|
Strip Cropping
Strip cropping is a method of farming which involves cultivating a field partitioned into long, narrow strips which are alternated in a crop rotation system. It is used when a slope is too steep or when there is no alternative method of preventing soil erosion. The most common crop choices for strip cropping are closely sown crops such as hay, wheat, or other forages which are alternated with strips of row crops, such as corn, soybeans, cotton, or sugar beets. The forages serve primarily as cover crops. In certain systems, strips in particularly-eroded areas are used to grow permanent protective vegetation, but in most systems, all strips are alternated on an annual basis. Dimensions The width of strips is determined by a number of factors, with the two most important being the average wind velocity in a specific site and the features of the slope, particularly the gradient. Each strip typically ranges from 25 feet (7.6 m) to 75 feet (23 m) in width, but certain conditions may ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strip Farming In Wisconsin, USA, 1957
Strip, Strips or Stripping may refer to: Places * Aouzou Strip, a strip of land following the northern border of Chad that had been claimed and occupied by Libya * Caprivi Strip, narrow strip of land extending from the Okavango Region of Namibia to the Zambezi River * Gaza Strip, narrow strip of land along the Mediterranean, in the Middle East * Las Vegas Strip, section of Las Vegas Boulevard South * Strip District, Pittsburgh, a neighborhood in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania * Sunset Strip, 1.5-mile stretch of Sunset Boulevard in West Hollywood, California, US * Tarfaya Strip (Cape Juby Strip), a strip of land between Morocco and the Western Sahara along the Atlantic Ocean * Toledo strip, formerly contested area between Ohio and Michigan; see Toledo War Arts, entertainment, and media Comics * Strip (comics), a comics anthology published by Marvel UK in 1990 * Comic strip, a sequence of drawings arranged in interrelated panels to display brief humor or form a narrative * Sunday st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade (slope)
The grade (US) or gradient (UK) (also called stepth, slope, incline, mainfall, pitch or rise) of a physical feature, landform or constructed line is either the elevation angle of that surface to the horizontal plane, horizontal or its tangent. It is a special case of the slope, where zero indicates horizontal plane, horizontality. A larger number indicates higher or steeper degree of "tilt". Often slope is calculated as a ratio of "rise" to "run", or as a fraction ("rise over run") in which ''run'' is the horizontal distance (not the distance along the slope) and ''rise'' is the vertical distance. Slopes of existing physical features such as canyons and hillsides, bank (geography), stream and river banks, and stream bed, beds are often described as grades, but typically the word "grade" is used for human-made surfaces such as roads, landscape grading, roof pitches, rail tracks, railroads, aqueduct (watercourse), aqueducts, and pedestrian or bicycle routes. The grade may refer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercropping
Intercropping is a multiple cropping practice that involves the cultivation of two or more crops simultaneously on the same field, a form of polyculture. The most common goal of intercropping is to produce a greater yield on a given piece of land by making use of resources or ecological processes that would otherwise not be utilized by a single crop. Methods The degree of spatial and temporal overlap in the two crops can vary somewhat, but both requirements must be met for a cropping system to be an intercrop. Numerous types of intercropping, all of which vary the temporal and spatial mixture to some degree, have been identified. Mixed intercropping Mixed intercropping consists of multiple crops freely mixed in the available space. In the 21st century, it remains a common practice in Ethiopia, Eritrea, Georgia (country), Georgia, and a few other places. Freely mixed intercropping has been practiced for thousands of years. In medieval England, farmers mixed oat and barley, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
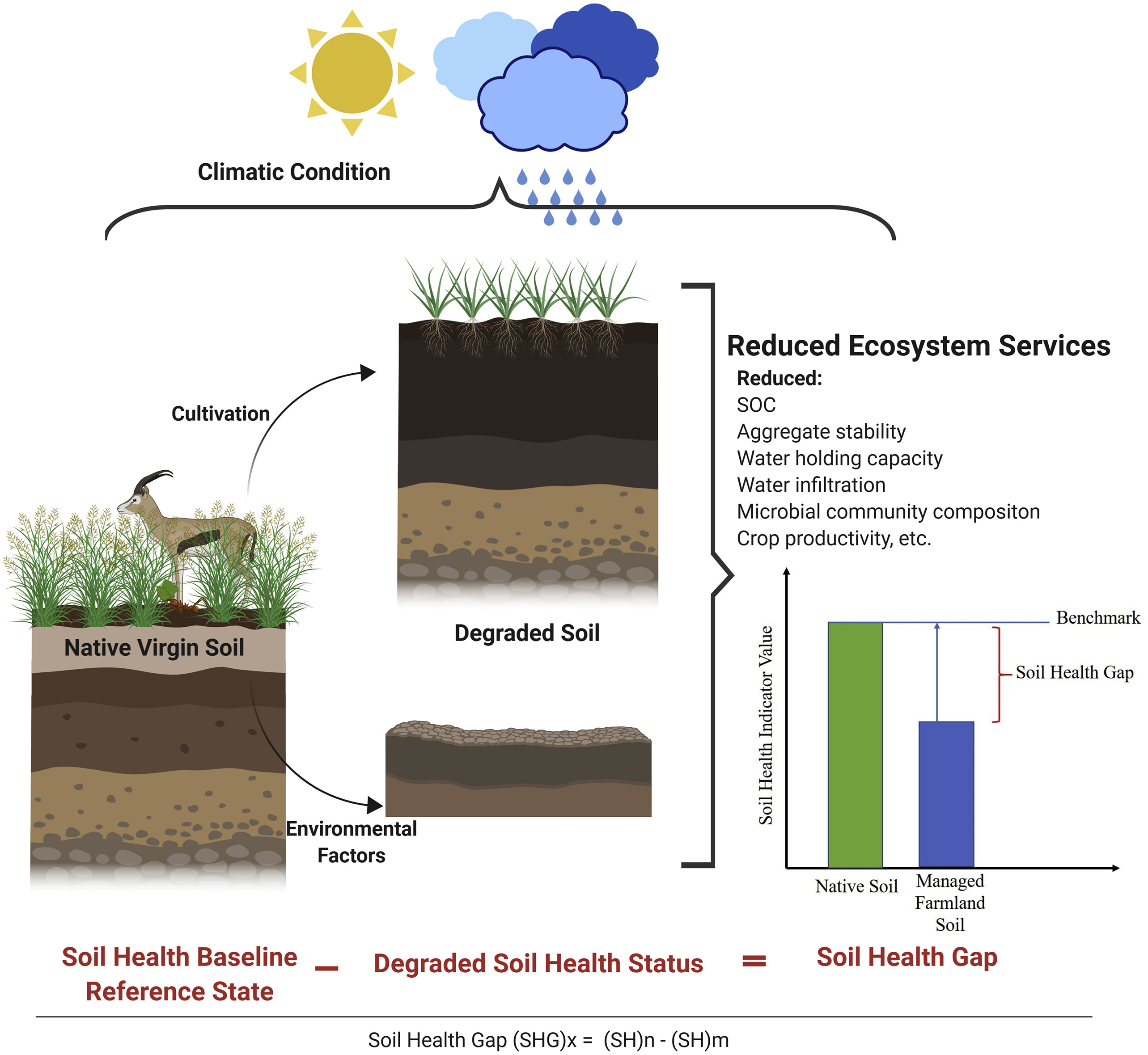
Soil Health
Soil health is a state of a soil meeting its range of ecosystem functions as appropriate to its environment. In more colloquial terms, the health of soil arises from favorable interactions of all soil components (living and non-living) that belong together, as in microbiota, plants and animals. It is possible that a soil can be healthy in terms of ecosystem functioning but not necessarily serve crop production or human nutrition directly, hence the scientific debate on terms and measurements. Soil health testing is pursued as an assessment of this status but tends to be confined largely to agronomic objectives. Soil health depends on soil biodiversity (with a robust soil biology, soil biota), and it can be improved via soil management, especially by care to keep protective living covers on the soil and by natural (carbon-containing) soil amendments. Inorganic fertilizers do not necessarily damage soil health if they are not used in excess, and if they bring about a general improveme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prairie Strips
Prairie strips are strips of native perennial vegetation that are strategically integrated into row crop fields. This technique is used in conservation farming to improve biodiversity, and protect soil and water. Native prairie vegetation improves soil stability, reduces soil erosion and nutrient runoff, and concentrates more organic carbon in soil than corn and soybean crops. Research has found that strategically setting aside land in corn and soybean fields benefits biodiversity, water and soil in a greater extent than other types of perennial vegetation. 10% of a corn field set aside for native vegetation can reduce sediment movement by 95%. Phosphorus and nitrogen lost through run off are reduced by 90% and 85% respectively. Farmers can take odd areas or difficult-to-farm areas out of production as they integrate native plant species into farm fields as contour buffers and edge-of-field filters. In Iowa, most of the rich and fertile soils have been dedicated to corn and soy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midwestern United States
The Midwestern United States (also referred to as the Midwest, the Heartland or the American Midwest) is one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It was officially named the North Central Region by the U.S. Census Bureau until 1984. It is between the Northeastern United States and the Western United States, with Canada to the north and the Southern United States to the south. The U.S. Census Bureau's definition consists of 12 states in the north central United States: Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, Ohio, South Dakota, and Wisconsin. The region generally lies on the broad Interior Plain between the states occupying the Appalachian Mountain range and the states occupying the Rocky Mountain range. Major rivers in the region include, from east to west, the Ohio River, the Upper Mississippi River, and the Missouri River. The 2020 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, second-largest country by total area, with the List of countries by length of coastline, world's longest coastline. Its Canada–United States border, border with the United States is the world's longest international land border. The country is characterized by a wide range of both Temperature in Canada, meteorologic and Geography of Canada, geological regions. With Population of Canada, a population of over 41million people, it has widely varying population densities, with the majority residing in List of the largest population centres in Canada, urban areas and large areas of the country being sparsely populated. Canada's capital is Ottawa and List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Prairies
The Canadian Prairies (usually referred to as simply the Prairies in Canada) is a region in Western Canada. It includes the Canadian portion of the Great Plains and the Prairie provinces, namely Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. These provinces are partially covered by grasslands, plains, and Upland and lowland#Lowland, lowlands, mostly in the southern regions. The northernmost reaches of the Canadian Prairies are less dense in population, marked by forests and more variable topography. If the region is defined to include areas only covered by prairie land, the corresponding region is known as the Interior Plains. Physical or ecological aspects of the Canadian Prairies extend to northeastern British Columbia, but that area is not included in political use of the term. The prairies in Canada are a biome of Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands, temperate grassland and shrubland within the prairie ecoregion of Canada that consists of Canadian Aspen Forests and Parkland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Plains
The Great Plains is a broad expanse of plain, flatland in North America. The region stretches east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, and grassland. They are the western part of the Interior Plains, which include the mixed grass prairie, the tallgrass prairie between the Great Lakes and Appalachian Plateau, and the Taiga Plains Ecozone, Taiga Plains and Boreal Plains Ecozone, Boreal Plains ecozones in Northern Canada. "Great Plains", or Western Plains, is also the ecoregion of the Great Plains or the western portion of the Great Plains, some of which in the farthest west is known as the High Plains. The Great Plains lie across both the Central United States and Western Canada, encompassing: *Most or all of the U.S. states of Kansas, Nebraska, and North Dakota, North and South Dakota; *Eastern parts of the U.S. states of Colorado, Montana, and Wyoming; *Parts of the U.S. states of New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas; *Sometimes western parts of Iowa, Minnesot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Farming
Dry or dryness most often refers to: * Lack of rainfall, which may refer to **Arid regions **Drought * Dry or dry area, relating to legal prohibition of selling, serving, or imbibing alcoholic beverages * Dry humor, deadpan * Dryness (medical) * Dryness (taste), the lack of sugar in a drink, especially an alcoholic one * Dry direct sound without reverberation Dry or DRY may also refer to: Places * Dry Brook (other), various rivers * Dry Creek (other), various rivers and towns * Dry, Loiret, a commune of the Loiret ''département'' in France * Dry River (other), various rivers and towns Art, entertainment, and media Film and television * ''Dry'' (2014 film), a Nigerian film directed by Stephanie Linus * ''Dry'' (2022 film), an Italian film directed by Paolo Virzì * ''The Dry'' (film), a 2020 film directed by Robert Connolly and based on the novel by Jane Harper ** '' Force of Nature: The Dry 2'', a 2024 sequel film * ''The Dry'' (TV series) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cover Crops
In agriculture, cover crops are plants that are planted to cover the soil rather than for the purpose of being harvested. Cover crops manage soil erosion, soil fertility, soil quality, water, weeds, pests, diseases, biodiversity and wildlife in an agroecosysteman ecological system managed and shaped by humans. Cover crops can increase microbial activity in the soil, which has a positive effect on nitrogen availability, nitrogen uptake in target crops, and crop yields. Cover crops reduce water pollution risks and remove CO2 from the atmosphere. Cover crops may be an off-season crop planted after harvesting the cash crop. Cover crops are nurse crops in that they increase the survival of the main crop being harvested, and are often grown over the winter. In the United States, cover cropping may cost as much as $35 per acre. Soil erosion Although cover crops can perform multiple functions in an agroecosystem simultaneously, they are often grown for the sole purpose of preventi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |