|
City University Test
The City University test (also known as TCU test or CU test) is a color vision test used to detect color vision deficiency. Unlike commonly used Ishihara test, City University test can be used to detect all types of color vision defects. Description The commonly used Ishihara test is used to detect mainly congenital red-green color blindness, but its usefulness is limited in detecting acquired color vision deficiencies. But City University test contains test plates that can be used to detect all types of color vision deficiencies. The TCU test was derived from Farnsworth D15 color arrangement test. The test consists of 10 plates, containing a central colored dot surrounded by four peripheral dots of different colors. The subject is asked to choose the dot closest to the central hue. Among the four peripheral dots, three peripheral colors are designed in such a way that, it makes confusion with the central color in protan, deutan and tritan deficiency. The fourth color is an adj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology (, ) is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and surgery of eye diseases and disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency training specific to that field. In the United States, following graduation from medical school, one must complete a four-year residency in ophthalmology to become an ophthalmologist. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat ailments, such as eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care—medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training and many inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optometry
Optometry is the healthcare practice concerned with examining the eyes for visual defects, prescribing corrective lenses, and detecting eye abnormalities. In the United States and Canada, optometrists are those that hold a post-baccalaureate four-year Doctor of Optometry degree. They are trained and licensed to practice medicine for eye related conditions, in addition to providing refractive (optical) eye care. Within their scope of practice, optometrists are considered physicians and bill medical insurance(s) (example: Medicare) accordingly. In the United Kingdom, optometrists may also provide medical care (e.g. prescribe medications and perform various surgeries) for eye-related conditions in addition to providing refractive care. The Doctor of Optometry degree is rarer in the UK. Many optometrists participate in academic research for eye-related conditions and diseases. In addition to prescribing glasses and contact lenses for vision related deficiencies, optometrists are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
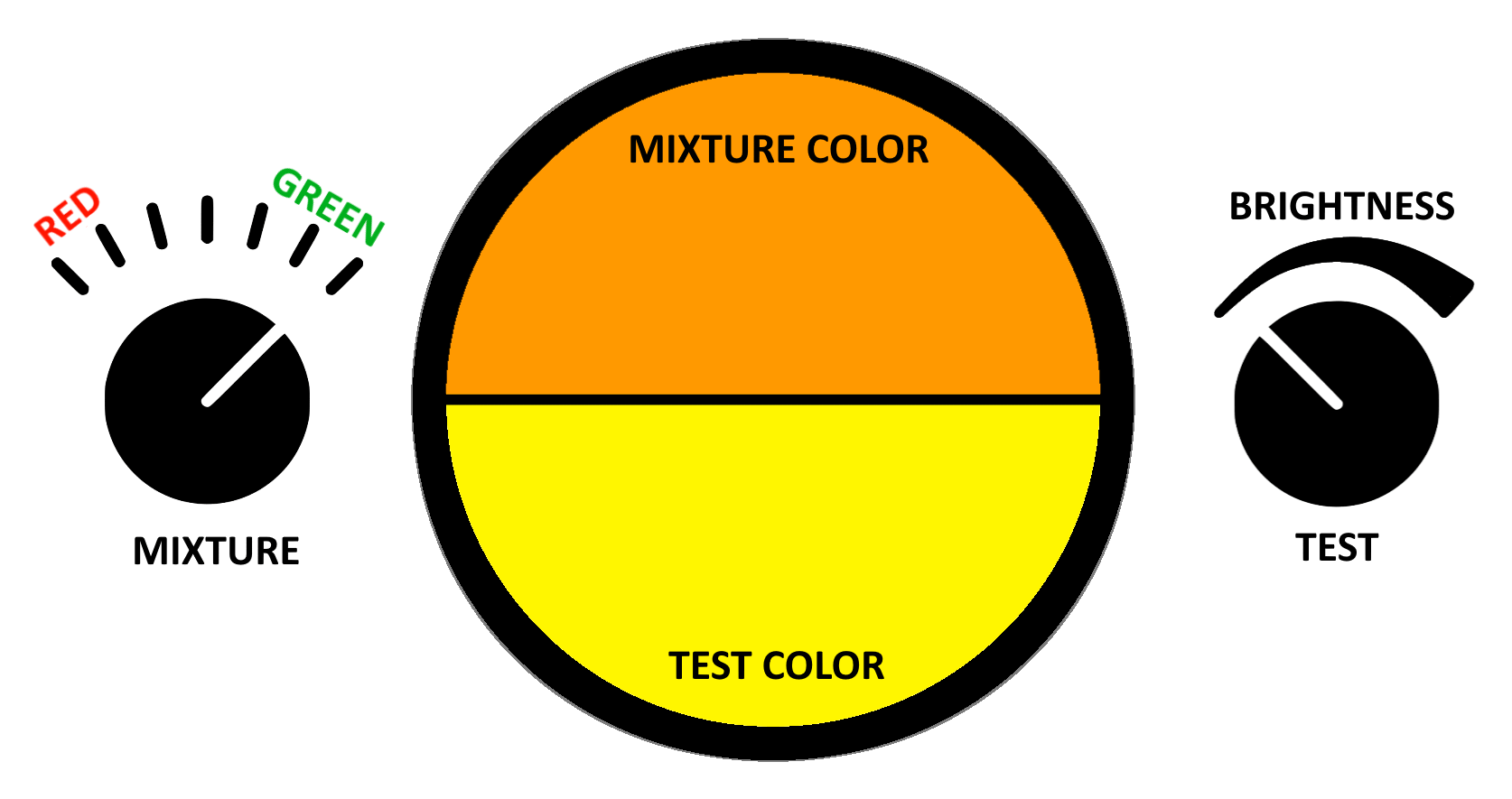
Color Vision Test
A color vision test is used for measuring color vision against a standard. These tests are most often used to diagnose color vision deficiencies ("CVD"; color blindness''), though several of the standards are designed to categorize normal color vision into sub-levels. With the large prevalence of color vision deficiencies (8% of males) and the Color blindness#Occupations, wide range of professions that restrict hiring the colorblind for safety or aesthetic reasons, clinical color vision standards must be designed to be fast and simple to implement. Color vision standards for academic use trade speed and simplicity for accuracy and precision. Applications Color vision standards are used to evaluate the color vision of a subject. They are most commonly applied to job applicants during pre-job screening. The evaluation may be to select against the color blindness, color vision deficient for roles where basic color vision is required, or to select for individuals with superior color v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Vision Deficiency
Color blindness, color vision deficiency (CVD) or color deficiency is the decreased ability to color vision, see color or differences in color. The severity of color blindness ranges from mostly unnoticeable to full absence of color perception. Color blindness is usually a Sex linkage, sex-linked Heredity, inherited problem or variation in the functionality of one or more of the three classes of cone cells in the retina, which mediate color vision. The most common form is caused by a genetic condition called congenital red–green color blindness (including protan and deutan types), which affects ''up to'' 1 in 12 males (8%) and 1 in 200 females (0.5%). The condition is more prevalent in males, because the opsin genes responsible are located on the X chromosome. Rarer genetic conditions causing color blindness include congenital blue–yellow color blindness (tritan type), blue cone monochromacy, and achromatopsia. Color blindness can also result from physical or chemical dam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishihara Test
The Ishihara test is a color vision test for detection of red–green color deficiencies. It was named after its designer, Shinobu Ishihara, a professor at the University of Tokyo, who first published his tests in 1917.S. Ishihara, Tests for color-blindness (Handaya, Tokyo, Hongo Harukicho, 1917). The test consists of a number of Ishihara plates, which are a type of pseudoisochromatic plate. Each plate depicts a solid circle of colored dots appearing randomized in color and size. Within the pattern are dots which form a number or shape clearly visible to those with normal color vision, and invisible, or difficult to see, to those with a red–green color vision deficiency. Other plates are intentionally designed to reveal numbers only to those with a red–green color vision deficiency, and be invisible to those with normal red–green color vision. The full test consists of 38 plates, but the existence of a severe deficiency is usually apparent after only a few plates. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Survey Of Ophthalmology
''Survey of Ophthalmology'' is a review journal dedicated to publishing reviews of ophthalmological topics by established authorities in that particular field. It is a strictly refereed journal with a bi-monthly publication schedule. The procedure of evaluating and inviting specific topics is done primarily by selecting current academics with a record of innovative and original research, supported by publications in international peer journals. See also *'' Archives of Ophthalmology'' *'' Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science'' *List of medical journals Medical journals are published regularly to communicate new research to clinicians, medical scientists, and other healthcare workers. This article lists academic journals that focus on the practice of medicine or any medical specialty. Jour ... External links * Ophthalmology journals Elsevier academic journals Review journals Bimonthly journals English-language journals Academic journals established in 1956< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protanomaly
Color blindness, color vision deficiency (CVD) or color deficiency is the decreased ability to see color or differences in color. The severity of color blindness ranges from mostly unnoticeable to full absence of color perception. Color blindness is usually a sex-linked inherited problem or variation in the functionality of one or more of the three classes of cone cells in the retina, which mediate color vision. The most common form is caused by a genetic condition called congenital red–green color blindness (including protan and deutan types), which affects ''up to'' 1 in 12 males (8%) and 1 in 200 females (0.5%). The condition is more prevalent in males, because the opsin genes responsible are located on the X chromosome. Rarer genetic conditions causing color blindness include congenital blue–yellow color blindness (tritan type), blue cone monochromacy, and achromatopsia. Color blindness can also result from physical or chemical damage to the eye, the optic nerve, pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |