|
National Institute For Space Research
The National Institute for Space Research (, INPE) is a research unit of the Brazilian Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation (Brazil), Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovations, the main goals of which are fostering scientific research and technological applications and qualifying personnel in the fields of Outer space, space and atmospheric sciences, Aerospace engineering, space engineering, and space technology. While INPE is the civilian research center for aerospace activities, the Brazilian Air Force's Brazilian Aerospace Technical Center (CTA), General Command for Aerospace Technology is the military arm. INPE is located in the city of São José dos Campos, São Paulo. History On August 13, 1961, President of Brazil, President Jânio Quadros signed a decree which created the Organizing Group for the National Commission on Space Activities (COGNAE). This group would give rise to the current National Institute for Space Research. COGNAE, which shortly after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jânio Quadros
Jânio da Silva Quadros (; 25 January 1917 – 16 February 1992) was a Brazilian lawyer and politician who served as the 22nd president of Brazil from 31 January to 25 August 1961, when he resigned from office. He also served as the 24th and 36th mayor of São Paulo, and the 18th governor of the state of São Paulo. Quadros was known for his populist style of government and eccentric behavior. As president, he focused on economic reform and attempted to root out corruption. He also pursued an independent foreign policy, trying to balance Brazil's relations between the United States and the Eastern Bloc. Although he was elected by a huge margin, his term was marked by uncertainty and political instability, culminating in his resignation. That unexpected move caused a national crisis, with the presidency being assumed by João Goulart after the Legality Campaign. Early life Quadros was born in Campo Grande, Mato Grosso do Sul, on January 25, 1917, to Gabriel Quadros and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
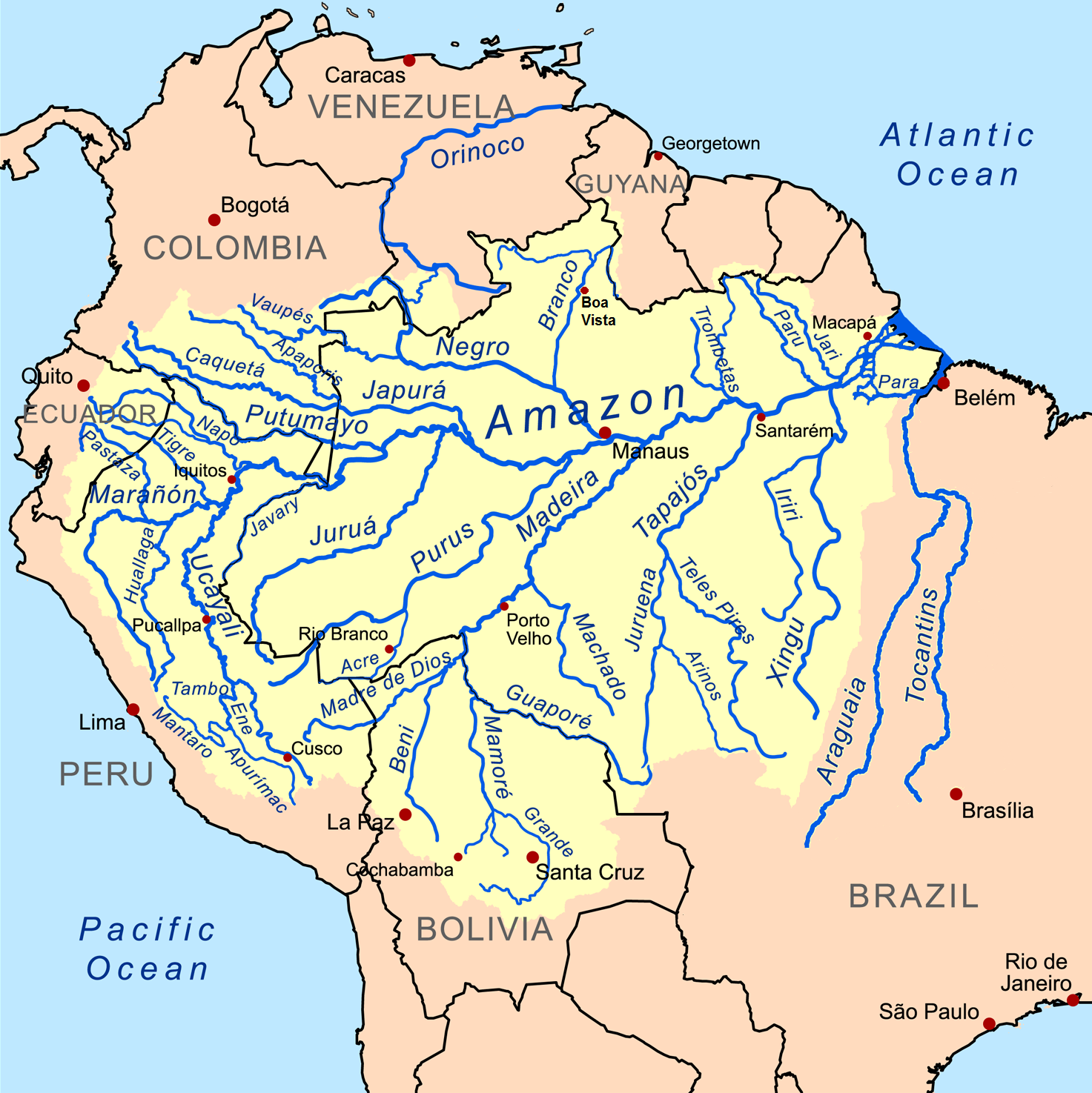
Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributary, tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela, as well as the territory of French Guiana. Most of the basin is covered by the Amazon rainforest, also known as Amazon rainforest, Amazonia. With a area of dense tropical forest, it is the largest rainforest in the world. Geography The Amazon River begins in the Andes, Andes Mountains at the west of the basin with its main tributary the Marañón River and Apurímac River, Apurimac River in Peru. The highest point in the Drainage divide, watershed of the Amazon is the second biggest peak of Yerupajá at . The Amazon River Basin occupies the entire central and eastern area of South America, lying to the east of the Andes mountain range and extending from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China–Brazil Earth Resources Satellite Program
The China–Brazil Earth Resources Satellite program (CBERS) is a technological cooperation program between Brazil and China which develops and operates Earth observation satellites. History The basis for the space cooperation between China and Brazil was established in May 1984, when both countries signed a complementary agreement to the cooperation framework agreement in science and technology. In July 1988, China and Brazil signed the protocol establishing the joint research and production of the China-Brazil Earth Resources Satellites (CBERS). Brazil, emerging from a long military regime, sought to abandon the Cold War logic and establish new international partnerships. China was dedicated to its great internal reform, but was also seeking international partnerships to develop advanced technologies. The agreement was advantageous for both countries. Brazil had the chance to develop medium-size satellites at a time when it was only capable of building small ones (100 kg size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
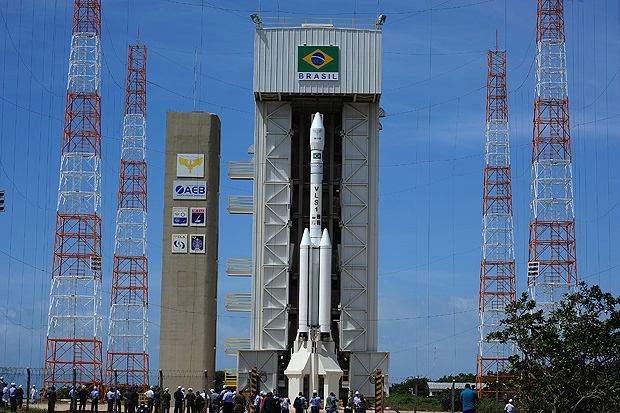
Brazilian Space Program
The Brazilian space program is the rocketry and space exploration programs conducted by Brazil from 1961, under GOCNAE (Group for the Organization of the National Commission on Space Activities) until the creation of the Brazilian Space Agency in 1994. It has significant capabilities in launch vehicles, launch sites, and satellite manufacturing. It is based at the National Institute for Space Research (INPE), under the Ministry of Science and Technology (MCT). Upon its founding the program was under complete military control, which hindered its development, as other countries (such as the United States) blocked technological development due to concerns over missile proliferation. In 1994, the space program was transferred to civilian control under the Brazilian Space Agency. History Since 1964, in an attempt to build a satellite launch vehicle ( ''Veículo Lançador de Satélite--VLS''), Brazil has developed a series of sounding (research) rockets, named Sonda I, II, III, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications Satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a Transponder (satellite communications), transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a Radio receiver, receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellations in low Earth orbit, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently. The radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by Line-of-sight propagation, line of sight and so are obstructe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geostationary Orbit
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular orbit, circular geosynchronous orbit in altitude above Earth's equator, in radius from Earth's center, and following the retrograde and prograde motion, direction of Earth's rotation. An object in such an orbit has an orbital period equal to Earth's rotational period, one sidereal time, sidereal day, and so to ground observers it appears motionless, in a fixed position in the sky. The concept of a geostationary orbit was popularised by the science fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke in the 1940s as a way to revolutionise telecommunications, and the first satellite to be placed in this kind of orbit was launched in 1963. Communications satellites are often placed in a geostationary orbit so that Earth-based satellite dish, satellite antennas do not have to rotate to track t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an physical object, object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Earth and other planets. Remote sensing is used in numerous fields, including geophysics, geography, land surveying and most Earth science disciplines (e.g. exploration geophysics, hydrology, ecology, meteorology, oceanography, glaciology, geology). It also has military, intelligence, commercial, economic, planning, and humanitarian applications, among others. In current usage, the term ''remote sensing'' generally refers to the use of satellite- or airborne-based sensor technologies to detect and classify objects on Earth. It includes the surface and the atmosphere and oceans, based on wave propagation, propagated signals (e.g. electromagnetic radiation). It may be split into "active" remote sensing (when a signal is emitted b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Satellite
A weather satellite or meteorological satellite is a type of Earth observation satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth. Satellites are mainly of two types: polar orbiting (covering the entire Earth asynchronously) or geostationary (hovering over the same spot on the equator). While primarily used to detect the development and movement of storm systems and other cloud patterns, meteorological satellites can also detect other phenomena such as city lights, fires, effects of pollution, auroras, sand and dust storms, snow cover, ice mapping, boundaries of ocean currents, and energy flows. Other types of environmental information are collected using weather satellites. Weather satellite images helped in monitoring the volcanic ash cloud from Mount St. Helens and activity from other volcanoes such as Mount Etna. Smoke from fires in the western United States such as Colorado and Utah have also been monitored. El Niño and its effects on wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Observation Satellite
An Earth observation satellite or Earth remote sensing satellite is a satellite used or designed for Earth observation (EO) from orbit, including spy satellites and similar ones intended for non-military uses such as environmental monitoring, meteorology, cartography and others. The most common type are Earth imaging satellites, that take satellite images, analogous to aerial photographs; some EO satellites may perform remote sensing without forming pictures, such as in GNSS radio occultation. The first occurrence of satellite remote sensing can be dated to the launch of the first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, by the Soviet Union on October 4, 1957. Sputnik 1 sent back radio signals, which scientists used to study the ionosphere. The United States Army Ballistic Missile Agency launched the first American satellite, Explorer 1, for NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on January 31, 1958. The information sent back from its radiation detector led to the discovery of the Earth's Van ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunication
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of transmission may be divided into communication channels for multiplexing, allowing for a single medium to transmit several concurrent Session (computer science), communication sessions. Long-distance technologies invented during the 20th and 21st centuries generally use electric power, and include the electrical telegraph, telegraph, telephone, television, and radio. Early telecommunication networks used metal wires as the medium for transmitting signals. These networks were used for telegraphy and telephony for many decades. In the first decade of the 20th century, a revolution in wireless communication began with breakthroughs including those made in radio communications by Guglielmo Marconi, who won the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics. Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteorology
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agriculture, construction, weather warnings and disaster management. Along with climatology, atmospheric physics and atmospheric chemistry, meteorology forms the broader field of the atmospheric sciences. The interactions between Earth's atmosphere and its oceans (notably El Niño and La Niña) are studied in the interdisciplinary field of hydrometeorology. Other interdisciplinary areas include biometeorology, space weather and planetary meteorology. Marine weather forecasting relates meteorology to maritime and coastal safety, based on atmospheric interactions with large bodies of water. Meteorologists study meteorological phenomena driven by solar radiation, Earth's rotation, ocean currents and other factors. These include everyday ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |