Coulee Region on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Driftless Area, a topographical and cultural region in the American
,
"Driftless Area Initiative"
,
, Iowa Department of Natural Resources (IDNR), Retrieved July 7, 2007 much of the incised Paleozoic Plateau of Wisconsin and northwestern Illinois has no evidence of glaciation. Numerous glacial advances throughout the world occurred during the most recent
The northern and eastern lobes were in part diverted around the area by the Watersmeet Dome, an ancient uplifted area of
Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. ...
, comprises southwestern Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
, southeastern Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minne ...
, northeastern Iowa
Iowa () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wiscon ...
, and the extreme northwestern corner of Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Roc ...
.
Never covered by ice during the last ice age, the area lacks the characteristic glacial deposits known as drift. Its landscape is characterized by steep hills, forested ridges, deeply carved river valleys, and karst geology with spring-fed waterfalls and cold-water trout streams. Ecologically, the Driftless Area's flora and fauna are more closely related to those of the Great Lakes region
The Great Lakes region of North America is a binational Canada, Canadian–United States, American region that includes portions of the eight U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York (state), New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania ...
and New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian province ...
than those of the broader Midwest and central Plains regions. The steep riverine landscape of both the Driftless Area proper and the surrounding Driftless-like region are the result of early glacial advances that forced preglacial rivers that flowed into the Great Lakes southward, causing them to carve a gorge across bedrock cuesta
A cuesta (from Spanish ''cuesta'' "slope") is a hill or ridge with a gentle slope on one side, and a steep slope on the other. In geology the term is more specifically applied to a ridge where a harder sedimentary rock overlies a softer laye ...
s, thereby forming the modern incised upper Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it ...
valley. The region has elevations ranging from 603 to 1,719 feet (184 to 524 m) at Blue Mound State Park
Blue Mound State Park is a state park in Wisconsin, United States, located atop the largest hill in the southern half of the state, near the village of Blue Mounds. The park features a pair of observation towers affording views of the Wisconsin ...
, and together with the Driftless-like region, covers .
Geologic origin
Retreating glaciers leave behind material called drift composed of silt, clay, sand, gravel, and boulders. Glacial drift includes unsorted material calledtill
image:Geschiebemergel.JPG, Closeup of glacial till. Note that the larger grains (pebbles and gravel) in the till are completely surrounded by the matrix of finer material (silt and sand), and this characteristic, known as ''matrix support'', is d ...
and layers deposited by meltwater streams called outwash
An outwash plain, also called a sandur (plural: ''sandurs''), sandr or sandar, is a plain formed of glaciofluvial deposits due to meltwater outwash at the terminus of a glacier. As it flows, the glacier grinds the underlying rock surface and ...
. While drift from early (pre-Illinoian
The Pre-Illinoian Stage is used by Quaternary geologists for the early and middle Pleistocene glacial and interglacial periods of geologic time in North America from ~2.5–0.2 Ma (million years ago).
North America
As the oldest stage in th ...
) glaciations has been found in some parts of the region,"Regional Landscape Ecosystems of Michigan, Minnesota, and Wisconsin: Section IV. Driftless Area",
USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, ...
, Retrieved July 13, 2007; another government site"Driftless Area Initiative"
,
USDA
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of com ...
, retrieved July 15, 2007, gives and "Yellow River State Forest", Iowa Department of Natural Resources (IDNR), Retrieved July 7, 2007 much of the incised Paleozoic Plateau of Wisconsin and northwestern Illinois has no evidence of glaciation. Numerous glacial advances throughout the world occurred during the most recent
Quaternary glaciation
The Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, is an alternating series of glacial and interglacial periods during the Quaternary period that began 2.58 Ma (million years ago) and is ongoing. Although geologists describ ...
(also known as the Pleistocene glaciation). The Upper Midwest
The Upper Midwest is a region in the northern portion of the U.S. Census Bureau's Midwestern United States. It is largely a sub-region of the Midwest. Although the exact boundaries are not uniformly agreed-upon, the region is defined as referrin ...
and Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five la ...
region of North America was repeatedly covered by advancing and retreating glaciers throughout this period. The Driftless Area escaped much of the scouring and depositional action by the continental glaciers that occurred during the last ice age, which created significant differences in the topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary s ...
and drainage patterns within the unglaciated area compared to adjacent glaciated regions.
The region has been subjected to large floods from the melting Laurentide Ice Sheet
The Laurentide Ice Sheet was a massive sheet of ice that covered millions of square miles, including most of Canada and a large portion of the Northern United States, multiple times during the Quaternary glacial epochs, from 2.58 million year ...
and subsequent catastrophic discharges from its proglacial lake
In geology, a proglacial lake is a lake formed either by the damming action of a moraine during the retreat of a melting glacier, a glacial ice dam, or by meltwater trapped against an ice sheet due to isostatic depression of the crust around th ...
s, such as Glacial Lake Wisconsin
Glacial Lake Wisconsin was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed from approximately 18,000 to 14,000 years ago, at the end of the last ice age, in the central part of present-day Wisconsin in the United States.
Formation and demise
Before ...
, Glacial Lake Agassiz, Glacial Lake Grantsburg
The proglacial lakes of Minnesota were lakes created in what is now the U.S. state of Minnesota in central North America in the waning years of the last glacial period. As the Laurentide Ice Sheet decayed at the end of the Wisconsin glaciation, l ...
, and Glacial Lake Duluth.
The last phases of the Wisconsin Glaciation
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cor ...
involved several major lobes of the Laurentide Ice Sheet: the Des Moines lobe, which flowed down toward Des Moines
Des Moines () is the capital and the most populous city in the U.S. state of Iowa. It is also the county seat of Polk County. A small part of the city extends into Warren County. It was incorporated on September 22, 1851, as Fort Des Moine ...
on the west; the Superior lobe and its sublobes on the north; and the Green Bay lobe and Lake Michigan lobes on the east.The northern and eastern lobes were in part diverted around the area by the Watersmeet Dome, an ancient uplifted area of
Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ag ...
rock underlain by basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of a ...
in northern Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
and western upper Michigan. The southward movement of the continental glacier was also hindered by the great depths of the Lake Superior
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh w ...
basin and the adjacent highlands of the Bayfield Peninsula The Bayfield Peninsula is a peninsula on Lake Superior. It is located in Bayfield County, Wisconsin USA. It is the northernmost region of mainland Wisconsin, with the south shore of Lake Superior to the west and the Chequamegon Bay to the east. T ...
, Gogebic Range, Porcupine Mountains
The Porcupine Mountains, or Porkies, are a group of small mountains spanning the northwestern Upper Peninsula of Michigan in Ontonagon and Gogebic counties, near the shore of Lake Superior. The Porcupine Mountains were named by the native O ...
, Keweenaw Peninsula
The Keweenaw Peninsula ( , sometimes locally ) is the northernmost part of Michigan's Upper Peninsula. It projects into Lake Superior and was the site of the first copper boom in the United States, leading to its moniker of " Copper Country." As ...
, and the Huron Mountains along the north rim of the Superior Upland bordering Lake Superior. The Green Bay and Lake Michigan lobes were also partially blocked by the bedrock of the Door Peninsula, which presently separates Green Bay from Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that ...
.
Another factor that may have contributed to the lack of glaciation of the Driftless area is the fractured, permeable bedrock within the Paleozoic Plateau underlying it, which would have promoted below-ground drainage of subglacial water that would otherwise have lubricated the underside of the glacial ice sheet. The dewatering of the underside of the ice sheet would have inhibited forward movement of the glacier into the Driftless Area, especially from the west.
In the adjacent glaciated regions, the glacial retreat left behind drift, which buried all former topographical features. Surface water was forced to carve out new stream beds. This process was absent in the Driftless Area, where the original drainage systems persisted during and after the ice age. Water erosion continued carving the existing gullies, ravine
A ravine is a landform that is narrower than a canyon and is often the product of streambank erosion.
 Overall, the region is characterized by an eroded
Overall, the region is characterized by an eroded
,
"River Geomorphology and Floodplain Habitats", p. 1 (*.pdf)
"The Geology of the MNRRA Corridor"
p. 26, Other rivers affected by this geologic process are:
*In Wisconsin, the Chippewa, Trempealeau, La Crosse,
Other rivers affected by this geologic process are:
*In Wisconsin, the Chippewa, Trempealeau, La Crosse,
 The climate is humid continental, displaying both the cool summer and warm summer subtypes as one travels from north to south. The
The climate is humid continental, displaying both the cool summer and warm summer subtypes as one travels from north to south. The  The Midwest Driftless Area Restoration Effort is a multi-agency cooperative effort to restore the landscape.
The main issues are water pollution from agricultural and animal runoff, and erosion. Many farmers in the region utilize
The Midwest Driftless Area Restoration Effort is a multi-agency cooperative effort to restore the landscape.
The main issues are water pollution from agricultural and animal runoff, and erosion. Many farmers in the region utilize 
 The Driftless Area contains more than half of the world's
The Driftless Area contains more than half of the world's
 The bioregion's economic and cultural characteristics were federally recognized with the granting of the Upper Mississippi River Valley (UMRV) viticultural area, the largest designated winemaking region in the country, by the Treasury Division's Tax and Trade Bureau in 2009. The petition for designation maintains the position that the region is a cohesive whole for marketing wine, and is now used to market other products.
In addition to wine-grape production and wine-making, the region, especially in southeast Minnesota, is known for apple production. Tobacco was also once a key crop of the Driftless, as its topography and sandy, nutrient-rich soil are suitable for its growth.
The Driftless Region Food and Farm Project, in partnership with the
The bioregion's economic and cultural characteristics were federally recognized with the granting of the Upper Mississippi River Valley (UMRV) viticultural area, the largest designated winemaking region in the country, by the Treasury Division's Tax and Trade Bureau in 2009. The petition for designation maintains the position that the region is a cohesive whole for marketing wine, and is now used to market other products.
In addition to wine-grape production and wine-making, the region, especially in southeast Minnesota, is known for apple production. Tobacco was also once a key crop of the Driftless, as its topography and sandy, nutrient-rich soil are suitable for its growth.
The Driftless Region Food and Farm Project, in partnership with the
 Due to the presence of
Due to the presence of
 Corresponding to the southeast geological region of Minnesota, the colloquial "Driftless Area" (though the whole region was glaciated) begins at about Fort Snelling. Starting as a narrow sliver against the Mississippi, it widens to the west as one goes south. The western boundary is the Bemis-Altamont moraine."Rochester Plateau Subsection"
Corresponding to the southeast geological region of Minnesota, the colloquial "Driftless Area" (though the whole region was glaciated) begins at about Fort Snelling. Starting as a narrow sliver against the Mississippi, it widens to the west as one goes south. The western boundary is the Bemis-Altamont moraine."Rochester Plateau Subsection"

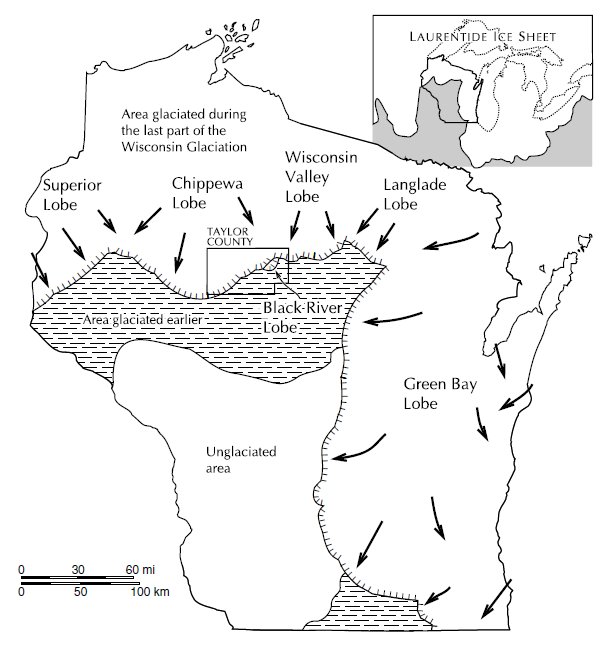 Around 85% of the Driftless Area lies within Wisconsin, comprising much of the southwestern quarter of the state. The border is defined by the catchment of the Chippewa River on the north, and somewhat west (or east, depending on if the southwestern portion of Wisconsin's
Around 85% of the Driftless Area lies within Wisconsin, comprising much of the southwestern quarter of the state. The border is defined by the catchment of the Chippewa River on the north, and somewhat west (or east, depending on if the southwestern portion of Wisconsin's
 An area in northeast Iowa that shares similar topographic characteristics to the Driftless Area in southeastern Wisconsin is the Paleozoic Plateau. For counties inland from the Mississippi, evidence is largely confined to the valleys of streams and rivers. It encompasses all of Allamakee, and part of Clayton, Fayette,
An area in northeast Iowa that shares similar topographic characteristics to the Driftless Area in southeastern Wisconsin is the Paleozoic Plateau. For counties inland from the Mississippi, evidence is largely confined to the valleys of streams and rivers. It encompasses all of Allamakee, and part of Clayton, Fayette,
Quaternary Geology of the Paleozoic Plateau Region of Northeastern Iowa
, Retrieved July 30, 2007 A line east of the most easterly tributaries of the Wapsipinicon River defines the western boundary of the landform region, with the catchment of the Maquoketa River south of Bellevue serving as a southern boundary. The most western tributaries of the Upper Iowa,
 The Illinois portion of the Driftless Area is confined mainly to
The Illinois portion of the Driftless Area is confined mainly to "Illinois' Natural Divisions"
,
This portion lacks any true urban center.
"Decoding the Driftless" movie
2018, created by Sustainable Driftless, Inc., dedicated to inspiring resource conservation and
The Driftless Area: A Landscape of Opportunities
"Driftless Area National Wildlife Refuge"
Retrieved July 23, 2007
Retrieved July 7, 2007
Retrieved July 7, 2007
Driftless Area Initiative
Retrieved July 2, 2014
Wisconsin Geological and Natural History Survey map showing extent of last glaciation
Driftless Region Food and Farm Project
Driftless Area Magazine
{{Continental Glaciations Regions of Wisconsin Pleistocene Geology of Wisconsin Geology of Illinois Geology of Iowa Geology of Minnesota Regions of Illinois Regions of Iowa Regions of Minnesota
Geology
 Overall, the region is characterized by an eroded
Overall, the region is characterized by an eroded plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ...
, with bedrock overlain by varying thicknesses of loess. Most characteristically, the branching river valleys are deeply dissected. The bluffs lining this reach of the Mississippi River currently climb to nearly . In Minnesota, pre-Illinoian-age till was probably removed by natural means prior to the deposition of loess. The sedimentary rocks of the valley walls date to the Paleozoic Era
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ''z ...
and are often covered with colluvium or loess.Regional Landscape Ecosystems of Michigan, Minnesota, and Wisconsin, Section IV, Driftless Area,
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an List of federal agencies in the United States, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government within the United States Department of the Interior, U.S. Department of ...
, Retrieved July 9, 2007 (A statement from this copyright-free site has been freely paraphrased.) Bedrock
In geology, bedrock is solid rock that lies under loose material ( regolith) within the crust of Earth or another terrestrial planet.
Definition
Bedrock is the solid rock that underlies looser surface material. An exposed portion of be ...
, where not directly exposed, is very near the surface and is composed of "primarily Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. ...
dolomite, limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms wh ...
, and sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
in Minnesota, with Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ag ...
sandstone, shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especia ...
, and dolomite exposed along the valley walls of the Mississippi River." In the east, the Baraboo Range
The Baraboo Range is a syncline located in Columbia and Sauk Counties, Wisconsin. It consists of highly eroded Precambrian metamorphic rock. It is about long and varies from 5 to in width. The Wisconsin River, previously traveling in a north ...
, an ancient, profoundly eroded monadnock
An inselberg or monadnock () is an isolated rock hill, knob, ridge, or small mountain that rises abruptly from a gently sloping or virtually level surrounding plain.
In Southern Africa a similar formation of granite is known as a koppie ...
in south central Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
, consists primarily of Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of th ...
quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock which was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tec ...
and rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained ( aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals ( phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The min ...
. The area has not undergone much tectonic action, as all the visible layers of sedimentary rock are approximately horizontal.
Karst topography
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathering-resistant ...
is found throughout the Driftless area. This is characterized by cave
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea ...
s and cave systems, disappearing streams, blind valleys, underground streams
A subterranean river is a river that runs wholly or partly beneath the ground surface – one where the riverbed does not represent the surface of the Earth. It is distinct from an aquifer, which may flow like a river but is contained within a ...
, sinkhole
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are locally also known as ''vrtače'' and shakeholes, and to openi ...
s, springs
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season), a season of the year
* Spring (device), a mechanical device that stores energy
* Spring (hydrology), a natural source of water
* Spring (mathematics), a geometric surface in the shape of a he ...
, and cold streams. Disappearing streams occur where surface waters sink down into the earth through fractured bedrock or a sinkhole, either joining an aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials ( gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characteri ...
, or becoming an underground stream. Blind valleys are formed by disappearing streams and lack an outlet to any other stream. Sinkholes result from the collapse of a cave's roof, and surface water can flow directly into them. Disappearing streams can re-emerge as large, cold springs. Cold streams with cold springs as their sources are superb trout
Trout are species of freshwater fish belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', '' Salmo'' and '' Salvelinus'', all of the subfamily Salmoninae of the family Salmonidae. The word ''trout'' is also used as part of the name of some non-sa ...
habitat. Due to the rapid movement of underground water through regions with karst topography, groundwater contamination
Groundwater pollution (also called groundwater contamination) occurs when pollutants are released to the ground and make their way into groundwater. This type of water pollution can also occur naturally due to the presence of a minor and unwanted ...
is a major concern in the Driftless area.
Rivers
The Mississippi River passes through the Driftless Area between and includingPool 2
Pool may refer to:
Water pool
* Swimming pool, usually an artificial structure containing a large body of water intended for swimming
* Reflecting pool, a shallow pool designed to reflect a structure and its surroundings
* Tide pool, a rocky pool ...
and Pool 13
Pool may refer to:
Water pool
* Swimming pool, usually an artificial structure containing a large body of water intended for swimming
* Reflecting pool, a shallow pool designed to reflect a structure and its surroundings
* Tide pool, a rocky po ...
.
As rivers and streams approach their confluence with the Mississippi, their canyons grow progressively steeper and deeper, particularly in the last in their journey to their mouths. The change in elevation above sea level from ridgetops lining a stream to its confluence with the main-stem Mississippi can reach well past in only a few miles. The Waukon Municipal Airport is reliably established as being above sea level. The Army Corps of Engineers maintains a river level in Pool 9 of about above sea level, which covers Lansing
Lansing () is the capital of the U.S. state of Michigan. It is mostly in Ingham County, although portions of the city extend west into Eaton County and north into Clinton County. The 2020 census placed the city's population at 112,644, making ...
. Maps and signs issued by the Iowa Department of Transportation
The Iowa Department of Transportation (Iowa DOT) is the government organization in the U.S. state of Iowa responsible for the organization, construction, and maintenance of the primary highway system. Located in Ames, Iowa, DOT is also respons ...
indicate Waukon and Lansing are apart on Iowa Highway 9
Iowa Highway 9 is the most northern of Iowa's east–west highways, traversing the entire northern tier of counties. It runs from the eastern terminus of South Dakota Highway 42 at the South Dakota border east of Sioux Falls, South Dakota near ...
. This is a drop of more than in less than (and this along a very minor tributary of the Mississippi). "The role of isostatic rebound
Post-glacial rebound (also called isostatic rebound or crustal rebound) is the rise of land masses after the removal of the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, which had caused isostatic depression. Post-glacial rebound ...
on the process of stream incision in the area is not clearly understood."
There are many small towns in the Driftless Area, especially in river valleys, at or upstream from the Mississippi. Small towns in a deep steep valley going down to the Mississippi are at risk every 50 to 100 years or so of a major flood, as with the wreck of Gays Mills, Wisconsin
Gays Mills is a village in Crawford County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 491 at the 2010 census.
History
In 1847 James B. Gay, a native of Indiana, built a dam and a sawmill on the Kickapoo River, which proved to be a flourish ...
, in August 2007, or the holding of the levee in Houston, Minnesota
Houston is a city in Houston County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 997 at the 2020 census.
History
The community was named after Sam Houston, first president of the Republic of Texas.
In 1852, William McSpadden platted the ori ...
, (on the South Fork Root River) at the same time. Metropolitan areas have flood walls (''See'' 2007 Midwest flooding
The 2007 Midwest flooding was a major flooding event that occurred in the Midwestern United States in the third week of August 2007. While Hurricane Dean was affecting the Yucatán Peninsula and the Gulf of Mexico, and Tropical Storm Erin was af ...
). In August 2018, the region yet again experienced record-breaking flooding in valley towns such as Coon Valley, Wisconsin, La Farge, Wisconsin and Viola, Wisconsin. The Kickapoo River flood stage is 13 feet but was recorded as high as 23 feet during the 2018 flood which was declared a statewide emergency. Many community members were rescued by boats sent by the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources
The Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (WDNR) is a government agency of the U.S. state of Wisconsin charged with conserving and managing Wisconsin's natural resources. The Wisconsin Natural Resources Board has the authority to set policy ...
. Days later, when two dams in Ontario, Wisconsin broke, it created flood water downstream in Readstown, Wisconsin
Readstown is a village in Vernon County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 415 at the 2010 census.
Geography
Readstown is located at (43.448544, -90.760708).
According to the United States Census Bureau, the village has a total area ...
, Soldiers Grove, Wisconsin
Soldiers Grove is a village situated along the Kickapoo River in Crawford County, Wisconsin, in the United States. The population was 592 at the 2010 census. The town is notable for having relocated its central business district due to flooding ...
and Gays Mills, Wisconsin
Gays Mills is a village in Crawford County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 491 at the 2010 census.
History
In 1847 James B. Gay, a native of Indiana, built a dam and a sawmill on the Kickapoo River, which proved to be a flourish ...
.
The history of this portion of the Upper Mississippi River dates back to an origin "as an ice-marginal stream during what had been referred to as the “ Nebraskan glaciation.”" Current terminology would place this outdated and abandoned period in the Pre-Illinoian Stage. The level of erosion often exposes Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ag ...
limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms wh ...
of about 510 million years of age. Evidence from soil borings and recent Lidar
Lidar (, also LIDAR, or LiDAR; sometimes LADAR) is a method for determining ranges (variable distance) by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected light to return to the receiver. It can also be ...
imagery in the lower Wisconsin River
The Wisconsin River is a tributary of the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. At approximately 430 miles (692 km) long, it is the state's longest river. The river's name, first recorded in 1673 by Jacques Marquette as "Meskou ...
valley in the Driftless area suggests that the river in the valley used to flow towards the east, rather than its present westerly course towards its confluence with the Mississippi River. This has led to the new hypothesis that the ancient Upper Mississippi River (also named the Wyalusing River) at one time flowed east through the current Wisconsin River valley and into the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five la ...
/ Saint Laurence River system somewhere near the Door Peninsula. The hypothesis posits that the flow of the ancient Wyalusing River was ultimately captured by the ancestral Mississippi River to the south when that river eroded through the Military Ridge near Wyalusing State Park
Wyalusing State Park is a Wisconsin state park at the confluence of the Mississippi and Wisconsin rivers in the town of Wyalusing, just south of Prairie du Chien.
Wyalusing means "home of the warrior" in the Lenape language spoken by Mun ...
, possibly as a result of an ancient ice sheet in a previous continental glaciation blocking the Wyalusing River to the east. The resulting Proglacial lake
In geology, a proglacial lake is a lake formed either by the damming action of a moraine during the retreat of a melting glacier, a glacial ice dam, or by meltwater trapped against an ice sheet due to isostatic depression of the crust around th ...
would have filled the Wyalusing River valley until it overtopped the Military Ridge, ultimately carving through the ridge and draining the lake. This resulted in the ancient Upper Mississippi River changing course and flowing south towards the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United S ...
, as it does currently, instead of east into the Saint Lawrence River and the North Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Afr ...
. The Stream capture
Stream capture, river capture, river piracy or stream piracy is a geomorphological phenomenon occurring when a stream or river drainage system or watershed is diverted from its own bed, and flows instead down the bed of a neighbouring stream. ...
hypothesis for the Upper Mississippi River would have created a substantial diversion of water from the Great Lakes Basin
The Great Lakes Basin consists of the Great Lakes and the surrounding lands of the states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin in the United States, and the province of Ontario in Canada, whose dir ...
and the Saint Lawrence River, reducing the inflow of fresh water into the North Atlantic with possible impacts to Ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contou ...
s and Climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologica ...
.
The Mississippi River trench is one of the few places in the Driftless Area where the bedrock is very deep below the surface, and is overlain by large amounts of sediment. As home to the formation of a substantial portion of the gorge of the Upper Mississippi, this enormous quantity of sediment goes down at least under the present riverbottom at the confluence of the Wisconsin River
The Wisconsin River is a tributary of the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. At approximately 430 miles (692 km) long, it is the state's longest river. The river's name, first recorded in 1673 by Jacques Marquette as "Meskou ...
. In contrast, as the Mississippi exits the Driftless Area "between Fulton and Muscatine, [... (Pool 13
Pool may refer to:
Water pool
* Swimming pool, usually an artificial structure containing a large body of water intended for swimming
* Reflecting pool, a shallow pool designed to reflect a structure and its surroundings
* Tide pool, a rocky po ...
)], it flows over or near bedrock."Charles Theiling"River Geomorphology and Floodplain Habitats", p. 1 (*.pdf)
USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, ...
, Retrieved July 12, 2007 "The course of the upper Mississippi River along the margin of the Driftless Area of southeastern Minnesota is believed to have been established during pre-Wisconsin time, when a glacial advance from the west displaced the river eastward from central Iowa to its present position."Thomas Madigan"The Geology of the MNRRA Corridor"
p. 26,
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an List of federal agencies in the United States, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government within the United States Department of the Interior, U.S. Department of ...
, Retrieved July 23, 2007
 Other rivers affected by this geologic process are:
*In Wisconsin, the Chippewa, Trempealeau, La Crosse,
Other rivers affected by this geologic process are:
*In Wisconsin, the Chippewa, Trempealeau, La Crosse, Black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ha ...
, Baraboo, Pecatonica, and Wisconsin River
The Wisconsin River is a tributary of the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. At approximately 430 miles (692 km) long, it is the state's longest river. The river's name, first recorded in 1673 by Jacques Marquette as "Meskou ...
s, along with the Wisconsin River's tributary, the Kickapoo River;
*In Minnesota: the Whitewater
Whitewater forms in a rapid context, in particular, when a river's gradient changes enough to generate so much turbulence that air is trapped within the water. This forms an unstable current that froths, making the water appear opaque and ...
, Cannon
A cannon is a large-caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder duri ...
, Zumbro
The Zumbro River is a tributary of the Mississippi River in the Driftless Area of southeastern Minnesota in the United States. It is longU.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, access ...
, and Root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the sur ...
rivers;
*In Iowa: the Upper Iowa (and Paint Creek), Yellow
Yellow is the color between green and orange on the spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a dominant wavelength of roughly 575585 nm. It is a primary color in subtractive color systems, used in painting or color printing. In ...
, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
, and Maquoketa rivers;
*In Illinois: the Apple River and the Galena River (a.k.a. the Fever River).
Although lying just to the north of the Driftless Area, the Saint Croix
Saint Croix; nl, Sint-Kruis; french: link=no, Sainte-Croix; Danish and no, Sankt Croix, Taino: ''Ay Ay'' ( ) is an island in the Caribbean Sea, and a county and constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincor ...
in Wisconsin and Minnesota is another important river that affected the area, as it was the outlet for Glacial Lake Duluth, forerunner to Lake Superior
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh w ...
, when the eastern outlet was blocked by the continental ice sheet. All major rivers in and adjacent to the Driftless Area have deep, dramatic canyons giving testimony to the immense quantity of water which once surged through them as a result of the nearby melting Glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such a ...
s associated with the miles-high Ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at ...
s during recurring Ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gre ...
s. Other examples include the Wisconsin River, which drained Glacial Lake Wisconsin
Glacial Lake Wisconsin was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed from approximately 18,000 to 14,000 years ago, at the end of the last ice age, in the central part of present-day Wisconsin in the United States.
Formation and demise
Before ...
, and Glacial River Warren (whose bed is now occupied by the Minnesota River
The Minnesota River ( dak, Mnísota Wakpá) is a tributary of the Mississippi River, approximately 332 miles (534 km) long, in the U.S. state of Minnesota. It drains a watershed of in Minnesota and about in South Dakota and Iowa.
It ris ...
), which drained the colossal Glacial Lake Agassiz. There was ample water to dig a very deep, hundreds-of-miles-long gash into the North American bedrock where the Upper Mississippi River now flows.
Ecosystem
 The climate is humid continental, displaying both the cool summer and warm summer subtypes as one travels from north to south. The
The climate is humid continental, displaying both the cool summer and warm summer subtypes as one travels from north to south. The United States Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of com ...
has the region falling mainly in zone 5a, with the northern fringe being 4b. A few patches in Wisconsin are 4a.
Prior to European settlement in the 19th century, the vegetation consisted of tallgrass prairie
The tallgrass prairie is an ecosystem native to central North America. Historically, natural and anthropogenic fire, as well as grazing by large mammals (primarily bison) provided periodic disturbances to these ecosystems, limiting the encroachm ...
and bur oak savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
on ridgetops and dry upper slopes, sugar maple
''Acer saccharum'', the sugar maple, is a species of flowering plant in the soapberry and lychee family Sapindaceae. It is native to the hardwood forests of eastern Canada and eastern United States. Sugar maple is best known for being the prima ...
-basswood
''Tilia americana'' is a species of tree in the family Malvaceae, native to eastern North America, from southeast Manitoba east to New Brunswick, southwest to northeast Oklahoma, southeast to South Carolina, and west along the Niobrara River ...
- oak forest on moister slopes, sugar maple-basswood forests in protected valleys and on north-facing slopes, wet prairies along the rivers and some mesic prairie
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the ...
on the floodplain farther back from the river. There were probably also oak forests that contained no sugar maple. Marsh and floodplain forests were also common on river flood plains. Prairie was restricted primarily to the broader ridge tops, which were unfavorable sites for trees due to thin soils and shallow bedrock, rapid drainage, and desiccating winds; all these conditions were also good for carrying fires across the landscape. Prairies also occurred on steep slopes with south or southwest aspect (''see'' goat prairie {{Short description, Type of grassland
Goat prairies, sometimes termed hill prairies, or dry prairies are found mainly along the valley of the Upper Mississippi River in the Driftless Area, but can occur elsewhere. Normally a variant of tallgrass ...
). Natural fire, which has long been vigorously suppressed, was essential for the regeneration of such prairies.
Evidence of ancient extinct ice age animals that once inhabited the Driftless Area has been discovered over the years. An example of extinct Pleistocene megafauna in the area is the Boaz mastodon, a composite skeleton of two separate mastodon
A mastodon ( 'breast' + 'tooth') is any proboscidean belonging to the extinct genus ''Mammut'' (family Mammutidae). Mastodons inhabited North and Central America during the late Miocene or late Pliocene up to their extinction at the end of th ...
s found in the 1890s in southwestern Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
. Although evidence exists that mastodons inhabited mostly coniferous spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' (), a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal ( taiga) regions of the Earth. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the sub ...
forests associated with the taiga
Taiga (; rus, тайга́, p=tɐjˈɡa; relates to Mongolic and Turkic languages), generally referred to in North America as a boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces ...
biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
, it is likely that most or all of the Driftless Area was at times covered by tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mo ...
and permafrost
Permafrost is ground that continuously remains below 0 °C (32 °F) for two or more years, located on land or under the ocean. Most common in the Northern Hemisphere, around 15% of the Northern Hemisphere or 11% of the global surfac ...
during periods of glacial maximums.
 The Midwest Driftless Area Restoration Effort is a multi-agency cooperative effort to restore the landscape.
The main issues are water pollution from agricultural and animal runoff, and erosion. Many farmers in the region utilize
The Midwest Driftless Area Restoration Effort is a multi-agency cooperative effort to restore the landscape.
The main issues are water pollution from agricultural and animal runoff, and erosion. Many farmers in the region utilize contour plowing
Contour bunding or contour farming or Contour ploughing is the farming practice of plowing and/or planting across a slope following its elevation contour lines. These contour lines create a water break which reduces the formation of rills and ...
, strip cropping, and other agricultural practices to reduce soil erosion due to the hilly terrain. Water pollution is particularly critical in karsted regions such as this, in that it can degrade or destroy prime cold water fish habitat. Soil erosion presents the Army Corps of Engineers with a particular problem, in that it requires them to dredge the Mississippi River shipping channels to keep them open. Trout Unlimited is part of this effort, if only because of the superb cold-water streams the region supports. A symposium was held in October 2007 in Decorah, Iowa
Decorah is a city in and the county seat of Winneshiek County, Iowa, United States. The population was 7,587 at the time of the 2020 census. Decorah is located at the intersection of State Highway 9 and U.S. Route 52, and is the largest commu ...
, "to share the results of research, management and monitoring work in the Driftless Area." The Nature Conservancy
The Nature Conservancy (TNC) is a global environmental organization headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. it works via affiliates or branches in 79 countries and territories, as well as across every state in the US.
Founded in 1951, The Natu ...
is also interested.

 The Driftless Area contains more than half of the world's
The Driftless Area contains more than half of the world's algific talus slopes
Algific talus slopes comprise a very rare, fragile ecosystem and habitat initially stated to exist only in the Driftless Area of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Illinois, and especially, Iowa.+Algific
Taiga and boreal forests in the United States
Ecore ...
, a type of small, isolated ecosystem. These refugia create cool summer and fall microclimates which host species usually found further north. They contain at least one endangered species, the Iowa Pleistocene Snail, and a threatened plant, the Northern monkshood
''Aconitum noveboracense'', also known as northern blue monkshood or northern wild monkshood, is a flowering plant belonging to the buttercup family (Ranunculaceae). Members of its genus (''Aconitum'') are also known as wolfsbane.
The United ...
. The Driftless Area National Wildlife Refuge
Driftless Area National Wildlife Refuge is a United States National Wildlife Refuge in northeastern Iowa, southwestern Wisconsin and northwestern Illinois. It is a non-contiguous collection of parcels in the vicinity of the Upper Mississippi Ri ...
was primarily carved out of the Upper Mississippi River National Wildlife and Fish Refuge
The Upper Mississippi River National Wildlife and Fish Refuge is a ,algific talus slopes
Algific talus slopes comprise a very rare, fragile ecosystem and habitat initially stated to exist only in the Driftless Area of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Illinois, and especially, Iowa.+Algific
Taiga and boreal forests in the United States
Ecore ...
are present. These trees survive in the cooler microclimate
A microclimate (or micro-climate) is a local set of atmospheric conditions that differ from those in the surrounding areas, often with a slight difference but sometimes with a substantial one. The term may refer to areas as small as a few squa ...
produced at these locations outside of their current range further north.
A particularly noteworthy annual event is the rising of fishflies, a kind of mayfly
Mayflies (also known as shadflies or fishflies in Canada and the upper Midwestern United States, as Canadian soldiers in the American Great Lakes region, and as up-winged flies in the United Kingdom) are aquatic insects belonging to the order ...
endemic to the Mississippi valley in the region. These are aquatic insects attracted to light, which rise by the millions as adults to mate, only to die within hours.
Wildlife is abundant with opportunities for hunting whitetail deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced t ...
and wild turkey
The wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') is an upland ground bird native to North America, one of two extant species of turkey and the heaviest member of the order Galliformes. It is the ancestor to the domestic turkey, which was originally ...
. Fishing, particularly for brown trout
The brown trout (''Salmo trutta'') is a European species of salmonid fish that has been widely introduced into suitable environments globally. It includes purely freshwater populations, referred to as the riverine ecotype, ''Salmo trutta'' morp ...
, brook trout, and rainbow trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead (sometimes called "steelhead trout") is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coast ...
in tributaries, and species such as channel catfish
The channel catfish (''Ictalurus punctatus'') is North America's most numerous catfish species. It is the official fish of Kansas, Missouri, Iowa, Nebraska, and Tennessee, and is informally referred to as a "channel cat". In the United States, th ...
in the Mississippi is available, with ice fishing
Ice fishing is the practice of catching fish with lines and fish hooks or spears through an opening in the ice on a frozen body of water. Ice fishers may fish in the open or in heated enclosures, some with bunks and amenities.
Shelters
Lo ...
in winter.
Other characteristics
The Driftless Area is part of the Mississippi Flyway. Many birds fly over the river in large flocks, going north in spring and south in autumn. There are very few natural lakes in the region, these being found in adjoining areas of glacial till, drift and in moraines; the region is extraordinarily well drained, and there is rarely a place where even a pond can naturally form. There are also very few dams in that the valley walls and floors are very often fissured or crumbly, or very porous, providing very poor anchors for a dam or making it difficult to keep any kind of reservoir appropriately filled. There are no realwaterfall
A waterfall is a point in a river or stream where water flows over a vertical drop or a series of steep drops. Waterfalls also occur where meltwater drops over the edge of a tabular iceberg or ice shelf.
Waterfalls can be formed in severa ...
s, but some very strong springs bear the name.
A modern, man-made characteristic is the comparatively twisty nature of highways in the region, such as in Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virgini ...
, in contrast to the usually rigid east-west/north-south alignment elsewhere in the Midwest. Here, the roads switchback up stream valleys or travel over ridge tops. The route of U.S. Highway 20
U.S. Route 20 or U.S. Highway 20 (US 20) is an east–west United States Numbered Highway that stretches from the Pacific Northwest east to New England. The "0" in its route number indicates that US 20 is a major coast-to-coast route. ...
through the Driftless, and particularly in Illinois, is a good example.
Economy
Agriculture
The natural characteristics of the Driftless Area provide good conditions for growing crops and grazing livestock. In recent years, the region has generated much public interest in the organic and artisanal food market. Organic dairy and beef production is of particular economic significance to the Driftless. Organic Valley, the largest organic dairy cooperative in the United States, was founded and is headquartered in La Farge, Wisconsin. The region's cheese production boasts specialty cheeses such as raw-milk artisan cheese, which is made from unpasteurized milk. Organic dairy generally fits best with a grass-based milk production system. The bioregion's economic and cultural characteristics were federally recognized with the granting of the Upper Mississippi River Valley (UMRV) viticultural area, the largest designated winemaking region in the country, by the Treasury Division's Tax and Trade Bureau in 2009. The petition for designation maintains the position that the region is a cohesive whole for marketing wine, and is now used to market other products.
In addition to wine-grape production and wine-making, the region, especially in southeast Minnesota, is known for apple production. Tobacco was also once a key crop of the Driftless, as its topography and sandy, nutrient-rich soil are suitable for its growth.
The Driftless Region Food and Farm Project, in partnership with the
The bioregion's economic and cultural characteristics were federally recognized with the granting of the Upper Mississippi River Valley (UMRV) viticultural area, the largest designated winemaking region in the country, by the Treasury Division's Tax and Trade Bureau in 2009. The petition for designation maintains the position that the region is a cohesive whole for marketing wine, and is now used to market other products.
In addition to wine-grape production and wine-making, the region, especially in southeast Minnesota, is known for apple production. Tobacco was also once a key crop of the Driftless, as its topography and sandy, nutrient-rich soil are suitable for its growth.
The Driftless Region Food and Farm Project, in partnership with the University of Wisconsin-Madison
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which ...
Center for Integrated Agricultural Systems, is a coalition of sustainable-agriculture farmers, processors, distributors, chefs, planning commissions, and other participants. The project seeks to define the culinary identity of the region and further direct the development of agritourism.
Mining
Fine-grained silica sand is typical of the Driftless and is mined for use primarily inhydraulic fracturing
Fracking (also known as hydraulic fracturing, hydrofracturing, or hydrofracking) is a well stimulation technique involving the fracturing of bedrock formations by a pressurized liquid. The process involves the high-pressure injection of "frac ...
, commonly known as "fracking".
 Due to the presence of
Due to the presence of sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
bedrock at or near the surface, sand mining
Sand mining is the extraction of sand, mainly through an open pit (or sand pit) but sometimes mined from beaches and inland dunes or dredged from ocean and river beds. Sand is often used in manufacturing, for example as an abrasive or in concr ...
is an industrial activity in the Driftless, with Wisconsin at the forefront of the industry. The sandstone contains quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical ...
(silica) sand grains of the ideal hardness, shape, and size, which make it optimal for use in hydraulic fracturing by the petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
and natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon ...
industries. The mining activity involves quarrying the sandstone bedrock by blasting with dynamite, crushing the rock, washing, drying, and grading the resulting sand, and transporting the sand out of the region via barge or train. In 2017, there were 73 frac sand mines in operation in Wisconsin alone, and there are currently five operating industrial sand mines in Minnesota; the proliferation of sand mines in the region created new jobs and generated economic activity. But the prominence of industry has raised concerns about impacts on water quality, air pollution caused by silica dust, noise and light pollution
Light pollution is the presence of unwanted, inappropriate, or excessive use of artificial lighting. In a descriptive sense, the term ''light pollution'' refers to the effects of any poorly implemented lighting, during the day or night. Light po ...
, heavy truck traffic, and the destruction of hills and ridges for which the region is known. Recently, industry changes have caused companies such as Hi-Crush, Covia
Unimin (known as Covia since 2018) Corporation is a wholly owned subsidiary of global industrial minerals company SCR- of Belgium. Unimin operates 44 mining and mineral processing facilities in the United States, Mexico and Canada. In Mexico, the ...
, Superior Silica Sands— all with operations in Wisconsin—to liquidate their frac sand mines and declare bankruptcy.
Geographic extent
Minnesota
 Corresponding to the southeast geological region of Minnesota, the colloquial "Driftless Area" (though the whole region was glaciated) begins at about Fort Snelling. Starting as a narrow sliver against the Mississippi, it widens to the west as one goes south. The western boundary is the Bemis-Altamont moraine."Rochester Plateau Subsection"
Corresponding to the southeast geological region of Minnesota, the colloquial "Driftless Area" (though the whole region was glaciated) begins at about Fort Snelling. Starting as a narrow sliver against the Mississippi, it widens to the west as one goes south. The western boundary is the Bemis-Altamont moraine."Rochester Plateau Subsection"Minnesota Department of Natural Resources
The Minnesota Department of Natural Resources, or Minnesota DNR, is the agency of the U.S. state of Minnesota charged with conserving and managing the state's natural resources. The agency maintains areas such as state parks, state forests, rec ...
, Retrieved July 23, 2007 Another more easily located reference to the western boundary is the approximate line of Minnesota State Highway 56.
The upland plateau lies west of the incised tributaries to the Mississippi. The historic vegetation was mixed woodland, with occasional goat prairie {{Short description, Type of grassland
Goat prairies, sometimes termed hill prairies, or dry prairies are found mainly along the valley of the Upper Mississippi River in the Driftless Area, but can occur elsewhere. Normally a variant of tallgrass ...
s on southwesterly facing slopes. In the western section is "an old plateau covered by loess ..along the eastern border and pre-Wisconsin age glacial till
image:Geschiebemergel.JPG, Closeup of glacial till. Note that the larger grains (pebbles and gravel) in the till are completely surrounded by the matrix of finer material (silt and sand), and this characteristic, known as ''matrix support'', is d ...
in the central and western parts. The western portion is a gently rolling glacial till plain that is covered by loess in places."
The counties involved include all or part of
Dakota
Dakota may refer to:
* Dakota people, a sub-tribe of the Sioux
** Dakota language, their language
Dakota may also refer to:
Places United States
* Dakota, Georgia, an unincorporated community
* Dakota, Illinois, a town
* Dakota, Minnesota ...
,
Goodhue,
Rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly '' Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and ''Porteresia'', both wild and domestica ...
,
Wabasha
Wabasha is a city and the county seat of Wabasha County, Minnesota. The population was 2,559 at the time of the 2020 census. It is on the Mississippi River, near its confluence with the Zumbro River.
Name
Wabasha is named after the Mdewakant ...
,
Winona Winona, Wynona or Wynonna may refer to:
Places Canada
* Winona, Ontario
United States
* Winona, Arizona
* Winona, Indiana
* Winona Lake, Indiana
* Winona, Kansas
* Winona, Michigan
* Winona County, Minnesota
** Winona, Minnesota, the seat of Wi ...
,
Olmsted,
Dodge
Dodge is an American brand of automobiles and a division of Stellantis, based in Auburn Hills, Michigan. Dodge vehicles have historically included performance cars, and for much of its existence Dodge was Chrysler's mid-priced brand above P ...
,
Houston
Houston (; ) is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in Texas, the Southern United States#Major cities, most populous city in the Southern United States, the List of United States cities by population, fourth-most pop ...
,
Fillmore Fillmore may refer to:
Places Canada
* Fillmore, Saskatchewan
* Rural Municipality of Fillmore No. 96, Saskatchewan
United States
* Fillmore, California
* Fillmore District, San Francisco, California
* Fillmore, Louisiana
* Fillmore, Illino ...
, and
Mower
A mower is a person or machine that cuts (mows) grass or other plants that grow on the ground. Usually mowing is distinguished from reaping, which uses similar implements, but is the traditional term for harvesting grain crops, e.g. with reapers ...
. Aside from the southeastern suburban sprawl of the Twin Cities
Twin cities are a special case of two neighboring cities or urban centres that grow into a single conurbation – or narrowly separated urban areas – over time. There are no formal criteria, but twin cities are generally comparable in stat ...
, Rochester
Rochester may refer to:
Places Australia
* Rochester, Victoria
Canada
* Rochester, Alberta
United Kingdom
*Rochester, Kent
** City of Rochester-upon-Medway (1982–1998), district council area
** History of Rochester, Kent
** HM Prison ...
is the main urban area. Additional communities include Red Wing, Lake City, Winona Winona, Wynona or Wynonna may refer to:
Places Canada
* Winona, Ontario
United States
* Winona, Arizona
* Winona, Indiana
* Winona Lake, Indiana
* Winona, Kansas
* Winona, Michigan
* Winona County, Minnesota
** Winona, Minnesota, the seat of Wi ...
, La Crescent, Chatfield, Lanesboro, Rushford, Houston
Houston (; ) is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in Texas, the Southern United States#Major cities, most populous city in the Southern United States, the List of United States cities by population, fourth-most pop ...
and Caledonia
Caledonia (; ) was the Latin name used by the Roman Empire to refer to the part of Great Britain () that lies north of the River Forth, which includes most of the land area of Scotland. Today, it is used as a romantic or poetic name for all ...
.
Glacial River Warren, in whose bed the Minnesota River
The Minnesota River ( dak, Mnísota Wakpá) is a tributary of the Mississippi River, approximately 332 miles (534 km) long, in the U.S. state of Minnesota. It drains a watershed of in Minnesota and about in South Dakota and Iowa.
It ris ...
now flows, entered the "Driftless Area" just downriver from present-day Minneapolis-Saint Paul, at Fort Snelling, over River Warren Falls, "an impressive 2700 feet (823 m) across and 175 feet (53 m) tall, over 10 times as wide as Niagara falls" (this has since receded to become Saint Anthony Falls). The region is characterized "by the absence of glacial drift deposits, the sculpted topography, and the presence of the ancient limestone immediately beneath the soil and in cliff outcroppings." The Minnesota Driftless Area did not reach the Twin Cities or any areas to the north or west of them; rather, the Twin Cities marked the edge of glaciation, with substantial terminal moraine
A terminal moraine, also called end moraine, is a type of moraine that forms at the Glacier terminus, terminal (edge) of a glacier, marking its maximum advance. At this point, debris that has accumulated by plucking and abrasion, has been pushed ...
s overlying the region.
The largest protected area is Richard J. Dorer Memorial Hardwood State Forest
The Richard J. Dorer Memorial Hardwood State Forest is a reserve of current and former forest in Minnesota's Driftless Area. Only of the land is state owned, with the remainder owned by private individuals and community groups, governed by ease ...
, which contains some state-owned land, but is mostly private, controlled by state conservation easements.
Wisconsin

 Around 85% of the Driftless Area lies within Wisconsin, comprising much of the southwestern quarter of the state. The border is defined by the catchment of the Chippewa River on the north, and somewhat west (or east, depending on if the southwestern portion of Wisconsin's
Around 85% of the Driftless Area lies within Wisconsin, comprising much of the southwestern quarter of the state. The border is defined by the catchment of the Chippewa River on the north, and somewhat west (or east, depending on if the southwestern portion of Wisconsin's Central Plain Central Plain or Central Plains may refer to:
Regions
* Zhongyuan, a plain in Northern China in the lower reaches of the Yellow River which was the cradle of Chinese civilisation
** Central Plains Economic Zone
* Central Plain (Wisconsin), one ...
is included) of the north-south line of the Wisconsin River
The Wisconsin River is a tributary of the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. At approximately 430 miles (692 km) long, it is the state's longest river. The river's name, first recorded in 1673 by Jacques Marquette as "Meskou ...
. Where the Wisconsin River turns west to join the Mississippi, the area to the south, including the whole of Grant County as well as most of Lafayette County, are part of the Driftless Area.
The rugged terrain comprising most of the Driftless Area is distinct from the rest of Wisconsin, and is known locally as the Coulee Region. The steep ridges, numerous rock outcroppings, and deep, narrow valleys in the Driftless Area are in marked contrast with the rest of the state, where glaciers have modified the landscape. The hilly unglaciated landscape is well represented in Wisconsin's Coulee Experimental State Forest
Coulee Experimental State Forest is a state forest located in La Crosse County, Wisconsin, United States. It is administered by the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources. The hilly terrain within the state forest is an excellent representatio ...
, Wildcat Mountain State Park, Governor Dodge State Park
Governor Dodge State Park is a Wisconsin state park outside Dodgeville in Iowa County, Wisconsin. Named after Henry Dodge, the first governor of the Wisconsin Territory, the park contains geologic features indicative of the Driftless Area. It ...
, Perrot State Park, and the Kickapoo Valley Reserve.
Karst topography
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathering-resistant ...
is most prominent in Wisconsin. Eagle Cave
Eagle Cave is an onyx cave located near Blue River, Wisconsin, in Richland County, Wisconsin
Richland County is a county in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. As of the 2020 census, the population was 17,304. Its county seat is Richland Center. ...
in Blue River, WI and Cave of the Mounds, near Blue Mounds, WI
Blue Mounds is a village in Dane County, Wisconsin, United States. As of the 2020 census, the village had a population of 948. The village is adjacent to the Town of Blue Mounds, and is part of the Madison Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Blue Moun ...
, are better known examples.
The Driftless Area is located in all or part of
Pierce,
Pepin,
Eau Claire Eau Claire (French for "clear water", ''pl.'' ''eaux claires'') is the name of a number of locations and features in North America. The name is pronounced as if it were spelled "O'Clare".
Place names (Canada)
Communities
*Eau Claire, Calgary, a n ...
,
Buffalo,
Trempealeau,
Jackson,
La Crosse,
Monroe,
Juneau,
Vernon,
Richland,
Sauk,
Crawford,
Iowa
Iowa () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wiscon ...
,
Dane,
Green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 Nanometre, nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by ...
,
Grant
Grant or Grants may refer to:
Places
*Grant County (disambiguation)
Australia
* Grant, Queensland, a locality in the Barcaldine Region, Queensland, Australia
United Kingdom
* Castle Grant
United States
*Grant, Alabama
* Grant, Inyo County, ...
, and
Lafayette counties. If the less restrictive definition of the Driftless Area is used (which includes the unglaciated southwestern portion of Wisconsin's Central Plain Central Plain or Central Plains may refer to:
Regions
* Zhongyuan, a plain in Northern China in the lower reaches of the Yellow River which was the cradle of Chinese civilisation
** Central Plains Economic Zone
* Central Plain (Wisconsin), one ...
), then Adams
Adams may refer to:
* For persons, see Adams (surname)
Places United States
*Adams, California
*Adams, California, former name of Corte Madera, California
*Adams, Decatur County, Indiana
*Adams, Kentucky
*Adams, Massachusetts, a New England town ...
and portions of southern Wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of ligni ...
and Portage
Portage or portaging (Canada: ; ) is the practice of carrying water craft or cargo over land, either around an obstacle in a river, or between two bodies of water. A path where items are regularly carried between bodies of water is also called a ...
counties are also included. La Crosse is the principal urban area wholly within the Driftless Area, while the larger Madison Madison may refer to:
People
* Madison (name), a given name and a surname
* James Madison (1751–1836), fourth president of the United States
Place names
* Madison, Wisconsin, the state capital of Wisconsin and the largest city known by this ...
's far western suburbs are located on the edges of the area. Small cities and towns are scattered throughout the region. Numerous Amish
The Amish (; pdc, Amisch; german: link=no, Amische), formally the Old Order Amish, are a group of traditionalist Anabaptist Christian church fellowships with Swiss German and Alsatian origins. They are closely related to Mennonite churches ...
settlements are also located within Wisconsin's Driftless Area.
The U.S. Army maintains a presence at Fort McCoy, Wisconsin
Fort McCoy is a United States Army installation on between Sparta and Tomah, Wisconsin, in Monroe County. In 1909, there were two separate camps named Camp Emory Upton and Camp Robinson; in 1926, these camps were joined together to form Ca ...
in Monroe County between Sparta
Sparta (Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referred ...
and Tomah immediately south of the Black River State Forest. The property is used mainly for military training exercises, although troops have also been based there for deployments overseas.
The Coulee Region portion of the Driftless Area comprises much of Wisconsin's Western Upland geographical region. The most rugged part of Wisconsin's Driftless area is also called the Ocooch Mountains.
Largely rural in character, land cover is forest, farmland, and grassland/pasture; modest wetlands are found in river valleys, and along the Mississippi. Row crop farming is less encountered than elsewhere in the state. Away from the Mississippi, Wisconsin, and other major rivers, much of the terrain is gently rolling, supporting dairy farms. In other areas, the rugged nature of the topography in the region is not conducive to farming, except on ridge tops and in river valleys. The sides of the ridges are often too steep for farming, and are usually forested. The Coulee Experimental State Forest
Coulee Experimental State Forest is a state forest located in La Crosse County, Wisconsin, United States. It is administered by the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources. The hilly terrain within the state forest is an excellent representatio ...
near La Crosse was created in part to test soil conservation
Soil conservation is the prevention of loss of the topmost layer of the soil from erosion or prevention of reduced fertility caused by over usage, acidification, salinization or other chemical soil contamination.
Slash-and-burn and other un ...
practices to prevent soil erosion in the hilly Driftless Area.
The northeastern portion of the Driftless area was covered by or bordered by Glacial Lake Wisconsin
Glacial Lake Wisconsin was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed from approximately 18,000 to 14,000 years ago, at the end of the last ice age, in the central part of present-day Wisconsin in the United States.
Formation and demise
Before ...
during the Wisconsin glaciation
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cor ...
. The steep-sided rocky bluffs present in Roche-a-Cri State Park and Mill Bluff State Park
Mill Bluff State Park is a state park in west-central Wisconsin, United States. It is located in eastern Monroe and western Juneau counties, near the village of Camp Douglas. A unit of the Ice Age National Scientific Reserve, the park protects ...
are Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ag ...
outliers of the Franconia cuesta
A cuesta (from Spanish ''cuesta'' "slope") is a hill or ridge with a gentle slope on one side, and a steep slope on the other. In geology the term is more specifically applied to a ridge where a harder sedimentary rock overlies a softer laye ...
to the southwest and were once islands or sea stacks in the ancient lake. The flat plain in which these bluffs lie is located in the southwest portion of Wisconsin's Central Plain Central Plain or Central Plains may refer to:
Regions
* Zhongyuan, a plain in Northern China in the lower reaches of the Yellow River which was the cradle of Chinese civilisation
** Central Plains Economic Zone
* Central Plain (Wisconsin), one ...
geographic region, and was created in part by sediments falling to the bottom of Glacial Lake Wisconsin
Glacial Lake Wisconsin was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed from approximately 18,000 to 14,000 years ago, at the end of the last ice age, in the central part of present-day Wisconsin in the United States.
Formation and demise
Before ...
. This flat plain consists of sandy deposits and contains many bog
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and muskeg; a ...
s that were left over from Glacial Lake Wisconsin. Many of these bogs have been converted into cranberry
Cranberries are a group of evergreen dwarf shrubs or trailing vines in the subgenus ''Oxycoccus'' of the genus '' Vaccinium''. In Britain, cranberry may refer to the native species '' Vaccinium oxycoccos'', while in North America, cranber ...
marshes, helping to make Wisconsin a leader in cranberry production. The remainder of the sand plain consists of forest and irrigated farmland. The Dells of the Wisconsin River
The Dells of the Wisconsin River, also called the Wisconsin Dells (from Old English �dæle��, modern English “dale”), meaning “valley”, is a 5-mile (8-km) gorge on the Wisconsin River in south-central Wisconsin, USA. It is noted for i ...
were carved through the bedrock during the sudden draining of Glacial Lake Wisconsin at the end of the last ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gre ...
.
Due to the lack of natural lakes in the Coulee region, several large artificial lakes have been created for flood control and recreational purposes, including Dutch Hollow Lake
Dutch Hollow Lake is a man-made reservoir located in the Town of La Valle, ( Sauk County), Wisconsin, United States. Created by developers in the 1970s by impounding the water of Dutch Hollow Creek,
it is now a public-access lake regulated by ...
and Lake Redstone
Lake Redstone is in La Valle in northern Sauk County of Wisconsin, United States.
Lake Redstone is a reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to s ...
in Sauk County, Blackhawk Lake in Iowa County, and Yellowstone Lake (in Yellowstone State Park) in Lafayette County. Plans for a large reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.
Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including control ...
on the Kickapoo River at La Farge, Wisconsin were dropped in 1975 after much controversy due to cost-benefit and environmental concerns. Land previously acquired for the reservoir became the Kickapoo Valley Reserve, an 8,569 acre public forest and wildlife area.
Wazee Lake, at 355 feet (108 m) deep, is Wisconsin's deepest inland lake, and is located in Jackson County in the northeast portion of the Driftless area. The artificial lake lies in the former open pit Jackson County Iron Mine and is the centerpiece of the Wazee Lake Recreation Area. Due to its great depth, vertical underwater cliffs, clear water, and submerged mining features, the lake is popular with scuba
Scuba may refer to:
* Scuba diving
** Scuba set, the equipment used for scuba (Self-Contained Underwater Breathing Apparatus) diving
* Scuba, an in-memory database developed by Facebook
* Submillimetre Common-User Bolometer Array Two instruments ...
divers.
The highest point in the Driftless area is West Blue Mound, with an elevation of . The feature is located in Blue Mound State Park
Blue Mound State Park is a state park in Wisconsin, United States, located atop the largest hill in the southern half of the state, near the village of Blue Mounds. The park features a pair of observation towers affording views of the Wisconsin ...
, in Iowa County.
During the 19th and early 20th centuries, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metals, heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale of mineral hardness#Intermediate ...
and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic t ...
mining was a major industrial activity in the Driftless Area, drawing many foreign immigrants to settle in the region to work in the mines. Early miners often lived in the mine tunnels, leading outsiders to compare them to the burrowing badger
Badgers are short-legged omnivores in the family Mustelidae (which also includes the otters, wolverines, martens, minks, polecats, weasels, and ferrets). Badgers are a polyphyletic rather than a natural taxonomic grouping, being united ...
; a nickname that eventually came to be used for all Wisconsin residents. An example of an early lead shot tower and smelting house is preserved in Tower Hill State Park.
Due to the influx of early miners, the lead mining region became Wisconsin's most populous area at the time. The first capitol of the Wisconsin Territory
The Territory of Wisconsin was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 3, 1836, until May 29, 1848, when an eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Wisconsin. Belmont was ...
was located for a short time at Belmont
Belmont may refer to:
People
* Belmont (surname)
Places
* Belmont Abbey (disambiguation)
* Belmont Historic District (disambiguation)
* Belmont Hotel (disambiguation)
* Belmont Park (disambiguation)
* Belmont Plantation (disambiguation)
* Belmon ...
, Lafayette County in the heart of the lead mining region. The site of the first capitol is preserved at the First Capitol Historic Site
First Capitol Historic Site is a free-admission historic museum located outside Belmont, Wisconsin, United States. The museum includes two of the buildings first used by legislators to meet in Wisconsin Territory. Currently owned and operated by th ...
.
Three units of the Ice Age National Scientific Reserve
The Ice Age National Scientific Reserve is an affiliated area of the National Park System of the United States comprising nine sites in Wisconsin that preserve geological evidence of glaciation. To protect the scientific and scenic value ...
are located within or adjacent to the Driftless Area: Devil's Lake State Park, Mill Bluff State Park
Mill Bluff State Park is a state park in west-central Wisconsin, United States. It is located in eastern Monroe and western Juneau counties, near the village of Camp Douglas. A unit of the Ice Age National Scientific Reserve, the park protects ...
, and Cross Plains State Park. In addition, the Ice Age Trail follows the Terminal moraine
A terminal moraine, also called end moraine, is a type of moraine that forms at the Glacier terminus, terminal (edge) of a glacier, marking its maximum advance. At this point, debris that has accumulated by plucking and abrasion, has been pushed ...
of the maximum glacial extent from the last ice age and enters the Driftless Area in several locations.
Other notable natural features include the Baraboo Range
The Baraboo Range is a syncline located in Columbia and Sauk Counties, Wisconsin. It consists of highly eroded Precambrian metamorphic rock. It is about long and varies from 5 to in width. The Wisconsin River, previously traveling in a north ...
(consisting of two heavily forested, steep, rocky quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock which was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tec ...
ridges with mountain-type scenery), rock formations in Natural Bridge State Park (Wisconsin), the forested bluffs, floodplains, islands, and sandbars in the Lower Wisconsin River State Riverway, the confluence of the Wisconsin River
The Wisconsin River is a tributary of the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. At approximately 430 miles (692 km) long, it is the state's longest river. The river's name, first recorded in 1673 by Jacques Marquette as "Meskou ...
with the Mississippi River at Wyalusing State Park
Wyalusing State Park is a Wisconsin state park at the confluence of the Mississippi and Wisconsin rivers in the town of Wyalusing, just south of Prairie du Chien.
Wyalusing means "home of the warrior" in the Lenape language spoken by Mun ...
, Trempealeau Mountain State Natural Area
Trempealeau Mountain State Natural Area is a Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources-designated State Natural Area consisting of a 425-foot conical rock mound surrounded on three sides by the Mississippi and Trempealeau Rivers. It is one of ...
in the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it ...
valley at Perrot State Park, and the gorge and rock formations surrounding the Wisconsin River at the Dells of the Wisconsin River
The Dells of the Wisconsin River, also called the Wisconsin Dells (from Old English �dæle��, modern English “dale”), meaning “valley”, is a 5-mile (8-km) gorge on the Wisconsin River in south-central Wisconsin, USA. It is noted for i ...
. The Black River State Forest protects a large area of the North Woods, rocky bluffs, sandy plains, and river shoreline on the northeastern edge of the Driftless Area that provides habitat for several wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly u ...
packs and one of Wisconsin's reintroduced elk herds.
Iowa
 An area in northeast Iowa that shares similar topographic characteristics to the Driftless Area in southeastern Wisconsin is the Paleozoic Plateau. For counties inland from the Mississippi, evidence is largely confined to the valleys of streams and rivers. It encompasses all of Allamakee, and part of Clayton, Fayette,
An area in northeast Iowa that shares similar topographic characteristics to the Driftless Area in southeastern Wisconsin is the Paleozoic Plateau. For counties inland from the Mississippi, evidence is largely confined to the valleys of streams and rivers. It encompasses all of Allamakee, and part of Clayton, Fayette, Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacen ...
, Winneshiek, Howard
Howard is an English-language given name originating from Old French Huard (or Houard) from a Germanic source similar to Old High German ''*Hugihard'' "heart-brave", or ''*Hoh-ward'', literally "high defender; chief guardian". It is also prob ...
, Dubuque
Dubuque (, ) is the county seat of Dubuque County, Iowa, United States, located along the Mississippi River. At the time of the 2020 census, the population of Dubuque was 59,667. The city lies at the junction of Iowa, Illinois, and Wisconsin, a r ...
, and Jackson Counties. Dubuque
Dubuque (, ) is the county seat of Dubuque County, Iowa, United States, located along the Mississippi River. At the time of the 2020 census, the population of Dubuque was 59,667. The city lies at the junction of Iowa, Illinois, and Wisconsin, a r ...
is the only metropolitan area.
The region is distinct from the "Iowan Erosion Surface to the west and the Southern Iowa Drift Plain to the south."Stephanie A. Tassier-Surine, ( Iowa Department of Natural Resources, Geological Survey Bureau)Quaternary Geology of the Paleozoic Plateau Region of Northeastern Iowa
, Retrieved July 30, 2007 A line east of the most easterly tributaries of the Wapsipinicon River defines the western boundary of the landform region, with the catchment of the Maquoketa River south of Bellevue serving as a southern boundary. The most western tributaries of the Upper Iowa,
Yellow
Yellow is the color between green and orange on the spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a dominant wavelength of roughly 575585 nm. It is a primary color in subtractive color systems, used in painting or color printing. In ...
and Turkey Rivers flow east and south from the vicinity of this moraine.
Outside of Dubuque
Dubuque (, ) is the county seat of Dubuque County, Iowa, United States, located along the Mississippi River. At the time of the 2020 census, the population of Dubuque was 59,667. The city lies at the junction of Iowa, Illinois, and Wisconsin, a r ...
, this region of Iowa is thinly populated. In the western section, agriculture and livestock raising are the norm. As one travels east, and as the valleys tumble down to the Mississippi, much of the land is virtually wild, with a great deal of it publicly owned. The state maintains an extensive number of wildlife management areas, along with state forests and state parks.
The most impressive area is on the Mississippi, between Pikes Peak State Park
Pikes Peak State Park is a state park of Iowa, US, featuring a bluff overlooking the Upper Mississippi River opposite the confluence of the Wisconsin River. The park is operated by the Iowa Department of Natural Resources. It is nearly a thou ...
, opposite the Wisconsin River down to Guttenberg, where bluffs lining the river reach their maximum height. This is apparently an Iowa continuation of Military Ridge, a catchment-defining divide in Wisconsin that was used for the Military Ridge Road, a portion of which is included in Military Ridge State Trail, both across the River in Wisconsin.
Effigy Mounds National Monument
Effigy Mounds National Monument preserves more than 200 prehistoric mounds built by pre-Columbian
Mound Builder cultures, mostly in the first millennium CE, during the later part of the Woodland period of pre-Columbian North America.
Numerous e ...
is at the heart of a network of adjacent parks, state forests, preserves, as well as national wildlife refuges, all of which preserve and illustrate the features of the Driftless, where "patchy remnants of Pre-Illinoian glacial drift more than 500,000 years old recently have been discovered in the area." Additional protected areas are Cold Water Spring State Preserve near Decorah
Decorah is a city in and the county seat of Winneshiek County, Iowa, United States. The population was 7,587 at the time of the 2020 census. Decorah is located at the intersection of State Highway 9 and U.S. Route 52, and is the largest communi ...
, Maquoketa Caves State Park northwest of Maquoketa, Bellevue State Park adjacent to Bellevue, White Pine Hollow State Forest (which protects Iowa's only remaining groves of old-growth white pine
''Pinus'', the pines, is a genus of approximately 111 extant tree and shrub species. The genus is currently split into two subgenera: subgenus ''Pinus'' (hard pines), and subgenus ''Strobus'' (soft pines). Each of the subgenera have been furthe ...
trees) near Dubuque, and the Yellow River State Forest
Yellow River State Forest, (YRSF), is mostly forested land owned by the Iowa Department of Natural Resources. It is located in the southeastern corner of Allamakee County, the most northeasterly of Iowa's counties. It is adjacent to the Uppe ...
in the southeastern corner of Allamakee County, Iowa
Allamakee County () is the northeasternmost county in the U.S. state of Iowa. As of the 2020 census, the population was 14,061. Its county seat is Waukon.
History
Allamakee County was formed on February 20, 1847. The derivation of the name i ...
.
Illinois
 The Illinois portion of the Driftless Area is confined mainly to
The Illinois portion of the Driftless Area is confined mainly to Jo Daviess County
Jo Daviess County () is the northwesternmost county in the U.S. state of Illinois. According to the 2010 census, it had a population of 22,678. Its county seat is Galena.
Jo Daviess County is part of the Tri-State Area and is located near ...
; western parts of Carroll County (the Mississippi River bluffs characteristic of the Driftless terminate around Savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
) and a tiny portion of northwest Whiteside County
Whiteside County is a county located in the U.S. state of Illinois. According to the 2010 census, it had a population of 58,498. Its county seat is Morrison. The county is bounded on the west by the Mississippi River. Whiteside County comprises ...
are also included. The region contains the highest points in the state, of which "the most notable are Charles Mound and Benton Mound, rising to heights of and respectively." The region "has many sinkholes and sinkhole ponds.",
Illinois Department of Natural Resources
The Illinois Department of Natural Resources (IDNR) is the code department of the Illinois state government that operates the state parks and state recreation areas, enforces the fishing and game laws of Illinois, regulates Illinois coal mines, ...
, Retrieved July 12, 2007East Dubuque
East Dubuque is a city in Jo Daviess County, Illinois, Jo Daviess County, Illinois, United States. The population was 1,505 at the 2020 census, down from 1,704 in 2010. East Dubuque is located alongside the Mississippi River. Across the river is t ...
is really a part of metropolitan Dubuque
Dubuque (, ) is the county seat of Dubuque County, Iowa, United States, located along the Mississippi River. At the time of the 2020 census, the population of Dubuque was 59,667. The city lies at the junction of Iowa, Illinois, and Wisconsin, a r ...
, while Galena
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver.
Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It cry ...
retains the character of a small Midwestern county seat.
The valley of the Apple River has a major canyon, with Apple River Canyon occupying much of it. The mouth of this river, near Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
adjacent to the former Savanna Army Depot, comes close to the southern end of the Driftless Area on the eastern side of the Mississippi (''see'' Lock and Dam No. 13).
As in Wisconsin, the Illinois portion of the driftless area was a major early center for Lead
Lead is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metals, heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale of mineral hardness#Intermediate ...
and Zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic t ...
mining. The city of Galena, Illinois
Galena is the largest city in and the county seat of Jo Daviess County, Illinois, with a population of 3,308 at the 2020 census. A section of the city is listed on the National Register of Historic Places as the Galena Historic District. The c ...
was named after the lead sulfide mineral Galena
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver.
Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It cry ...
.
References
External links
"Decoding the Driftless" movie
2018, created by Sustainable Driftless, Inc., dedicated to inspiring resource conservation and
sustainable growth
Sustainable development is an organizing principle for meeting human development goals while also sustaining the ability of natural systems to provide the natural resources and ecosystem services on which the economy and society depend. The d ...
in the Driftless Region.
* A Sand County Almanac
''A Sand County Almanac: And Sketches Here and There'' is a 1949 non-fiction book by American ecologist, forester, and environmentalist Aldo Leopold. Describing the land around the author's home in Sauk County, Wisconsin, the collection of es ...
: A book written by Aldo Leopold
Aldo Leopold (January 11, 1887 – April 21, 1948) was an American writer, philosopher, naturalist, scientist, ecologist, forester, conservationist, and environmentalist. He was a professor at the University of Wisconsin and is best known for his ...
about the flora and fauna in the Coulee region.
The Driftless Area: A Landscape of Opportunities
"Driftless Area National Wildlife Refuge"
Retrieved July 23, 2007
Retrieved July 7, 2007
Retrieved July 7, 2007
Driftless Area Initiative
Retrieved July 2, 2014
Wisconsin Geological and Natural History Survey map showing extent of last glaciation
Driftless Region Food and Farm Project
Driftless Area Magazine
{{Continental Glaciations Regions of Wisconsin Pleistocene Geology of Wisconsin Geology of Illinois Geology of Iowa Geology of Minnesota Regions of Illinois Regions of Iowa Regions of Minnesota