|
Wang Mang
Wang Mang (45 BCE6 October 23 CE), courtesy name Jujun, officially known as the Shijianguo Emperor (), was the founder and the only emperor of the short-lived Chinese Xin dynasty. He was originally an official and consort kin of the Han dynasty and later seized the throne in 9 CE. The Han dynasty was restored after his overthrow, and his rule marked the separation between the Western Han dynasty (before Xin) and Eastern Han dynasty (after Xin). Traditional Chinese historiography viewed Wang as a tyrant and usurper, while more recently, some historians have portrayed him as a visionary and selfless social reformer. During his reign, he abolished slavery and initiated a land redistribution program. Though a learned Confucian scholar who sought to implement the harmonious society he saw in the Chinese classics, his efforts ended in chaos. Wang Mang's late reign saw large-scale peasant rebellions, most notably the revolt of the Red Eyebrows. In October 23 CE, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang (surname)
Wang () is the pinyin romanization of Chinese, romanization of the common Chinese surname (''Wáng''). It has a mixture of various origin with uncertain lineage of family history, however it is currently the list of common Chinese surnames, most common surname in Mainland China, one of the most common surnames in Asia, with more than 107 million in Asia. It is the 8th name listed in the famous Hundred Family Surnames. [Public Security Bureau Statistics: 'Wang' Found China's #1 'Big Family', Includes 92.88m People]." 24 Apr 2007. Accessed 27 Mar 2012. A separate surname (''Wāng'') is also romanized as Wang. Wang also has less common unrelated origins in the North Germanic languages, Scandinavian and Germanic languages. Population and distribution Wáng is one of the most common surnames in the ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Guangwu Of Han
Emperor Guangwu of Han (; 15 January 5 BC29 March AD 57), born Liu Xiu (), courtesy name Wenshu (), was a Chinese monarch. He served as an emperor of the Han dynasty by restoring the dynasty in AD 25, thus founding the Eastern Han dynasty. He ruled over parts of China at first since his dynasty was formed through rebellion against the short-lived Xin dynasty, and through suppression and conquest of regional warlords, the whole of China proper was consolidated by the time of his death in AD 57. During his reign, Taoism was made the official religion of China, and the Chinese folk religion began to decline. Liu Xiu was one of the many descendants of the Han imperial family. Following the usurpation of the Han throne by Wang Mang and the ensuing civil war during the disintegration of Wang's Xin dynasty, he emerged as one of several descendants of the fallen dynasty claiming the imperial throne. After assembling forces and proclaiming himself emperor in the face of competitors, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empress Xu (Cheng)
Empress Xu (許皇后) (personal name unknown, but likely Xu Kua ��誇 (died December 8 BC) was an empress during the Han dynasty, who came from a powerful family. She was initially loved by her husband Emperor Cheng, but she eventually lost favor, and as a result of the machinations of her eventual successor, Empress Zhao Feiyan, she was deposed. After she was removed, she tried in vain to regain a measure of dignity by conspiring with her husband's cousin Chunyu Zhang (淳于長), but that conspiracy would eventually lead to her being forced to commit suicide. Family background and marriage to then-Crown Prince Ao Empress Xu was a daughter of Xu Jia (許嘉), the Marquess of Ping'en and a brother of Emperor Xuan's first wife Empress Xu Pingjun, who was the mother of Emperor Yuan. Emperor Yuan frequently grieved for his mother because she was murdered while he was still young by Huo Guang's wife Xian (顯), so he resolved to marry a daughter of the Xu clan to his son, Crow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empress Zhao Feiyan
Zhao Feiyan (, ? – September or October 1 BC),Peterson, Barbara Bennett & He Hong Fei & Han Tie & Wang Jiyu & Zhang Guangyu. (1999) ''Notable Women of China'' "M.E. Sharpe". pp. 87–90. . formally Empress Xiaocheng (孝成皇后), was a Chinese courtesan and empress. She was an empress during the Han dynasty. Her husband was Emperor Cheng. She was known in the collective consciousness of Chinese society more for her beauty than for the regal presence that she and her sister, the Consort Zhao Hede engaged in and exuded, but unlike most of the famous beauties in Chinese history (such as the Four Beauties), she was often vilified by her own sisters. She was often contrasted with Yang Guifei, the concubine of Emperor Xuanzong of Tang, because she was known for her slender build while Yang was known for her full build. This led to the Chinese idiom ''huanfei yanshou'' (環肥燕瘦, literally "fat Huan, thin Fei"), describing the range of beauty types. Later, the idiom was applie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marches
In medieval Europe, a march or mark was, in broad terms, any kind of borderland, as opposed to a state's "heartland". More specifically, a march was a border between realms or a neutral buffer zone under joint control of two states in which different laws might apply. In both of these senses, marches served a political purpose, such as providing warning of military incursions or regulating cross-border trade. Marches gave rise to the titles marquess (masculine) or marchioness (feminine). Etymology The word "march" derives ultimately from a Proto-Indo-European root *''merg-'', meaning "edge, boundary". The root *''merg-'' produced Latin ''margo'' ("margin"), Old Irish ''mruig'' ("borderland"), Welsh ''bro'' ("region, border, valley") and Persian and Armenian '' marz'' ("borderland"). The Proto-Germanic ''*marko'' gave rise to the Old English word ''mearc'' and Frankish ''marka'', as well as Old Norse ''mǫrk'' meaning "borderland, forest", and derived from ''merki'' "boundary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquess
A marquess (; ) is a nobleman of high hereditary rank in various European peerages and in those of some of their former colonies. The German-language equivalent is Markgraf (margrave). A woman with the rank of a marquess or the wife (or widow) of a marquess is a marchioness () or marquise (). These titles are also used to translate equivalent Asian styles, as in Imperial China and Imperial Japan. Etymology The word ''marquess'' entered the English language from the Old French ("ruler of a border area") in the late 13th or early 14th century. The French word was derived from ("frontier"), itself descended from the Middle Latin ("frontier"), from which the modern English word ''March (territory), march'' also descends. The distinction between governors of frontier territories and interior territories was made as early as the founding of the Roman Empire when some provinces were set aside for administration by the senate and more unpacified or vulnerable provinces were adm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empress Dowager
Empress dowager (also dowager empress or empress mother; ) is the English language translation of the title given to the mother or widow of a monarch, especially in regards to Chinese, Japanese, Korean, or Vietnamese monarchs in the Chinese cultural sphere. The term however, is applied well beyond just East Asia. The title was also given occasionally to another woman of the same generation, while a woman from the previous generation was sometimes given the title of grand empress dowager (). An empress dowager wielded power over the harem and imperial family. Numerous empress dowagers held regency during the reign of underage emperors. Many of the most prominent empress dowagers also extended their control for long periods after the emperor was old enough to govern. This was a source of political turmoil according to the traditional view of Chinese history. In Europe, the title dowager empress was given to the wife of a deceased Emperor of Russia or Holy Roman Emperor. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Cheng Of Han
Emperor Cheng of Han, personal name Liu Ao (劉驁; 51 BC – 17 April 7 BC), was an emperor of the Chinese Han dynasty ruling from 33 until 7 BC. He succeeded his father, Emperor Yuan. Under Emperor Cheng, the Han dynasty continued its growing disintegration as the emperor's maternal relatives from the Wang clan increased their grip on the levers of power and on governmental affairs as encouraged by the previous emperor. Corruption and greedy officials continued to plague the government and, as a result, rebellions broke out throughout the country. Emperor Cheng died childless after a reign of 26 years; both of his sons by concubines had died in infancy. One of them starved to death and another was suffocated in prison. The babies and their mothers were killed by the order of Emperor Cheng's favorite consort Zhao Hede, with the implied consent of the emperor. He was succeeded by his nephew, Emperor Ai, whose death was followed by Wang Mang's rise to power. Birth and caree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
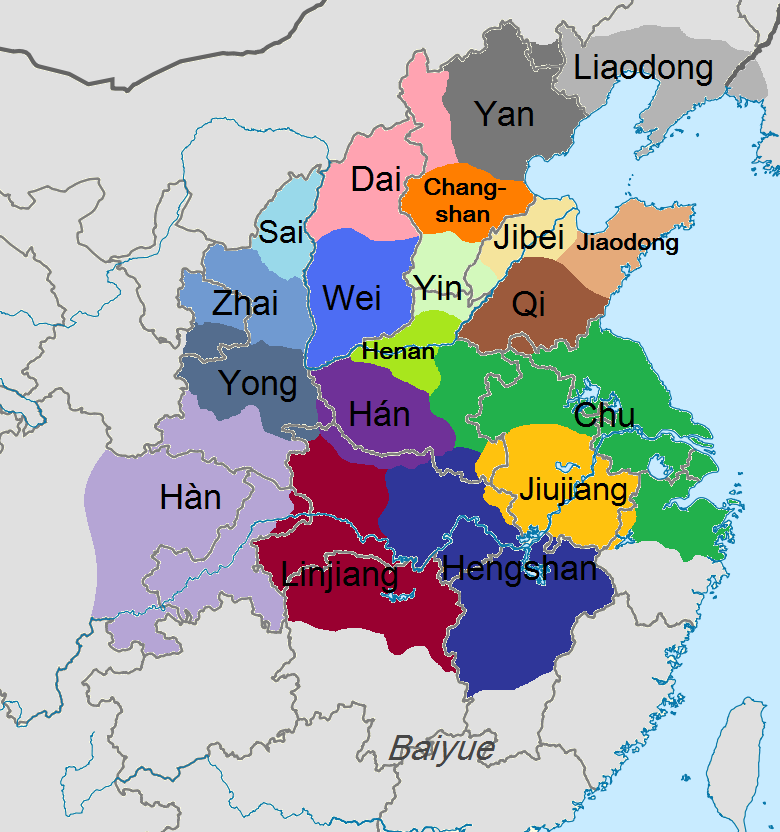
Eighteen Kingdoms
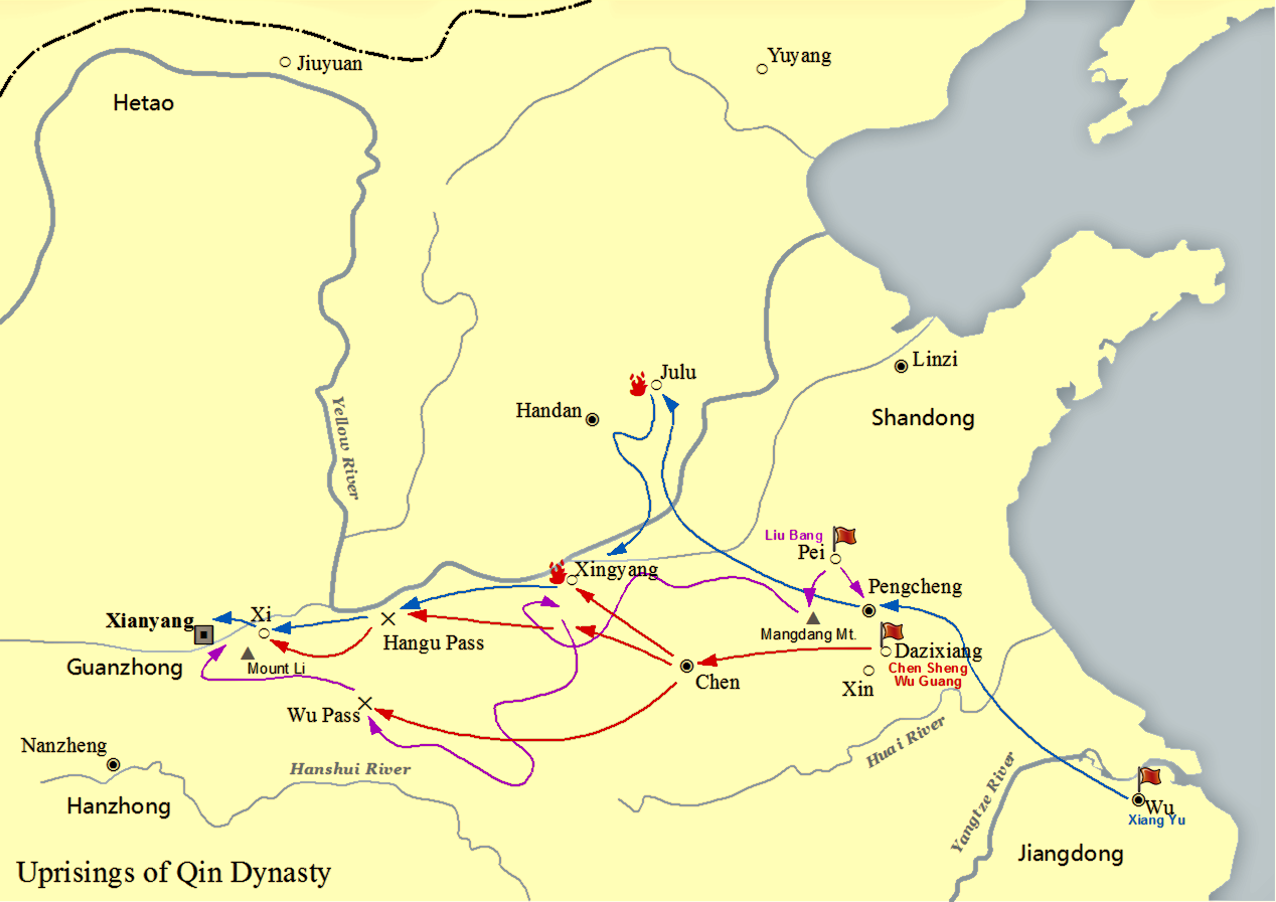
The historiographical term "Eighteen Kingdoms" ( zh, t=十八國), also translated as "Eighteen States", refers to the eighteen '' fengjian'' states in China created by military leader Xiang Yu in 206 BCE, after the collapse of the Qin dynasty.林达礼,中华五千年大事记, 台南大孚书局, 1982, p. 56 The establishment and abolishment of the Eighteen Kingdoms marked the beginning and end of a turbulent interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention. The details of the feudal division are as follows: The Eighteen Kingdoms were short-lived. Almost immediately rebellion broke out in Qi, after which Tian Rong conquered Jiaodong and Jibei, reuniting the old Qi state. Meanwhile, Xiang Yu had Emperor Yi of Chu and King Han Cheng of Hán killed. Thereafter, Liu Bang of Hàn conquered the lands of the Three Qins, thereby formally starting the Chu–Han Contention. Following many battles and changing alliances, Han defeated Chu and subdued all other kingdoms, where Liu Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jian Of Qi
Tian Jian, commonly known as "Jian, King of Qi" (), was the last king of the Qi state. Life Tian Jian succeeded his father, King Xiang, who died in 265 BC. He reigned for 44 years. At the time he acceded to the throne, Qi was one of the wealthiest states, and it was on the seacoast far from the most aggressive state, Qin. For years, Tian Jian's mother acted as his advisor. On her deathbed she wanted to tell her son which ministers she thought were the best. But when the writing materials arrived she could no longer tell him. After she died, Hou Sheng (后勝) became his prime minister. It was alleged by some sources that Hou Sheng was in the pay of the state of Qin. In Strategies of the Warring States, The Book of Qi One famous anecdote is that after the Battle of Changping in 260 BC, in which, according to the historian Sima Qian, 450,000 soldiers of the state of Zhao were killed by the Qin army, King Jian was advised: "Zhao is a hedge that protects Qi... just as the lips ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiang Yu
Xiang Yu (), born Xiang Ji, was a Chinese warlord who founded and led the short-lived ancient Chinese states, kingdom-state of Western Chu during the interregnum period between the Qin dynasty, Qin and Han dynasty, Han dynasties of China, dynasties known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC). A nobleman of the former state of Chu, Xiang Yu rebelled against the Qin dynasty under the command of his uncle Xiang Liang, and was granted the title of "Duke of Lu" () by Emperor Yi of Chu, King Huai II of the restoring Chu state in 208 BC. The following year, he led an outnumbered Chu army to victory at the Battle of Julu against the Qin armies led by Zhang Han (Qin dynasty), Zhang Han. After the fall of Qin, Xiang Yu divided the country into a federacy of Eighteen Kingdoms, among which he was self-titled as the "Hegemon-King of Western Chu" () and ruled a vast region spanning central and eastern China, with Pengcheng as his capital. Although a formidable warrior and milita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |