Commandery Of Dai on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dai Commandery was a
 Dai Commandery was first established around 300BC during China's
Dai Commandery was first established around 300BC during China's
 Dai Commandery was one of the divisions of the
Dai Commandery was one of the divisions of the
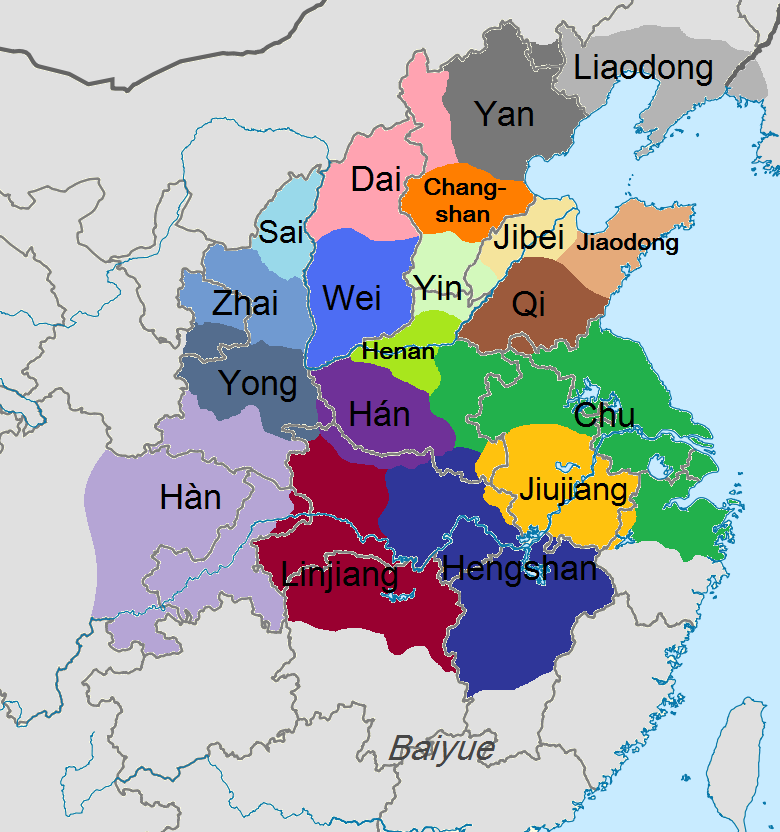 During the interregnum following Qin's collapse, Dai was one of the
During the interregnum following Qin's collapse, Dai was one of the
 Under the Han, Dai Prefecture formed part of the
Under the Han, Dai Prefecture formed part of the
《代郡》
at Baike.com {{Han dynasty provinces Former commanderies of China Commanderies of the Qin dynasty Commanderies of the Han dynasty Commanderies of the Jin dynasty (266–420) Commanderies of the Sui dynasty
commandery
In the Middle Ages, a commandery (rarely commandry) was the smallest administrative division of the European landed properties of a military order. It was also the name of the house where the knights of the commandery lived.Anthony Luttrell and G ...
(''jùn'') of the state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
of Zhao established BC and of northern imperial Chinese dynasties until the time of the Emperor Wen of the Sui dynasty
The Sui dynasty ( ) was a short-lived Dynasties of China, Chinese imperial dynasty that ruled from 581 to 618. The re-unification of China proper under the Sui brought the Northern and Southern dynasties era to a close, ending a prolonged peri ...
(r. AD581–604). It occupied lands in what is now Hebei
Hebei is a Provinces of China, province in North China. It is China's List of Chinese administrative divisions by population, sixth-most populous province, with a population of over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. It bor ...
, Shanxi
Shanxi; Chinese postal romanization, formerly romanised as Shansi is a Provinces of China, province in North China. Its capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level cities are Changzhi a ...
, and Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of China. Its border includes two-thirds of the length of China's China–Mongolia border, border with the country of Mongolia. ...
. Its seat
A seat is a place to sit. The term may encompass additional features, such as back, armrest, head restraint but may also refer to concentrations of power in a wider sense (i.e " seat (legal entity)"). See disambiguation.
Types of seat
The ...
was usually at Dai or Daixian
Dai County, also known by its Chinese name Daixian, is a county in Xinzhou, Shanxi Province, China. Its county seat at Shangguan is also known as Daixian. The county has an area of and had a population of 178,870 at the time of the 2020 c ...
(near present-day Yuzhou in Hebei
Hebei is a Provinces of China, province in North China. It is China's List of Chinese administrative divisions by population, sixth-most populous province, with a population of over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. It bor ...
), although it was moved to Gaoliu (present-day Yanggao
Yanggao County is a CPRC, county in the northeast of Shanxi province, China, bordering Inner Mongolia to the northwest and Hebei province to the east. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Datong.
History
Yanggao was f ...
in Shanxi
Shanxi; Chinese postal romanization, formerly romanised as Shansi is a Provinces of China, province in North China. Its capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level cities are Changzhi a ...
) during the Eastern Han
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
.
Name
The name derives from the White Di kingdom of Dai, conquered by the Zhao family of Jin.History
Zhao Kingdom
 Dai Commandery was first established around 300BC during China's
Dai Commandery was first established around 300BC during China's Warring States period
The Warring States period in history of China, Chinese history (221 BC) comprises the final two and a half centuries of the Zhou dynasty (256 BC), which were characterized by frequent warfare, bureaucratic and military reforms, and ...
by the state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
of Zhao's King Yong, posthumously known as the Wuling ("Martial-&-Numinous") King.. The commandery seat—then known as Dai—was southwest of present-day Yuzhou in Hebei
Hebei is a Provinces of China, province in North China. It is China's List of Chinese administrative divisions by population, sixth-most populous province, with a population of over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. It bor ...
.. It was the former capital of the independent state of Dai, which had been conquered by King Yong's ancestors around 476BC.. He created Dai Commandery along with its companion commanderies of Yanmen
Yanmen Pass, also known by its Chinese name Yanmenguan and as Xixingguan, is a mountain pass which includes three fortified gatehouses along the Great Wall of China. The area was a strategic choke point in ancient and medieval China, contro ...
and Yunzhong
Yunzhong Commandery was a historical commandery of China. Its territories were located between the Great Wall and Yin Mountains, and correspond to part of modern-day Hohhot, Baotou and Ulanqab prefectures in Inner Mongolia.
The commandery was cr ...
to consolidate his conquests from invasions of the Loufan ( t s ''Lóufán'') and " forest nomads" ( ''Línhú'') in 306 and 304BC.
Following the Qin conquest
Conquest involves the annexation or control of another entity's territory through war or Coercion (international relations), coercion. Historically, conquests occurred frequently in the international system, and there were limited normative or ...
of Zhao, Zhao Jia attempted to regroup at Dai, declaring himself its king. This Kingdom of Dai was ended by Qin in 222BC, just prior to the declaration of the Qin Empire
The Qin dynasty ( ) was the first imperial dynasty of China. It is named for its progenitor state of Qin, a fief of the confederal Zhou dynasty (256 BC). Beginning in 230 BC, the Qin under King Ying Zheng engaged in a series ...
two years later.
Qin Empire
 Dai Commandery was one of the divisions of the
Dai Commandery was one of the divisions of the Qin Empire
The Qin dynasty ( ) was the first imperial dynasty of China. It is named for its progenitor state of Qin, a fief of the confederal Zhou dynasty (256 BC). Beginning in 230 BC, the Qin under King Ying Zheng engaged in a series ...
. Its seat—then known as Daixian—continued to be near present-day Yuzhou..
Eighteen Kingdoms
 During the interregnum following Qin's collapse, Dai was one of the
During the interregnum following Qin's collapse, Dai was one of the Eighteen Kingdoms
The historiographical term "Eighteen Kingdoms" ( zh, t=十八國), also translated as "Eighteen States", refers to the eighteen '' fengjian'' states in China created by military leader Xiang Yu in 206 BCE, after the collapse of the Qin dynasty.� ...
established by Xiang Yu
Xiang Yu (), born Xiang Ji, was a Chinese warlord who founded and led the short-lived ancient Chinese states, kingdom-state of Western Chu during the interregnum period between the Qin dynasty, Qin and Han dynasty, Han dynasties of China, d ...
. It was ruled by Zhao Xie Zhao may refer to:
* Zhao (surname) (赵), a Chinese surname
** commonly spelled Chao in Taiwan or up until the early 20th century in other regions
** Chiu, from the Cantonese pronunciation
** Cho (Korean surname), represent the Hanja 趙 (Chine ...
and Chun Yu.
Western Han Empire
province
A province is an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire, Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of Bingzhou
Bingzhou, or Bing Province, was a location in ancient China. According to legend, when Yu the Great (–2100 BC) tamed the flood, he divided the land of China into the Nine Provinces. Historical texts such as the ''Rites of Zhou'', and "Treatise ...
and oversaw 18 counties, both within and beyond the Great Wall
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand Li (unit), ''li'' long wall") is a series of fortifications in China. They were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection agains ...
. Along with Yunzhong
Yunzhong Commandery was a historical commandery of China. Its territories were located between the Great Wall and Yin Mountains, and correspond to part of modern-day Hohhot, Baotou and Ulanqab prefectures in Inner Mongolia.
The commandery was cr ...
and Yanmen
Yanmen Pass, also known by its Chinese name Yanmenguan and as Xixingguan, is a mountain pass which includes three fortified gatehouses along the Great Wall of China. The area was a strategic choke point in ancient and medieval China, contro ...
, it also formed part of the Principality of Dai, used as an imperial appanage
An appanage, or apanage (; ), is the grant of an estate, title, office or other thing of value to a younger child of a monarch, who would otherwise have no inheritance under the system of primogeniture (where only the eldest inherits). It was ...
. The ''Book of Han
The ''Book of Han'' is a history of China finished in 111 CE, covering the Western, or Former Han dynasty from the first emperor in 206 BCE to the fall of Wang Mang in 23 CE. The work was composed by Ban Gu (32–92 CE), ...
'' records Dai Commandery having 278,754 people living in 56,771 households. The Han administration kept the seat at Daixian near present-day Yuzhou and continued the Qin-era counties (renaming "New Pingshu County" to simply " Pingshu County"), with the addition of:
Xin Empire
Under the short-livedXin dynasty
The Xin dynasty (; ), also known as Xin Mang () in Chinese historiography, was a short-lived Dynasties in Chinese history, Chinese imperial dynasty which lasted from 9 to 23 AD, established by the Han dynasty consort kin Wang Mang, who usurped th ...
established by Wang Mang
Wang Mang (45 BCE6 October 23 CE), courtesy name Jujun, officially known as the Shijianguo Emperor (), was the founder and the only emperor of the short-lived Chinese Xin dynasty. He was originally an official and consort kin of the ...
, several of the Han counties were renamed.
Eastern Han Empire
Under theEastern Han
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
, Dai Commandery formed part of the province
A province is an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire, Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of Youzhou
You Prefecture or You Province, also known by its Chinese name Youzhou, was a prefecture ('' zhou'') in northern China during its imperial era.
"You Province" was cited in some ancient sources as one of the nine or twelve original provinces o ...
. Its seat—then known as Gaoliu—was southwest of present-day Yanggao
Yanggao County is a CPRC, county in the northeast of Shanxi province, China, bordering Inner Mongolia to the northwest and Hebei province to the east. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Datong.
History
Yanggao was f ...
in northeastern Shanxi
Shanxi; Chinese postal romanization, formerly romanised as Shansi is a Provinces of China, province in North China. Its capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level cities are Changzhi a ...
.
Wei Kingdom
During China'sThree Kingdoms period
The Three Kingdoms of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu dominated China from AD 220 to 280 following the end of the Han dynasty. This period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and followed by the Western Jin dynasty. Academically, the ...
, Wei returned the commandery seat to Daixian (near present-day Yuzhou, Hebei
Hebei is a Provinces of China, province in North China. It is China's List of Chinese administrative divisions by population, sixth-most populous province, with a population of over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. It bor ...
).
Sixteen Kingdoms
During China'sSixteen Kingdoms
The Sixteen Kingdoms (), less commonly the Sixteen States, was a chaotic period in Chinese history from AD 304 to 439 when northern China fragmented into a series of short-lived dynastic states. The majority of these states were founded b ...
period, both Later Yan
Yan, known in historiography as the Later Yan (; 384 – 407 or 409), was a dynastic state of China ruled by the Xianbei people during the era of Sixteen Kingdoms.
The prefix "Later" to distinguish them from the Former Yan before them and othe ...
and the Northern Wei
Wei (), known in historiography as the Northern Wei ( zh, c=北魏, p=Běi Wèi), Tuoba Wei ( zh, c=拓跋魏, p=Tuòbá Wèi), Yuan Wei ( zh, c=元魏, p=Yuán Wèi) and Later Wei ( zh, t=後魏, p=Hòu Wèi), was an Dynasties of China, impe ...
had commanderies named Dai. Northern Wei's lay to the west, with its seat at Pingcheng (present-day Datong
Datong is a prefecture-level city in northern Shanxi Province, China. It is located in the Datong Basin at an elevation of and borders Inner Mongolia to the north and west and Hebei to the east. As of the 2020 census, it had a population o ...
, Shanxi
Shanxi; Chinese postal romanization, formerly romanised as Shansi is a Provinces of China, province in North China. Its capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level cities are Changzhi a ...
).
Separate from these, Tuoba Yilu
Tuoba Yilu (; died 316) was the chieftain of the western Tuoba territory from 295 to 307, supreme chieftain of the Tuoba from 307 to 316, Duke of Dai from 310 to 315, and first ruler of the Dai kingdom from 315 to 316. He was the son of Tuoba Sham ...
was declared " Duke of Dai" () by the Jin in AD310 and (vassal) "King of Dai
Prince or King of Dai was an ancient and medieval Chinese title.
King of Dai is sometimes used to describe the heads of the Baidi state of Dai north of the Zhou Kingdom that was conquered by the Zhao clan of Jin. It was used as the title for t ...
" by the same court in 315. This Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were an ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. The Xianbei were likely not of a single ethnicity, but rather a multiling ...
Kingdom of Dai lasted until 376, and its dynasts were responsible for the later state of Northern Wei. It held some lands in northern Shanxi and Hebei but was mostly to their north in what is now Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of China. Its border includes two-thirds of the length of China's China–Mongolia border, border with the country of Mongolia. ...
, with their capital at Shengle
Shengle () was the capital of the Xianbei-led Dai state and the first capital of the Northern Wei dynasty in the 4th century. The ruins of ancient Shengle is located at present-day Xiyaozi and Tuchengzi village, in the town of , in Horinger Cou ...
(northwest of present-day Horinger
Horinger (Mongolian language, Mongolian: ; zh, s=和林格尔县) is a Counties of China, county of Inner Mongolia, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, North China, it is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Hohhot, the capita ...
).
Sui Empire
Dai Commandery continued until its abolishment under the Wen Emperor of Sui, who replaced it in 585 withDai Prefecture
Dai Prefecture, also known by its Chinese language, Chinese name Daizhou, was a Zhou (country subdivision), prefecture (''zhou'') of imperial China in what is now northern Shanxi. It existed intermittently from AD585 to 1912. Its eponymous seat ...
, whose seat was at Guangwu or Yanmen (present-day Daixian
Dai County, also known by its Chinese name Daixian, is a county in Xinzhou, Shanxi Province, China. Its county seat at Shangguan is also known as Daixian. The county has an area of and had a population of 178,870 at the time of the 2020 c ...
, Shanxi
Shanxi; Chinese postal romanization, formerly romanised as Shansi is a Provinces of China, province in North China. Its capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level cities are Changzhi a ...
)..
Notes
References
Citations
Bibliography
* . * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * .External links
《代郡》
at Baike.com {{Han dynasty provinces Former commanderies of China Commanderies of the Qin dynasty Commanderies of the Han dynasty Commanderies of the Jin dynasty (266–420) Commanderies of the Sui dynasty