Columbian Exchange on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Columbian exchange, also known as the Columbian interchange, was the widespread transfer of plants, animals, and diseases between the
 In 1972, Alfred W. Crosby, an American historian at the
In 1972, Alfred W. Crosby, an American historian at the
 The Spanish were the first Europeans to grow cacao, in 1590. Though cacao was usually consumed by European populations in the form of sweets and was at first treated as an expensive luxury item,
The Spanish were the first Europeans to grow cacao, in 1590. Though cacao was usually consumed by European populations in the form of sweets and was at first treated as an expensive luxury item,
File:The Florentine Codex- The Conquest of Mexico.png, Spanish conquest of Mexico, 1519–1521, with
While mesoamerican peoples, Mayas in particular, already practiced apiculture, producing wax and
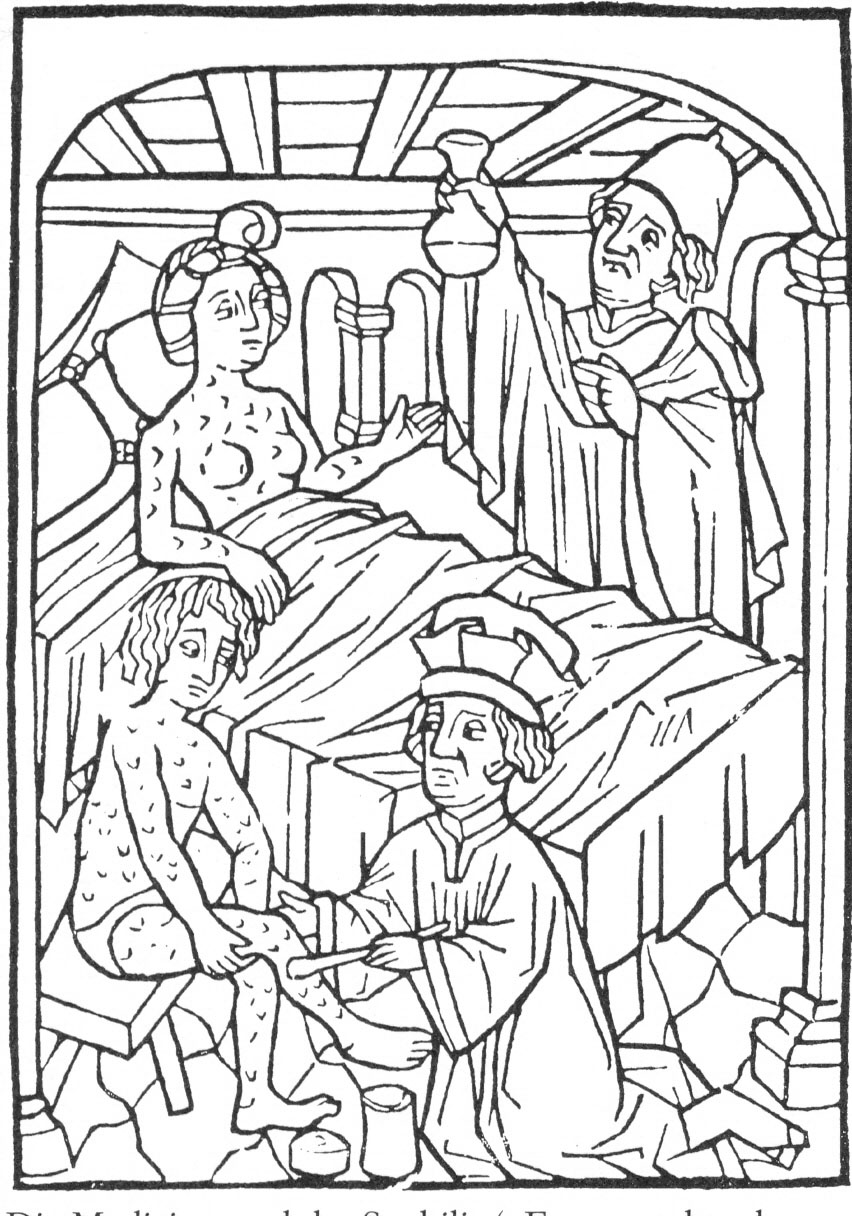 The first manifestation of the Columbian exchange may have been the spread of
The first manifestation of the Columbian exchange may have been the spread of 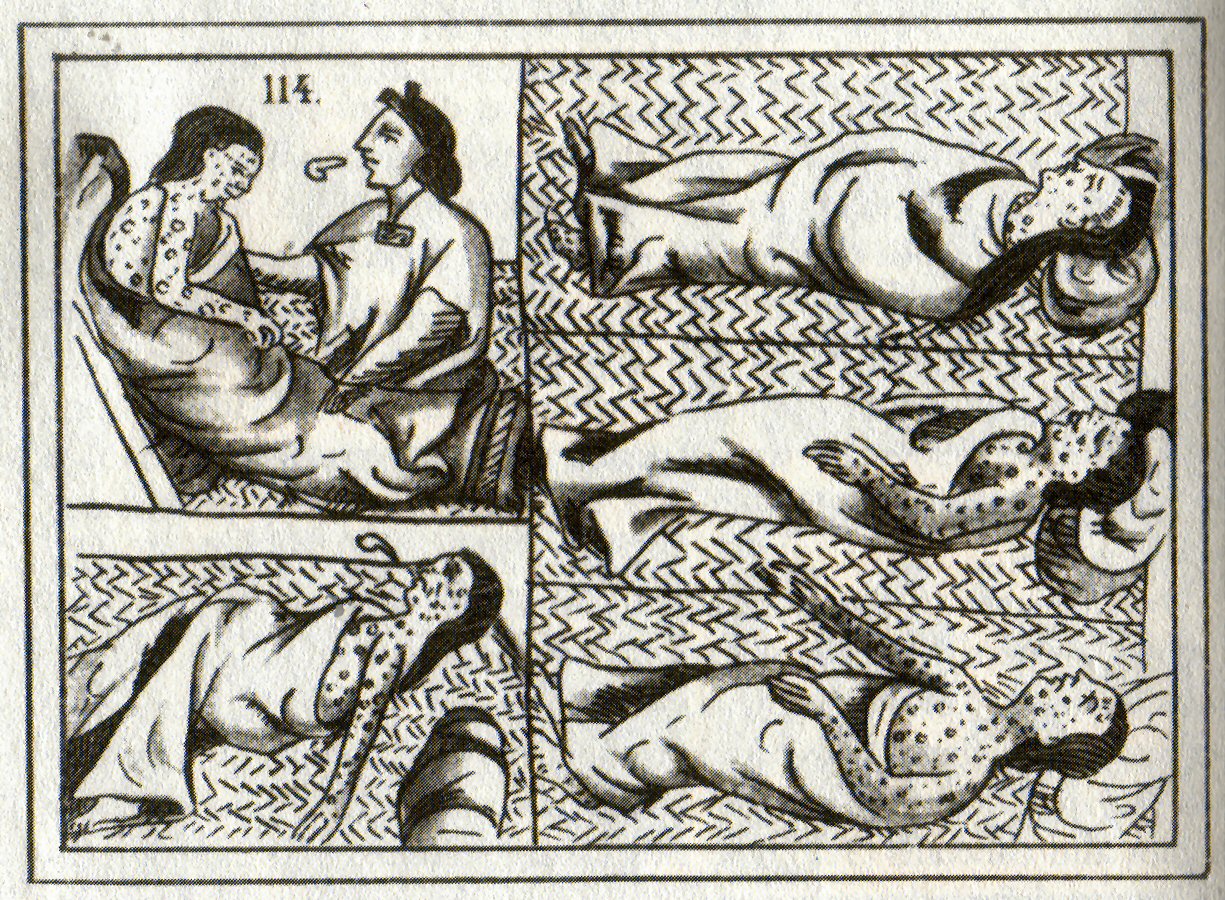 In 1518,
In 1518,
 The Atlantic slave trade consisted of the involuntary immigration of 11.7 million Africans, primarily from West Africa, to the Americas between the 16th and 19th centuries, far outnumbering the about 3.4 million Europeans who migrated, most voluntarily, to the New World between 1492 and 1840. The prevalence of African slaves in the New World was related to the demographic decline of New World peoples and the need of European colonists for labor. Another reason for the demand for slaves was the cultivation of crops such as sugar cane suitable for the climatic conditions of the new lands. The Africans were less likely to die, too, from those diseases that had been brought to the New World. Enslaved Africans helped shape an emerging African-American culture in the New World. They participated in both skilled and unskilled labor. For example, slaves were involved in handicraft production. They could also work as ordinary workers, and as managers of small enterprises in the commercial or industrial sphere. Their descendants gradually developed an ethnicity that drew from the numerous African tribes as well as European nationalities. The descendants of African slaves make up a majority of the population in some Caribbean countries, notably
The Atlantic slave trade consisted of the involuntary immigration of 11.7 million Africans, primarily from West Africa, to the Americas between the 16th and 19th centuries, far outnumbering the about 3.4 million Europeans who migrated, most voluntarily, to the New World between 1492 and 1840. The prevalence of African slaves in the New World was related to the demographic decline of New World peoples and the need of European colonists for labor. Another reason for the demand for slaves was the cultivation of crops such as sugar cane suitable for the climatic conditions of the new lands. The Africans were less likely to die, too, from those diseases that had been brought to the New World. Enslaved Africans helped shape an emerging African-American culture in the New World. They participated in both skilled and unskilled labor. For example, slaves were involved in handicraft production. They could also work as ordinary workers, and as managers of small enterprises in the commercial or industrial sphere. Their descendants gradually developed an ethnicity that drew from the numerous African tribes as well as European nationalities. The descendants of African slaves make up a majority of the population in some Caribbean countries, notably
The Columbian Exchange: Plants, Animals, and Disease between the Old and New Worlds
by Alfred W. Crosby (2009) * '' 1491: New Revelations of the Americas Before Columbus'', New York: Alfred A. Knopf, by Charles C. Mann (2005); a
Google Books
* Specht, Joshua; Stockland, Etienne (2017). ''The Columbian Exchange''. CRC Press. *
Indian Givers: How the Indians of the Americas Transformed the World
' by Jack Weatherford (2010)
Foods that Changed the World
—Steven R. King {{DEFAULTSORT:Columbian exchange Age of Discovery Agricultural revolutions History of Europe History of agriculture History of globalization History of Indigenous peoples of the Americas History of the Americas History of the Atlantic Ocean Horticulture Introduced species Spanish colonization of the Americas Spanish exploration in the Age of Discovery Transatlantic cultural exchange Western culture
New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
(the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
) in the Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the 180th meridian.- The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Geopolitically, ...
, and the Old World
The "Old World" () is a term for Afro-Eurasia coined by Europeans after 1493, when they became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously ...
(Afro-Eurasia
Afro-Eurasia (also Afroeurasia and Eurafrasia) is a landmass comprising the continents of Africa, Asia, and Europe. The terms are compound (linguistics), compound words of the names of its constituent parts. Afro-Eurasia has also been called th ...
) in the Eastern Hemisphere, from the late 15th century on. It is named after the explorer Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus (; between 25 August and 31 October 1451 – 20 May 1506) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed Voyages of Christopher Columbus, four Spanish-based voyages across the At ...
and is related to the European colonization and global trade following his 1492 voyage. Some of the exchanges were deliberate while others were unintended. Communicable diseases of Old World origin resulted in an 80 to 95 percent reduction in the Indigenous population of the Americas from the 15th century onwards, and their extinction in the Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
.
The cultures of both hemispheres were significantly impacted by the migration of people, both free and enslaved, from the Old World to the New. European colonists and African slaves replaced Indigenous populations across the Americas, to varying degrees. The number of Africans taken to the New World was far greater than the number of Europeans moving there in the first three centuries after Columbus.
The new contacts among the global population resulted in the interchange of many species of crop
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. In other words, a crop is a plant or plant product that is grown for a specific purpose such as food, Fiber, fibre, or fuel.
When plants of the same spe ...
s and livestock
Livestock are the Domestication, domesticated animals that are raised in an Agriculture, agricultural setting to provide labour and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, Egg as food, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The t ...
, which supported increases in food production and population in the Old World. American crops such as maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
, potato
The potato () is a starchy tuberous vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are underground stem tubers of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'', a perennial in the nightshade famil ...
es, tomato
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible Berry (botany), berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originate ...
es, tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', common name, commonly called cassava, manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America, from Brazil, Paraguay and parts of the Andes. Although ...
, sweet potatoes, and chili pepper
Chili peppers, also spelled chile or chilli ( ), are varieties of fruit#Berries, berry-fruit plants from the genus ''Capsicum'', which are members of the nightshade family Solanaceae, cultivated for their pungency. They are used as a spice to ...
s became important crops around the world. Old World rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
, wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
, sugar cane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
, and livestock
Livestock are the Domestication, domesticated animals that are raised in an Agriculture, agricultural setting to provide labour and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, Egg as food, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The t ...
, among other crops, became important in the New World.
The term was first used in 1972 by the American historian and professor Alfred W. Crosby in his environmental history book '' The Columbian Exchange''. It was rapidly adopted by other historians and by journalists.
Etymology
 In 1972, Alfred W. Crosby, an American historian at the
In 1972, Alfred W. Crosby, an American historian at the University of Texas at Austin
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public university, public research university in Austin, Texas, United States. Founded in 1883, it is the flagship institution of the University of Texas System. With 53,082 stud ...
, published the book '' The Columbian Exchange'', thus coining the term. His primary focus was mapping the biological and cultural transfers that occurred between the Old and New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
s. He studied the effects of Columbus's voyages between the two – specifically, the global diffusion of crops, seeds, and plants from the New World to the Old, which radically transformed agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
in both regions.
His research made a lasting contribution to the way scholars understand the variety of contemporary ecosystems that arose due to these transfers. His 1986 book '' Ecological Imperialism'' presented further research in the field.
Background
The scientific consensus is that humans first came to the New World fromSiberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
thousands of years ago. There is little additional evidence of contacts between the peoples of the Old World and those of the New World, although the literature speculating on pre-Columbian trans-oceanic journeys is extensive. The first inhabitants of the New World brought with them small domestic dogs and, possibly, a container, the calabash, both of which persisted in their new home. The medieval explorations, visits, and brief residence of the Norsemen
The Norsemen (or Northmen) were a cultural group in the Early Middle Ages, originating among speakers of Old Norse in Scandinavia. During the late eighth century, Scandinavians embarked on a Viking expansion, large-scale expansion in all direc ...
in Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ...
, Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
, and Vinland
Vinland, Vineland, or Winland () was an area of coastal North America explored by Vikings. Leif Erikson landed there around 1000 AD, nearly five centuries before the voyages of Christopher Columbus and John Cabot. The name appears in the V ...
in the late 10th century and 11th century had no known impact on the Americas, though the small perennial '' Rumex acetosella'' (sheep's sorrel) appeared in Greenland at that time.
Many scientists accept that possible contact between Polynesians and coastal peoples in South America around the year 1200 resulted in genetic similarities and the adoption by Polynesians of an American crop, the sweet potato. However, it was only with the first voyage of the Italian explorer Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus (; between 25 August and 31 October 1451 – 20 May 1506) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed Voyages of Christopher Columbus, four Spanish-based voyages across the At ...
and his crew to the Americas in 1492 that the Columbian exchange began, resulting in major transformations in the cultures and livelihoods of the peoples in both hemispheres.
Biological exchanges
Of plants
Because of the new trading resulting from the Columbian exchange, several plants native to the Americas spread around the world, includingpotato
The potato () is a starchy tuberous vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are underground stem tubers of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'', a perennial in the nightshade famil ...
es, maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
, tomato
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible Berry (botany), berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originate ...
es, and tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
. Before 1500, potatoes were not grown outside of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
. By the 18th century, they were cultivated and consumed widely in Europe and had become important crops in both India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
and North America. Potatoes eventually became an important staple food in the diets of many Europeans, contributing to an estimated 12 to 25% of the population growth in Afro-Eurasia between 1700 and 1900. The introduction of the potato to the Old World accounts for 47 percent of the increase in urbanization between 1700 and 1900. Cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', common name, commonly called cassava, manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America, from Brazil, Paraguay and parts of the Andes. Although ...
was introduced from South America by the Portuguese in the 16th century, and gradually replaced sorghum
''Sorghum bicolor'', commonly called sorghum () and also known as great millet, broomcorn, guinea corn, durra, imphee, jowar, or milo, is a species in the Poaceae, grass genus ''Sorghum (genus), Sorghum'' cultivated for its grain. The grain i ...
and millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most millets belong to the tribe Paniceae.
Millets are important crops in the Semi-arid climate, ...
as Africa's most important food crop. Spanish colonizers of the 16th century introduced new staple crops to Asia from the Americas, including maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
and sweet potatoes, contributing to population growth there. On a larger scale, the introduction of potatoes and maize to the Old World improved people's nutrition throughout the Eurasian landmass, enabling more varied and abundant food production. Cassava and maize can have negative consequences when overused (for example, the nutritional diseases pellagra and konzo).
The discovery of the Americas provided the Old World with new arable landscapes suitable for growing sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
and coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially a ...
. Coffee, introduced in the Americas circa 1720 from Africa and the Middle East, and sugarcane, introduced from the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
to the Spanish West Indies
The Spanish West Indies, Spanish Caribbean or the Spanish Antilles (also known as "Las Antillas Occidentales" or simply "Las Antillas Españolas" in Spanish) were Spanish territories in the Caribbean. In terms of governance of the Spanish Empir ...
, subsequently became the primary commodity crops and exported goods of extensive Latin America
Latin America is the cultural region of the Americas where Romance languages are predominantly spoken, primarily Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Latin America is defined according to cultural identity, not geogr ...
n plantations. Introduced to India by the Portuguese, chili pepper
Chili peppers, also spelled chile or chilli ( ), are varieties of fruit#Berries, berry-fruit plants from the genus ''Capsicum'', which are members of the nightshade family Solanaceae, cultivated for their pungency. They are used as a spice to ...
s and potatoes from South America in turn became integral parts of Indian cuisine
Indian cuisine consists of a variety of regional and traditional cuisines native to the Indian subcontinent. Given the diversity in soil, climate, culture, ethnic groups, and occupations, these cuisines vary substantially and use locally av ...
, and starting the process of making curry an international dish.
Because crops traveled widely but at least initially their endemic fungi did not, for a limited time yields were somewhat higher in the new regions to which they were introduced, a form of ecological release or "". However, the exchange of pathogens has continued alongside globalization, and crops have declined back toward their endemic yields.
 The Spanish were the first Europeans to grow cacao, in 1590. Though cacao was usually consumed by European populations in the form of sweets and was at first treated as an expensive luxury item,
The Spanish were the first Europeans to grow cacao, in 1590. Though cacao was usually consumed by European populations in the form of sweets and was at first treated as an expensive luxury item, chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cocoa beans that can be a liquid, solid, or paste, either by itself or to flavoring, flavor other foods.
Cocoa beans are the processed seeds of the cacao tree (''Theobroma cacao''); unprocesse ...
helped with fatigue and provided energy. As for vanilla
Vanilla is a spice derived from orchids of the genus ''Vanilla (genus), Vanilla'', primarily obtained from pods of the flat-leaved vanilla (''Vanilla planifolia, V. planifolia'').
''Vanilla'' is not Autogamy, autogamous, so pollination ...
, the pods of the plant after chemical treatment acquired an aroma, which was then used both in cooking and in perfumery.
Rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
, originally domesticated in China, became widely planted in the New World; European planters there relied upon the skills of African slaves to cultivate it. Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
, South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
, Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...
, and Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territo ...
were major centers of rice production during the colonial era. Enslaved Africans brought their knowledge of water control, milling, winnowing, and other agrarian practices to the fields. This widespread knowledge among African slaves eventually made rice a staple food in the New World.
Citrus fruit
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering plant, flowering trees and shrubs in the family Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as Orange (fruit), oranges, Mandarin orange, mandarins, lemons, grapefruits, ...
s and grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began approximately 8,0 ...
s were brought to the Americas from the Mediterranean. At first, planters struggled to adapt these crops to New World climates, but by the late 19th century they were cultivated more consistently. Banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large treelike herbaceous flowering plants in the genus '' Musa''. In some countries, cooking bananas are called plantains, distinguishing the ...
s were introduced into the Americas in the 16th century by Portuguese sailors, who brought them from West Africa. Despite this early introduction, they were little consumed in the Americas as late as the 1880s, when large plantations were established in the Caribbean. The Manila galleon
The Manila galleon (; ) refers to the Spain, Spanish trading Sailing ship, ships that linked the Philippines in the Spanish East Indies to Mexico (New Spain), across the Pacific Ocean. The ships made one or two round-trip voyages per year betwe ...
trading network introduced American plants such as chayote and papaya into Southeast Asia; these were incorporated into the cuisines there.
Long before the arrival of the Spaniards, cultivators brought wild tomato
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible Berry (botany), berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originate ...
es from Central America to South America. Soon after Columbus's visit, tomatoes were brought to Spain, and from there to other European countries, including Italy. In 1544, Pietro Andrea Mattioli, a Tuscan physician and botanist, wrote that the tomato was eaten fried in oil there. The first Italian cookbook to include tomato sauce, ''Lo Scalco alla Moderna'' ("The Modern Steward"), was written by Italian chef Antonio Latini and was published in two volumes in 1692 and 1694. In 1790, the use of tomato sauce with pasta appeared for the first time, in the Italian cookbook ''L'Apicio Moderno'' ("The Modern Apicius
''Apicius'', also known as ''De re culinaria'' or ''De re coquinaria'' (''On the Subject of Cooking''), is a collection of Food and dining in the Roman Empire, Roman cookery recipes, which may have been compiled in the fifth century CE, or ea ...
"), by chef Francesco Leonardi.''L'Arte della cucina in Italia'', Emilio Faccioli, Einaudi, Milano, 1987
Alongside the intentional introductions of cultivated plants that were Crosby's focus, many wild plants including weeds of cultivation, such as dandelions and grass
Poaceae ( ), also called Gramineae ( ), is a large and nearly ubiquitous family (biology), family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos, the grasses of natural grassland and spe ...
es, were transferred in both directions, permanently affecting the ecology of many parts of the world.
Of animals
Initially, the Columbian exchange of animals largely went in one direction, from Europe to the New World, as the Eurasian regions had domesticated many more animals.Horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 mi ...
s, donkeys, mule
The mule is a domestic equine hybrid between a donkey, and a horse. It is the offspring of a male donkey (a jack) and a female horse (a mare). The horse and the donkey are different species, with different numbers of chromosomes; of the two ...
s, pigs
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), also called swine (: swine) or hog, is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is named the domestic pig when distinguishing it from other members of the genus '' Sus''. Some authorities cons ...
, cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are calle ...
, sheep
Sheep (: sheep) or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to d ...
, goats
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a species of goat-antelope that is mostly kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the famil ...
, chickens, dogs, cats
The cat (''Felis catus''), also referred to as the domestic cat or house cat, is a small domesticated carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species of the family Felidae. Advances in archaeology and genetics have shown that the ...
, and bees were rapidly adopted by native peoples for transport, food, and other uses. The Plains Indians, for example, made extensive use of horses for hunting.
horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 mi ...
s, pigs, cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are calle ...
, and sheep
Sheep (: sheep) or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to d ...
being landed from ships. Florentine Codex.
File:George Catlin - Buffalo hunt.jpg, Native Americans learned to use horses, dramatically expanding their hunting range. George Catlin, 1844
honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several species of bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of pl ...
from a variety of bees, such as '' Melipona'' or '' Trigona'', European bees ('' Apis mellifera'')—were more productive, delivering a honey with less water content and allowing for easier extraction from beehives—were introduced in New Spain, becoming an important part of farming production.
The Mapuche
The Mapuche ( , ) also known as Araucanians are a group of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging e ...
of Araucanía were fast to adopt the horse from the Spanish, and improve their military capabilities as they fought the Arauco War
The Arauco War was a long-running conflict between colonial Spaniards and the Mapuche people, mostly fought in the Araucanía region of Chile. The conflict began at first as a reaction to the Spanish conquerors attempting to establish cities a ...
against Spanish colonizers. Until the arrival of the Spanish, the Mapuches had largely maintained chilihueques ( llamas) as livestock. The Spanish introduction of sheep caused some competition between the two domesticated species. Anecdotal evidence of the mid-17th century shows that by then sheep far outnumbered llamas. The decline of llamas reached a point in the late 18th century when only the Mapuche from Mariquina and the Huequén next to Angol
Angol is a commune and capital city of the Malleco Province in the Araucanía Region of southern Chile. It is located at the foot of the Cordillera de Nahuelbuta and next to the Vergara River, that permitted communications by small boats to the ...
raised the species. In the Chiloé Archipelago
The Chiloé Archipelago (, , ) is a group of islands lying off the coast of Chile, in the Los Lagos Region. It is separated from mainland Chile by the Chacao Channel in the north, the Sea of Chiloé in the east and the Gulf of Corcovado in the s ...
the introduction of pigs by the Spanish proved a success. They could feed on the abundant shellfish and algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
exposed by the large tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables ...
s.
In the other direction, the turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, from North America, and the Muscovy duck, from Mexico and South America, were New World domestic animals transferred to Europe.
Of diseases
 The first manifestation of the Columbian exchange may have been the spread of
The first manifestation of the Columbian exchange may have been the spread of syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The prim ...
from the native people of the Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere, located south of the Gulf of Mexico and southwest of the Sargasso Sea. It is bounded by the Greater Antilles to the north from Cuba ...
to Europe. The history of syphilis has been well-studied, but the origin of the disease remains a subject of debate. There are two primary hypotheses: one proposes that syphilis was carried to Europe from the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
by the crew of Christopher Columbus in the early 1490s, while the other proposes that syphilis previously existed in Europe but went unrecognized. The first written descriptions of syphilis in the Old World came in 1493. The first large outbreak of syphilis in Europe occurred in 1494–1495 among the army of Charles VIII during its invasion of Naples. Many of the crew members who had served with Columbus had joined this army. After the victory, Charles's largely mercenary army returned to their respective homes, spreading "the Great Pox" across Europe, which killed up to five million people.
The Columbian exchange of diseases towards the New World was far deadlier. The peoples of the Americas had previously had no exposure to Old World diseases and little or no immunity to them. An epidemic of swine influenza beginning in 1493 killed many of the Taino people inhabiting Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
islands. The pre-contact population of the island of Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ) is an island between Geography of Cuba, Cuba and Geography of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico in the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and the second-largest by List of C ...
was probably at least 500,000, but by 1526, fewer than 500 were still alive. Spanish exploitation was part of the cause of the near-extinction of the native people. In 1518,
In 1518, smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
was first recorded in the Americas and became the deadliest imported Old World disease. Forty percent of the 200,000 people living in the Aztec
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the Post-Classic stage, post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central ...
capital of Tenochtitlan
, also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear, but the date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th annivers ...
, later Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city of Mexico, as well as the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North America. It is one of the most important cultural and finan ...
, are estimated to have died of smallpox in 1520 during the war of the Aztecs with conquistador Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquis of the Valley of Oaxaca (December 1485 – December 2, 1547) was a Spanish ''conquistador'' who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions o ...
. Epidemics, possibly of smallpox, spread from Central America
Central America is a subregion of North America. Its political boundaries are defined as bordering Mexico to the north, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Central America is usually ...
, devastated the population of the Inca Empire
The Inca Empire, officially known as the Realm of the Four Parts (, ), was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The History of the Incas, Inca ...
a few years before the arrival of the Spanish. The ravages of Old World diseases and Spanish exploitation reduced the Mexican population from an estimated 20 million to barely more than a million in the 16th century.
The Indigenous population of Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
decreased from about 9 million in the pre-Columbian era, to 600,000 in 1620. An estimated 80–95 percent of the Native American population died in epidemics within the first 100–150 years following 1492. Nunn and Qian also refer to the calculations of the scientist David Cook: in some cases no one survived due to diseases. The deadliest Old World diseases in the Americas were smallpox, measles
Measles (probably from Middle Dutch or Middle High German ''masel(e)'', meaning "blemish, blood blister") is a highly contagious, Vaccine-preventable diseases, vaccine-preventable infectious disease caused by Measles morbillivirus, measles v ...
, whooping cough
Whooping cough ( or ), also known as pertussis or the 100-day cough, is a highly contagious, Vaccine-preventable diseases, vaccine-preventable Pathogenic bacteria, bacterial disease. Initial symptoms are usually similar to those of the common c ...
, chicken pox, bubonic plague, typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposu ...
, and malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
. Yellow fever was brought to the Americas from Africa, probably by the slave trade. Many people in Africa had acquired immunity. Europeans suffered higher rates of death than did people of African descent when exposed to yellow fever in the Americas, as numerous epidemics swept the colonies and sugar plantations.
On the other hand, European exploration of tropical areas was aided by the New World discovery of quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg ...
, the first effective treatment for malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
. Cinchona
''Cinchona'' (pronounced or ) is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae containing at least 23 species of trees and shrubs. All are native to the Tropical Andes, tropical Andean forests of western South America. A few species are ...
trees from the Andes were processed and quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg ...
was obtained from their bark. Europeans suffered from this disease, but some Indigenous populations had developed at least partial resistance to it. In Africa, resistance to malaria has been associated with other genetic changes among sub-Saharan Africans and their descendants, which can cause sickle-cell disease. The resistance of sub-Saharan Africans to malaria in the southern United States and the Caribbean contributed greatly to the specific character of the Africa-sourced slavery in those regions.
Cultural exchanges
Clash of cultures
The movement of people between New and Old Worlds caused cultural exchanges, extending to what Pieter Emmer has called "a clash of cultures". This involved the transfer of European values to Indigenous cultures, such as the concept ofprivate property
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental Capacity (law), legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property, which is owned by a state entity, and from Collective ownership ...
in regions where property was often viewed as communal, universal monogamy
Monogamy ( ) is a social relation, relationship of Dyad (sociology), two individuals in which they form a mutual and exclusive intimate Significant other, partnership. Having only one partner at any one time, whether for life or #Serial monogamy ...
(though many Indigenous peoples were already monogamous), the role of women and children in the social system, and different concepts of labor, including slavery. Christianity was brought to the Indigenous peoples by priests and monks from Europe. Tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
was used in the Old World as medicine and currency, while in the New World, it was the subject of religious customs. Some New World peoples such as the Mapuche
The Mapuche ( , ) also known as Araucanians are a group of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging e ...
of Araucania resisted the adoption of Spanish technology, holding to their ancestral customs. Indigenous people have often been seen as static recipients of transatlantic encounters, but thousands of Native Americans crossed the ocean during the sixteenth century, some by choice.
Atlantic slave trade
 The Atlantic slave trade consisted of the involuntary immigration of 11.7 million Africans, primarily from West Africa, to the Americas between the 16th and 19th centuries, far outnumbering the about 3.4 million Europeans who migrated, most voluntarily, to the New World between 1492 and 1840. The prevalence of African slaves in the New World was related to the demographic decline of New World peoples and the need of European colonists for labor. Another reason for the demand for slaves was the cultivation of crops such as sugar cane suitable for the climatic conditions of the new lands. The Africans were less likely to die, too, from those diseases that had been brought to the New World. Enslaved Africans helped shape an emerging African-American culture in the New World. They participated in both skilled and unskilled labor. For example, slaves were involved in handicraft production. They could also work as ordinary workers, and as managers of small enterprises in the commercial or industrial sphere. Their descendants gradually developed an ethnicity that drew from the numerous African tribes as well as European nationalities. The descendants of African slaves make up a majority of the population in some Caribbean countries, notably
The Atlantic slave trade consisted of the involuntary immigration of 11.7 million Africans, primarily from West Africa, to the Americas between the 16th and 19th centuries, far outnumbering the about 3.4 million Europeans who migrated, most voluntarily, to the New World between 1492 and 1840. The prevalence of African slaves in the New World was related to the demographic decline of New World peoples and the need of European colonists for labor. Another reason for the demand for slaves was the cultivation of crops such as sugar cane suitable for the climatic conditions of the new lands. The Africans were less likely to die, too, from those diseases that had been brought to the New World. Enslaved Africans helped shape an emerging African-American culture in the New World. They participated in both skilled and unskilled labor. For example, slaves were involved in handicraft production. They could also work as ordinary workers, and as managers of small enterprises in the commercial or industrial sphere. Their descendants gradually developed an ethnicity that drew from the numerous African tribes as well as European nationalities. The descendants of African slaves make up a majority of the population in some Caribbean countries, notably Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican ...
and Jamaica
Jamaica is an island country in the Caribbean Sea and the West Indies. At , it is the third-largest island—after Cuba and Hispaniola—of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean. Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, west of Hispaniola (the is ...
, and a sizeable minority in most American countries.
See also
* Arab Agricultural Revolution * Early impact of Mesoamerican goods in Iberian society *Great American Interchange
The Great American Biotic Interchange (commonly abbreviated as GABI), also known as the Great American Interchange and the Great American Faunal Interchange, was an important late Cenozoic paleozoogeographic biotic interchange event in which land ...
* List of food plants native to the Americas
* Pre-Columbian trans-oceanic contact theories
* Transformation of culture
References
Sources
* :* * * * *Further reading
The Columbian Exchange: Plants, Animals, and Disease between the Old and New Worlds
by Alfred W. Crosby (2009) * '' 1491: New Revelations of the Americas Before Columbus'', New York: Alfred A. Knopf, by Charles C. Mann (2005); a
Google Books
* Specht, Joshua; Stockland, Etienne (2017). ''The Columbian Exchange''. CRC Press. *
Indian Givers: How the Indians of the Americas Transformed the World
' by Jack Weatherford (2010)
External links
*Foods that Changed the World
—Steven R. King {{DEFAULTSORT:Columbian exchange Age of Discovery Agricultural revolutions History of Europe History of agriculture History of globalization History of Indigenous peoples of the Americas History of the Americas History of the Atlantic Ocean Horticulture Introduced species Spanish colonization of the Americas Spanish exploration in the Age of Discovery Transatlantic cultural exchange Western culture