Dai Commandery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dai Commandery was a commandery (''jùn'') of the state of Zhao established BC and of northern imperial Chinese dynasties until the time of the Emperor Wen of the
 The name derives from the
The name derives from the
 Dai Commandery was first established around 300BC during China's
Dai Commandery was first established around 300BC during China's
 Dai Commandery was one of the divisions of the
Dai Commandery was one of the divisions of the
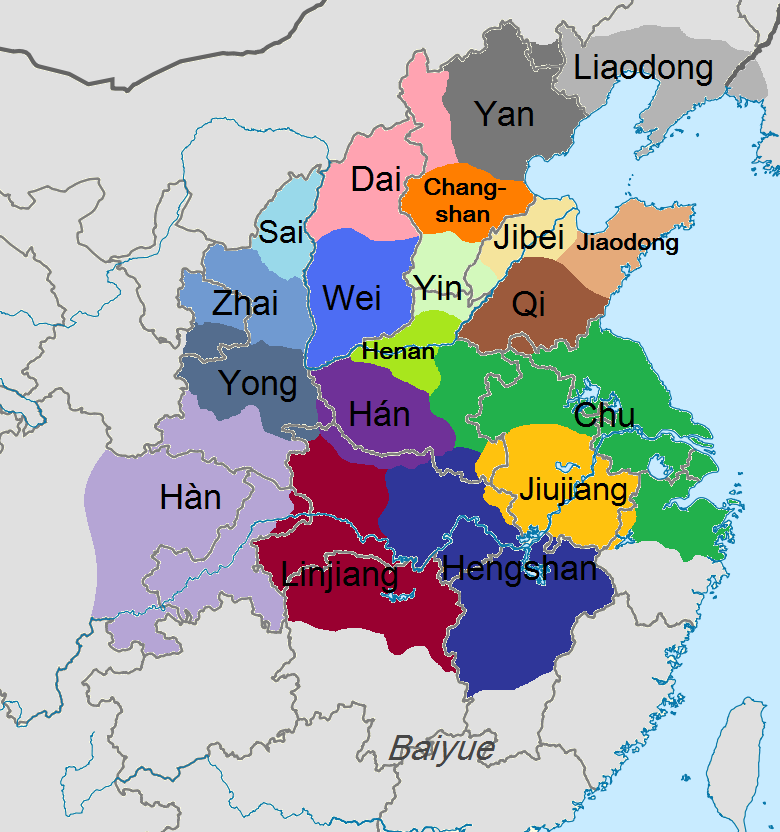 During the interregnum following Qin's collapse, Dai was one of the
During the interregnum following Qin's collapse, Dai was one of the
 Under the Han, Dai Prefecture formed part of the
Under the Han, Dai Prefecture formed part of the
《代郡》
at Baike.com {{Han dynasty provinces Former commanderies of China Commanderies of the Qin dynasty Commanderies of the Han dynasty Commanderies of the Jin dynasty (266–420) Commanderies of the Sui dynasty
Sui dynasty
The Sui dynasty (, ) was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China that lasted from 581 to 618. The Sui unified the Northern and Southern dynasties, thus ending the long period of division following the fall of the Western Jin dynasty, and layi ...
(r. AD581–604). It occupied lands in what is now Hebei, Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-lev ...
, and Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for ...
. Its seat
A seat is a place to sit. The term may encompass additional features, such as back, armrest, head restraint but also headquarters in a wider sense.
Types of seat
The following are examples of different kinds of seat:
* Armchair (furniture), ...
was usually at Dai or Daixian (near present-day Yuzhou in Hebei), although it was moved to Gaoliu (present-day Yanggao
Yanggao County is a county in the northeast of Shanxi province, China, bordering Inner Mongolia to the northwest and Hebei province to the east. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Datong.
History
Yanggao was formerl ...
in Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-lev ...
) during the Eastern Han
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a wa ...
.
Name
 The name derives from the
The name derives from the White Di
The Di or Beidi (Northern Di) were various ethnic groups who lived north of the Chinese (''Huaxia'') realms during the Zhou dynasty. Although initially described as nomadic, they seem to have practiced a mixed pastoral, agricultural, and hunting ...
kingdom of Dai, conquered by the Zhao family of Jin.
History
Zhao Kingdom
 Dai Commandery was first established around 300BC during China's
Dai Commandery was first established around 300BC during China's Warring States Period
The Warring States period () was an era in ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded with the Qin wars of conquest ...
by the state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* '' Our ...
of Zhao's King Yong, posthumously known as the Wuling ("Martial-&-Numinous") King.. The commandery seat—then known as Dai—was southwest of present-day Yuzhou in Hebei.. It was the former capital of the independent state of Dai, which had been conquered by King Yong's ancestors around 476BC.. He created Dai Commandery along with its companion commanderies of Yanmen
Yanmen Pass, also known by its Chinese name Yanmenguan and as Xixingguan, is a mountain pass which includes three fortified gatehouses along the Great Wall of China. The area was a strategic choke point in ancient and medieval China, contr ...
and Yunzhong
Yunzhong Commandery ( zh, 雲中郡) was a historical commandery of China. Its territories were located between the Great Wall and Yin Mountains, and correspond to part of modern-day Hohhot, Baotou and Ulanqab prefectures in Inner Mongolia.
The ...
to consolidate his conquests from invasions of the Loufan ( t s ''Lóufán'') and " forest nomads" ( ''Línhú'') in 306 and 304BC.
Following the Qin conquest
Conquest is the act of military subjugation of an enemy by force of arms.
Military history provides many examples of conquest: the Roman conquest of Britain, the Mauryan conquest of Afghanistan and of vast areas of the Indian subcontinent, t ...
of Zhao, Zhao Jia attempted to regroup at Dai, declaring himself its king. This Kingdom of Dai was ended by Qin in 222BC, just prior to the declaration of the Qin Empire
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin state (modern Gansu and Shaanxi), the ...
two years later.
Qin Empire
 Dai Commandery was one of the divisions of the
Dai Commandery was one of the divisions of the Qin Empire
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin state (modern Gansu and Shaanxi), the ...
. Its seat—then known as Daixian—continued to be near present-day Yuzhou..
Eighteen Kingdoms
 During the interregnum following Qin's collapse, Dai was one of the
During the interregnum following Qin's collapse, Dai was one of the Eighteen Kingdoms
The historiographical term "Eighteen Kingdoms" ( zh, t=十八國), also translated to as "Eighteen States", refers to the eighteen ''fengjian'' states in China created by military leader Xiang Yu in 206 BCE, after the collapse of the Qin dynasty. ...
established by Xiang Yu
Xiang Yu (, –202 BC), born Xiang Ji (), was the Hegemon-King (Chinese: 霸王, ''Bà Wáng'') of Western Chu during the Chu–Han Contention period (206–202 BC) of China. A noble of the Chu state, Xiang Yu rebelled against the Qin dyna ...
. It was ruled by Zhao Xie and Chun Yu.
Western Han Empire
province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outsi ...
of Bingzhou and oversaw 18 counties, both within and beyond the Great Wall
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against various nomadic grou ...
. Along with Yunzhong
Yunzhong Commandery ( zh, 雲中郡) was a historical commandery of China. Its territories were located between the Great Wall and Yin Mountains, and correspond to part of modern-day Hohhot, Baotou and Ulanqab prefectures in Inner Mongolia.
The ...
and Yanmen
Yanmen Pass, also known by its Chinese name Yanmenguan and as Xixingguan, is a mountain pass which includes three fortified gatehouses along the Great Wall of China. The area was a strategic choke point in ancient and medieval China, contr ...
, it also formed part of the Principality of Dai
Prince or King of Dai was an ancient and medieval Chinese title.
King of Dai is sometimes used to describe the heads of the Baidi state of Dai north of the Zhou Kingdom that was conquered by the Zhao clan of Jin. It was used as the title for t ...
, used as an imperial appanage
An appanage, or apanage (; french: apanage ), is the grant of an estate, title, office or other thing of value to a younger child of a sovereign, who would otherwise have no inheritance under the system of primogeniture. It was common in much ...
. The ''Book of Han
The ''Book of Han'' or ''History of the Former Han'' (Qián Hàn Shū,《前汉书》) is a history of China finished in 111AD, covering the Western, or Former Han dynasty from the first emperor in 206 BCE to the fall of Wang Mang in 23 CE. ...
'' records Dai Commandery having 278,754 people living in 56,771 households. The Han administration kept the seat at Daixian near present-day Yuzhou and continued the Qin-era counties (renaming "New Pingshu County" to simply "Pingshu County
''Pingshu'' () or ''pinghua'' () refers to the traditional Han Chinese performing art of storytelling with no musical accompaniment. It is better known as ''pingshu'' in northern China and ''pinghua'' in southern China.
Performing art
Pingsh ...
"), with the addition of:
Xin Empire
Under the short-livedXin dynasty
The Xin dynasty (; ), also known as Xin Mang () in Chinese historiography, was a short-lived Chinese imperial dynasty which lasted from 9 to 23 AD, established by the Han dynasty consort kin Wang Mang, who usurped the throne of the Emperor Ping ...
established by Wang Mang
Wang Mang () (c. 45 – 6 October 23 CE), courtesy name Jujun (), was the founder and the only emperor of the short-lived Chinese Xin dynasty. He was originally an official and consort kin of the Han dynasty and later seized the thro ...
, several of the Han counties were renamed.
Eastern Han Empire
Under theEastern Han
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a wa ...
, Dai Commandery formed part of the province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outsi ...
of Youzhou. Its seat—then known as Gaoliu—was southwest of present-day Yanggao
Yanggao County is a county in the northeast of Shanxi province, China, bordering Inner Mongolia to the northwest and Hebei province to the east. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Datong.
History
Yanggao was formerl ...
in northeastern Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-lev ...
.
Wei Kingdom
During China'sThree Kingdoms Period
The Three Kingdoms () from 220 to 280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the dynastic states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The Three Kingdoms period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and was followed by the Wester ...
, Wei
Wei or WEI may refer to:
States
* Wey (state) (衛, 1040–209 BC), Wei in pinyin, but spelled Wey to distinguish from the bigger Wei of the Warring States
* Wei (state) (魏, 403–225 BC), one of the seven major states of the Warring States per ...
returned the commandery seat to Daixian (near present-day Yuzhou, Hebei).
Sixteen Kingdoms
During China'sSixteen Kingdoms Period
The Sixteen Kingdoms (), less commonly the Sixteen States, was a chaotic period in Chinese history from AD 304 to 439 when northern China fragmented into a series of short-lived dynastic states. The majority of these states were founded by ...
, both Later Yan
Yan, known in historiography as the Later Yan (; 384 – 407 or 409) was a dynastic state of China ruled by the Xianbei people, located in modern-day northeast China, during the era of Sixteen Kingdoms.
All rulers of the Later Yan declared them ...
and the Northern Wei had commanderies named Dai. Northern Wei's lay to the west, with its seat at Pingcheng (present-day Datong
Datong is a prefecture-level city in northern Shanxi Province in the People's Republic of China. It is located in the Datong Basin at an elevation of and borders Inner Mongolia to the north and west and Hebei to the east. As of the 2020 cen ...
, Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-lev ...
).
Separate from these, Tuoba Yilu was declared "Duke of Dai
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ...
" () by the Jin in AD310 and (vassal) "King of Dai
Prince or King of Dai was an ancient and medieval Chinese title.
King of Dai is sometimes used to describe the heads of the Baidi state of Dai north of the Zhou Kingdom that was conquered by the Zhao clan of Jin. It was used as the title for t ...
" by the same court in 315. This Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were a Proto-Mongolic ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into t ...
Kingdom of Dai lasted until 376, and its dynasts were responsible for the later state of Northern Wei. It held some lands in northern Shanxi and Hebei but was mostly to their north in what is now Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for ...
, with their capital at Shengle (northwest of present-day Horinger).
Sui Empire
Dai Commandery continued until its abolishment under the Wen Emperor of Sui, who replaced it in 585 withDai Prefecture
Dai Prefecture, also known by its Chinese name Daizhou, was a prefecture (''zhou'') of imperial China in what is now northern Shanxi. It existed intermittently from AD585 to 1912. Its eponymous seat Daizhou was located at Shangguan in Dai Cou ...
, whose seat was at Guangwu or Yanmen (present-day Daixian, Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-lev ...
)..
Notes
References
Citations
Bibliography
* . * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * .External links
《代郡》
at Baike.com {{Han dynasty provinces Former commanderies of China Commanderies of the Qin dynasty Commanderies of the Han dynasty Commanderies of the Jin dynasty (266–420) Commanderies of the Sui dynasty