Didemnins on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Didemnins are cyclic depsipeptide compounds isolated from a
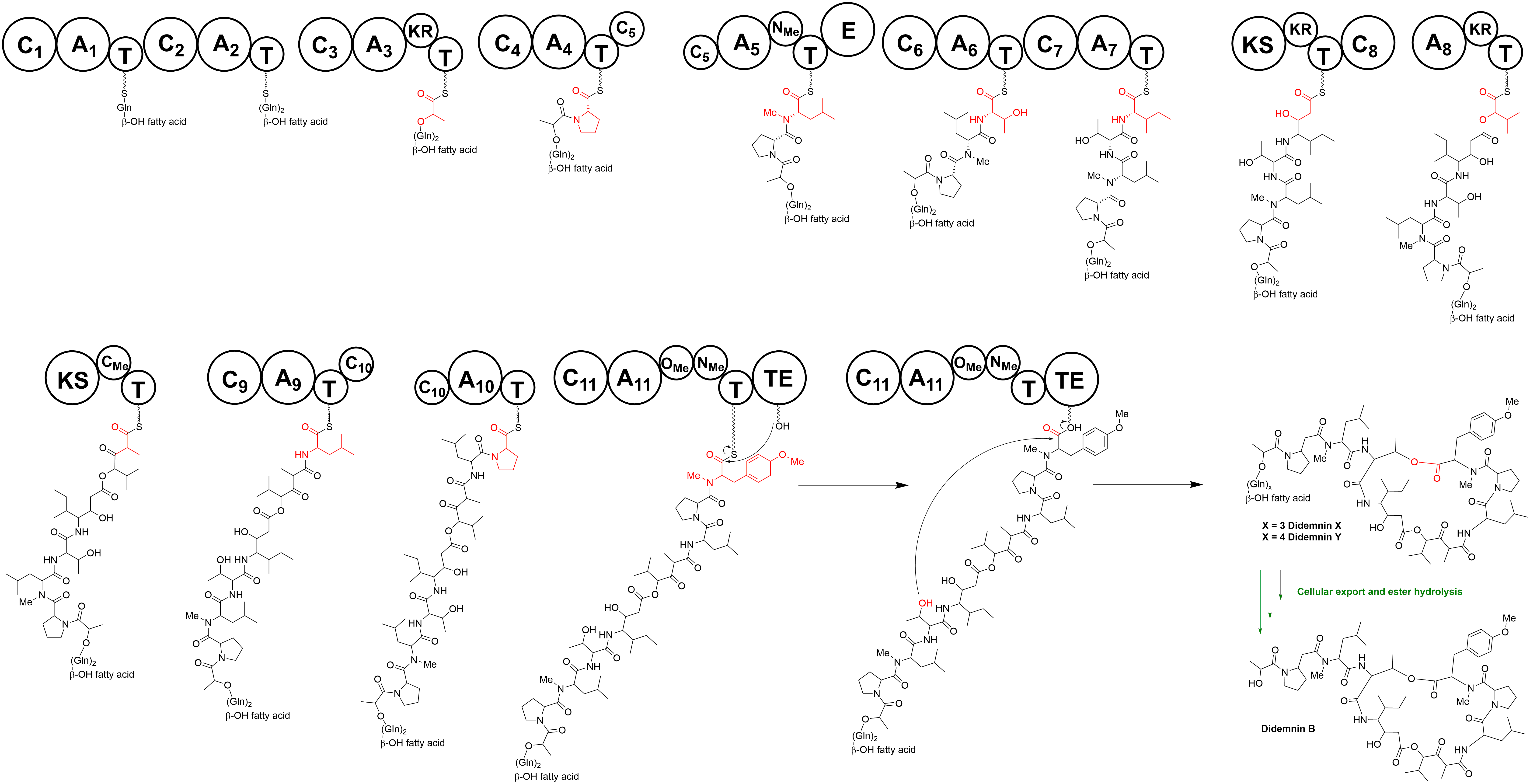 The proposed pathway of the biosynthesis of didemnin B starts on Did A. Modules 1 and 2 both incorporate a glycine on a β-OH fatty acid. On DidB, the adenylation (A) domain is loaded by pyruvate and subsequently reduced in its cis conformation by the ketoreductase (KR) domain, yielding the lactate bounded to the thiolation (T) domain. Monomodular didC incorporates proline, before tridomain didD elongates the peptide chain with 3 amino acids. The adenylation (A) domain of didD is loaded with leucine and subsequently N-methylated by the methyltransferase (MT) domain and converted into N-methylated D-leucine by the epimerase (E) domain. The N-methylated leucine is the only D-amino acid in didemnin B. The second module on didD incorporates threonine and the third module on the domain attached isoleucine, assembling the tetrapeptide (Pro)-(N-Me-D-Leu)-(Thr)-(Ile). DidE is a PKS, but lacks an acyltransferase (AT) domain. Module 8 on didE attaches a ketide-extended β-hydroxy-γ-isostatin. It is suggested that the didemnin PKS mobilizes AT domain FabD from a Fatty Acid Synthase (FAS), since there iis no AT domain present in the didemin genome. The DidF A domain is loaded with 2-oxoisovaleric acid and incorporates α-hydroxy acid 2-hydroxyisovaleric acid. Module 10 on PKS DidG adds a second round of malonate extension. The MT domain on DidG adds an α-methyl group to this residue. Monomodular domains DidH, DidI and DidJ elongate the chain with respectively leucine, proline and tyrosine. The two MT domains on DidJ methylates tyrosine twice, to yield N-methyl-O-methyl-tyrosine, finalizing the assembly of linear didemnin B. The Thioesterase (TE) domain on module DidJ releases the product in its cyclized form.
The proposed pathway of the biosynthesis of didemnin B starts on Did A. Modules 1 and 2 both incorporate a glycine on a β-OH fatty acid. On DidB, the adenylation (A) domain is loaded by pyruvate and subsequently reduced in its cis conformation by the ketoreductase (KR) domain, yielding the lactate bounded to the thiolation (T) domain. Monomodular didC incorporates proline, before tridomain didD elongates the peptide chain with 3 amino acids. The adenylation (A) domain of didD is loaded with leucine and subsequently N-methylated by the methyltransferase (MT) domain and converted into N-methylated D-leucine by the epimerase (E) domain. The N-methylated leucine is the only D-amino acid in didemnin B. The second module on didD incorporates threonine and the third module on the domain attached isoleucine, assembling the tetrapeptide (Pro)-(N-Me-D-Leu)-(Thr)-(Ile). DidE is a PKS, but lacks an acyltransferase (AT) domain. Module 8 on didE attaches a ketide-extended β-hydroxy-γ-isostatin. It is suggested that the didemnin PKS mobilizes AT domain FabD from a Fatty Acid Synthase (FAS), since there iis no AT domain present in the didemin genome. The DidF A domain is loaded with 2-oxoisovaleric acid and incorporates α-hydroxy acid 2-hydroxyisovaleric acid. Module 10 on PKS DidG adds a second round of malonate extension. The MT domain on DidG adds an α-methyl group to this residue. Monomodular domains DidH, DidI and DidJ elongate the chain with respectively leucine, proline and tyrosine. The two MT domains on DidJ methylates tyrosine twice, to yield N-methyl-O-methyl-tyrosine, finalizing the assembly of linear didemnin B. The Thioesterase (TE) domain on module DidJ releases the product in its cyclized form.
tunicate
Tunicates are marine invertebrates belonging to the subphylum Tunicata ( ). This grouping is part of the Chordata, a phylum which includes all animals with dorsal nerve cords and notochords (including vertebrates). The subphylum was at one time ...
( ascidian, or sea-squirt) of the genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
'' Trididemnum'' (family of Didemnidæ) that were collected in the Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere, located south of the Gulf of Mexico and southwest of the Sargasso Sea. It is bounded by the Greater Antilles to the north from Cuba ...
. They were first isolated in 1978 at the University of Illinois
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC, U of I, Illinois, or University of Illinois) is a public university, public land-grant university, land-grant research university in the Champaign–Urbana metropolitan area, Illinois, United ...
.
Although more than nine didemnins (didemnins A-E, G, X and Y) have been isolated from the extract of ''Trididemnum solidum'', didemnin B is the one that possesses the most potent biological activities. It is a strong antiviral agent against both DNA and RNA virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
es such as herpes simplex virus type 1, a strong immunosuppressant that shows some potential in skin graft and is also very cytotoxic. It shows strong activity against murine
The Old World rats and mice, part of the subfamily Murinae in the family Muridae, comprise at least 519 species. Members of this subfamily are called murines. In terms of species richness, this subfamily is larger than all mammal families excep ...
leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia; pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and produce high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or '' ...
cells. Large amounts of didemnin B were chemically synthesized and it was advanced to clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel v ...
s by the National Cancer Institute
The National Cancer Institute (NCI) coordinates the United States National Cancer Program and is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which is one of eleven agencies that are part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. ...
. It has completed phase II human clinical trials
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel v ...
against adenocarcinoma of the kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
, advanced epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
ovarian cancer, and metastatic breast cancer. Unfortunately, the compound exhibited high toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacteria, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect o ...
through a high incidence of anaphylactic reactions in patients and trials were terminated.
The didemnin analog plitidepsin was in phase II clinical trials as of 2003.
Biosynthesis
The biosynthesis of depsipeptide Didemnin is governed by a hybrid non-ribosomal peptide synthetase-polyketide synthetase (NRPS-PKS) pathway. The didemnin mega-synthetase consists of 10 proteins, of which 8 NRPS and 2 PKS, covering 13 modules in total.Xu Y.,''et al.'' ''J. Am. Chem. Soc'' 2012, ''20'', 8625–8632. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja301735a The proposed pathway of the biosynthesis of didemnin B starts on Did A. Modules 1 and 2 both incorporate a glycine on a β-OH fatty acid. On DidB, the adenylation (A) domain is loaded by pyruvate and subsequently reduced in its cis conformation by the ketoreductase (KR) domain, yielding the lactate bounded to the thiolation (T) domain. Monomodular didC incorporates proline, before tridomain didD elongates the peptide chain with 3 amino acids. The adenylation (A) domain of didD is loaded with leucine and subsequently N-methylated by the methyltransferase (MT) domain and converted into N-methylated D-leucine by the epimerase (E) domain. The N-methylated leucine is the only D-amino acid in didemnin B. The second module on didD incorporates threonine and the third module on the domain attached isoleucine, assembling the tetrapeptide (Pro)-(N-Me-D-Leu)-(Thr)-(Ile). DidE is a PKS, but lacks an acyltransferase (AT) domain. Module 8 on didE attaches a ketide-extended β-hydroxy-γ-isostatin. It is suggested that the didemnin PKS mobilizes AT domain FabD from a Fatty Acid Synthase (FAS), since there iis no AT domain present in the didemin genome. The DidF A domain is loaded with 2-oxoisovaleric acid and incorporates α-hydroxy acid 2-hydroxyisovaleric acid. Module 10 on PKS DidG adds a second round of malonate extension. The MT domain on DidG adds an α-methyl group to this residue. Monomodular domains DidH, DidI and DidJ elongate the chain with respectively leucine, proline and tyrosine. The two MT domains on DidJ methylates tyrosine twice, to yield N-methyl-O-methyl-tyrosine, finalizing the assembly of linear didemnin B. The Thioesterase (TE) domain on module DidJ releases the product in its cyclized form.
The proposed pathway of the biosynthesis of didemnin B starts on Did A. Modules 1 and 2 both incorporate a glycine on a β-OH fatty acid. On DidB, the adenylation (A) domain is loaded by pyruvate and subsequently reduced in its cis conformation by the ketoreductase (KR) domain, yielding the lactate bounded to the thiolation (T) domain. Monomodular didC incorporates proline, before tridomain didD elongates the peptide chain with 3 amino acids. The adenylation (A) domain of didD is loaded with leucine and subsequently N-methylated by the methyltransferase (MT) domain and converted into N-methylated D-leucine by the epimerase (E) domain. The N-methylated leucine is the only D-amino acid in didemnin B. The second module on didD incorporates threonine and the third module on the domain attached isoleucine, assembling the tetrapeptide (Pro)-(N-Me-D-Leu)-(Thr)-(Ile). DidE is a PKS, but lacks an acyltransferase (AT) domain. Module 8 on didE attaches a ketide-extended β-hydroxy-γ-isostatin. It is suggested that the didemnin PKS mobilizes AT domain FabD from a Fatty Acid Synthase (FAS), since there iis no AT domain present in the didemin genome. The DidF A domain is loaded with 2-oxoisovaleric acid and incorporates α-hydroxy acid 2-hydroxyisovaleric acid. Module 10 on PKS DidG adds a second round of malonate extension. The MT domain on DidG adds an α-methyl group to this residue. Monomodular domains DidH, DidI and DidJ elongate the chain with respectively leucine, proline and tyrosine. The two MT domains on DidJ methylates tyrosine twice, to yield N-methyl-O-methyl-tyrosine, finalizing the assembly of linear didemnin B. The Thioesterase (TE) domain on module DidJ releases the product in its cyclized form.
See also
*Trabectedin
Trabectedin, sold under the brand name Yondelis, is an antitumor chemotherapy medication for the treatment of advanced soft-tissue sarcoma and ovarian cancer.
The most common adverse reactions include nausea, fatigue, vomiting, constipation, de ...
References