DOCP on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
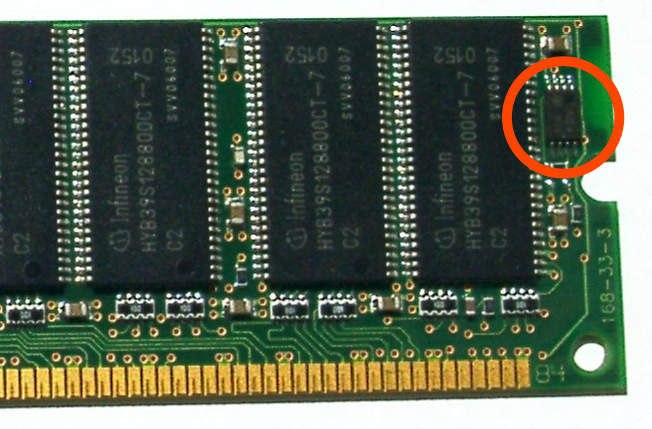 The first SPD specification was issued by JEDEC and tightened up by Intel as part of its
The first SPD specification was issued by JEDEC and tightened up by Intel as part of its
"SPDs for DDR SDRAM"JEDEC Standard 21-C section 4.1.2.10
"Specific SPDs for DDR2 SDRAM"JEDEC Standard 21-C section 4.1.2.11
"Serial Presence Detect (SPD) for DDR3 SDRAM Modules"JEDEC Standard 21-C section 4.1.2
"SERIAL PRESENCE DETECT STANDARD, General Standard"JEDEC Standard 21-C section 4.1.2.5
"Specific PDs for Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM)" while some of the remainder is earmarked for manufacturer identification. However, a 256-byte EEPROM is generally provided. A number of uses have been made of the remaining space. Memory generally comes with conservative timing recommendations in the SPD ROM, to ensure basic functionality on all systems. Enthusiasts often spend considerable time manually adjusting the memory timings for higher speed. Enabling special configurations such as Intel XMP or AMD EXPO often requires additional testing to ensure system stability and may void CPU warranty if used out of the manufacturer’s published specifications.
dmidecode
program that can decode information about memory (and other things) and runs on
spdmem(4)
since version 4.3 to provide information about memory modules. The driver was ported from NetBSD, where it is available since release 5.0. *
computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, hardware and softw ...
, serial presence detect (SPD) is a standardized way to automatically access information about a memory module
In computing, a memory module or RAM stick is a printed circuit board on which Computer memory, memory integrated circuits are mounted.
Memory modules permit easy installation and replacement in electronic systems, especially computers such as ...
. Earlier 72-pin SIMM
A SIMM (single in-line memory module) is a type of memory module used in computers from the early 1980s to the early 2000s. It is a printed circuit board upon which multiple random-access memory Integrated circuit chips are attached to one or ...
s included five pins that provided five bits of ''parallel presence detect'' (PPD) data, but the 168-pin DIMM
A DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) is a popular type of memory module used in computers. It is a printed circuit board with one or both sides (front and back) holding DRAM chips and pins. The vast majority of DIMMs are manufactured in compl ...
standard changed to a serial presence detect to encode more information.
When an ordinary modern computer is turned on, it starts by doing a power-on self-test
A power-on self-test (POST) is a process performed by firmware or software routines immediately after a computer or other digital electronic device is powered on.
POST processes may set the initial state of the device from firmware and detec ...
(POST). Since about the mid-1990s, this process includes automatically configuring the hardware currently present. SPD is a memory hardware feature that makes it possible for the computer to know what memory is present, and what memory timings
Memory timings or RAM timings describe the timing information of a memory module or the onboard LPDDRx. Due to the inherent qualities of VLSI and microelectronics, memory chips require time to fully execute commands. Executing commands too quickl ...
to use to access the memory.
Some computers adapt to hardware changes completely automatically. In most cases, there is a special optional procedure for accessing BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is a type of firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization d ...
parameters, to view and potentially make changes in settings. It may be possible to control how the computer uses the memory SPD data—to choose settings, selectively modify memory timings, or possibly to completely override the SPD data (see overclocking
In computing, overclocking is the practice of increasing the clock rate of a computer to exceed that certified by the manufacturer. Commonly, operating voltage is also increased to maintain a component's operational stability at accelerated sp ...
).
Stored information
For a memory module to support SPD, theJEDEC
The Joint Electron Device Engineering Council (JEDEC) Solid State Technology Association is a consortium of the semiconductor industry headquartered in Arlington County, Virginia, Arlington, United States. It has over 300 members and is focused ...
standards require that certain parameters be in the lower 128 bytes of an EEPROM
EEPROM or E2PROM (electrically erasable programmable read-only memory) is a type of non-volatile memory. It is used in computers, usually integrated in microcontrollers such as smart cards and remote keyless systems, or as a separate chip d ...
located on the memory module. These bytes contain timing parameters, manufacturer, serial number and other useful information about the module. Devices utilizing the memory automatically determine key parameters of the module by reading this information. For example, the SPD data on an SDRAM
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal.
DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the ...
module might provide information about the CAS latency
Column address strobe latency, also called CAS latency or CL, is the delay in clock cycles between the READ command and the moment data is available. In asynchronous DRAM, the interval is specified in nanoseconds (absolute time). In synchronou ...
so the system can set this correctly without user intervention.
The SPD EEPROM firmware is accessed using SMBus
The System Management Bus (SMBus or SMB) is a single-ended simple two-wire bus for the purpose of lightweight communication. Most commonly it is found in chipsets of computer motherboards for communication with the power source for ON/OFF instru ...
, a variant of the I2C protocol. This reduces the number of communication pins on the module to just two: a clock signal and a data signal. The EEPROM shares ground pins with the RAM, has its own power pin, and has three additional pins (SA0–2) to identify the slot, which are used to assign the EEPROM a unique address in the range 0x50–0x57. Not only can the communication lines be shared among 8 memory modules, the same SMBus is commonly used on motherboards for system health monitoring tasks such as reading power supply voltages, CPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes instructions of a computer program, such as arithmetic, log ...
temperatures, and fan speeds.
SPD EEPROMs also respond to I2C addresses 0x30–0x37 if they have not been write protected, and an extension (TSE series) uses addresses 0x18–0x1F to access an optional on-chip temperature sensor. All those values are seven-bit I2C addresses formed by a Device Type Identifier Code prefix (DTIC) with SA0-2: to read (1100) from slot 3, one uses 110 0011 = 0x33. With a final R/W bit it forms the 8-bit Device Select Code. Note that the semantics of slot-id is different for write-protection operations: for them they can be not passed by the SA pins at all.
Before SPD, memory chips were spotted with parallel presence detect (PPD). PPD used a separate pin for each bit of information, which meant that only the speed and density of the memory module could be stored because of the limited space for pins.
SDR SDRAM
 The first SPD specification was issued by JEDEC and tightened up by Intel as part of its
The first SPD specification was issued by JEDEC and tightened up by Intel as part of its PC100
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal.
DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the ea ...
memory specification introduced in 1998. Most values specified are in binary-coded decimal
In computing and electronic systems, binary-coded decimal (BCD) is a class of binary encodings of decimal numbers where each digit is represented by a fixed number of bits, usually four or eight. Sometimes, special bit patterns are used f ...
form. The most significant nibble
In computing, a nibble, or spelled nybble to match byte, is a unit of information that is an aggregation of four- bits; half of a byte/ octet. The unit is alternatively called nyble, nybl, half-byte or tetrade. In networking or telecommuni ...
can contain values from 10 to 15, and in some cases extends higher. In such cases, the encodings for 1, 2 and 3 are instead used to encode 16, 17 and 18. A most significant nibble of 0 is reserved to represent "undefined".
The SPD ROM defines up to three DRAM timings, for three CAS latencies specified by set bits in byte 18. First comes the highest CAS latency (fastest clock), then two lower CAS latencies with progressively lower clock speeds.
DDR SDRAM
The DDR DIMM SPD format is an extension of the SDR SDRAM format. Mostly, parameter ranges are rescaled to accommodate higher speeds.DDR2 SDRAM
The DDR2 SPD standard makes a number of changes, but is roughly similar to the above. One notable deletion is the confusing and little-used support for DIMMs with two ranks of different sizes. For cycle time fields (bytes 9, 23, 25 and 49), which are encoded inBCD
BCD may refer to:
Computing
* Binary-coded decimal, a representation of decimal digits in binary
** BCD (character encoding), a 6-bit superset of binary-coded decimal derived from the binary encoding of the same name
* Boot Configuration Data, th ...
, some additional encodings are defined for the tenths digit to represent some common timings exactly:
DDR3 SDRAM
The DDR3 SDRAM standard significantly overhauls and simplifies the SPD contents layout. Instead of a number of BCD-encoded nanosecond fields, some "timebase" units are specified to high precision, and various timing parameters are encoded as multiples of that base unit. Further, the practice of specifying different time values depending on the CAS latency has been dropped; now there are just a single set of timing parameters. Revision 1.1 lets some parameters be expressed as a "medium time base" value plus a (signed, −128 +127) "fine time base" correction. Generally, the medium time base is 1/8 ns (125 ps), and the fine time base is 1, 2.5 or 5 ps. For compatibility with earlier versions that lack the correction, the medium time base number is usually rounded up and the correction is negative. Values that work this way are: The memory capacity of a module can be computed from bytes 4, 7 and 8. The module width (byte 8) divided by the number of bits per chip (byte 7) gives the number of chips per rank. That can then be multiplied by the per-chip capacity (byte 4) and the number of ranks of chips on the module (usually 1 or 2, from byte 7).DDR4 SDRAM
The DDR4 SDRAM "Annex L" standard for SPD changes the EEPROM module used. Instead of the old AT24C02-compatible 256-byte EEPROMs, JEDEC now defines a new nonstandard EE1004 type with two pages at the SMBus level each with 256 bytes. The new memory still uses the old 0x50–0x57 addresses, but two additional address at 0x36 (SPA0) and 0x37 (SPA1) are now used to receive commands to select the currently-active page for the bus, a form ofbank switching
Bank switching is a technique used in computer design to increase the amount of usable memory beyond the amount directly addressable by the Processor (computing), processor instructions. It can be used to configure a system differently at diffe ...
. Internally each logical page is further divided into two physical blocks of 128 bytes each, totaling four blocks and 512 bytes. Other semantics for "special" address ranges remain the same, although write protection is now addressed by blocks and a high voltage at SA0 is now required to change its status.
Annex L defines a few different layouts that can be plugged into a 512-byte (of which a maximum of 320 bytes are defined) template, depending on the type of the memory module. The bit definitions are similar to DDR3.
DDR5 SDRAM
Preliminary table for DDR5, based on JESD400-5 specification. DDR5 expands the SPD table to 1024-byte. SPD of DDR5 is using the I3C bus.Extensions
The JEDEC standard only specifies some of the SPD bytes. The truly critical data fits into the first 64 bytes,JEDEC Standard 21-C section 4.1.2.4"SPDs for DDR SDRAM"JEDEC Standard 21-C section 4.1.2.10
"Specific SPDs for DDR2 SDRAM"JEDEC Standard 21-C section 4.1.2.11
"Serial Presence Detect (SPD) for DDR3 SDRAM Modules"JEDEC Standard 21-C section 4.1.2
"SERIAL PRESENCE DETECT STANDARD, General Standard"JEDEC Standard 21-C section 4.1.2.5
"Specific PDs for Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM)" while some of the remainder is earmarked for manufacturer identification. However, a 256-byte EEPROM is generally provided. A number of uses have been made of the remaining space. Memory generally comes with conservative timing recommendations in the SPD ROM, to ensure basic functionality on all systems. Enthusiasts often spend considerable time manually adjusting the memory timings for higher speed. Enabling special configurations such as Intel XMP or AMD EXPO often requires additional testing to ensure system stability and may void CPU warranty if used out of the manufacturer’s published specifications.
Enhanced Performance Profiles (EPP)
Enhanced Performance Profiles is an extension of SPD, developed byNvidia
Nvidia Corporation ( ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and incorporated in Delaware. Founded in 1993 by Jensen Huang (president and CEO), Chris Malachowsky, and Curti ...
and Corsair, which includes additional information for higher-performance operation of DDR2 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR2 SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) interface. It is a JEDEC standard (JESD79-2); first published in September 2003. DDR2 succeed ...
, including supply voltages and command timing information not included in the JEDEC SPD spec. The EPP information is stored in the same EEPROM, but in bytes 99–127, which are unused by standard DDR2 SPD.
The parameters are particularly designed to fit the memory controller on the nForce 5, nForce 6 and nForce 7 chipsets. Nvidia encourages support for EPP in the BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is a type of firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization d ...
for its high-end motherboard chipsets. This is intended to provide "one-click overclocking
In computing, overclocking is the practice of increasing the clock rate of a computer to exceed that certified by the manufacturer. Commonly, operating voltage is also increased to maintain a component's operational stability at accelerated sp ...
" to get better performance with minimal effort.
Nvidia's name for EPP memory that has been qualified for performance and stability is "SLI-ready memory". The term "SLI-ready-memory" has caused some confusion, as it has nothing to do with SLI video. One can use EPP/SLI memory with a single video card (even a non-Nvidia card), and one can run a multi-card SLI video setup without EPP/SLI memory.
An extended version, EPP 2.0, supports DDR3 memory as well.
Intel Extreme Memory Profile (XMP)
A similar,Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer compo ...
-developed JEDEC SPD extension was developed for DDR3 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR3 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high bandwidth (" double data rate") interface, and has been in use since 2007. It is the higher-spe ...
DIMMs, later used in DDR4
Double Data Rate 4 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR4 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory with a high bandwidth ("double data rate") interface.
Released to the market in 2014, it is a variant of dynamic rando ...
and DDR5 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 5 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR5 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory. Compared to its predecessor DDR4 SDRAM, DDR5 was planned to reduce power consumption, while doubling bandwidth. Th ...
as well. XMP uses bytes 176–255, which are unallocated by JEDEC, to encode higher-performance memory timings.
Later, AMD developed AMP, an equivalent technology to XMP, for use in its "Radeon Memory" line of memory modules optimized for use in AMD platforms. Furthermore, motherboard developers implemented their own technologies to allow their AMD-based motherboards to read XMP profiles: MSI offers A-XMP, ASUS has DOCP (Direct Over Clock Profile), and Gigabyte has EOCP (Extended Over Clock Profile).
The header contains the following data. Most importantly, it contains a "medium timebase" value MTB, as a rational number of nanoseconds (common values are 1/8, 1/12 and 1/16 ns). Many other later timing values are expressed as an integer number of MTB units.
Also included in the header is the number of DIMMs per memory channel that the profile is designed to support; including more DIMMs may not work well.
All data above are for DDR3 (XMP 1.1); DDR4 specs are not yet available.
AMD Extended Profiles for Overclocking (EXPO)
AMD's Extended Profiles for Overclocking (EXPO) is a JEDEC SPD extension developed forDDR5
Double Data Rate 5 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR5 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory. Compared to its predecessor DDR4 SDRAM, DDR5 was planned to reduce power consumption, while doubling bandwidth. The ...
DIMMs to apply a one-click automatic overclocking profile to system memory. AMD EXPO-certified DIMMs include optimised timings that optimise the performance of its Zen 4
Zen 4 is the name for a CPU microarchitecture designed by AMD, released on September 27, 2022. It is the successor to Zen 3 and uses TSMC's N6 process for I/O dies, N5 process for CCDs, and N4 process for APUs.
Zen 4 powers Ryzen 7000 per ...
processors. Unlike Intel's closed standard XMP, the EXPO standard is open and royalty-free. It can be used on Intel platforms. At launch in September 2022, there are 15 partner RAM kits with EXPO-certification available reaching up to 6400 MT/s.
Vendor-specific memory
A common misuse is to write information to certain memory regions to bind vendor-specific memory modules to a specific system.Fujitsu Technology Solutions
Fujitsu Technology Solutions GmbH (FTS) is a Munich-based information technology vendor in the so-called "EMEIA" markets: Europe, the Middle East, India and Africa. A subsidiary of Fujitsu in Tokyo, FTS was founded in 2009 when the parent firm b ...
is known to do this. Adding different memory module to the system usually results in a refusal or other counter-measures (like pressing F1 on every boot).
02 0E 00 01-00 00 00 EF-02 03 19 4D-BC 47 C3 46 ...........M.G.F 53 43 00 04-EF 4F 8D 1F-00 01 70 00-01 03 C1 CF SC...O....p.....This is the output of a 512 MB memory module from Micron Technologies, branded for Fujitsu-Siemens Computers, note the "FSC" string. The system BIOS rejects memory modules that don't have this information starting at offset 128h. Some Packard Bell AMD laptops also use this method, in this case the symptoms can vary but it can lead to a flashing cursor rather than a beep pattern. Incidentally this can also be a symptom of BIOS corruption as well. Though upgrading a 2 GB to a 4 GB can also lead to issues.
Reading and writing SPD information
Memory module manufacturers write the SPD information to theEEPROM
EEPROM or E2PROM (electrically erasable programmable read-only memory) is a type of non-volatile memory. It is used in computers, usually integrated in microcontrollers such as smart cards and remote keyless systems, or as a separate chip d ...
on the module. Motherboard BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is a type of firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization d ...
es read the SPD information to configure the memory controller. There exist several programs that are able to read and modify SPD information on most, but not all motherboard chipsets.
dmidecode
program that can decode information about memory (and other things) and runs on
Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
, FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free-software Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). The first version was released in 1993 developed from 386BSD, one of the first fully functional and free Unix clones on affordable ...
, NetBSD
NetBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). It was the first open-source BSD descendant officially released after 386BSD was fork (software development), forked. It continues to ...
, OpenBSD
OpenBSD is a security-focused operating system, security-focused, free software, Unix-like operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). Theo de Raadt created OpenBSD in 1995 by fork (software development), forking NetBSD ...
, BeOS
BeOS is a discontinued operating system for personal computers that was developed by Be Inc. It was conceived for the company's BeBox personal computer which was released in 1995. BeOS was designed for multitasking, multithreading, and a graph ...
, Cygwin
Cygwin ( ) is a free and open-source Unix-like environment and command-line interface (CLI) for Microsoft Windows. The project also provides a software repository containing open-source packages. Cygwin allows source code for Unix-like operati ...
and Solaris
Solaris is the Latin word for sun.
It may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Literature, television and film
* ''Solaris'' (novel), a 1961 science fiction novel by Stanisław Lem
** ''Solaris'' (1968 film), directed by Boris Nirenburg
** ''Sol ...
. dmidecode does not access SPD information directly; it reports the SMBIOS
In computing, the System Management BIOS (SMBIOS) specification defines data structures (and access methods) that can be used to read management information produced by the BIOS of a computer. This eliminates the need for the operating system to ...
data about the memory. This information may be limited or incorrect.
* On Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
systems and FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free-software Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). The first version was released in 1993 developed from 386BSD, one of the first fully functional and free Unix clones on affordable ...
, the user space
A modern computer operating system usually uses virtual memory to provide separate address spaces or regions of a single address space, called user space and kernel space. This separation primarily provides memory protection and hardware prote ...
program decode-dimms provided by i2c-tools decodes and prints information on any memory with SPD information in the computer. It requires SMBus
The System Management Bus (SMBus or SMB) is a single-ended simple two-wire bus for the purpose of lightweight communication. Most commonly it is found in chipsets of computer motherboards for communication with the power source for ON/OFF instru ...
controller support in the kernel, the EEPROM kernel driver, and also that the SPD EEPROMs are connected to the SMBus. On older Linux distributions, decode-dimms.pl was available as part of lm_sensors
lm_sensors (Linux-monitoring sensors) is a free open-source software-tool for Linux that provides tools and drivers for monitoring temperatures, voltage, humidity, and fans. It can also detect chassis intrusions.
Issues
During 2001/2004, the ...
.
* OpenBSD has included a driverspdmem(4)
since version 4.3 to provide information about memory modules. The driver was ported from NetBSD, where it is available since release 5.0. *
Coreboot
coreboot, formerly known as LinuxBIOS, is a software project aimed at replacing proprietary firmware (BIOS or UEFI) found in most computers with a lightweight firmware designed to perform only the minimum number of tasks necessary to load and r ...
reads and uses SPD information to initialize all memory controller
A memory controller, also known as memory chip controller (MCC) or a memory controller unit (MCU), is a digital circuit that manages the flow of data going to and from a computer's main memory. When a memory controller is integrated into anothe ...
s in a computer with timing, size and other properties.
* Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
systems use programs like HWiNFO, CPU-Z
CPU-Z is a freeware system profiler, system profiling and system monitor, monitoring application for Microsoft Windows and Android (operating system), Android that detects the central processing unit, Random access memory, RAM, motherboard chipse ...
and Speccy
Speccy, developed by Piriform Software, is a freeware utility software and runs under Microsoft Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, Vista and Windows XP, XP for both IA-32 and x64 versions of these operating systems, w ...
, which can read and display DRAM module information from SPD.
Chipset-independent reading and writing of SPD information is done by accessing the memory's EEPROM directly with eeprom programmer hardware and software.
A not so common use for old laptops is as generic SMBus readers, as the internal EEPROM on the module can be disabled once the BIOS has read it so the bus is essentially available for use. The method used is to pull low the A0,A1 lines so the internal memory shuts down, allowing the external device to access the SMBus. Once this is done, a custom Linux build or DOS application can then access the external device. A common use is recovering data from LCD panel memory chips to retrofit a generic panel into a proprietary laptop.
On some chips it is also a good idea to separate write protect lines so that the onboard chips do not get wiped during reprogramming.
A related technique is rewriting the chip on webcams often included with many laptops as the bus speed is substantially higher and can even be modified so that 25x compatible chips can be read back for later cloning of the uEFI in the event of a chip failure.
This unfortunately only works on DDR3 and below, as DDR4 uses different security and can usually only be read. Its possible to use a tool like SPDTool or similar and replace the chip with one that has its WP line free so it can be altered in situ.
On some chipsets the message "Incompatible SMBus driver?" may be seen so read is also prevented.
RGB LED control
Some memory modules (especially on Gaming PCs) support RGB LEDs that are controlled by proprietary SMBus commands. This allows LED color control without additional connectors and cables. Kernel drivers from multiple manufacturers required to control the lights have been exploited to gain access ranging from full kernel memory access, to MSR and I/O port control numerous times in 2020 alone.On older equipment
Some older equipment require the use ofSIMM
A SIMM (single in-line memory module) is a type of memory module used in computers from the early 1980s to the early 2000s. It is a printed circuit board upon which multiple random-access memory Integrated circuit chips are attached to one or ...
s with ''parallel'' presence detect (more commonly called simply ''presence detect'' or PD). Some of this equipment uses non-standard PD coding, IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
computers and Hewlett-Packard
The Hewlett-Packard Company, commonly shortened to Hewlett-Packard ( ) or HP, was an American multinational information technology company. It was founded by Bill Hewlett and David Packard in 1939 in a one-car garage in Palo Alto, California ...
LaserJet
LaserJet is a line of laser printers sold by HP Inc. (originally Hewlett-Packard) since 1984. The LaserJet was the world's first commercially successful laser printer. Canon supplies both mechanisms and cartridges for most HP laser printers; s ...
and other printers in particular.
See also
*Transducer electronic data sheet
IEEE 1451 is a set of smart transducer interface standards developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Instrumentation and Measurement Society's Sensor Technology Technical Committee describing a set of open, common, ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Serial Presence Detect Computer memory