof, or a separate pavilion in a garden or park. The actual structure can be of any form or style, including a turret, a cupola or an open gallery. The term may be also used for a paved terrace or just a place with a good viewpoint, but no actual building. It has also been used as a name for a whole building, as in the Belvedere, Vienna, a huge palace, or Belvedere Castle, a folly in Central Park in New York. Examples On the hillside above the Vatican Palace (–1490), Antonio del Pollaiuolo built a small pavilion ( in Italian) named the ''palazzetto'' or the Belvedere for Pope Innocent VIII. Some years later Donato Bramante linked the Vatican with the Belvedere, a commission from Pope Julius II, by creating the Cortile del Belvedere ("Courtyard of the Belvedere"), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exedra
An exedra (: exedras or exedrae) is a semicircular architecture, architectural recess or platform, sometimes crowned by a semi-dome, and either set into a building's façade or free-standing. The original Greek word ''ἐξέδρα'' ('a seat out of doors') was applied to a room that opened onto a stoa, ringed with curved high-backed stone benches, a suitable place for conversation. An exedra may also be expressed by a curved break in a colonnade, perhaps with a semicircular seat. The exedra would typically have an apse, apsidal podium that supported the stone bench. The free-standing (open air) exedra, often supporting bronze portrait sculpture, is a familiar Hellenistic structure, characteristically sited along shrine, sacred ways or in open places in sanctuaries, such as at Delos or Epidaurus. Some Hellenistic exedras were built in relation to a city's agora, as in Priene. Monument architects have also used this free-standing style in modern times. Rise The exedra achieved pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Sebastian
Sebastian (; ) was an early Christianity, Christian saint and martyr. According to traditional belief, he was killed during the Diocletianic Persecution of Christians. He was initially tied to a post or tree and shot with arrows, though this did not kill him. He was, according to tradition, rescued and healed by Irene of Rome, which became a popular subject in 17th-century painting. In all versions of the story, shortly after his recovery he went to Diocletian to warn him about his sins, and as a result he was clubbed to death. He is venerated in the Roman Catholic Church, Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Church as the patron saint of athletics, archery, and plagues. The oldest record of the details of Sebastian's martyrdom is found in the ''Chronograph of 354'', which mentions him as a martyr, venerated on January 20. He is also mentioned in a sermon on Psalm 118 by 4th-century bishop Ambrose, Ambrose of Milan: in his sermon, Ambrose stated that Sebas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acts Of The Martyrs
Acts of the Martyrs () are accounts of the suffering and death of Christian martyrs which were collected and used in early Catholic church liturgies, as attested by Augustine of Hippo, Saint Augustine."Acts of the Martyrs." Cross, F. L., ed. The Oxford dictionary of the Christian church. New York: Oxford University Press. 2005 Their authenticity varies, the most reliable derive from accounts of trials such as that of Cyprian and Justina, Saint Cyprian or of the Scillitan Martyrs. Although, some claim that the latter has been embellished with miraculous and apocryphal material. As it stands, few of these trial accounts survive. A second, the , includes the martyrdoms of Saint Ignatius of Antioch, Martyrdom of Polycarp, Saint Polycarp, and the Martyrs of Lyons, the famous ''Saints Perpetua and Felicitas, Acts of Perpetua and Felicitas'', and the Passion of Saint Irenaeus. In these accounts, miraculous elements are restricted, which proved to be unpopular and was often later embellish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villa Of Domitian
The Villa of Domitian, known as Albanum Domitiani or Albanum Caesari in Latin, was a vast and sumptuous Roman villa or palace built by emperor Domitian (r. 81–96 AD). It was situated from Rome, high in the Alban Hills where summer temperatures are more comfortable. It faced west overlooking the sea and Ostia Antica, Ostia. To travellers on the via Appia it would have made an impressive sight. It gained a notorious reputation among ancient authors from Domitian's rule but this may have been unjust. It was one of several palaces developed by Domitian outside Rome, such as that Villa of Domitian (Sabaudia), "at Circeii" (Sabaudia). Today the remains of the villa are located mostly within the papal Villa Barberini property, the most prominent of the villas in the pontifical estate of Castel Gandolfo, and the rest in the towns of Castel Gandolfo and Albano Laziale. The Villa Barberini gardens are open to visitors. The remains have not been excavated and a complete plan is not a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Villa Of Pliny "in Tuscis"
The Villa of Pliny ''in Tuscis'' was a large, elaborate ancient Roman villa-estate that belonged to the Plinys (Pliny the Elder and Pliny the Younger). It is located at Colle Plinio near San Giustino, Umbria, Italy. He called it his villa ''in Tuscis'' (in Tuscany) and often mentioned it in letters. It is now an important archaeological site even though parts have been destroyed in the past by farming. It was identified by tile-stamps with the names of the Plinys (CPS: Caius Plinius Secundus and CPCS: Caius Plinius Caecilius Secundus) and by an inscription mentioning a freedwoman named ''Plinia'' Chreste, clearly with Pliny as patron. Pliny the Younger wrote that "I prefer my Tuscan villa to those which I possess at Tusculum, Tiber, and Præneste. ... I enjoy here a cosier, more profound and undisturbed retirement than anywhere else". Pliny the Younger also had two villas near Lake Como, Pliny's Comedy and Tragedy villas, and another at Laurentum. It was located under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chariot Racing
Chariot racing (, ''harmatodromía''; ) was one of the most popular Ancient Greece, ancient Greek, Roman Empire, Roman, and Byzantine Empire, Byzantine sports. In Greece, chariot racing played an essential role in aristocratic funeral games from a very early time. With the institution of formal races and permanent racetracks, chariot racing was adopted by many Greek states and their religious festivals. Horses and chariots were very costly. Their ownership was a preserve of the wealthiest aristocrats, whose reputations and status benefitted from offering such extravagant, exciting displays. Their successes could be further broadcast and celebrated through commissioned odes and other poetry. In standard Greek racing practise, each chariot held a single driver and was pulled by four horses, or sometimes two. Drivers and horses risked serious injury or death through collisions and crashes; this added to the excitement and interest for spectators. Most charioteers were slaves or cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |