|
Coypu
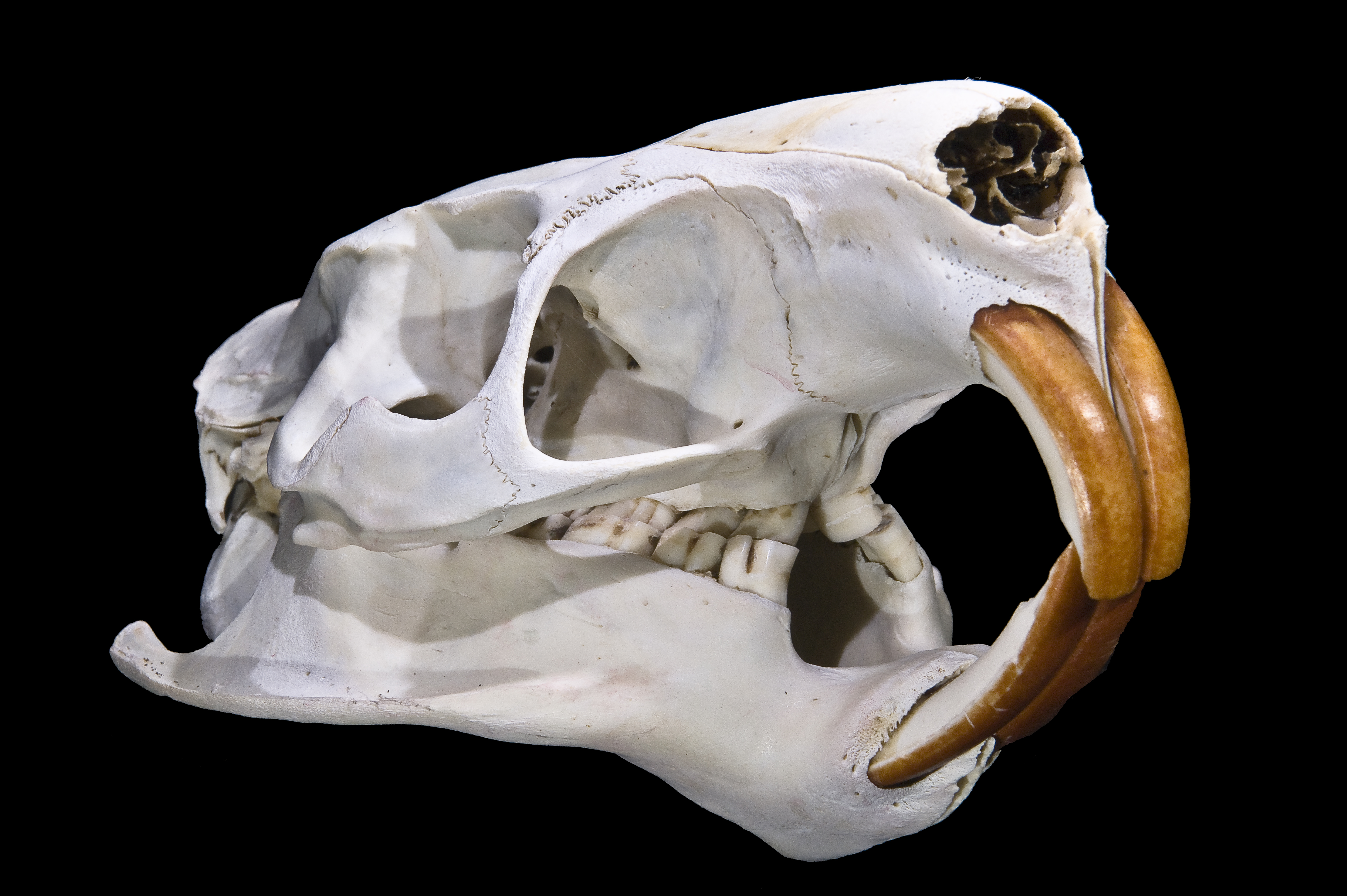
The nutria (''Myocastor coypus''), also known as the coypu, is a large, herbivorous, semiaquatic rodent. Classified for a long time as the only member of the family Myocastoridae, ''Myocastor'' is now included within Echimyidae, the family of the spiny rats. The nutria lives in burrows alongside stretches of water, and feeds on river plant stems. Originally native to subtropical and temperate South America, it has since been introduced to North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa, primarily by fur farmers. Although it is still hunted and trapped for its fur in some regions, its destructive burrowing and feeding habits often bring it into conflict with humans, and it is considered an invasive species. Nutria also transmit various diseases to humans and animals mainly through water contamination. Etymology The genus name ''Myocastor'' derives from the two Ancient Greek words (), meaning "rat, mouse", and (), meaning "beaver". Literally, therefore, the name ''Myocastor'' mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutria Population In Weilerswist, Germany Low Res
The nutria (''Myocastor coypus''), also known as the coypu, is a large, herbivorous, semiaquatic rodent. Classified for a long time as the only member of the family Myocastoridae, ''Myocastor'' is now included within Echimyidae, the family of the spiny rats. The nutria lives in burrows alongside stretches of water, and feeds on river plant stems. Originally native to subtropical and temperate South America, it has since been introduced to North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa, primarily by fur farmers. Although it is still hunted and trapped for its fur in some regions, its destructive burrowing and feeding habits often bring it into conflict with humans, and it is considered an invasive species. Nutria also transmit various diseases to humans and animals mainly through water contamination. Etymology The genus name ''Myocastor'' derives from the two Ancient Greek words (), meaning "rat, mouse", and (), meaning "beaver". Literally, therefore, the name ''Myocastor'' me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocastorini
Myocastorini is a tribe of echimyid rodents, proposed in 2017, and containing the five extant genera ''Callistomys'', ''Hoplomys'', ''Myocastor'', ''Proechimys'', and ''Thrichomys ''Thrichomys'' is a genus of South American rodents in the family Echimyidae. It contains at least five species, found in Bolivia, Brazil and Paraguay. They are as follows: * Common punaré (''Thrichomys apereoides'') * Foster's punaré (''Thrich ...''. Definition Myocastorini members share long upper incisor roots (except ''Callistomys''), and mid- to long-sized lower incisor roots. These five genera share either four (''Callistomys'', ''Thrichomys'') or five (''Hoplomys'', ''Myocastor'', ''Proechimys'') lophids on the lower deciduous fourth premolar, three roots anchoring the upper molars, and well-connected lophs on cheek teeth. Members display a variety of lifestyles including terrestrial (''Hoplomys'', ''Proechimys'', ''Thrichomys''), arboreal (''Callistomys''), and amphibious (''Myocastor'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echimyidae
Echimyidae is the family of neotropical spiny rats and their fossil relatives. This is the most species-rich family of hystricognath rodents. It is probably also the most ecologically diverse, with members ranging from fully arboreal to terrestrial to fossorial to semiaquatic habits. They presently exist mainly in South America; three members of the family also range into Central America, and the hutias are found in the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean. Species of the extinct subfamily Heteropsomyinae formerly lived on Cuba, Hispaniola, and Puerto Rico in the Antilles, probably until the arrival of Europeans. Characteristics In general form, most spiny rats resemble rats, although they are more closely related to guinea pigs and chinchillas. Most species have stiff, pointed hairs, or spines, that presumably serve for protection from predators. Many echimyids can break off their tails when attacked. This action may confuse predators long enough for the spiny r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for New Zealand, Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/richochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include Mouse, mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Rabbits, hares, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutria Fur
Nutria fur, also known as coypu fur, is used in the fashion industry. It comes from the nutria, a South American rodent and cousin of the beaver. History of the fur The nutria is a semi-aquatic mammal native to South America. It first became internationally popular as a fur in the 1930s, when it was worn by Hollywood stars such as Greta Garbo. It resembles beaver, with stiff guard hairs and a soft, short undercoat. It was originally imported to the southern United States – possibly as early as the 19th century, although in larger numbers from the 1950s – to reduce the population of muskrat. Some escaped and found the swamps of Louisiana ideal territory, leading to their common name of swamp rat. With the decline in the fur market in the 1980s, the population mushroomed and threatened the stability of the wetland ecosystem by eating away the plants that hold the swamp together. Treatment Typically, nutria is sheared or plucked for the fur trade. It can be dyed a variety of col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Ignacio Molina
Fr. Juan Ignacio Molina (; (June 24, 1740 – September 12, 1829) was a Chilean Jesuit priest, naturalist, historian, translator, geographer, botanist, ornithologist, and linguist. He is usually referred to as Abate Molina (a form of Abbot Molina), and is also sometimes known by the Italian form of his name, Giovanni Ignazio Molina. He was one of the precursors of the theory of the gradual evolution of species, 44 years before Darwin, who repeatedly quoted him in "The Origin of Species". Biography Early years Molina was born at Guaraculén, a big farm located near Villa Alegre ( General Captaincy of Chile), where he lived until he was 5 years old. In the current province of Linares, in the Maule Region of Chile. His parents were Agustín Molina and Francisca González Bruna. From an early age he was attracted to the nature of his environment, and in addition to his school work, he enjoyed observing nature on the family farm, which he visited periodically, alternating wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Kerr (writer)
Dr Robert Kerr FRSE FAS FRCSE (20 October 1757 – 11 October 1813) was a Scottish surgeon, writer on scientific and other subjects, and translator. Life Kerr was born in 1757 in Bughtridge, Roxburghshire, the son of James Kerr, a jeweller, who served as MP for Edinburgh 1747–1754, and his wife Elizabeth. He was sent to the High School in Edinburgh. He studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh and practised at the Edinburgh Foundling Hospital as a surgeon. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh in 1788. His proposers were Alexander Fraser Tytler, James Russell and Andrew Dalzell. At this time he lived at Foresters Wynd off the Royal Mile in Edinburgh. He translated several scientific works into English, such as Antoine Lavoisier's work of 1789, '' Traité Élémentaire de Chimie'', published under the title ''Elements of Chemistry in a New Systematic Order containing All the Modern Discoveries'', in 1790. In 1792, he published ''The Animal Kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire
Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire (15 April 177219 June 1844) was a French naturalist who established the principle of "unity of composition". He was a colleague of Jean-Baptiste Lamarck and expanded and defended Lamarck's evolutionary theories. Geoffroy's scientific views had a transcendental flavor (unlike Lamarck's materialistic views) and were similar to those of German morphologists like Lorenz Oken. He believed in the underlying unity of organismal design, and the possibility of the transmutation of species in time, amassing evidence for his claims through research in comparative anatomy, paleontology, and embryology. He is considered as a predecessor of the evo-devo evolutionary concept. Life and early career Geoffroy was born at Étampes (in present-day Essonne), and studied at the Collège de Navarre, in Paris, where he studied natural philosophy under M. J. Brisson. He then attended the lectures of Daubenton at the College de France and Fourcroy at the Jardin de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiloé Island
Chiloé Island ( es, Isla de Chiloé, , ) also known as Greater Island of Chiloé (''Isla Grande de Chiloé''), is the largest island of the Chiloé Archipelago off the west coast of Chile, in the Pacific Ocean. The island is located in southern Chile, in the Los Lagos Region. Of roughly rectangular shape, the southwestern half of the island is a wilderness of contiguous forests and swamps. Mountains in the island form a belt running from the northwestern to the southeastern corner of the island. Cordillera del Piuchén make up the northern mountains and the more subdued Cordillera de Pirulil gathers the southern mountains. The landscape of the northeastern sectors of Chiloé Island is dominated by rolling hills with a mosaic of pastures, forests and cultivated fields. While the western shores are rocky and relatively straight, the eastern and northern shores contain many inlets, bays and peninsulas, and it is here where all towns and cities lie. Geographically, the bulk of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers in the west and deserts, tablelands and steppes to the east. Patagonia is bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and many bodies of water that connect them, such as the Strait of Magellan, the Beagle Channel, and the Drake Passage to the south. The Colorado and Barrancas rivers, which run from the Andes to the Atlantic, are commonly considered the northern limit of Argentine Patagonia. The archipelago of Tierra del Fuego is sometimes included as part of Patagonia. Most geographers and historians locate the northern limit of Chilean Patagonia at Huincul Fault, in Araucanía Region.Manuel Enrique Schilling; Richard WalterCarlson; AndrésTassara; Rommulo Vieira Conceição; Gustavo Walter B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nipple
The nipple is a raised region of tissue on the surface of the breast from which, in females, milk leaves the breast through the lactiferous ducts to feed an infant. The milk can flow through the nipple passively or it can be ejected by smooth muscle contractions that occur along with the ductal system. The nipple is surrounded by the areola, which is often a darker colour than the surrounding skin. A nipple is often called a teat when referring to non-humans. Nipple or teat can also be used to describe the flexible mouthpiece of a baby bottle. In humans, the nipples of both males and females can be stimulated as part of sexual arousal. In many cultures, human female nipples are sexualized, or "regarded as sex objects and evaluated in terms of their physical characteristics and sexiness." Anatomy In mammals, a nipple (also called mammary papilla or teat) is a small projection of skin containing the outlets for 15–20 lactiferous ducts arranged cylindrically around the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)




