Decadence on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Decadence was a late-19th-century movement emphasizing the need for
Decadence was a late-19th-century movement emphasizing the need for

 Heliogabalus is also the subject of '' The Roses of Heliogabalus'' (1888) by Sir Lawrence Alma-Tadema, which, according to Professor Rosemary Barrow, represents "the artist s��most glorious revel in Roman Decadence." To Barrow, " e authenticity of the cene��perhaps had little importance for the artist meaning thatits appeal is the entertaining and extravagant vision it gives of later imperial Rome." Barrow also makes a point to mention "that Alma-Tadema’s Roman-subject paintings end to��make use of historical, literary and archaeological sources" within themselves. Thus, the presence of roses within the painting as opposed to the original "'violets and other flowers'" of the source material emphasizes how "the Roman world…h ldextra connotations of revelry and luxuriant excess" about them.
Heliogabalus is also the subject of '' The Roses of Heliogabalus'' (1888) by Sir Lawrence Alma-Tadema, which, according to Professor Rosemary Barrow, represents "the artist s��most glorious revel in Roman Decadence." To Barrow, " e authenticity of the cene��perhaps had little importance for the artist meaning thatits appeal is the entertaining and extravagant vision it gives of later imperial Rome." Barrow also makes a point to mention "that Alma-Tadema’s Roman-subject paintings end to��make use of historical, literary and archaeological sources" within themselves. Thus, the presence of roses within the painting as opposed to the original "'violets and other flowers'" of the source material emphasizes how "the Roman world…h ldextra connotations of revelry and luxuriant excess" about them.
 The philosophy of decadence comes from the work of German philosopher
The philosophy of decadence comes from the work of German philosopher

 Modernism tends to belittle popular culture through its oppressive nature, which can be seen as elitist and controlling, as it privileges certain works of art above others. As a result, postmodern artists and writers developed a contempt for the canon, rejecting tradition and
Modernism tends to belittle popular culture through its oppressive nature, which can be seen as elitist and controlling, as it privileges certain works of art above others. As a result, postmodern artists and writers developed a contempt for the canon, rejecting tradition and
 The historian
The historian
'' Aufheben''. Summer 1993. One who directly opposed the idea of decadence as expressed by Lenin was José Ortega y Gasset in '' The Revolt of the Masses'' (1930). He argued that the " mass man" had the notion of material progress and scientific advance deeply inculcated to the extent that it was an expectation. He also argued that contemporary progress was opposite the true decadence of the
Collection of the articles of the International Communist Current on the Theory of Decadence
{{authority control Art movements Concepts in ethics Modern art Political theories
 Decadence was a late-19th-century movement emphasizing the need for
Decadence was a late-19th-century movement emphasizing the need for sensationalism
In journalism and mass media, sensationalism is a type of editorial tactic. Events and topics in news stories are selected and worded to excite the greatest number of readers and viewers. This style of news reporting encourages biased or emoti ...
, egocentricity, and bizarre, artificial, perverse, and exotic sensations and experiences. By extension, it may refer to a decline in art, literature, science, technology, and work ethics, or (very loosely) to self-indulgent behavior.
Usage of the term sometimes implies moral censure
A censure is an expression of strong disapproval or harsh criticism. In parliamentary procedure, it is a debatable main motion that could be adopted by a majority vote. Among the forms that it can take are a stern rebuke by a legislature, a sp ...
, or an acceptance of the idea, met with throughout the world since ancient times
Ancient history is a time period from the History of writing, beginning of writing and recorded human history through late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the development of Sumerian language, ...
, that such declines are objectively observable and that they inevitably precede the destruction of the society in question; for this reason, modern historians use it with caution. The word originated in Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. It was also the administrative language in the former Western Roman Empire, Roman Provinces of Mauretania, Numidi ...
''(dēcadentia)'', appeared in 16th-century French, and entered English soon afterwards. It bore the neutral meaning of decay, decrease, or decline until the late 19th century, when the influence of new theories of social degeneration
Social degeneration was a widely influential concept at the interface of the social and biological sciences in the 18th and 19th centuries. During the 18th century, scientific thinkers including Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon, Johann Fri ...
contributed to its modern meaning.
The idea that a society or institution is declining is called declinism
Declinism is the belief that a society or institution is tending towards wiktionary:decline, decline. Particularly, it is the predisposition, caused by cognitive biases such as rosy retrospection, to view the past more favourably and the future mor ...
. This may be caused by the predisposition, caused by cognitive bias
A cognitive bias is a systematic pattern of deviation from norm (philosophy), norm or rationality in judgment. Individuals create their own "subjective reality" from their perception of the input. An individual's construction of reality, not the ...
es such as rosy retrospection
Rosy retrospection is a proposed Psychology, psychological phenomenon of recalling the past more positively than it was actually experienced.
The highly False memory, unreliable nature of human memory is well documented and accepted amongst psycho ...
, to view the past more favourably and future more negatively. Declinism has been described as "a trick of the mind" and as "an emotional strategy, something comforting to snuggle up to when the present day seems intolerably bleak." Other cognitive factors contributing to the popularity of declinism may include the reminiscence bump as well as both the positivity effect and negativity bias.
In literature, the Decadent movement
The Decadent movement (from the French language, French ''décadence'', ) was a late 19th-century Art movement, artistic and literary movement, literary movement, centered in Western Europe, that followed an aesthetic ideology of excess and artif ...
began in France's ''fin de siècle
"''Fin de siècle''" () is a French term meaning , a phrase which typically encompasses both the meaning of the similar English idiom '' turn of the century'' and also makes reference to the closing of one era and onset of another. Without co ...
'' intermingling with Symbolism and the Aesthetic movement
Aestheticism (also known as the aesthetic movement) was an art movement in the late 19th century that valued the appearance of literature, music, fonts and the arts over their functions. According to Aestheticism, art should be produced to b ...
while spreading throughout Europe and the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
. The Decadent title was originally used as a criticism but it was soon triumphantly adopted by some of the writers themselves. The Decadents praised artifice over nature and sophistication over simplicity, defying contemporary discourses of decline by embracing subjects and styles that their critics considered morbid and over-refined. Some of these writers were influenced by the tradition of the Gothic novel
Gothic fiction, sometimes referred to as Gothic horror (primarily in the 20th century), is a literary aesthetic of fear and haunting. The name of the genre is derived from the Renaissance era use of the word "gothic", as a pejorative to mean ...
and by the poetry and fiction of Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic who is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales involving mystery and the macabre. He is widely re ...
.
History
Ancient Rome
Decadence is a popular criticism of the culture of thelater Roman Empire
In historiography, the Late or Later Roman Empire, traditionally covering the period from 284 CE to 641 CE, was a time of significant transformation in Roman governance, society, and religion. Diocletian's reforms, including the establishment of t ...
's elites, seen also in much of its earlier historiography
Historiography is the study of the methods used by historians in developing history as an academic discipline. By extension, the term ":wikt:historiography, historiography" is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiog ...
and 19th and early 20th century art depicting Roman life. This criticism describes the later Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
as reveling in luxury, in its extreme characterized by corrupting "extravagance, weakness, and sexual deviance", as well as "orgies and sensual excesses".

Victorian-era artwork on Roman decadence
According to Professor Joseph Bristow ofUCLA
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Its academic roots were established in 1881 as a normal school then known as the southern branch of the C ...
, decadence in Rome and the Victorian-era movement are connected through the idea of "decadent historicism." In particular, decadent historicism refers to the "interest among…1880s and 1890s writers in the enduring authority of perverse personas from the past" including the later Roman era. As such, Bristow's argument references how Heliogabalus, the title subject of Simeon Solomon
Simeon Solomon (9 October 1840 – 14 August 1905) was a British painter associated with the Pre-Raphaelites who was noted for his depictions of Jewish life and same-sex desire. His career was cut short as a result of public scandal following h ...
's painting ''Heliogabalus, High Priest of the Sun'' (1866), was "a decadent icon" for the Victorian movement. Bristow also notes that " e image f the paintingsummons many qualities linked with fin-de-siècle decadence longside his��queerness thus "inspir nglate-Victorian writers s��they…imagine anew sexual modernity."
 Heliogabalus is also the subject of '' The Roses of Heliogabalus'' (1888) by Sir Lawrence Alma-Tadema, which, according to Professor Rosemary Barrow, represents "the artist s��most glorious revel in Roman Decadence." To Barrow, " e authenticity of the cene��perhaps had little importance for the artist meaning thatits appeal is the entertaining and extravagant vision it gives of later imperial Rome." Barrow also makes a point to mention "that Alma-Tadema’s Roman-subject paintings end to��make use of historical, literary and archaeological sources" within themselves. Thus, the presence of roses within the painting as opposed to the original "'violets and other flowers'" of the source material emphasizes how "the Roman world…h ldextra connotations of revelry and luxuriant excess" about them.
Heliogabalus is also the subject of '' The Roses of Heliogabalus'' (1888) by Sir Lawrence Alma-Tadema, which, according to Professor Rosemary Barrow, represents "the artist s��most glorious revel in Roman Decadence." To Barrow, " e authenticity of the cene��perhaps had little importance for the artist meaning thatits appeal is the entertaining and extravagant vision it gives of later imperial Rome." Barrow also makes a point to mention "that Alma-Tadema’s Roman-subject paintings end to��make use of historical, literary and archaeological sources" within themselves. Thus, the presence of roses within the painting as opposed to the original "'violets and other flowers'" of the source material emphasizes how "the Roman world…h ldextra connotations of revelry and luxuriant excess" about them.
Decadent movement
Decadence was the name given to a number of late nineteenth-century writers who valued artifice over the earlier Romantics' naïve view of nature. Some of them triumphantly adopted the name, referring to themselves as Decadents. For the most part, they were influenced by the tradition of theGothic novel
Gothic fiction, sometimes referred to as Gothic horror (primarily in the 20th century), is a literary aesthetic of fear and haunting. The name of the genre is derived from the Renaissance era use of the word "gothic", as a pejorative to mean ...
and by the poetry and fiction of Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic who is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales involving mystery and the macabre. He is widely re ...
, and were associated with Symbolism and/or Aestheticism.
This concept of decadence dates from the eighteenth century, especially from Montesquieu
Charles Louis de Secondat, baron de La Brède et de Montesquieu (18 January 168910 February 1755), generally referred to as simply Montesquieu, was a French judge, man of letters, historian, and political philosopher.
He is the principal so ...
and Wilmot. It was taken up by critics as a term of abuse after Désiré Nisard used it against Victor Hugo
Victor-Marie Hugo, vicomte Hugo (; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French Romanticism, Romantic author, poet, essayist, playwright, journalist, human rights activist and politician.
His most famous works are the novels ''The Hunchbac ...
and Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century. The purpose of the movement was to advocate for the importance of subjec ...
in general. A later generation of Romantics, such as Théophile Gautier
Pierre Jules Théophile Gautier ( , ; 30 August 1811 – 23 October 1872) was a French poet, dramatist, novelist, journalist, and art and literary critic.
While an ardent defender of Romanticism, Gautier's work is difficult to classify and rema ...
and Charles Baudelaire
Charles Pierre Baudelaire (, ; ; 9 April 1821 – 31 August 1867) was a French poet, essayist, translator and art critic. His poems are described as exhibiting mastery of rhythm and rhyme, containing an exoticism inherited from the Romantics ...
took the word as a badge of pride, as a sign of their rejection of what they saw as banal "progress." In the 1880s, a group of French writers
Chronological list of French language authors (regardless of nationality), by date of birth. For an alphabetical list of writers of French nationality (broken down by genre), see French writers category.
Middle Ages
* Turold (eleventh centu ...
referred to themselves as Decadents. The classic novel from this group is Joris-Karl Huysmans
Charles-Marie-Georges Huysmans (, ; 5 February 1848 – 12 May 1907) was a French novelist and art critic who published his works as Joris-Karl Huysmans (, variably abbreviated as J. K. or J.-K.). He is most famous for the novel (1884, pub ...
' '' Against Nature'', often seen as the first great decadent work, though others attribute this honor to Baudelaire's works.
In Britain and Ireland the leading figure associated with the Decadent movement was Irish writer, Oscar Wilde
Oscar Fingal O'Fflahertie Wills Wilde (16 October 185430 November 1900) was an Irish author, poet, and playwright. After writing in different literary styles throughout the 1880s, he became one of the most popular and influential playwright ...
. Other significant figures include Arthur Symons, Aubrey Beardsley
Aubrey Vincent Beardsley ( ; 21 August 187216 March 1898) was an English illustrator and author. His black ink drawings were influenced by Woodblock printing in Japan, Japanese woodcuts, and depicted the grotesque, the decadent, and the erotic. ...
and Ernest Dowson
Ernest Christopher Dowson (2 August 186723 February 1900) was an English poet, novelist, and short-story writer who is often associated with the Decadent movement.
Biography
Ernest Dowson was born in Lee, London, Lee, then in Kent, in 1867. His ...
.
The Symbolist movement has frequently been confused with the Decadent movement. Several young writers were derisively referred to in the press as "decadent" in the mid-1880s. Jean Moréas' manifesto was largely a response to this polemic
Polemic ( , ) is contentious rhetoric intended to support a specific position by forthright claims and to undermine the opposing position. The practice of such argumentation is called polemics, which are seen in arguments on controversial to ...
. A few of these writers embraced the term while most avoided it. Although the aesthetics of Symbolism and Decadence can be seen as overlapping in some areas, the two remain distinct.
1920s Berlin
This "''fertile culture''" ofBerlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
extended onwards until Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
rose to power in early 1933 and stamped out any and all resistance to the Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party ( or NSDAP), was a far-right politics, far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported the ideology of Nazism. Its precursor ...
. Likewise, the German far-right decried Berlin as a haven of degeneracy. A new culture had developed in and around Berlin throughout the previous decade, including architecture and design (Bauhaus
The Staatliches Bauhaus (), commonly known as the , was a German art school operational from 1919 to 1933 that combined Decorative arts, crafts and the fine arts.Oxford Dictionary of Art and Artists (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 4th edn., ...
, 1919–33), a variety of literature ( Döblin, ''Berlin Alexanderplatz
''Berlin Alexanderplatz'' () is a 1929 novel by Alfred Döblin. It is considered one of the most important and innovative works of the Weimar culture, Weimar Republic. In a 2002 poll of 100 noted writers, the book was named among the top 100 bo ...
'', 1929), film (Lang
Lang may refer to:
*Lang (surname), a surname of independent Germanic or Chinese origin
Places
* Lang Island (Antarctica), East Antarctica
* Lang Nunatak, Antarctica
* Lang Sound, Antarctica
* Lang Park, a stadium in Brisbane, Australia
* Lang, ...
, ''Metropolis
A metropolis () is a large city or conurbation which is a significant economic, political, and cultural area for a country or region, and an important hub for regional or international connections, commerce, and communications.
A big city b ...
'', 1927, Dietrich, '' Der blaue Engel'', 1930), painting ( Grosz), and music ( Brecht and Weill, ''The Threepenny Opera
''The Threepenny Opera'' ( ) is a 1928 German "play with music" by Bertolt Brecht, adapted from a translation by Elisabeth Hauptmann of John Gay's 18th-century English ballad opera, '' The Beggar's Opera'', and four ballads by François V ...
'', 1928), criticism (Benjamin
Benjamin ( ''Bīnyāmīn''; "Son of (the) right") blue letter bible: https://www.blueletterbible.org/lexicon/h3225/kjv/wlc/0-1/ H3225 - yāmîn - Strong's Hebrew Lexicon (kjv) was the younger of the two sons of Jacob and Rachel, and Jacob's twe ...
), philosophy/psychology (Jung
Carl Gustav Jung ( ; ; 26 July 1875 – 6 June 1961) was a Swiss psychiatrist, psychotherapist, and psychologist who founded the school of analytical psychology. A prolific author of over 20 books, illustrator, and correspondent, Jung was a c ...
), and fashion. This culture was considered decadent and disruptive by rightists.
Film
A film, also known as a movie or motion picture, is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, emotions, or atmosphere through the use of moving images that are generally, sinc ...
was making huge technical and artistic strides during this period of time in Berlin, and gave rise to the influential movement called German Expressionism
Expressionism is a modernist movement, initially in poetry and painting, originating in Northern Europe around the beginning of the 20th century. Its typical trait is to present the world solely from a subjective perspective, distorting it radi ...
. " Talkies", the sound films, were also becoming more popular with the general public across Europe, and Berlin was producing very many of them.
Berlin in the 1920s also proved to be a haven for English-language writers such as W. H. Auden, Stephen Spender
Sir Stephen Harold Spender (28 February 1909 – 16 July 1995) was an English poet, novelist and essayist whose work concentrated on themes of social injustice and the class struggle. He was appointed U.S. Poet Laureate Consultant in Poetry ...
and Christopher Isherwood, who wrote a series of 'Berlin novels', inspiring the play '' I Am a Camera'', which was later adapted into a musical, ''Cabaret
Cabaret is a form of theatrical entertainment featuring music song, dance, recitation, or drama. The performance venue might be a pub, casino, hotel, restaurant, or nightclub with a stage for performances. The audience, often dining or drinking, ...
'', and an Academy Award
The Academy Awards, commonly known as the Oscars, are awards for artistic and technical merit in film. They are presented annually by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (AMPAS) in the United States in recognition of excellence ...
winning film of the same name. Spender's semi-autobiographical novel '' The Temple'' evokes the attitude and atmosphere of the place at the time.
Decadent nihilistic art
 The philosophy of decadence comes from the work of German philosopher
The philosophy of decadence comes from the work of German philosopher Arthur Schopenhauer
Arthur Schopenhauer ( ; ; 22 February 1788 – 21 September 1860) was a German philosopher. He is known for his 1818 work ''The World as Will and Representation'' (expanded in 1844), which characterizes the Phenomenon, phenomenal world as ...
(1788–1860), however, Friedrich Nietzsche
Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche (15 October 1844 – 25 August 1900) was a German philosopher. He began his career as a classical philology, classical philologist, turning to philosophy early in his academic career. In 1869, aged 24, Nietzsche bec ...
(1844–1900), a specific philosopher of decadence, conceptualized modern decadence on a more influential scale. Holding decadence to be in any condition, ultimately limiting what something or someone can be, Nietzsche used his exploration in nihilism to critique traditional values and morals that threatened the decline in art, literature, and science. Nihilism
Nihilism () encompasses various views that reject certain aspects of existence. There have been different nihilist positions, including the views that Existential nihilism, life is meaningless, that Moral nihilism, moral values are baseless, and ...
, generally, is the rejection of moral principles, ultimately believing that life is meaningless. Nihilism, for Nietzsche, was the ultimate fate of Western civilization as old values lost their influence and purpose, in turn, disappeared among society. Predicting a rise in decadence and aesthetic nihilism, creators would renounce the pursuit of beauty and instead welcome the incomprehensible chaos. In art, there have been movements connected to nihilism, such as cubism and surrealism, that pushes for abandoned viewpoints to ultimately tap into the potential of one's conscious mind. Because of this, paintings like 1875-76's "''L’Absinthe''" by Edgar Degas
Edgar Degas (, ; born Hilaire-Germain-Edgar De Gas, ; 19 July 183427 September 1917) was a French Impressionist artist famous for his pastel drawings and oil paintings.
Degas also produced bronze sculptures, prints, and drawings. Degas is e ...
and 1915's " Black Square" by Kazimir Malevich
Kazimir Severinovich Malevich (
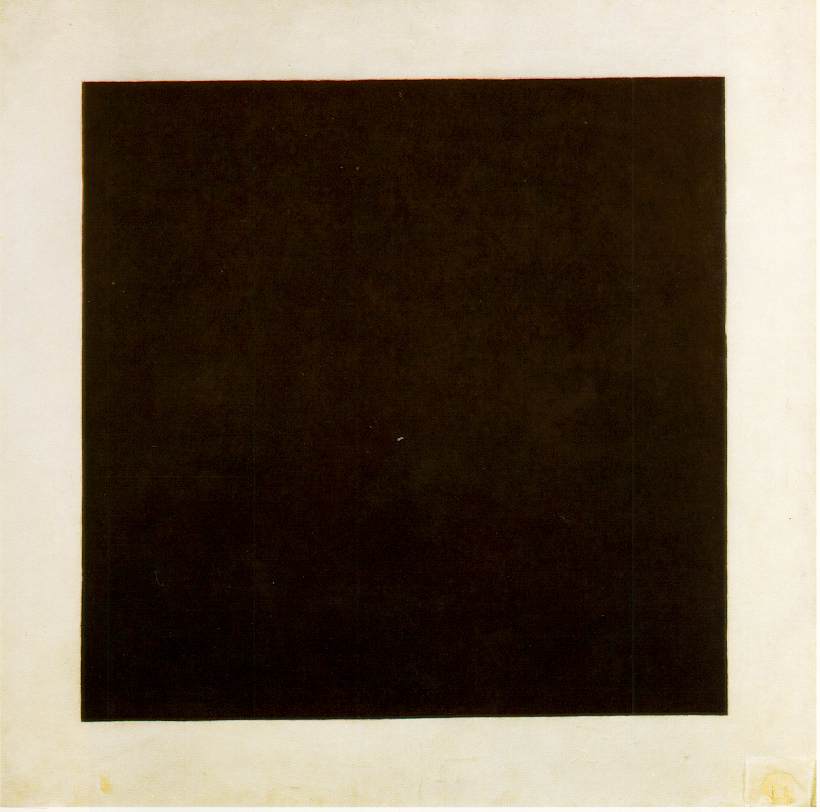
were created. ''L’Absinthe,'' which first showed in 1876, was mocked and called disgusting when panned by critics. Some say the painting is a blow to morality, as a glass filled with Absinthe, an alcoholic drink, rests in front of a woman at a table. Taken to be in bad faith and quite uncouth, Degas's art took decadence as a way to portray ambiguity in random subjects that seem to be drifting between depression and euphoria. Using nihilism in a synonymously way, Degas denoted his paintings to a general mood of despair, mainly at existence as a whole. Comparing this piece to Kazimir Malevich's "Black Square," abstract nihilistic art in the Western tradition was only beginning to take shape as the 20th century came about. Malevich's perception of this piece embraced a philosophy connected to Suprematism – a new realism in painting that evokes non-objectivity to experience "white emptiness of a liberated nothing," as said by Malevich himself. In nihilism, life has, in a sense, no truth, therefore no action is objectively preferable to another. Malevich's decadent painting shows the complete abandonment of depicting reality, and instead creates his own world of new form. When the painting was first exhibited, the public was in chaos, as society was in its first World War and Malevich reflected a new social revolution as a symbol of a new tomorrow, disregarding the past to move forward. Because of this painting and Degas's, decadence can be portrayed as a physiological foundation for nihilism, bringing out a term called "Decadent Nihilism:" existing beyond the world, and that of vain virtues. According to Nietzsche, Western metaphysical and nihilistic thought is decadent because of its confirmation from 'others' (apart from oneself) based on ideas of a nihilistic God. The extreme position an artist takes is what makes their pieces decadent.
Decadent aesthetics
Controversy
Vladimir Nabokov's ''Lolita'' (1955) Aesthetics falling under the category of decadence often include controversy. An example of a controversial style founded through decadent literary influence is the novel, ''Lolita
''Lolita'' is a 1955 novel written by Russian-American novelist Vladimir Nabokov. The protagonist and narrator is a French literature professor who moves to New England and writes under the pseudonym Humbert Humbert. He details his obsession ...
'', by Vladimir Nabokov
Vladimir Vladimirovich Nabokov ( ; 2 July 1977), also known by the pen name Vladimir Sirin (), was a Russian and American novelist, poet, translator, and entomologist. Born in Imperial Russia in 1899, Nabokov wrote his first nine novels in Rus ...
, a Russian-American citizen. ''Lolita'', while expressing the prose through a pedophile's narration, directly expresses Nabokov's discourse with decadent literature. According to Will Norman from the University of Kent
The University of Kent (formerly the University of Kent at Canterbury, abbreviated as UKC) is a Collegiate university, collegiate public university, public research university based in Kent, United Kingdom. The university was granted its roya ...
, the novel makes many references to prominent historical figures related to decadence, such as Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic who is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales involving mystery and the macabre. He is widely re ...
and Charles Baudelaire
Charles Pierre Baudelaire (, ; ; 9 April 1821 – 31 August 1867) was a French poet, essayist, translator and art critic. His poems are described as exhibiting mastery of rhythm and rhyme, containing an exoticism inherited from the Romantics ...
. Norman states, "... Lolita ''emerges as the risky reinstatement of a transatlantic decadent tradition, in which the failure of temporal and ethical containment disrupts a dominant narrative of modernism's history in American letters"''. ''Lolita'' purposefully exemplifies a moral decline, while simultaneously disregarding the ethics of Nabokov’s time. The emphasis on its temporal standing in history captures an intermediate state of decadent literature itself. Norman describes that "... Nabokov reproduces the tension between American regionalism and modernist cosmopolitanism
Cosmopolitanism is the idea that all human beings are members of a single community. Its adherents are known as cosmopolitan or cosmopolite. Cosmopolitanism is both prescriptive and aspirational, believing humans can and should be " world citizen ...
in his own 'Edgar H. Humbert', as the European aesthete embarks on his road-trip with Dolores...". The text exemplifies Nabokov's desire to replicate the many social disparities of American culture while using his character, H. Humbert, to demonstrate a lack of moral judgement. Norman continues, "Nabokov's text positions ''itself'' as the dynamic historical agent, importing Poe wholesale (from caricature through to complex literary intellectual) into the present and facilitating his critique in the hands of the reader". Leaving the judgement in the hands of the reader, Nabokov uses ''Lolita'' to work through the complexities that decadence presents for ethical or moral obligations to society. Norman concludes, "''Lolita'' joins American works such as William Faulkner
William Cuthbert Faulkner (; September 25, 1897 – July 6, 1962) was an American writer. He is best known for William Faulkner bibliography, his novels and short stories set in the fictional Yoknapatawpha County, Mississippi, a stand-in fo ...
's ''The Sound and the Fury
''The Sound and the Fury'' is a novel by the American author William Faulkner. It employs several narrative styles, including stream of consciousness. Published in 1929, ''The Sound and the Fury'' was Faulkner's fourth novel, and was not immedi ...
'' (1929) and F. Scott Fitzgerald's '' Tender Is the Night'' (1934) which assimilate themes of incest and sexual pathology into their decadent aesthetics, with the effect of bringing European temporalities into conflict with American social modernity". Using a controversial method, Nabokov employs decadent aesthetics to document a moment of historical transition.
Women in decadence
Not only do the stylistic choices of literature in decadence cause ethical debate, but the presence of women in literature also causes controversy in politics. Viola Parente-Čapková, a Lecturer from the university in Prague, Czech Republic, argues that women writers following decadent literary structure have been overlooked due to their simultaneous influence of thefeminist movement
The feminist movement, also known as the women's movement, refers to a series of social movements and political campaigns for Radical politics, radical and Liberalism, liberal reforms on women's issues created by inequality between men and wom ...
. The belief that women could not separate morality from their writing due to their purposeful prose to argue for women's rights suggests a theme of misogyny, in which men excluded women from being considered Decadent writers because of the possibility of a desire for social change.
Social change
Decadence offers a world-view, in that "it is an ideological phenomenon originating in the experience of a particular group, and it became the aesthetics of the upper-middle class". Changes in European industrialization and urbanization led to the development of the proletariat, nuclear family, and entrepreneurial class . The values of Decadence formed as an opposition to "those of an earlier and supposedly more vital bourgeoisie". Aesthetically, progress turns into decay, activity becomes play instead of goal-oriented work, and art becomes a way of life. To individuals that observe the changes in social structure after rapid industrialization, the idea of progress becomes something to rebel against, because this real-world progress seems to be leaving them behind.Modern-day perspectives
Postmodernist connection to decadence
Nearly a century after the supposed end of the decadent period itself, the spirit and drive of it continued in the next end of the century. Unknowingly following in the footsteps of the decadents before them, postmodernists have subscribed to many of the same habits. Both groups have found themselves simultaneously exhausted by all the new experiences of society while still putting all their efforts into experiencing it all. Thepostmodernist
Postmodernism encompasses a variety of artistic, Culture, cultural, and philosophical movements that claim to mark a break from modernism. They have in common the conviction that it is no longer possible to rely upon previous ways of depicting ...
is simultaneously aware of their desire for modernist
Modernism was an early 20th-century movement in literature, visual arts, and music that emphasized experimentation, abstraction, and Subjectivity and objectivity (philosophy), subjective experience. Philosophy, politics, architecture, and soc ...
disintegration all while enjoying the products of their dying predecessor. This ravenous eye for the new is reflective of the lives of the practicing decadent, where they too enjoyed all the new experiences offered by their own time's modernity. Both events were deeply intertwined with expanding globalization
Globalization is the process of increasing interdependence and integration among the economies, markets, societies, and cultures of different countries worldwide. This is made possible by the reduction of barriers to international trade, th ...
. As seen in the lives of decadents in their literary and visual art pursuit and creation, so too has the postmodernist been given more global connection and experience. During the rise of postmodernism, there has been a clear concentration of power and wealth that supported globalization. This resurgence of power to apply has restructured the desires of the disintegration-loving postmodernist, indulging themselves in all the newness of globalized life. This renewed interest in a global view of the world brought along a renewed interest in different forms of artistic representation as well.

 Modernism tends to belittle popular culture through its oppressive nature, which can be seen as elitist and controlling, as it privileges certain works of art above others. As a result, postmodern artists and writers developed a contempt for the canon, rejecting tradition and
Modernism tends to belittle popular culture through its oppressive nature, which can be seen as elitist and controlling, as it privileges certain works of art above others. As a result, postmodern artists and writers developed a contempt for the canon, rejecting tradition and essentialism
Essentialism is the view that objects have a set of attributes that are necessary to their Identity (philosophy), identity. In early Western thought, Platonic idealism held that all things have such an "essence"—an Theory of forms, "idea" or "f ...
. This disdain for privilege extended to the fields of philosophy, science, and of course, politics. Pierre Bourdieu
Pierre Bourdieu (, ; ; ; 1 August 1930 – 23 January 2002) was a French sociologist and public intellectual. Bourdieu's contributions to the sociology of education, the theory of sociology, and sociology of aesthetics have achieved wide influ ...
provides some insight into the attitudes of this new sub-class and its relation to post-modern theorists, embodied through students of bourgeois descent. They began to pursue their artistic interests at their schools after being shadowed academically. They are victims of verdicts which, like those of the school, appeal to reason and science to block off the paths leading (back) to power, and are quick to denounce science, power, the power of science, and above all perhaps a power which, like the triumphant technology of the moment, appeals to science to legitimate itself. This postmodern way of thought is guided by an anti-institutional temperament that flees competitions and hierarchies. These systems allow art to become confined by labels – postmodern work is difficult to define. In the name of the fight against 'taboos' and the liquidation of 'complexes' they adopt the most external and most easily borrowed aspects of the intellectual life-style, liberated manners, cosmetic or sartorial outrages, emancipated poses and postures, and systematically apply the cultivated disposition to not-yet-legitimate culture (cinema, strip cartoons, the underground), to every-day life (street art), the personal sphere (sexuality, cosmetics, child-rearing, leisure) and the existential (the relation to nature, love, death). Their craft evolves into a way of being that directly criticizes modernist attitudes, and enables postmodern artists and writers with a newfound sense of freedom through rebellion.
Jacques Barzun
 The historian
The historian Jacques Barzun
Jacques Martin Barzun (; November 30, 1907 – October 25, 2012) was a French-born American historian known for his studies of the history of ideas and cultural history. He wrote about a wide range of subjects, including baseball, mystery novels, ...
(1907–2012) gives a definition of decadence which is independent from moral judgement. In his bestseller '' From Dawn to Decadence: 500 Years of Western Cultural Life'' (published 2000) he describes decadent eras as times when "the forms of art as of life seem exhausted, the stages of development have been run through. Institutions function painfully." He emphasizes that "decadent" in his view is "not a slur" but "a technical label".
With reference to Barzun, ''New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'' columnist Ross Douthat
Ross Gregory Douthat ( ; born November 28, 1979) is a conservative American author and ''New York Times'' columnist. He was a senior editor of '' The Atlantic''. He has written on religion, politics, and society.
Early life and education
Ross Gr ...
characterizes decadence as a state of "economic stagnation, institutional decay and cultural and intellectual exhaustion at a high level of material prosperity and technological development". Douthat sees the West in the 21st century in an "age of decadence", marked by stalemate and stagnation. He is the author of the book ''The Decadent Society'', published by Simon & Schuster
Simon & Schuster LLC (, ) is an American publishing house owned by Kohlberg Kravis Roberts since 2023. It was founded in New York City in 1924, by Richard L. Simon and M. Lincoln Schuster. Along with Penguin Random House, Hachette Book Group US ...
in 2020.
Pria Viswalingam
Pria Viswalingam, an Australian documentary and film maker, sees the western world in decay since the late 1960s. Viswalingam is the author of the six-episode documentary TV series ''Decadence: The Meaninglessness of Modern Life'', broadcast in 2006 and 2007, and the 2011 documentary film ''Decadence: The Decline of the Western World''. According to Viswalingam, western culture started in 1215 with theMagna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter"), sometimes spelled Magna Charta, is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the Archbishop of Canterbury, Cardin ...
, continued to the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, the Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
, the founding of the United States, the Enlightenment and culminated with the social revolutions of the 1960s.
Since 1969, the year of the moon landing
A Moon landing or lunar landing is the arrival of a spacecraft on the surface of the Moon, including both crewed and robotic missions. The first human-made object to touch the Moon was Luna 2 in 1959.
In 1969 Apollo 11 was the first cr ...
, the My Lai massacre, the Woodstock Festival
The Woodstock Music and Art Fair, commonly referred to as Woodstock, was a music festival held from August 15 to 18, 1969, on Max Yasgur's dairy farm in Bethel, New York, southwest of the town of Woodstock, New York, Woodstock. Billed as "a ...
and the Altamont Free Concert
The Altamont Speedway Free Festival was a counterculture rock concert in the United States, held on Saturday, December 6, 1969, at the Altamont Speedway outside of Tracy, California. Approximately 300,000 attended the concert, with some an ...
, "decadence depicts the west's decline". As symptoms he names increasing suicide rates, addiction to anti-depressants
Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction.
Common side effects of antidepressants include dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, akathisia, sex ...
, exaggerated individualism, broken families and a loss of religious faith as well as "treadmill consumption, growing income-disparity, b-grade leadership" and money as the only benchmark for value.
Use in Marxism
Leninism
According toVladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov ( 187021 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, politician and political theorist. He was the first head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 until Death and state funeral of ...
, capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
had reached its highest stage and could no longer provide for the general development of society. He expected reduced vigor in economic activity and a growth in unhealthy economic phenomena, reflecting capitalism's gradually decreasing capacity to provide for social needs and preparing the ground for socialist
Socialism is an economic ideology, economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse Economic system, economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes ...
revolution in the West. Politically, World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
proved the decadent nature of the advanced capitalist countries to Lenin, that capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
had reached the stage where it would destroy its own prior achievements more than it would advance.Decadence: The Theory of Decline or the Decline of Theory? (Part I)'' Aufheben''. Summer 1993. One who directly opposed the idea of decadence as expressed by Lenin was José Ortega y Gasset in '' The Revolt of the Masses'' (1930). He argued that the " mass man" had the notion of material progress and scientific advance deeply inculcated to the extent that it was an expectation. He also argued that contemporary progress was opposite the true decadence of the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
.
Left communism
Decadence is an important aspect of contemporary left communist theory. Similar to Lenin's use of it, left communists, coming from the Communist International themselves started in fact with a theory of decadence in the first place, yet the communist left sees the theory of decadence at the heart of Marx's method as well, expressed in famous works such as ''The Communist Manifesto
''The Communist Manifesto'' (), originally the ''Manifesto of the Communist Party'' (), is a political pamphlet written by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, commissioned by the Communist League and originally published in London in 1848. The ...
'', ''Grundrisse
The ''Grundrisse der Kritik der Politischen Ökonomie'' (, ), often simply the ''Grundrisse'' (, ), is an unfinished manuscript by the German philosopher Karl Marx. The series of seven notebooks was rough-drafted by Marx, chiefly for purposes ...
'', ''Das Kapital
''Capital: A Critique of Political Economy'' (), also known as ''Capital'' or (), is the most significant work by Karl Marx and the cornerstone of Marxian economics, published in three volumes in 1867, 1885, and 1894. The culmination of his ...
'' but most significantly in '' Preface to the Critique of Political Economy''.Marx, Karl (1859). ''A Contribution to the Critique of Political Economy.'' Progress Publishers.
Contemporary left communist theory defends that Lenin was mistaken on his definition of imperialism (although how grave his mistake was and how much of his work on imperialism is valid varies from groups to groups) and Rosa Luxemburg
Rosa Luxemburg ( ; ; ; born Rozalia Luksenburg; 5 March 1871 – 15 January 1919) was a Polish and naturalised-German revolutionary and Marxist theorist. She was a key figure of the socialist movements in Poland and Germany in the early 20t ...
to be basically correct on this question, thus accepting capitalism as a world epoch similarly to Lenin, but a world epoch from which no capitalist state can oppose or avoid being a part of. On the other hand, the theoretical framework of capitalism's decadence varies between different groups while left communist organizations like the International Communist Current hold a basically Luxemburgist analysis that makes an emphasis on the world market and its expansion, others hold views more in line with those of Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov ( 187021 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, politician and political theorist. He was the first head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 until Death and state funeral of ...
, Nikolai Bukharin
Nikolai Ivanovich Bukharin (; rus, Николай Иванович Бухарин, p=nʲɪkɐˈlaj ɪˈvanəvʲɪdʑ bʊˈxarʲɪn; – 15 March 1938) was a Russian revolutionary, Soviet politician, and Marxist theorist. A prominent Bolshevik ...
and most importantly Henryk Grossman and Paul Mattick with an emphasis on monopolies and the falling rate of profit
In economics and finance, the profit rate is the relative profitability of an investment project, a capitalist enterprise or a whole capitalist economy. It is similar to the concept of rate of return on investment.
Historical cost ''vs.'' mark ...
.
See also
* Acedia *Anomie
In sociology, anomie or anomy () is a social condition defined by an uprooting or breakdown of any moral values, standards or guidance for individuals to follow. Anomie is believed to possibly evolve from conflict of belief systems and causes b ...
* Behavioral sink
* Bread and circuses
* Buraiha
* Competence (human resources)
Competence is the set of demonstrable personal characteristics or KSAOs (Knowledge, Skills, Abilities, and Other characteristics) that enable job performance at a high level with consistency and minimal difficulty. Competency in human resources ...
* Kleptocracy
Kleptocracy (from Greek , "thief", or , "I steal", and from , "power, rule"), also referred to as thievocracy, is a government whose corrupt leaders (kleptocrats) use political power to expropriate the wealth of the people and land the ...
* Late capitalism
The concept of late capitalism (in German: ''Spätkapitalismus''), also known as late-stage capitalism, was first used by the German social scientist Werner Sombart (1863–1941) in 1928, to describe the new capitalist order emerging at that tim ...
* Moral relativism
Moral relativism or ethical relativism (often reformulated as relativist ethics or relativist morality) is used to describe several Philosophy, philosophical positions concerned with the differences in Morality, moral judgments across different p ...
* Privilege hazard
* Societal collapse
Societal collapse (also known as civilizational collapse or systems collapse) is the fall of a complex human society characterized by the loss of cultural identity and of social complexity as an Complex adaptive system, adaptive system, the downf ...
* Twilight of the Idols
* The Decline of the West
* Degenerate art
References
Further reading
* Richard Gilman, ''Decadence: The Strange Life of an Epithet'' (1979). * Matei Calinescu, ''Five Faces of Modernity''. * Mario Praz, ''The Romantic Agony'' (1930). *Jacques Barzun
Jacques Martin Barzun (; November 30, 1907 – October 25, 2012) was a French-born American historian known for his studies of the history of ideas and cultural history. He wrote about a wide range of subjects, including baseball, mystery novels, ...
, '' From Dawn to Decadence'', (2000).
* A. E. Carter, ''The Idea of Decadence in French Literature'' (1978).
* Michael Murray, ''Jacques Barzun: Portrait of a Mind'' (2011).
External links
Collection of the articles of the International Communist Current on the Theory of Decadence
{{authority control Art movements Concepts in ethics Modern art Political theories