Cosegregation To Adjacency on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Cosegregation, in
Cosegregation, in
 An alternative method to using Normalized Linkage Disequilibrium is Normalized Pointwise Mutual Information (NPMI). NPMI measures how closely two loci are associated by taking the log of their joint cosegregation probability, , divided by their independent probabilities, . This log is then divided by the log of their joint probability, to normalize the result.
An alternative method to using Normalized Linkage Disequilibrium is Normalized Pointwise Mutual Information (NPMI). NPMI measures how closely two loci are associated by taking the log of their joint cosegregation probability, , divided by their independent probabilities, . This log is then divided by the log of their joint probability, to normalize the result.
Both NLD and NPMI range between -1 and 1 and reflect how the joint cosegregation probability deviates from what would be expected if the two loci were independent. However, they differ in scope as NLD measures linear relationships, while NPMI can capture more complex, non-linear relationships between the loci.
 Fortunately, not only is it able to scale dataset sizes well, it is able to take as many loci of focus that are required to determine the interaction probability. Provided that adding each loci adds a single computation to the equation, a linear time complexity is the result. The picture below shows how the amount of loci affects the detection frequency equation.
Fortunately, not only is it able to scale dataset sizes well, it is able to take as many loci of focus that are required to determine the interaction probability. Provided that adding each loci adds a single computation to the equation, a linear time complexity is the result. The picture below shows how the amount of loci affects the detection frequency equation.
 Finally, the numerical value that results can assist in drawing multiple conclusions including radial position, compaction, and the most influential contacts.
Finally, the numerical value that results can assist in drawing multiple conclusions including radial position, compaction, and the most influential contacts.
 Effective cosegregation analysis depends largely on having a strong supporting dataset because even small inaccuracies can be compounded by cosegregation. A complete understanding of the material is necessary as cosegregation only provides connections between datapoints. The interpretation of those connections must be done through another method. For example, locus cosegregation can give a score of genes that commonly interact with each other, but no matter how strong those relationships are, the results of quantitative cosegregation can seem to support either a correlated, anti-correlated or independent relationships. It is important to be aware of this and follow up cosegregation analysis with another form of analysis, such as normalized linkage disequilibrium to correct for the compounding effect cosegregation can have on negligible variations in the detection frequency of the data.
Effective cosegregation analysis depends largely on having a strong supporting dataset because even small inaccuracies can be compounded by cosegregation. A complete understanding of the material is necessary as cosegregation only provides connections between datapoints. The interpretation of those connections must be done through another method. For example, locus cosegregation can give a score of genes that commonly interact with each other, but no matter how strong those relationships are, the results of quantitative cosegregation can seem to support either a correlated, anti-correlated or independent relationships. It is important to be aware of this and follow up cosegregation analysis with another form of analysis, such as normalized linkage disequilibrium to correct for the compounding effect cosegregation can have on negligible variations in the detection frequency of the data.
 For example, imagine a simple form of cancer that is trigged by a small number of genes. Here we are examining a suspect gene and three other genes that are suspected to be involved in the processes. This chart shows a hypothetical data set of 10 people and their cancer status as well as if they possess the four genes of interest. Looking at the graph, there is a clear connection between the suspect gene and Gene A. There is also a less obvious interaction between the suspect gene and Gene C that only takes place when Gene B is absent. It is entirely possible that co-segregation would have a hard time determining that relationship. Gene B is commonly present with Gene A and that combination does result in cancer. In a real data set with hundreds or even thousands of genes being examined, one could erroneously conclude that Gene B contributes to the cancer when, in reality it does not and can actually prevent it.
Another limitation of this technique is that many mapping tools measure not only specific physical interactions between genes but also random contacts, the latter being much more common between genes with smaller linear genomic distance this could lead to inflated co-segregation scores. GAM has helped to resolve this issue because in GAM the detection of genomic windows is independent of any interactions with other regions. This allows for an expected interaction value to be calculated and combining this with the co-segregation results to filter out the noise of random connections this will provide a cleaner result.Also an advantage of using GAM is the reduced sample size needed compared to analyze data compared to
For example, imagine a simple form of cancer that is trigged by a small number of genes. Here we are examining a suspect gene and three other genes that are suspected to be involved in the processes. This chart shows a hypothetical data set of 10 people and their cancer status as well as if they possess the four genes of interest. Looking at the graph, there is a clear connection between the suspect gene and Gene A. There is also a less obvious interaction between the suspect gene and Gene C that only takes place when Gene B is absent. It is entirely possible that co-segregation would have a hard time determining that relationship. Gene B is commonly present with Gene A and that combination does result in cancer. In a real data set with hundreds or even thousands of genes being examined, one could erroneously conclude that Gene B contributes to the cancer when, in reality it does not and can actually prevent it.
Another limitation of this technique is that many mapping tools measure not only specific physical interactions between genes but also random contacts, the latter being much more common between genes with smaller linear genomic distance this could lead to inflated co-segregation scores. GAM has helped to resolve this issue because in GAM the detection of genomic windows is independent of any interactions with other regions. This allows for an expected interaction value to be calculated and combining this with the co-segregation results to filter out the noise of random connections this will provide a cleaner result.Also an advantage of using GAM is the reduced sample size needed compared to analyze data compared to
 The image above depicts the conversion from a cosegregation matrix to an adjacency matrix is one use of a matrix in genome architecture mapping where scientists are using cryosectioning to find
The image above depicts the conversion from a cosegregation matrix to an adjacency matrix is one use of a matrix in genome architecture mapping where scientists are using cryosectioning to find
plotly.express
in Python. Using co-segregation, heat maps are used to visualize a matrix that contains values of either 1 or 0 to visualize the commonalities between 2 or more variables. "The primary benefit of using heat maps is that they make otherwise dull or impenetrable data understandable. Many people understand heat maps intuitively, without even needing to be told that those warmer colors indicate a denser focus of interactions." In the limitation section, there are two heat maps (also put below for easy viewing) shown depicting the difference between normalized and un-normalized data. Showing the difference in the graphs would help the researcher identify different patterns based on the intensity of the color gradients as well as the clustering of data points. Cosegregation results as seen above can have different forms and visualizing them in heat maps can aid researchers in understanding which genomes are connected similar to matrices.
 The heat map below is a different representation of the data which uses the normalized linkage table instead of the resulting adjacency matrix. This visualization gives more variation (from -1 to 1 instead of only 0 or 1) and better shows the advantages of using a heat map.
The heat map below is a different representation of the data which uses the normalized linkage table instead of the resulting adjacency matrix. This visualization gives more variation (from -1 to 1 instead of only 0 or 1) and better shows the advantages of using a heat map.
 One limitation to heat maps are that some software does not allow the use of locating specific points on the graph, especially if there are many variables. There are coding libraries such as plotly.express that can create interactive heat maps where the programmer can hover over specified points on a graph and read the exact dependent variable's value. Another limitation is that heat maps do not represent real-time data. Since heat maps work by aggregating data over time, it does not show recent changes in behavior compared to the more dominant patterns already present.
One limitation to heat maps are that some software does not allow the use of locating specific points on the graph, especially if there are many variables. There are coding libraries such as plotly.express that can create interactive heat maps where the programmer can hover over specified points on a graph and read the exact dependent variable's value. Another limitation is that heat maps do not represent real-time data. Since heat maps work by aggregating data over time, it does not show recent changes in behavior compared to the more dominant patterns already present.
/ref> In genetics, network diagrams can be created using cosegregation adjacency matrices. To convert an adjacency matrix to a network diagram, one must translate the matrix elements into visual nodes and edges, where non-zero values indicate connections between nodes, thereby creating a graphical representation of the genetic interactions. Below is an image of a network diagram created using the
 Cosegregation, in
Cosegregation, in genealogy
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kin ...
, refers to the tendency of two or more genes
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
located close together on the same chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
to be inherited together during cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell (biology), cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukar ...
. Due to their physical proximity, these genes are considered genetically linked and are likely to be inherited together.
In genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian ...
, the term may also refer to the estimated probability of interaction between multiple loci or specific regions within a target gene. This probability is assessed using data derived from nuclear profiles (NPs), which are thin slices taken from a cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (; : nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have #Anucleated_cells, ...
. Within each NP, the presence or absence of particular loci is evaluated.
These interaction probabilities—referred to as cosegregation values—are used in mathematical models such as SLICE and normalized linkage disequilibrium Linkage disequilibrium, often abbreviated to LD, is a term in population genetics referring to the association of genes, usually linked genes, in a population. It has become an important tool in medical genetics and other fields
In defining LD, it ...
. These models contribute to the generation of 3D genome architecture maps as part of genome architecture mapping
In molecular biology, genome architecture mapping (GAM) is a cryosectioning method to Gene mapping, map Colocalization, colocalized DNA regions in a Ligation (molecular biology), ligation independent manner. It overcomes some limitations of Chromos ...
(GAM) techniques. The resulting 3D renderings provide insights into genomic density and the radial positioning of loci within the nucleus.
History
Some of the earliest known studies that have used cosegregation in genealogy dates back to the early 1980s. Around this time, scientists were conducting experiments on vegetative organisms to see if there are unique sequences ofchloroplast DNA
Chloroplast DNA (cpDNA), also known as plastid DNA (ptDNA) is the DNA located in chloroplasts, which are photosynthetic organelles located within the cells of some eukaryotic organisms. Chloroplasts, like other types of plastid, contain a genome s ...
. The process of the experiment was to track the chloroplast gene in each generation by clustering the genes in nucleoids
The nucleoid (meaning '' nucleus-like'') is an irregularly shaped region within the prokaryotic cell that contains all or most of the genetic material. The chromosome of a typical prokaryote is circular, and its length is very large compared to ...
to reduce the number of segregated units. This study was done at the Duke University
Duke University is a Private university, private research university in Durham, North Carolina, United States. Founded by Methodists and Quakers in the present-day city of Trinity, North Carolina, Trinity in 1838, the school moved to Durham in 1 ...
in the Zoology Department where Karen P. VanWinkle-Swift utilized Pedigree Diagrams to show how the traits and sequences were passed down from parent to child.
In genetics, Cosegregation in Genome architecture mapping
In molecular biology, genome architecture mapping (GAM) is a cryosectioning method to Gene mapping, map Colocalization, colocalized DNA regions in a Ligation (molecular biology), ligation independent manner. It overcomes some limitations of Chromos ...
(GAM) is another process being used to identify the compaction and adjacency of genomic windows. In a study from 2017, cosegregation was used to understand gene-expression-specific contacts in organizing the genome in mammalian nuclei in the larger process of GAM. The results of the study produced complex 3D structures that displayed interactions under certain regions of chromatin contacts and proved that GAM is a useful tool in the genome biologist's skill set that expands the ability to finely dissect 3D chromatin structures, cell types and valuable human samples. A study in 2021 "discovered extensive 'melting' of long genes when they are highly expressed and/or have high chromatin accessibility. The contacts most specific of neuron subtypes contain genes associated with specialized processes, such as addiction and synaptic plasticity, which harbour putative binding sites for neuronal transcription factors within accessible chromatin regions." Both of these studies used mice as models due to their anatomical, physiological, and genetic similarity to humans.
Usage
In genetics, Cosegregation is best suited for cases where multiple factors' interactions are under consideration. It can show how different factors are linked and highlight their interactions and connections. For example, if a genetic disorder was identified as related to a certain gene, but is not always present when that gene is, then a cosegregation analysis could help identify other genes that interact with the suspect gene more often than normal. This could lead researchers to discover the combination of genes that manifest the genetic disorder. Cosegregation is being actively used in medical fields likecancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
research. It can highlight the strongest connections between genes in cases where cancer develops. This is useful because there often isn't a single gene causing cancer. Rather, cancer can be caused by a multitude of gene combinations. Cosegregation helps to show links between genes that could be forming these combinations.
Examples of using cosegregation in genetics
An example of an application using cosegregation would be finding thenormalized
Normalization or normalisation refers to a process that makes something more normal or regular. Science
* Normalization process theory, a sociological theory of the implementation of new technologies or innovations
* Normalization model, used in ...
linkage disequilibrium Linkage disequilibrium, often abbreviated to LD, is a term in population genetics referring to the association of genes, usually linked genes, in a population. It has become an important tool in medical genetics and other fields
In defining LD, it ...
(NLD) between two loci. Given a 2D dataset (row = genomic window slice, column = nuclear profile (NP)) a "1" was displayed if an NP existed in a window or a "0" otherwise. From this data, the NLD could be found using the base disequilibrium and its theorized maximum (). The amount of NPs present in loci (genomic windows) and , is then used to find the , and and the co-segregation which is, . After the NLD is found between two loci, it was then placed into another dataset to be visualized and then analyzed to determine how interconnected a loci is.
This example was executed using python
Python may refer to:
Snakes
* Pythonidae, a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia
** ''Python'' (genus), a genus of Pythonidae found in Africa and Asia
* Python (mythology), a mythical serpent
Computing
* Python (prog ...
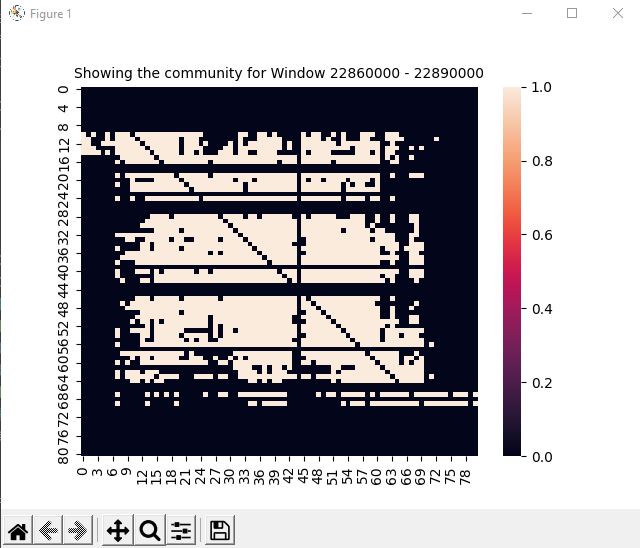
for computation and visualization of the given data and results and in finding the NLD. Using the NLD further analysis can be done to place the windows into "communities". To showcase this a graph to the right will show the community of one of the windows with the highest centrality
In graph theory and network analysis, indicators of centrality assign numbers or rankings to nodes within a graph corresponding to their network position. Applications include identifying the most influential person(s) in a social network, ke ...
which uses the average of the window's NLDs.
 An alternative method to using Normalized Linkage Disequilibrium is Normalized Pointwise Mutual Information (NPMI). NPMI measures how closely two loci are associated by taking the log of their joint cosegregation probability, , divided by their independent probabilities, . This log is then divided by the log of their joint probability, to normalize the result.
An alternative method to using Normalized Linkage Disequilibrium is Normalized Pointwise Mutual Information (NPMI). NPMI measures how closely two loci are associated by taking the log of their joint cosegregation probability, , divided by their independent probabilities, . This log is then divided by the log of their joint probability, to normalize the result.Both NLD and NPMI range between -1 and 1 and reflect how the joint cosegregation probability deviates from what would be expected if the two loci were independent. However, they differ in scope as NLD measures linear relationships, while NPMI can capture more complex, non-linear relationships between the loci.
Formula
This formula can be easily programmed into code as seen in thepseudo-code
In computer science, pseudocode is a description of the steps in an algorithm using a mix of conventions of programming languages (like assignment operator, conditional operator, loop) with informal, usually self-explanatory, notation of action ...
in the figure to the right. The code was written to satisfy the Example described above.
Advantages
Given a large dataset of nuclear profiles, cosegregation is easily scalable given its simplistic mathematical formulas. The larger the data set that is provided, the more accurate the following equations will be. As depicted in the photo below, the amount of data being added to the equation merely adds linear time adjustments to the original equation. Fortunately, not only is it able to scale dataset sizes well, it is able to take as many loci of focus that are required to determine the interaction probability. Provided that adding each loci adds a single computation to the equation, a linear time complexity is the result. The picture below shows how the amount of loci affects the detection frequency equation.
Fortunately, not only is it able to scale dataset sizes well, it is able to take as many loci of focus that are required to determine the interaction probability. Provided that adding each loci adds a single computation to the equation, a linear time complexity is the result. The picture below shows how the amount of loci affects the detection frequency equation.
 Finally, the numerical value that results can assist in drawing multiple conclusions including radial position, compaction, and the most influential contacts.
Finally, the numerical value that results can assist in drawing multiple conclusions including radial position, compaction, and the most influential contacts.
Limitations
 Effective cosegregation analysis depends largely on having a strong supporting dataset because even small inaccuracies can be compounded by cosegregation. A complete understanding of the material is necessary as cosegregation only provides connections between datapoints. The interpretation of those connections must be done through another method. For example, locus cosegregation can give a score of genes that commonly interact with each other, but no matter how strong those relationships are, the results of quantitative cosegregation can seem to support either a correlated, anti-correlated or independent relationships. It is important to be aware of this and follow up cosegregation analysis with another form of analysis, such as normalized linkage disequilibrium to correct for the compounding effect cosegregation can have on negligible variations in the detection frequency of the data.
Effective cosegregation analysis depends largely on having a strong supporting dataset because even small inaccuracies can be compounded by cosegregation. A complete understanding of the material is necessary as cosegregation only provides connections between datapoints. The interpretation of those connections must be done through another method. For example, locus cosegregation can give a score of genes that commonly interact with each other, but no matter how strong those relationships are, the results of quantitative cosegregation can seem to support either a correlated, anti-correlated or independent relationships. It is important to be aware of this and follow up cosegregation analysis with another form of analysis, such as normalized linkage disequilibrium to correct for the compounding effect cosegregation can have on negligible variations in the detection frequency of the data.
 For example, imagine a simple form of cancer that is trigged by a small number of genes. Here we are examining a suspect gene and three other genes that are suspected to be involved in the processes. This chart shows a hypothetical data set of 10 people and their cancer status as well as if they possess the four genes of interest. Looking at the graph, there is a clear connection between the suspect gene and Gene A. There is also a less obvious interaction between the suspect gene and Gene C that only takes place when Gene B is absent. It is entirely possible that co-segregation would have a hard time determining that relationship. Gene B is commonly present with Gene A and that combination does result in cancer. In a real data set with hundreds or even thousands of genes being examined, one could erroneously conclude that Gene B contributes to the cancer when, in reality it does not and can actually prevent it.
Another limitation of this technique is that many mapping tools measure not only specific physical interactions between genes but also random contacts, the latter being much more common between genes with smaller linear genomic distance this could lead to inflated co-segregation scores. GAM has helped to resolve this issue because in GAM the detection of genomic windows is independent of any interactions with other regions. This allows for an expected interaction value to be calculated and combining this with the co-segregation results to filter out the noise of random connections this will provide a cleaner result.Also an advantage of using GAM is the reduced sample size needed compared to analyze data compared to
For example, imagine a simple form of cancer that is trigged by a small number of genes. Here we are examining a suspect gene and three other genes that are suspected to be involved in the processes. This chart shows a hypothetical data set of 10 people and their cancer status as well as if they possess the four genes of interest. Looking at the graph, there is a clear connection between the suspect gene and Gene A. There is also a less obvious interaction between the suspect gene and Gene C that only takes place when Gene B is absent. It is entirely possible that co-segregation would have a hard time determining that relationship. Gene B is commonly present with Gene A and that combination does result in cancer. In a real data set with hundreds or even thousands of genes being examined, one could erroneously conclude that Gene B contributes to the cancer when, in reality it does not and can actually prevent it.
Another limitation of this technique is that many mapping tools measure not only specific physical interactions between genes but also random contacts, the latter being much more common between genes with smaller linear genomic distance this could lead to inflated co-segregation scores. GAM has helped to resolve this issue because in GAM the detection of genomic windows is independent of any interactions with other regions. This allows for an expected interaction value to be calculated and combining this with the co-segregation results to filter out the noise of random connections this will provide a cleaner result.Also an advantage of using GAM is the reduced sample size needed compared to analyze data compared to chromosome conformation capture
Chromosome conformation capture techniques (often abbreviated to 3C technologies or 3C-based methods) are a set of molecular biology methods used to analyze the spatial organization of chromatin in a cell. These methods quantify the number of in ...
methods. It also benefits from not needing ligation
Ligation may refer to:
* Ligation (molecular biology), the covalent linking of two ends of DNA or RNA molecules
* Chemical ligation, the chemoselective condensation of unprotected peptides
* In medicine, the making of a ligature (tie)
* Tubal liga ...
, which is not guaranteed to occur in a consistent manner
Visualizations
Matrices
Matrices
Matrix (: matrices or matrixes) or MATRIX may refer to:
Science and mathematics
* Matrix (mathematics), a rectangular array of numbers, symbols or expressions
* Matrix (logic), part of a formula in prenex normal form
* Matrix (biology), the ...
are a rectangular structured array of numbers (entries) where the entries can be summed, subtracted, multiplied, and divided using the standard math operations. In the case of co-segregation, Graph theory
In mathematics and computer science, graph theory is the study of ''graph (discrete mathematics), graphs'', which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph in this context is made up of ''Vertex (graph ...
is used to see if a variable shares an edge or vertex with another variable on a network of nodes. Graph theory is the mathematical study of objects using pairwise relations that is shown through connected nodes called vertices that are connected to other nodes by edges.
 The image above depicts the conversion from a cosegregation matrix to an adjacency matrix is one use of a matrix in genome architecture mapping where scientists are using cryosectioning to find
The image above depicts the conversion from a cosegregation matrix to an adjacency matrix is one use of a matrix in genome architecture mapping where scientists are using cryosectioning to find colocalization In fluorescence microscopy, colocalization refers to observation of the spatial overlap between two (or more) different fluorescent labels, each having a separate emission wavelength, to see if the different "targets" are located in the same area of ...
between DNA regions, genomes, and/or alleles. In that example, cosegregation is being used to describe the linkage of data to each other in terms of the distance between specific windows in a genome. The values in the cosegregation matrix were found using the formula above. Comparing windows , the formula seeks to find the intersection of Nuclear Profiles between the respective windows. The genomic windows would be the nodes and the adjacency graph is the matrix depiction of the edges connecting each node.
Heat maps
Aheat map
A heat map (or heatmap) is a 2-dimensional data visualization technique that represents the magnitude of individual values within a dataset as a color. The variation in color may be by hue or intensity.
In some applications such as crime analy ...
is a visual representation of a matrix of that can show different phenomenons on a two-dimensional scale. Heat maps have a range of color intensities based on the values and scale given from the data. Coding-wise, heat maps can be created using libraries such aplotly.express
in Python. Using co-segregation, heat maps are used to visualize a matrix that contains values of either 1 or 0 to visualize the commonalities between 2 or more variables. "The primary benefit of using heat maps is that they make otherwise dull or impenetrable data understandable. Many people understand heat maps intuitively, without even needing to be told that those warmer colors indicate a denser focus of interactions." In the limitation section, there are two heat maps (also put below for easy viewing) shown depicting the difference between normalized and un-normalized data. Showing the difference in the graphs would help the researcher identify different patterns based on the intensity of the color gradients as well as the clustering of data points. Cosegregation results as seen above can have different forms and visualizing them in heat maps can aid researchers in understanding which genomes are connected similar to matrices.

 The heat map below is a different representation of the data which uses the normalized linkage table instead of the resulting adjacency matrix. This visualization gives more variation (from -1 to 1 instead of only 0 or 1) and better shows the advantages of using a heat map.
The heat map below is a different representation of the data which uses the normalized linkage table instead of the resulting adjacency matrix. This visualization gives more variation (from -1 to 1 instead of only 0 or 1) and better shows the advantages of using a heat map.
 One limitation to heat maps are that some software does not allow the use of locating specific points on the graph, especially if there are many variables. There are coding libraries such as plotly.express that can create interactive heat maps where the programmer can hover over specified points on a graph and read the exact dependent variable's value. Another limitation is that heat maps do not represent real-time data. Since heat maps work by aggregating data over time, it does not show recent changes in behavior compared to the more dominant patterns already present.
One limitation to heat maps are that some software does not allow the use of locating specific points on the graph, especially if there are many variables. There are coding libraries such as plotly.express that can create interactive heat maps where the programmer can hover over specified points on a graph and read the exact dependent variable's value. Another limitation is that heat maps do not represent real-time data. Since heat maps work by aggregating data over time, it does not show recent changes in behavior compared to the more dominant patterns already present.
Network Diagrams
Anetwork diagram
Graph drawing is an area of mathematics and computer science combining methods from geometric graph theory and information visualization to derive two-dimensional depictions of graphs arising from applications such as social network analysis, c ...
is a visual representation of a network, which consists of distinct nodes and edges, or the interactions between these nodes./ref> In genetics, network diagrams can be created using cosegregation adjacency matrices. To convert an adjacency matrix to a network diagram, one must translate the matrix elements into visual nodes and edges, where non-zero values indicate connections between nodes, thereby creating a graphical representation of the genetic interactions. Below is an image of a network diagram created using the
NetworkX
NetworkX is a Python (programming language), Python library for studying Graph (discrete mathematics), graphs and Network theory, networks. NetworkX is free software released under the BSD-new, BSD-new license.
History
NetworkX began developm ...
library in Python.

References
{{Reflist Genetics concepts Classical genetics