Corfu ( , ) or Kerkyra (, ) is a
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
island in the
Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea (, ; or , ; , ) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including Basilicata, Calabria, Sicily, and the Salento peninsula to the west, ...
, of the
Ionian Islands
The Ionian Islands (Modern Greek: , ; Ancient Greek, Katharevousa: , ) are a archipelago, group of islands in the Ionian Sea, west of mainland Greece. They are traditionally called the Heptanese ("Seven Islands"; , ''Heptanēsa'' or , ''Heptanē ...
;
including its
small satellite islands, it forms the margin of Greece's northwestern frontier.
The island is part of the
Corfu regional unit, and is administered by three municipalities with the islands of
Othonoi
Othonoi (, also rendered as Othoni, ) is a small inhabited list of Greek islands, Greek island in the Ionian Sea, located northwest of Corfu, and is the westernmost point of Greece. Othonoi is the largest and most populated of the Diapontian Isl ...
,
Ereikoussa
Ereikoussa () is an island and a former community of the Ionian Islands, Greece. It is one of the Diapontian Islands; an island complex to the northwest of Corfu. Since the 2019 local government reform it is part of the municipality of Central ...
, and
Mathraki
Mathraki (, ) is an island and a former community of the Ionian Islands (region), Ionian Islands, Greece. It is one of the Diapontian Islands. Since the 2019 local government reform, it is part of the municipality of Central Corfu and Diapontian Is ...
.
The principal city of the island (pop. 32,095) is also named
Corfu
Corfu ( , ) or Kerkyra (, ) is a Greece, Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands; including its Greek islands, small satellite islands, it forms the margin of Greece's northwestern frontier. The island is part of the Corfu (regio ...
.
Corfu is home to the
Ionian University
The Ionian University (IU; ) is a university located in the Ionian Islands (region), Ionian Islands, Greece. It is one of the newest institutions of Higher Education in Greece, created in 1984 pursuant to presidential order 83/84 ΦΕΚ 31 Α/2 ...
.
The island is bound up with the
history of Greece
The history of Greece encompasses the history of the territory of the modern nation-state of Greece as well as that of the Greek people and the areas they inhabited and ruled historically. The scope of Greek habitation and rule has varied thro ...
from the beginnings of
Greek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories conc ...
, and is marked by numerous battles and conquests. Ancient
Korkyra took part in the
Battle of Sybota
The Battle of Sybota () took place in 433 BC between Corcyra (modern Corfu) and Corinth. It was one of the immediate catalysts for the Peloponnesian War.
History
Corinth had been in dispute with Corcyra, an old Corinthian colony which no longer ...
which was a catalyst for the
Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancien ...
, and, according to Thucydides, the largest naval battle between Greek city states until that time.
Thucydides
Thucydides ( ; ; BC) was an Classical Athens, Athenian historian and general. His ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts Peloponnesian War, the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been d ...
also reports that Korkyra was one of the three great naval powers of Greece in the fifth century BCE, along with
Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
and
Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
. Ruins of ancient Greek temples and other archaeological sites of the ancient city of Korkyra are located in
Palaiopolis.
Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
castles punctuating strategic locations across the island are a legacy of struggles in the Middle Ages against invasions by pirates and the
Ottomans
Ottoman may refer to:
* Osman I, historically known in English as "Ottoman I", founder of the Ottoman Empire
* Osman II, historically known in English as "Ottoman II"
* Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empir ...
. Two of these castles enclose its capital, which is the only city in Greece to be surrounded in such a way. As a result, Corfu's capital has been officially declared a ''kastropolis'' ("castle city") by the Greek government.
From medieval times and into the 17th century, the island, as part of the
Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
since 1204, successfully repulsed the Ottomans during several sieges, was recognised as a bulwark of the European States against the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
and became one of the most fortified places in Europe.
The fortifications of the island were used by the Venetians to defend against Ottoman intrusion into the
Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Se ...
. In November 1815 Corfu came under British rule following the
Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
, and in 1864 was ceded to
modern Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
by the
British government
His Majesty's Government, abbreviated to HM Government or otherwise UK Government, is the central government, central executive authority of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. along with the remaining islands of the
United States of the Ionian Islands
The United States of the Ionian Islands was a Greeks, Greek state (polity), state and Protectorate#Amical_protection, amical protectorate of the United Kingdom between 1815 and 1864. The succession of states, successor state of the Septinsular R ...
under the
Treaty of London. Corfu is the origin of the
Ionian Academy, the first university of the modern Greek state, and the
Nobile Teatro di San Giacomo di Corfù, the first Greek theatre and
opera house
An opera house is a theater building used for performances of opera. Like many theaters, it usually includes a stage, an orchestra pit, audience seating, backstage facilities for costumes and building sets, as well as offices for the institut ...
of modern Greece.
Ioannis Kapodistrias
Count Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias (; February 1776 –27 September 1831), sometimes anglicized as John Capodistrias, was a Greek statesman who was one of the most distinguished politicians and diplomats of 19th-century Europe.
Kapodistrias's ...
, the first governor of independent Greece after the revolution of 1821, founder of the modern Greek state, and a distinguished European diplomat, was born in Corfu.
In 2007, the city's old town was added to the
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage List
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritag ...
, following a recommendation by
ICOMOS.
The
1994 European Union summit was held in Corfu.
The island is a popular tourist destination.
Name
The Greek name, ''Kerkyra'' or ''
Korkyra'', is related to two powerful water deities:
Poseidon
Poseidon (; ) is one of the twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and mythology, presiding over the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 He was the protector of seafarers and the guardian of many Hellenic cit ...
, god of the sea, and
Asopos, an important Greek mainland river.
According to myth, Poseidon fell in love with the beautiful nymph Korkyra, daughter of Asopos and river nymph
Metope
A metope (; ) is a rectangular architectural element of the Doric order, filling the space between triglyphs in a frieze
, a decorative band above an architrave.
In earlier wooden buildings the spaces between triglyphs were first open, and ...
, and abducted her.
Poseidon brought Korkyra to the hitherto unnamed island and, in marital bliss, offered her name to the place: ''Korkyra'',
which gradually evolved to ''Kerkyra'' (
Doric).
They had a child, Phaiax, after whom the inhabitants of the island were named ''
Phaiakes'' (in
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
, ''Phaeaciani''). Corfu is known as the island of the
Phaeacians
Scheria or Scherie (; or ), also known as Phaeacia () or Faiakia, was a region in Greek mythology, first mentioned in Homer's ''Odyssey'' as the home of the Phaeacians and the last destination of Odysseus in his 10-year journey before returning h ...
.
The name ''Corfù'' is a Venetian and Italian version of the
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
Κορυφώ (Koryphō), meaning "city of the peaks". It derives from the
Byzantine Greek
Medieval Greek (also known as Middle Greek, Byzantine Greek, or Romaic; Greek: ) is the stage of the Greek language between the end of classical antiquity in the 5th–6th centuries and the end of the Middle Ages, conventionally dated to the F ...
Κορυφαί (Koryphai) (crests or peaks), denoting the two peaks of ''Palaio Frourio''.
Geography

Corfu is located in the northwestern corner of Greece. The northeastern edge of Corfu lies off the
coast
A coast (coastline, shoreline, seashore) is the land next to the sea or the line that forms the boundary between the land and the ocean or a lake. Coasts are influenced by the topography of the surrounding landscape and by aquatic erosion, su ...
of
Sarandë
Sarandë (; sq-definite, Saranda; ) is a List of cities and towns in Albania, city in the Republic of Albania and the seat of Sarandë Municipality. Geographically, the city is located on an open sea gulf of the Ionian Sea within the Mediterrane ...
,
Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
, separated by straits varying in width from . The southeast side of the island lies off the coast of
Thesprotia
Thesprotia (; , ) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the Epirus region. Its capital and largest town is Igoumenitsa. Thesprotia is named after the Thesprotians, an ancient Greek tribe that inhabited the region in antiquity.
His ...
, Greece. Its shape resembles a
sickle
A sickle, bagging hook, reaping-hook or grasshook is a single-handed agricultural tool designed with variously curved blades and typically used for harvesting or reaping grain crops, or cutting Succulent plant, succulent forage chiefly for feedi ...
(''drepanē, δρεπάνι''), to which it was compared by the ancients: the concave side, with the city and harbour of Corfu in the centre, lies toward the Albanian coast.
[ With the island's area estimated at ,][
]

 The second range culminates in the mountain of Santi Jeca, or Santa Decca, as it is called by misinterpretation of the Greek designation ''Άγιοι Δέκα'' (Hagioi Deka), or the Ten Saints. The whole island, composed as it is of various limestone formations, presents great diversity of surface.
The second range culminates in the mountain of Santi Jeca, or Santa Decca, as it is called by misinterpretation of the Greek designation ''Άγιοι Δέκα'' (Hagioi Deka), or the Ten Saints. The whole island, composed as it is of various limestone formations, presents great diversity of surface.[ Beaches are found in Agios Gordis, the Korission Lagoon, Agios Georgios, Marathia, Kassiopi, Sidari, Palaiokastritsa and many others. Corfu is located near the ]Kefalonia
Kefalonia or Cephalonia (), formerly also known as Kefallinia or Kephallonia (), is the largest of the Ionian Islands in western Greece and the 6th-largest island in Greece after Crete, Euboea, Lesbos, Rhodes and Chios. It is also a separate regio ...
geological fault formation; earthquakes have occurred.
Corfu's coastline spans including capes; its highest point is Mount Pantokrator (); and the second Stravoskiadi, at . The full extent of capes and promontories take in Agia Aikaterini, Drastis to the north, Lefkimmi and Asprokavos to the southeast, and Megachoro to the south. Two islands are also to be found at a middle point of Gouvia and Corfu Bay, which extends across much of the eastern shore of the island; are known as Lazareto and Ptychia (or Vido).
Diapontia Islands
 The
The Diapontia Islands
The Diapontian Islands or Diapontia Islands (, also known as Othonoi Islands () are a Greek island group in the Ionian Sea. They are located northwest of Corfu. The main and the only inhabited islands of the archipelago are Othoni, Ereikoussa and ...
(Greek: Διαπόντια νησιά) are located in the northwest of Corfu, (6 km away) and about
from the Italian coast. The main islands are Othonoi
Othonoi (, also rendered as Othoni, ) is a small inhabited list of Greek islands, Greek island in the Ionian Sea, located northwest of Corfu, and is the westernmost point of Greece. Othonoi is the largest and most populated of the Diapontian Isl ...
, Ereikoussa
Ereikoussa () is an island and a former community of the Ionian Islands, Greece. It is one of the Diapontian Islands; an island complex to the northwest of Corfu. Since the 2019 local government reform it is part of the municipality of Central ...
and Mathraki
Mathraki (, ) is an island and a former community of the Ionian Islands (region), Ionian Islands, Greece. It is one of the Diapontian Islands. Since the 2019 local government reform, it is part of the municipality of Central Corfu and Diapontian Is ...
.
Lazaretto Island
Lazaretto Island, formerly known as St. Dimitrios, is located off the coast northeast of the city Corfu
Corfu ( , ) or Kerkyra (, ) is a Greece, Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands; including its Greek islands, small satellite islands, it forms the margin of Greece's northwestern frontier. The island is part of the Corfu (regio ...
. Lazaretto has an area of and comes under the administration of the Greek National Tourist Organization. During Venetian rule in the early 16th century, a monastery was built on the islet and a leprosarium established later in the century, after which the island was named. In 1798, during the French occupation, the islet was occupied by the Russo Russo may refer to:
* Russo (surname)
* Russo (footballer, 1915–1980), full name Adolpho Milman, Brazilian football forward and manager
* Russo (footballer, born 1976), full name Ricardo Soares Florêncio, Brazilian football defender
* Russo brot ...
-Turkish fleet, who ran it as a military hospital. During the period of British rule
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent,
*
* lasting from 1858 to 1947.
*
* It is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
* or dire ...
, in 1814, the leprosarium was once again opened after renovations, and following Enosis
''Enosis'' (, , "union") is an irredentist ideology held by various Greek communities living outside Greece that calls for them and the regions that they inhabit to be incorporated into the Greek state. The idea is related to the Megali Idea ...
in 1864 the leprosarium again saw occasional use.World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the Axis occupation of Greece
The occupation of Greece by the Axis Powers () began in April 1941 after Nazi Germany Battle of Greece, invaded the Kingdom of Greece in order to assist its ally, Fascist Italy (1922–1943), Italy, in their Greco-Italian War, ongoing war that w ...
established a Nazi concentration camp
From 1933 to 1945, Nazi Germany operated more than a thousand concentration camps (), including subcamp (SS), subcamps on its own territory and in parts of German-occupied Europe.
The first camps were established in March 1933 immediately af ...
there for the prisoners of the Greek resistance,
Climate
Corfu has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate ( ), also called a dry summer climate, described by Köppen and Trewartha as ''Cs'', is a temperate climate type that occurs in the lower mid-latitudes (normally 30 to 44 north and south latitude). Such climates typic ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
: ''Csa'') featuring hot, dry summers and mild to cool, very rainy winters, which are much wetter than other Greek islands
Greece has many islands, with estimates ranging from somewhere around 1,200 to 6,000, depending on the minimum size to take into account. The number of inhabited islands is variously cited as between 166 and 227.
The largest Greek island by ...
. The highest temperature ever recorded is on 24 July 2007 while the lowest is on 17 January 2012.
Biodiversity
Flora
Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
identifies six plants that adorn the garden of Alcinous
In Greek mythology, Alcinous (also Alcinoüs; ; ''Alkínoos'' ) was a son of Nausithous and brother of Rhexenor. After the latter's death, he married his brother's daughter Arete who bore him Nausicaa, Halius, Clytoneus and Laodamas. In ...
: wild olive, pear, pomegranate
The pomegranate (''Punica granatum'') is a fruit-bearing deciduous shrub in the family Lythraceae, subfamily Punica, Punicoideae, that grows between tall. Rich in symbolic and mythological associations in many cultures, it is thought to have o ...
, apple, fig and grape vine
''Vitis'' (grapevine) is a genus of 81 accepted species of vining plants in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The genus consists of species predominantly from the Northern Hemisphere. It is economically important as the source of grapes, bot ...
. Of these the apple and the pear are very inferior in Corfu; the others thrive, together with all the fruit trees known in Southern Europe
Southern Europe is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, C ...
, with addition of the kumquat
Kumquats ( ), or cumquats in Australian English, are a group of small, angiosperm, fruit-bearing trees in the family Rutaceae. Their taxonomy is disputed. They were previously classified as forming the now-historical genus ''Fortunella'' or plac ...
, loquat
The loquat (''Eriobotrya japonica'', Chinese: 枇杷; Pinyin: pípá) is a large evergreen shrub or tree grown commercially for its orange fruit. It is also cultivated as an ornamental plant.
The loquat is in the family Rosaceae, subfamily Spi ...
and prickly pear and, in some spots, the banana. Olive trees dominate and their combination with cypress trees compose the typical Corfiot landscape. When undisturbed by cultivation,[ the high maquis is the major natural vegetation type followed by deciduous oak forests and to a lesser extent, pine forests. In total more than 1800 plant species have been recorded.
]
Fauna
Corfu is a continental island; its fauna is similar to that of the opposite mainland.
Birds
Avifauna is extensive, with around 300 bird species recorded since the 19th century. Species vary in size from the greater flamingo
The greater flamingo (''Phoenicopterus roseus'') is the most widespread and largest species of the flamingo family. Common in the Old World, they are found in Northern (coastal) and Sub-Saharan Africa, the Indian Subcontinent (south of the Him ...
to the goldcrest
The goldcrest (''Regulus regulus'') is a very small passerine bird in the kinglet family. Its colourful golden Crest (feathers), crest feathers, as well as being called the "king of the birds" in European folklore, gives rise to its Englis ...
. Some species have become extinct, such as the rock partridge and the grey partridge
The grey partridge (''Perdix perdix'') is a bird in the pheasant family Phasianidae of the order Galliformes, gallinaceous birds. The scientific name is the Latin for "partridge".
Taxonomy
The grey partridge formally described in 1758 by the S ...
, or no longer breed on the island, like the eastern imperial eagle
The eastern imperial eagle (''Aquila heliaca'') is a large bird of prey that breeds in southeastern Europe and extensively through West and Central Asia. Most populations are migratory and winter in northeastern Africa, the Middle East and South a ...
, the white-tailed eagle
The white-tailed eagle (''Haliaeetus albicilla''), sometimes known as the 'sea eagle', is a large bird of prey, widely distributed across temperate Eurasia. Like all eagles, it is a member of the family Accipitridae (or accipitrids) which also ...
, the Bonelli's eagle, the griffon vulture
The Eurasian griffon vulture (''Gyps fulvus'') is a large Old World vulture in the bird of prey family Accipitridae. It is also known as the griffon vulture, although this term is sometimes used for the genus as a whole. It is not to be confuse ...
and the Egyptian vulture.
Mammals
Around 40 species of mammals live on the island and in the sea around it. Fin whale
The fin whale (''Balaenoptera physalus''), also known as the finback whale or common rorqual, is a species of baleen whale and the second-longest cetacean after the blue whale. The biggest individual reportedly measured in length, wi ...
s, sperm whale
The sperm whale or cachalot (''Physeter macrocephalus'') is the largest of the toothed whales and the largest toothed predator. It is the only living member of the Genus (biology), genus ''Physeter'' and one of three extant species in the s ...
s, Cuvier's beaked whale
Cuvier's beaked whale, goose-beaked whale, or ziphius (''Ziphius cavirostris'') is the most widely distributed of all beaked whales in the family Beaked whale, Ziphiidae. It is smaller than most baleen whales—and indeed the larger Toothed whal ...
s, common bottlenose dolphin
The common bottlenose dolphin or Atlantic bottlenose dolphin (''Tursiops truncatus'') is one of three species of bottlenose dolphin in the genus ''Tursiops''. The common bottlenose dolphin is a very familiar dolphin due to the wide exposure it re ...
s, short-beaked common dolphin
The common dolphin (''Delphinus delphis'') is the most abundant cetacean in the world, with a global population of about six million. Despite this fact and its vernacular name, the common dolphin is not thought of as the archetypal dolphin, wit ...
s, striped dolphin
The striped dolphin (''Stenella coeruleoalba'') is a dolphin found in temperate and tropical waters of all the world's oceans. It is a member of the oceanic dolphin family, Delphinidae.
Taxonomy
The striped dolphin, also known as the euphrosy ...
s and Risso's dolphin
Risso's dolphin (''Grampus griseus'') is a marine mammal and dolphin, the only species of the genus ''Grampus''. Some of the most closely related species to these dolphins include: pilot whales (''Globicephala'' spp.), pygmy killer whales (''Fere ...
s are the regularly present cetaceans. Monk seals appear from time to time without breeding there anymore. Eurasian otter
The Eurasian otter (''Lutra lutra''), also known as the European otter, Eurasian river otter, European river otter, common otter, and Old World otter, is a semiaquatic mammal native to Eurasia and the Maghreb. The most widely distributed member o ...
s still survive in the lagoons and streams of Corfu.[Stille, M., Gasteratos, I. & B. Stille 2021: Larger mammals of Corfu, Ionian Islands, Greece – status and potential threats. Russian Journal of Theriology 20(2): 204-214.] The golden jackal
The golden jackal (''Canis aureus''), also called the common jackal, is a wolf-like canid that is native to Eurasia. The golden jackal's coat varies in color from a pale creamy yellow in summer to a dark tawny beige in winter. It is smaller a ...
was very common till the 1960s, but after persecution it became extinct, with the last individuals observed in the first half of the 1990s. Recent sightings indicate a recolonization effort from the nearby mainland.Wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a Suidae, suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The speci ...
s were exterminated after 2000, after farmers complained about crop damage, but at the moment they recolonized Corfu, swimming from the mainland.Red fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe and Asia, plus ...
es, beech marten
The beech marten (''Martes foina''), also known as the stone marten, house marten or white breasted marten, is a species of marten native to much of Europe and Central Asia, though it has established a feral population in North America. It is li ...
s, least weasel
The least weasel (''Mustela nivalis''), little weasel, common weasel, or simply weasel is the smallest member of the genus ''Mustela,'' Family (biology), family Mustelidae and Order (biology), order Carnivora. It is native to Eurasia, North Ame ...
s, European hare
The European hare (''Lepus europaeus''), also known as the brown hare, is a species of hare native to Europe and parts of Asia. It is among the largest hare species and is adapted to temperate, open country. Hares are herbivorous and feed mainly ...
s, northern white-breasted hedgehogs are quite widespread, as some of the smaller mammals like the European edible dormouse
The European edible dormouse also known as the European dormouse or European fat dormouse (''Glis glis'') is a large dormouse and one of only two living species in the genus ''Glis (genus), Glis'', found in most of Europe and parts of western Asi ...
, the hazel dormouse
The hazel dormouse or common dormouse (''Muscardinus avellanarius'') is a small dormouse species native to Europe and the only living species in the genus ''Muscardinus''.
Distribution and habitat
The hazel dormouse is native to northern Europe ...
, the house mouse
The house mouse (''Mus musculus'') is a small mammal of the rodent family Muridae, characteristically having a pointed snout, large rounded ears, and a long and almost hairless tail. It is one of the most abundant species of the genus '' Mus''. A ...
, the yellow-necked mouse
The yellow-necked mouse (''Apodemus flavicollis''), also called yellow-necked field mouse or yellow-necked wood mouse, is closely related to the wood mouse, with which it was long confused. It was only recognised as a separate species in 1894. I ...
, the western broad-toothed field mouse, the wood mouse
The wood mouse (''Apodemus sylvaticus'') is a Muridae, murid rodent native to Europe and northwestern Africa. It is closely related to the yellow-necked mouse (''Apodemus flavicollis'') but differs in that it has no band of yellow fur around the ...
, the lesser white-toothed shrew, the etruscan shrew
The Etruscan shrew (''Suncus etruscus''), also known as the Etruscan pygmy shrew, white-toothed pygmy shrew and Savi's pygmy shrew, is the smallest known extant mammal by mass, weighing only about on average. (The bumblebee bat is regarded as t ...
, as well as several species of bats.Coypu
The nutria () or coypu () (''Myocastor coypus'') is a herbivore, herbivorous, semiaquatic rodent from South America.
Classified for a long time as the only member of the family Myocastoridae, ''Myocastor'' has since been included within Echimy ...
s, fallow deer
Fallow deer is the common name for species of deer in the genus ''Dama'' of subfamily Cervinae. There are two living species, the European fallow deer (''Dama dama''), native to Europe and Anatolia, and the Persian fallow deer (''Dama mesopotamic ...
, red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or Hart (deer), hart, and a female is called a doe or hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Ir ...
, Indian crested porcupine
The Indian crested porcupine (''Hystrix indica'') is a hystricomorph rodent species native to southern Asia and the Middle East. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List. It belongs to the Old World porcupine family, Hystricidae.
Des ...
s, Siberian chipmunk
The Siberian chipmunk (''Eutamias sibiricus''), also called common chipmunk, is a species of chipmunk native to northern Asia from central Russia to China, Korea, and Hokkaidō in northern Japan. It was imported from South Korea and introduced i ...
s and raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the North American, northern or common raccoon (also spelled racoon) to distinguish it from Procyonina, other species of raccoon, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest ...
s have been observed recently, but they are escapees and only the coypu and the raccoon have established viable populations.
Amphibians and reptiles
Eight species of amphibians and 31 species of reptiles live or have been recorded on and around Corfu.
The Greek newt, the Macedonian crested newt, the common toad
The common toad, European toad, or in Anglophone parts of Europe, simply the toad (''Bufo bufo'', from Latin ''bufo'' "toad"), is a toad found throughout most of Europe (with the exception of Ireland, Iceland, parts of Scandinavia, and some List ...
, the European green toad, the European tree frog
The European tree frog (''Hyla arborea'') is a small tree frog. As traditionally defined, it was found throughout much of Europe, Asia and northern Africa, but based on molecular genetic and other data several populations formerly included in it ...
, the agile frog, the Epirus water frog and the Greek marsh frog are the representatives of the Amphibia Class.
Loggerhead sea turtle
The loggerhead sea turtle (''Caretta caretta'') is a species of sea turtle, oceanic turtle distributed throughout the world. It is a marine reptile, belonging to the Family (biology), family Cheloniidae. The average loggerhead measures around ...
s nest on the sandy beaches. On land, the Hermann's tortoise is widespread, while the marginated tortoise's status is unclear. In freshwater wetlands European pond terrapins and Balkan terrapins are common, but the last few years face the competition of the introduced pond slider.
Lizard species include typical lizards and geckos like the starred agama, the Mediterranean house gecko
The Mediterranean house gecko (''Hemidactylus turcicus'') is a species of house gecko native to the Mediterranean region, from which it has spread to many parts of the world including parts of East Africa, South America, the Caribbean, and the ...
, the moorish gecko, the Dalmatian algyroides, the common wall lizard, the Balkan wall lizard, the Balkan green lizard, the European green lizard
The European green lizard (''Lacerta viridis'') is a large lizard distributed across European midlatitudes from Slovenia and eastern Austria to as far east as the Black Sea coasts of Ukraine and Turkey. It is often seen sunning on rocks or lawns, ...
and the snake-eyed skink as also the legless Greek slow worm and the European glass lizard.
Of the snakes of Corfu, only the nose-horned viper is potentially dangerous. The harmless snake list includes the European worm snake, the javelin sand boa, the Dahl's whip snake, the Balkan whip snake, the Caspian whip snake, the four-lined snake, the Aesculapian snake #REDIRECT Aesculapian snake
{{redirect category shell, {{R from another capitalisation{{R from move ...
, the leopard snake, the grass snake
The grass snake (''Natrix natrix''), sometimes called the ringed snake or water snake, is a Eurasian semi-aquatic non- venomous colubrid snake. It is often found near water and feeds almost exclusively on amphibians.
Subspecies
Many subspecie ...
, the dice snake, the European cat snake, the eastern Montpellier snake.
Dragonflies
Corfu has a rich and diverse dragonfly fauna and 39 out of Europe’s 143 species are presently confirmed to have breeding populations on the island, four of them quite recent additions. The Dainty Bluet ('' Coenagion scitulum'') and the Blue-eye ('' Erythromma lindenii'') were reported for the first time in 2013, the Black Pennant ('' Selysiothemis nigra'') was in 2009, and the Bladetail ('' Lindenia tetraphylla'') in 2014. The “Critically Endangered” Greek Red Damsel ('' Pyrrhosoma elisabethae'') and the “Near Threatened” Eastern Spectre ('' Caliaeshna microstigma'') also have breeding populations on the island but are severely threatened by habitat loss. Some species reported from the island in the beginning of the 20th century have not been found in recent years, and may have been lost to the island. Dragonflies are used as indicators for water quality as their larvae are very sensitive to pollution.
Butterflies
There are 75 (plus) known species of Corfiot butterfly. Of particular interest are the southern swallowtail, southern festoon, Oberthür's grizzled skipper, Lulworth skipper, eastern orange tip, Krueper's small white, eastern baton blue and the tree grayling, many of which are of near threatened status. Before the turn of the century, not much had been published about the butterfly fauna of Corfu, and there were only a few short and obscure scientific articles. Recent interest grew when a Facebook discussion page (now called Corfu Butterfly Conservation) was created on 27 April 2014. Since that time, a group of responsible butterfly enthusiasts has grown (731 members at the time of writing) who share their passion for the butterflies and moths found on the island. It is through this work that more is being discovered about the distribution and abundance of butterflies across the island.
= Corfu Butterfly Conservation
=
Corfu Butterfly Conservation (CBC) was launched in April 2019. The group is composed of concerned residents, island visitors and scientists from throughout Europe. Their goals are to produce robust scientific data that can be used to influence policy and protect habitat for the benefit of Corfu's butterflies and the wider natural environment, as well as to stimulate public interest in butterfly conservation.
CBC launched its website (www.corfubutterflyconservation.org, funded by the Royal Entomological Society
The Royal Entomological Society is a learned society devoted to the study of insects. It aims to disseminate information about insects and to improve communication between entomologists.
The society was founded in 1833 as the Entomological S ...
's Goodman Award) on the 1 January 2021 to coincide with the launch of the Corfu Butterfly Survey. The website describes the 75 species of butterflies that have been confirmed by members of CBC from the island. It outlines the value of butterflies as indicators of the island's biodiversity status and encourages enthusiasts to record their sightings on this website, as participants of the survey.community interest company
A community interest company (CIC, pronounced "see-eye-see", or colloquially, "kick") is a form of social enterprise in the United Kingdom intended "for people wishing to establish businesses which trade with a social purpose..., or to carry on ...
(No.13813164) and so its identity changed from being a project to that of an organisation.
History
Early history
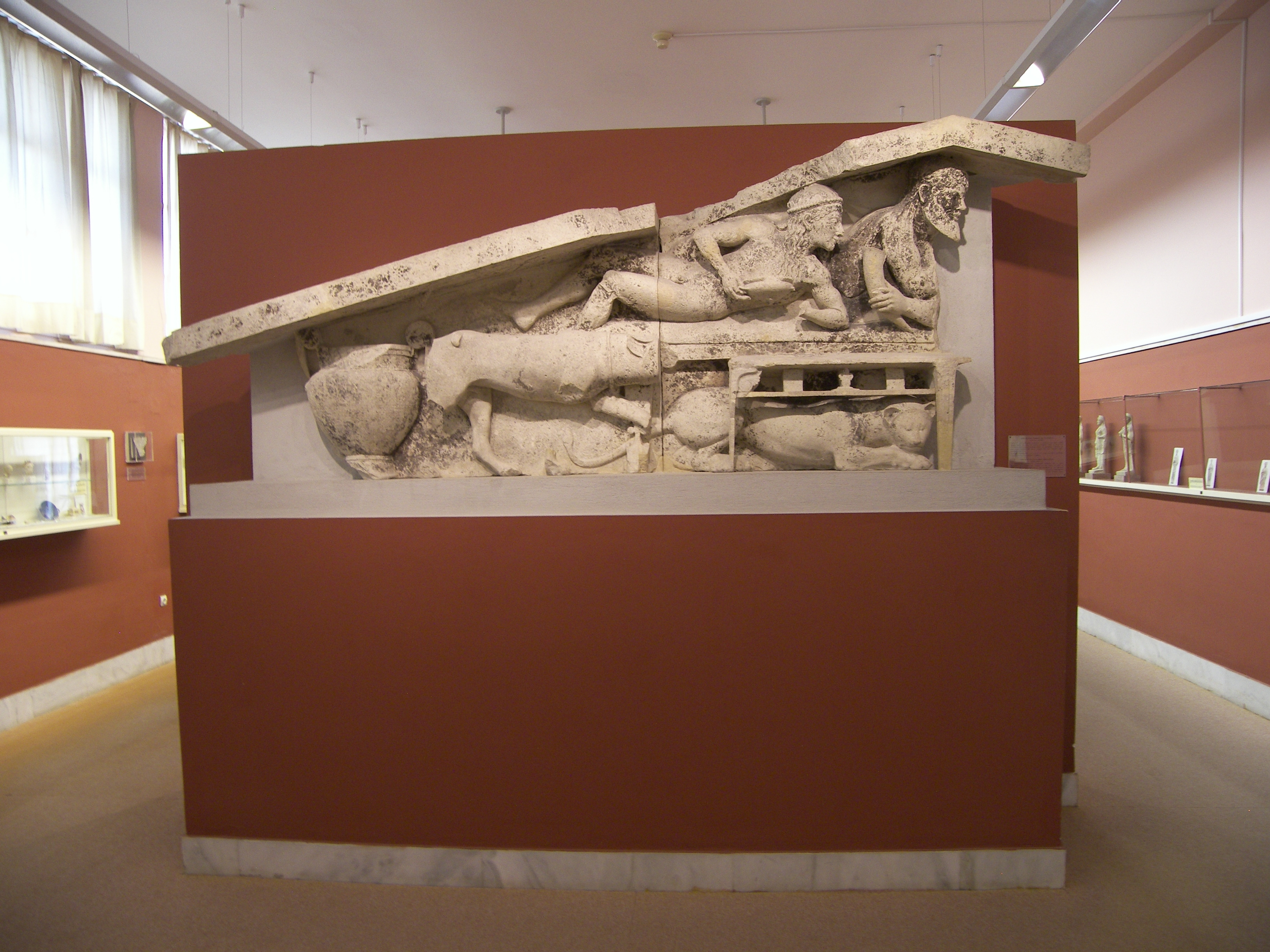 The earliest reference to Corfu is the
The earliest reference to Corfu is the Mycenaean Greek
Mycenaean Greek is the earliest attested form of the Greek language. It was spoken on the Greek mainland and Crete in Mycenaean Greece (16th to 12th centuries BC). The language is preserved in inscriptions in Linear B, a script first atteste ...
word ''ko-ro-ku-ra-i-jo (''"man from Kerkyra") written in Linear B
Linear B is a syllabary, syllabic script that was used for writing in Mycenaean Greek, the earliest Attested language, attested form of the Greek language. The script predates the Greek alphabet by several centuries, the earliest known examp ...
syllabic script, c. 1300 BC. According to Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
, Corcyra
Corfu ( , ) or Kerkyra (, ) is a Greece, Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands; including its Greek islands, small satellite islands, it forms the margin of Greece's northwestern frontier. The island is part of the Corfu (regio ...
(Κόρκυρα) was the Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
ic island of Scheria
Scheria or Scherie (; or ), also known as Phaeacia () or Faiakia, was a region in Greek mythology, first mentioned in Homer's ''Odyssey'' as the home of the Phaeacians and the last destination of Odysseus in his 10-year journey before returning h ...
(Σχερία),[''Strab. vi. p. 407''] and its earliest inhabitants were the Phaeacians
Scheria or Scherie (; or ), also known as Phaeacia () or Faiakia, was a region in Greek mythology, first mentioned in Homer's ''Odyssey'' as the home of the Phaeacians and the last destination of Odysseus in his 10-year journey before returning h ...
(Φαίακες). The island has indeed been identified by some scholars with Scheria
Scheria or Scherie (; or ), also known as Phaeacia () or Faiakia, was a region in Greek mythology, first mentioned in Homer's ''Odyssey'' as the home of the Phaeacians and the last destination of Odysseus in his 10-year journey before returning h ...
, the island of the Phaeacians described in Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
's ''Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; ) is one of two major epics of ancient Greek literature attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest surviving works of literature and remains popular with modern audiences. Like the ''Iliad'', the ''Odyssey'' is divi ...
'', though conclusive and irrefutable evidence for this theory has not been found. Apollonius of Rhodes
Apollonius of Rhodes ( ''Apollṓnios Rhódios''; ; fl. first half of 3rd century BC) was an ancient Greek literature, ancient Greek author, best known for the ''Argonautica'', an epic poem about Jason and the Argonauts and their quest for the Go ...
depicts the island in ''Argonautica
The ''Argonautica'' () is a Greek literature, Greek epic poem written by Apollonius of Rhodes, Apollonius Rhodius in the 3rd century BC. The only entirely surviving Hellenistic civilization, Hellenistic epic (though Aetia (Callimachus), Callim ...
'' as a place visited by the Argonauts. Jason
Jason ( ; ) was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece is featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He was married to the sorceress Med ...
and Medea
In Greek mythology, Medea (; ; ) is the daughter of Aeëtes, King Aeëtes of Colchis. Medea is known in most stories as a sorceress, an accomplished "wiktionary:φαρμακεία, pharmakeía" (medicinal magic), and is often depicted as a high- ...
were married there in 'Medea's Cave'. Apollonius named the island ''Drepane'', Greek for "sickle", since it was thought to hide the sickle that Cronus
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Cronus, Cronos, or Kronos ( or ; ) was the leader and youngest of the Titans, the children of Gaia (Earth) and Uranus (mythology), Uranus (Sky). He overthrew his father and ruled dur ...
used to castrate his father Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It is a gaseous cyan-coloured ice giant. Most of the planet is made of water, ammonia, and methane in a Supercritical fluid, supercritical phase of matter, which astronomy calls "ice" or Volatile ( ...
, from whose blood the Phaeacians were descended. In an alternative account, Apollonius identifies the buried sickle as a scythe belonging to Demeter
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Demeter (; Attic Greek, Attic: ''Dēmḗtēr'' ; Doric Greek, Doric: ''Dāmā́tēr'') is the Twelve Olympians, Olympian goddess of the harvest and agriculture, presiding over cro ...
, yet the name ''Drepane'' probably originated in the sickle-shape of the island. According to a scholiast
Scholia (: scholium or scholion, from , "comment", "interpretation") are grammatical, critical, or explanatory comments – original or copied from prior commentaries – which are inserted in the margin of the manuscript of ancient au ...
, commenting on the passage in ''Argonautica'', the island was first of all called Macris after the nurse of Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, myth, Dionysus (; ) is the god of wine-making, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, festivity, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, and theatre. He was also known as Bacchus ( or ; ...
who fled there from Euboea
Euboea ( ; , ), also known by its modern spelling Evia ( ; , ), is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete, and the sixth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by ...
.
Some scholars have asserted that Corfu is '' Taphos'', the island of the Lelegian Taphians.Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
(VI, 269), the Liburnians
The Liburnians or Liburni () were an ancient tribe inhabiting the district called Liburnia, a coastal region of the northeastern Adriatic between the rivers ''Arsia'' ( Raša) and ''Titius'' ( Krka) in what is now Croatia. According to Strabo ...
were masters of the island ''Korkyra'' (Corfu) for a time, until the 8th century BC. They reportedly were expelled from Korkyra by the Corinthians.
At a date no doubt previous to the foundation of Syracuse
Syracuse most commonly refers to:
* Syracuse, Sicily, Italy; in the province of Syracuse
* Syracuse, New York, USA; in the Syracuse metropolitan area
Syracuse may also refer to:
Places
* Syracuse railway station (disambiguation)
Italy
* Provi ...
, Corfu was peopled by settlers from Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
, probably 730 BC, but it appears to have previously received a stream of emigrants from Eretria
Eretria (; , , , , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers ...
. The commercially advantageous location of Corcyra on the way between Greece and Magna Grecia
Magna Graecia refers to the Greek-speaking areas of southern Italy, encompassing the modern Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania, and Sicily. These regions were extensively settled by Greeks beginning in the 8th century ...
, and its fertile lowlands in the southern section of the island favoured its growth and, influenced perhaps by the presence of non-Corinthian settlers, its people, quite contrary to the usual practice of Corinthian colonies, maintained an independent and even hostile attitude towards the mother city.[
This opposition came to a head in the early part of the 7th century BC, when their fleets fought the first naval battle recorded in Greek history: 665 BC according to ]Thucydides
Thucydides ( ; ; BC) was an Classical Athens, Athenian historian and general. His ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts Peloponnesian War, the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been d ...
. These hostilities ended in the conquest of Corcyra by the Corinthian tyrant Periander
Periander (; ; died c. 585 BC) was the second tyrant of the Cypselid dynasty that ruled over ancient Corinth. Periander's rule brought about a prosperous time in Corinth's history, as his administrative skill made Corinth one of the wealthiest city ...
(Περίανδρος) who induced his new subjects to join in the colonization of Apollonia and Anactorium. The island soon regained its independence and thenceforth devoted itself to a purely mercantile policy. During the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
invasion of 480 BC it manned the second largest Greek fleet (60 ships), but took no active part in the war. In 435 BC it was again involved in a quarrel with Corinth over the control of Epidamnus
Epidamnos ''(Ancient Greek: Επίδαμνος, Albanian: Epidamn)'', later known as Dyrrachium ''(Latin: Dyrrhachium, Greek: Δυρράχιον, Albanian: Dyrrah)'', was a prominent city on the Adriatic coast, located in modern-day Durrës, Alb ...
, and sought assistance from Athens (see Battle of Sybota
The Battle of Sybota () took place in 433 BC between Corcyra (modern Corfu) and Corinth. It was one of the immediate catalysts for the Peloponnesian War.
History
Corinth had been in dispute with Corcyra, an old Corinthian colony which no longer ...
).[
This new alliance was one of the chief immediate causes of the ]Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancien ...
, in which Corcyra was of considerable use to the Athenians
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
as a naval station, but did not render much assistance with its fleet. The island was nearly lost to Athens by two attempts of the oligarchic faction to effect a revolution; on each occasion the popular party ultimately won the day and took a most bloody revenge on its opponents (427 BC and 425 BC).[
During the Sicilian campaigns of Athens Corcyra served as a supply base; after a third abortive rising of the oligarchs in 410 BC it practically withdrew from the war. In 375 BC it again joined the Athenian alliance; two years later it was besieged by a ]Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas rive ...
n force, but in spite of the devastation of its flourishing countryside held out successfully until relieved. In the Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
period Corcyra was exposed to attack from several sides.[
In 303 BC, after a vain siege by ]Cassander
Cassander (; ; 355 BC – 297 BC) was king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia from 305 BC until 297 BC, and '' de facto'' ruler of southern Greece from 317 BC until his death.
A son of Antipater and a contemporary of Alexander the ...
,[ the island was occupied for a short time by the Lacedaemonian general ]Cleonymus of Sparta
Cleonymus () was a member of the Spartan royal family of the Agiad dynasty.
Biography
Cleonymus was the second son of Cleomenes II and a pretender to the Spartan throne. He did not succeed his father (died 309/308 BC), allegedly because he was ...
, then regained its independence and later it was attacked and conquered by Agathocles of Syracuse
Agathocles (, ''Agathoklḗs''; 361–289 BC) was a tyrant of Syracuse, Sicily, Syracuse from 317 BC and king of much of Sicily from 304 BC until his death. Agathocles began his career as a military officer, and raised his profile as a supp ...
. He offered Corfu as dowry to his daughter Lanassa on her marriage to Pyrrhus, King of Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
. The island then became a member of the Epirotic alliance. It was then perhaps that the settlement of Cassiope
''Cassiope'' is a genus of 18 small shrubby species in the family Ericaceae. It is the sole genus in the subfamily Cassiopoideae. They are native to the Arctic and north temperate montane regions. The genus is named after Cassiopeia of Greek ...
was founded to serve as a base for the King of Epirus' expeditions. The island remained in the Epirotic alliance until 255 BC when it became independent after the death of Alexander
Alexander () is a male name of Greek origin. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here ar ...
, last King of Epirus. In 229 BC, following the naval battle of Paxos, it was captured by the Illyrians
The Illyrians (, ; ) were a group of Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking people who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo-Balkan languages, Paleo-Balkan populations, alon ...
, but was speedily delivered by a Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
fleet and remained a Roman naval station until at least 189 BC. At this time, it was governed by a prefect (presumably nominated by the consuls), but in 148 BC it was attached to the province of Macedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
. In 31 BC, it served Octavian
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in ...
(Augustus) as a base against Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman people, Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the Crisis of the Roman Republic, transformation of the Roman Republic ...
.[
]
Roman and medieval history
 Christianity arrived in Corfu early; two disciples of
Christianity arrived in Corfu early; two disciples of Saint Paul
Paul, also named Saul of Tarsus, commonly known as Paul the Apostle and Saint Paul, was a Christian apostle ( AD) who spread the teachings of Jesus in the first-century world. For his contributions towards the New Testament, he is generally ...
, Jason of Tarsus and Sosipatrus of Patras, taught the Gospel, and according to tradition the city of Corfu and much of the island converted to Christianity. Their relics were housed in the old cathedral (at the site of the current Old Fortress, before a dedicated church was built for them .
During Late Antiquity (late Roman/early Byzantine period), the island formed part of the province of Epirus Vetus in the praetorian prefecture of Illyricum. In 551, during the Gothic War (535–554), Gothic War, the Ostrogoths raided the island and destroyed the city of Corfu, then known as ''Chersoupolis'' (Χερσούπολις, "city on the promontory") because of its location between Garitsa Bay and Kanoni. Over the next centuries, the main settlement was moved north, to the location of the current Old Fortress, where the rocky hills offered natural protection against raids. From the twin peaks of the new site, the medieval city received its new name, ''Korypho'' (Κορυφώ, "city on the peak") or ''Korphoi'' (Κορφοί, "peaks"), whence the modern Western name of "Corfu". The previous site of the city, now known as ''Palaiopolis'' (Παλαιόπολις, "old city"), continued to be inhabited for several centuries, however.
From at least the early 9th century, Corfu and the other Ionian Islands formed part of the theme (Byzantine district), theme of Cephallenia (theme), Cephallenia. This naval theme provided a defensive bulwark for Byzantium against western threats, but also played a major role in securing the sealanes to the Byzantine Catepanate of Italy, possessions in southern Italy. Indeed, traveller reports from throughout the middle Byzantine period (8th–12th centuries) make clear that Corfu was "an important staging post for travels between East and West". Indeed, the medieval name of Corfu first appears (Latinized ''Coryphus'') in Liutprand of Cremona's account of his 968 embassy to the Byzantine court. Corfu enjoyed relative peace and safety during the Macedonian dynasty (867–1054), which allowed the construction of a monumental church to Saints Iason and Sosipatrus outside the city wall of Palaiopolis. Nevertheless, in 933, the city, led by its archbishop, Arsenios, withstood a Saracen attack; Arsenios was canonized and became the city's patron saint.
The peace and prosperity of the Macedonian era ended with another Saracen attack in 1033, but more importantly with the emergence of a new threat: following the Norman conquest of Southern Italy, the ambitious Norman monarchs set their sights on expansion in the East. Three times on the space of a century Corfu was the first target and served as a staging area for the Byzantine–Norman wars, Norman invasions of Byzantium. The first Norman occupation from 1081 to 1084 was ended only after the Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos secured the aid of the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
, in exchange to wide-ranging commercial concessions to Venetian merchants. The admiral George of Antioch captured Corfu again in 1147, and it took a ten-month siege for Manuel I Komnenos to recover the island in 1149. In the third invasion in 1185, the island was again captured by William II of Sicily, but was soon regained by Isaac II Angelos.
During the break-up of the Byzantine Empire the island was occupied by Genoa, Genoese privateers (1197–1207), who in turn were expelled by the Venetians. In 1214 it passed to the Greek despotate of Epirus, despots of Epirus,[ who gave it to Manfred of Sicily as a dowry in 1259. At his death in 1267 it passed to the Capetian House of Anjou, House of Anjou. Thus, Corfu became a part of the Angevin Kingdom of Albania (medieval), Kingdom of Albania that was established and ruled by Frankish Charles I of Anjou, Charles of Anjou of the royal Capetian dynasty. Under the latter, the island suffered considerably from the inroads of various adventurers.][
The island was one of the first places in Europe in which Romani people settled. In about 1360, a fiefdom, called the ''Feudum Acinganorum'' was established, with mainly Romani serfs. From 1386, Corfu was controlled by the ]Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
, which in 1401 acquired formal sovereignty and retained it until the French Occupation of 1797.[ Corfu became central for the propagation of the activities of the Filiki Etaireia among the Greek Diaspora and philhellenic societies across Europe, through nobles like ]Ioannis Kapodistrias
Count Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias (; February 1776 –27 September 1831), sometimes anglicized as John Capodistrias, was a Greek statesman who was one of the most distinguished politicians and diplomats of 19th-century Europe.
Kapodistrias's ...
and Dionysios Romas.
Venetian rule
 From medieval times and into the 17th century, the island was recognised as a bulwark of the European States against the
From medieval times and into the 17th century, the island was recognised as a bulwark of the European States against the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
and became one of the most fortified places in Europe.Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Se ...
. Corfu repulsed several Ottoman Empire, Ottoman sieges, before passing under United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, British United States of the Ionian Islands, rule following the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
.[ and subjected to four notable sieges in Siege of Corfu (1537), 1537, 1571, 1573 and Siege of Corfu (1716), 1716, in which the strength of the city defences asserted itself time after time. The effectiveness of the powerful Venetian fortifications as well as the strength of some old Byzantine castles in Angelokastro (Corfu), Angelokastro, Kassiopi Castle, Gardiki Castle, Corfu, Gardiki and elsewhere, were additional factors that enabled Corfu to remain free. Will Durant claimed that Corfu owed to the ]Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
the fact that it was one of the few parts of Greece never conquered by the Ottomans.
A series of attempts by the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans to take the island began in 1431 when Ottoman troops under Ali Bey Evrenosoglu, Ali Bey landed on the island. The Ottomans tried to take the city castle and raided the surrounding area, but were repulsed. The Siege of Corfu (1716), second great siege of Corfu took place in 1716, during the last Ottoman–Venetian War (1714–18). After the conquest of the Peloponnese in 1715, the Ottoman fleet appeared in Buthrotum opposite Corfu. On 8 July the Ottoman fleet, carrying 33,000 men, sailed to Corfu from Buthrotum and established a beachhead at Ipsos.
The Siege of Corfu (1716), second great siege of Corfu took place in 1716, during the last Ottoman–Venetian War (1714–18). After the conquest of the Peloponnese in 1715, the Ottoman fleet appeared in Buthrotum opposite Corfu. On 8 July the Ottoman fleet, carrying 33,000 men, sailed to Corfu from Buthrotum and established a beachhead at Ipsos.
Venetian policies and legacy
Corfu's urban architecture differs from that of other major Greek cities, because of Corfu's unique history. From 1386 to 1797, Corfu was ruled by Venetian nobility; much of the city reflects this era when the island belonged to the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
, with multi-storeyed buildings on narrow lanes. The Old Town of Corfu has clear Venetian influence and is amongst the List of World Heritage Sites in Greece, World Heritage Sites in Greece. It was in the Venetian period that the city saw the erection of the first opera house ( Nobile Teatro di San Giacomo di Corfù) in Greece.
Many Venetian-speaking families settled in Corfu during these centuries; they were called Corfiot Italians, and until the second half of the 20th century the ''Venetian language, Veneto da mar'' was spoken in Corfu. During this time, the local Greek language assimilated a large number of Italian and Venetian words, many of which are still common today. The internationally renowned Venetian-born British photographer Felice Beato (1832–1909) is thought to have spent much of his childhood in Corfu. Also many Italian Jews took refuge in Corfu during the Venetian centuries and spoke their own language (Italkian), a mixture of Hebrew-Italian in a Venetian or Apulian dialect with some Greek words.
Venetians promoted the Catholic Church during their four centuries of rule in Corfu. Today the majority of Corfiots are Greek Orthodox, but the small Catholic minority (5%), living harmoniously with the Orthodox community, owes its faith to these origins. These contemporary Catholics are mostly families who came from Malta, but also from Italy, and today the Catholic community numbers about 4,000 ( of Maltese descent), who live almost exclusively in the Venetian "Citadel" of Corfu City. Like other native Greek Catholics, they celebrate Easter using the same calendar as the Greek Orthodox church. The Cathedral of Saint James and Saint Christopher, Cathedral of St. James and St. Christopher in Corfu City is the see of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Corfu, Zakynthos and Cephalonia.
The island served also as a refuge for Greek scholars, and in 1732, it became the home of the first academy of modern Greece.[ A Corfu cleric and scholar, Nikephoros Theotokis (1732–1800) became renowned in Greece as an educator, and in Russia (where he moved later in his life) as an Orthodox archbishop.
The island's culture absorbed Venetian influence in a variety of ways; like other Ionian islands (see Cuisine of the Ionian islands), its local cuisine took in such elements and today's Corfiot cooking includes Venetian delicacies and recipes: "Pastitsada", deriving from the Venetian "Pastissada" (Italian: "Spezzatino") and the most popular dish in the island of Corfu, "Sofrito", "Strapatsada", "Savoro", "Bianco" and "Mandolato".
File:Corfu Pinargenti 1573.jpg, Venetian Old Fortress, Map 1573
File:Venetian blazon in Corfu.jpg, Venetian blazon with the Lion of Saint Mark, as frequently found on the New Fortress walls
File:Παλιό Φρούριο και Παλιά Πόλη από το Νέο Φρούριο.JPG, Panoramic view of Corfu (city) from the New Fortress
File:Detail of the south wing of the entrance at Kassiopi Castle.JPG, Detail of the south wing of the entrance at Kassiopi Castle
File:View of Kassiopi village from the castle.JPG, View of Kasiopi village from the castle
]
19th century
 By the 1797 Treaty of Campo Formio, Corfu was ceded to the French Revolution, French, who occupied it for two years as the ''French departments of Greece, département'' of Corcyre, until they were Siege of Corfu (1798–1799), expelled by a joint Russian Empire, Russian-Ottoman squadron under Admiral Ushakov. For a short time it became the capital of a self-governing federation of the Septinsular Republic, Heptanesos ("Seven Islands"), under Ottoman suzerainty; in 1807 after the Treaty of Tilsit its faction-ridden government was again replaced by a French administration under governor François-Xavier Donzelot, and in 1809 it was besieged in vain by a Royal Navy, British Royal Navy fleet, which had captured all the other Ionian islands.
By the 1797 Treaty of Campo Formio, Corfu was ceded to the French Revolution, French, who occupied it for two years as the ''French departments of Greece, département'' of Corcyre, until they were Siege of Corfu (1798–1799), expelled by a joint Russian Empire, Russian-Ottoman squadron under Admiral Ushakov. For a short time it became the capital of a self-governing federation of the Septinsular Republic, Heptanesos ("Seven Islands"), under Ottoman suzerainty; in 1807 after the Treaty of Tilsit its faction-ridden government was again replaced by a French administration under governor François-Xavier Donzelot, and in 1809 it was besieged in vain by a Royal Navy, British Royal Navy fleet, which had captured all the other Ionian islands.[
Following the final defeat of Napoleon at the Battle of Waterloo, the Ionian Islands became a British protectorate, protectorate of the United Kingdom by the Treaty of Paris (1815), Treaty of Paris of 5 November 1815 as the ]United States of the Ionian Islands
The United States of the Ionian Islands was a Greeks, Greek state (polity), state and Protectorate#Amical_protection, amical protectorate of the United Kingdom between 1815 and 1864. The succession of states, successor state of the Septinsular R ...
. Corfu became the seat of the British Lord High Commissioner of the Ionian Islands.[ The population of the island was 66,000 by 1848.The period of British rule led to investment in new roads, an improved water supply system, and the expansion of the Ionian Academy into a university. During this period the Greek language became the official language.
Following a plebiscite the Second National Assembly of the Greeks at Athens elected a new king, Prince Wilhelm (William) of Denmark, who took the name George I of the Hellenes, George I and brought with him the Ionian Islands as a coronation gift from Britain. On 29 March 1864, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom, Kingdom of Greece, Greece, Second French Empire, France and Russian Empire, Russia signed the Treaty of London, pledging the transfer of sovereignty to Greece upon ratification. Thus, on 21 May, by proclamation of the Lord High Commissioner, the Ionian Islands were united with Greece.]
British Lord High Commissioners during the protectorate
 This is a list of the British High Commissioners of the Ionian Islands; (as well as the transitional Greek Governor, appointed a year prior to Enosis (Union) with Greece in 1864).
This is a list of the British High Commissioners of the Ionian Islands; (as well as the transitional Greek Governor, appointed a year prior to Enosis (Union) with Greece in 1864).[:ca:Història de Corfú]
*Sir James Campbell, 1st Baronet, Sir James Campbell 1814–1816
*Sir Thomas Maitland (1759–1824) 1815–1823
*Frederick Adam, Sir Frederick Adam (1781–1853) 1823–1832
*Alexander Woodford, Sir Alexander Woodford (1782–1870) 1832
*George Nugent-Grenville, 2nd Baron Nugent (1788–1850) 1832–1835
*Howard Douglas (1776–1861) 1835–1840
*James Alexander Stewart-Mackenzie (1784–1843) 1840–1843
*John Colborne, 1st Baron Seaton (1778–1863) 1843–1849
*Henry George Ward, Sir Henry George Ward (1797–1860) 1849–1855
*John Young, 1st Baron Lisgar, Sir John Young (1807–1876) 1855–1859
*William Ewart Gladstone (1809–1898) 1859
*Henry Knight Storks, Sir Henry Knight Storks (1811–1874) 1859–1863
*Count Dimitrios Nikolaou Karousos, President of the United States of the Ionian Islands, Ionian Parliament (1799–1873) 1863–1864
First World War
 During the First World War, the island served as a refuge for the Serbian army that retreated there on Allies of World War I, Allied forces' ships from a homeland occupied by the Austrians, Germans and Bulgarians. During their stay, a large portion of Serbian soldiers died from exhaustion, food shortage, and various diseases. Most of their remains were buried at sea near the island of Vido, a small island at the mouth of Corfu port, and a monument of thanks to the Greek nation has been erected at Vido by the grateful Serbs; consequently, the waters around Vido Island are known by the Serbian people as the Blue Tomb (in Serbian, Плава Гробница, Plava Grobnica), after a poem written by Milutin Bojić following World War I.
During the First World War, the island served as a refuge for the Serbian army that retreated there on Allies of World War I, Allied forces' ships from a homeland occupied by the Austrians, Germans and Bulgarians. During their stay, a large portion of Serbian soldiers died from exhaustion, food shortage, and various diseases. Most of their remains were buried at sea near the island of Vido, a small island at the mouth of Corfu port, and a monument of thanks to the Greek nation has been erected at Vido by the grateful Serbs; consequently, the waters around Vido Island are known by the Serbian people as the Blue Tomb (in Serbian, Плава Гробница, Plava Grobnica), after a poem written by Milutin Bojić following World War I.[
]
Interwar period
In 1923, after a diplomatic dispute between Italy and Greece, Italian forces bombarded and occupied Corfu. The League of Nations settled this Corfu incident in Italy's favour.
Second World War
Italian occupation and resistance
 During the Greco-Italian War, Corfu was occupied by the Italians in April 1941. They administered Corfu and the Ionian islands as a separate entity from Greece until September 1943, following Benito Mussolini's orders of fulfilling Italian Italia irredenta, Irredentism and making Corfu part of the Kingdom of Italy. During the Second World War the 10th Mechanized Infantry Brigade (Greece), 10th Infantry Regiment of the Hellenic Army, Greek Army, composed mainly of Corfiot soldiers,
During the Greco-Italian War, Corfu was occupied by the Italians in April 1941. They administered Corfu and the Ionian islands as a separate entity from Greece until September 1943, following Benito Mussolini's orders of fulfilling Italian Italia irredenta, Irredentism and making Corfu part of the Kingdom of Italy. During the Second World War the 10th Mechanized Infantry Brigade (Greece), 10th Infantry Regiment of the Hellenic Army, Greek Army, composed mainly of Corfiot soldiers,
German bombing and occupation
Upon the Fall of the Fascist regime in Italy, fall of Italian fascism in 1943, the Nazis moved to take control of the island. On 14 September 1943, Corfu was bombarded by the Luftwaffe. The Nazi bombing raids destroyed most of the city's buildings, including churches, homes, and whole city blocks, especially in the Jewish quarter Evraiki. Other losses included the city's market (αγορά) and the hotel Bella Venezia. The worst losses were the historic buildings of the Ionian Academy (Ιόνιος Ακαδημία), the Municipal Theatre of Corfu, Municipal Theatre (which in 1901 had replaced the '' Nobile Teatro di San Giacomo di Corfù''), the Municipal Library, and the Ionian Parliament.[United States Holocaust Memorial Museum](_blank)
on the Holocaust in Corfu. Also contains information about the Nazi collaborator mayor Kollas. In early June 1944, while the Allies bombed Corfu as a diversion from the Operation Overlord, Normandy landings, the Gestapo rounded up the Jews of the city, temporarily incarcerated them at the old fort (Palaio Frourio), and on 10 June sent them to Auschwitz concentration camp#Auschwitz II-Birkenau, Auschwitz II, where most of them were Extermination camp#Gassings, murdered by gas.[From the interview of Holocaust survivors, a survivor in the film "Shoah (film), Shoah"] Approximately two hundred out of a total population of 1,900 escaped.[United States Holocaust Memorial Museum](_blank)
: "[...]two hundred of the 2,000 Corfu Jews found sanctuary with Christian families[...]" In ''Evraiki'' (Εβραική, meaning ''Jewish quarter''), there is currently a synagogue with about 65 members, who still speak their original Italkian language.
Liberation
 Corfu was liberated by British Armed Forces, British troops, specifically the 40th Royal Marine Commando, which landed in Corfu on 14 October 1944, as the Germans were evacuating Greece. The Royal Navy swept the Corfu Channel for mines in 1944 and 1945, and found it to be free of mines.
Corfu was liberated by British Armed Forces, British troops, specifically the 40th Royal Marine Commando, which landed in Corfu on 14 October 1944, as the Germans were evacuating Greece. The Royal Navy swept the Corfu Channel for mines in 1944 and 1945, and found it to be free of mines.
Post–World War and modern Corfu
After World War II and the Greek Civil War, the island was rebuilt under the general programme of reconstruction of the Greek Government (Ανοικοδόμησις) and many elements of its classical architecture remain. Its economy grew but a portion of its inhabitants left the island for other parts of the country; buildings erected during Italian occupation – such as schools or government buildings – were put back to civic use. In 1956 Maria Desylla Kapodistria, relative of first Governor (head of state) of Greece Ioannis Kapodistrias
Count Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias (; February 1776 –27 September 1831), sometimes anglicized as John Capodistrias, was a Greek statesman who was one of the most distinguished politicians and diplomats of 19th-century Europe.
Kapodistrias's ...
, was elected mayor of Corfu
Corfu ( , ) or Kerkyra (, ) is a Greece, Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands; including its Greek islands, small satellite islands, it forms the margin of Greece's northwestern frontier. The island is part of the Corfu (regio ...
and became the first female mayor in Greece.[Municipality of Corfu from the Internet archive](_blank)
Quote: "In the elections of 1954 Stamatios Desillas was elected Mayor for a second term and remained in office until his death, Christmas Day 1955. Soon after a bye-election took place in Corfu in which the widow of the deceased Maria Desilla – Kapodistria, was elected Mayor with 5,365 votes in a total of 10,207. Maria Desilla became Mayor of Corfu on 15 April 1956 until 9 May 1959. She was the first female Mayor in Greece." The Corfu General Hospital was also constructed;Ionian University
The Ionian University (IU; ) is a university located in the Ionian Islands (region), Ionian Islands, Greece. It is one of the newest institutions of Higher Education in Greece, created in 1984 pursuant to presidential order 83/84 ΦΕΚ 31 Α/2 ...
was established in 1984.
Architecture
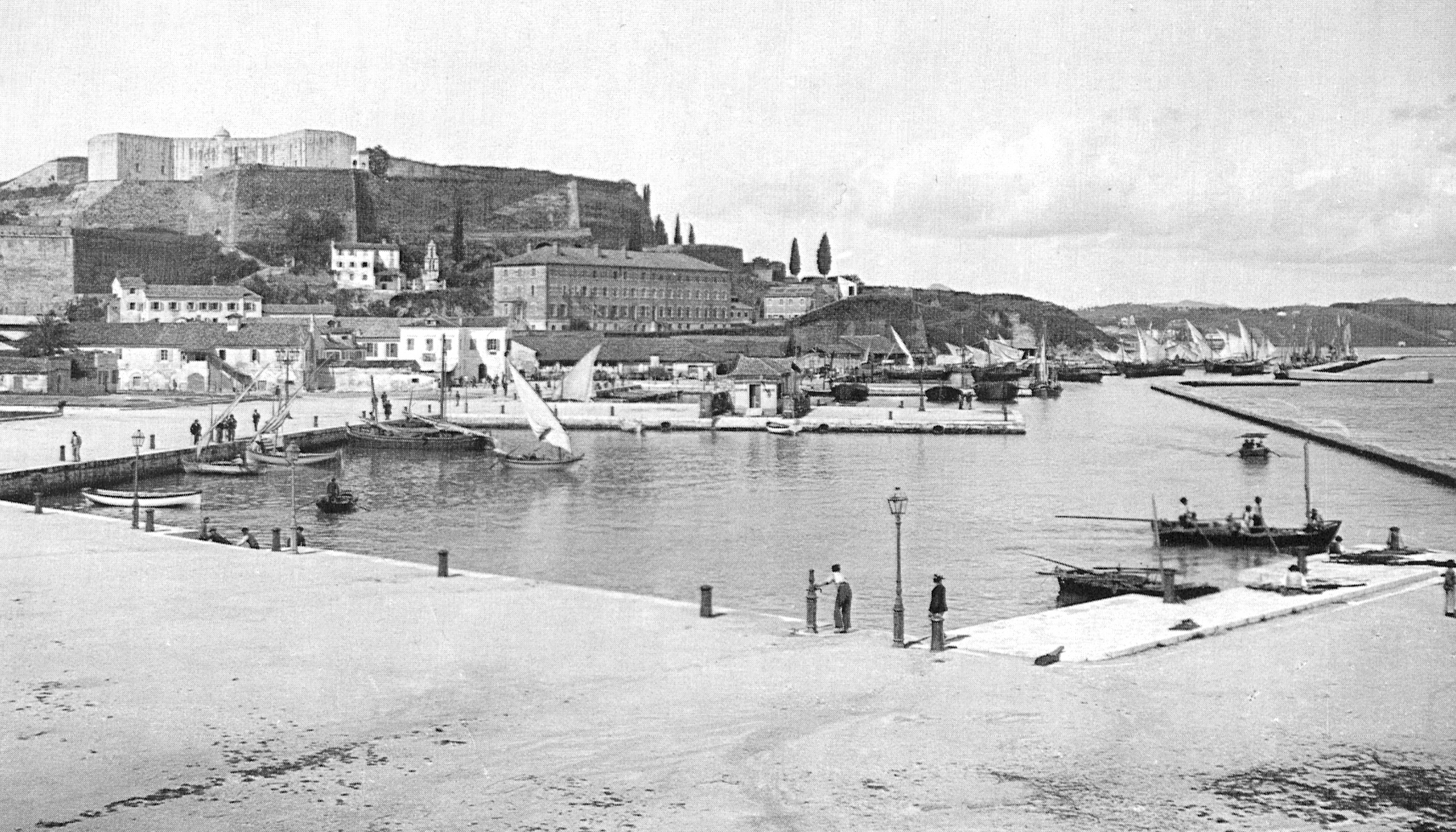
Venetian influence
 Corfu's urban architecture influence derives from Venice, reflecting the fact that from 1386 to 1797 the island was ruled by the Venetians. The architecture of the Old Town of Corfu along with its narrow streets, the , has clear Venetian influence and is amongst the List of World Heritage Sites in Greece, World Heritage Sites in Greece. Other notable Venetian-era buildings include the Nobile Teatro di San Giacomo di Corfù, the first Greek opera house, and ''Liston'', a multi-level commercial and residential building, with an arched colonnade at ground level, lined with cafes and restaurants on its east side, and restaurants and other stores on its west side. Liston's main thoroughfare is often the site of parades and other mass gatherings. Liston is on the edge of the ''Spianada'' (Esplanade), the vast main plaza and park which incorporates a cricket field, a pavilion, and Maitland's monument. Also notable are the Old and New forts, the recently restored Palace of Sts. Michael and George, formerly the residence of the British colonial governor and the seat of the Ionian Senate, and the summer Palace of ''Mon Repos, Corfu, Mon Repos'', formerly the property of the Greek royal family and birthplace of the Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh. The Park of Mon Repos is built on part of the Palaiopolis of Kerkyra, where excavations were conducted by the Greek Archaeological Service in collaboration with academics and universities internationally. Examples of the finds can be found in the Museum of the Palace of Mon Repos and at the Archaeological Museum of Corfu.
Corfu's urban architecture influence derives from Venice, reflecting the fact that from 1386 to 1797 the island was ruled by the Venetians. The architecture of the Old Town of Corfu along with its narrow streets, the , has clear Venetian influence and is amongst the List of World Heritage Sites in Greece, World Heritage Sites in Greece. Other notable Venetian-era buildings include the Nobile Teatro di San Giacomo di Corfù, the first Greek opera house, and ''Liston'', a multi-level commercial and residential building, with an arched colonnade at ground level, lined with cafes and restaurants on its east side, and restaurants and other stores on its west side. Liston's main thoroughfare is often the site of parades and other mass gatherings. Liston is on the edge of the ''Spianada'' (Esplanade), the vast main plaza and park which incorporates a cricket field, a pavilion, and Maitland's monument. Also notable are the Old and New forts, the recently restored Palace of Sts. Michael and George, formerly the residence of the British colonial governor and the seat of the Ionian Senate, and the summer Palace of ''Mon Repos, Corfu, Mon Repos'', formerly the property of the Greek royal family and birthplace of the Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh. The Park of Mon Repos is built on part of the Palaiopolis of Kerkyra, where excavations were conducted by the Greek Archaeological Service in collaboration with academics and universities internationally. Examples of the finds can be found in the Museum of the Palace of Mon Repos and at the Archaeological Museum of Corfu.[R. Winkes (editor), Kerkyra. Artifacts from the Palaiopolis, Providence 2004.]
The Achilleion
 In 1889, Elisabeth of Bavaria, Empress Elisabeth of Austria built a summer palace in the region of Gastouri (Γαστούρι) to the south of the city, naming it Achilleion (Corfu), Achílleion (Αχίλλειον) after the
In 1889, Elisabeth of Bavaria, Empress Elisabeth of Austria built a summer palace in the region of Gastouri (Γαστούρι) to the south of the city, naming it Achilleion (Corfu), Achílleion (Αχίλλειον) after the Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
ic hero Achilles. The structure is filled with paintings and statues of Achilles, both in the main hall and in the gardens, depicting scenes of the Trojan War. The palace, with the Neoclassicism, neoclassical Greek statues that surround it, is a monument to Platonism, platonic romanticism as well as escapism. It served as a refuge for the grieving Empress following the tragic death of her only son Rudolf, Crown Prince of Austria, Crown Prince, Rudolf.
 The Imperial gardens on the hill look over the surrounding green hills and valleys and the
The Imperial gardens on the hill look over the surrounding green hills and valleys and the Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea (, ; or , ; , ) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including Basilicata, Calabria, Sicily, and the Salento peninsula to the west, ...
. The centrepiece of the gardens is a marble statue on a high pedestal, of the mortally wounded Achilles (Greek language, Greek: Αχιλλεύς Θνήσκων, ''Achilleús Thnēskōn'', Achilles Dying) without hubris and wearing only a simple cloth and an ancient Greek hoplite helmet. This statue was carved by German sculptor Ernst Gustav Herter.
The hero is presented devoid of rank or status, and seems notably human, though heroic, as he is forever trying to pull Paris (mythology), Paris's arrow from his heel. His classically depicted face is full of pain. He gazes skyward, as if to seek help from Twelve Olympians, Olympus. According to Greek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories conc ...
, his mother Thetis was a goddess.
In contrast, at the great staircase in the main hall is a giant painting of the triumphant Achilles full of hubris, pride. Dressed in full royal military regalia and erect on his racing chariot, he pulls the lifeless body of Hector of Troy in front of the stunned crowd watching helplessly from inside the walls of the Trojan citadel.
In 1898, Empress Sissi was assassinated at the age of 60 by an Italian anarchist, Luigi Lucheni, in Geneva, Switzerland. After her death, the palace was sold to the German Empire, German Kaiser William II, German Emperor, Wilhelm II. Following the Kaiser's purchase of the Achilleion, he invited archaeologist Reinhard Kekulé von Stradonitz, a friend and advisor, to come to Corfu to advise him where to position the huge statue of Achilles which he commissioned. The famous salute to Achilles from the Kaiser, which had been inscribed at the statue's base, was also created by Kekulé. The inscription read:
Kaiser's Bridge
German Wilhelm II of Germany, Kaiser Wilhelm II was also fond of taking holidays in Corfu. Having purchased the Achilleion in 1907 after Sissi's death, he appointed Carl Ludwig Sprenger as the botanical architect of the Palace, and also built a bridge later named by the locals after him—the "Kaiser's bridge" (Greek: η γέφυρα του Κάιζερ transliterated as: i gefyra tou Kaizer)—to access the beach without traversing the road forming the island's main artery to the south. The bridge, arching over the road, spanned the distance between the lower gardens of Achilleion and the nearby beach; its remains are an important landmark on the highway. The bridge's central section was demolished by the Wehrmacht in 1944, during the German occupation of World War II, to allow for the passage of an enormous cannon, forming part of the Nazi defences in the southeastern coast of Corfu.[Corfu map](_blank)
: The bridge was destroyed during a German attack in World War II. The remains can still be seen today.
Urban landscape
Old town
The Old Town of Corfu (city), Corfu city is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. In several parts of the old city, buildings of the Venice, Venetian era are to be found. The old city's architectural character is strongly influenced by the Venetian style, coming as it did under Venetian rule for a long period; its small and ancient side streets, and the old buildings' trademark arches are particularly reminiscent of Venice.
The city of Corfu
Corfu ( , ) or Kerkyra (, ) is a Greece, Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands; including its Greek islands, small satellite islands, it forms the margin of Greece's northwestern frontier. The island is part of the Corfu (regio ...
stands on the broad part of a peninsula, whose termination in the Venetian citadel () is cut off from it by an artificial moat, fosse formed in a natural gully, with a seawater moat at the bottom,[ that now serves as a marina and is called the ''Contrafossa''. In the old town there are many narrow streets paved with cobblestones. These streets are known as (), and the older amongst them sometimes follow the gentle irregularities of the ground; while many are too narrow for vehicular traffic. A promenade rises by the seashore towards the bay of Garitsa (Γαρίτσα), together with an esplanade between the city and the citadel known as ''Spianada'' with the arcade () to its west side, where restaurants and bistros abound.]
Ano and Kato Plateia and the music pavilion
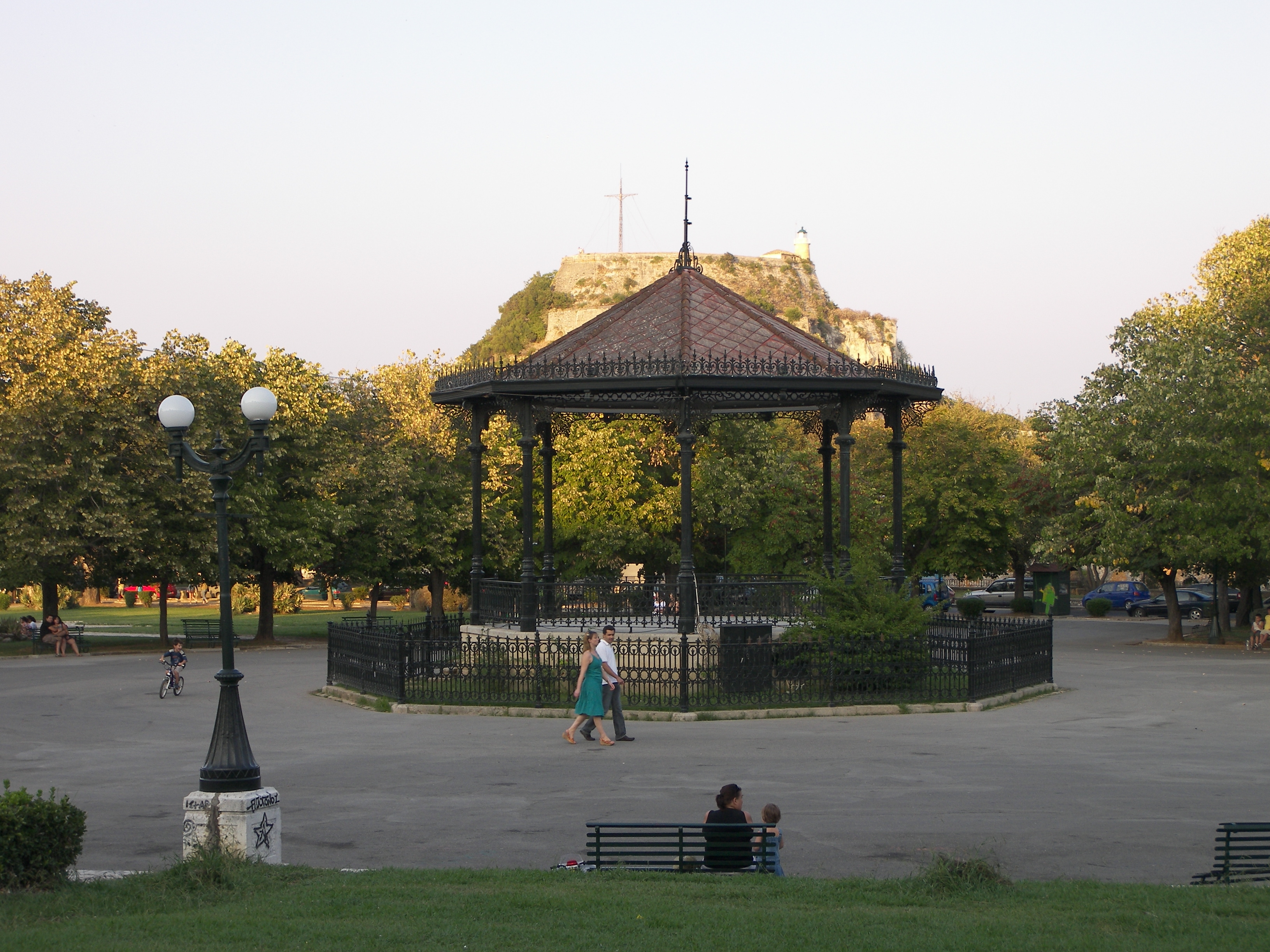 Near the old Venetian Citadel a large square called ''Spianada'' is also to be found, divided by a street in two parts: "Ano Plateia" (literally: "Upper square") and "Kato Plateia" (literally: "Lower square"), (Ανω Πλατεία and Κάτω Πλατεία in Greek). This is the biggest square in South-Eastern Europe and one of the largest in Europe, and replete with green spaces and interesting structures, such as a Roman-style rotunda from the era of British administration, known as the ''Maitland monument'', built to commemorate Sir Thomas Maitland. An ornate music pavilion is also present, where the local "Philharmonikes" (Philharmonic Orchestras) (Φιλαρμονικές), mount classical performances in the artistic and musical tradition for which the island is well known. "Kato Plateia" also serves as a venue where cricket matches are held from time to time. In Greece, cricket is unique to Corfu, as it was once a British protectorate.
Near the old Venetian Citadel a large square called ''Spianada'' is also to be found, divided by a street in two parts: "Ano Plateia" (literally: "Upper square") and "Kato Plateia" (literally: "Lower square"), (Ανω Πλατεία and Κάτω Πλατεία in Greek). This is the biggest square in South-Eastern Europe and one of the largest in Europe, and replete with green spaces and interesting structures, such as a Roman-style rotunda from the era of British administration, known as the ''Maitland monument'', built to commemorate Sir Thomas Maitland. An ornate music pavilion is also present, where the local "Philharmonikes" (Philharmonic Orchestras) (Φιλαρμονικές), mount classical performances in the artistic and musical tradition for which the island is well known. "Kato Plateia" also serves as a venue where cricket matches are held from time to time. In Greece, cricket is unique to Corfu, as it was once a British protectorate.
Palaia Anaktora and its gardens
Just to the north of "Kato Plateia" lie the "Palaia Anaktora" (Παλαιά Ανάκτορα: literally "Old Palaces"): a large complex of buildings of Roman architectural style which formerly housed the Kings of Greece, and prior to that the List of Lord High Commissioners of the Ionian Islands, British Governors of the island. It was then called the Palace of Saints Michael and George. The Order of St. Michael and St. George was founded here in 1818 with motto ''auspicium melioris aevi'',
Churches
In the city, there are thirty-seven Greek churches, the most important of which are the city's cathedral, the church dedicated to Our Lady of the Cave (η Παναγία Σπηλιώτισσα (hē Panagia Spēliōtissa)); Saint Spyridon Church, wherein lies the preserved body of the patron saint of the island; and finally the suburban church of St Jason and St Sosipater (Αγιοι Ιάσων και Σωσίπατρος), reputedly the oldest in the island,[ and named after the two saints probably the first to preach Christianity to the Corfiots.
]
Pontikonisi
The nearby island, known as Pontikonisi (Greek meaning "mouse island"), though small is very green with abundant trees, and at its highest natural elevation (excluding its trees or man-made structures, such as the monastery), stands at about . Pontikonisi is home of the monastery of Pantokrator (Μοναστήρι του Παντοκράτορος); the white stone staircase of the monastery, viewed from afar, gives the impression of a (mouse) tail, which lent the island its name.
Archaeology
Palaiopolis
In the city of Corfu, the ruins of the ancient city of Korkyra, also known as ''Palaiopolis'', include ancient temples which were excavated at the location of the palace of Mon Repos, which was built on the ruins of the Palaiopolis. The temples are: Kardaki Temple, Temple of Artemis, Corfu, Temple of Artemis, and the Temple of Hera, Mon Repos, Temple of Hera. Hera's temple is situated at the western limits of Mon Repos, close to Kardaki Temple and to the northwest.
Kardaki Temple
 Kardaki Temple is an Archaic Greece, Archaic Doric order, Doric Greek temple, temple in Corfu, Greece, built around 500 BC in the ancient city of Korkyra (or Corcyra), in what is known today as the location Kardaki in the hill of Analipsi in Corfu.
Kardaki Temple is an Archaic Greece, Archaic Doric order, Doric Greek temple, temple in Corfu, Greece, built around 500 BC in the ancient city of Korkyra (or Corcyra), in what is known today as the location Kardaki in the hill of Analipsi in Corfu.Poseidon
Poseidon (; ) is one of the twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and mythology, presiding over the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 He was the protector of seafarers and the guardian of many Hellenic cit ...
has not been established.
Temple of Artemis
 The Temple of Artemis is an Archaic Greece, Archaic Greek temple in Corfu, built in around 580 BC in the ancient city of Korkyra (or Corcyra), in what is known today as the suburb of Garitsa. The temple was dedicated to Artemis. It is known as the first Doric order, Doric temple exclusively built with limestone, stone.
The Temple of Artemis is an Archaic Greece, Archaic Greek temple in Corfu, built in around 580 BC in the ancient city of Korkyra (or Corcyra), in what is known today as the suburb of Garitsa. The temple was dedicated to Artemis. It is known as the first Doric order, Doric temple exclusively built with limestone, stone.[: "The island of Corfu, to the northwest of present-day Greece, off the coast of Albania, was an early colony of the city of Corinth and was under Corinthian control when its Temple of Artemis was constructed. A milestone in Greek architecture, this was the first building that was truly Doric. Many if not all of its Doric characteristics had appeared in earlier structures but here they were used for the first time as an ensemble."] Very few Greek temple reliefs from the Archaic period have survived, and the large fragments of the group from the pediment are the earliest significant survivals.
The temple was a peripteral–styled building with a pseudodipteral configuration. Its perimeter was rectangular, with width of and length with an eastward orientation so that light could enter the interior of the temple at sunrise.[.]
The Metope (architecture), metope of the temple was probably decorated, since remnants of reliefs featuring Achilles and Memnon (mythology), Memnon were found in the ancient ruins.[.] The temple has been described as a milestone of Ancient Greek architecture and one of 150 masterpieces of Western world, Western architecture.[ The Corfu temple architecture may have influenced the design of an archaic sanctuary structure found at the Sant'Omobono Area, Sant'Omobono archaeological site in Rome, dating from the time of the Etruscans, which incorporates similar design elements.][.] If still in use by the 4th-century, the temple would have been closed during the persecution of pagans in the late Roman Empire, when the Christian Emperors issued edicts prohibiting non-Christian worship. Kaiser Wilhelm II, while vacationing at his summer palace of Achilleion in Corfu and while Europe was preparing for war, was involved in excavations at the site of the ancient temple.
Temple of Hera
 The Temple of Hera or Heraion is an Archaic Greece, archaic Greek temple, temple in Corfu, built around 610 BC in the ancient city of Korkyra (or Corcyra), in what is known today as ''Palaiopolis'', and lies within the ground of the Mon Repos, Corfu, Mon Repos estate.
The Temple of Hera or Heraion is an Archaic Greece, archaic Greek temple, temple in Corfu, built around 610 BC in the ancient city of Korkyra (or Corcyra), in what is known today as ''Palaiopolis'', and lies within the ground of the Mon Repos, Corfu, Mon Repos estate.
Tomb of Menecrates
 The Tomb of Menecrates or Monument of Menecrates is an Archaic Greece, Archaic cenotaph in Corfu, built around 600 BC in the ancient city of Korkyra (or Corcyra).
The Tomb of Menecrates or Monument of Menecrates is an Archaic Greece, Archaic cenotaph in Corfu, built around 600 BC in the ancient city of Korkyra (or Corcyra).
Other archaeological sites
In Cassiope
''Cassiope'' is a genus of 18 small shrubby species in the family Ericaceae. It is the sole genus in the subfamily Cassiopoideae. They are native to the Arctic and north temperate montane regions. The genus is named after Cassiopeia of Greek ...
, the only other city of ancient importance, its name is still preserved by the village of Kassiopi, and there are some rude remains of building on the site; but the temple of Zeus Cassius for which it was celebrated has totally disappeared.
Castles
The castles of Corfu, located at strategic points on the island helped defend the island from many invaders and they were instrumental in repulsing repeated Turkish invasions, making Corfu one of the few places in Greece never to be conquered by the Ottomans.
Palaio Frourio
 The ''old citadel'' (in Greek ''Palaio Frourio'' (Παλαιό Φρούριο) is an old Venetian fortress built on an artificial islet with fortifications surrounding its entire perimeter, although some sections, particularly on the east side, are slowly being eroded and falling into the sea. Nonetheless, the interior has been restored and is in use for cultural events, such as concerts (συναυλίες) and Sound and Light Productions (Ηχος και Φως), when historical events are recreated using sound and light special effects. These events take place amidst the ancient fortifications, with the Ionian Sea in the background. The central high point of the citadel rises like a giant natural obelisk complete with a military observation post at the top, with a giant #Early history, cross at its apex; at the foot of the observatory lies St. George's church, in a classical style punctuated by six Doric Order, Doric columns,
The ''old citadel'' (in Greek ''Palaio Frourio'' (Παλαιό Φρούριο) is an old Venetian fortress built on an artificial islet with fortifications surrounding its entire perimeter, although some sections, particularly on the east side, are slowly being eroded and falling into the sea. Nonetheless, the interior has been restored and is in use for cultural events, such as concerts (συναυλίες) and Sound and Light Productions (Ηχος και Φως), when historical events are recreated using sound and light special effects. These events take place amidst the ancient fortifications, with the Ionian Sea in the background. The central high point of the citadel rises like a giant natural obelisk complete with a military observation post at the top, with a giant #Early history, cross at its apex; at the foot of the observatory lies St. George's church, in a classical style punctuated by six Doric Order, Doric columns,
Neo Frourio
 The ''new citadel'' or ''Neo Frourio'' (Νέο Φρούριο, "New Fortress") is a huge complex of fortifications built by the British during their United States of the Ionian Islands, rule of the island (1815–63) dominating the northeastern part of the city. The huge walls of the fortress loom over the landscape as one travels from ''Neo Limani'' (Νέο Λιμάνι, "New Port") to the city, taking the road that passes through the fishmarket (ψαραγορά). The new citadel was until recently a restricted area due to the presence of a naval garrison, but old restrictions have been lifted and it is now open to the public, with tours possible through the maze of medieval corridors and fortifications. The winged Lion of St Mark, the symbol of Venice, can be seen at regular intervals adorning the fortifications.
The ''new citadel'' or ''Neo Frourio'' (Νέο Φρούριο, "New Fortress") is a huge complex of fortifications built by the British during their United States of the Ionian Islands, rule of the island (1815–63) dominating the northeastern part of the city. The huge walls of the fortress loom over the landscape as one travels from ''Neo Limani'' (Νέο Λιμάνι, "New Port") to the city, taking the road that passes through the fishmarket (ψαραγορά). The new citadel was until recently a restricted area due to the presence of a naval garrison, but old restrictions have been lifted and it is now open to the public, with tours possible through the maze of medieval corridors and fortifications. The winged Lion of St Mark, the symbol of Venice, can be seen at regular intervals adorning the fortifications.
Angelokastro
Angelokastro ( (Castle of Angelos or Castle of the Angel); ) is a Byzantine castle on the island's northwest coast.[: "On a precipitous rocky peak dominating a wide range of coastline around Palaeokastritsa stand the crumbling walls and battlements of the twelfth-century Byzantine Fortress of Angelokastro, not far from the village of Krini." (p. 163); "After a siege lasting a year the invaders were finally driven away by the defenders of the fortress who were helped by the inhabitants of the neighbouring villages. Again, during the first great siege of Corfu by the Turks in 1537, Angelocastro successfully resisted attack. About 3,000 villagers had sought refuge within the fortress to escape the fate of the inhabitants of other parts of the island who were ... In 1571, when they once more invaded Corfu, the Ottomans again unsuccessfully attacked, Angelocastro, where 4,000 people had taken refuge. During the second great siege of the city by the Ottomans in 1716, Angelokastro once again served as a refuge for the ... During the course of the centuries Angelocastro played an important part in the defence of the island. In 1403 a force of Genoese soldiers, under the command of the French condottiere Boucicaut, landed at Palaeokastritsa and attacked ... The fortress existed in 1272 when it was formally taken over by the Italian Giordano di San Felice in the name of the Angevin rulers of Naples, who held the island of Corfu from 1267 to 1386." (p. 164); "... Angelocastro was probably built during the reign of the Byzantine Emperor Manuel Comnenos (1143 - 1180)." (p. 164); "This was used as a hermitage and was converted into a chapel, probably around the end of the eighteenth century" (p. 165); "From the top of Angelocastro the view sweeps far and wide over the hills across the breadth of Corfu, to the town, the Eastern Channel and the mountains on the mainland, over a sheer drop of a thousand feet to the sea below" (p. 325).]Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Se ...
and presented a formidable strategic vantage point to the occupant of the castle.
Angelokastro formed a defensive triangle with the castles of Gardiki Castle, Corfu, Gardiki and Kassiopi Castle, Kassiopi, which covered Corfu's defences to the south, northwest and northeast. The castle never fell, despite frequent sieges and attempts at conquering it through the centuries, and played a decisive role in defending the island against pirate incursions and during three sieges of Corfu by the Ottomans, significantly contributing to their defeat. During invasions it helped shelter the local peasant population. The villagers also fought against the invaders playing an active role in the defence of the castle. Angelokastro, located at the western frontier of the Empire, was instrumental in repulsing the Ottomans during the first great siege of Corfu in 1537, in the siege of 1571 and the second great siege of Corfu in 1716 causing the Ottomans to fail at penetrating the defences of Corfu in the North. Consequently the Turks were never able to create a beachhead and to occupy the island.
Gardiki Castle
 Gardiki Castle () is a 13th-century Byzantine castle on the southwestern coast of Corfu and the only surviving medieval fortress on the southern part of the island.
Gardiki Castle () is a 13th-century Byzantine castle on the southwestern coast of Corfu and the only surviving medieval fortress on the southern part of the island.
Kassiopi Castle
 Kassiopi Castle () is a castle on the northeastern coast of Corfu overseeing the fishing village of Kassiopi. It was one of three Byzantine-period castles that defended the island before the Republic of Venice, Venetian era (1386–1797). The castles formed a defensive triangle, with Gardiki Castle, Corfu, Gardiki guarding the island's south, Kassiopi the northeast and Angelokastro (Corfu), Angelokastro the northwest.
Kassiopi Castle () is a castle on the northeastern coast of Corfu overseeing the fishing village of Kassiopi. It was one of three Byzantine-period castles that defended the island before the Republic of Venice, Venetian era (1386–1797). The castles formed a defensive triangle, with Gardiki Castle, Corfu, Gardiki guarding the island's south, Kassiopi the northeast and Angelokastro (Corfu), Angelokastro the northwest.
Municipalities
The three present municipalities of Corfu and Diapontia Islands were formed in the 2019 local government reform from the former municipality Corfu.
Education
Ionian Academy
 The Ionian Academy was an institution that maintained the tradition of Greek education while the rest of Greece was still under Ottoman rule. The academy was established by the French during their administration of the island as the ''French departments of Greece, département'' of Corcyre,
The Ionian Academy was an institution that maintained the tradition of Greek education while the rest of Greece was still under Ottoman rule. The academy was established by the French during their administration of the island as the ''French departments of Greece, département'' of Corcyre,
Ionian University
 The Ionian University was established in 1984, in recognition, by the administration of Andreas Papandreou, of Corfu's contribution to Education in Greece, as the seat of the first Greek university in modern times, the Ionian Academy. The university opened its doors to students in 1985 and today comprises three Schools and six Departments offering undergraduate and post-graduate degree programmes and summer schools.
The Ionian University was established in 1984, in recognition, by the administration of Andreas Papandreou, of Corfu's contribution to Education in Greece, as the seat of the first Greek university in modern times, the Ionian Academy. The university opened its doors to students in 1985 and today comprises three Schools and six Departments offering undergraduate and post-graduate degree programmes and summer schools.
Student activism
In the modern era, beginning with its massive student protests during World War II against fascist occupation, and continuing in the fight against the dictatorship of Georgios Papadopoulos (1967–1974), students in Corfu have played a vanguard role in protesting for Freedom (political), freedom and democracy in Greece, against both internal and external oppression. For Corfiotes a recent example of such heroism is that of geology student Kostas Georgakis, who set himself ablaze in Genoa, Italy on 19 September 1970, in a protest against the Greek military junta of 1967-1974.
Culture
Corfu has a long musical, theatrical, and operatic tradition. The operas performed in Corfu were at par with their European counterparts. The phrase "applaudito in Corfu" (applauded in Corfu) was a measure of high accolade for an opera performed on the island. The Nobile Teatro di San Giacomo di Corfù was the first theatre and opera house of modern Greece and the place where the first Greek opera, Spyridon Xyndas' ''The Parliamentary Candidate'' (based on an exclusively Greek libretto) was performed.
Museums and libraries
 The most notable of Corfu's museums and libraries are located in the city; these include:
The most notable of Corfu's museums and libraries are located in the city; these include: *The Public Library of Corfu is located at the old English Barracks, in Palaio Frourio.
*The Reading Society of Corfu has an extensive library of old Corfu manuscripts and rare books.
*The Serbian Museum of Corfu (, ''Serbian House'') houses rare exhibits about the Serbian soldiers' tragic fate during the First World War. The remnants of the Serbian Army of about 150,000 soldiers together with their government in exile, found refuge and shelter in Corfu, following the collapse of the Serbian Front as a result of the Austro-Hungarian attack of 6 October 1915. Exhibits include photographs from the three years stay of the Serbians in Corfu, together with other exhibits such as uniforms, arms and ammunition of the Serbian army, Serbian regimental flags, religious artifacts, surgical tools and other decorations of the Kingdom of Serbia.
*Solomos Museum and the Corfiot Studies Society.
*The Public Library of Corfu is located at the old English Barracks, in Palaio Frourio.
*The Reading Society of Corfu has an extensive library of old Corfu manuscripts and rare books.
*The Serbian Museum of Corfu (, ''Serbian House'') houses rare exhibits about the Serbian soldiers' tragic fate during the First World War. The remnants of the Serbian Army of about 150,000 soldiers together with their government in exile, found refuge and shelter in Corfu, following the collapse of the Serbian Front as a result of the Austro-Hungarian attack of 6 October 1915. Exhibits include photographs from the three years stay of the Serbians in Corfu, together with other exhibits such as uniforms, arms and ammunition of the Serbian army, Serbian regimental flags, religious artifacts, surgical tools and other decorations of the Kingdom of Serbia.
*Solomos Museum and the Corfiot Studies Society.
Patron Saint Spyridon
Saint Spyridon the Thaumaturgy, Thaumaturgist (Miracle-worker, Θαυματουργός) is the patron saint (πολιούχος) of the city and the island. St. Spyridon is revered for the miracle of expelling the plague (πανώλη) from the island, among many other miracles attributed to him. It is believed by the faithful that on its way from the island the plague scratched one of the fortification stones of the old citadel to indicate its fury at being expelled; to St. Spyridon is also attributed the role of saving the island at the Siege of Corfu (1716), second great siege of Corfu in 1716.[ ''As far as his theatrical activities were concerned, the end of 1716 was a high point for Vivaldi. In November, he managed to have the Ospedale della Pietà perform his first great oratorio, Juditha Triumphans devicta Holofernis barbaric . This work was an allegorical description of the victory of the Venetians (the Christians) over the Turks (the barbarians) in August 1716.'']
Hence Spyridon is a popular first name for Greek males born on the island and/or to islanders.
Music
Musical history
While much of present-day Greece was under Ottoman rule, the Ionian Islands enjoyed a Golden Age in music and opera. Corfu was the capital city of a Venetian protectorate and it benefited from a unique musical and theatrical heritage. Then in the 19th century, as a Protectorate, British Protectorate, Corfu developed a musical heritage of its own and which constitutes the nucleus of modern Greek musical history. Until the early 18th century, musical life took place in city and village squares, with performances of straight or musical comedies – known as Momaries or Bobaries. From 1720, Corfu became the possessor of the first theatre in post-1452 Greece. It was the Teatro San Giacomo (now the City Hall) named after the nearby Roman Catholic cathedral (completed in 1691).
The island was also the center of the Ionian School (music), Ionian School of music, the musical production of a group of Heptanesian composers, whose heyday was from the early 19th century till approximately the 1950s. It was the first school of classical music in Greece and it was a heavy influence for the later Greek music scene, after the Greek War of Independence, independence.
The three Philharmonics
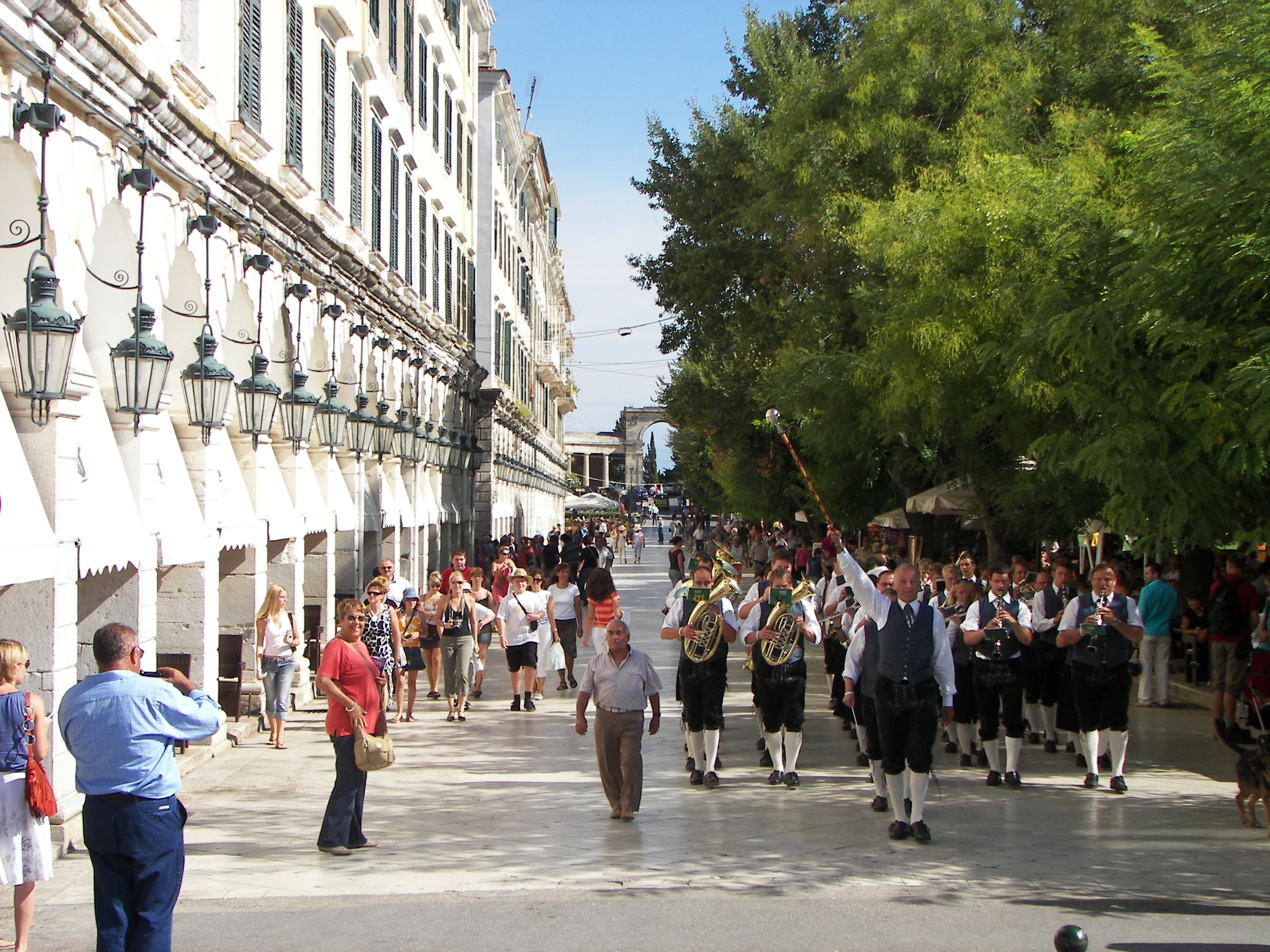 Corfu's Philharmonic Societies provide free instruction in music, and continue to attract young recruits. There are nineteen such marching wind bands throughout the island.
Corfu's Philharmonic Societies provide free instruction in music, and continue to attract young recruits. There are nineteen such marching wind bands throughout the island.
Corfu city is home to the three most prestigious bands – in order of seniority:
*the Philharmonic Society of Corfu use dark blue uniforms with dark red accents, and blue and red helmet plumes. It is usually called the ''Old Philharmonic'' or simply the ''Paliá'' ("Old"). Founded 12 September 1840.
*the Nikolaos Mantzaros, Mantzaros Philharmonic Society use blue uniforms with blue and white helmet plumes. It is commonly called the ''Néa'' ("New"). Founded 25 October 1890.
*the John Capodistria, Capodistria Philharmonic Union use bright red and black uniforms and plumes. It is commonly called the ''Cónte Capodístria'' or simply the ''Cónte'' ("Count"). It is the juniormost of the three (founded 18 April 1980).
All three maintain two major bands each, the main marching bands that can field up to 200 musicians on grand occasions, and the 60-strong student ''bandinas'' meant for lighter fare and on-the-job training.
The bands give regular summer weekend promenade concerts at the Spianada Green gazebo, "''pálko''", and have a prominent part in the yearly Holy Week ceremonies.
Ionian University music department
 Since the early 1990s a music department has been established at the
Since the early 1990s a music department has been established at the Ionian University
The Ionian University (IU; ) is a university located in the Ionian Islands (region), Ionian Islands, Greece. It is one of the newest institutions of Higher Education in Greece, created in 1984 pursuant to presidential order 83/84 ΦΕΚ 31 Α/2 ...
. Aside from its academic activities, concerts in Corfu and abroad, and musicological research in the field of Neo-Hellenic Music, the Department organizes an international music academy every summer, which gathers together both international students and professors specialising in Brass instrument, brass, strings (music), strings, singing, jazz and musicology.
Theatres and operatic tradition
Teatro di San Giacomo
Under Republic of Venice, Venetian rule, the Corfiotes developed a fervent appreciation of Italian opera, which was the real source of the extraordinary (given conditions in the mainland of Greece) musical development of the island during this era.[Birth of Greek opera Paper](_blank)
Kostas Kardamis "San Giacomo and Greek ottocento"XI Convegno Annuale di Società Italiana di Musicologia Lecce, 22–24 October 2004 The opera house of Corfu during the 18th and 19th centuries was the Nobile Teatro di San Giacomo di Corfù, Nobile Teatro di San Giacomo, named after the neighbouring Catholic cathedral; it was later converted into the City Hall.opera house
An opera house is a theater building used for performances of opera. Like many theaters, it usually includes a stage, an orchestra pit, audience seating, backstage facilities for costumes and building sets, as well as offices for the institut ...
of Greece in modern times and the place where the first Greek opera (based on an exclusively Greek libretto), Spyridon Xyndas' ''The Parliamentary Candidate'' was performed.[History of the theatre](_blank)
from Corfu cityhall
Municipal Theatre of Corfu
The Municipal Theatre of Corfu () was the main theatre and opera house
An opera house is a theater building used for performances of opera. Like many theaters, it usually includes a stage, an orchestra pit, audience seating, backstage facilities for costumes and building sets, as well as offices for the institut ...
in Corfu.[History of the municipal theatre](_blank)
from Corfu cityhall Opened in 1902, the theatre was the successor of Nobile Teatro di San Giacomo di Corfù which became the Corfu city hall. It was destroyed during a Luftwaffe aerial bombardment in 1943.
Festivities
Easter
On Good Friday, from the early afternoon onward, the bands of the three Philharmonic Societies, separated into squads, accompany the Epitaphios (liturgical), Epitaph processions of the city churches. Late in the afternoon, the squads come together to form one band in order to accompany the Epitaphios (liturgical), Epitaph procession of the cathedral, while the funeral marches that the bands play differ depending on the band; the Old Philharmonic play Albinoni's ''Adagio'', the Mantzaros play Giuseppe Verdi, Verdi's ''Marcia Funebre'' from Don Carlo, and the Capodistria play Frédéric Chopin, Chopin's ''Funeral March'' and Angelo Mariani (conductor), Mariani's ''Sventura''.
Ta Karnavalia
Another venerable Corfu tradition is known as the Carnival or ''Ta Karnavalia''. Venetian in origin, festivities include a parade featuring the main attraction of ''Karnavalos'', a rather grotesque figure with a large head and smiling face, leading a diverse procession of colourful Float (parade), floats.
Cultural depictions
In myth
*It is in Corfu that Heracles, just before embarking on his ten labours, slept with the naiad Melite (naiad), Melite; their son was Hyllus (not to be confused with Hyllus, the leader of the Heraclids, also a son of Heracles).Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
's Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; ) is one of two major epics of ancient Greek literature attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest surviving works of literature and remains popular with modern audiences. Like the ''Iliad'', the ''Odyssey'' is divi ...
, Kerkyra is the island of the Phaeacians
Scheria or Scherie (; or ), also known as Phaeacia () or Faiakia, was a region in Greek mythology, first mentioned in Homer's ''Odyssey'' as the home of the Phaeacians and the last destination of Odysseus in his 10-year journey before returning h ...
, (Phaiakes) wherein Odysseus (Ulysses) meets Nausicaa, Nausica, the daughter of King Alcinous, Alkinoos. The bay of Palaiokastritsa is considered to be the place where Odysseus disembarked.
In literature
*British naturalist Gerald Durrell wrote three books about his 1935–1940 childhood on Corfu: ''My Family and Other Animals''; ''Birds, Beasts and Relatives''; and ''The Garden of the Gods''. His brother, literary author Lawrence Durrell, also wrote a volume about Corfu: ''Prospero's Cell: A Guide to the Landscape and Manners of the Island of Corcyra (Corfu)''.
*Mary Stewart (novelist), Mary Stewart's novel ''This Rough Magic'' is set in Corfu.
*Prospero's island in Shakespeare's final play, ''The Tempest'', is often said to have been based on Corfu.
*Letitia Elizabeth Landon twice wrote of Corfu as an island paradise: the first poem appeared in ''Fisher's Drawing Room Scrap Book'' for 1835, to a picture by Thomas Allom; and the second in the same publication for 1838, to a picture by Charles Bentley (painter), Charles Bentley titled ''Corfu and Manduchio from Mount Olivet''. A third poem of hers, paired with and based on an engraving of a painting by Samuel Prout depicting a city scene in Corfu, was published in the ''Scrap Book'' for 1837.
*Humbert Humbert's first love, Annabel Leigh, is said to have died of typhus in Corfu in a scene of Vladimir Nabokov's ''Lolita''.
*Albert Cohen (novelist), Albert Cohen wrote three books which are partially or entirely set in Corfu. They are: ''Mangeclous'', ''Les Valeureux'', and ''Belle du Seigneur''. Cohen himself was born on the island.
*Voltaire references two monks from Corfu in Chapter XXVIII of Candide
In film
*Corfu was one of the main locations featured in the 1970 film ''The Executioner (1970 film), The Executioner'' starring George Peppard and Joan Collins.
*Corfu was one of the settings of ''The Burglars'', a 1971 film starring Jean-Paul Belmondo and Omar Sharif.
*''The Countess of Corfu'' ('), a 1972 film starring Rena Vlahopoulou and Alekos Alexandrakis, was filmed in Corfu.
*Much of the 1978 Billy Wilder film ''Fedora (1978 film), Fedora'' is set in Corfu and filmed on location.
*Some scenes of the 1978 film ''The Greek Tycoon'' starring Anthony Quinn and Jacqueline Bisset were filmed in Corfu. The film is a fictionalized account of the life of the Greek shipping magnate, Aristotle Onassis.
*The 1980 French comedy ''Jupiter's Thigh'' starring Annie Girardot and Philippe Noiret includes some scenes in Corfu Town.
*The 1981 James Bond movie ''For Your Eyes Only (film), For Your Eyes Only'' has a number of scenes filmed in Corfu. The most memorable scene of the film to be bound with the island is of the underwater ancient Greek temple, with a huge turtle swimming in front of the camera; a casino scene was also filmed at the Achilleion (Corfu), Achilleion.
In popular culture
 Corfu is one of the locations in the legend of Simon and Milo, where Simon falls in love temporarily. It is the setting of the 1998 song "Mediterranean Lady" by Prozzak. The island is alluded to several times in David Foster Wallace's 1987 novel, ''The Broom of the System''. Drake (entertainer), Drake mentions Corfu in a song. It is also mentioned in Brian Jacques' adventure novel, Voyage of Slaves.
Corfu is one of the locations in the legend of Simon and Milo, where Simon falls in love temporarily. It is the setting of the 1998 song "Mediterranean Lady" by Prozzak. The island is alluded to several times in David Foster Wallace's 1987 novel, ''The Broom of the System''. Drake (entertainer), Drake mentions Corfu in a song. It is also mentioned in Brian Jacques' adventure novel, Voyage of Slaves.
Tourism
Corfiotes have a long history of hospitality to foreign residents and visitors, typified in the 20th century by Gerald Durrell's childhood reminiscence ''My Family and Other Animals''. The north east coast has largely been developed by a few British holiday companies, with large expensive holiday villas. Package holiday resorts exist on the north, east and southwest coasts. Since 2021 there is an extra service added for visitors of the island calle
The Corfu Island Pass©
This official discount pass of Corfu gives everyone visiting Corfu a discount on sightseeing tours, rentals and cruises.
At the other end of the island, the southern resort of Kavos also provides tourist facilities.
St George South to the west boasts the largest sandy beach on the island coupled with a selection of all-inclusive package hotels and traditional corfiot villas and flats. The Korission lake nature reserve also provides a stopover for European birds migrating south.
Up until the early 20th century, it was mainly visited by the European royals and elites, including Emperor Wilhelm II of Germany and Empress Elisabeth of Austria; today it is also widely visited by middle class families (primarily from the UK, Scandinavia and Germany). With the advent of the jet airliner bringing these groups relatively affordable 'package holidays', Corfu was one of the primary destinations for this new form of mass tourism. It is still popular with the ultra-wealthy however, and in the island's northeast the homeowners include members of the Rothschild family and Russian oligarchs.
Transport
The island is linked by two highways: GR-24 in the northwest and GR-25 in the south.
*Greek National Road 24, Cen., NW, Corfu – Palaiokastritsa
*Greek National Road 25, Cen., S, SE, Corfu – Lefkimi
Corfu has ferry services both by traditional ferries to Gaios in the island of Paxoi and as far as Patras and both traditional ferries and advanced retractable airfoil, hydrodynamic-flow, high-speed ferries called "Flying Dolphins" to Igoumenitsa and Sarandë
Sarandë (; sq-definite, Saranda; ) is a List of cities and towns in Albania, city in the Republic of Albania and the seat of Sarandë Municipality. Geographically, the city is located on an open sea gulf of the Ionian Sea within the Mediterrane ...
in neighbouring Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
. The small port of Lefkimmi is also to be found at the southernmost tip of the island on Cape Kavos, offering a ferry boat, ferry service to the mainland.
The Ioannis Kapodistrias International Airport, named after Ioannis Kapodistrias
Count Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias (; February 1776 –27 September 1831), sometimes anglicized as John Capodistrias, was a Greek statesman who was one of the most distinguished politicians and diplomats of 19th-century Europe.
Kapodistrias's ...
, a Corfiot and European diplomat, and the first governor of the independent Greek state, is located around three kilometres south of Kerkyra, just half a kilometre north of Pontikonisi. The approach and landing, in a northeasterly direction, afford passengers aerial views of ''Pontikonisi'' and Vlaheraina Monastery, also taking in the hills of ''Kanoni'', as the runway employed for landing lies a few hundred metres from these local landmarks. The airport offers domestic flights from Olympic Airlines (OA 600, 602 and 606), and Aegean Airlines (A3 402, 404 and 406). Seaplanes, Air Sea Lines, a Greek seaplane operator, offers scheduled flights from Corfu to Paxoi, Lefkada, Ithaki, Kefalonia, Ioannina, Patras and Brindisi in Italy.
The buses to the main places on the island run about six times a day between the city and Glyfada, Sidari, Paleokastritsa, Roda and Acharavi, Lefkimmi, Lefkimmi and Piri. Other coaches drive up to twice a day to Athens and Thessaloniki. City buses run through the city to the Airport, Achilleion, Gouvia, Afra, Pelekas and some other places of interest.
The Diapontia Islands
The Diapontian Islands or Diapontia Islands (, also known as Othonoi Islands () are a Greek island group in the Ionian Sea. They are located northwest of Corfu. The main and the only inhabited islands of the archipelago are Othoni, Ereikoussa and ...
are accessible by boat with regular services from Corfu port and Agios Stefanos Avliotes and by ferry from Corfu city port.
Economy
 Corfu is mostly planted with olive groves and vineyards and has been producing olive oil and wine since antiquity. The main wine grape varietals found in Corfu are the indigenous white ''Kakotrýgēs'' and red ''Petrokóritho'', the Cefalonian white ''Robóla'', the Aegean Sea, Aegean ''Moscháto'' (white Muscat (grape and wine), muscat), the Achaean ''Mavrodáphnē'' and others.
Corfu is mostly planted with olive groves and vineyards and has been producing olive oil and wine since antiquity. The main wine grape varietals found in Corfu are the indigenous white ''Kakotrýgēs'' and red ''Petrokóritho'', the Cefalonian white ''Robóla'', the Aegean Sea, Aegean ''Moscháto'' (white Muscat (grape and wine), muscat), the Achaean ''Mavrodáphnē'' and others.kumquat
Kumquats ( ), or cumquats in Australian English, are a group of small, angiosperm, fruit-bearing trees in the family Rutaceae. Their taxonomy is disputed. They were previously classified as forming the now-historical genus ''Fortunella'' or plac ...
and bergamot oranges, which are extensively used in making spoon sweets and liqueurs. Corfu also produces local animal products, such as Corfiote ''graviéra'' (a variant of Gruyère (cheese), gruyere) and "''Corfu''" cheese (a variant of Grana (cheese), Grana); "Corfu butter" (''Boútyro Kerkýras''), an intensely flavored cooking and baking butter made of ewe's milk; and the ''noúmboulo'' salami made of pork and lard and flavored with orange peel, oregano, thyme and other aromatic herbs, which are also burned for smoking.
Local culinary specialties include ''sofrito'' (a veal rump roast of Venice, Venetian origin), ''pastitsáda'' (bucatini pasta served with diced veal cooked in a tomato sauce), ''bourdétto'' (cod cooked in a Capsicum, peppery sauce), ''mándoles'' (caramelized almonds), ''pastéli'' (honey bars made with sesame, almonds or pistachios), ''mandoláto'' (a "pastéli" made of crushed almonds, sugar, honey and vanilla), and ''tzitzibíra'', the local ginger beer, a remnant of the British era. There are three breweries in Corfu and one bed layers factory.
The island has again become an important Port#Port of call, port of call and has a considerable trade in olive oil.
International relations
Twin towns – sister cities
* Asha, Cyprus, Asha, Cyprus
* Bari, Italy
* Belgrade, Serbia
* Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, Bethlehem, United States
* Famagusta, Cyprus
* Ioannina, Greece
* Kruševac, Serbia
* Meißen, Germany (1996)Sarandë
Sarandë (; sq-definite, Saranda; ) is a List of cities and towns in Albania, city in the Republic of Albania and the seat of Sarandë Municipality. Geographically, the city is located on an open sea gulf of the Ionian Sea within the Mediterrane ...
, Albania
* Tai'an, China
* Tremetousia, Cyprus
* Troisdorf, Germany (1996)[
* Vathy, Samos, Vathy, Greece
]
Notable people
Ancient and medieval
*Ptolichus (5th century BCE), ancient Greek sculptor
*Peithias (5th century BCE), leader during the Peleponnesian War
*Philiscus of Corcyra, Philiscus ( 3rd century BCE), tragic poet, born in Corfu
*Philomena (291–304 CE), Virgin (title)#Virgin martyrs, virgin martyr and saint
*Arsenius of Corfu, Arsenius (), bishop and saint
Modern
 *Princess Alexia of Greece and Denmark, born in Corfu
*Panos Aravantinos, artist, born in Corfu
*Marie Aspioti, magazine publisher and cultural figure who influenced the literary and cultural life of post-war Corfu
*Felice Beato, 19th-century photographer, born in Corfu
*Giacomo Casanova, lived on the island as an officer of the Venetian army
*Tilemachos Chytiris, Greek politician, Member of the Hellenic Parliament
*Albert Cohen (novelist), Albert Cohen, Swiss-French author, born in Corfu
*Spiro Çomora, Albanian playwright, born in Corfu
*Haim Corfu, Israeli politician, was born in Jerusalem, his family name testifying to his family's origin
*Nikos Dendias, Greek lawyer and politician, has been Member of the Hellenic Parliament and has served as Minister for National Defence (Greece), Minister for National Defence and Minister of Foreign Affairs (Greece), Minister for Foreign Affairs
*Maria Desylla-Kapodistria, relative of Ioannis Kapodistrias, mayor of Corfu and first female mayor of Greece
*Princess Alexia of Greece and Denmark, born in Corfu
*Panos Aravantinos, artist, born in Corfu
*Marie Aspioti, magazine publisher and cultural figure who influenced the literary and cultural life of post-war Corfu
*Felice Beato, 19th-century photographer, born in Corfu
*Giacomo Casanova, lived on the island as an officer of the Venetian army
*Tilemachos Chytiris, Greek politician, Member of the Hellenic Parliament
*Albert Cohen (novelist), Albert Cohen, Swiss-French author, born in Corfu
*Spiro Çomora, Albanian playwright, born in Corfu
*Haim Corfu, Israeli politician, was born in Jerusalem, his family name testifying to his family's origin
*Nikos Dendias, Greek lawyer and politician, has been Member of the Hellenic Parliament and has served as Minister for National Defence (Greece), Minister for National Defence and Minister of Foreign Affairs (Greece), Minister for Foreign Affairs
*Maria Desylla-Kapodistria, relative of Ioannis Kapodistrias, mayor of Corfu and first female mayor of GreeceIoannis Kapodistrias
Count Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias (; February 1776 –27 September 1831), sometimes anglicized as John Capodistrias, was a Greek statesman who was one of the most distinguished politicians and diplomats of 19th-century Europe.
Kapodistrias's ...
, first Governor of Greece, born in Corfu
*Giorgos Katsaros, noted Greek musician and songwriter
*Nikos Kourkoulos, Greek theatrical and film actor
*Spyridon Lambros, history professor and former Prime Minister of Greece, born in Corfu
*Petros Lantzas, Greek rebel, spy and privateer
*Vicky Leandros, international pop star, born in Corfu
*Andreas Mandelis, expert on photonics, member of the Canadian Academy of Engineering, awarded the 2014 Killam Prize
*Nikolaos Mantzaros, Greek composer, born in Corfu
*Aristedes Metallinos, sculptor
*George Metallinos, Greek Orthodox theologian, priest (protoiereus, protopresbyter), historian, author and professor
*Margarita Miniati (1821–1897), Greek scholar and writer, born in Corfu
*Andreas Mustoxydis, Andreas Moustoxydis, historian and philologist, born in Corfu
*Rena Pagrati, Greek film, television and theatre actress
*Vangelis Petsalis, Greek classical musician and composer, born in Corfu
*Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh (1921–2021), born Prince Philippos of Greece and Denmark, in Corfu
*Spiros Pizanis, famous Greek painter
*, first publisher of Dionysios Solomos, born in Corfu
*Henry Ponsonby (1825–1895), Private Secretary to the Sovereign, private secretary to Queen Victoria
*Alfredo Ragona (born 1922), Greek footballer
*Georgios Rallis (1918–2006), prime minister, son of Ioannis Rallis and Zaira, daughter of George Theotoki
*Alexander Rossi (artist), Alexander Rossi, artist, born in Corfu
*Sakis Rouvas, Greek singer and athlete, born in Corfu
*Spyridon Samaras, Greek composer, born in Corfu
*Georgios Samartzis, Greek painter and musician, associated with the Heptanese School of painting
*Johann Matthias von der Schulenburg, Austrian general and aristocrat, successfully defended the island against the Ottoman Turks during the siege of 1716 as leader of the Venetian forces in Corfu
*Edith Somerville, Edith Œnone Somerville (1858-1949), Irish novelist, born in Corfu
*Nikolaos Sophianos, was a Greek humanist and cartographer, born in Corfu
*Carl Ludwig Sprenger, German botanist, lived in Corfu
*Theodore Stephanides, Greek poet, author, doctor and naturalist, born in Corfu
*Anthony Stevens (Jungian analyst), Anthony Stevens, Jungian analyst, lived in Corfu
*Xenophon Stratigos, Greek military officer
*Georgios Theotokis, former Prime Minister of Greece, born in Corfu
*Ioannis Theotokis, Greek politician, born in Corfu
*Nikephoros Theotokis (1732–1800), Greek educator and Russian archbishop, born in Corfu
*Nikolaos Ventouras, Greek artist and engraver
*Rena Vlahopoulou, Greek actress and singer, born in Corfu
*Stylianos Vlasopoulos, scion of the aristocratic Vlassopoulos dynasty of Corfu
*Eugenios Voulgaris, Greek scholar, born in Corfu
*Sotirios Voulgaris (1857–1932), silversmith and businessman, founder of the Bulgari jewellery store that later became the luxury fashion company Bulgari
*Petros Vrailas Armenis, Greek philosopher, politician, diplomat and former owner of the predecessor of the Achilleion (Corfu), Achilleion palace, born in Corfu
*Wilhelm II of Germany, bought Achilleion after Sissi's death
*Spyridon Xyndas (1812–1896), Greek composer and musician, born in Corfu
Gallery
File:Cape Fonias, Corfu 3.JPG, Cape Drastis at the northwest tip of Corfu island
File:Corfu Chalikiopoulou Lagoon R01.jpg, Chalikiopoulou Lagoon (or Lake Chalikiopoulou), south of Corfu town
File:Venetian Shipyard in Gouvia, Corfu.jpg, Venetian arsenal, Gouvia
File:Corfu Annunziata R02.jpg, Old tower, Corfu town
File:Corfu panorama bgiu.jpg, Panorama of the Old Town of Corfu
File:Corfu venetian quarter overview bgiu.jpg, Venetian quarter, Corfu town
File:Narrow street corfu.jpg, ''Odós Ipeirou'' in Corfu old town
File:Corfu Evgeniou Voulgareos R01.jpg, Historic building in ''Evgeniou Voulgareos'' street
File:St. George's Church.jpg, View of St. George's Temple at the Old Fortress, Corfu, Old Fortress
File:Corfu Mon Repos R01.jpg, Mon Repos, Corfu, Mon Repos
File:Corfu Achilleion R11.jpg, Gardens of Achilleion (Corfu), Achilleion
File:Achilleion Terrace Corfu(1).jpg, Statues at the Achilleion (Corfu), Achilleion terrace
File:Villa Rossa in Corfu.jpg, ''Villa Rossa'', landmark of Corfu city
File:Corfu Pelekas R02.jpg, Pelekas village
File:Kaiser's Bridge in Corfu ca. 1918.jpg, Kaiser's Bridge in Corfu c. 1918
File:Krf i Starata tvrdina.jpg, Workers on Corfu. The image shows the Old Fortress. First World War
See also
*Aspioti-ELKA
*Cuisine of the Ionian islands
*Heptanese School (painting)
*Hercules (vehicles)
*Korčula
*Music of the Heptanese
*Temple of Hera, Mon Repos
Explanatory notes
Citations
General and cited sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*Siebert, Diana: ''Aller Herren Außenposten. Korfu von 1797 bis 1944''. Köln, 2016
External links
Municipality of Corfu
(official site)
Corfu Butterfly ConservationCorfugo WebsiteCorfu island pass
(official site)
{{Authority control
Corfu,
Corfu (regional unit)
Corinthian colonies
Euboean colonies
Islands of Greece
Jewish communities in Italy
Places in Greek mythology
Mediterranean port cities and towns in Greece
Populated places in Corfu (regional unit)
Provinces of Greece
Septinsular Republic
Territories of the Republic of Venice

 The second range culminates in the mountain of Santi Jeca, or Santa Decca, as it is called by misinterpretation of the Greek designation ''Άγιοι Δέκα'' (Hagioi Deka), or the Ten Saints. The whole island, composed as it is of various limestone formations, presents great diversity of surface. Beaches are found in Agios Gordis, the Korission Lagoon, Agios Georgios, Marathia, Kassiopi, Sidari, Palaiokastritsa and many others. Corfu is located near the
The second range culminates in the mountain of Santi Jeca, or Santa Decca, as it is called by misinterpretation of the Greek designation ''Άγιοι Δέκα'' (Hagioi Deka), or the Ten Saints. The whole island, composed as it is of various limestone formations, presents great diversity of surface. Beaches are found in Agios Gordis, the Korission Lagoon, Agios Georgios, Marathia, Kassiopi, Sidari, Palaiokastritsa and many others. Corfu is located near the  The
The  Christianity arrived in Corfu early; two disciples of
Christianity arrived in Corfu early; two disciples of 
 From medieval times and into the 17th century, the island was recognised as a bulwark of the European States against the
From medieval times and into the 17th century, the island was recognised as a bulwark of the European States against the  The Siege of Corfu (1716), second great siege of Corfu took place in 1716, during the last Ottoman–Venetian War (1714–18). After the conquest of the Peloponnese in 1715, the Ottoman fleet appeared in Buthrotum opposite Corfu. On 8 July the Ottoman fleet, carrying 33,000 men, sailed to Corfu from Buthrotum and established a beachhead at Ipsos. The same day, the Venetian fleet encountered the Ottoman fleet off the Corfu Channel and defeated it in the ensuing naval battle. On 19 July, after taking a few outlying forts, the Ottoman army reached the hills around the city of Corfu and laid siege to it. Despite repeated assaults and heavy fighting, the Ottomans were unable to breach the defences and were forced to raise the siege after 22 days. The 5,000 Venetians and foreign mercenaries, together with 3,000 Corfiotes, under the leadership of Count Johann Matthias von der Schulenburg, von der Schulenburg who commanded the defence of the island, were victorious once more. The success was owed in no small part to the extensive fortifications, where Venetian castle engineering had proven itself once again against considerable odds. The repulse of the Ottomans was widely celebrated in Europe, Corfu being seen as a bastion of western culture, Western civilization against the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman tide. Today, however, this role is often relatively unknown or ignored, but was celebrated in ''Juditha triumphans'' by the Venetian composer Antonio Vivaldi.
The Siege of Corfu (1716), second great siege of Corfu took place in 1716, during the last Ottoman–Venetian War (1714–18). After the conquest of the Peloponnese in 1715, the Ottoman fleet appeared in Buthrotum opposite Corfu. On 8 July the Ottoman fleet, carrying 33,000 men, sailed to Corfu from Buthrotum and established a beachhead at Ipsos. The same day, the Venetian fleet encountered the Ottoman fleet off the Corfu Channel and defeated it in the ensuing naval battle. On 19 July, after taking a few outlying forts, the Ottoman army reached the hills around the city of Corfu and laid siege to it. Despite repeated assaults and heavy fighting, the Ottomans were unable to breach the defences and were forced to raise the siege after 22 days. The 5,000 Venetians and foreign mercenaries, together with 3,000 Corfiotes, under the leadership of Count Johann Matthias von der Schulenburg, von der Schulenburg who commanded the defence of the island, were victorious once more. The success was owed in no small part to the extensive fortifications, where Venetian castle engineering had proven itself once again against considerable odds. The repulse of the Ottomans was widely celebrated in Europe, Corfu being seen as a bastion of western culture, Western civilization against the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman tide. Today, however, this role is often relatively unknown or ignored, but was celebrated in ''Juditha triumphans'' by the Venetian composer Antonio Vivaldi.
 By the 1797 Treaty of Campo Formio, Corfu was ceded to the French Revolution, French, who occupied it for two years as the ''French departments of Greece, département'' of Corcyre, until they were Siege of Corfu (1798–1799), expelled by a joint Russian Empire, Russian-Ottoman squadron under Admiral Ushakov. For a short time it became the capital of a self-governing federation of the Septinsular Republic, Heptanesos ("Seven Islands"), under Ottoman suzerainty; in 1807 after the Treaty of Tilsit its faction-ridden government was again replaced by a French administration under governor François-Xavier Donzelot, and in 1809 it was besieged in vain by a Royal Navy, British Royal Navy fleet, which had captured all the other Ionian islands.
Following the final defeat of Napoleon at the Battle of Waterloo, the Ionian Islands became a British protectorate, protectorate of the United Kingdom by the Treaty of Paris (1815), Treaty of Paris of 5 November 1815 as the
By the 1797 Treaty of Campo Formio, Corfu was ceded to the French Revolution, French, who occupied it for two years as the ''French departments of Greece, département'' of Corcyre, until they were Siege of Corfu (1798–1799), expelled by a joint Russian Empire, Russian-Ottoman squadron under Admiral Ushakov. For a short time it became the capital of a self-governing federation of the Septinsular Republic, Heptanesos ("Seven Islands"), under Ottoman suzerainty; in 1807 after the Treaty of Tilsit its faction-ridden government was again replaced by a French administration under governor François-Xavier Donzelot, and in 1809 it was besieged in vain by a Royal Navy, British Royal Navy fleet, which had captured all the other Ionian islands.
Following the final defeat of Napoleon at the Battle of Waterloo, the Ionian Islands became a British protectorate, protectorate of the United Kingdom by the Treaty of Paris (1815), Treaty of Paris of 5 November 1815 as the  This is a list of the British High Commissioners of the Ionian Islands; (as well as the transitional Greek Governor, appointed a year prior to Enosis (Union) with Greece in 1864).:ca:Història de Corfú
*Sir James Campbell, 1st Baronet, Sir James Campbell 1814–1816
*Sir Thomas Maitland (1759–1824) 1815–1823
*Frederick Adam, Sir Frederick Adam (1781–1853) 1823–1832
*Alexander Woodford, Sir Alexander Woodford (1782–1870) 1832
*George Nugent-Grenville, 2nd Baron Nugent (1788–1850) 1832–1835
*Howard Douglas (1776–1861) 1835–1840
*James Alexander Stewart-Mackenzie (1784–1843) 1840–1843
*John Colborne, 1st Baron Seaton (1778–1863) 1843–1849
*Henry George Ward, Sir Henry George Ward (1797–1860) 1849–1855
*John Young, 1st Baron Lisgar, Sir John Young (1807–1876) 1855–1859
*William Ewart Gladstone (1809–1898) 1859
*Henry Knight Storks, Sir Henry Knight Storks (1811–1874) 1859–1863
*Count Dimitrios Nikolaou Karousos, President of the United States of the Ionian Islands, Ionian Parliament (1799–1873) 1863–1864
This is a list of the British High Commissioners of the Ionian Islands; (as well as the transitional Greek Governor, appointed a year prior to Enosis (Union) with Greece in 1864).:ca:Història de Corfú
*Sir James Campbell, 1st Baronet, Sir James Campbell 1814–1816
*Sir Thomas Maitland (1759–1824) 1815–1823
*Frederick Adam, Sir Frederick Adam (1781–1853) 1823–1832
*Alexander Woodford, Sir Alexander Woodford (1782–1870) 1832
*George Nugent-Grenville, 2nd Baron Nugent (1788–1850) 1832–1835
*Howard Douglas (1776–1861) 1835–1840
*James Alexander Stewart-Mackenzie (1784–1843) 1840–1843
*John Colborne, 1st Baron Seaton (1778–1863) 1843–1849
*Henry George Ward, Sir Henry George Ward (1797–1860) 1849–1855
*John Young, 1st Baron Lisgar, Sir John Young (1807–1876) 1855–1859
*William Ewart Gladstone (1809–1898) 1859
*Henry Knight Storks, Sir Henry Knight Storks (1811–1874) 1859–1863
*Count Dimitrios Nikolaou Karousos, President of the United States of the Ionian Islands, Ionian Parliament (1799–1873) 1863–1864
 During the First World War, the island served as a refuge for the Serbian army that retreated there on Allies of World War I, Allied forces' ships from a homeland occupied by the Austrians, Germans and Bulgarians. During their stay, a large portion of Serbian soldiers died from exhaustion, food shortage, and various diseases. Most of their remains were buried at sea near the island of Vido, a small island at the mouth of Corfu port, and a monument of thanks to the Greek nation has been erected at Vido by the grateful Serbs; consequently, the waters around Vido Island are known by the Serbian people as the Blue Tomb (in Serbian, Плава Гробница, Plava Grobnica), after a poem written by Milutin Bojić following World War I.
During the First World War, the island served as a refuge for the Serbian army that retreated there on Allies of World War I, Allied forces' ships from a homeland occupied by the Austrians, Germans and Bulgarians. During their stay, a large portion of Serbian soldiers died from exhaustion, food shortage, and various diseases. Most of their remains were buried at sea near the island of Vido, a small island at the mouth of Corfu port, and a monument of thanks to the Greek nation has been erected at Vido by the grateful Serbs; consequently, the waters around Vido Island are known by the Serbian people as the Blue Tomb (in Serbian, Плава Гробница, Plava Grobnica), after a poem written by Milutin Bojić following World War I.
 During the Greco-Italian War, Corfu was occupied by the Italians in April 1941. They administered Corfu and the Ionian islands as a separate entity from Greece until September 1943, following Benito Mussolini's orders of fulfilling Italian Italia irredenta, Irredentism and making Corfu part of the Kingdom of Italy. During the Second World War the 10th Mechanized Infantry Brigade (Greece), 10th Infantry Regiment of the Hellenic Army, Greek Army, composed mainly of Corfiot soldiers, was assigned the task of defending Corfu. The regiment took part in ''Operation Latzides'', which was an unsuccessful attempt to stem the forces of the Italians. After Greece's surrender to the Axis, the island came under Italian control and occupation. On the first Sunday of November 1941, high school students from all over Corfu took part in student protests against the occupying Italian army; these student protests of the island were among the first acts of overt popular Greek Resistance, Resistance in occupied Greece and a rare phenomenon even by wartime European standards. Subsequently, a considerable number of Corfiots escaped to Epirus (region), Epirus in mainland Greece and enlisted as Partisan (military), partisans in Ethnikos Laikos Apeleftherotikos Stratos, ELAS and Ethnikos Dimokratikos Ellinikos Syndesmos, EDES, in order to join the resistance movement gathering in the mainland.
During the Greco-Italian War, Corfu was occupied by the Italians in April 1941. They administered Corfu and the Ionian islands as a separate entity from Greece until September 1943, following Benito Mussolini's orders of fulfilling Italian Italia irredenta, Irredentism and making Corfu part of the Kingdom of Italy. During the Second World War the 10th Mechanized Infantry Brigade (Greece), 10th Infantry Regiment of the Hellenic Army, Greek Army, composed mainly of Corfiot soldiers, was assigned the task of defending Corfu. The regiment took part in ''Operation Latzides'', which was an unsuccessful attempt to stem the forces of the Italians. After Greece's surrender to the Axis, the island came under Italian control and occupation. On the first Sunday of November 1941, high school students from all over Corfu took part in student protests against the occupying Italian army; these student protests of the island were among the first acts of overt popular Greek Resistance, Resistance in occupied Greece and a rare phenomenon even by wartime European standards. Subsequently, a considerable number of Corfiots escaped to Epirus (region), Epirus in mainland Greece and enlisted as Partisan (military), partisans in Ethnikos Laikos Apeleftherotikos Stratos, ELAS and Ethnikos Dimokratikos Ellinikos Syndesmos, EDES, in order to join the resistance movement gathering in the mainland.
 Corfu was liberated by British Armed Forces, British troops, specifically the 40th Royal Marine Commando, which landed in Corfu on 14 October 1944, as the Germans were evacuating Greece. The Royal Navy swept the Corfu Channel for mines in 1944 and 1945, and found it to be free of mines. A large minefield was laid there shortly afterwards by the newly communist Albania and gave rise to the Corfu Channel Incident. This incident led to the The Corfu Channel Case (United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland v. People's Republic of Albania), Corfu Channel Case, where the United Kingdom opened a case against the People's Republic of Albania at the International Court of Justice.
Corfu was liberated by British Armed Forces, British troops, specifically the 40th Royal Marine Commando, which landed in Corfu on 14 October 1944, as the Germans were evacuating Greece. The Royal Navy swept the Corfu Channel for mines in 1944 and 1945, and found it to be free of mines. A large minefield was laid there shortly afterwards by the newly communist Albania and gave rise to the Corfu Channel Incident. This incident led to the The Corfu Channel Case (United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland v. People's Republic of Albania), Corfu Channel Case, where the United Kingdom opened a case against the People's Republic of Albania at the International Court of Justice.
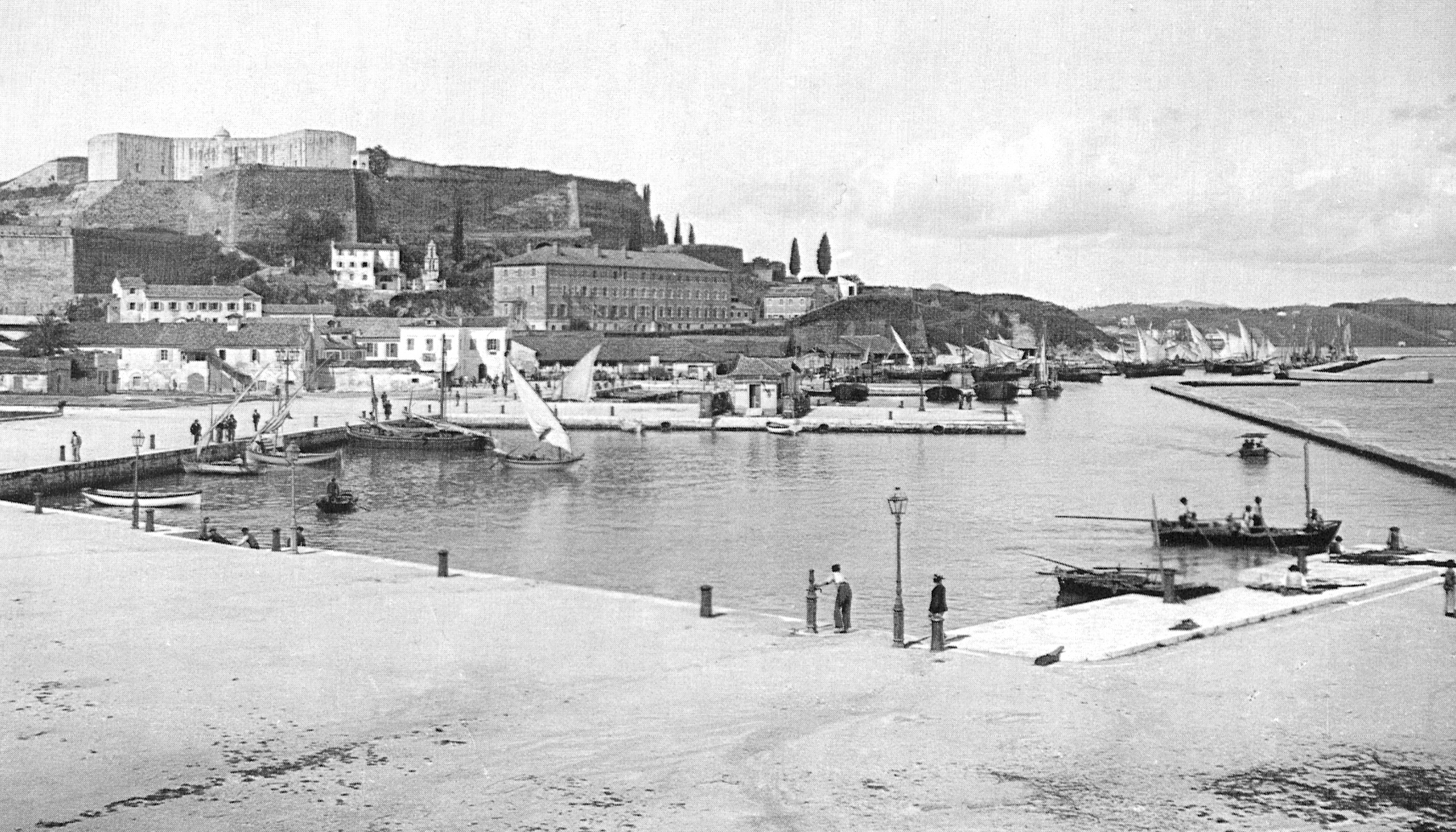
 Corfu's urban architecture influence derives from Venice, reflecting the fact that from 1386 to 1797 the island was ruled by the Venetians. The architecture of the Old Town of Corfu along with its narrow streets, the , has clear Venetian influence and is amongst the List of World Heritage Sites in Greece, World Heritage Sites in Greece. Other notable Venetian-era buildings include the Nobile Teatro di San Giacomo di Corfù, the first Greek opera house, and ''Liston'', a multi-level commercial and residential building, with an arched colonnade at ground level, lined with cafes and restaurants on its east side, and restaurants and other stores on its west side. Liston's main thoroughfare is often the site of parades and other mass gatherings. Liston is on the edge of the ''Spianada'' (Esplanade), the vast main plaza and park which incorporates a cricket field, a pavilion, and Maitland's monument. Also notable are the Old and New forts, the recently restored Palace of Sts. Michael and George, formerly the residence of the British colonial governor and the seat of the Ionian Senate, and the summer Palace of ''Mon Repos, Corfu, Mon Repos'', formerly the property of the Greek royal family and birthplace of the Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh. The Park of Mon Repos is built on part of the Palaiopolis of Kerkyra, where excavations were conducted by the Greek Archaeological Service in collaboration with academics and universities internationally. Examples of the finds can be found in the Museum of the Palace of Mon Repos and at the Archaeological Museum of Corfu.R. Winkes (editor), Kerkyra. Artifacts from the Palaiopolis, Providence 2004.
Corfu's urban architecture influence derives from Venice, reflecting the fact that from 1386 to 1797 the island was ruled by the Venetians. The architecture of the Old Town of Corfu along with its narrow streets, the , has clear Venetian influence and is amongst the List of World Heritage Sites in Greece, World Heritage Sites in Greece. Other notable Venetian-era buildings include the Nobile Teatro di San Giacomo di Corfù, the first Greek opera house, and ''Liston'', a multi-level commercial and residential building, with an arched colonnade at ground level, lined with cafes and restaurants on its east side, and restaurants and other stores on its west side. Liston's main thoroughfare is often the site of parades and other mass gatherings. Liston is on the edge of the ''Spianada'' (Esplanade), the vast main plaza and park which incorporates a cricket field, a pavilion, and Maitland's monument. Also notable are the Old and New forts, the recently restored Palace of Sts. Michael and George, formerly the residence of the British colonial governor and the seat of the Ionian Senate, and the summer Palace of ''Mon Repos, Corfu, Mon Repos'', formerly the property of the Greek royal family and birthplace of the Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh. The Park of Mon Repos is built on part of the Palaiopolis of Kerkyra, where excavations were conducted by the Greek Archaeological Service in collaboration with academics and universities internationally. Examples of the finds can be found in the Museum of the Palace of Mon Repos and at the Archaeological Museum of Corfu.R. Winkes (editor), Kerkyra. Artifacts from the Palaiopolis, Providence 2004.
 The Imperial gardens on the hill look over the surrounding green hills and valleys and the
The Imperial gardens on the hill look over the surrounding green hills and valleys and the  Kardaki Temple is an Archaic Greece, Archaic Doric order, Doric Greek temple, temple in Corfu, Greece, built around 500 BC in the ancient city of Korkyra (or Corcyra), in what is known today as the location Kardaki in the hill of Analipsi in Corfu. The temple features several architectural peculiarities that point to a Doric origin. The temple at Kardaki is unusual because it has no frieze, following perhaps architectural tendencies of Sicilian temples.
It is considered to be the only Greek temple of Doric architecture that does not have a frieze. The spacing of the temple columns has been described as "abnormally wide". The temple also lacked both porch and adyton, and the lack of a triglyph and metope frieze may be indicative of Ionians, Ionian influence. The temple at Kardaki is considered an important and to a certain degree mysterious topic on the subject of early ancient Greek architecture. Its association with the worship of Apollo or
Kardaki Temple is an Archaic Greece, Archaic Doric order, Doric Greek temple, temple in Corfu, Greece, built around 500 BC in the ancient city of Korkyra (or Corcyra), in what is known today as the location Kardaki in the hill of Analipsi in Corfu. The temple features several architectural peculiarities that point to a Doric origin. The temple at Kardaki is unusual because it has no frieze, following perhaps architectural tendencies of Sicilian temples.
It is considered to be the only Greek temple of Doric architecture that does not have a frieze. The spacing of the temple columns has been described as "abnormally wide". The temple also lacked both porch and adyton, and the lack of a triglyph and metope frieze may be indicative of Ionians, Ionian influence. The temple at Kardaki is considered an important and to a certain degree mysterious topic on the subject of early ancient Greek architecture. Its association with the worship of Apollo or  The Temple of Artemis is an Archaic Greece, Archaic Greek temple in Corfu, built in around 580 BC in the ancient city of Korkyra (or Corcyra), in what is known today as the suburb of Garitsa. The temple was dedicated to Artemis. It is known as the first Doric order, Doric temple exclusively built with limestone, stone. It is also considered the first building to have incorporated all of the elements of the Doric order, Doric architectural style.: "The island of Corfu, to the northwest of present-day Greece, off the coast of Albania, was an early colony of the city of Corinth and was under Corinthian control when its Temple of Artemis was constructed. A milestone in Greek architecture, this was the first building that was truly Doric. Many if not all of its Doric characteristics had appeared in earlier structures but here they were used for the first time as an ensemble." Very few Greek temple reliefs from the Archaic period have survived, and the large fragments of the group from the pediment are the earliest significant survivals.
The temple was a peripteral–styled building with a pseudodipteral configuration. Its perimeter was rectangular, with width of and length with an eastward orientation so that light could enter the interior of the temple at sunrise. It was one of the largest temples of its time..
The Metope (architecture), metope of the temple was probably decorated, since remnants of reliefs featuring Achilles and Memnon (mythology), Memnon were found in the ancient ruins.. The temple has been described as a milestone of Ancient Greek architecture and one of 150 masterpieces of Western world, Western architecture. The Corfu temple architecture may have influenced the design of an archaic sanctuary structure found at the Sant'Omobono Area, Sant'Omobono archaeological site in Rome, dating from the time of the Etruscans, which incorporates similar design elements.. If still in use by the 4th-century, the temple would have been closed during the persecution of pagans in the late Roman Empire, when the Christian Emperors issued edicts prohibiting non-Christian worship. Kaiser Wilhelm II, while vacationing at his summer palace of Achilleion in Corfu and while Europe was preparing for war, was involved in excavations at the site of the ancient temple.
The Temple of Artemis is an Archaic Greece, Archaic Greek temple in Corfu, built in around 580 BC in the ancient city of Korkyra (or Corcyra), in what is known today as the suburb of Garitsa. The temple was dedicated to Artemis. It is known as the first Doric order, Doric temple exclusively built with limestone, stone. It is also considered the first building to have incorporated all of the elements of the Doric order, Doric architectural style.: "The island of Corfu, to the northwest of present-day Greece, off the coast of Albania, was an early colony of the city of Corinth and was under Corinthian control when its Temple of Artemis was constructed. A milestone in Greek architecture, this was the first building that was truly Doric. Many if not all of its Doric characteristics had appeared in earlier structures but here they were used for the first time as an ensemble." Very few Greek temple reliefs from the Archaic period have survived, and the large fragments of the group from the pediment are the earliest significant survivals.
The temple was a peripteral–styled building with a pseudodipteral configuration. Its perimeter was rectangular, with width of and length with an eastward orientation so that light could enter the interior of the temple at sunrise. It was one of the largest temples of its time..
The Metope (architecture), metope of the temple was probably decorated, since remnants of reliefs featuring Achilles and Memnon (mythology), Memnon were found in the ancient ruins.. The temple has been described as a milestone of Ancient Greek architecture and one of 150 masterpieces of Western world, Western architecture. The Corfu temple architecture may have influenced the design of an archaic sanctuary structure found at the Sant'Omobono Area, Sant'Omobono archaeological site in Rome, dating from the time of the Etruscans, which incorporates similar design elements.. If still in use by the 4th-century, the temple would have been closed during the persecution of pagans in the late Roman Empire, when the Christian Emperors issued edicts prohibiting non-Christian worship. Kaiser Wilhelm II, while vacationing at his summer palace of Achilleion in Corfu and while Europe was preparing for war, was involved in excavations at the site of the ancient temple.
 The Tomb of Menecrates or Monument of Menecrates is an Archaic Greece, Archaic cenotaph in Corfu, built around 600 BC in the ancient city of Korkyra (or Corcyra). The tomb and the funerary sculpture of a lion were discovered in 1843 during demolition works by the British Army who were demolishing a Venetian fortress in the location of Garitsa hill in Corfu. The tomb is dated to the 6th century BC.
The lion is dated at the end of the 7th century BC and it is one of the earliest funerary lions ever found. The tomb and the lion were found in an area which was part of the necropolis of ancient Korkyra, which was discovered by the British army at the time. According to an Ancient Greek inscription found on the grave, the tomb was a monument built by the ancient Korkyreans in honour of their proxenos (ambassador) Menecrates, son of Tlasios, from Oeiantheia. Menecrates was the ambassador of ancient Korkyra to Oeiantheia, modern day Galaxidi or Ozolian Locris, and he was lost at sea. In the inscription it is also mentioned that the brother of Menecrates, Praximenes, had arrived from Oeiantheia to assist the people of Korkyra in building the monument to his brother.
The Tomb of Menecrates or Monument of Menecrates is an Archaic Greece, Archaic cenotaph in Corfu, built around 600 BC in the ancient city of Korkyra (or Corcyra). The tomb and the funerary sculpture of a lion were discovered in 1843 during demolition works by the British Army who were demolishing a Venetian fortress in the location of Garitsa hill in Corfu. The tomb is dated to the 6th century BC.
The lion is dated at the end of the 7th century BC and it is one of the earliest funerary lions ever found. The tomb and the lion were found in an area which was part of the necropolis of ancient Korkyra, which was discovered by the British army at the time. According to an Ancient Greek inscription found on the grave, the tomb was a monument built by the ancient Korkyreans in honour of their proxenos (ambassador) Menecrates, son of Tlasios, from Oeiantheia. Menecrates was the ambassador of ancient Korkyra to Oeiantheia, modern day Galaxidi or Ozolian Locris, and he was lost at sea. In the inscription it is also mentioned that the brother of Menecrates, Praximenes, had arrived from Oeiantheia to assist the people of Korkyra in building the monument to his brother.
 The ''old citadel'' (in Greek ''Palaio Frourio'' (Παλαιό Φρούριο) is an old Venetian fortress built on an artificial islet with fortifications surrounding its entire perimeter, although some sections, particularly on the east side, are slowly being eroded and falling into the sea. Nonetheless, the interior has been restored and is in use for cultural events, such as concerts (συναυλίες) and Sound and Light Productions (Ηχος και Φως), when historical events are recreated using sound and light special effects. These events take place amidst the ancient fortifications, with the Ionian Sea in the background. The central high point of the citadel rises like a giant natural obelisk complete with a military observation post at the top, with a giant #Early history, cross at its apex; at the foot of the observatory lies St. George's church, in a classical style punctuated by six Doric Order, Doric columns, as opposed to the Hagia Sophia, Byzantine architectural style of the greater part of Greek Orthodox churches.
The ''old citadel'' (in Greek ''Palaio Frourio'' (Παλαιό Φρούριο) is an old Venetian fortress built on an artificial islet with fortifications surrounding its entire perimeter, although some sections, particularly on the east side, are slowly being eroded and falling into the sea. Nonetheless, the interior has been restored and is in use for cultural events, such as concerts (συναυλίες) and Sound and Light Productions (Ηχος και Φως), when historical events are recreated using sound and light special effects. These events take place amidst the ancient fortifications, with the Ionian Sea in the background. The central high point of the citadel rises like a giant natural obelisk complete with a military observation post at the top, with a giant #Early history, cross at its apex; at the foot of the observatory lies St. George's church, in a classical style punctuated by six Doric Order, Doric columns, as opposed to the Hagia Sophia, Byzantine architectural style of the greater part of Greek Orthodox churches.
 The ''new citadel'' or ''Neo Frourio'' (Νέο Φρούριο, "New Fortress") is a huge complex of fortifications built by the British during their United States of the Ionian Islands, rule of the island (1815–63) dominating the northeastern part of the city. The huge walls of the fortress loom over the landscape as one travels from ''Neo Limani'' (Νέο Λιμάνι, "New Port") to the city, taking the road that passes through the fishmarket (ψαραγορά). The new citadel was until recently a restricted area due to the presence of a naval garrison, but old restrictions have been lifted and it is now open to the public, with tours possible through the maze of medieval corridors and fortifications. The winged Lion of St Mark, the symbol of Venice, can be seen at regular intervals adorning the fortifications.
The ''new citadel'' or ''Neo Frourio'' (Νέο Φρούριο, "New Fortress") is a huge complex of fortifications built by the British during their United States of the Ionian Islands, rule of the island (1815–63) dominating the northeastern part of the city. The huge walls of the fortress loom over the landscape as one travels from ''Neo Limani'' (Νέο Λιμάνι, "New Port") to the city, taking the road that passes through the fishmarket (ψαραγορά). The new citadel was until recently a restricted area due to the presence of a naval garrison, but old restrictions have been lifted and it is now open to the public, with tours possible through the maze of medieval corridors and fortifications. The winged Lion of St Mark, the symbol of Venice, can be seen at regular intervals adorning the fortifications.
 Gardiki Castle () is a 13th-century Byzantine castle on the southwestern coast of Corfu and the only surviving medieval fortress on the southern part of the island. It was built by a ruler of the Despotate of Epirus, and was one of three castles which defended the island before the Republic of Venice, Venetian era (1401–1797).
The location of Gardiki at the narrow southwest flank of Corfu provided protection to the fields and the southern lowlands of Corfu and in combination with Kassiopi Castle on the northeastern coast of the island and Byzantine Angelokastro (Corfu), Angelokastro protecting the northwestern shore of Corfu, formed a triangular line of defence which protected Corfu during the pre-Venetian era.
Gardiki Castle () is a 13th-century Byzantine castle on the southwestern coast of Corfu and the only surviving medieval fortress on the southern part of the island. It was built by a ruler of the Despotate of Epirus, and was one of three castles which defended the island before the Republic of Venice, Venetian era (1401–1797).
The location of Gardiki at the narrow southwest flank of Corfu provided protection to the fields and the southern lowlands of Corfu and in combination with Kassiopi Castle on the northeastern coast of the island and Byzantine Angelokastro (Corfu), Angelokastro protecting the northwestern shore of Corfu, formed a triangular line of defence which protected Corfu during the pre-Venetian era.
 The Ionian University was established in 1984, in recognition, by the administration of Andreas Papandreou, of Corfu's contribution to Education in Greece, as the seat of the first Greek university in modern times, the Ionian Academy. The university opened its doors to students in 1985 and today comprises three Schools and six Departments offering undergraduate and post-graduate degree programmes and summer schools.
The Ionian University was established in 1984, in recognition, by the administration of Andreas Papandreou, of Corfu's contribution to Education in Greece, as the seat of the first Greek university in modern times, the Ionian Academy. The university opened its doors to students in 1985 and today comprises three Schools and six Departments offering undergraduate and post-graduate degree programmes and summer schools.
 The most notable of Corfu's museums and libraries are located in the city; these include:
*Archaeological Museum of Corfu, The Archaeological Museum, inaugurated in 1967, was constructed to house the exhibit of the huge Gorgon pediment of the Temple of Artemis (Corfu), Artemis temple in the ancient city of Korkyra, excavated at Palaiopolis in the early 20th century. The pediment has been described by ''The New York Times'' as the "finest example of Archaic Greece, archaic temple sculpture extant". Kaiser Wilhelm II had developed a "lifelong obsession" with the Gorgon sculpture, dating from seminars on Greek Archaeology the Kaiser attended while at the University of Bonn. The seminars were given by archaeologist Reinhard Kekulé von Stradonitz, who later became the Kaiser's advisor. In 1994, two more halls were added to the museum, where new discoveries from the excavations of the ancient city and the Garitsa cemetery are exhibited.
*The Museum of Asian art of Corfu is located at the Palace of St. Michael and St. George (mainly Chinese and Japanese Arts); its unique collection is housed in 15 rooms, taking in over 12,000 artifacts, including a Greco-Buddhist art collection that shows the influence of Alexander the Great on Buddhist culture as far as Pakistan (see Greco-Buddhism).
*The Banknote Museum, located in Saint Spyridon, Aghios Spyridon square, features a complete collection of Greek banknotes from independence to the adoption of the euro in 2002.
*The Byzantine Museum of Antivouniotissa, a church converted into a museum featuring rare Byzantine art.
*Kapodistrias Museum. Ioannis Kapodistrias' summer home in Koukourisa in his birthplace of Corfu has been converted to a museum commemorating his life and accomplishments and has been named in his honour. Donated by Maria Desylla Kapodistria, grand niece of Ioannis Kapodistrias, former mayor of Corfu and first female mayor of Greece.
*The Music Museum of the Philharmonic Society of Corfu is located in the building of the Philharmonic Society and features scores, instruments, paintings and documents related to the music history of Corfu and the 19th-century Ionian Islands.
The most notable of Corfu's museums and libraries are located in the city; these include:
*Archaeological Museum of Corfu, The Archaeological Museum, inaugurated in 1967, was constructed to house the exhibit of the huge Gorgon pediment of the Temple of Artemis (Corfu), Artemis temple in the ancient city of Korkyra, excavated at Palaiopolis in the early 20th century. The pediment has been described by ''The New York Times'' as the "finest example of Archaic Greece, archaic temple sculpture extant". Kaiser Wilhelm II had developed a "lifelong obsession" with the Gorgon sculpture, dating from seminars on Greek Archaeology the Kaiser attended while at the University of Bonn. The seminars were given by archaeologist Reinhard Kekulé von Stradonitz, who later became the Kaiser's advisor. In 1994, two more halls were added to the museum, where new discoveries from the excavations of the ancient city and the Garitsa cemetery are exhibited.
*The Museum of Asian art of Corfu is located at the Palace of St. Michael and St. George (mainly Chinese and Japanese Arts); its unique collection is housed in 15 rooms, taking in over 12,000 artifacts, including a Greco-Buddhist art collection that shows the influence of Alexander the Great on Buddhist culture as far as Pakistan (see Greco-Buddhism).
*The Banknote Museum, located in Saint Spyridon, Aghios Spyridon square, features a complete collection of Greek banknotes from independence to the adoption of the euro in 2002.
*The Byzantine Museum of Antivouniotissa, a church converted into a museum featuring rare Byzantine art.
*Kapodistrias Museum. Ioannis Kapodistrias' summer home in Koukourisa in his birthplace of Corfu has been converted to a museum commemorating his life and accomplishments and has been named in his honour. Donated by Maria Desylla Kapodistria, grand niece of Ioannis Kapodistrias, former mayor of Corfu and first female mayor of Greece.
*The Music Museum of the Philharmonic Society of Corfu is located in the building of the Philharmonic Society and features scores, instruments, paintings and documents related to the music history of Corfu and the 19th-century Ionian Islands.
 *The Public Library of Corfu is located at the old English Barracks, in Palaio Frourio.
*The Reading Society of Corfu has an extensive library of old Corfu manuscripts and rare books.
*The Serbian Museum of Corfu (, ''Serbian House'') houses rare exhibits about the Serbian soldiers' tragic fate during the First World War. The remnants of the Serbian Army of about 150,000 soldiers together with their government in exile, found refuge and shelter in Corfu, following the collapse of the Serbian Front as a result of the Austro-Hungarian attack of 6 October 1915. Exhibits include photographs from the three years stay of the Serbians in Corfu, together with other exhibits such as uniforms, arms and ammunition of the Serbian army, Serbian regimental flags, religious artifacts, surgical tools and other decorations of the Kingdom of Serbia.
*Solomos Museum and the Corfiot Studies Society.
*The Public Library of Corfu is located at the old English Barracks, in Palaio Frourio.
*The Reading Society of Corfu has an extensive library of old Corfu manuscripts and rare books.
*The Serbian Museum of Corfu (, ''Serbian House'') houses rare exhibits about the Serbian soldiers' tragic fate during the First World War. The remnants of the Serbian Army of about 150,000 soldiers together with their government in exile, found refuge and shelter in Corfu, following the collapse of the Serbian Front as a result of the Austro-Hungarian attack of 6 October 1915. Exhibits include photographs from the three years stay of the Serbians in Corfu, together with other exhibits such as uniforms, arms and ammunition of the Serbian army, Serbian regimental flags, religious artifacts, surgical tools and other decorations of the Kingdom of Serbia.
*Solomos Museum and the Corfiot Studies Society.
 Since the early 1990s a music department has been established at the
Since the early 1990s a music department has been established at the  Corfu is one of the locations in the legend of Simon and Milo, where Simon falls in love temporarily. It is the setting of the 1998 song "Mediterranean Lady" by Prozzak. The island is alluded to several times in David Foster Wallace's 1987 novel, ''The Broom of the System''. Drake (entertainer), Drake mentions Corfu in a song. It is also mentioned in Brian Jacques' adventure novel, Voyage of Slaves.
Corfu is one of the locations in the legend of Simon and Milo, where Simon falls in love temporarily. It is the setting of the 1998 song "Mediterranean Lady" by Prozzak. The island is alluded to several times in David Foster Wallace's 1987 novel, ''The Broom of the System''. Drake (entertainer), Drake mentions Corfu in a song. It is also mentioned in Brian Jacques' adventure novel, Voyage of Slaves.
 Corfu is mostly planted with olive groves and vineyards and has been producing olive oil and wine since antiquity. The main wine grape varietals found in Corfu are the indigenous white ''Kakotrýgēs'' and red ''Petrokóritho'', the Cefalonian white ''Robóla'', the Aegean Sea, Aegean ''Moscháto'' (white Muscat (grape and wine), muscat), the Achaean ''Mavrodáphnē'' and others.
Modern times have seen the introduction of specialist cultivation supported by the mild climate, like the
Corfu is mostly planted with olive groves and vineyards and has been producing olive oil and wine since antiquity. The main wine grape varietals found in Corfu are the indigenous white ''Kakotrýgēs'' and red ''Petrokóritho'', the Cefalonian white ''Robóla'', the Aegean Sea, Aegean ''Moscháto'' (white Muscat (grape and wine), muscat), the Achaean ''Mavrodáphnē'' and others.
Modern times have seen the introduction of specialist cultivation supported by the mild climate, like the  *Princess Alexia of Greece and Denmark, born in Corfu
*Panos Aravantinos, artist, born in Corfu
*Marie Aspioti, magazine publisher and cultural figure who influenced the literary and cultural life of post-war Corfu
*Felice Beato, 19th-century photographer, born in Corfu
*Giacomo Casanova, lived on the island as an officer of the Venetian army
*Tilemachos Chytiris, Greek politician, Member of the Hellenic Parliament
*Albert Cohen (novelist), Albert Cohen, Swiss-French author, born in Corfu
*Spiro Çomora, Albanian playwright, born in Corfu
*Haim Corfu, Israeli politician, was born in Jerusalem, his family name testifying to his family's origin
*Nikos Dendias, Greek lawyer and politician, has been Member of the Hellenic Parliament and has served as Minister for National Defence (Greece), Minister for National Defence and Minister of Foreign Affairs (Greece), Minister for Foreign Affairs
*Maria Desylla-Kapodistria, relative of Ioannis Kapodistrias, mayor of Corfu and first female mayor of Greece
*Mathew Devaris, scholar, born in Corfu
*Tommaso Diplovataccio, Greco-Italian jurist, publisher and politician, born in Corfu
*Eleni Doika, Greek Olympic gymnast, born in Corfu
*Viktor Dousmanis, Hellenic Army officer, born in Corfu
*Panagiotis Doxaras, painter, pioneer of the Heptanese School (painting), Heptanese School of painting, worked and died in Corfu
*Gerald Durrell, British naturalist and younger brother of Lawrence Durrell, lived in Corfu
*Lawrence Durrell, British writer and older brother of Gerald Durrell, lived in Corfu
*Elisabeth of Bavaria ("Sissi"), Empress of Austria, built Achilleion as summer palace
*Thomas Flanginis, wealthy Greek lawyer and merchant in Venice, who founded the Flanginian School, a Greek college where many teachers were trained
*Mario Frangoulis, Greek vocalist, famous for his refined tenor vocals
*Kostas Georgakis, student, martyr of the resistance against the Greek military junta of 1967–1974, born in Corfu
*Angela Gerekou, actress, singer and politician, born in Corfu, wife of Tolis Voskopoulos
*Angelos Giallinas, Greek landscape painter, known primarily for his watercolors
*Spyridon Gianniotis, Olympic silver medalist in swimming, raised in Corfu with father from Corfu
*Gaetano Giuffrè, composer and conductor, born in Corfu
*Spyros Gogolos, footballer, born in Corfu
*Angelos Grammenos, Greek actor, television director and singer
*Ian Hamilton (British Army officer), Ian Hamilton, British Army officer, led the 1915 Gallipoli campaign, Gallipoli Landings, born in Corfu
*Markos Antonios Katsaitis (1717–1787), Greek scholar, geographer and lawyer born in Corfu
*Augustinos Kapodistrias, younger brother of Ioannis Kapodistrias, soldier and politician, born in Corfu
*
*Princess Alexia of Greece and Denmark, born in Corfu
*Panos Aravantinos, artist, born in Corfu
*Marie Aspioti, magazine publisher and cultural figure who influenced the literary and cultural life of post-war Corfu
*Felice Beato, 19th-century photographer, born in Corfu
*Giacomo Casanova, lived on the island as an officer of the Venetian army
*Tilemachos Chytiris, Greek politician, Member of the Hellenic Parliament
*Albert Cohen (novelist), Albert Cohen, Swiss-French author, born in Corfu
*Spiro Çomora, Albanian playwright, born in Corfu
*Haim Corfu, Israeli politician, was born in Jerusalem, his family name testifying to his family's origin
*Nikos Dendias, Greek lawyer and politician, has been Member of the Hellenic Parliament and has served as Minister for National Defence (Greece), Minister for National Defence and Minister of Foreign Affairs (Greece), Minister for Foreign Affairs
*Maria Desylla-Kapodistria, relative of Ioannis Kapodistrias, mayor of Corfu and first female mayor of Greece
*Mathew Devaris, scholar, born in Corfu
*Tommaso Diplovataccio, Greco-Italian jurist, publisher and politician, born in Corfu
*Eleni Doika, Greek Olympic gymnast, born in Corfu
*Viktor Dousmanis, Hellenic Army officer, born in Corfu
*Panagiotis Doxaras, painter, pioneer of the Heptanese School (painting), Heptanese School of painting, worked and died in Corfu
*Gerald Durrell, British naturalist and younger brother of Lawrence Durrell, lived in Corfu
*Lawrence Durrell, British writer and older brother of Gerald Durrell, lived in Corfu
*Elisabeth of Bavaria ("Sissi"), Empress of Austria, built Achilleion as summer palace
*Thomas Flanginis, wealthy Greek lawyer and merchant in Venice, who founded the Flanginian School, a Greek college where many teachers were trained
*Mario Frangoulis, Greek vocalist, famous for his refined tenor vocals
*Kostas Georgakis, student, martyr of the resistance against the Greek military junta of 1967–1974, born in Corfu
*Angela Gerekou, actress, singer and politician, born in Corfu, wife of Tolis Voskopoulos
*Angelos Giallinas, Greek landscape painter, known primarily for his watercolors
*Spyridon Gianniotis, Olympic silver medalist in swimming, raised in Corfu with father from Corfu
*Gaetano Giuffrè, composer and conductor, born in Corfu
*Spyros Gogolos, footballer, born in Corfu
*Angelos Grammenos, Greek actor, television director and singer
*Ian Hamilton (British Army officer), Ian Hamilton, British Army officer, led the 1915 Gallipoli campaign, Gallipoli Landings, born in Corfu
*Markos Antonios Katsaitis (1717–1787), Greek scholar, geographer and lawyer born in Corfu
*Augustinos Kapodistrias, younger brother of Ioannis Kapodistrias, soldier and politician, born in Corfu
*