Color Task on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
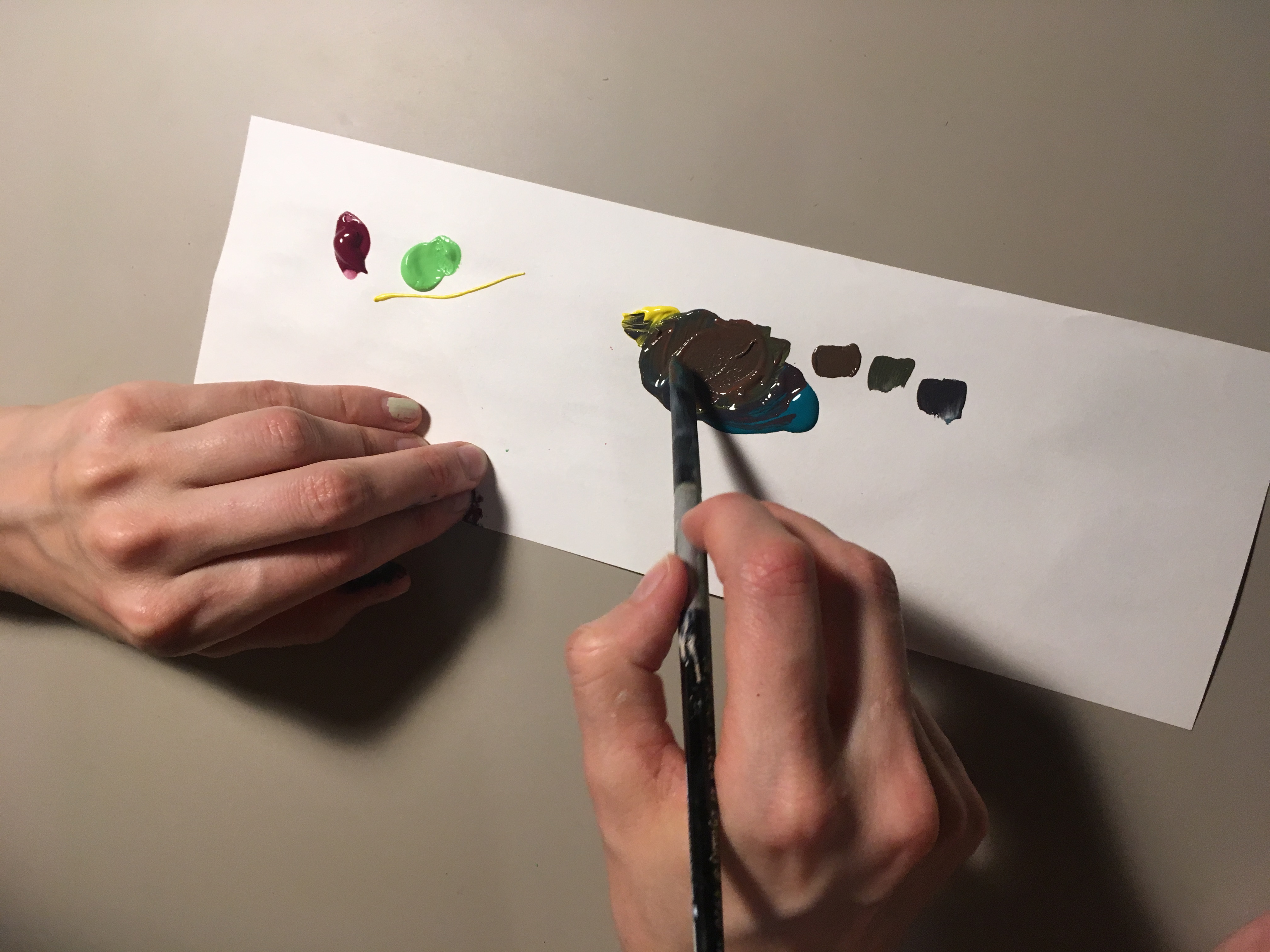 Color tasks are tasks that involve the recognition of
Color tasks are tasks that involve the recognition of
 Comparative color tasks require a subject to differentiate two colors. Simple examples include many
Comparative color tasks require a subject to differentiate two colors. Simple examples include many
 Generally, in order to communicate colors, they must first be converted into a meaningful
Generally, in order to communicate colors, they must first be converted into a meaningful
 Aesthetic color tasks require aesthetic judgments of colors, usually in terms of color harmony, where color combinations can be selected to be pleasing or flattering. Alternatively, colors can be selected for their evocative qualities (such as warmth or coolness). Aesthetic color tasks are necessary in
Aesthetic color tasks require aesthetic judgments of colors, usually in terms of color harmony, where color combinations can be selected to be pleasing or flattering. Alternatively, colors can be selected for their evocative qualities (such as warmth or coolness). Aesthetic color tasks are necessary in
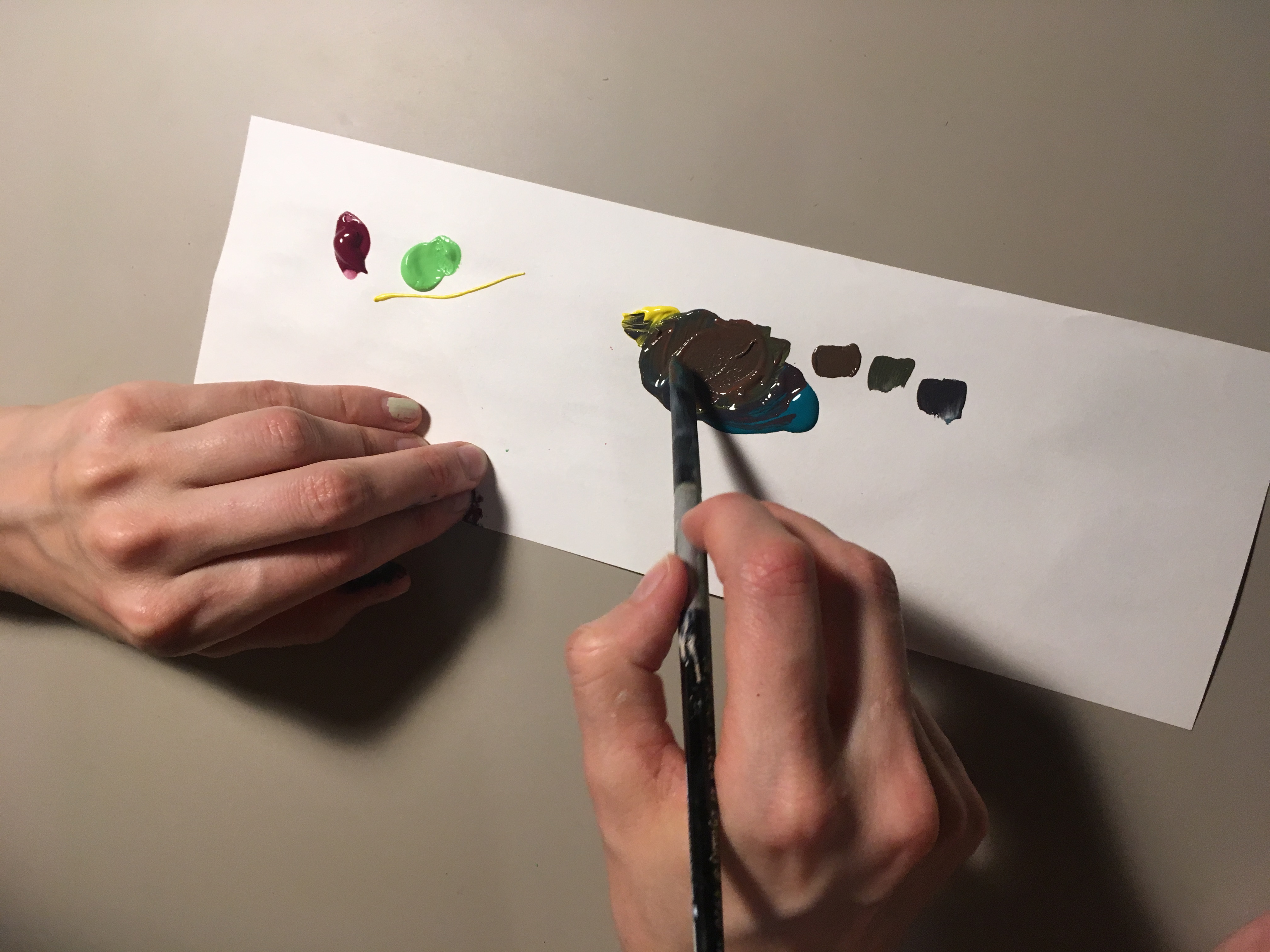 Color tasks are tasks that involve the recognition of
Color tasks are tasks that involve the recognition of colors
Color (or colour in Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is the visual perception based on the electromagnetic spectrum. Though color is not an inherent property of matter, color perception is related to an object's light absorpt ...
. Color tasks can be classified according to how the color is interpreted. Cole describes four categories of color tasks:
* Comparative – When multiple colors must be compared, such as with mixing paint
* Connotative – When colors are given an implicit meaning, such as red = stop
* Denotative – When identifying colors, for example by name, such as “where is the yellow ball?”
* Aesthetic – When colors look nice – or convey an emotional response – but don’t carry explicit meaning
Earlier classification of color tasks did not attempt to be comprehensive, and mainly differentiated between color matching/ordering, pseudoisochromatic plates and color-naming. In Cole's definitions, the latter would be denotative color tasks and the others would be comparative color tasks.
Color blindness
Color blindness
Color blindness, color vision deficiency (CVD) or color deficiency is the decreased ability to color vision, see color or differences in color. The severity of color blindness ranges from mostly unnoticeable to full absence of color percept ...
(or color vision deficiency) is a defect of normal color vision
Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different frequencies independently of light intensity.
Color perception is a part of the larger visual system and is mediated by a co ...
. Because color blindness is a symptom of several genetic and acquired conditions, the severity can range drastically from monochromacy
Monochromacy (from Greek ''mono'', meaning "one" and ''chromo'', meaning "color") is the ability of organisms to perceive only light intensity without respect to spectral composition. Organisms with monochromacy lack color vision and can only ...
(no color vision) to anomalous trichromacy (can be as mild as being indistinguishable from normal color vision). Congenital (genetic) color blindness causes difficulty in all four kinds of color tasks. However, cerebral color blindness may cause issues only in some types of color tasks, and other conditions that do not affect color vision can still affect color vision tasks (e.g. anomia).
Comparative
color vision tests
A color vision test is used for measuring color vision against a standard. These tests are most often used to diagnose color vision deficiencies ("CVD"; color blindness''), though several of the standards are designed to categorize normal color vi ...
, which are specifically modeled as comparative tasks. For example, the Ishihara test and other pseudoisochromatic plates require a direct comparison (and therefore discrimination) of foreground and background colors to be able to read the embedded number/character.
Arrangement tests such as the Farnsworth D-15 also requires comparison of adjacent colors to be able to arrange them in a meaningful spectrum
A spectrum (: spectra or spectrums) is a set of related ideas, objects, or properties whose features overlap such that they blend to form a continuum. The word ''spectrum'' was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of co ...
. In addition to being able to distinguish two colors, arrangement tests also require measuring color difference and decision making based on this parameter. Despite the increased complexity of this task, they were not differentiated by Cole, though were by others.
''Comparative'' tasks are the "purest" tasks that rely almost solely on color perception without interference of linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds ...
, culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
or memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembe ...
. Sometimes, color blindness derived from brain damage (such as cerebral achromatopsia) can affect the other color tasks while leaving the comparative color tasks untouched.
Other examples of comparative color tasks include:
* Distinguishing red fruits from green foliage
* Paint mixing
Paint mixing is the practice of mixing components or colors of paint to combine them into a working material and achieve a desired hue. The components that go into paint mixing depend on the function of the product sought to be produced. For examp ...
* Reading colored data with legends
* Painting/drawing realistic subjects
Connotative
Connotative color tasks require the subject to infer implicit information from a color. In addition to color vision, connotative color tasks require either cultural or natural knowledge to interpret the color's meaning. An example of a connotative color task based on cultural meaning aretraffic light
Traffic lights, traffic signals, or stoplights – also known as robots in South Africa, Zambia, and Namibia – are signaling devices positioned at intersection (road), road intersections, pedestrian crossings, and other locations in order t ...
s, which require the test taker to not only recognize the color, but also to interpret the meaning of the color ( red means stop). Examples of connotative color tasks based on natural meaning are interpretation of skin tone (blushing
Blushing or erubescence is the reddening of a person's face due to psychological reasons. It is normally involuntary and triggered by emotional stress associated with passion, embarrassment, shyness, fear, anger, or romantic stimulation.
S ...
, sunburn
Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and other animals include red or reddish skin tha ...
, pallor
Pallor is a pale color of the skin that can be caused by illness, emotional shock or stress, stimulant use, or anemia, and is the result of a reduced amount of oxyhaemoglobin and may also be visible as pallor of the conjunctivae of the eye ...
, etc.) and interpretation of food edibility ( ripeness, doneness
Doneness is a gauge of how thoroughly cooked a cut of meat is based on its color, juiciness, and internal temperature. The gradations are most often used in reference to beef (especially steaks and roasts) but are also applicable to other types ...
, etc.).
Denotative
color term
A color term (or color name) is a word or phrase that refers to a specific color. The color term may refer to human perception of that color (which is affected by visual context) which is usually defined according to the Munsell color system, or ...
or description. Anything that requires this conversion, either from color to description (color naming) or vice versa, is a denotative color task. Denotative color tasks involve both color perception and linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds ...
. Aphasia
Aphasia, also known as dysphasia, is an impairment in a person's ability to comprehend or formulate language because of dysfunction in specific brain regions. The major causes are stroke and head trauma; prevalence is hard to determine, but aph ...
or color anomia
Anomic aphasia, also known as dysnomia, nominal aphasia, and amnesic aphasia, is a mild, fluent type of aphasia where individuals have word retrieval failures and cannot express the words they want to say (particularly nouns and verbs). By cont ...
can also lead to a failure to perform denotative color tasks even when color vision is normal. Some color vision tests comprise denotative tasks, such as lantern tests, which require the subject to name the colors of lights.
Aesthetic
 Aesthetic color tasks require aesthetic judgments of colors, usually in terms of color harmony, where color combinations can be selected to be pleasing or flattering. Alternatively, colors can be selected for their evocative qualities (such as warmth or coolness). Aesthetic color tasks are necessary in
Aesthetic color tasks require aesthetic judgments of colors, usually in terms of color harmony, where color combinations can be selected to be pleasing or flattering. Alternatively, colors can be selected for their evocative qualities (such as warmth or coolness). Aesthetic color tasks are necessary in architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
, interior decoration, graphic design
Graphic design is a profession, academic discipline and applied art that involves creating visual communications intended to transmit specific messages to social groups, with specific objectives. Graphic design is an interdisciplinary branch of ...
, advertising
Advertising is the practice and techniques employed to bring attention to a Product (business), product or Service (economics), service. Advertising aims to present a product or service in terms of utility, advantages, and qualities of int ...
, matching clothes, abstract art
Abstract art uses visual language of shape, form, color and line to create a Composition (visual arts), composition which may exist with a degree of independence from visual references in the world. ''Abstract art'', ''non-figurative art'', ''non- ...
, and other applications. Aesthetic tasks are not generally tested for, since aesthetic tasks are highly subjective.
See also
* City University test * Color agnosia *Color anomia
Anomic aphasia, also known as dysnomia, nominal aphasia, and amnesic aphasia, is a mild, fluent type of aphasia where individuals have word retrieval failures and cannot express the words they want to say (particularly nouns and verbs). By cont ...
References
{{reflist task Color vision Agnosia