Demographics Of Nepal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The current population of
The current population of
 Source: ''UN World Population Prospects''
Source: ''UN World Population Prospects''



 Nepali was the national language and
Nepali was the national language and
 Since Nepal's unification, various indigenous languages have come under threat of extinction as the government of Nepal has marginalized their use through strict policies designed to promote Nepali as the official language. Indigenous languages which have gone extinct or are critically threatened include Byangsi, Chonkha, and Longaba. Since democracy was restored in 1990, however, the government has worked to improve the marginalization of these languages. Tribhuvan University began surveying and recording threatened languages in 2010 and the government intends to use this information to include more languages on the next Nepali census.
Since Nepal's unification, various indigenous languages have come under threat of extinction as the government of Nepal has marginalized their use through strict policies designed to promote Nepali as the official language. Indigenous languages which have gone extinct or are critically threatened include Byangsi, Chonkha, and Longaba. Since democracy was restored in 1990, however, the government has worked to improve the marginalization of these languages. Tribhuvan University began surveying and recording threatened languages in 2010 and the government intends to use this information to include more languages on the next Nepali census.
 Nepal defines itself as a secular nation according to
Nepal defines itself as a secular nation according to

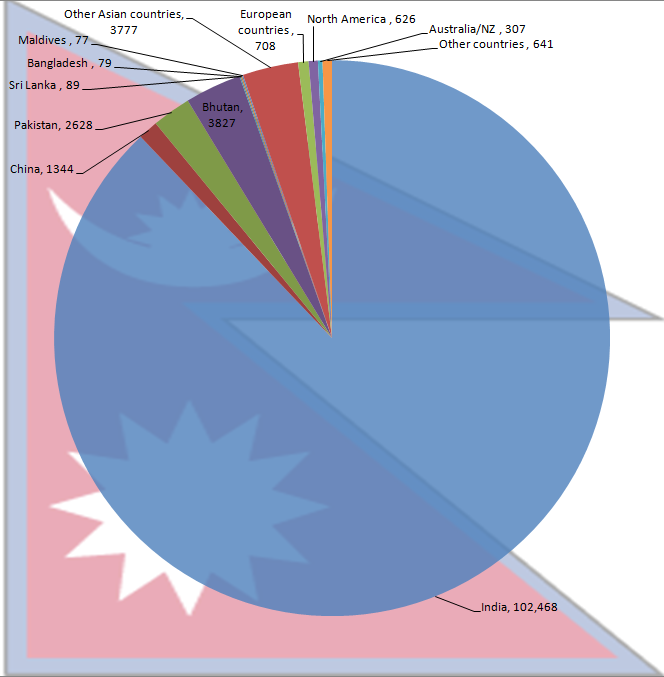 According to the 2001 census, there were 116,571 foreign born citizens in Nepal; 90% of them were of Indian origin followed by Bhutan, Pakistan and China. This number does not include the refugees from Bhutan and Tibet, nor does it include 4 million indian immigrants who were given Nepali citizenship in 2008 after the promulgation of the New Constitution of Nepal.
According to the 2001 census, there were 116,571 foreign born citizens in Nepal; 90% of them were of Indian origin followed by Bhutan, Pakistan and China. This number does not include the refugees from Bhutan and Tibet, nor does it include 4 million indian immigrants who were given Nepali citizenship in 2008 after the promulgation of the New Constitution of Nepal.
Nepal Encyclopedia Ethnicity Page
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Demographics Of Nepal Gurkhas
 The current population of
The current population of Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
is 29,164,578 as per the 2021 census. The population growth rate is 0.92% per year.
In the 2011 census, Nepal's population was approximately 26 million people with a population growth rate of 1.35% and a median age of 21.6 years.
In 2016, the female median age was approximately 25 years old and the male median age was approximately 22 years old. Only 4.4% of the population is estimated to be more than 65 years old, comprising 681,252 females and 597,628 males. 61% of the population is between 15 and 64 years old, and 34.6% is younger than 14 years.
In 2011, the birth rate
Birth rate, also known as natality, is the total number of live childbirth, human births per 1,000 population for a given period divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registr ...
is estimated to be 22.17 births per 1,000 people with an infant mortality
Infant mortality is the death of an infant before the infant's first birthday. The occurrence of infant mortality in a population can be described by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the number of deaths of infants under one year of age ...
rate of 46 deaths per 1,000 live births. Compared to the infant mortality rate in 2006 of 48 deaths per 1000 live births, the 2011 IMR is a slight decrease within that 5-year period. Infant mortality rate in Nepal is higher in rural regions at 44 deaths per 1000 live births, whereas in urban regions the IMR is lower at 40 deaths per 1000 live births. This difference is due to a lack of delivery assistance services in rural communities compared to their urban counterparts who have better access to hospitals and neonatal clinics.
Life expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where '' ...
at birth is estimated to be 67.44 years for females and 64.94 years for males. The mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular Statistical population, population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically ...
is estimated to be 681 deaths per 100,000 people.
Net migration rate
The net migration rate is the difference between the number of immigrants (people coming into an area) and the number of emigrants (people leaving an area) per year divided by the population. When the number of immigrants is larger than the num ...
is estimated to be 61 migrants per 100,000 people.
According to the 2000 census, 65.9% of the total population is literate
Literacy is the ability to read and write, while illiteracy refers to an inability to read and write. Some researchers suggest that the study of "literacy" as a concept can be divided into two periods: the period before 1950, when literacy was ...
.
Population growth
The population of Nepal has been steadily rising in recent decades. In the June 2001 census, there was a population of about 23 million in Nepal. The population increased by 5 million from the preceding 1991 census; the growth rate is 2.3%. The current population is roughly 30 million which contributes to an increase of about 3 million people every 5 years. Sixty caste and linguistic subgroups have formed throughout time with the waves ofmigration
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
from Tibet and India. There was a moderate amount of immigration early in Nepal's history, then the population essentially remained the same without any significant fluctuations for over one hundred years. Natural disasters and the following government resettlement programs in the 1950s led to a spike in internal migration from the hills to the Terai region. In the 1980s the Western Chitwan Valley became a major transportation hub for all of Nepal. Along with this major change came a dramatic increase in government services, business expansion, and growing employment, especially in the agricultural industry. The valley's population grew rapidly through both in-migration and natural increase.
Vital statistics
UN estimates
CBR = crude birth rate (per 1000); CDR = crude death rate (per 1000); NC = natural change (per 1000); TFR = total fertility rate (number of children per woman); IMR = infant mortality rate per 1000 births Source:UN DESA
The United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) is part of the United Nations Secretariat and is responsible for the follow-up to major United Nations Summits and Conferences, as well as services to the United Nations Econ ...
, World Population Prospects, 2022
Structure of the population
Life expectancy
Demographic and Health Survey
Total fertility rate (TFR) (wanted fertility rate) and crude birth rate (CBR): The following demographic statistics are from the 2011 Nepal Demographic and Health Survey (NDHS). Median birth intervals (median number of months since preceding birth) :Total: 36.2 :Rural: 35.9 :Urban: 40.3 (2011) Median age at first birth :Median age: 20.1 (2011) Fertility rate – past trend and present :Total fertility rate: 4.6 children born/woman (1996) :Total fertility rate: 4.1 children born/woman (2001) :Total fertility rate: 3.1 children born/woman (2006) :Total fertility rate: 2.6 children born/woman :Rural fertility rate: 2.8 children born/woman :Urban fertility rate: 1.6 children born/woman (2011) Ideal family size – mean ideal number of children :Overall (female/male): 2.1 / 2.3 :Currently married (female/male): 2.2 / 2.3 :Urban (female/male): 1.9 / 2.0 :Rural (female/male): 2.2 / 2.3 (2011) Ideal family size by gender and age group :Below is a table of the ideal family size by gender and age for 2011.Ethnic and regional equity

 Nepali was the national language and
Nepali was the national language and Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
became a required school subject. Children who spoke Nepali natively and who were exposed to Sanskrit had much better chances of passing the national examinations at the end of high school, which meant they had better employment prospects and could continue into higher education. Children who natively spoke local languages of the Madhesh
Madhesi, or variants, may refer to:
*Madesi tribe, an indigenous group of Native Americans
*Madheshi people, several Nepali people
*Madhesh Province
Madhesh Province () is a Provinces of Nepal, province of Nepal in the Terai region with an are ...
and Hills
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct summit, and is usually applied to peaks which are above elevation compared to the relative landmass, though not as prominent as mountains. Hills fall und ...
, or Tibetan dialects prevailing in the high mountains were at a considerable disadvantage. This history of exclusion coupled with poor prospects for improvement created grievances that encouraged many in ethnic communities such as Madhesi and Tharu in the Tharuhat and Madhesh
Madhesi, or variants, may refer to:
*Madesi tribe, an indigenous group of Native Americans
*Madheshi people, several Nepali people
*Madhesh Province
Madhesh Province () is a Provinces of Nepal, province of Nepal in the Terai region with an are ...
and Kham Magar
The Kham Magars (खाम मगर), also known in scholarship as the Northern Magars, are a (Tibeto-Burman languages, Tibeto-Burman language) Magar Kham language or Kham Kura speaking indigenous ethnic tribal community native to Nepal. In g ...
in the mid-western hills to support the Unified Communist Party of Nepal (Maoist)
The Communist Party of Nepal (Maoist Centre) (), abbreviated CPN (Maoist Centre) or CPN (MC), is the third largest political party in Nepal and a member party of Samajbadi Morcha. It was founded in 1994 after breaking away from the Communi ...
and various other armed Maoist opposition groups such as the JTMM during and after the Nepali Civil War. The negotiated end to this war forced King Gyanendra to abdicate in 2008. Issues of ethnic and regional equity have tended to dominate the agenda of the new republican government and continue to be divisive. Today, even after the end of a 10-year-old Maoist conflict, the upper caste dominates every field in Nepal. Although Newars are low in numbers, their urban living habitat gives them a competitive advantage. Kayastha of Madhesh are the toppers in Human Development Index. From a gender perspective, Newari women are the most literate and lead in every sector. Brahmin and Chhetri women have experienced less social and economic mobility compared to Newari women. Specifically, Brahmin women experience less equality due to their predominately rural living conditions which deprives them of access to certain educational and healthcare advantages.
Languages
Nepal's diverse linguistic heritage evolved from three major language groups: Indo-Aryan,Tibeto-Burman languages
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non- Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people spe ...
, and various indigenous language
An indigenous language, or autochthonous language, is a language that is native to a region and spoken by its indigenous peoples. Indigenous languages are not necessarily national languages but they can be; for example, Aymara is both an indigen ...
isolates. According to the 2001 national census, 92 different living languages are spoken in Nepal (a 93rd category was "unspecified"). Based upon the 2011 census, the major languages spoken in Nepal (percentage spoken out of the mother tongue language) includes
Nepali (derived from Khas
Khas peoples or Khas Tribes, (; ) popularly known as Khashiya are an Indo-Aryan ethno-linguistic group native to the Himalayan region of the Indian subcontinent, in what is now the South Asian country of Nepal, as well as the Indian stat ...
bhasa) is an Indo-Aryan language and is written in Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; in script: , , ) is an Indic script used in the Indian subcontinent. It is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental Writing systems#Segmental systems: alphabets, writing system), based on the ancient ''Brāhmī script, Brā ...
script. Nepali was the language of the house of Gorkhas in the late 18th century and became the official, national language that serves as the ''lingua franca'' among Nepali of different ethnolinguistic groups. Maithili, Bhojpuri
Bhojpuri may refer to:
* Bhojpuri language, an Indo-Aryan language of India and Nepal
* Bhojpuri grammar, grammatical rules of the language
* Bhojpuri nouns, nouns of the language
* Bhojpuri people, people who speak the language
* Bhojpuri region ...
, Bajjika
Bajjika is an Indo-Aryan language variety spoken in parts of Bihar, India and in Nepal. It is also classified as a dialect of Maithili language and is known as Western Maithili.
Territory and speakers
Bajjika language is spoken in the north-w ...
and Awadhi languages are spoken in the southern Terai
The Terai or Tarai is a lowland region in parts of southern Nepal and northern India that lies to the south of the outer foothills of the Himalayas, the Sivalik Hills and north of the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
This lowland belt is characterised by ...
. There has been a surge in the number and percentage of people who understand English. Majority of the urban and a significant number of the rural schools are English-medium schools. Higher education in technical, medical, scientific and engineering fields are entirely in English. Nepal Bhasa
Newar (; , ) is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Newar people, the indigenous inhabitants of Nepal Mandala, which consists of the Kathmandu Valley and surrounding regions in Nepal. The language is known officially in Nepal as Nepal Bhas ...
, the mother-tongue of the Newars, is widely used and spoken in and around Kathmandu Valley
The Kathmandu Valley (), also known as the Nepal Valley or Nepa Valley (, Newar language, Nepal Bhasa: 𑐣𑐾𑐥𑐵𑑅 𑐐𑐵𑑅, नेपाः गाः), National Capital Area, is a bowl-shaped valley located in the Himalayas, Hima ...
and in major Newar trade towns across Nepal.
Other languages, particularly in the Inner Terai hill and mountain regions, are remnants of the country's pre-unification history of dozens of political entities isolated by mountains and gorges. These languages typically are limited to an area spanning about one day's walk. Beyond that distance, dialects and languages lose mutual intelligibility. However, there are some major languages spoken by indigenous peoples in the region: Magar and Gurung in the west-central hills, Tamang in the east-centre and Limbu in the east. In the high Himalayas are spoken various Tibetan languages, including Bhotia.
 Since Nepal's unification, various indigenous languages have come under threat of extinction as the government of Nepal has marginalized their use through strict policies designed to promote Nepali as the official language. Indigenous languages which have gone extinct or are critically threatened include Byangsi, Chonkha, and Longaba. Since democracy was restored in 1990, however, the government has worked to improve the marginalization of these languages. Tribhuvan University began surveying and recording threatened languages in 2010 and the government intends to use this information to include more languages on the next Nepali census.
Since Nepal's unification, various indigenous languages have come under threat of extinction as the government of Nepal has marginalized their use through strict policies designed to promote Nepali as the official language. Indigenous languages which have gone extinct or are critically threatened include Byangsi, Chonkha, and Longaba. Since democracy was restored in 1990, however, the government has worked to improve the marginalization of these languages. Tribhuvan University began surveying and recording threatened languages in 2010 and the government intends to use this information to include more languages on the next Nepali census.
Religion
As of the 2021 census, 81.19% of the Nepali population wasHindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
, 8.21% Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
, 5.09% Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
, 3.17% Kiratist/Yumaist, 1.76% Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
, and 0.9% followed other or no religion.
 Nepal defines itself as a secular nation according to
Nepal defines itself as a secular nation according to Constitution of Nepal
The Constitution of Nepal () is the present governing Constitution of Nepal.
Nepal is governed according to the Constitution which came into effect on 20 September 2015, replacing the Interim Constitution of 2007. The constitution of Nepal is di ...
It is common for many Hindus in the country to also worship Buddhist deities simultaneously with Hindu traditions. The notion of religion in Nepal is more fluid than other countries, particularly Western countries. The Nepali people build their social networks through their religious celebrations, which are a central part to the whole of communities within the country.
There is a general idea held by the Nepali people that there is an omnipotent, transcendental "moral order" that is sacred to Hinduism. This idea exists along with the constant presence of chaos and disorder in the material world. In the northwestern region of the country, this all-encompassing state of disorder in the world is synonymous with human affliction, which the religious shamans are believed to alleviate.
Kathmandu Valley is home to the Newars, a major ethnic group in Nepal. The city Bhaktapur is located inside of Kathmandu Valley. Bhaktapur was once an independent Hindu Kingdom. Individual homes typically have at least one shrine devoted to personal deities, with an altar displaying flowers, fruit, and oil among other offerings to the Gods. The perimeter of Kathmandu Valley is lined with shrines devoted to Hindu goddesses, whose purpose is to protect the city from chaotic events. At least one shrine can be found on the vast majority of streets in Kathmandu. The people of Nepal do not feel the need to segregate or compete based upon religion, so Hindu and Buddhist shrines are often coexisting in the same areas. The areas outside of the city are perceived to always possess some form of wild or disordered nature, so the Nepali people inside of the city lines regularly worship the Hindu gods through public ceremonies.
The Hindu god Vishnu is believed to symbolise moral order in the Newar society. The natural human shortcomings in maintaining this moral order is believed to be represented by the Hindu god Shiva. The destruction of Shiva is neutralised by the preserver Vishnu, who tips the scales to restore order. In recent times, there has been a rise in political violence, specifically Maoist violence. This increased violence, along with the widespread poverty, has caused the Nepali to seek stability and peace in religion.
Nepal's constitution continues long-standing legal provisions prohibiting discrimination against other religions (but also proselytization). The king was deified as the earthly manifestation of the Hindu god Vishnu
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation ( ...
. On May 19, 2006, the government faced a constitutional crisis
In political science, a constitutional crisis is a problem or conflict in the function of a government that the constitution, political constitution or other fundamental governing law is perceived to be unable to resolve. There are several variat ...
, the House of Representatives which had been just reformed, having been previously dissolved, declared Nepal a "secular state
is an idea pertaining to secularity, whereby a state is or purports to be officially neutral in matters of religion, supporting neither religion nor irreligion. A secular state claims to treat all its citizens equally regardless of relig ...
".
The 2001 census identified 80.6% of the population as Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
and 10.7% as Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
(although many people labeled Hindu or Buddhist often practice a syncretic
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the theology and mythology of religion, thus ...
blend of Hinduism, Buddhism, or animist
Animism (from meaning 'breath, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct spiritual essence. Animism perceives all things—animals, plants, rocks, rivers, weather systems, human handiwork, and in ...
traditions), 4.2% of the population was Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
, 3.6% of the population followed the indigenous Kirat Mundhum
Kirat Mundhum, (Nepali language, Nepali: किरात मुन्धुम) also known as Kiratism, or Kirati Mundhum, is a traditional belief of the Kirati people, Kirati ethnic groups of Nepal, Darjeeling and Sikkim, majorly practiced by Yak ...
religion and Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
was practiced by 0.45% of the population.
Buddhist and Hindu shrines and festivals are respected and celebrated by most Nepali. Certain animist practises of old indigenous religions continue to survive to the modern era.
Migration
Emigration

Nepali in the United Kingdom
In the 2001 census, approximately 6,000 Nepali were living in the UK. According to latest figure fromOffice for National Statistics
The Office for National Statistics (ONS; ) is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the Parliament of the United Kingdom, UK Parliament.
Overview
The ONS is responsible fo ...
estimates that 51,000 Nepal-born people are currently resident in the UK. There has been increasing interest in the opportunities offered in the UK by the Nepali, especially education. Between the years of 2001 to 2006, there were 7,500 applications for student visas.
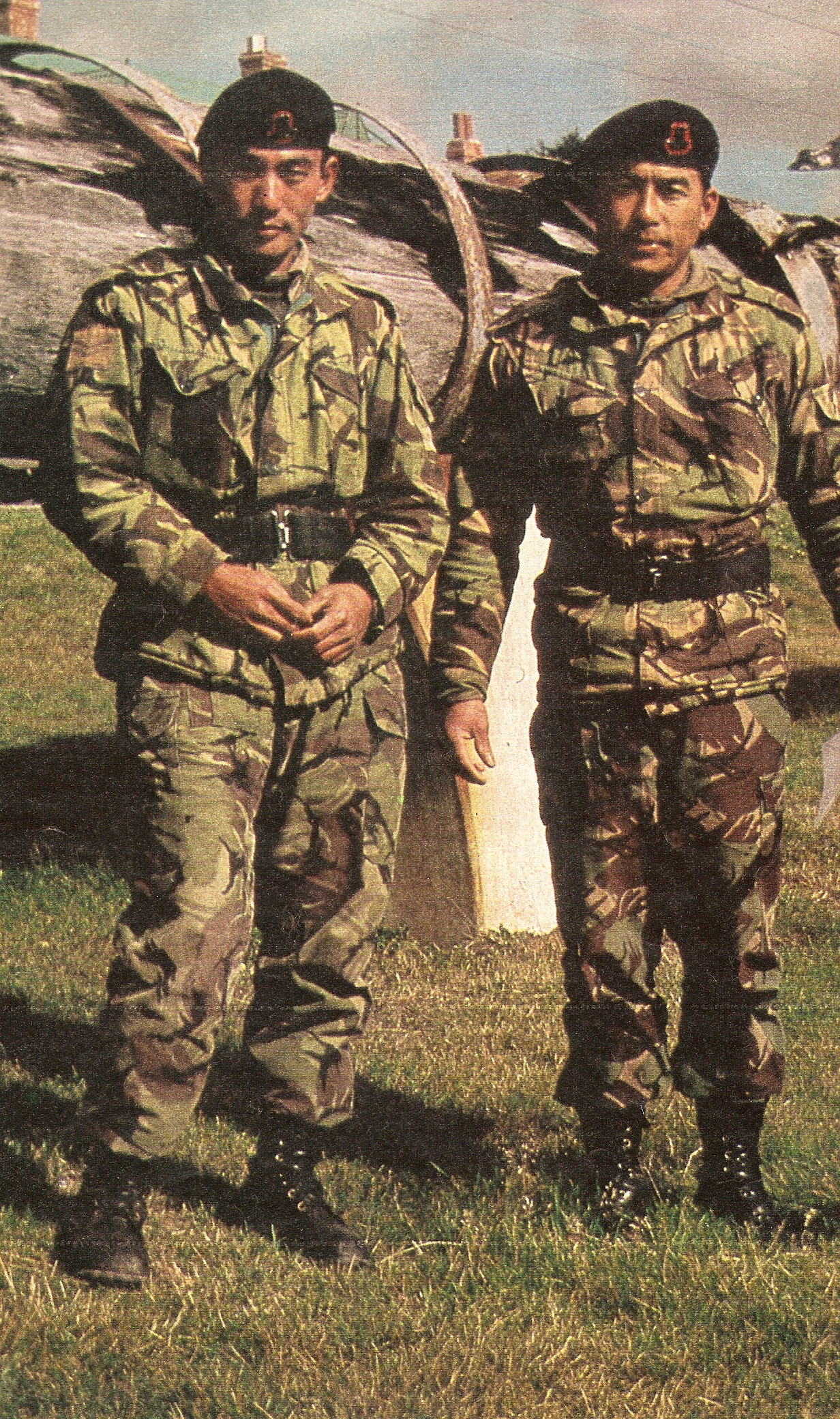
Nepali in Hong Kong
The Nepali people residing in Hong Kong are primarily made up of children of ex-Gurkha
The Gurkhas or Gorkhas (), with the endonym Gorkhali ( Nepali: गोर्खाली ), are soldiers native to the Indian subcontinent, chiefly residing within Nepal and some parts of North India.
The Gurkha units consist of Nepali and ...
s; born in Hong Kong during their parents' service with the British Army
The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 25,742 Army Reserve (United Kingdom), volunteer reserve perso ...
's Brigade of Gurkhas
Brigade of Gurkhas is the collective name which refers to all the units in the British Army that are composed of Gurkha, Nepalese Gurkha soldiers. The brigade draws its heritage from Gurkha units that originally served in the British Indian Arm ...
, which was based in Hong Kong from the 1970s until the handover
In cellular telecommunications, handover, or handoff, is the process of transferring an ongoing call or data session from one channel connected to the core network to another channel. In satellite communications it is the process of transf ...
. Large groups of Nepali people can be found in Shek Kong
Shek Kong is an area north of Tai Mo Shan, located near Kam Tin and Pat Heung, in Yuen Long District, New Territories, Hong Kong, hosting Shek Kong San Tsuen, Shek Kong Barracks and Shek Kong Airfield.
The area named after an old walled village ...
and Yuen Long District
Yuen Long District (Hong Kong Government Cantonese Romanisation, formerly Un Long) is one of the districts of Hong Kong, districts of Hong Kong. Located in the northwest of the New Territories, it had a population of 662,000 in 2021.
Geogra ...
off of the main bases of the British army. Many ex-Gurkhas remained in Hong Kong after the end of their service under the sponsorship of their Hong Kong-born children, who held right of abode
The right of abode is an individual's freedom from immigration control in a particular country. A person who has the right of abode in a country does not need permission from the government to enter the country and can live and work there witho ...
.
Nepali of middle age or older generations in Hong Kong are predominantly found in security
Security is protection from, or resilience against, potential harm (or other unwanted coercion). Beneficiaries (technically referents) of security may be persons and social groups, objects and institutions, ecosystems, or any other entity or ...
, while those of younger generations are predominantly found in the business industry.
Mostly the people from Kirati
The Kirati people, also spelled as Kirat or Kirant or Kiranti, are Tibeto-Burman ethnolinguistic groups living in the Himalayas, mostly the Eastern Himalaya extending eastward from Nepal to North East India (predominantly in the Indian state ...
ethnic groups
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, rel ...
such as Rai and Limbu
Limbu may refer to:
* Limbu people, an indigenous tribe living in Nepal, Sikkim (India) and Bhutan
** Limbu language, their Sino-Tibetan language
*** Limbu script
**** Limbu (Unicode block)
* Rambahadur Limbu
Rambahadur Limbu, (; 8 July 1939 � ...
are the ones residing in Hong Kong
Hong Kong)., Legally Hong Kong, China in international treaties and organizations. is a special administrative region of China. With 7.5 million residents in a territory, Hong Kong is the fourth most densely populated region in the wor ...
and other neighbouring nations such as Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
and Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
.
Nepali overseas
Nepali migrants abroad have suffered tremendous hardships, including some 7,500 deaths in theMiddle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
and Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
alone since the year 2000, some 3,500 in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
.
Immigration
 According to the 2001 census, there were 116,571 foreign born citizens in Nepal; 90% of them were of Indian origin followed by Bhutan, Pakistan and China. This number does not include the refugees from Bhutan and Tibet, nor does it include 4 million indian immigrants who were given Nepali citizenship in 2008 after the promulgation of the New Constitution of Nepal.
According to the 2001 census, there were 116,571 foreign born citizens in Nepal; 90% of them were of Indian origin followed by Bhutan, Pakistan and China. This number does not include the refugees from Bhutan and Tibet, nor does it include 4 million indian immigrants who were given Nepali citizenship in 2008 after the promulgation of the New Constitution of Nepal.
See also
*Ethnic groups in Nepal
Ethnic groups in Nepal are delineated using Languages of Nepal, language, ethnic identity or the caste system in Nepal. They are categorized by common culture and endogamy. Endogamy carves out ethnic groups in Nepal.
Broad ethnic categories of ...
References
External links
Nepal Encyclopedia Ethnicity Page
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Demographics Of Nepal Gurkhas