Deforestation In Brazil on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An estimated 30% of deforestation is due to small farmers; the rate of deforestation in areas they inhabit is greater than in areas occupied by medium and large ranchers, who own 89% of the Legal Amazon's private land. This underlines the importance of using previously cleared land for agriculture, rather than the usual, politically easier path of distributing still-forested areas. The number of small farmers versus large landholders fluctuates with economic and demographic pressures.
An estimated 30% of deforestation is due to small farmers; the rate of deforestation in areas they inhabit is greater than in areas occupied by medium and large ranchers, who own 89% of the Legal Amazon's private land. This underlines the importance of using previously cleared land for agriculture, rather than the usual, politically easier path of distributing still-forested areas. The number of small farmers versus large landholders fluctuates with economic and demographic pressures.
 Deforestation in Brazil has been linked with an extractive
Deforestation in Brazil has been linked with an extractive
mongabay.com. Removal of The Brazilian government granted land to approximately 150,000 families in the Amazon between 1995 and 1998. Poor farmers were also encouraged by the government through programmes such as the National Institute for Colonization and Agrarian Reform in Brazil (INCRA) to farm unclaimed forest land and after a five-year period were given a title and the right to sell the land. The productivity of the soil following forest removal for farming lasts only a year or two before the fields become infertile and farmers must clear new areas of forest to maintain their income. In 1995, nearly half (48%) of the deforestation in Brazil was attributed to poorer farmers clearing lots under in size.
The Brazilian government granted land to approximately 150,000 families in the Amazon between 1995 and 1998. Poor farmers were also encouraged by the government through programmes such as the National Institute for Colonization and Agrarian Reform in Brazil (INCRA) to farm unclaimed forest land and after a five-year period were given a title and the right to sell the land. The productivity of the soil following forest removal for farming lasts only a year or two before the fields become infertile and farmers must clear new areas of forest to maintain their income. In 1995, nearly half (48%) of the deforestation in Brazil was attributed to poorer farmers clearing lots under in size.
 Deforestation and loss of biodiversity have led to high risks of irreversible changes to the Amazon's tropical forests. It has been suggested by modeling studies that the deforestation may be approaching a " tipping point", after which large-scale "savannization" or desertification of the Amazon will take place, with catastrophic consequences for the world's climate, due to a self-perpetuating collapse of the region's biodiversity and
Deforestation and loss of biodiversity have led to high risks of irreversible changes to the Amazon's tropical forests. It has been suggested by modeling studies that the deforestation may be approaching a " tipping point", after which large-scale "savannization" or desertification of the Amazon will take place, with catastrophic consequences for the world's climate, due to a self-perpetuating collapse of the region's biodiversity and
 Between July and October 1987, about of rainforest was burned in the states of
Between July and October 1987, about of rainforest was burned in the states of
 The pressure on deforestation in the Amazon has affected the trade and agricultural productivity in Brazil. One of the leading countries in the demand for agricultural products has been China. The interest from China comes from Brazil's port investments and land infrastructure, which will ensure a fast and efficient transport network for China. This increased demand from China involves a two-step process, using remote-sensing data. The first step of the process comes from international trade flow data, which is used to compute the differential growth in Chinese demand for each product (excluding Brazil). The second step takes the Chinese-product-specific demand growth to municipalities in Brazil based on their production composition in 1995. The data used was sourced from MapBiomas in Brazil, which classifies the land use based on 30-meter LANDSAT images. The exposure to trade with China mitigated the deforestation impacts from new soy technology. In table 2 column 4 in the image to the right, there is a change in the coefficients associated with Chinese demand. Regions that were heavily impacted by both trade and technology shocks saw less deforestation and slower cropland expansion compared to areas that were only influenced by genetically engineered (GE) soy. This suggests that the deforestation effects of GE soy are mitigated in areas with greater exposure to technological advancements and increased demand from China.
The pressure on deforestation in the Amazon has affected the trade and agricultural productivity in Brazil. One of the leading countries in the demand for agricultural products has been China. The interest from China comes from Brazil's port investments and land infrastructure, which will ensure a fast and efficient transport network for China. This increased demand from China involves a two-step process, using remote-sensing data. The first step of the process comes from international trade flow data, which is used to compute the differential growth in Chinese demand for each product (excluding Brazil). The second step takes the Chinese-product-specific demand growth to municipalities in Brazil based on their production composition in 1995. The data used was sourced from MapBiomas in Brazil, which classifies the land use based on 30-meter LANDSAT images. The exposure to trade with China mitigated the deforestation impacts from new soy technology. In table 2 column 4 in the image to the right, there is a change in the coefficients associated with Chinese demand. Regions that were heavily impacted by both trade and technology shocks saw less deforestation and slower cropland expansion compared to areas that were only influenced by genetically engineered (GE) soy. This suggests that the deforestation effects of GE soy are mitigated in areas with greater exposure to technological advancements and increased demand from China.

 In the
In the
''Conservation news and environmental science news.'' 26 Jan 2009. In 2006, Brazil proposed a
In 2006, Brazil proposed a
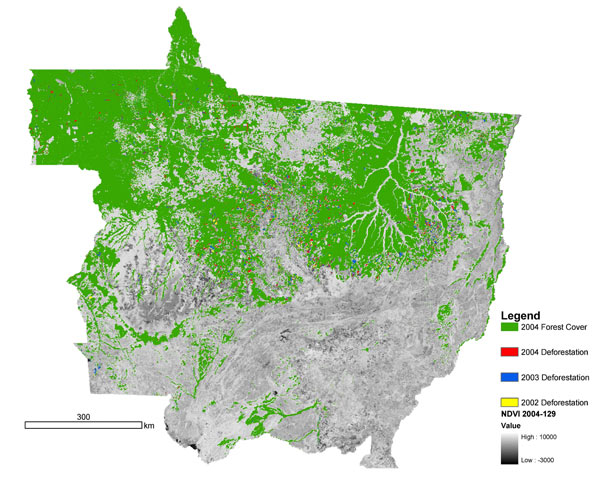 To diminish deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon, some organisations have argued that large financial resources are required to give illegal loggers an economic incentive to pursue other areas of activity. The
To diminish deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon, some organisations have argued that large financial resources are required to give illegal loggers an economic incentive to pursue other areas of activity. The 
INPE
The Amazon's deforestation has been seen to be at its highest levels since 2008. This could have long-term implications for the health of the region and its significant impact on the functionality of the global ecosystem
Models
suggest that the Amazon may be reaching a tipping point due to the deforestation and rising temperatures. Under
Images of deforestation in the Amazon
Reversing deforestation in Brazil? an academic article
Mecanismos y actors Sociales en la deforestación de la Amazonia brasileña
*
Cattle Ranching in the Amazon Region
. Yale School of Forestry & Environmental Studies {{Americas topic, Deforestation in Environmental issues in Brazil
Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
once had the highest deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
rate in the world, and recent data still shows high rates of deforestation. Between 2001 and 2023, Brazil lost 68.9 Mha of tree cover (13% of its total tree cover lost since 2000), and in 2022, Brazilian forest loss accounted for 43% of global deforestation. In 2005, Brazil still had the largest area of forest removed annually. Since 1970, over of the Amazon rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, also called the Amazon jungle or Amazonia, is a Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, moist broadleaf tropical rainforest in the Amazon biome that covers most of the Amazon basin of South America. This basin ...
have been destroyed. In 2001, the Amazon was approximately , which is only 87% of the Amazon's original size. According to official data, about 729,000 km² have already been deforested in the Amazon biome, which corresponds to 17% of the total. 300,000 km² have been deforested in the last 20 years.
Rainforests have decreased in size primarily due to deforestation. Between May 2000 and August 2006, Brazil lost nearly of forest, an area larger than Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
. According to the Living Planet Report
The ''Living Planet Report'' is published every two years by the World Wide Fund for Nature since 1998. It is based on the Living Planet Index and ecological footprint calculations.
The ''Living Planet Report'' is the world's leading, scien ...
2010, deforestation continues at an alarming rate. At the Convention on Biological Diversity
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty. The Convention has three main goals: the conservation of biological diversity (or biodiversity); the sustainable use of its ...
's 9th Conference, 67 ministers signed up to help achieve zero net deforestation by 2020. Due to deforestation the Amazon was a net emitter of greenhouse gas in the 2010s.
The effects include "severe financial losses, social setbacks, and biodiversity loss". Economic losses due to deforestation in Brazil could reach around 317 billion dollars per year, approximately 7 times higher in comparison to the cost of all commodities produced through deforestation. In 2023 the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
, published a report named: "A Balancing Act for Brazil’s Amazonian States: An Economic Memorandum" proposing non-deforestation based economic program in the region of the Amazon rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, also called the Amazon jungle or Amazonia, is a Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, moist broadleaf tropical rainforest in the Amazon biome that covers most of the Amazon basin of South America. This basin ...
.
History
The deforestation of the Atlantic forest, or ''Mata Atlântica'', dates back to Portuguese colonization and the subsequent rapid development of urban centers. Before human-modification, the forest covered around 17% of Brazil's area. Unlike the Amazon, which has only faced extreme deforestation in recent years, the Atlantic Forest has been a long-lasting target for land development, speculation, and agricultural endeavors. Starting during the sixteenth century, the forest began facing pressure due to the unsustainable development of coffee, sugarcane, brazilwood, and cattle in the region. In the 1940s Brazil began a program of national development in the Amazon Basin. President Getúlio Vargas declared emphatically that: Before the 1960s, much of the forest remained intact due to restrictions on access to the Amazon beyond partial clearing along the river banks. The poor soil madeplantation
Plantations are farms specializing in cash crops, usually mainly planting a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Plantations, centered on a plantation house, grow crops including cotton, cannabis, tob ...
-based agriculture unprofitable. The key point in deforestation of the Amazon came when colonists established farms in the forest in the 1960s. They farmed based on crop cultivation and used the slash and burn
Slash-and-burn agriculture is a form of shifting cultivation that involves the cutting and burning of plants in a forest or woodland to create a field called a swidden. The method begins by cutting down the trees and woody plants in an area. T ...
method. The colonists were unable to successfully manage their fields and the crops due to weed invasion and loss of soil fertility
Soil fertility refers to the ability of soil to sustain agricultural plant growth, i.e. to provide plant habitat and result in sustained and consistent yields of high quality.
.Watkins and Griffiths, J. (2000). Forest Destruction and Sustainable Agriculture in the Brazilian Amazon: a Literature Review (Doctoral dissertation, The University of Reading, 2000). Dissertation Abstracts International, 15-17 Soils in the Amazon are productive for only a very short period of time after the land is cleared, so farmers there must constantly move and clear more and more land.
Amazonian colonization
475px, Map of the year each country achieved List of sovereign states by date of formation, independence.
Colonization (British English: colonisation) is a process of establishing occupation of or control over foreign territories or peoples f ...
was dominated by cattle raising, not only because grass did grow in the poor soil, but also because ranching required little labor, generated decent profit, and awarded social status
Social status is the relative level of social value a person is considered to possess. Such social value includes respect, honour, honor, assumed competence, and deference. On one hand, social scientists view status as a "reward" for group members ...
. However, farming led to extensive deforestation and environmental damage. Williams, M. (2006). ''Deforesting the Earth: From Prehistory to Global Crisis''. Chicago, IL: The University of Chicago Press.
 An estimated 30% of deforestation is due to small farmers; the rate of deforestation in areas they inhabit is greater than in areas occupied by medium and large ranchers, who own 89% of the Legal Amazon's private land. This underlines the importance of using previously cleared land for agriculture, rather than the usual, politically easier path of distributing still-forested areas. The number of small farmers versus large landholders fluctuates with economic and demographic pressures.
An estimated 30% of deforestation is due to small farmers; the rate of deforestation in areas they inhabit is greater than in areas occupied by medium and large ranchers, who own 89% of the Legal Amazon's private land. This underlines the importance of using previously cleared land for agriculture, rather than the usual, politically easier path of distributing still-forested areas. The number of small farmers versus large landholders fluctuates with economic and demographic pressures.
Causes
 Deforestation in Brazil has been linked with an extractive
Deforestation in Brazil has been linked with an extractive economic growth
In economics, economic growth is an increase in the quantity and quality of the economic goods and Service (economics), services that a society Production (economics), produces. It can be measured as the increase in the inflation-adjusted Outp ...
model that relies on factor accumulation (labor, capital, land) rather than total factor productivity
In economics, total-factor productivity (TFP), also called multi-factor productivity, is usually measured as the ratio of aggregate output (e.g., GDP) to aggregate inputs. Under some simplifying assumptions about the production technology, growt ...
, where Brazil's frontier expansion in the "arc of deforestation" is a manifestation of land accumulation. Under this model, with a strong focus on commodities exports, deforestation is an economic choice, often linked to cattle ranching, mining, soybean production or logging, and influenced by factors raising the external competitiveness of Amazonian farmers, ranging from infrastructure development (especially roads) to a depreciating real exchange rate. Land grabbing
Land grabbing is the large-scale acquisition of land through buying or leasing of large pieces of land by domestic and Multinational corporation, transnational companies, governments, and individuals.
While used broadly throughout history, land g ...
in the Amazon is associated with the rational expectation that this growth model will continue to raise rural land prices, creating incentives to grab public lands.
Cattle ranching and infrastructure
Livestock and agriculture have never been very strong in the Amazon: the area has a bad soil and climate for planting, and cattle, although they reach the margins of the forest, are actually spread throughout the country, being the areas that have less cattle throughout Brazil, coastal regions and the Amazon. States likeGoiás
Goiás () is a Brazilian States of Brazil, state located in the Central-West Region, Brazil, Central-West region. Goiás borders the Federal District (Brazil), Federal District and the states of (from north clockwise) Tocantins, Bahia, Minas Ge ...
, Mato Grosso do Sul
Mato Grosso do Sul ( ) is one of Federative units of Brazil, Brazil's 27 federal units, located in the southern part of the Central-West Region, Brazil, Central-West Region, bordering five Brazilian states: Mato Grosso (to the north), Goiás and ...
and Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is one of the 27 federative units of Brazil, being the fourth largest state by area and the second largest in number of inhabitants with a population of 20,539,989 according to the 2022 Brazilian census, 2022 census. Located in ...
have a lot of cattle. The annual rate of deforestation in the Amazon region continued to increase from 1990 to 2003 because of factors at local, national, and international levels. Seventy per cent of formerly forested land in the Amazon, and 91% of land deforested since 1970, is used for livestock pasture
Pasture (from the Latin ''pastus'', past participle of ''pascere'', "to feed") is land used for grazing.
Types of pasture
Pasture lands in the narrow sense are enclosed tracts of farmland, grazed by domesticated livestock, such as horses, c ...
. The Brazilian government initially attributed 38% of all forest loss
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then land conversion, converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or u ...
between 1966 and 1975 to large-scale cattle ranching
A ranch (from /Mexican Spanish) is an area of land, including various structures, given primarily to ranching, the practice of raising grazing livestock such as cattle and sheep. It is a subtype of farm. These terms are most often applied to li ...
. According to the Center for International Forestry Research (CIFOR), "between 1990 and 2001 the percentage of Europe's processed meat imports that came from Brazil rose from 40 to 74 percent" and by 2003 "for the first time ever, the growth in Brazilian cattle production, 80 percent of which was in the Amazon was largely export driven."
Forest removal to make way for cattle ranching
A ranch (from /Mexican Spanish) is an area of land, including various structures, given primarily to ranching, the practice of raising grazing livestock such as cattle and sheep. It is a subtype of farm. These terms are most often applied to li ...
was the leading cause of deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon from the mid-1960s on. In addition to Vargas's earlier goal of commercial development, the devaluation of the Brazilian real
The Brazilian real (plural, pl. '; currency symbol, sign: R$; ISO 4217, code: BRL) is the official currency of Brazil. It is subdivided into 100 centavos. The Central Bank of Brazil is the central bank and the issuing authority. The real repl ...
against the dollar
Dollar is the name of more than 25 currencies. The United States dollar, named after the international currency known as the Spanish dollar, was established in 1792 and is the first so named that still survives. Others include the Australian d ...
had the result of doubling the price of beef
Beef is the culinary name for meat from cattle (''Bos taurus''). Beef can be prepared in various ways; Cut of beef, cuts are often used for steak, which can be cooked to varying degrees of doneness, while trimmings are often Ground beef, grou ...
in reals; this gave ranchers a widespread incentive to increase the size of their cattle ranches and areas under pasture for mass beef production, resulting in large areas of forest removal."Deforestation in the Amazon."mongabay.com. Removal of
forest cover
Forest cover is the amount of trees that covers a particular area of land. It may be measured as relative (in percent) or absolute (in square kilometres/ square miles). Nearly a third of the world's land surface is covered with forest, with clos ...
for cattle farming in Brazil was also seen by developers as an economic investment during periods of high inflation, when appreciation of cattle prices provided a way to outpace the interest earned on money left in the bank. Brazilian beef was more competitive on the world market at a time when extensive improvements in the road network in the Amazonas (such as the introduction of the Trans-Amazonian Highway in the early 1970s) gave potential developers access to vast areas of previously inaccessible forest. This coincided with lower transportation costs due to cheaper fuels such as ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
, which lowered the costs of shipping the beef and further incentivized the development of remote forested areas.
Cattle ranching is not an environmentally friendly investment because cattle emit large amounts of methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
. These emissions play a major role in climate change because methane's ability to trap heat is 20 times greater than that of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
in a time horizon of 100 years and exponentially higher in shorter time horizons. One cow can emit up to 130 gallons of methane a day, just by belching.
 The Brazilian government granted land to approximately 150,000 families in the Amazon between 1995 and 1998. Poor farmers were also encouraged by the government through programmes such as the National Institute for Colonization and Agrarian Reform in Brazil (INCRA) to farm unclaimed forest land and after a five-year period were given a title and the right to sell the land. The productivity of the soil following forest removal for farming lasts only a year or two before the fields become infertile and farmers must clear new areas of forest to maintain their income. In 1995, nearly half (48%) of the deforestation in Brazil was attributed to poorer farmers clearing lots under in size.
The Brazilian government granted land to approximately 150,000 families in the Amazon between 1995 and 1998. Poor farmers were also encouraged by the government through programmes such as the National Institute for Colonization and Agrarian Reform in Brazil (INCRA) to farm unclaimed forest land and after a five-year period were given a title and the right to sell the land. The productivity of the soil following forest removal for farming lasts only a year or two before the fields become infertile and farmers must clear new areas of forest to maintain their income. In 1995, nearly half (48%) of the deforestation in Brazil was attributed to poorer farmers clearing lots under in size.
Mining
Mining has also increased deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon, particularly since the 1980s, with miners often clearing forest to open the mines or to provide building material, collecting wood for fuel and subsistence agriculture. In February 2017, the Brazilian government provided a reservation with a surface of for deforestation, to attract foreign mining investors. In September 2017, the government withdrew this permission.Soybean production
Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
is currently the second-largest global producer of soybeans
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean. Soy is a staple crop, the world's most grown legume, and an important animal feed.
Soy is a key source of f ...
after the United States, mostly for livestock
Livestock are the Domestication, domesticated animals that are raised in an Agriculture, agricultural setting to provide labour and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, Egg as food, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The t ...
feed. As stated in the Constitution of Brazil
The Constitution of the Federative Republic of Brazil () is the Constitution, supreme law of Brazil. It is the foundation and source of the legal authority underlying the existence of Brazil and the federal government of Brazil. It replaced the ...
, clearing land for crops or fields is considered an "effective use" of land and is the first step toward land ownership. Cleared property is also valued 5–10 times more than forested land, and for that reason is valuable to the owner whose ultimate objective is resale. The soy industry is an important exporter for Brazil; therefore, the needs of soy farmers have been used to validate many of the controversial transportation projects being developed in the Amazon.
However, the Amazonian soil is of very low quality for plantations: it has few nutrients and the soil is sterile after two or three years of planting. In 2020, only 5% of the country's agricultural production came from the Northern Region. Most of the soy plantation in the country is practiced in the region of Cerrado
The Cerrado () is a vast ecoregion of Tropics, tropical savanna in central Brazil, being present in the states of Goiás, Mato Grosso do Sul, Mato Grosso, Tocantins, Maranhão, Piauí, Bahia, Minas Gerais, São Paulo (state), São Paulo, Paraná ...
, a savanna with little vegetation that was barren and where agriculture was impractical until a few years ago. Thanks to EMBRAPA, Brazil adapted plants for cultivation in this region, since Brazil has many terrible biomes for the practice of agriculture and livestock, such as the Semi-Arid Region of the Northeast, the Amazon Forest itself or the mountainous plateaus in the Southeast.
Cargill
Cargill, Incorporated is an American multinational food corporation based in Minnetonka, Minnesota, Minnetonka, Minnesota, and incorporated in Wilmington, Delaware. Founded in 1865 by William Wallace Cargill, it is the largest privately held c ...
, a multinational company which controls the majority of the soya bean trade in Brazil, has been criticized, along with fast food chains like McDonald's, by Greenpeace
Greenpeace is an independent global campaigning network, founded in Canada in 1971 by a group of Environmental movement, environmental activists. Greenpeace states its goal is to "ensure the ability of the Earth to nurture life in all its biod ...
for accelerating the deforestation of the Amazon. Cargill is the main supplier of soya beans to large fast food companies such as McDonald's which use the soy products to feed their cattle and chickens. As fast-food chains expand, the chains must increase the quantity of their livestock in order to produce more products. In order to meet the resulting demand for soya, Cargill has expanded its soy production by clear-cutting parts of the Amazon.
A report by Greenpeace mentions that European supermarket giant Tesco
Tesco plc () is a British multinational groceries and general merchandise retailer headquartered in the United Kingdom at its head offices in Welwyn Garden City, England. The company was founded by Jack Cohen (businessman), Sir Jack Cohen in ...
told Greenpeace that 99% of its soya footprint is made up of animal feed. This is responsible for more than 500,000 tonnes of soya imports into the UK each year, making up more than a sixth of the total.
The same report by Greenpeace also mentions that animal feed for meat production is Europe's largest contribution to deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
, with soya imports representing 47% of Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
’s deforestation footprint, compared to 14% for pasture expansion for livestock and 10% for palm oil. Greenpeace called for "a new EU law to protect forests by keeping any product that comes from forest destruction off the European market."
In 2020, the Amsterdam Declarations Partnership (which includes Germany, France, Denmark, Italy, Norway, the UK and the Netherlands) sent an open letter to vice president Hamilton Mourão, stating that Brazil's backwards moves in environmental protection were threatening Europe's desire to source its food sustainably.
The first two highways, the Rodovia Belém-Brasília (1958) and the Cuiabá
Cuiabá () is the capital city and the largest city of the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso. It is located near the geographical centre of South America and also forms the metropolitan area of Mato Grosso, along with the neighbouring town of Várz ...
-Porto Velho
Porto Velho (, ''Old Port'') is the capital (political), capital of the Brazilian States of Brazil, state of Rondônia, in the upper Amazon River basin. The population is 460,434 people (as of the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics, ...
(1968), were the only federal highways in the Legal Amazon to be paved and passable year-round before the late 1990s. These two highways are said to be "at the heart of the ‘arc of deforestation’" that is the epicenter of deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon. The Belém-Brasília Highway attracted nearly two million settlers in its first twenty years. The success of the Belém-Brasília highway in opening up the forest was re-enacted as paved roads continued to be developed, unleashing the irrepressible spread of settlement. The completion of the roads were followed by a wave of resettlement and the settlers had a significant effect on the forest.
Scientists using NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
satellite data have found that clearing for mechanized cropland has recently become a significant force in Brazilian Amazon deforestation. This change in land use may alter the region's climate and the land's ability to absorb carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
. Researchers found that in 2003, the peak year of deforestation, more than 20 percent of the Mato Grosso
Mato Grosso ( – ) is one of the states of Brazil, the List of Brazilian states by area, third largest by area, located in the Central-West Region, Brazil, Central-West region. The state has 1.66% of the Brazilian population and is responsible ...
state's forests were converted to cropland. This finding suggests that the recent cropland expansion in the region is contributing to further deforestation. In 2005, soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean. Soy is a staple crop, the world's most grown legume, and an important animal feed.
Soy is a key source o ...
prices fell by more than 25 percent and some areas of Mato Grosso showed a decrease in large deforestation events, although the central agricultural zone continued to clear forests. But, deforestation rates could return to the high levels seen in 2003 as soybean and other crop prices begin to rebound in international markets. Brazil has become a leading worldwide producer of grains
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit ( caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and le ...
including soybean, which accounts for 5% of the nation's exports. This new driver of forest loss suggests that the rise and fall of prices for other crops, beef and timber may also have a significant impact on future land use in the region, according to the study.
Logging
The export of tree trunks native to the Amazon (selling fresh wood, that is, without any type of processing), is an illegal activity in Brazil. However, it is common to see, in Europe, the sale of furniture produced with illegal Brazilian woods, such asjacaranda
''Jacaranda'' is a genus of 49 species of flowering plants in the family Bignoniaceae, native to tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas while cultivated around the world. The generic name is also used as the common name.
The species ' ...
and mahogany
Mahogany is a straight- grained, reddish-brown timber of three tropical hardwood species of the genus ''Swietenia'', indigenous to the AmericasBridgewater, Samuel (2012). ''A Natural History of Belize: Inside the Maya Forest''. Austin: Universit ...
. Timber arrives illegally in Europe and the countries of the continent do not take action to block these imports. Logging in Brazil's Amazon is economically motivated. The economic opportunity for developing regions is driven by timber export and demand for charcoal. Charcoal-producing ovens use large amounts of timber. In one month, the Brazilian government destroyed 800 illegal ovens in Tailândia. These 800 ovens were estimated to consume about 23,000 trees per month. Logging for timber export is selective, since only a few species, such as mahogany, have commercial value and are harvested. Selective logging still does a lot of damage to the forest. For every tree harvested, 5-10 other trees are logged, to transport the logs through the forest. Also, a falling tree takes down a lot of other small trees. A logged forest contains significantly fewer species than areas where selective logging has not taken place. A forest disturbed by selective logging is also significantly more vulnerable to fire.
Logging in the Amazon, in theory, is controlled and only strictly licensed individuals are allowed to harvest the trees in selected areas. In practice, illegal logging
Illegal logging is the harvest, transportation, purchase, or sale of timber in violation of laws. The harvesting procedure itself may be illegal, including using corrupt means to gain access to forests; extraction without permission, or from a p ...
is widespread in Brazil. Up to 60 to 80 percent of all logging in Brazil is estimated to be illegal, with 70% of the timber cut wasted in the mills. Most illegal logging companies are international companies that don't replant the trees and the practice is extensive. Expensive wood such as mahogany is illegally exported to profit these companies. Fewer trees mean that less photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
will occur and therefore oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
levels drop. Carbon dioxide emissions increase, as this gas is released from a tree when it's cut down and burned or left to rot. A tree can absorb as much as 48 pounds of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
per year so illegal logging has a major impact on climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
.
To combat this destruction, the Brazilian government has stopped issuing new permits for logging. Unauthorized harvesting has continued nonetheless. Efforts to prevent cutting down forests include payments to landowners. Instead of banning logging altogether, the government hopes payments of comparable sums will dissuade owners from further deforestation.
Weak non-commodities sectors
Brazil's legacy ofimport substitution industrialization
Import substitution industrialization (ISI) is a protectionist trade and economics, economic policy that advocates replacing foreign imports with domestic production. It is based on the premise that a country should attempt to reduce its foreign ...
is reflected in an imbalance where export-oriented commodities sectors are much stronger than more domestically oriented and protected manufacturing and services: between 1996 and 2022 labor productivity in agriculture grew by 5.8% in agriculture and 2.9% in mining, while it fell by 0.8% in manufacturing, with mixed experience in services. Yet on the agricultural frontier in the Amazon the Jevons paradox
In economics, the Jevons paradox (; sometimes Jevons effect) occurs when technological advancements make a resource more efficient to use (thereby reducing the amount needed for a single application); however, as the cost of using the resourc ...
implies that agricultural productivity growth accelerates deforestation. Stronger productivity gains in manufacturing and services, the more urban sectors which are critical for an urbanized population like Brazil's, would take pressure off the agricultural frontier in the Amazon.
The COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
has increased deforestation in Brazil. The government has been preoccupied by the global pandemic, and unchecked illegal activity has taken place. “The trend line is shooting upward compared to a year that was already historic in terms of a rise in deforestation,” said federal prosecutor Ana Carolina Haliuc Bragança.“If state entities don’t adopt very decisive measures, we’re looking at a likely tragedy.”
Climate change
Climate change plays a significant role in the wildfires in thePantanal
The Pantanal () is a natural region encompassing the world's largest tropical wetland area, and the world's largest Flooded grasslands and savannas, flooded grasslands. It is located mostly within the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul, but i ...
.
Effects
 Deforestation and loss of biodiversity have led to high risks of irreversible changes to the Amazon's tropical forests. It has been suggested by modeling studies that the deforestation may be approaching a " tipping point", after which large-scale "savannization" or desertification of the Amazon will take place, with catastrophic consequences for the world's climate, due to a self-perpetuating collapse of the region's biodiversity and
Deforestation and loss of biodiversity have led to high risks of irreversible changes to the Amazon's tropical forests. It has been suggested by modeling studies that the deforestation may be approaching a " tipping point", after which large-scale "savannization" or desertification of the Amazon will take place, with catastrophic consequences for the world's climate, due to a self-perpetuating collapse of the region's biodiversity and ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
s. In 2018, about 17% of the Amazon rainforest was already destroyed. Research suggests that upon reaching about 20–25%, the tipping point to flip it into a non-forest ecosystems (in eastern, southern and central Amazonia) could be reached.
The result of passing the tipping point will be catastrophic for both and will hurt global food security. Carlos Nobres, a climate scientist, said: “Brazil should be battling the most o protect the Amazon because it has the most to lose,”. Experts note that avoiding deforestation and climate change is a top interest of the agricultural sector. This is something that's only been expedited by the current president of Brazil, Jair Bolsonaro, with major staff and budgeting cuts in relation to environmental enforcement.
Climate change
 Between July and October 1987, about of rainforest was burned in the states of
Between July and October 1987, about of rainforest was burned in the states of Pará
Pará () is a Federative units of Brazil, state of Brazil, located in northern Brazil and traversed by the lower Amazon River. It borders the Brazilian states of Amapá, Maranhão, Tocantins (state), Tocantins, Mato Grosso, Amazonas (Brazilian st ...
, Mato Grosso
Mato Grosso ( – ) is one of the states of Brazil, the List of Brazilian states by area, third largest by area, located in the Central-West Region, Brazil, Central-West region. The state has 1.66% of the Brazilian population and is responsible ...
, Rondônia
Rondônia () is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the northern subdivision of the country (central-western part). It is bordered by Acre (state), Acre in the west,
Amazonas, Brazil, Amazonas in the north, Mato Grosso in the east, and Bo ...
, and Acre
The acre ( ) is a Unit of measurement, unit of land area used in the Imperial units, British imperial and the United States customary units#Area, United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one Chain (unit), ch ...
releasing more than 500 million tons of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
, 44 million tons of carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
, and millions of tons of nitrogen oxide
Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
Charge-neutral
*Nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen(II) oxide, or nitrogen monoxide
* Nitrogen dioxide (), nitrogen(IV) oxide
* Nitrogen trioxide (), o ...
s and other poisonous chemicals into the atmosphere.
Carbon present in the trees is essential for ecosystem development and plays a key role in the regional and global climate. Fallen leaves from deforestation leave behind a mass of dead plant material known as slash, which on decomposition provides a food source for invertebrates. This has the indirect effect of increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
levels through respiration and microbial activity. Simultaneously the organic carbon in the soil structure becomes depleted; the presence of carbon plays a vital role in the functioning of life in any ecosystem.
Biodiversity
Rainforests are the oldest ecosystems on earth. Rainforest plants and animals continue to evolve, developing into the most diverse and complex ecosystems on earth. Living in limited areas, most of these species are endemic, found nowhere else in the world. In tropical rainforests, an estimated 90% of the species of the ecosystem live in the canopy. Since tropical rainforests are estimated to hold 50% of the planet's species, the canopy of rainforests worldwide may hold 45% of life on Earth. The Amazon rainforest borders eight countries, and has the world's largest river basin and is the source of 1/5 of the Earth's river water. It has the world's greatest diversity of birds and freshwater fish. The Amazon is home to more species of plants and animals than any other terrestrial ecosystem on the planet—perhaps 30% of the world's species are found there. More than 300 species of mammals are found in the Amazon, the majority of them bats and rodents. The Amazon basin contains more freshwater fish species than anywhere else in the world—more than 3,000 species. More than 1,500 bird species are also found there. Frogs are overwhelmingly the most abundant amphibians in the rainforest. Species interdependence takes many forms in the forest, from species relying on other species for pollination and seed dispersal to predator-prey relationships and symbiotic relationships. Each species that disappears from the ecosystem may weaken the survival chances of another, while the loss of akeystone species
A keystone species is a species that has a disproportionately large effect on its natural environment relative to its abundance. The concept was introduced in 1969 by the zoologist Robert T. Paine. Keystone species play a critical role in main ...
—an organism that links many other species together—could cause a significant disruption in the functioning of the entire system.
Indigenous people
A WRI report mentions that “tenure-secure” indigenous lands generates billions and sometimes trillions of dollars’ worth of benefits in the form ofcarbon sequestration
Carbon sequestration is the process of storing carbon in a carbon pool. It plays a crucial role in Climate change mitigation, limiting climate change by reducing the amount of Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, carbon dioxide in the atmosphe ...
, reduced pollution, clean water and more. It says that
tenure-secure indigenous lands have low deforestation rates, they help to reduce GHG emissions, control erosion and flooding by anchoring soil, and provide a suite of other local, regional and global “ecosystem services
Ecosystem services are the various benefits that humans derive from Ecosystem, ecosystems. The interconnected Biotic_material, living and Abiotic, non-living components of the natural environment offer benefits such as pollination of crops, clean ...
.”
However, many of these communities find themselves on the front lines of the deforestation crisis, and their lives and livelihoods threatened.
On March 30, 2020, land defender Zezico Guajajara's body was found near his village. Zezico was a member of the protected Guajajara Tribe in the Amazon who started the Guardians of the Forest in 2012.
The Yanomami people, one of the largest Indigenous groups in Brazil, have seen their lands increasingly threatened by illegal deforestation and mining activities. Satellite data shows over 2,000 hectares of their land have been deforested for illegal gold mining between 2019 and 2022.
Land degradation
Deforestation for the export oftimber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into uniform and useful sizes (dimensional lumber), including beams and planks or boards. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, window frames). ...
removes valuable protection for the soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
s in a dynamic ecosystem; thus regions are prone to desertification
Desertification is a type of gradual land degradation of Soil fertility, fertile land into arid desert due to a combination of natural processes and human activities.
The immediate cause of desertification is the loss of most vegetation. This i ...
and silting of river banks as rivers become clogged with eroded
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is disti ...
soils in sparse areas. If too much timber is cut, soil that once had sufficient cover can get baked and dry out in the sun, leading to erosion and degradation of soil fertility; this means farmers cannot profit from their land even after clearing it. According to the United Nations Environmental Programme (UNEP) in 1977, deforestation is a major cause of desertification and in 1980 threatened 35% of the world's land surface and 20% of the world's population.
From 2003-2019, carbon losses due to soil erosion from land degradation have increased in the Brazilian Amazon. In this time frame, carbon loss totaled 3,042 MtC. Degradation has accounted for 44% of carbon losses with 56% coming from deforestation. Activities like logging, fire, mining and oil extraction have led to increased numbers in the area. These combined effects have hindered forests' ability to absorb carbon. For Brazil, it is important to reduce standing pressure on standing forests, which is where tree species and plants compete for light, air, water and nutrients. They need to create financial mechanisms to help landowners incentivize conservation of forests on private lands. A mechanism could be established under Brazil’s Forest Code with the environmental reserve quotas. The Brazilian Forest Code requires landowners in the Amazon to maintain 35 to 80 percent of their property under native vegetation.
Pollution
Exploitation of forests for mining activities such asgold mining
Gold mining is the extraction of gold by mining.
Historically, mining gold from Alluvium, alluvial deposits used manual separation processes, such as gold panning. The expansion of gold mining to ores that are not on the surface has led to mor ...
has also significantly increased the risk of mercury poisoning and contamination of the ecosystem and water. Mercury poisoning
Mercury poisoning is a type of metal poisoning due to exposure to mercury. Symptoms depend upon the type, dose, method, and duration of exposure. They may include muscle weakness, poor coordination, numbness in the hands and feet, skin rashe ...
can affect the food chain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web, often starting with an autotroph (such as grass or algae), also called a producer, and typically ending at an apex predator (such as grizzly bears or killer whales), detritivore (such as ...
and affect wildlife
Wildlife refers to domestication, undomesticated animals and uncultivated plant species which can exist in their natural habitat, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wilderness, wild in an area without being species, introdu ...
both on land and in the rivers. It can also affect plants and the crops of farmers trying to farm forest areas. Pollution may result from mine sludge and affect the functioning of the river system when exposed soil is blown in the wind and can have a significant impact on aquatic populations further affected by dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aqua ...
building in the region. Dams may have a profound impact on migrating fish and ecological life and leave plains prone to flooding and leaching.
In August 2019, smoke from wildfires in Brazil's rainforests became so thick that it arrived in São Paulo
São Paulo (; ; Portuguese for 'Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul') is the capital of the São Paulo (state), state of São Paulo, as well as the List of cities in Brazil by population, most populous city in Brazil, the List of largest cities in the ...
and plunged the city into darkness in the middle of the day for an hour, prompting the spread of the hashtag "prayforamazonia" on social media.
Drought
The deforestation of the Amazon has already had a significant negative impact on Brazil's freshwater supply, harming, among others, the agricultural industry that has contributed to the clearing of the forests. In 2005, parts of the Amazon basin experienced the worst drought in more than a century. This has been the result of two factors: # The rainforest provides much of therainfall
Rain is a form of precipitation where water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. ...
in Brazil, even in areas far from it. Deforestation increased the impacts of the droughts of 2005, 2010, and 2015–2016.
# The rainforest, by inducing rainfall and helping with water storage, provides freshwater to the rivers that give water to Brazil and other countries.
Even modest increases in Amazon forest loss may reduce water supplies in Brazilian cities and in neighboring countries. More massive deforestation could alter water supplies as far away as Africa or California.
As of 2020 deforestation in Brazil is close to reach a tipping point after which the forest will change to savanna. The result of passing such tipping point will be catastrophic for the agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
and hydroelectricity in Brazil. Already both sectors are severely hurt. For example, the rainy season has been shortened by 15 – 30 days in 40 years, the amount of rainfall decreased, the harvest became lower in many areas, the mega dam Belo Monte can produce less power. In the future, the soya sector can lose 40% of productivity even in areas with low risk, the hydroelectric sector more than 80%. The lack of water can cause water conflict between the different sectors of the economy. Also passing the tipping point will hurt global food security.
Rainforests are home to a wide range of animal and plant species and an enormous biodiversity. They are also hugely important for absorbing carbon dioxide and returning it to oxygen. The loss of the Amazon rainforests would mean an acceleration of climate change and cause the world's weather patterns to be much more unstable.
Carlos Nobre, a climate scientist says: “Brazil should be battling the most o protect the Amazonbecause it has the most to lose.” Experts note that avoiding deforestation and climate change is a top interest of the agricultural sector because it existence depending on it.
A 2022 study found that 28% of the agricultural land in Brazil is no more climatically optimal due to climate change and to change in local climate as a result of deforestation. The number will go to 51% by 2030 and 74% by 2060 if the change in climate will continue in the same way. Brazil has a strong interest in forest conservation as its agriculture sector directly depends on its forests.
Temperature
In 2019, a group of scientists published research suggesting that in a "business as usual" scenario, the deforestation of the Amazon Rainforest would raise the temperature in Brazil by 1.45 degrees. They wrote: "Increased temperatures in already hot locations may increase human mortality rates andelectricity demand
World energy supply and consumption refers to the global supply of energy resources and its consumption. The system of global energy supply consists of the energy development, refinement, and trade of energy. Energy supplies may exist in var ...
s, reduce agricultural yields and water resources
Water resources are natural resources of water that are potentially useful for humans, for example as a source of drinking water supply or irrigation water. These resources can be either Fresh water, freshwater from natural sources, or water produ ...
, and contribute to biodiversity collapse, particularly in tropical regions. Furthermore, local warming may cause shifts in species distributions, including for species involved in infectious disease transmissions." The authors of the paper say that deforestation is already causing a rise in the temperature.
Economic effects
According to theWorld Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
, economic losses due to deforestation in Brazil could reach around 317 billion dollars per year, approximately 7 times higher in comparison to the cost of all commodities produced through deforestation.
As of 2024, the Amazon drought continues to be an issue economically for Brazil. With dried up rivers as well as forest fires, the productivity of work in the Amazon has gone down. The Brazilian Legal Amazon (LAM) covers 60% of the national territory, with 23% of it already being deforested. This deforestation is driven by factors including agriculture, soy cultivation, cattle ranching, and logging. These activities are often incentivized by government policies and market demands, leading to increased land clearing by deforestation.
The demand for these products outside of the Amazon has put pressure on the use of natural resources and led to the reshaping of the socio-economic landscapes. The main economic driving force has been from foreign countries and Brazil itself. This export-driven deforestation is responding to the rapid pressure on natural resources.
 The pressure on deforestation in the Amazon has affected the trade and agricultural productivity in Brazil. One of the leading countries in the demand for agricultural products has been China. The interest from China comes from Brazil's port investments and land infrastructure, which will ensure a fast and efficient transport network for China. This increased demand from China involves a two-step process, using remote-sensing data. The first step of the process comes from international trade flow data, which is used to compute the differential growth in Chinese demand for each product (excluding Brazil). The second step takes the Chinese-product-specific demand growth to municipalities in Brazil based on their production composition in 1995. The data used was sourced from MapBiomas in Brazil, which classifies the land use based on 30-meter LANDSAT images. The exposure to trade with China mitigated the deforestation impacts from new soy technology. In table 2 column 4 in the image to the right, there is a change in the coefficients associated with Chinese demand. Regions that were heavily impacted by both trade and technology shocks saw less deforestation and slower cropland expansion compared to areas that were only influenced by genetically engineered (GE) soy. This suggests that the deforestation effects of GE soy are mitigated in areas with greater exposure to technological advancements and increased demand from China.
The pressure on deforestation in the Amazon has affected the trade and agricultural productivity in Brazil. One of the leading countries in the demand for agricultural products has been China. The interest from China comes from Brazil's port investments and land infrastructure, which will ensure a fast and efficient transport network for China. This increased demand from China involves a two-step process, using remote-sensing data. The first step of the process comes from international trade flow data, which is used to compute the differential growth in Chinese demand for each product (excluding Brazil). The second step takes the Chinese-product-specific demand growth to municipalities in Brazil based on their production composition in 1995. The data used was sourced from MapBiomas in Brazil, which classifies the land use based on 30-meter LANDSAT images. The exposure to trade with China mitigated the deforestation impacts from new soy technology. In table 2 column 4 in the image to the right, there is a change in the coefficients associated with Chinese demand. Regions that were heavily impacted by both trade and technology shocks saw less deforestation and slower cropland expansion compared to areas that were only influenced by genetically engineered (GE) soy. This suggests that the deforestation effects of GE soy are mitigated in areas with greater exposure to technological advancements and increased demand from China.
NASA survey

 In the
In the American Meteorological Society
The American Meteorological Society (AMS) is a scientific and professional organization in the United States promoting and disseminating information about the atmospheric, oceanic, and hydrologic sciences. Its mission is to advance the atmosph ...
'' Journal of Climate'', two research meteorologists at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C., in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959, as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC ...
, Andrew Negri and Robert Adler, have analysed the impact of deforestation on climatic patterns in the Amazon using data and observatory readings collected from NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission over many years.
Working with the University of Arizona
The University of Arizona (Arizona, U of A, UArizona, or UA) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Tucson, Arizona, United States. Founded in 1885 by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, it ...
and the North Carolina State University
North Carolina State University (NC State, North Carolina State, NC State University, or NCSU) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Raleigh, North Carolina, United States. Founded in 1887 and p ...
, Negri said, "In deforested areas, the land heats up faster and reaches a higher temperature, leading to localized upward motions that enhance the formation of clouds and ultimately produce more rainfall".
They also examined cloud cover
Cloud cover (also known as cloudiness, cloudage, or cloud amount) refers to the fraction of the sky obscured by clouds on average when observed from a particular location. Okta is the usual unit for measurement of the cloud cover. The cloud c ...
in deforested areas. In comparison with areas still unaffected by deforestation, they found a significant increase in cloud cover and rainfall
Rain is a form of precipitation where water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. ...
during the August–September wet season
The wet season (sometimes called the rainy season or monsoon season) is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. Generally, the season lasts at least one month. The term ''green season'' is also sometimes used a ...
where the forest had been cleared. The height or existence of plants and trees in the forest directly affects the aerodynamics
Aerodynamics () is the study of the motion of atmosphere of Earth, air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dynamics and its subfield of gas dynamics, and is an ...
of the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
, and precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
in the area. In addition, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a Private university, private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of moder ...
developed a series of detailed computer simulation models of rainfall patterns in the Amazon during the 1990s and concluded that forest removal also leaves soil exposed to the sun, and the increased temperature on the surface enhances evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the Interface (chemistry), surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. A high concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evapora ...
and increases moisture in the air.
Rates
Deforestation rates in the Brazilian Amazon have slowed dramatically since peaking in 2004 at 27,423 square kilometers per year. By 2009, deforestation had fallen to around 7,000 square kilometers per year, a decline of nearly 75 percent from 2004, according to Brazil'sNational Institute for Space Research
The National Institute for Space Research (, INPE) is a research unit of the Brazilian Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation (Brazil), Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovations, the main goals of which are fostering scientific r ...
(''Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais'', or INPE),National Institute for Space Research (INPE) (2010) which produces deforestation figures annually.
Their deforestation estimates are derived from 100 to 220 images taken during the dry season in the Amazon by the China–Brazil Earth Resources Satellite program
The China–Brazil Earth Resources Satellite program (CBERS) is a technological cooperation program between Brazil and China which develops and operates Earth observation satellites.
History
The basis for the space cooperation between China a ...
(CBS), and may only consider the loss of the Amazon rainforest – not the loss of natural fields or savanna within the Amazon biome. According to INPE, the original Amazon rainforest biome in Brazil of 4,100,000 km2 was reduced to 3,403,000 km2 by 2005 – representing a loss of 17.1%.
In 2018, Brazil released its worst annual deforestation figures in a decade amid fears that the situation might worsen when the avowedly anti-environmentalist president-elect Jair Bolsonaro
Jair Messias Bolsonaro (; born 21 March 1955) is a Brazilian politician and former military officer who served as the 38th president of Brazil from 2019 to 2023. He previously served as a member of Brazil's Chamber of Deputies (Brazil), Chamb ...
took power. Between August 2017 and July 2018, 7,900 km2 were deforested, according to preliminary figures from the environment ministry based on satellite monitoring – a 13.7% rise from the previous year and the biggest area of forest cleared since 2008. The area is equivalent to 987,000 football pitch
A football pitch or soccer field is the playing surface for the game of association football. Its dimensions and markings are defined by Law 1 of the Laws of the Game (association football), Laws of the Game, "The Field of Play". The pitch is ty ...
es. Deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon rose more than 88% in June 2019 compared with the same month in 2018. In the year 2019 approximately 9,762 square kilometers of the Amazonian forest were destroyed, 30% more than in the previous year. Environmental groups, scientists accused the policy of the government of Bolsonaro that rejected the blames. In January 2020, deforestation more than doubled compared with the previous year. From August 2020 to July 2021, INPE recorded 13,235sq km of deforestation. In January 2022, according to government data, Brazil recorded the most deforestation in the Amazon rainforest for the month of January since the current data series began in 2015/2016.
Estimates of the rates of deforestation in the Amazon rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, also called the Amazon jungle or Amazonia, is a Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, moist broadleaf tropical rainforest in the Amazon biome that covers most of the Amazon basin of South America. This basin ...
from 1970 to 2022 are given in the table below, based on data from the National Institute for Space Research and the Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, , translates ...
(FAO).
Measures to combat deforestation
By the end of the 1980s, the removal of Brazil's forests had become a serious global issue, not only because of the loss of biodiversity and ecological disruption, but also because of the large amounts ofcarbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
(CO2) released from burned forests and the loss of a valuable sink
A sink (also known as ''basin'' in the UK) is a bowl-shaped plumbing fixture for washing hands, dishwashing, and other purposes. Sinks have a tap (faucet) that supplies hot and cold water and may include a spray feature to be used for fas ...
to absorb global CO2 emissions. At the 1992 UN Framework Convention on Climate Change, deforestation became a key issue addressed at the summit in Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro, or simply Rio, is the capital of the Rio de Janeiro (state), state of Rio de Janeiro. It is the List of cities in Brazil by population, second-most-populous city in Brazil (after São Paulo) and the Largest cities in the America ...
. Plans for the compensated reduction (CR) of greenhouse gas emissions from tropical forests were set up to give nations like Brazil an incentive to curb their rate of deforestation.
"We are encouraging the Brazilian government to fully endorse the Compensated Reduction proposal", said scientist Paulo Moutinho, coordinator of the climate change program of the Amazon (IPAM), an NGO research institute in Brazil.
On May 11, 1994, NASA scientists, Compton Tucker and David Skole concluded that satellite observations showed a reduction in the rate of forest removal between 1992 and 1993 and that World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
estimates of 600,000 square km2 (12%) cleared to that point appeared to be too high. The NASA assessment concurred with the findings of the Brazilian National Space Research Institute (INPE) of an estimated 280,000 km2 (5%) in the same period.
The following year (1995) deforestation nearly doubled; this has been attributed to the accidental fire following the El Niño
EL, El or el may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Fictional entities
* El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit
* Eleven (''Stranger Things'') (El), a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things''
* El, fami ...
-related drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, ...
rather than active logging; the following year again showed a major drop. In 2002, Brazil ratified the Kyoto Agreement as a developing nation
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreeme ...
listed in the non-Annex I countries. These countries do not have carbon emission quotas in the agreement as developed nations do. President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva
Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva (; born Luiz Inácio da Silva; 27 October 1945), known Mononym, mononymously as Lula, is a Brazilian politician, trade unionist and former metalworker who has served as the 39th president of Brazil since 2023. A mem ...
reiterated that Brazil: "is in charge of looking after the Amazon"."Brazil will forge its own path for developing the Amazon."''Conservation news and environmental science news.'' 26 Jan 2009.
 In 2006, Brazil proposed a
In 2006, Brazil proposed a direct finance
Direct finance is a method of financing where borrowers borrow funds directly from the financial market without using a third party service, such as a financial intermediary. This is different from indirect financing where a financial intermediar ...
project to deal with the Reduced Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation in Developing Countries, or REDD, issue, recognizing that deforestation contributes to 20% of the world's greenhouse gas emissions. The competing proposal for the REDD issue was a carbon emission credit system, where reduced deforestation would receive "marketable emissions credits". In effect, developed countries could reduce their carbon emissions, and approach their emissions quota by investing in the reforestation of developing rainforest countries. Instead, Brazil's 2006 proposal would draw from a fund based on donor country contributors.
By 2005, forest removal had fallen to of forest compared to in 2003 and on July 5, 2007, Brazilian president Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva announced at the International Conference on Biofuels in Brussels
Brussels, officially the Brussels-Capital Region, (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) is a Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium#Regions, region of Belgium comprising #Municipalit ...
that more than 20 million hectares of conservation units to protect the forest and more efficient fuel production had allowed the rate of deforestation to fall by 52% in the three years since 2004.
The academic evidence suggests that the creation of public lands, through the assignment of property rights, reduces incentives to deforest land for agricultural conversion and contributes to lower land-related conflict.
In 2005, Brazilian Environment Minister Marina da Silva announced that of forest had been felled in the previous year, compared with more than in 2003 and 2004. Between 2005 and 2006 there was a 41% drop in deforestation; nonetheless, Brazil still had the largest area of forest removed annually on the planet.
These methods have also reduced the illegal appropriation of land and logging, encouraging the use of land for sustainable timber harvesting.
At the end of August 2019 after an international outcry and warning from experts that fires can increase even more, the Brazilian government of Jair Bolsonaro
Jair Messias Bolsonaro (; born 21 March 1955) is a Brazilian politician and former military officer who served as the 38th president of Brazil from 2019 to 2023. He previously served as a member of Brazil's Chamber of Deputies (Brazil), Chamb ...
begun to take measures to stop the fires in the Amazon rainforest. The measures include:
* 60 day ban for clearing forest with fires.
* Sending 44,000 soldiers to fight the fires.
* Accepting 4 planes from Chile for battle the fires.
* Accepting 12 million dollars of aid from the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
government
* Softening his position about aid from the G7.
* Appealing for a Latin America conference to preserve the Amazon
2019
 To diminish deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon, some organisations have argued that large financial resources are required to give illegal loggers an economic incentive to pursue other areas of activity. The
To diminish deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon, some organisations have argued that large financial resources are required to give illegal loggers an economic incentive to pursue other areas of activity. The World Wide Fund for Nature
The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) is a Swiss-based international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named th ...
(WWF) estimated in 2007 that a total of approximately US$547.2 million (1 billion Brazilian reais) per year would be required from international sources to compensate the forest developers and establish a highly organized framework to fully implement forest governance and monitoring, and the foundation of new protected forest areas in the Amazon for future sustainability.

Non-governmental organization
A non-governmental organization (NGO) is an independent, typically nonprofit organization that operates outside government control, though it may get a significant percentage of its funding from government or corporate sources. NGOs often focus ...
s (NGOs) such as WWF have been active in the region, and WWF Brazil formed an alliance with eight other Brazilian NGOs who aimed to completely halt deforestation in the Amazon by 2015. However, deforestation continues; in July 2019, the rate reached a four-year high. Deforestation has rapidly increased over 30 percent since 2018 according to thINPE
The Amazon's deforestation has been seen to be at its highest levels since 2008. This could have long-term implications for the health of the region and its significant impact on the functionality of the global ecosystem
Models
suggest that the Amazon may be reaching a tipping point due to the deforestation and rising temperatures. Under
Jair Bolsonaro
Jair Messias Bolsonaro (; born 21 March 1955) is a Brazilian politician and former military officer who served as the 38th president of Brazil from 2019 to 2023. He previously served as a member of Brazil's Chamber of Deputies (Brazil), Chamb ...
's government, who took office in January 2019, policies surrounding deforestation have relaxed. Bolsonaro and other senior figures have encouraged the exploitation of the Amazon rainforest, denigrated critics and denied man-made climate change. Some environmental laws have been weakened and there has been a cut in funding and personnel at key government agencies and a firing of the heads of the agency's state bodies.
In 2019 an initiative has been made by the NGO RioTerra and the organization Reforest’Action. This initiative is intended to make more efforts to reduce deforestation and restore degraded areas. Slash-and-burn farming is a big part of the problem in the fight against deforestation, and this is something that is focused on in this project. The goal is to plant 120,000 trees, use agroforestry to reduce deforestation, help diversify forest fruit production, store carbon to fight climate change, and provide food security. Agroforestry is a way of agriculture in forested areas combining planting and managing trees with farming and cattle ranching. The project should benefit from multiple environmental problems caused by deforestation like conserving biodiversity, improving the water cycle and generating income for the local population from the sale of non-wood products and fruit providing more food security. Not to mention that the trees act as carbon storage, caused by cutting and burning trees. Besides that, the planting of trees helps restore cleared or burned areas of land and make agroforestry possible.2023
In 2023 theWorld Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
, published a report named: "A Balancing Act for Brazil’s Amazonian States: An Economic Memorandum". The report stating, that economic losses due to deforestation in Brazil could reach around 317 billion dollars per year, approximately 7 times higher in comparison to the cost of all commodities produced through deforestation, proposed another economic program in the region of the Amazon rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, also called the Amazon jungle or Amazonia, is a Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, moist broadleaf tropical rainforest in the Amazon biome that covers most of the Amazon basin of South America. This basin ...
. For example, it proposed to link cities with help of rivers and not roads.
See also
* 2018 in Brazil * 2019 Amazon rainforest wildfires *Agriculture in Brazil
The agricultural sector in Brazil is historically one of the principal bases of Economy of Brazil, Brazil's economy. In 2024, Brazil was the second-biggest grain exporter in the world, with 19% of the international market share, and the fourth ...
* Amazon rainforest § Deforestation
* Brazilian Institute of Environment and Renewable Natural Resources (IBAMA)
* Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism
* Coffee plantation
Plantations are farms specializing in cash crops, usually mainly planting a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Plantations, centered on a plantation house, grow crops including cotton, cannabis, tobacco ...
* Coffee production in Brazil
* Deforestation of the Amazon Rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, spanning an area of 3,000,000 km2 (1,200,000 sq mi), is the world's largest rainforest. It encompasses the largest and most biodiverse tropical rainforest on the planet, representing over half of all rainforests. The ...
* Environment of Brazil
* Environmental issues in Brazil
* Environmental history of Latin America
* Stern Review's cost estimates of climate change
* Rainforest Alliance
The Rainforest Alliance is an international non-governmental organization (NGO) with staff in more than 20 countries and operations in more than 70 countries. It was founded in 1987 by Daniel Katz, an American environmental activist, who serve ...
References
External links
Images of deforestation in the Amazon
Reversing deforestation in Brazil? an academic article
Mecanismos y actors Sociales en la deforestación de la Amazonia brasileña
*
Cattle Ranching in the Amazon Region
. Yale School of Forestry & Environmental Studies {{Americas topic, Deforestation in Environmental issues in Brazil
Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
Forestry in Brazil
Environmental disasters in South America
Environmental racism