Demographics Of Israel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The demographics of Israel, monitored by the

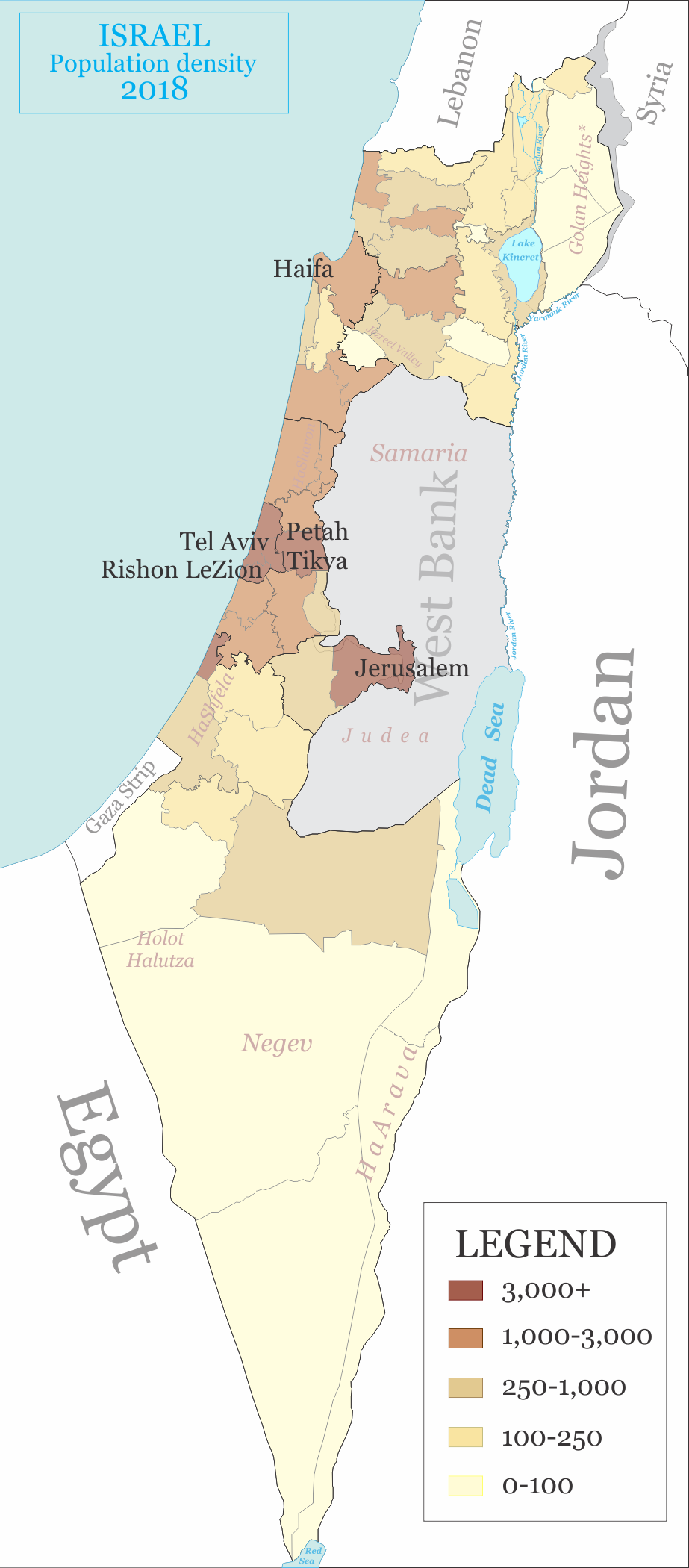 Geographic deployment, as of 2018:
* Central District: 24.5% (2,196,100)
*
Geographic deployment, as of 2018:
* Central District: 24.5% (2,196,100)
*
 The
The
/ref>
 2021 :
* Total: 19.7 births/1,000 population
* Jews and others: 19.1 births/1,000 population
* Muslims: 23.4 births/1,000 population
* Christians: 13.3 births/1,000 population
* Druze: 15.8 births/1,000 population
Births, in absolute numbers, by mother's religion
Between the mid-1980s and 2000, the
2021 :
* Total: 19.7 births/1,000 population
* Jews and others: 19.1 births/1,000 population
* Muslims: 23.4 births/1,000 population
* Christians: 13.3 births/1,000 population
* Druze: 15.8 births/1,000 population
Births, in absolute numbers, by mother's religion
Between the mid-1980s and 2000, the

 As of 2019:
* Total population: 82.8 years
* Male: 81 years
* Female: 84.7 years
As of 2019:
* Total population: 82.8 years
* Male: 81 years
* Female: 84.7 years
 The most prominent
The most prominent
 Arab citizens of Israel are those Arab residents of Mandatory Palestine that remained within Israel's borders following the
Arab citizens of Israel are those Arab residents of Mandatory Palestine that remained within Israel's borders following the
 In Israel, there are also a few thousand
In Israel, there are also a few thousand  Ethnic
Ethnic
 The number and status of African migrants in Israel is disputed and controversial, but it is estimated that at least 70,000 refugees mainly from
The number and status of African migrants in Israel is disputed and controversial, but it is estimated that at least 70,000 refugees mainly from
, on cbs.gov.il
Official website
of the
Population of Israel
by the Tourism Ministry
Israel
''
Issues in Israeli Society
at the
Israel Central Bureau of Statistics
The Israel Central Bureau of Statistics (, ''HaLishka HaMerkazit LiStatistika''; ), abbreviated CBS, is an Israeli government office established in 1949 to carry out research and publish statistical data on all aspects of Israeli life, including ...
, encompass various attributes that define the nation's populace. Since its establishment in 1948, Israel has witnessed significant changes in its demographics. Formed as a homeland for the Jewish people, Israel has attracted Jewish immigrants from Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas.
The Israel Central Bureau of Statistics
The Israel Central Bureau of Statistics (, ''HaLishka HaMerkazit LiStatistika''; ), abbreviated CBS, is an Israeli government office established in 1949 to carry out research and publish statistical data on all aspects of Israeli life, including ...
defines the population of Israel as including Jews living in all of the West Bank
The West Bank is located on the western bank of the Jordan River and is the larger of the two Palestinian territories (the other being the Gaza Strip) that make up the State of Palestine. A landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
and Palestinians in East Jerusalem
East Jerusalem (, ; , ) is the portion of Jerusalem that was Jordanian annexation of the West Bank, held by Jordan after the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, as opposed to West Jerusalem, which was held by Israel. Captured and occupied in 1967, th ...
but excluding Palestinians anywhere in the rest of the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, and foreign workers anywhere in Israel. As of December 2023, this calculation stands at approximately 9,842,000 of whom:
*73.2% (about 7,208,000 people) are Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
, including about 503,000 living outside the self-defined borders of the State of Israel in the West Bank
The West Bank is located on the western bank of the Jordan River and is the larger of the two Palestinian territories (the other being the Gaza Strip) that make up the State of Palestine. A landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
*21.1% (around 2,080,000 people) are Israeli citizens classified as Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
, some identifying as Palestinian
Palestinians () are an Arab ethnonational group native to the Levantine region of Palestine.
*: "Palestine was part of the first wave of conquest following Muhammad's death in 632 CE; Jerusalem fell to the Caliph Umar in 638. The indigenous p ...
, and including Druze
The Druze ( ; , ' or ', , '), who Endonym and exonym, call themselves al-Muwaḥḥidūn (), are an Arabs, Arab Eastern esotericism, esoteric Religious denomination, religious group from West Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic ...
, Circassians
The Circassians or Circassian people, also called Cherkess or Adyghe (Adyghe language, Adyghe and ), are a Northwest Caucasian languages, Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation who originated in Circassia, a region and former country in t ...
, all other Muslims, Christian Arabs
Arab Christians () are the Arabs who adhere to Christianity. The number of Arab Christians who live in the Middle East was estimated in 2012 to be between 10 and 15 million. Arab Christian communities can be found throughout the Arab world, bu ...
, Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
(which Israel considers "Arab")
*An additional 5.7% (roughly 554,000 people) are classified as "others". This diverse group comprises those with Jewish ancestry but not recognized as Jewish by religious law, non-Jewish family members of Jewish immigrants, Christians other than Arabs and Armenians, and residents without a distinct ethnic or religious categorization.
Israel's annual population growth rate stood at 2.0% in 2015, more than three times faster than the OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
average of around 0.6%. With an average of three children per woman, Israel also has the highest fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
in the OECD by a considerable margin and much higher than the OECD average of 1.7.
Definitions
The definition of what constitutes the population of Israel varies depending on which territories are counted and which population groups are counted in each territory. TheIsrael Central Bureau of Statistics
The Israel Central Bureau of Statistics (, ''HaLishka HaMerkazit LiStatistika''; ), abbreviated CBS, is an Israeli government office established in 1949 to carry out research and publish statistical data on all aspects of Israeli life, including ...
(CBS) definition of the Area of the State of Israel:
*includes East Jerusalem
East Jerusalem (, ; , ) is the portion of Jerusalem that was Jordanian annexation of the West Bank, held by Jordan after the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, as opposed to West Jerusalem, which was held by Israel. Captured and occupied in 1967, th ...
since 1967, which Israel unilaterally annexed
*includes the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights, or simply the Golan, is a basaltic plateau at the southwest corner of Syria. It is bordered by the Yarmouk River in the south, the Sea of Galilee and Hula Valley in the west, the Anti-Lebanon mountains with Mount Hermon in t ...
since 1982, which Israel unilaterally annexed
*excludes the West Bank other than East Jerusalem
The CBS' definition of the Population of Israel, however:
*includes non-Israeli Palestinians (as well as Israeli Arabs/Palestinians) in East Jerusalem who have permission to live there
*includes Israeli settlers
Israeli may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the State of Israel
* Israelis, citizens or permanent residents of the State of Israel
* Modern Hebrew, a language
* ''Israeli'' (newspaper), published from 2006 to 2008
* Guni Israeli (b ...
and others with Israeli residency permits living in the Area C of West Bank
*excludes Palestinian/Arab/other residents of Area C and East Jerusalem who do not have Israeli citizenship or residence
*excludes persons who are not registered (from 2008 on) and/or entered illegally, and foreign workers.
Population
Total population
(most current update from the Israeli Central Bureau for Statistics, via live feed) ''Note:'' includes over 200,000 Israelis and 250,000 Arabs inEast Jerusalem
East Jerusalem (, ; , ) is the portion of Jerusalem that was Jordanian annexation of the West Bank, held by Jordan after the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, as opposed to West Jerusalem, which was held by Israel. Captured and occupied in 1967, th ...
, about 421,400 Jewish settlers on the West Bank, and about 42,000 in the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights, or simply the Golan, is a basaltic plateau at the southwest corner of Syria. It is bordered by the Yarmouk River in the south, the Sea of Galilee and Hula Valley in the west, the Anti-Lebanon mountains with Mount Hermon in t ...
(July 2007 estimate). Does not include Arab populations in the West Bank
The West Bank is located on the western bank of the Jordan River and is the larger of the two Palestinian territories (the other being the Gaza Strip) that make up the State of Palestine. A landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
and Gaza Strip
The Gaza Strip, also known simply as Gaza, is a small territory located on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea; it is the smaller of the two Palestinian territories, the other being the West Bank, that make up the State of Palestine. I ...
. Does not include 222,000 foreigners living in the country.
Density
 Geographic deployment, as of 2018:
* Central District: 24.5% (2,196,100)
*
Geographic deployment, as of 2018:
* Central District: 24.5% (2,196,100)
* Tel Aviv District
The Tel Aviv District (; ) is the geographically smallest yet also the most densely populated of the six administrative districts of Israel, with a population of 1.35 million residents. It is 98.9% Jewish and 1.10% Arab (0.7% Muslim, 0.4% Chris ...
: 15.9% (1,427,200)
* Northern District: 16.2% (1,448,100)
* Southern District: 14.5% (1,302,000)
* Haifa District
Haifa District () is an administrative district surrounding the city of Haifa in Israel. The district is one of the seven administrative districts of Israel, and its capital is Haifa. The district land area is 864 km2 (299.3 mi2).
D ...
: 11.5% (1,032,800)
* Jerusalem District
The Jerusalem District (; ) is one of the six administrative districts of Israel. The district capital is Jerusalem and its total land area is 652 km2. The population of 1,159,900 is 66.3% Jewish and 32.1% Arab. A fifth (21%) of the Arab ...
: 12.6% (1,133,700)
* Judea and Samaria Area
The Judea and Samaria Area (; ) is an administrative division used by the State of Israel to refer to the entire West Bank, which has been occupied by Israel since 1967, but excludes East Jerusalem (see Jerusalem Law). Its area is split int ...
(West Bank) (Israelis only): 4.8% (427,800)
Population growth rate
* 2.0% (2016) During the 1990s, the Jewishpopulation growth rate
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to 8.2 billion in 2025. Actual global human population growth amounts to around 70 million annu ...
was about 3% per year, as a result of massive immigration to Israel, primarily from the republics of the former Soviet Union
The post-Soviet states, also referred to as the former Soviet Union or the former Soviet republics, are the independent sovereign states that emerged/re-emerged from the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Prior to their independence, they ...
. There is also a very high population growth rate among certain Jewish groups, especially adherents of Orthodox Judaism
Orthodox Judaism is a collective term for the traditionalist branches of contemporary Judaism. Theologically, it is chiefly defined by regarding the Torah, both Torah, Written and Oral Torah, Oral, as literally revelation, revealed by God in Ju ...
. The growth rate of the Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
population in Israel is 2.2%, while the growth rate of the Jewish population in Israel is 1.8%. The growth rate of the Arab population has slowed from 3.8% in 1999 to 2.2% in 2013, and for the Jewish population, the growth rate declined from 2.7% to its lowest rate of 1.4% in 2005. Due to a rise in fertility of the Jewish population since 1995 and immigration, the growth rate has since risen to 1.8%.
Fertility
 The
The total fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
(TFR) of a population is the average number of children that an average woman would have, in her lifetime.
* 3.01 children born/woman (2019)
Jewish total fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
increased by 10.2% during 1998–2009, and was recorded at 2.90 during 2009. During the same time period, Arab TFR decreased by 20.5%. Muslim TFR was measured at 3.73 for 2009, and 2.9 for 2022.
In 2000, the Jewish and Arab TFRs in Jerusalem were 3.79 and 4.43 respectively. By 2009, the Jewish TFR in Jerusalem was measured higher than the Arab TFR (2010: 4.26 vs 3.85, 2009: 4.16 vs 3.87). As of 2021, the Jewish and Arab TFRs in Jerusalem were 4.4 and 3.1 respectively. TFR for Arab residents in the West Bank was measured at 2.91 in 2013, while that for the Jewish residents was reported at 5.10 children per woman.
The ethnic group with highest recorded TFR is the Bedouin of Negev. Their TFR was reported at 10.06 in 1998, and 5.73 in 2009. TFR is also very high among Haredi Jews. For Ashkenazi
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; also known as Ashkenazic Jews or Ashkenazim) form a distinct subgroup of the Jewish diaspora, that Ethnogenesis, emerged in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium Common era, CE. They traditionally spe ...
Haredim, the TFR rose from 6.91 in 1980 to 8.51 in 1996. The figure for 2008 is estimated to be even higher. TFR for Sephardi
Sephardic Jews, also known as Sephardi Jews or Sephardim, and rarely as Iberian Peninsular Jews, are a Jewish diaspora population associated with the historic Jewish communities of the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal) and their descendant ...
/ Mizrahi Haredim rose from 4.57 in 1980 to 6.57 in 1996. In 2020 the overall Jewish TFR in Israel (3.00) was for the first time measured higher than Arab Muslim TFR (2.99).
As of 2022, the fertility rates in Israeli cities dominated by specific demographic groups were: Haredi 6.1, Bedouin 4.4, Jewish non-Haredi 2.4, Arab 2.2, Druze 1.8.הדמוגרפיה של ישראל 2023: ירידות בפריון, בהגירה ובתמותה/ref>
Birth rate
fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
in the Muslim sector was stable at 4.6–4.7 children per woman; after 2001, a gradual decline became evident, reaching 3.51 children per woman in 2011. By point of comparison, in 2011, there was a rising fertility rate of 2.98 children among the Jewish population.
Life expectancy
 As of 2019:
* Total population: 82.8 years
* Male: 81 years
* Female: 84.7 years
As of 2019:
* Total population: 82.8 years
* Male: 81 years
* Female: 84.7 years
Infant mortality rate
* Total: 4.03 deaths/1,000 live births * Male: 4.20 deaths/1,000 live births * Female: 3.84 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Age structure
The table shows population estimates by sex and age group, as of July 1, 2019. It includes data for East Jerusalem and Israeli residents in certain other territories under occupation by Israeli military forces since June 1967. Data refer to Israeli citizens and permanent residents who are listed in the Population Register.Median age
The Jewish median age in Jerusalem district and the West Bank are 24.9 and 19.7, respectively, and both account for 16% of the Jewish population, but 24% of 0- to 4-year-olds. The lowest median age in Israel, and one of the lowest in the world, is found in two of the West Bank's biggest Jewish cities:Modi'in Illit
Modi'in Illit (; , lit. "Upper Modi'in") is a Haredi Judaism, Haredi Jewish-Israeli settlement organized as a city council (Israel), city council in the West Bank, situated midway between Jerusalem and Tel Aviv.
Built on the land of five Palest ...
(11), Beitar Illit (11) followed by Bedouin towns in the Negev (15.2).
Cities
Within Israel's system of local government, an urban municipality can be granted acity council
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as a city council, town council, town board, community council, borough counc ...
by the Israeli Interior Ministry when its population exceeds 20,000. The term "city" does not generally refer to local councils or urban agglomeration
An urban area is a human settlement with a high population density and an infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas originate through urbanization, and researchers categorize them as cities, towns, conurbations or suburbs. In urbani ...
s, even though a defined city often contains only a small portion of an urban area or metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region consisting of a densely populated urban area, urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories which share Industry (economics), industries, commercial areas, Transport infrastructure, transport network ...
's population.
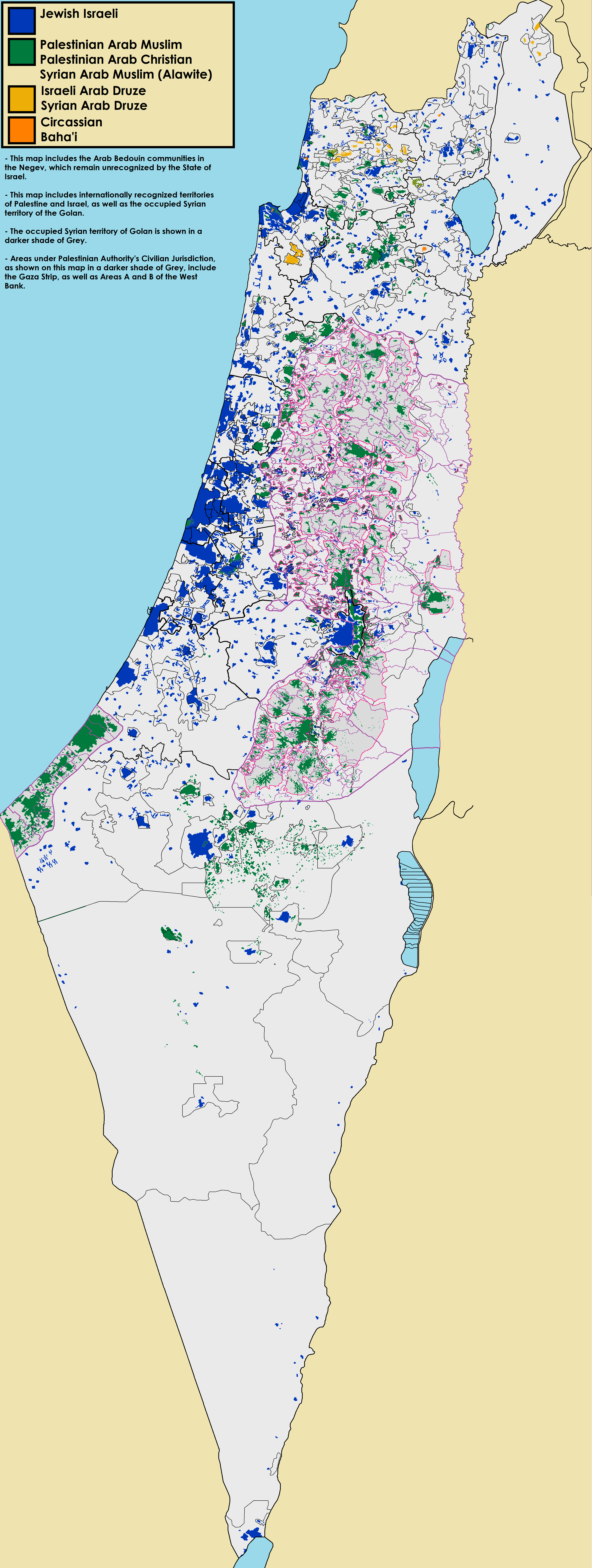
Ethnic and religious groups
Statistics

ethnic
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
and religious groups that live in Israel at present and that are Israeli citizens or nationals are as follows:
Jews
According to Israel's Central Bureau of Statistics, in 2008, of Israel's 7.3 million people, 75.6 percent were Jews of any background. Among them, 70.3 percent were Sabras (born in Israel), mostly second- or third-generation Israelis, and the rest areolim
''Aliyah'' (, ; ''ʿălīyyā'', ) is the immigration of Jews from the diaspora to, historically, the geographical Land of Israel or the Palestine region, which is today chiefly represented by the State of Israel. Traditionally described ...
(Jewish immigrants to Israel)—20.5 percent from Europe and the Americas, and 9.2 percent from Asia and Africa, including the Arab countries
The Arab world ( '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, comprises a large group of countries, mainly located in West Asia and North Africa. While the majority of people in ...
.
According to Israel's Central Bureau of Statistics, in April 2023, of Israel's 9.7 million people, 73.5 percent, or 7.145 million, were Jews of any background.
There are no government statistics categorizing Israeli Jews as "Ashkenazi", "Mizrahi", etc, but studies and estimates have been conducted. In a 2019 study, in a sample meant to be representative of the Israeli Jewish population, about 44.9% percent of Israel's Jewish population were categorized as Mizrahi (defined as having grandparents born in North Africa or Asia), 31.8% were categorized as Ashkenazi
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; also known as Ashkenazic Jews or Ashkenazim) form a distinct subgroup of the Jewish diaspora, that Ethnogenesis, emerged in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium Common era, CE. They traditionally spe ...
(defined as having grandparents born in Europe, the Americas, Oceania and South Africa), 12.4% as "Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
" (defined as having progenitors who came from the ex-USSR in 1989 or later), about 3% as Beta Israel
Beta Israel, or Ethiopian Jews, is a Jewish group originating from the territory of the Amhara Region, Amhara and Tigray Region, Tigray regions in northern Ethiopia, where they are spread out across more than 500 small villages over a wide ter ...
(Ethiopia) and 7.9% as a mix of these, or other Jewish groups. Note that this methodology isn't exact: See, for example, Bulgarian or Greek Jews
The history of the Jews in Greece can be traced back to at least the fourth century BCE. The oldest and the most characteristic Jewish group that has inhabited Greece are the Romaniotes, also known as "Greek Jews." The term "Greek Jew" is pre ...
, who would be categorized as Ashkenazi according to this definition, although they are overwhelmingly Sephardic.
The paternal lineage of the Jewish population of Israel as of 2015 is as follows:
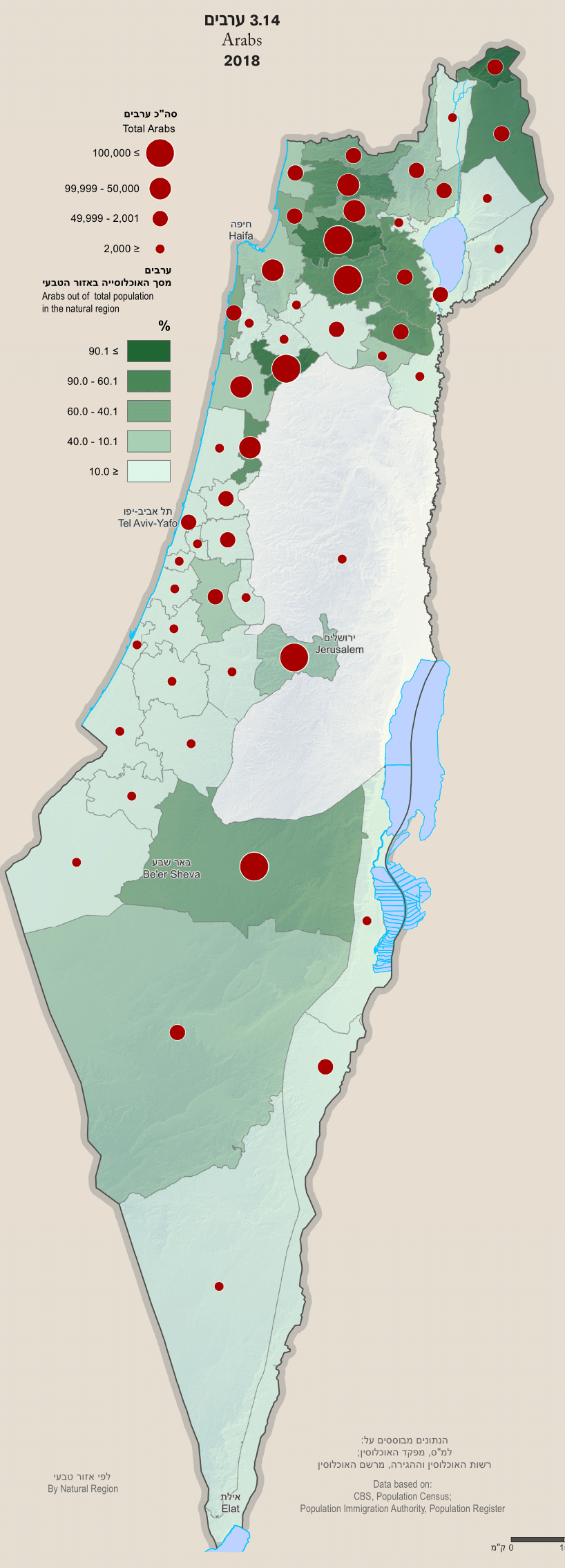
Arabs
 Arab citizens of Israel are those Arab residents of Mandatory Palestine that remained within Israel's borders following the
Arab citizens of Israel are those Arab residents of Mandatory Palestine that remained within Israel's borders following the 1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War, also known as the First Arab–Israeli War, followed the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war in Mandatory Palestine as the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. The civil war becam ...
and the establishment of the State of Israel
The Israeli Declaration of Independence, formally the Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel (), was proclaimed on 14 May 1948 (5 Iyar 5708), at the end of the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war phase and ...
. It is including those born within the state borders subsequent to this time, as well as those who had left during the establishment of the state (or their descendants), who have since re-entered by means accepted as lawful residence by the Israeli state (primarily family reunifications).
In 2019, the official number of Arab residents in Israel was 1,890,000 people, representing 21% of Israel's population. This figure includes 209,000 Arabs (14% of the Israeli Arab population) in East Jerusalem, also counted in the Palestinian statistics, although 98 percent of East Jerusalem Palestinians have either Israeli residency or Israeli citizenship.
Arab Muslims
Most Arab citizens of Israel are Muslim, particularly of the Sunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
branch of Islam. A small minority are Ahmadiyya
Ahmadiyya, officially the Ahmadiyya Muslim Jama'at (AMJ), is an Islamic messianic movement originating in British India in the late 19th century. It was founded by Mirza Ghulam Ahmad (1835–1908), who said he had been divinely appointed a ...
sect and there are also some Alawites
Alawites () are an Arab ethnoreligious group who live primarily in the Levant region in West Asia and follow Alawism, a sect of Islam that splintered from early Shia as a ''ghulat'' branch during the ninth century. Alawites venerate Ali ...
(affiliated with Shia Islam) in the northernmost village of Ghajar with Israeli citizenship. As of 2019, Arab citizens of Israel composed 21 percent of the country's total population. About 82 percent of the Arab population in Israel are Sunni Muslims, a very small minority are Shia Muslims, another 9 percent are Druze
The Druze ( ; , ' or ', , '), who Endonym and exonym, call themselves al-Muwaḥḥidūn (), are an Arabs, Arab Eastern esotericism, esoteric Religious denomination, religious group from West Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic ...
, and around 9 percent are Christian (mostly Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
and Catholic denominations).
Bedouin
The Arab Muslim citizens of Israel include also the Bedouins, who are divided into two main groups: the Bedouin in the north of Israel, who live in villages and towns for the most part, and the Bedouin in the Negev
The Negev ( ; ) or Naqab (), is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southern end is the Gulf of Aqaba and the resort town, resort city ...
, who include half-nomadic and inhabitants of towns and Unrecognized villages. According to the Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs
The Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs (; ) is one of the most important Cabinet of Israel, ministries in the Government of Israel, Israeli government. The ministry's role is to implement Israel's foreign policy, and promote economic, cultural ...
, as of 1999, 110,000 Bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu ( ; , singular ) are pastorally nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia (Iraq). The Bedouin originated in the Sy ...
s live in the Negev, 50,000 in the Galilee and 10,000 in the central region of Israel. The vast majority of Arab Bedouins of Israel practice Sunni Islam.
Ahmadiyya
The Ahmadiyya community
Ahmadiyya, officially the Ahmadiyya Muslim Jama'at (AMJ), is an Islamic messianic movement originating in British India in the late 19th century. It was founded by Mirza Ghulam Ahmad (1835–1908), who said he had been divinely appointed a ...
was first established in the region in the 1920s, in what was then Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine was a British Empire, British geopolitical entity that existed between 1920 and 1948 in the Palestine (region), region of Palestine, and after 1922, under the terms of the League of Nations's Mandate for Palestine.
After ...
. There is a large community in Kababir, a neighborhood on Mount Carmel
Mount Carmel (; ), also known in Arabic as Mount Mar Elias (; ), is a coastal mountain range in northern Israel stretching from the Mediterranean Sea towards the southeast. The range is a UNESCO biosphere reserve. A number of towns are situat ...
in Haifa
Haifa ( ; , ; ) is the List of cities in Israel, third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropolitan area i ...
. It is unknown how many Israeli Ahmadis there are, although it is estimated there are about 2,200 Ahmadis in Kababir alone.
Arab Christians
As of December 2013, about 161,000 Israeli citizens practiced Christianity, together comprising about 2% of the total population. The largest group consists of Melkite
The term Melkite (), also written Melchite, refers to various Eastern Christian churches of the Byzantine Rite and their members originating in West Asia. The term comes from the common Central Semitic root ''m-l-k'', meaning "royal", referrin ...
s (about 60% of Israel's Christians), followed by the Greek Orthodox (about 30%), with the remaining ca. 10% spread between the Roman Catholic (Latin), Maronite, Anglican, Lutheran, Armenian, Syriac, Ethiopian, Coptic and other denominations.
Druze
The Arab citizens of Israel include also the Druze
The Druze ( ; , ' or ', , '), who Endonym and exonym, call themselves al-Muwaḥḥidūn (), are an Arabs, Arab Eastern esotericism, esoteric Religious denomination, religious group from West Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic ...
, who numbered at an estimated 143,000 in April 2019. All of the Druze
The Druze ( ; , ' or ', , '), who Endonym and exonym, call themselves al-Muwaḥḥidūn (), are an Arabs, Arab Eastern esotericism, esoteric Religious denomination, religious group from West Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic ...
living in what was then British Mandate Palestine became Israeli citizens after the declaration of the State of Israel. Druze serve prominently in the Israel Defense Forces
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; , ), alternatively referred to by the Hebrew-language acronym (), is the national military of the State of Israel. It consists of three service branches: the Israeli Ground Forces, the Israeli Air Force, and ...
, and are represented in mainstream Israeli politics and business as well, unlike Muslim or Christian Arabs who are not required to and generally choose not to serve in the Israeli army. Though a few individuals identify themselves as "Palestinian Druze", the vast majority of Druze do not consider themselves to be 'Palestinian', and consider their Israeli identity stronger than their Arab identity
Arab identity () is the objective or subjective state of Identity (social science), perceiving oneself as an Arab and as relating to being Arab. Like other Cultural identity, cultural identities, it relies on a common culture, a traditional linea ...
. A 2017 Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
poll reported that the majority of the Israeli Druze identified as ethnically Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
.
Syriac Christians
Arameans In 2014, Israel decided to recognize the Aramaic community within its borders as a national minority, allowing some of theChristians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
in Israel to be registered as "Aramean" instead of "Arab". As of October 2014, some 600 Israelis requested to be registered as Arameans, with several thousand eligible for the status – mostly members of the Maronite community with some Assyrians as well.
The Maronite Christian community in Israel of around 7,000 resides mostly in the Galilee, with a presence in Haifa, Nazareth and Jerusalem. It is largely composed of families that lived in Upper Galilee
The Upper Galilee (, ''HaGalil Ha'Elyon''; , ''Al Jaleel Al A'alaa'') is a geographical region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Part of the larger Galilee region, it is characterized by its higher elevations and mountainous terra ...
in villages such as Jish
Jish (, ), also known by its Hebrew name of Gush Halab (, ), or by its classical name of Gischala, is a local council in Upper Galilee, located on the northeastern slopes of Mount Meron, north of Safed, in Israel's Northern District. In , it ...
long before the establishment of Israel in 1948. In the year 2000, the community was joined by a group of Lebanese SLA militia members and their families, who fled Lebanon after 2000 withdrawal of IDF from South Lebanon.
Assyrians
There are around 1,000 Assyrians
Assyrians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to Mesopotamia, a geographical region in West Asia. Modern Assyrians share descent directly from the ancient Assyrians, one of the key civilizations of Mesopotamia. While they are distinct from ot ...
living in Israel, mostly in Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
and Nazareth
Nazareth is the largest Cities in Israel, city in the Northern District (Israel), Northern District of Israel. In its population was . Known as "the Arab capital of Israel", Nazareth serves as a cultural, political, religious, economic and ...
. Assyrians are an Aramaic
Aramaic (; ) is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, Sinai, southeastern Anatolia, and Eastern Arabia, where it has been continually written a ...
speaking, Eastern Rite Christian minority who are descended from the ancient Mesopotamians
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
. The old Syriac Orthodox
The Syriac Orthodox Church (), also informally known as the Jacobite Church, is an Oriental Orthodox denomination that originates from the Church of Antioch. The church currently has around 4-5 million followers. The church upholds the Mia ...
monastery of Saint Mark lies in Jerusalem. Other than followers of the Syriac Orthodox Church, there are also followers of the Assyrian Church of the East
The Assyrian Church of the East (ACOE), sometimes called the Church of the East and officially known as the Holy Apostolic Catholic Assyrian Church of the East, is an Eastern Christianity, Eastern Syriac Christianity, Syriac Christian denomin ...
and the Chaldean Catholic Church
The Chaldean Catholic Church is an Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern Catholic Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites, particular church (''sui iuris'') in full communion with the Holy See and the rest of the Catholic Church, and is ...
living in Israel.
Other citizens
Copts Some 1,000 Israeli citizens belong to the Coptic community, originating in Egypt. Samaritans TheSamaritans
Samaritans (; ; ; ), are an ethnoreligious group originating from the Hebrews and Israelites of the ancient Near East. They are indigenous to Samaria, a historical region of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah that ...
are an ethnoreligious group of the Levant. Ancestrally, they claim descent from a group of Israelite inhabitants who have connections to ancient Samaria from the beginning of the Babylonian Exile up to the beginning of the Common Era. 2007 population estimates show that 712 Samaritans live half in Holon, Israel and half at Mount Gerizim
Mount Gerizim ( ; ; ; , or ) is one of two mountains in the immediate vicinity of the State of Palestine, Palestinian city of Nablus and the biblical city of Shechem. It forms the southern side of the valley in which Nablus is situated, the nor ...
in the West Bank. The Holon community holds Israeli citizenship, while the Gerizim community resides at an Israeli-controlled enclave, holding dual Israeli-Palestinian citizenship.
Armenians
About 4,000 Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
reside in Israel mostly in Jerusalem (including in the Armenian Quarter
The Armenian Quarter (, ; , ''Harat al-Arman''; , ''Ha-Rova ha-Armeni'') is one of the four sectors of the walled Old City of Jerusalem. Located in the southwestern corner of the Old City, it can be accessed through the Zion Gate and Jaffa G ...
), but also in Tel Aviv, Haifa and Jaffa. Armenians have a Patriarchate in Jerusalem and churches in Jerusalem, Haifa and Jaffa. Although Armenians of Old Jerusalem have Israeli identity cards, they are officially holders of Jordanian passports.
Circassians
Circassians
The Circassians or Circassian people, also called Cherkess or Adyghe (Adyghe language, Adyghe and ), are a Northwest Caucasian languages, Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation who originated in Circassia, a region and former country in t ...
, living mostly in Kfar Kama
Kfar Kama (, , ) is a Circassian town located in the Lower Galilee of Israel's northern district, located along road 767, that leads from Kfar Tavor to the Kinneret. It is one of the only two Circassian towns in Israel, the other being Rehan ...
(2,000) and Reyhaniye (1,000). These two villages were a part of a greater group of Circassian villages around the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights, or simply the Golan, is a basaltic plateau at the southwest corner of Syria. It is bordered by the Yarmouk River in the south, the Sea of Galilee and Hula Valley in the west, the Anti-Lebanon mountains with Mount Hermon in t ...
. The Circassians in Israel enjoy, like Druze
The Druze ( ; , ' or ', , '), who Endonym and exonym, call themselves al-Muwaḥḥidūn (), are an Arabs, Arab Eastern esotericism, esoteric Religious denomination, religious group from West Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic ...
s, a ''status aparte''. Male Circassians (at their leader's request) are mandated for military service, while females are not.
People from post-Soviet states Ethnic
Ethnic Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
, Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
, and Belarusians
Belarusians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Belarus. They natively speak Belarusian language, Belarusian, an East Slavic language. More than 9 million people proclaim Belarusian ethnicity worldwide. Nearly 7.99&n ...
, immigrants from the former Soviet Union
The post-Soviet states, also referred to as the former Soviet Union or the former Soviet republics, are the independent sovereign states that emerged/re-emerged from the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Prior to their independence, they ...
, who were eligible to emigrate due to having, or being married to somebody who has, at least one Jewish grandparent and thus qualified for Israeli citizenship under the revised Law of Return
The Law of Return (, ''ḥok ha-shvūt'') is an Israeli law, passed on 5 July 1950, which gives Jews, people with one or more Jewish grandparent, and their spouses the right to Aliyah, relocate to Israel and acquire Israeli nationality law, Isra ...
. A number of these immigrants also belong to various ethnic groups from the Former Soviet Union such as Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
, Georgians
Georgians, or Kartvelians (; ka, ქართველები, tr, ), are a nation and Peoples of the Caucasus, Caucasian ethnic group native to present-day Georgia (country), Georgia and surrounding areas historically associated with the Ge ...
, Azeris, Uzbeks
The Uzbeks () are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia, being among the largest Turkic ethnic groups in the area. They comprise the majority population of Uzbekistan, next to Kazakhs, Kazakh and Karakalpaks, Karakalpak ...
, Moldovans
Moldovans, sometimes referred to as Moldavians (, , ), are an ethnic group native to Moldova, who mostly speak the Romanian language, also referred to locally as Moldovan language, Moldovan. Moldovans form significant communities in Romania, It ...
, Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
, among others. Some of them, having a Jewish father or grandfather, identify as Jews, but being non-Jewish by Orthodox in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Halakha
''Halakha'' ( ; , ), also Romanization of Hebrew, transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Judaism, Jewish religious laws that are derived from the Torah, Written and Oral Torah. ''Halakha'' is ...
(religious law), they are not recognized formally as Jews by the state. Most of them are in the mainstream of Israel culture and are called "expanded Jewish population". In addition, a certain number of former Soviet citizens, primarily women of Russian and Ukrainian ethnicity, emigrated to Israel, after marrying Muslim or Christian Arab citizens of Israel, who went to study in the former Soviet Union in the 1970s and 1980s. 1,557,698 people from the current Russia and Ukraine live in Israel.
Finns
Although most people of Finnish origin in Israel are Finnish Jews who immigrated to Israel, and their descendants, a small number of Finnish Christians moved to Israel in the 1940s before independence and gained citizenship following independence. For the most part, many of the original Finnish settlers intermarried with the other communities in the country, and therefore remain very small in number. A Moshav shitufi
A moshav shitufi (, lit. ''collective moshav'', pl. ''moshavim shitufiim'') is a type of cooperative State of Israel, Israeli village, whose organizational principles place it between the kibbutz and the moshav on the scale of cooperation.
Ideolo ...
near Jerusalem named Yad HaShmona, meaning the "Memorial for the Eight", was established in 1971 by a group of Finnish Christian-Israelis, although today, most members are Israeli, and are predominantly Hebrew speakers, and the moshav has become a center of Messianic Jews
Messianic Judaism is a syncretic Abrahamic religious sect that combines Christian theology with select elements of Judaism. It considers itself to be a form of Judaism but is generally considered to be a form of Christianity, including by al ...
.
Baháʼís
The population of followers of the Baháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the Baháʼí Faith and the unity of religion, essential worth of all religions and Baháʼí Faith and the unity of humanity, the unity of all people. Established by ...
in Israel is almost entirely made up of volunteers serving at the Baháʼí World Centre
The Baháʼí World Centre is the name given to the spiritual and administrative centre of the Baháʼí Faith, representing sites in or near the cities of Acre and Haifa, Israel.
Much of the international governance and coordination of the ...
. Bahá'u'lláh (1817–1892), the Faith's founder, was banished to Akka
Akka or AKKA may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Akka (film), ''Akka'' (film), a 1976 Indian Tamil film
* Akka (TV series), ''Akka'' (TV series), a 2014–2015 Indian Tamil soap opera
* Akka, a character in the children's novel ''The Wonderful ...
and died nearby where his shrine is located. During his lifetime he instructed his followers not to teach or convert those living in the area, and the Baháʼís descending from those original immigrants were later asked to leave and teach elsewhere. For nearly a century there has been a policy by Baháʼí leaders to not accept converts living in Israel. The 650 or so foreign national Baháʼís living in Israel are almost all on temporary duty serving at the shrines and administrative offices.
Vietnamese
The number of Vietnamese people
The Vietnamese people (, ) or the Kinh people (), also known as the Viet people or the Viets, are a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to modern-day northern Vietnam and Dongxing, Guangxi, southern China who speak Vietnamese language, Viet ...
in Israel and their descendants is estimated at 150 to 200. Most of them came to Israel in between 1976 and 1979, after prime minister Menachem Begin
Menachem Begin ( ''Menaḥem Begin'', ; (Polish documents, 1931–1937); ; 16 August 1913 – 9 March 1992) was an Israeli politician, founder of both Herut and Likud and the prime minister of Israel.
Before the creation of the state of Isra ...
authorized their admission to Israel and granted them political asylum. The Vietnamese people living in Israel are Israeli citizens who also serve in the Israel Defense Forces
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; , ), alternatively referred to by the Hebrew-language acronym (), is the national military of the State of Israel. It consists of three service branches: the Israeli Ground Forces, the Israeli Air Force, and ...
. Today, the majority of the community lives in the Gush Dan area in the center of Tel Aviv, but also a few dozen Vietnamese-Israelis or Israelis of Vietnamese origin live in Haifa
Haifa ( ; , ; ) is the List of cities in Israel, third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropolitan area i ...
, Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
, and Ofakim
Ofakim () is a city in the Southern District (Israel), Southern District of Israel, 20 kilometers (12.4 mi) west of Beersheba. It achieved municipal status in 1955. It has an area of 10,000 dunams (~3.9 sq mi; 10 km2). In , it had a populatio ...
.
African Hebrew Israelites of Jerusalem
The African Hebrew Israelite Nation of Jerusalem is a religious sect of Black Americans
Americans are the Citizenship of the United States, citizens and United States nationality law, nationals of the United States, United States of America.; ; Law of the United States, U.S. federal law does not equate nationality with Race (hu ...
, founded in 1960 by Ben Carter a metal worker in Chicago. The members of this sect believe they are descended from the tribes of Judah driven from the Holy Land by the Romans during the First Jewish War (70 AD), and who reportedly emigrated to West Africa before being taken as slaves to the United States. With a population of over 5,000, most members live in their own community in Dimona, Israel, with additional families in Arad, Mitzpe Ramon
Mitzpe Ramon (, Ramon Lookout; ) is a local council in the Negev desert of southern Israel. It is situated on the northern ridge at an elevation of 860 meters (2,800 feet) overlooking the world's largest erosion cirque, known as the M ...
, and the Tiberias
Tiberias ( ; , ; ) is a city on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee in northern Israel. A major Jewish center during Late Antiquity, it has been considered since the 16th century one of Judaism's Four Holy Cities, along with Jerusalem, Heb ...
area. The group believes that the ancient Israelites are the ancestors of Black Americans and that the actual Jews are "impostors". Some scholarship does consider them to be of subsaharan African origin, rather than Levantine. Their ancestors were Black Americans
Americans are the Citizenship of the United States, citizens and United States nationality law, nationals of the United States, United States of America.; ; Law of the United States, U.S. federal law does not equate nationality with Race (hu ...
who, after being expelled from Liberia
Liberia, officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to Guinea–Liberia border, its north, Ivory Coast to Ivory Coast–Lib ...
, illegally immigrated to Israel in the late 1960s using tourist visas, requesting that Israel provide them legal citizenship status. Israel granted their requests. The African Hebrew Israelites, like the Haredim
Haredi Judaism (, ) is a branch of Orthodox Judaism that is characterized by its strict interpretation of religious sources and its accepted (Jewish law) and traditions, in opposition to more accommodating values and practices. Its members are ...
and most Israeli Arabs
The Arab citizens of Israel form the country's largest ethnic minority. Their community mainly consists of former Mandatory Palestine citizens (and their descendants) who continued to inhabit the territory that was acknowledged as Israeli by ...
, are not required to serve in the military; however, some do.
Naturalized foreign workers
Some naturalized foreign worker
Foreign workers or guest workers are people who work in a country other than one of which they are a citizen. Some foreign workers use a guest worker program in a country with more preferred job prospects than in their home country. Guest worke ...
s and their children born in Israel, predominantly from the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
, Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
, Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
, Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
, China, Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
, Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, and South America (mainly Colombia).
Non-citizens
African migrants The number and status of African migrants in Israel is disputed and controversial, but it is estimated that at least 70,000 refugees mainly from
The number and status of African migrants in Israel is disputed and controversial, but it is estimated that at least 70,000 refugees mainly from Eritrea
Eritrea, officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa, with its capital and largest city being Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia in the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, south, Sudan in the west, and Dj ...
, Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
, South Sudan
South Sudan (), officially the Republic of South Sudan, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered on the north by Sudan; on the east by Ethiopia; on the south by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda and Kenya; and on the ...
, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
, and the Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire and officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital city of Yamoussoukro is located in the centre of the country, while its largest List of ci ...
reside and work in Israel. A count in late 2011 published in Ynet pointed out the number only in Tel Aviv is 40,000, which represents 10 percent of the city's population. The vast majority live in the southern parts of the city. There is a significant population in the southern Israeli cities of Eilat, Arad, and Beersheba.
Foreign workers
There are around 300,000 foreign workers, residing in Israel under temporary work visas, including Palestinians. Most of those foreign workers engage in agriculture and construction. The main groups of those foreign workers include the Chinese, Thai, Filipinos
Filipinos () are citizens or people identified with the country of the Philippines. Filipinos come from various Austronesian peoples, all typically speaking Filipino language, Filipino, Philippine English, English, or other Philippine language ...
, Nigerians
Nigerians or the Nigerian people are citizens of Nigeria or people with ancestry from Nigeria. The name Nigeria was derived from the Niger River running through the country. This name was allegedly coined in the late 19th century by British jo ...
, Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
, and Latin Americans
Latin Americans (; ) are the citizens of Latin American countries (or people with cultural, ancestral or national origins in Latin America).
Latin American countries and their diasporas are multi-ethnic and multi-racial. Latin Americans are ...
.
Other refugees
Approximately 100–200 refugees from Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
, Kosovo
Kosovo, officially the Republic of Kosovo, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe with International recognition of Kosovo, partial diplomatic recognition. It is bordered by Albania to the southwest, Montenegro to the west, Serbia to the ...
, Iraqi Kurdistan
Iraqi Kurdistan or Southern Kurdistan () refers to the Kurds, Kurdish-populated part of northern Iraq. It is considered one of the four parts of Greater Kurdistan in West Asia, which also includes parts of southeastern Turkey (Northern Kurdist ...
, and North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders China and Russia to the north at the Yalu River, Yalu (Amnok) an ...
were absorbed in Israel as refugees. Most of them were also given Israeli resident status, and currently reside in Israel. As of 2006, some 200 ethnic Kurdish refugees from Turkey resided in Israel as illegal immigrants, fleeing the Kurdish–Turkish conflict
Kurdish nationalism, Kurdish nationalist uprisings have periodically occurred in Turkey, beginning with the Turkish War of Independence and the consequent transition from the Ottoman Empire to the modern Turkish state and continuing to the pre ...
.
Languages
Due to its immigrant nature, Israel is one of the most multicultural and multilingual societies in the world.Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
is the official language of the country, and Arabic is given special status, while English and Russian are the two most widely spoken non-official languages. A certain degree of English is spoken widely, and is the language of choice for many Israeli businesses. Hebrew and English language are mandatory subjects in the Israeli school system, and most schools offer either Arabic, French, Spanish, German, Italian, or Russian.
Religion
According to a 2010Israel Central Bureau of Statistics
The Israel Central Bureau of Statistics (, ''HaLishka HaMerkazit LiStatistika''; ), abbreviated CBS, is an Israeli government office established in 1949 to carry out research and publish statistical data on all aspects of Israeli life, including ...
study of Israeli Jews aged over 18:
While the ultra-Orthodox, or Haredim, represented only 5% of Israel's population in 1990, they are expected to represent more than one-fifth of Israel's Jewish population by 2028. By 2022, Haredim were 13.3% of the population and enumerated 1,280,000.
Education
Education between ages 5 and 15 is compulsory. It is not free, but it is subsidized by the government, individual organizations (such as the Beit Yaakov System), or a combination. Parents are expected to participate in courses as well. The school system is organized into kindergartens, 6-year primary schools, and either 6-year secondary schools or 3-year junior secondary schools + 3-year senior secondary schools (depending on region), after which a comprehensive examination is offered for university admissions.Literacy
Age 15 and over can read and write (2011 estimate): * Total population: 97.8% * Male: 98.7% * Female: 96.8%Policy
Israel is the thirtieth-most-densely-crowded country in the world. In an academic article,Jewish National Fund
The Jewish National Fund (JNF; , ''Keren Kayemet LeYisrael''; previously , ''Ha Fund HaLeumi'') is a non-profit organizationProfessor Alon Tal, The Mitrani Department of Desert Ecology, The Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research, Ben Gurion ...
Board member Daniel Orenstein, argues that, as elsewhere, overpopulation is a stressor on the environment in Israel; he shows that environmentalists have conspicuously failed to consider the impact of population on the environment, and argues that overpopulation in Israel has not been appropriately addressed for ideological reasons.
Citizenship and Entry Law
TheCitizenship and Entry into Israel Law
The Citizenship and Entry into Israel Law (Temporary Order) 5763 is an Israeli law first passed on 31 July 2003. The law makes inhabitants of the West Bank and Gaza Strip ineligible for the automatic granting of Israeli citizenship and residency ...
(Temporary Order) 5763 was first passed on 31 July 2003, and has since been extended until 31 July 2008. The law places age restrictions for the automatic granting of Israeli citizenship and residency permits to spouses of Israeli citizens, such that spouses who are inhabitants of the West Bank and Gaza Strip are ineligible. On 8 May 2005, the Israeli ministerial committee for issues of legislation once again amended the Citizenship and Entry into Israel Law, to restrict citizenship and residence in Israel only to Palestinian men over the age of 35, and Palestinian women over the age of 25. Those in favor of the law say the law not only limits the possibility of the entrance of terrorists into Israel, but, as Ze'ev Boim
Ze'ev Boim (; 30 April 1943 – 18 March 2011) was an Israeli politician. He was the mayor of Kiryat Gat before becoming a Knesset member for Likud and later Kadima. Boim was Minister of Agriculture and Rural Development, Minister of Housing ...
asserts, allows Israel "to maintain the state's democratic nature, but also its Jewish nature" (i. e., its Jewish demographic majority). Critics, including the United Nations Committee on the Elimination of Racial Discrimination, say the law disproportionately affects Arab citizens of Israel
The Arab citizens of Israel form the country's largest ethnic minority. Their community mainly consists of former Palestinian Citizenship Order 1925, Mandatory Palestine citizens (and their descendants) who continued to inhabit the territory ...
, since Arabs in Israel are far more likely to have spouses from the West Bank and Gaza Strip than other Israeli citizens.
In the constitutional challenges to the Citizenship and Entry to Israel Law, the state, represented by the Attorney General, insisted that security was the only objective behind the law. The state also added that even if the law was intended to achieve demographic objectives, it is still in conformity with Israel's Jewish and democratic definition, and thus constitutional. In a 2012 ruling by the Supreme Court on the issue, some of the judges on the panel discussed demography, and were inclined to accept that demography is a legitimate consideration in devising family reunification policies that violate the right to family life.
Vital statistics
Current vital statistics
Migration
Immigration
In 2013 Israel had an estimated net migration rate of 1.81 migrant(s) per 1,000 population. Immigrants by last country of residence in recent years (according to CBS and theJewish Agency
The Jewish Agency for Israel (), formerly known as the Jewish Agency for Palestine, is the largest Jewish non-profit organization in the world. It was established in 1929 as the operative branch of the World Zionist Organization (WZO).
As an ...
):
Immigration from the USSR
During the 1970s about 163,000 people of Jewish descent immigrated to Israel from the USSR. LaterAriel Sharon
Ariel Sharon ( ; also known by his diminutive Arik, ; 26 February 192811 January 2014) was an Israeli general and politician who served as the prime minister of Israel from March 2001 until April 2006.
Born in Kfar Malal in Mandatory Palestin ...
, in his capacity as Minister of Housing & Construction and member of the Ministerial Committee for Immigration & Absorption, launched an unprecedented large-scale construction effort to accommodate the new Russian population in Israel so as to facilitate their smooth integration and encourage further Jewish immigration as an ongoing means of increasing the Jewish population of Israel. Between 1989 and 2006, about 979,000 Jews emigrated from the former Soviet Union to Israel.
Emigration
For many years definitive data on Israeli emigration was unavailable. In ''The Israeli Diaspora'' sociologist Stephen J. Gold maintains that calculation of Jewish emigration has been a contentious issue, explaining, "Since Zionism, the philosophy that underlies the existence of the Jewish state, calls for return home of the world's Jews, the opposite movement—Israelis leaving the Jewish state to reside elsewhere—clearly presents an ideological and demographic problem." In the past several decades, emigration (yerida
Yerida (, "descent") is emigration by Jews from the State of Israel (or in religious texts, Land of Israel). Yerida is the opposite of aliyah (, lit. "ascent"), which is immigration by Jews to Israel. Zionists are generally critical of the act ...
) has seen a considerable increase. From 1990 to 2005, 230,000 Israelis left the country; a large proportion of these departures included people who initially immigrated to Israel and then reversed their course (48% of all post-1990 departures and even 60% of 2003 and 2004 departures were former immigrants to Israel). 8% of Jewish immigrants in the post-1990 period left Israel, while 15% of non-Jewish immigrants did. In 2005 alone, 21,500 Israelis left the country and had not yet returned at the end of 2006; among them 73% were Jews, 5% Arabs, and 22% "Others" (mostly non-Jewish immigrants, with Jewish ancestry, from USSR). At the same time, 10,500 Israelis came back to Israel after over one year abroad; 84% were Jews, 9% Others, and 7% Arabs.
According to the Israel Central Bureau of Statistics, as of 2005, 650,000 Israelis had left the country for over one year and not returned. Of them, 530,000 are still alive today. This number does not include the children born overseas. It should also be noted that Israeli law grants citizenship only to the first generation of children born to Israeli emigrants.
Health
HIV/AIDS – adult prevalence rate
* 0.2% (2009 est.)Obesity – adult prevalence rate
* 26% of women and 40% of men are overweight. In both genders, obesity rate is 15% (as of 2011).Statistilite 133 – Women & Men in Israel – 1990–2011, on cbs.gov.il
Future projections
In June 2013, the Central Bureau of Statistics released a demographic report, projecting that Israel's population would grow to 11.4 million by 2035, with the Jewish population numbering 8.3 million, or 73% of the population, and the Arab population at 2.6 million, or 23%. This includes some 2.3 million Muslims (20% of the population), 185,000 Druze, and 152,000 Christians. The report predicts that the Israeli population growth rate will decline to 1.4% annually, with growth in the Muslim population remaining higher than the Jewish population until 2035, at which point the Jewish population will begin growing the fastest. In 2017, the Central Bureau of Statistics projected that Israel's population would rise to about 18 million by 2059, including 14.4 million Jews and 3.6 million Arabs. Of the Jewish population, about 5.25 million would beHaredi
Haredi Judaism (, ) is a branch of Orthodox Judaism that is characterized by its strict interpretation of religious sources and its accepted (Jewish law) and traditions, in opposition to more accommodating values and practices. Its members are ...
. Overall, the forecast projected that 49% of the population would be either Haredi Jews (29%) or Arabs (20%). It also projected a population of 20 million in 2065. Jews and other non-Arabs are expected to compose 81% of the population in 2065, and Arabs 19%. About 32% of the population is expected to be Haredi.
Other forecasts project that Israel could have a population as high as 23 million, or even 36 million, by 2050.
See also
*Aliyah
''Aliyah'' (, ; ''ʿălīyyā'', ) is the immigration of Jews from Jewish diaspora, the diaspora to, historically, the geographical Land of Israel or the Palestine (region), Palestine region, which is today chiefly represented by the Israel ...
* Crime in Israel
* Culture of Israel
The culture of Israel is closely associated with Jewish culture and rooted in the Jewish history of the diaspora and Zionist movement. It has also been influenced by Arab culture and the history and traditions of the Arab Israeli population and ...
* Demographic history of Palestine (region)
The population of the region of Palestine, which approximately corresponds to modern Israel and the Palestine, has varied in both size and ethnic composition throughout the history of Palestine.
Studies of Palestine's demographic changes over ...
* Demographics of the Middle East
The Demographics of the Middle East describes populations of the Middle East, a region covering western and northern parts of the Asian and African continents respectively.
Overview
;''Encyclopedia Britannica'' definition of Middle East
''Enc ...
* Demographics of the State of Palestine
* Health care in Israel
Healthcare in Israel is Universal health care, universal and participation in a medical insurance plan is compulsory. All Israeli residents are entitled to basic health care as a fundamental right. The Israeli healthcare system is based on the N ...
* Israel Central Bureau of Statistics
The Israel Central Bureau of Statistics (, ''HaLishka HaMerkazit LiStatistika''; ), abbreviated CBS, is an Israeli government office established in 1949 to carry out research and publish statistical data on all aspects of Israeli life, including ...
* Jewish population by country
the world's core Jewish population (those identifying as Jews above all else) was estimated at 15.8 million, which is approximately 0.2% of the 8 billion worldwide population. Israel hosts the largest core Jewish population in the world with ...
* Standard of living in Israel
* Women in Israel
References
Further reading
* * * Book review by John Waterbury. *Videos of academic lectures posted on the official YouTube VOD (video on demand) channel of ''Tel Aviv University
Tel Aviv University (TAU) is a Public university, public research university in Tel Aviv, Israel. With over 30,000 students, it is the largest university in the country. Located in northwest Tel Aviv, the university is the center of teaching and ...
:''
** (28 min)
** (16 min)
** (31 min)
External links
Official website
of the
Israel Central Bureau of Statistics
The Israel Central Bureau of Statistics (, ''HaLishka HaMerkazit LiStatistika''; ), abbreviated CBS, is an Israeli government office established in 1949 to carry out research and publish statistical data on all aspects of Israeli life, including ...
Population of Israel
by the Tourism Ministry
Israel
''
The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a Reference work, reference resource produced by the United States' Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The off ...
''. Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA; ) is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States tasked with advancing national security through collecting and analyzing intelligence from around the world and ...
.
Issues in Israeli Society
at the
Jewish Agency for Israel
The Jewish Agency for Israel (), formerly known as the Jewish Agency for Palestine, is the largest Jewish non-profit organization in the world. It was established in 1929 as the operative branch of the World Zionist Organization (WZO).
As an ...
{{Subject bar, Israel, Society, d=y, auto=1