 Cursive (also known as joined-up writing) is any style of
Cursive (also known as joined-up writing) is any style of penmanship
Penmanship is the technique of writing with the hand using a writing instrument. Today, this is most commonly done with a pen, or pencil, but throughout history has included many different writing implement, implements. The various generic a ...
in which characters are written joined in a flowing manner, generally for the purpose of making writing faster, in contrast to block letters
Block letters (known as printscript, manuscript, print writing, printing or ball and stick in academics) are a sans-serif (or "gothic") style of writing Latin script in which the letters are individual glyphs, with no joining.
Elementary educat ...
. It varies in functionality and modern-day usage across languages and regions; being used both publicly in artistic and formal documents as well as in private communication. Formal cursive is generally joined, but casual cursive is a combination of joins and pen lifts. The writing style can be further divided as "looped", " italic", or "connected".
The cursive method is used with many alphabets due to infrequent pen lifting which allows increased writing speed. However, more elaborate or ornamental calligraphic styles of writing can be slower to reproduce. In some alphabets, many or all letters in a word are connected, sometimes making a word one single complex stroke.
History
Cursive is a style of penmanship in which the symbols of the language are written in a conjoined, or flowing, manner, generally for the purpose of making writing faster. This writing style is distinct from "print-script" usingblock letters
Block letters (known as printscript, manuscript, print writing, printing or ball and stick in academics) are a sans-serif (or "gothic") style of writing Latin script in which the letters are individual glyphs, with no joining.
Elementary educat ...
, in which the letters of a word are unconnected. Not all cursive copybooks join all letters; formal cursive is generally joined, but casual cursive is a combination of joins and pen lifts. In the Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
, Syriac, Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
, and Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Ea ...
scripts, many or all letters in a word are connected (while others must not), sometimes making a word one single complex stroke. In Hebrew cursive and Roman cursive, the letters are not connected. In Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
, there was a cursive alphabet, known as the 'Modi' script, used to write the Marathi language
Marathi (; , 𑘦𑘨𑘰𑘙𑘲, , ) is a Classical languages of India, classical Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language predominantly spoken by Marathi people in the Indian state of Maharashtra and is also spoken in Goa, and parts of Guj ...
.
Subclasses
Ligature
Ligature is writing the letters of words with lines connecting the letters so that one does not have to pick up the pen or pencil between letters. Commonly some of the letters are written in a looped manner to facilitate the connections. In common printed Greek texts, the modern small letter fonts are called "cursive" (as opposed to uncial) though the letters do not connect.Looped
 In ''looped cursive'' penmanship, some ascenders and descenders have loops which allows for the letters to link. This is generally what people refer to when they say "cursive" in the context of English. The letters in this style have their own unique characteristics. For example the lowercase ''t'' is taller, while the lowercase ''v'' and ''w'' are rounder. Also, the lowercase ''x'' links out at the baseline.
In ''looped cursive'' penmanship, some ascenders and descenders have loops which allows for the letters to link. This is generally what people refer to when they say "cursive" in the context of English. The letters in this style have their own unique characteristics. For example the lowercase ''t'' is taller, while the lowercase ''v'' and ''w'' are rounder. Also, the lowercase ''x'' links out at the baseline.
Italic
''Cursive italic'' penmanship—derived from chancery cursive—uses non-looped joins, and not all letters are joined. In italic cursive, there are no joins from g, j, q, or y, and a few other joins are discouraged. Italic penmanship became popular in the 15th-century Italian Renaissance. The term "italic" as it relates to handwriting is not to be confused withitalic type
In typography, italic type is a cursive font based on a stylised form of calligraphic handwriting. Along with blackletter and roman type, it served as one of the major typefaces in the history of Western typography.
Owing to the influence f ...
d letters. Many, but not all, letters in the handwriting of the Renaissance were joined, as most are today in cursive italic.
Origin
The origins of the cursive method are associated with the practical advantages of writing speed and infrequent pen-lifting to accommodate the limitations of the quill. Quills are fragile, easily broken, and will spatter unless used properly. They also run out of ink faster than most contemporary writing utensils. Steel dip pens followed quills; they were sturdier, but still had some limitations. The individuality of the provenance of a document (seeSignature
A signature (; from , "to sign") is a depiction of someone's name, nickname, or even a simple "X" or other mark that a person writes on documents as a proof of identity and intent. Signatures are often, but not always, Handwriting, handwritt ...
) was a factor also, as opposed to machine font
In metal typesetting, a font is a particular size, weight and style of a ''typeface'', defined as the set of fonts that share an overall design.
For instance, the typeface Bauer Bodoni (shown in the figure) includes fonts " Roman" (or "regul ...
. Cursive was also favoured because the writing tool was rarely taken off the paper.
The term ''cursive'' derives from Middle French
Middle French () is a historical division of the French language that covers the period from the mid-14th to the early 17th centuries. It is a period of transition during which:
* the French language became clearly distinguished from the other co ...
from Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. It was also the administrative language in the former Western Roman Empire, Roman Provinces of Mauretania, Numidi ...
, which literally means 'running'. This term in turn derives from Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
('to run, hasten'). Although by the 2010s, the use of cursive appeared to be on the decline, it seemed to be coming back into use.
Bengali
 In the Bengali cursive script
(also known in Bengali as "professional writing") the letters are more likely to be more curvy in appearance than in standard Bengali handwriting. Also, the horizontal supporting bar on each letter ( ''matra'') runs continuously through the entire word, unlike in standard handwriting. This cursive handwriting often used by literature experts differs in appearance from the standard Bengali alphabet as it is free hand writing, where sometimes the alphabets are complex and appear different from the standard handwriting.
In the Bengali cursive script
(also known in Bengali as "professional writing") the letters are more likely to be more curvy in appearance than in standard Bengali handwriting. Also, the horizontal supporting bar on each letter ( ''matra'') runs continuously through the entire word, unlike in standard handwriting. This cursive handwriting often used by literature experts differs in appearance from the standard Bengali alphabet as it is free hand writing, where sometimes the alphabets are complex and appear different from the standard handwriting.
Chinese
Cursive forms ofChinese characters
Chinese characters are logographs used Written Chinese, to write the Chinese languages and others from regions historically influenced by Chinese culture. Of the four independently invented writing systems accepted by scholars, they represe ...
are used in calligraphy; "running script" is the semi-cursive form and " rough script" (mistakenly called "grass script" due to literal misinterpretation) is the cursive. The running aspect of this script has more to do with the formation and connectedness of strokes ''within'' an individual character than with connections between characters as in Western connected cursive. The latter are rare in hanzi and in the derived Japanese kanji
are logographic Chinese characters, adapted from Chinese family of scripts, Chinese script, used in the writing of Japanese language, Japanese. They were made a major part of the Japanese writing system during the time of Old Japanese and are ...
characters which are usually well separated by the writer.
Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
File:ZhiYong1000charcter.jpg, One page of the album "Thousand Character classic in formal and Cursive script" attributed to Zhi Yong
English
Cursive writing was used in English before theNorman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, French people, French, Flemish people, Flemish, and Bretons, Breton troops, all led by the Du ...
. Anglo-Saxon charters
Anglo-Saxon charters are documents from the early medieval period in England which typically made a grant of land or recorded a privilege. The earliest surviving charters were drawn up in the 670s: the oldest surviving charters granted land to ...
typically include a boundary clause written in Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
in a cursive script. A cursive handwriting style— secretary hand—was widely used for both personal correspondence and official documents in England from early in the 16th century.
Cursive handwriting developed into something approximating its current form from the 17th century, but its use was neither uniform, nor standardized either in England itself or elsewhere in the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
. In the English colonies of the early 17th century, most of the letters are clearly separated in the handwriting of William Bradford, though a few were joined as in a cursive hand. In England itself, Edward Cocker had begun to introduce a version of the French '' ronde'' style, which was then further developed and popularized throughout the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
in the 17th and 18th centuries as round hand by John Ayers and William Banson.
Cursive writing in the United Kingdom
Today there is no standardised teaching script stipulated in the variousnational curriculum A national curriculum is a common programme of study in schools that is designed to ensure nationwide uniformity of content and standards in education. It is usually legislated by the national government, possibly in consultation with state or othe ...
s for schools in the United Kingdom, only that one font style needs to be used consistently throughout the school. Be School Ready – What Letter Font is Your Child’s School Teaching?online
, 29 August 2019, access date 30 March 2022 In both the cursive and the continuous cursive writing styles, letters are created through joining lines and curve shapes in a particular way. Once pupils have learnt how to clearly form single letters, they are taught how single letters can be joined to form a flowing script. Teach handwriting: The three handwriting stages
, access date 30 March 2022 Characteristics of cursive and continuous cursive scripts:What's The Difference between Cursive and Continuous Cursive Handwriting Fonts?
online
, 9 November 2017, access date 30 March 2022 Whether cursive or continuous cursive is to be favoured remains a subject of debate. While many schools in the United Kingdom are opting to teach continuous cursive throughout the year groups, often starting in Reception, critics have argued that conjoined writing styles leave many children struggling with the high level of gross and fine motor coordination required.
Cursive writing in North America
Development in the 18th and 19th centuries
In the American colonies, on the eve of their independence from theKingdom of Great Britain
Great Britain, also known as the Kingdom of Great Britain, was a sovereign state in Western Europe from 1707 to the end of 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the Kingd ...
, it is notable that Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
joined most, but not all the letters when drafting the United States Declaration of Independence
The Declaration of Independence, formally The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen States of America in the original printing, is the founding document of the United States. On July 4, 1776, it was adopted unanimously by the Second Continen ...
. However, a few days later, Timothy Matlack professionally re-wrote the presentation copy of the Declaration in a fully joined, cursive hand. Eighty-seven years later, in the middle of the 19th century, Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War ...
drafted the Gettysburg Address in a cursive hand that would not look out of place today.
Not all such cursive, then or now, joined all of the letters within a word.
In both the British Empire and the United States in the 18th and 19th centuries, before the typewriter, professionals used cursive for their correspondence. This was called a "fair hand", meaning it looked good, and firms trained all their clerks to write in exactly the same script.
Although women's handwriting had noticeably different particulars from men's, the general forms were not prone to rapid change. In the mid-19th century, most children were taught the contemporary cursive; in the United States, this usually occurred in second or third grade (around ages seven to nine). Few simplifications appeared as the middle of the 20th century approached.
After the 1960s, a movement originally begun by Paul Standard in the 1930s to replace looped cursive with cursive italic penmanship resurfaced. It was motivated by the claim that cursive instruction was more difficult than it needed to be; that conventional (looped) cursive was unnecessary, and it was easier to write in cursive italic. Because of this, various new forms of cursive italic appeared, including Getty-Dubay Italic, and Barchowsky Fluent Handwriting. In the 21st century, some of the surviving cursive writing styles are Spencerian, Palmer Method, Zaner-Bloser, and D'Nealian script.
Decline of English cursive in the United States
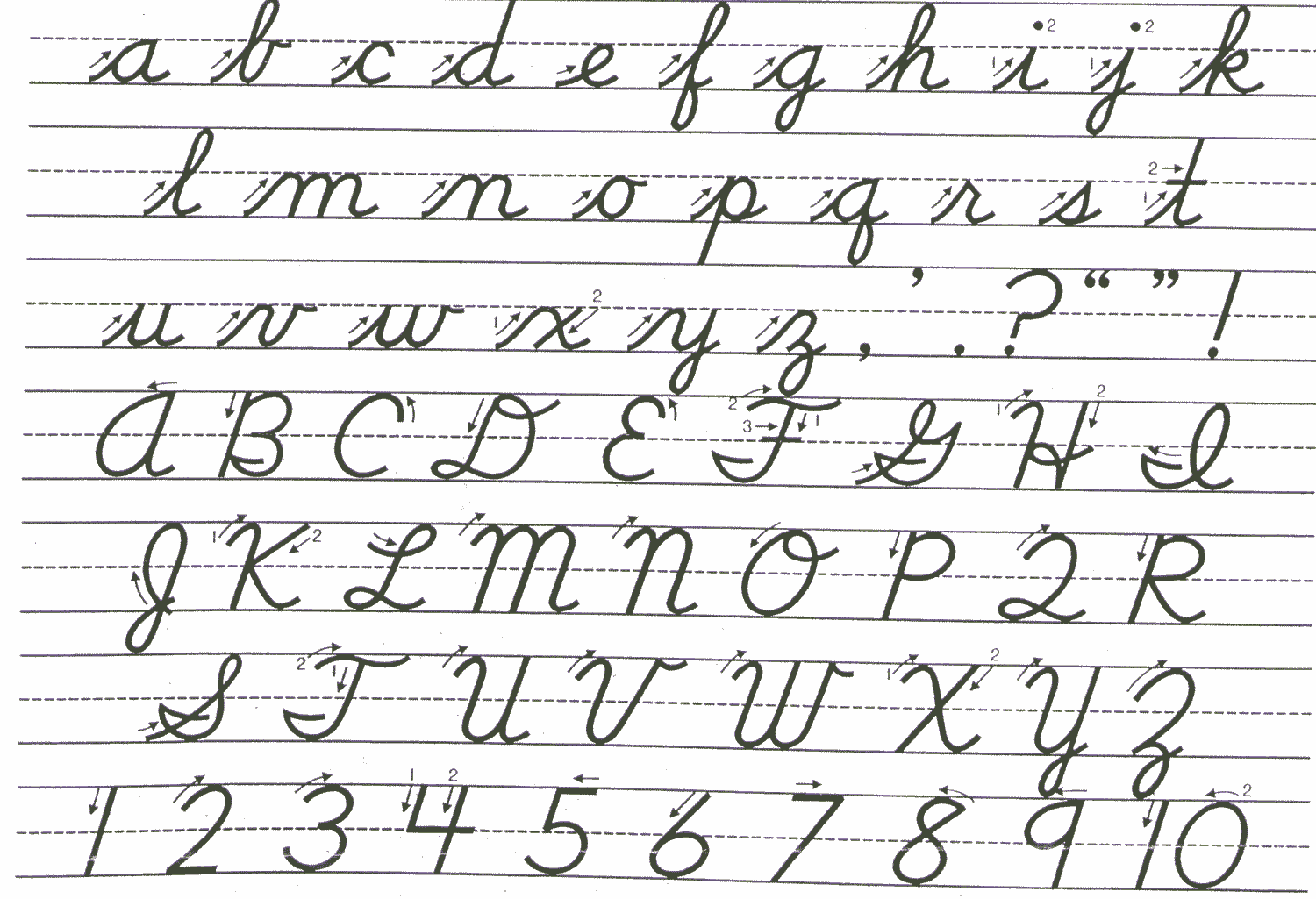 Numerous factors have impacted the declining use of English cursive in the United States. Largely, they have been technologically based, but in the 2000s cultural changes (such as diminished instruction of educators how to teach it) have also contributed to its marginalization. However, by the second decade of the 2000s “back to basics“ movements have emerged advocating for its preservation.
The declining emphasis on using cursive began in the 20th century, first from the introduction of the typewriter and its widespread adoption by the 1920s. The post-World War II proliferation of the inexpensive ballpoint pen added convenience to writing by hand and eliminated the flourishes liquid ink and flexible metal tips had allowed. In the digital era, the introduction of technologies such as the word processor and personal computer in the 1980s and smartphone in the 2000s have increasingly displaced all forms of handwriting, most significantly cursive.
Cursive has also been in decline throughout the 21st century because it is no longer perceived as necessary. The Fairfax Education Association, the largest teachers' union in Fairfax County, Virginia, has called cursive a "dying art".
On the 2006
Numerous factors have impacted the declining use of English cursive in the United States. Largely, they have been technologically based, but in the 2000s cultural changes (such as diminished instruction of educators how to teach it) have also contributed to its marginalization. However, by the second decade of the 2000s “back to basics“ movements have emerged advocating for its preservation.
The declining emphasis on using cursive began in the 20th century, first from the introduction of the typewriter and its widespread adoption by the 1920s. The post-World War II proliferation of the inexpensive ballpoint pen added convenience to writing by hand and eliminated the flourishes liquid ink and flexible metal tips had allowed. In the digital era, the introduction of technologies such as the word processor and personal computer in the 1980s and smartphone in the 2000s have increasingly displaced all forms of handwriting, most significantly cursive.
Cursive has also been in decline throughout the 21st century because it is no longer perceived as necessary. The Fairfax Education Association, the largest teachers' union in Fairfax County, Virginia, has called cursive a "dying art".
On the 2006 SAT
The SAT ( ) is a standardized test widely used for college admissions in the United States. Since its debut in 1926, its name and Test score, scoring have changed several times. For much of its history, it was called the Scholastic Aptitude Test ...
, an American university matriculation exam, only 15 percent of the students wrote their essay answers in cursive. However, students might be discouraged from using cursive on standardized tests because they will receive lower marks if their answers are hard to read, and some graders may have difficulties reading cursive. Nevertheless, in 2007, a survey of 200 teachers of first through third grades in all 50 American states, 90 percent of respondents said their schools required the teaching of cursive. In spite of this mandate, a nationwide survey in 2008 found elementary school teachers lacking formal training in teaching handwriting; only 12 percent reported having taken a course in how to teach it.
In 2012, the American states of Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the s ...
and Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
announced that their schools would no longer be required to teach cursive (but will still be permitted to), and instead will be required to teach "keyboard proficiency". Nationwide Common Core State Standards (which do not include instruction in cursive) were proposed in 2009 and had been adopted by 44 states as of July 2011—all of which have debated whether to augment them with cursive.
Conservation efforts and effects on the learning disabled
Despite the decline in the day-to-day use of cursive, it is being reintroduced to the curriculum of some schools in the United States.California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
passed cursive handwriting legislation in 2023, adding to a wave of state legislation between 2013 and 2023 that requires the incorporation of cursive handwriting into elementary education. Other states such as Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest and Mountain states, Mountain West subregions of the Western United States. It borders Montana and Wyoming to the east, Nevada and Utah to the south, and Washington (state), ...
, Kansas
Kansas ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the west. Kansas is named a ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
, North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
, South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
, New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, and Tennessee
Tennessee (, ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina t ...
had already mandated cursive in schools as a part of the Back to Basics program designed to maintain the integrity of cursive handwriting. Cursive instruction is required by grade 5 in Illinois, starting with the 2018–2019 school year.
Some argue that cursive is not worth teaching in schools and "in the 1960s cursive was implemented because of preference and not an educational basis; Hawaii and Indiana have replaced cursive instruction with 'keyboard proficiency' and 44 other states are currently weighing similar measures."
Many historical documents, such as the United States Constitution, are written in cursive. Some argue the inability to read cursive therefore precludes one from being able to fully appreciate such documents in their original format.
Maria Montessori
Maria Tecla Artemisia Montessori ( ; ; 31 August 1870 – 6 May 1952) was an Italians, Italian physician and educator best known for her philosophy of education (the Montessori method) and her writing on scientific pedagogy. At an early a ...
argued that writing with straight lines is more difficult than writing with curved lines and children would benefit from learning cursive first.
Students with dyslexia
Dyslexia (), previously known as word blindness, is a learning disability that affects either reading or writing. Different people are affected to different degrees. Problems may include difficulties in spelling words, reading quickly, wri ...
, who have difficulty learning to read because their brains have difficulty associating sounds and letter combinations efficiently, have found that cursive can help them with the decoding process because it integrates hand-eye coordination, fine motor skills, and other brain and memory functions. However, students with dysgraphia may be badly served, or even substantially hindered, by demands for cursive.
German
Up to the 19th century, (also known as ''German cursive'') was used in German-language longhand. Kurrent was not used exclusively, but rather in parallel to modern cursive (which is the same as English cursive). Writers used both cursive styles: location, contents and context of the text determined which style to use. A successor of , , was widely used in the period 1911–1941 until the Nazi Party banned it and its printed equivalent . German speakers brought up with continued to use it well into the post-war period. Today, three different styles of cursive writing are taught in German schools, the (introduced in 1953), the (1968), and the (1969). The German National Primary Schoolteachers' Union has proposed replacing all three with , a simplified form of non-cursive handwriting adopted byHamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th-lar ...
schools.
Greek
 The
The Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BC. It was derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and is the earliest known alphabetic script to systematically write vowels as wel ...
has had several cursive forms in the course of its development. In antiquity, a cursive form of handwriting was used in writing on papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can a ...
. It employed slanted and partly connected letter forms as well as many ligatures. Some features of this handwriting were later adopted into Greek minuscule, the dominant form of handwriting in the medieval and early modern era. In the 19th and 20th centuries, an entirely new form of cursive Greek, more similar to contemporary Western European cursive scripts, was developed.
Marathi
 Modi is a cursive script used to write Marathi that is thought to be derived from the
Modi is a cursive script used to write Marathi that is thought to be derived from the Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; in script: , , ) is an Indic script used in the Indian subcontinent. It is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental Writing systems#Segmental systems: alphabets, writing system), based on the ancient ''Brāhmī script, Brā ...
script. It was used alongside Devanagari until the 20th century as a shorthand script for quick writing in business and administration. Due to the promotion of the Balbodh
Balabodh (, , , translation: understood by children) is a slightly modified style of the Devanagari script used to write the Marathi language and the Korku language. What sets balabodha apart from the Devanagari script used for other languages i ...
variant of Devanagari as the standard writing system for Marathi, Modi largely fell out of use by the mid-20th century. Since then there have been attempts to revive this script.
A distinctive feature of this script is that the head stroke is written before the letters, in order to produce a "ruled page" for writing in lines. It has several characteristics that facilitate writing so that moving from one character to the next minimises lifting the pen from the paper for dipping in ink. Some characters are "broken" versions of their Devanagari counterparts. Many characters are more circular in shape. The long 'ī' (ई) and short 'u' (उ) are used in place of the short 'i' (इ) and long 'ū' (ऊ) respectively.
Roman
 ''Roman cursive'' is a form of handwriting (or a script) used in
''Roman cursive'' is a form of handwriting (or a script) used in ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Em ...
and to some extent into the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
. It is customarily divided into old (or ancient) cursive, and new cursive. Old Roman cursive, also called majuscule
Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals (more formally '' majuscule'') and smaller lowercase (more formally '' minuscule'') in the written representation of certain languages. The writing syste ...
cursive and capitalis cursive, was the everyday form of handwriting used for writing letters, by merchants writing business accounts, by schoolchildren learning the Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also known as the Roman alphabet, is the collection of letters originally used by the Ancient Rome, ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered except several letters splitting—i.e. from , and from � ...
, and even by emperors
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/ grand empress dowager), or a woman who rule ...
issuing commands. New Roman, also called minuscule cursive or later cursive, developed from old cursive. It was used from approximately the 3rd century to the 7th century, and uses letter forms that are more recognizable to modern eyes; "a", "b", "d", and "e" have taken a more familiar shape, and the other letters are proportionate to each other rather than varying wildly in size and placement on a line.
Russian
Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Ea ...
'' alphabet is used (instead of the block letters) when handwriting the modern Russian language
Russian is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language belonging to the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of the four extant East Slavic languages, and is ...
. While several letters resemble Latin counterparts, many of them represent different sounds. Most handwritten Russian, especially personal letters and schoolwork, uses the cursive Russian (Cyrillic) alphabet although use of block letters in private writing has been rising. Most children in Russian schools are taught in the first grade how to write using this Russian script.
Examples
Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
(1 May 1500)
File:Lessing Kleist-Brief.jpg, A letter from Lessing to Kleist, written in Kurrent (14 March 1758)
File:United States Declaration of Independence.jpg, United States Declaration of Independence
The Declaration of Independence, formally The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen States of America in the original printing, is the founding document of the United States. On July 4, 1776, it was adopted unanimously by the Second Continen ...
(4 July 1776)
File:Bold running hand script exemplar by Joseph Carstairs published 1820.jpg, Bold running hand exemplar by English chirographer Joseph Carstairs (1820)
File:Spencerian example.jpg, Example of classic American business handwriting known as Spencerian script (1884)
See also
* Asemic writing *Bastarda
Bastarda or bastard was a blackletter script used in France, the Burgundian Netherlands and Germany during the 14th and 15th centuries. The Burgundian variant of script can be seen as the court script of the Dukes of Burgundy. The particular ...
*Blackletter
Blackletter (sometimes black letter or black-letter), also known as Gothic script, Gothic minuscule or Gothic type, was a script used throughout Western Europe from approximately 1150 until the 17th century. It continued to be commonly used for ...
* Book hand
*Calligraphy
Calligraphy () is a visual art related to writing. It is the design and execution of lettering with a pen, ink brush, or other writing instruments. Contemporary calligraphic practice can be defined as "the art of giving form to signs in an e ...
* Chancery hand
* Court hand
* Cursive script (East Asia) (Grass script)
* D'Nealian Method
*Emphasis (typography)
In typography, emphasis is the strengthening of words in a text with a font in a different style from the rest of the text, to highlight them. It is the equivalent of Stress (linguistics)#Prosodic stress, prosody stress in speech.
Methods and ...
* Hand (writing style)
* Handwriting
* Hieratic and Cursive hieroglyphs
*History of writing
The history of writing traces the development of writing systems and how their use transformed and was transformed by different societies. The use of writing prefigures various social and psychological consequences associated with literacy a ...
*Italic script
Italic script, also known as chancery cursive and Italic hand, is a semi-cursive, slightly sloped style of handwriting and calligraphy that was developed during the Renaissance in Italy. It is one of the most popular styles used in contemporary ...
* Library hand
*Palaeography
Palaeography (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, UK) or paleography (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, US) (ultimately from , , 'old', and , , 'to write') is the study and academic disciplin ...
* Palmer Method
*Paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, Textile, rags, poaceae, grasses, Feces#Other uses, herbivore dung, or other vegetable sources in water. Once the water is dra ...
*Pen
PEN may refer to:
* (National Ecological Party), former name of the Brazilian political party Patriota (PATRI)
* PEN International, a worldwide association of writers
** English PEN, the founding centre of PEN International
** PEN America, located ...
* Ronde script (calligraphy)
* Rotunda (script)
* Round hand
* Secretary hand
*Shorthand
Shorthand is an abbreviated symbolic writing method that increases speed and brevity of writing as compared to Cursive, longhand, a more common method of writing a language. The process of writing in shorthand is called stenography, from the Gr ...
* Spencerian Method
* Sütterlin and Kurrent – German cursive
* Zaner-Bloser Method
References
External links
The Golden Age of American Penmanship
including scans of the January 1932 issue of Austin Norman Palmer's ''American Penman''
Normal and Bold Victorian Modern Cursive electronic fonts for downloading
a ''
Time
Time is the continuous progression of existence that occurs in an apparently irreversible process, irreversible succession from the past, through the present, and into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequ ...
'' magazine article on the demise of cursive handwritingOp-Art: The Write Stuff
a ''New York Times'' article on the advantages of italic hand over both full cursive and block printing
The Society for Italic Handwriting
supporters of teaching a simplified cursive hand
Has Technology Killed Cursive Handwriting?
�� Mashable, 11 June 2013
Why Cursive Still Matters in Education
State Library of Kansas' KGI Online Library *Twinkl. ''Cursive Handwriting''. Twinkl, n.d., https://www.twinkl.com/teaching-wiki/cursive-handwriting. Accessed 16 Dec. 2024. {{Authority control Calligraphy Penmanship Western calligraphy Writing