Coteaux du Languedoc on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Languedoc-Roussillon wine, including the ''
Languedoc-Roussillon wine, including the ''
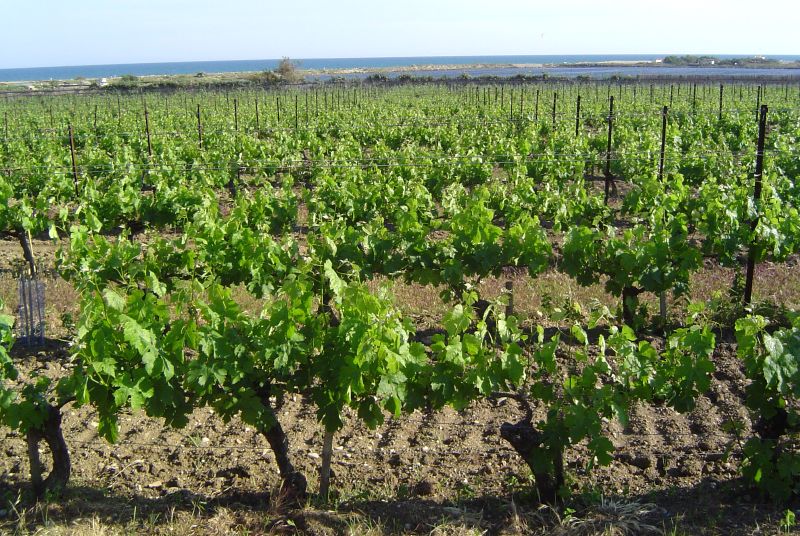 The history of Languedoc wines can be traced to the first
The history of Languedoc wines can be traced to the first 
vin de pays
''Vin de pays'' (, "country wine") was a French wine classification that was above the '' vin de table'' classification, but below the ''appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) classification and below the former '' vin délimité de qualité ...
'' labeled ''Vin de Pays d'Oc'', is produced in southern France. While "Languedoc" can refer to a specific historic region of France and Northern Catalonia
Northern Catalonia, North Catalonia, ; french: Catalogne (du) Nord ; oc, Catalonha (del) Nòrd; es, Cataluña (del) Norte) French Catalonia or Roussillon refers to the Catalan-speaking and Catalan-culture territory ceded to France by Spain t ...
, usage since the 20th century (especially in the context of wine) has primarily referred to the northern part of the Languedoc-Roussillon
Languedoc-Roussillon (; oc, Lengadòc-Rosselhon ; ca, Llenguadoc-Rosselló) is a former administrative region of France. On 1 January 2016, it joined with the region of Midi-Pyrénées to become Occitania. It comprised five departments, and b ...
région
France is divided into eighteen administrative regions (french: régions, singular ), of which thirteen are located in metropolitan France (in Europe), while the other five are overseas regions (not to be confused with the overseas collect ...
of France, an area which spans the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
coastline from the French border with Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
to the region of Provence
Provence (, , , , ; oc, Provença or ''Prouvènço'' , ) is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which extends from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the France–Italy border, Italian border ...
. The area has around under vines and is the single biggest wine-producing region
This list of wine-producing regions catalogues significant growing regions where vineyards are planted. Wine grapes mostly grow between the 30th and the 50th degree of latitude, in both the Northern and Southern hemispheres. Grapes will sometimes ...
in the world, being responsible for more than a third of France's total wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are ...
production.K. MacNeil ''The Wine Bible'' p. 293 Workman Publishing 2001 In 2001, the region produced more wine than the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
.K. MacNeil ''The Wine Bible'' p. 294 Workman Publishing 2001
History
 The history of Languedoc wines can be traced to the first
The history of Languedoc wines can be traced to the first vineyards
A vineyard (; also ) is a plantation of grape-bearing vines, grown mainly for winemaking, but also raisins, table grapes and non-alcoholic grape juice. The science, practice and study of vineyard production is known as viticulture. Vine ...
planted along the coast near Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in Southern France in the Occitanie region. It lies from Paris in the Aude department, of which it is a sub-prefecture. It is located about from the shores of the M ...
by the early Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, Albania, Greeks in Italy, ...
in the fifth century BC. Along with parts of Provence
Provence (, , , , ; oc, Provença or ''Prouvènço'' , ) is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which extends from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the France–Italy border, Italian border ...
, these are the oldest planted vineyards in France. The region of Languedoc has belonged to France since the thirteenth century and the Roussillon
Roussillon ( , , ; ca, Rosselló ; oc, Rosselhon ) is a historical province of France that largely corresponded to the County of Roussillon and part of the County of Cerdagne of the former Principality of Catalonia. It is part of th ...
was acquired from Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
in the mid-seventeenth century. The two regions were joined as one administrative region in the late 1980s.
From the 4th century through the 18th and early 19th centuries, the Languedoc had a reputation for producing high quality wine. In Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. ...
during the 14th century, wines from the St. Chinian area were prescribed in hospitals for their "healing powers".K. MacNeil ''The Wine Bible'' p. 295 Workman Publishing 2001 During the advent of the Industrial Age in the late 19th century, production shifted towards mass-produced ''le gros rouge''—cheap red wine that could satisfy the growing work force. The use of highly prolific grape varieties produced high yields and thin wines, which were normally blended with red wine from Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, religi ...
to give them more body.Assorted Editors ''The Pocket Wine Guide'' p. 84 Barnes & Noble, 2006
The phylloxera
Grape phylloxera is an insect pest of commercial grapevines worldwide, originally native to eastern North America. Grape phylloxera (''Daktulosphaira vitifoliae'' (Fitch 1855) belong to the family Phylloxeridae, within the order Hemiptera, ...
epidemic in the 19th century severely affected the Languedoc wine industry, killing off many of the higher quality ''Vitis vinifera
''Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, is a species of flowering plant, native to the Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean region, Central Europe, and southwestern Asia, from Morocco and Portugal north to southern Germany and east to northern ...
'' that were susceptible to the louse. American rootstock
A rootstock is part of a plant, often an underground part, from which new above-ground growth can be produced. It could also be described as a stem with a well developed root system, to which a bud from another plant is grafted. It can refer to a ...
that was naturally resistant to phylloxera did not take well to the limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms wh ...
soil on the hillside. In place of these vines, acres of the lower quality Aramon, Alicante Bouschet
Alicante Bouschet or Alicante Henri Bouschet is a wine grape variety that has been widely cultivated since 1866. It is a cross of Petit Bouschet (itself a cross of the very old variety Teinturier du Cher and Aramon) and Grenache.Carignan
Carignan (also known as Mazuelo, Bovale Grande, Cariñena, Carinyena, Samsó, Carignane, and Carignano) is a red grape variety of Spanish origin that is more commonly found in French wine but is widely planted throughout the western Medite ...
were planted.C. Fallis, editor ''The Encyclopedic Atlas of Wine'' p. 205 Global Book Publishing 2006
During both World Wars
A world war is an international conflict which involves all or most of the world's major powers. Conventionally, the term is reserved for two major international conflicts that occurred during the first half of the 20th century, World WarI (1914 ...
the Languedoc was responsible for providing the daily wine rations given to French soldiers. In 1962, Algeria gained its independence from France, bringing about an end to the blending of the stronger Algerian red wine to mask the thin ''le gros rouge''. This event, coupled with French consumers moving away from cheap red wines in the 1970s, has contributed to several decades of surplus wine production in France, with Languedoc as the largest contributor to the European "wine lake
The wine lake refers to a perceived overproduction of wine in the European Union, particularly around 2005–2007. The EU's Common Agricultural Policy contained a number of subsidies for wine producers, leading to a supply glut; this surplus forc ...
" and recurring European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
subsidies aimed at reducing production. These developments prompted many Languedoc producers to start refocusing on higher quality, but has also led to many local and regional protests, including violent ones from the infamous Comité Régional d'Action Viticole
Comité Régional d'Action Viticole (CRAV, ''Regional Committee for Viticultural Action''), or sometimes Comité d'action viticole (CAV, Committee for Viticultural Action) is a group of militant French wine producers. It has claimed responsibili ...
(CRAV).
Despite the general reputation as a mass producer and a consensus that the region is in the midst of an economic crisis, parts of the Languedoc wine industry are experiencing commercial success due to outside investment and an increased focus on quality. Sales have been improved by many vineyards that concentrate on creating a good brand name rather than relying on the sometimes infamous regional designations. Some vineyards have adopted the youngest batch of AOC
Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez (; ; born October 13, 1989), also known by her initials AOC, is an American politician and activist. She has served as the U.S. representative for New York's 14th congressional district since 2019, as a member of th ...
classifications developed in the late 1990s, while other vineyards eschew designated blends entirely and are instead shifting toward bottling single varietal wines
A varietal wine is a wine made primarily from a single named grape variety, and which typically displays the name of that variety on the wine label.The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition, 2000.winepros.com.au. ...
, a practice increasingly demanded by consumers in the large New World wine market.K. MacNeil ''The Wine Bible'' pp. 294–96 Workman Publishing 2001

Climate and geography
The Languedoc-Roussillon region shares many terrain and climate characteristics with the neighboring regions of SouthernRhône
The Rhône ( , ; wae, Rotten ; frp, Rôno ; oc, Ròse ) is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and southeastern France before discharging into the Mediterranean Sea. At Ar ...
and Provence
Provence (, , , , ; oc, Provença or ''Prouvènço'' , ) is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which extends from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the France–Italy border, Italian border ...
. The region stretches from the Banyuls AOC
Banyuls is a French ''appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) for a fortified apéritif or dessert wine made from old vines cultivated in terraces on the slopes of the Catalan Pyrenees in the Roussillon county of France, bordering, to the so ...
at the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
** Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Ca ...
border and Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
in the west, along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
to the river Rhône
The Rhône ( , ; wae, Rotten ; frp, Rôno ; oc, Ròse ) is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and southeastern France before discharging into the Mediterranean Sea. At Ar ...
and Provence in the east. The northern boundaries of the region sit on the Massif Central
The (; oc, Massís Central, ; literally ''"Central Massif"'') is a highland region in south-central France, consisting of mountains and plateaus. It covers about 15% of mainland France.
Subject to volcanism that has subsided in the last 10,00 ...
with the Cévennes
The Cévennes ( , ; oc, Cevenas) is a cultural region and range of mountains in south-central France, on the south-east edge of the Massif Central. It covers parts of the ''départements'' of Ardèche, Gard, Hérault and Lozère. Rich in geogr ...
mountain ranges and valleys dominating the area. Many vineyards are located along the river Hérault
Hérault (; oc, Erau, ) is a department of the region of Occitania, Southern France. Named after the Hérault River, its prefecture is Montpellier. It had a population of 1,175,623 in 2019.Kim Marcu
Languedoc Wakes Up
Wine Spectator March 31, 2000 Vineyards in the Languedoc are generally planted along the
Vineyards in the Languedoc are generally planted along the
 The five best known appellations in the Languedoc include Languedoc AOC (formerly known as the
The five best known appellations in the Languedoc include Languedoc AOC (formerly known as the
 The Languedoc-Roussillon area is home to numerous
The Languedoc-Roussillon area is home to numerous
 Wines from the Languedoc can carry an enormous number of names, ranging from broad regional designations like Vin de Pays d'Oc to very specific geographical classifications with restrictions on grape variety, like Corbières and Minervois. Since the 1990s, the INAO has been creating smaller AOC classifications which take into account the intricate
Wines from the Languedoc can carry an enormous number of names, ranging from broad regional designations like Vin de Pays d'Oc to very specific geographical classifications with restrictions on grape variety, like Corbières and Minervois. Since the 1990s, the INAO has been creating smaller AOC classifications which take into account the intricate
 The
The
The wines of Languedoc-Roussillon
– The official website of France (in English)
Regional Guide to Languedoc Wines
Languedoc Wine Map
Wine regions of France Languedoc-Roussillon {{Portal bar, Wine, France
Languedoc Wakes Up
Wine Spectator March 31, 2000
 Vineyards in the Languedoc are generally planted along the
Vineyards in the Languedoc are generally planted along the coastal plains
A coastal plain is flat, low-lying land adjacent to a sea coast. A fall line commonly marks the border between a coastal plain and a piedmont area. Some of the largest coastal plains are in Alaska and the southeastern United States. The Gulf Coa ...
of the Mediterranean while those in the Roussillon are to be found in the narrow valleys around the Pyrenees. The peak growing season (between May and August) is very dry and the majority of annual rainfall
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water ...
occurs during the winter. In the Languedoc, the plains area is the most arid and hottest region of France. The region's Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
is very conducive to growing a large amount of a wide variety of grapes, with vintners in the area excelling in mass production. The average annual temperature is . The ''tramontane'' inland wind from the northwest often accentuates the dry climate; drought is the most common threat to vine production, with French AOC
Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez (; ; born October 13, 1989), also known by her initials AOC, is an American politician and activist. She has served as the U.S. representative for New York's 14th congressional district since 2019, as a member of th ...
and European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
regulation prohibiting the use of irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been dev ...
.C. Fallis, editor ''The Encyclopedic Atlas of Wine'' p. 204 Global Book Publishing 2006 In December 2006, the French government responded to global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in a broader sense also includes ...
concerns and relaxed some of the irrigation regulations.
In 1999 severe weather
Severe weather is any dangerous meteorological phenomenon with the potential to cause damage, serious social disruption, or loss of human life. Types of severe weather phenomena vary, depending on the latitude, altitude, topography, and atmos ...
had damaging effects on the wine producing industry, including hail
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It is distinct from ice pellets (American English "sleet"), though the two are often confused. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is called a hailstone. Ice pellets generally fal ...
storms in May that affected Roussillon and a rain surge in mid November that saw a year's worth of rain fall in 36 hours in the areas of Corbières and Minervois
Minervois is an AOC in the Languedoc-Roussillon wine region, in the departments of the Aude and of the Herault. Historically, the region's capital has been the village of Minerve.
AOC regulations require the wine to be blended (at least 2 varie ...
in the western Languedoc.
The composition of soil in the Languedoc varies from the chalk, limestone and gravel based soils inland to more alluvial soils near the coast. Some of the more highly rated vineyards are laid on top of ancient riverbed stones similar to those of Châteauneuf-du-Pape
Châteauneuf-du-Pape (; Provençal: Castèu-Nòu-De-Papo) is a commune in the Vaucluse department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region in Southeastern France. The village lies about to the east of the Rhône and north of the town of Avi ...
.K. MacNeil ''The Wine Bible'' p. 297 Workman Publishing 2001
Appellations
 The five best known appellations in the Languedoc include Languedoc AOC (formerly known as the
The five best known appellations in the Languedoc include Languedoc AOC (formerly known as the Coteaux du Languedoc
Languedoc-Roussillon wine, including the ''vin de pays'' labeled ''Vin de Pays d'Oc'', is produced in southern France. While "Languedoc" can refer to a specific Languedoc, historic region of France and Northern Catalonia, usage since the 20th cen ...
), Corbières AOC
Corbières is an Appellation d'origine contrôlée (AOC) for wine in the Languedoc-Roussillon, France, and it is this region's largest AOC, responsible for 46 per cent of the region's AOC wine production in 2005. Red wine dominates the producti ...
, Faugères, Minervois AOC
Minervois is an AOC in the Languedoc-Roussillon wine region, in the departments of the Aude and of the Herault. Historically, the region's capital has been the village of Minerve.
AOC regulations require the wine to be blended (at least 2 vari ...
, and Saint-Chinian AOC {{no footnotes, date=March 2013
The Saint-Chinian is a French wine, from the Languedoc-Roussillon wine region of France. It is usually a blend of several grape varieties, and produced in red, rosé, and white versions. Since 1982, the name is pro ...
s. The vast majority of Languedoc wines are produced by wine cooperatives
A cooperative (also known as co-operative, co-op, or coop) is "an autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned and democratically-control ...
which number more than 500.K. MacNeil ''The Wine Bible'' p. 299 Workman Publishing 2001 However, the appellation system in the region is undergoing considerable changes with both new appellations being created and existing ones changing. One recent change is that the Coteaux du Languedoc has changed name to Languedoc and been extended to include also the Roussillon.
Within the larger Languedoc AOC appellations are several sub-districts, or Cru's, with distinct wine styles of their own. Some of these sub-districts have pending AOC applications to become appellations in their own right and some have been granted sub-appellations to the umbrella appellation Languedoc AOC. These include the Quatourze, La Clape
LA most frequently refers to Los Angeles, the second largest city in the United States.
La, LA, or L.A. may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* La (musical note), or A, the sixth note
* "L.A.", a song by Elliott Smith on ''Figur ...
, Montpeyroux, St. Saturnin
ST, St, or St. may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Stanza, in poetry
* Suicidal Tendencies, an American heavy metal/hardcore punk band
* Star Trek, a science-fiction media franchise
* Summa Theologica, a compendium of Catholic philosophy ...
, Picpoul de Pinet, Terrasses du Larzac Terrasses du Larzac is an Appellation d’origine contrôlée (AOC) within the Côteaux du Languedoc in Southern France ( French Occitania ) created in 2005 for red wines made from Syrah, Grenache and Mourvèdre grapes, with the acceptable additi ...
, and Pic St.-Loup.K. MacNeil ''The Wine Bible'' p. 300 Workman Publishing 2001
The boundary of the eastern Languedoc with the Southern Rhône Valley
The Rhône ( , ; wae, Rotten ; frp, Rôno ; oc, Ròse ) is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and southeastern France before discharging into the Mediterranean Sea. At Ar ...
wine region was moved slightly in 2004, with the result that Costières de Nîmes AOC
Costières de Nîmes is an Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée (AOC) for wines that are produced in an area between the ancient city of Nîmes and the western Rhône delta, in the French department of the Gard. Formerly part of the Languedoc regi ...
is now a Rhône appellation rather than a Languedoc one. In that year, INAO moved the responsibility for oversight of this appellation's wine to the regional committee of the Rhône valley. Local producers of Côtes du Rhône-styled wines made from Syrah
Syrah (), also known as Shiraz, is a dark-skinned grape variety grown throughout the world and used primarily to produce red wine. In 1999, Syrah was found to be the offspring of two obscure grapes from southeastern France, Dureza and Mondeus ...
and Grenache
Grenache () or Garnacha () is one of the most widely planted red wine grape varieties in the world.Niels Lillelund: ''Rhône-Vinene'' p. 25, JP Bøger – JP/Politikens Forlagshus A/S, 2004. . It ripens late, so it needs hot, dry conditi ...
lobbied for this change since the local winemaking traditions did not coincide with administrative borders, and presumably due to the greater prestige of Rhône wines in the marketplace. Such changes of borders between wine regions are very rare, so out of habit, Costières de Nîmes remains listed as a Languedoc wine in many publications.
Grapes
 The Languedoc-Roussillon area is home to numerous
The Languedoc-Roussillon area is home to numerous grape varieties
This list of grape varieties includes cultivated grapes, whether used for wine, or eating as a table grape, fresh or dried (raisin, currant, sultana). For a complete list of all grape species including those unimportant to agriculture, see Vit ...
, including many international varieties
An international variety is a grape variety that is widely planted in most of the major wine producing regions and has widespread appeal and consumer recognition. These are grapes that are highly likely to appear on wine labels as varietal wines ...
like Merlot
Merlot is a dark blue–colored wine grape variety, that is used as both a blending grape and for varietal wines. The name ''Merlot'' is thought to be a diminutive of ''merle'', the French name for the blackbird, probably a reference to t ...
, Cabernet Sauvignon
Cabernet Sauvignon () is one of the world's most widely recognized red wine grape varieties. It is grown in nearly every major wine producing country among a diverse spectrum of climates from Australia and British Columbia, Canada to Leban ...
, Sauvignon blanc
is a green-skinned grape variety that originates from the Bordeaux region of France. The grape most likely gets its name from the French words ''sauvage'' ("wild") and ''blanc'' ("white") due to its early origins as an indigenous grape in ...
, and Chardonnay
Chardonnay (, , ) is a green-skinned grape variety used in the production of white wine. The variety originated in the Burgundy wine region of eastern France, but is now grown wherever wine is produced, from England to New Zealand. For new ...
. The traditional Rhône grapes of Mourvedre, Grenache, Syrah
Syrah (), also known as Shiraz, is a dark-skinned grape variety grown throughout the world and used primarily to produce red wine. In 1999, Syrah was found to be the offspring of two obscure grapes from southeastern France, Dureza and Mondeus ...
, and Viognier
Viognier () is a white wine grape variety. It is the only permitted grape for the French wine Condrieu in the Rhône Valley.J. Robinson ''"The Oxford Companion to Wine"'' Third Edition pg 754 Oxford University Press 2006 Outside of the Rh ...
are also prominent.K. MacNeil ''The Wine Bible'' p. 298 Workman Publishing 2001
Chardonnay is a major white grape, used in the ''Vin de Pays d'Oc'' and the sparkling Crémant de Limoux. Others include Chenin blanc and Mauzac, which is also the principal grape in the sparkling Blanquette de Limoux
Limoux wine is produced around the city of Limoux in Languedoc in southwestern France. Limoux wine is produced under four ''Appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) designations: Blanquette de Limoux, Blanquette méthode ancestrale, Crémant de ...
. The sweet fortified wine
Fortified wine is a wine to which a distilled spirit, usually brandy, has been added. In the course of some centuries, winemakers have developed many different styles of fortified wine, including port, sherry, madeira, Marsala, Comma ...
s of the Muscat de Frontignan
Muscat ( ar, مَسْقَط, ) is the capital and most populated city in Oman. It is the seat of the Governorate of Muscat. According to the National Centre for Statistics and Information (NCSI), the total population of Muscat Governorate was 1 ...
and Muscat de St-Jean Minervois
Muscat ( ar, مَسْقَط, ) is the capital and most populated city in Oman. It is the seat of the Governorate of Muscat. According to the National Centre for Statistics and Information (NCSI), the total population of Muscat Governorate was ...
regions are made with the Muscat Blanc à Petits Grains
Muscat ( ar, مَسْقَط, ) is the capital and most populated city in Oman. It is the seat of the Governorate of Muscat. According to the National Centre for Statistics and Information (NCSI), the total population of Muscat Governorate was ...
grapes. In the Muscat de Rivesaltes AOC
Muscat de Rivesaltes is an ''Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée'' (AOC) for fortified wines (of the type ''vin doux naturel'') made in the Roussillon wine region of France. They are similar to Rivesaltes AOC wines, except for the grape varieties use ...
, fortified wines are made from Muscat of Alexandria
Muscat of Alexandria is a white wine grape that is a member of the Muscat family of ''Vitis vinifera''. It is considered an "ancient vine", and wine experts believe it is one of the oldest genetically unmodified vines still in existence.J. Robi ...
grapes.
Among the reds, Grenache, Syrah
Syrah (), also known as Shiraz, is a dark-skinned grape variety grown throughout the world and used primarily to produce red wine. In 1999, Syrah was found to be the offspring of two obscure grapes from southeastern France, Dureza and Mondeus ...
, Carignan, Cinsault
Cinsaut or Cinsault ( ) is a red wine grape whose heat tolerance and productivity make it important in Languedoc-Roussillon and the former French colonies of Algeria, Lebanon, and Morocco. It is often blended with grapes such as Grenache and ...
, and Mourvedre are major grapes of the Corbières, Faugères, Fitou
Fitou (; oc, Fitor) is a commune in the Aude department in southern France.
Population
Wine
Fitou has a red wine appellation; see Fitou AOC.
See also
* Corbières AOC
* Communes of the Aude department
The following is a list of the ...
, and Minervois
Minervois is an AOC in the Languedoc-Roussillon wine region, in the departments of the Aude and of the Herault. Historically, the region's capital has been the village of Minerve.
AOC regulations require the wine to be blended (at least 2 varie ...
AOCs. Cinsault is also commonly used in rosé
A rosé () is a type of wine that incorporates some of the color from the grape skins, but not enough to qualify it as a red wine. It may be the oldest known type of wine, as it is the most straightforward to make with the skin contact metho ...
production along with Lladoner Pelut
Grenache () or Garnacha () is one of the most widely planted red wine grape varieties in the world.Niels Lillelund: ''Rhône-Vinene'' p. 25, JP Bøger – JP/Politikens Forlagshus A/S, 2004. . It ripens late, so it needs hot, dry conditio ...
, Piquepoul noir
Piquepoul, Picpoul, or Picapoll is a variety (botany), variety of wine grape grown primarily in the Rhône (wine region), Rhone Valley and Languedoc wine, Languedoc regions of France as well as Catalonia, Spain. It exists both in dark-skinned ...
, Terret noir
Terret noir is a dark-skinned French wine grape variety grown primarily in the Rhône valley region of France. It is a mutation of the old ''Vitis vinifera'' vine Terret.J. Robinson ''Jancis Robinson's Guide to Wine Grapes'' pg 184 Oxford Unive ...
, and Grenache. Grenache is also the main grape used in the fortified wines of the Banyuls
Banyuls-sur-Mer (; ) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France. It was first settled by Greeks starting in 400 BCE.
Geography Location
Banyuls-sur-Mer is located in the canton of La Côte Vermeille and in the ar ...
and Rivesaltes region. Some of the oldest vines in France are Carignan
Carignan (also known as Mazuelo, Bovale Grande, Cariñena, Carinyena, Samsó, Carignane, and Carignano) is a red grape variety of Spanish origin that is more commonly found in French wine but is widely planted throughout the western Medite ...
grapes. Winemakers often use carbonic maceration
Carbonic maceration is a winemaking technique, often associated with the French wine region of Beaujolais, in which whole grapes are fermented in a carbon dioxide rich environment before crushing. Conventional alcoholic fermentation involve ...
to soften the tannin
Tannins (or tannoids) are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids.
The term ''tannin'' (from Anglo-Norman ''tanner ...
s.J. Robinson ''Jancis Robinson's Wine Course'' p. 199 Abbeville Press 2003
Other varieties that can be found include Roussanne
Roussanne is a white wine grape grown originally in the Rhône wine region in France, where it is often blended with Marsanne. It is the only other white variety, besides Marsanne, allowed in the northern Rhône appellations of Crozes-Hermita ...
, Marsanne
Marsanne is a white wine grape, most commonly found in the Northern Rhône region. It is often blended with Roussanne. In Savoie the grape is known as ''grosse roussette''. Outside France it is also grown in Switzerland (where it is known as ' ...
, Vermentino
Vermentino is a light-skinned wine grape variety, primarily found in Italian wine. It is widely planted in both Sardinia and Liguria, to some extent in Corsica, in Piedmont under the name Favorita, and in increasing amounts in Languedoc-Rouss ...
, Bourboulenc
Bourboulenc is a white wine grape variety primarily grown in southern France. The variety is found in the regions Southern Rhône, Provence and Languedoc.
Bourboulenc is a late-ripening grape variety with tight bunches of large grapes, that can ...
, Clairette blanche
Clairette blanche is a white wine grape variety most widely grown in the wine regions of Provence, Rhône and Languedoc in France. At the end of the 1990s, there were of Clairette blanche grown in France, although volumes are decreasing.
Cla ...
, Grenache blanc
Grenache blanc (also known as garnatxa blanca in Catalonia) is a variety of white wine grape that is related to the red grape Grenache. It is mostly found in Rhône wine blends and in northeast Spain. Its wines are characterized by high alcohol a ...
, Grenache gris, Piquepoul blanc
Piquepoul, Picpoul, or Picapoll is a variety of wine grape grown primarily in the Rhone Valley and Languedoc regions of France as well as Catalonia, Spain. It exists both in dark-skinned (Piquepoul noir) and light-skinned (Piquepoul b ...
, Piquepoul gris
Piquepoul, Picpoul, or Picapoll is a variety of wine grape grown primarily in the Rhone Valley and Languedoc regions of France as well as Catalonia, Spain. It exists both in dark-skinned (Piquepoul noir) and light-skinned (Piquepoul blanc) v ...
, and Macabeo
Macabeo, also called Viura or Macabeu (, ), is a white variety of wine grape.
It is widely grown in the Rioja region of northeastern Spain, the Cava producing areas south of Barcelona, and the Languedoc-Roussillon region of France. Spanish ...
.
Wines and taxonomy
 Wines from the Languedoc can carry an enormous number of names, ranging from broad regional designations like Vin de Pays d'Oc to very specific geographical classifications with restrictions on grape variety, like Corbières and Minervois. Since the 1990s, the INAO has been creating smaller AOC classifications which take into account the intricate
Wines from the Languedoc can carry an enormous number of names, ranging from broad regional designations like Vin de Pays d'Oc to very specific geographical classifications with restrictions on grape variety, like Corbières and Minervois. Since the 1990s, the INAO has been creating smaller AOC classifications which take into account the intricate microclimates
A microclimate (or micro-climate) is a local set of atmospheric conditions that differ from those in the surrounding areas, often with a slight difference but sometimes with a substantial one. The term may refer to areas as small as a few squa ...
and soil variations in the Languedoc-Roussillon. Younger appellations like the Cabardes and subregions like Minervois la Livinière, Corbières-Boutenac and St-Chinian-Berlou are much smaller in scope. While these new appellations have been praised for consistently improving their product, others have criticized the additions for further complicating an already esoteric system of classification.
The majority of wine produced in the Languedoc are labeled ''vin ordinaire
Table wine (rarely abbreviated TW) is a wine term with two different meanings: a style of wine and a quality level within wine classification.
In the United States, the term primarily designates a wine style: an ordinary wine which is not fortif ...
''. There is also sizable production of ''Vins Doux Naturels
Fortified wine is a wine to which a distilled spirit, usually brandy, has been added. In the course of some centuries, winemakers have developed many different styles of fortified wine, including port, sherry, madeira, Marsala, Comma ...
''.H. Johnson & J. Robinson ''The World Atlas of Wine'' p. 138 Mitchell Beazley Publishing 2005
Vins de Pays
The introduction of the ''vins de pays
''Vin de pays'' (, "country wine") was a French wine classification that was above the ''vin de table'' classification, but below the ''appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) classification and below the former '' vin délimité de qualité ...
,'' a classification produced under less stringent regulations than those of an AOC, opened up the Languedoc wine industry to the labeling of varietal wines and the blending of international varieties such as Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, Syrah and Chardonnay. Examples include Vin de pays d'Oc, Vin de pays d'Aude, Vin de pays de l'Hérault, and Vin de Pays du Gard. Winemakers such as Guy Anderson, Thierry Boudinaud and E. & J. Gallo Winery capitalized on this new horizon, producing wines like Fat Bastard
Fat Bastard is a fictional character in the second and third films of the ''Austin Powers'' series. A morbidly obese henchman hailing from Clydebank, Scotland, Fat Bastard serves Dr. Evil in his quest to destroy Austin Powers. The character i ...
and Red Bicyclette
Red Bicyclette is a French wine produced by the Sieur d'Arques cooperative and distributed in the United States by the E. & J. Gallo Winery. Its distinctive label appeals to consumers who prefer branded wines, labelled with the variety of grape ...
.G. Taber ''The Judgment of Paris: California vs France'' p. 286 Simon & Schuster
Vins Doux Naturels
''Vins Doux Naturels
Fortified wine is a wine to which a distilled spirit, usually brandy, has been added. In the course of some centuries, winemakers have developed many different styles of fortified wine, including port, sherry, madeira, Marsala, Comma ...
'' are "naturally sweet" wines that have been fortified
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''face ...
with brandy to stop fermentation, leaving residual sugar
The subjective sweetness of a wine is determined by the interaction of several factors, including the amount of sugar in the wine, but also the relative levels of alcohol, acids, and tannins. Sugars and alcohol enhance a wine's sweetness, wh ...
to add sweetness to the wine. The majority of Languedoc sweet white wines are made with a variety of Muscat
Muscat ( ar, مَسْقَط, ) is the capital and most populated city in Oman. It is the seat of the Governorate of Muscat. According to the National Centre for Statistics and Information (NCSI), the total population of Muscat Governorate was ...
grapes. The red fortified wines of the Banyuls are made from Grenache grapes, normally have an alcohol level between 16 and 17% and carry residual sugars in the 8 to 12% range.K. MacNeil ''The Wine Bible'' p. 301 Workman Publishing 2001
In Banyuls, winemakers use various methods to "bake" their wines to encourage deep raisin colors. Some winemakers utilize a solera
''Solera'' is a process for aging liquids such as wine, beer, vinegar, and brandy, by fractional blending in such a way that the finished product is a mixture of ages, with the average age gradually increasing as the process continues over man ...
system of transporting the wine among different size barrels of various ages that are left out in the sun to warm. Others will put the wine in large glass jars to expose it to direct sunlight. In addition to the dark color, the resulting wines often have a nutty, rancid taste called ''rancio''. In the Banyuls Grand Cru AOC the wine is required to be aged in wood barrels for two and a half years.J. Robinson ''Jancis Robinson's Wine Course'' p. 201 Abbeville Press 2003
Crémant de Limoux
 The
The crémant
Sparkling wine is a wine with significant levels of carbon dioxide in it, making it fizzy. While the phrase commonly refers to champagne, European Union countries legally reserve that term for products exclusively produced in the Champagne re ...
produced in the Languedoc is made according to the '' Méthode Traditionnelle'' – formerly known as méthode champenoise – the same method used to produce Champagne
Champagne (, ) is a sparkling wine originated and produced in the Champagne wine region of France under the rules of the appellation, that demand specific vineyard practices, sourcing of grapes exclusively from designated places within it, ...
. Méthode Traditionnelle includes a second fermentation in the bottle to encapture the carbon dioxide produced by the yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to consti ...
. Languedoc crémant is produced in the small villages around the town of Limoux
Limoux (; oc, Limós ) is a commune and subprefecture in the Aude department, a part of the ancient Languedoc province and the present-day Occitanie region in southern France. Its vineyards are famous for being first to produce sparkling w ...
. The wines are normally composed of 70% Mauzac and a 30% combination of Chardonnay
Chardonnay (, , ) is a green-skinned grape variety used in the production of white wine. The variety originated in the Burgundy wine region of eastern France, but is now grown wherever wine is produced, from England to New Zealand. For new ...
and Chenin blanc. AOC regulations require a year of aging
Ageing ( BE) or aging ( AE) is the process of becoming older. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi, whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biologically immortal. In ...
on the lees. The Blanquette de Limoux
Limoux wine is produced around the city of Limoux in Languedoc in southwestern France. Limoux wine is produced under four ''Appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) designations: Blanquette de Limoux, Blanquette méthode ancestrale, Crémant de ...
, when labelled ''méthode ancestrale'', is composed entirely of Mauzac, undergoes only one fermentation, and is aged approximately three months less on the lees before the bottling, the actual date being determined by the moon's cycle.K. MacNeil ''The Wine Bible Karen MacNeil (born 1954) is an American author, journalist, wine educator and consultant.
Career
MacNeil's first article, on the subject of the best butter on offer in New York delis, was published in ''The Village Voice.'' She transitioned to win ...
'' p. 302 Workman Publishing 2001
See also
*Wine label
Wine labels are important sources of information for consumers since they tell the type and origin of the wine. The label is often the only resource a buyer has for evaluating the wine before purchasing it. Certain information is ordinarily inclu ...
References
Further reading
* *External links
The wines of Languedoc-Roussillon
– The official website of France (in English)
Regional Guide to Languedoc Wines
Languedoc Wine Map
Wine regions of France Languedoc-Roussillon {{Portal bar, Wine, France