Cholesterol level on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cholesterol is the principal

 This molecule is then reduced to mevalonate by the enzyme
This molecule is then reduced to mevalonate by the enzyme  Mevalonate is finally converted to
Mevalonate is finally converted to 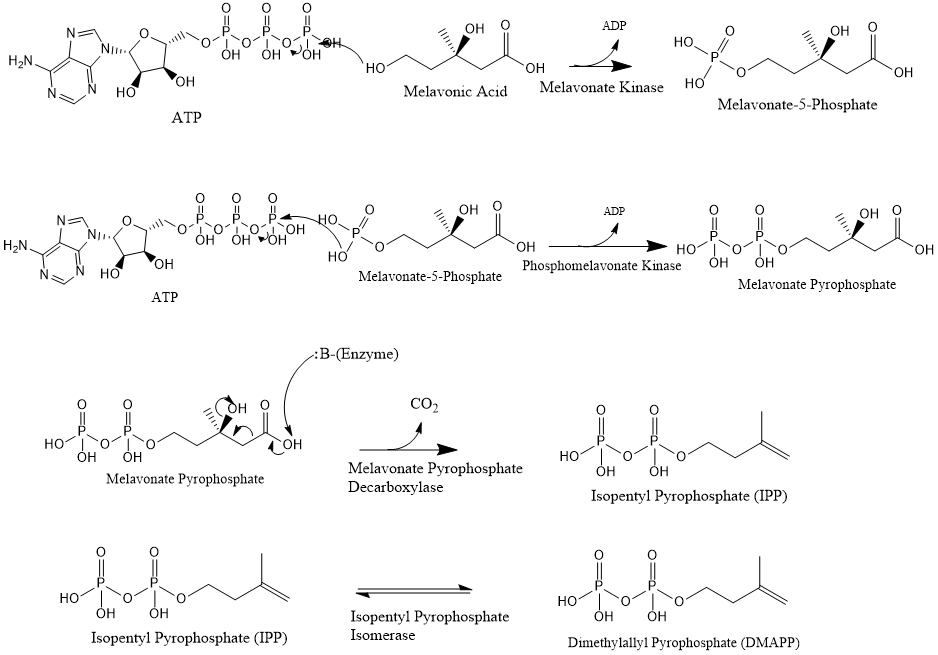 Three molecules of isopentenyl pyrophosphate condense to form
Three molecules of isopentenyl pyrophosphate condense to form  Two molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate then condense to form
Two molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate then condense to form 



 Finally,
Finally, 

 As an isolated molecule, cholesterol is only minimally soluble in
As an isolated molecule, cholesterol is only minimally soluble in
 According to the
According to the  Total cholesterol is defined as the sum of HDL, LDL, and VLDL. Usually, only the total, HDL, and triglycerides are measured. For cost reasons, the VLDL is usually estimated as one-fifth of the triglycerides and the LDL is estimated using the Friedewald formula (or a variant): estimated LDL = otal cholesterol− otal HDL− stimated VLDL Direct LDL measures are used when triglycerides exceed 400 mg/dL. The estimated VLDL and LDL have more error when triglycerides are above 400 mg/dL.
In the
Total cholesterol is defined as the sum of HDL, LDL, and VLDL. Usually, only the total, HDL, and triglycerides are measured. For cost reasons, the VLDL is usually estimated as one-fifth of the triglycerides and the LDL is estimated using the Friedewald formula (or a variant): estimated LDL = otal cholesterol− otal HDL− stimated VLDL Direct LDL measures are used when triglycerides exceed 400 mg/dL. The estimated VLDL and LDL have more error when triglycerides are above 400 mg/dL.
In the
 Cholesterol has 256
Cholesterol has 256
File:ConversColest.png, Cholesterol units conversion
File:Steroidogenesis.svg,
sterol
A sterol is any organic compound with a Skeletal formula, skeleton closely related to Cholestanol, cholestan-3-ol. The simplest sterol is gonan-3-ol, which has a formula of , and is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom on ...
of all higher animals, distributed in body tissues, especially the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
and spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
, and in animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesized
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme- catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthesis) serve ...
by all animal cells and is an essential structural and signaling
A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of data over some media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processing, information theory and biology.
...
component of animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
s. In vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s, hepatic cells
Hepatic stellate cells (HSC), also known as perisinusoidal cells or Ito cells (earlier ''lipocytes'' or ''fat-storing cells''), are pericytes found in the perisinusoidal space of the liver, also known as the space of Disse (a small area between t ...
typically produce the greatest amounts. In the brain, astrocytes
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" and , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of end ...
produce cholesterol and transport it to neurons
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
. It is absent among prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Gree ...
s (bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
and archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
), although there are some exceptions, such as ''Mycoplasma
''Mycoplasma'' is a genus of bacteria that, like the other members of the class ''Mollicutes'', lack a cell wall, and its peptidoglycan, around their cell membrane. The absence of peptidoglycan makes them naturally resistant to antibiotics ...
'', which require cholesterol for growth. Cholesterol also serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormone
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids (typically made in the adrenal cortex, hence ''cortico-'') and sex steroids (typically made in the gonads or placenta). Wit ...
s, bile acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver in peroxisomes. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine residues to give anions called bile ...
and vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
.
Elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood, especially when bound to low-density lipoprotein
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons (aka ULDL by the overall density ...
(LDL, often referred to as "bad cholesterol"), may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
.
François Poulletier de la Salle
François Poulletier de la Salle (30 September 1719 in Lyon – 20 March 1788 in Paris) was a French medical doctor and chemist. In about 1758, he isolated for the first time the crystals from cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal ste ...
first identified cholesterol in solid form in gallstone
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of ...
s in 1769. In 1815, chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul
Michel Eugène Chevreul (; 31 August 1786 – 9 April 1889) was a French chemist whose work contributed to significant developments in science, medicine, and art. Chevreul's early work with animal fats revolutionized soap and candle manufacturing ...
named the compound "cholesterine".
Etymology
The word ''cholesterol'' comes fromAncient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
''chole-'' 'bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), also known as gall, is a yellow-green/misty green fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is primarily composed of water, is pro ...
' and ''stereos'' 'solid', followed by the chemical
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combin ...
suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns and adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can ca ...
''-ol'' for an alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
.
Physiology
Cholesterol is essential for all animal life. While most cells are capable of synthesizing it, the majority of cholesterol is ingested or synthesized byhepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass.
These cells are involved in:
* Protein synthesis
* Protein storage
* Transformation of carbohydrates
* Synthesis of cholesterol, bi ...
s and transported in the blood to peripheral cells. The levels of cholesterol in peripheral tissues are dictated by a balance of uptake and export. Under normal conditions, brain cholesterol is separate from peripheral cholesterol, i.e., the dietary and hepatic cholesterol do not cross the blood brain barrier. Rather, astrocyte
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" and , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of en ...
s produce and distribute cholesterol in the brain.
De novo synthesis, both in astrocytes and hepatocytes, occurs by a complex 37-step process. This begins with the mevalonate or HMG-CoA reductase pathway
The mevalonate pathway, also known as the isoprenoid pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway is an essential metabolic pathway present in eukaryotes, archaea, and some bacteria. The pathway produces two five-carbon building blocks called isopentenyl ...
, the target of statin
Statins (or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) are a class of medications that lower cholesterol. They are prescribed typically to people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease.
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play ...
drugs, which encompasses the first 18 steps. This is followed by 19 additional steps to convert the resulting lanosterol
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast, plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol. In the eyes of vertebrates, lanosterol is a natural constituent, havin ...
into cholesterol. A human male weighing 68 kg (150 lb) normally synthesizes about 1 gram (1,000 mg) of cholesterol per day, and his body contains about 35 g, mostly contained within the cell membranes.
Typical daily cholesterol dietary intake for a man in the United States is 307 mg.
Most ingested cholesterol is esterified
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distinct ...
, which causes it to be poorly absorbed by the gut. The body also compensates for absorption of ingested cholesterol by reducing its own cholesterol synthesis. For these reasons, cholesterol in food, seven to ten hours after ingestion, has little, if any effect on concentrations of cholesterol in the blood. Surprisingly, in rats, blood cholesterol is inversely correlated with cholesterol consumption. The more cholesterol a rat eats the lower the blood cholesterol. During the first seven hours after ingestion of cholesterol, as absorbed fats are being distributed around the body within extracellular water by the various lipoprotein
A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly whose primary function is to transport hydrophobic lipid (also known as fat) molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids. They consist of a triglyceride and cholesterol center, sur ...
s (which transport all fats in the water outside cells), the concentrations increase.
Plants make cholesterol in very small amounts. In larger quantities they produce phytosterol
Phytosterols are phytosteroids, similar to cholesterol, that serve as structural components of biological membranes of plants. They encompass plant sterols and stanol ester, stanols. More than 250 sterols and related compounds have been identified ...
s, chemically similar substances which can compete with cholesterol for reabsorption in the intestinal tract, thus potentially reducing cholesterol reabsorption. When intestinal lining cells absorb phytosterols, in place of cholesterol, they usually excrete the phytosterol molecules back into the GI tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. T ...
, an important protective mechanism. The intake of naturally occurring phytosterols, which encompass plant sterols
A sterol is any organic compound with a Skeletal formula, skeleton closely related to Cholestanol, cholestan-3-ol. The simplest sterol is gonan-3-ol, which has a formula of , and is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom on ...
and stanols, ranges between ≈200–300 mg/day depending on eating habits. Specially designed vegetarian experimental diets have been produced yielding upwards of 700 mg/day.
Function
Membranes
Cholesterol is present in varying degrees in all animalcell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
s, but is absent in prokaryotes. It is required to build and maintain membranes and modulates membrane fluidity
In biology, membrane fluidity refers to the viscosity of the lipid bilayer of a cell membrane or a synthetic lipid membrane. Lipid packing can influence the fluidity of the membrane. Viscosity of the membrane can affect the rotation and diffusion ...
over the range of physiological temperatures. The hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
group of each cholesterol molecule interacts with water molecules surrounding the membrane, as do the polar heads of the membrane
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. Bi ...
phospholipid
Phospholipids are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typ ...
s and sphingolipid
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids containing a backbone of sphingoid bases, which are a set of aliphatic amino alcohols that includes sphingosine. They were discovered in brain extracts in the 1870s and were named after the mythological sp ...
s, while the bulky steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes t ...
and the hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and Hydrophobe, hydrophobic; their odor is usually fain ...
chain are embedded in the membrane, alongside the nonpolar
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end.
Polar molecules must contain one or more polar ...
fatty-acid chain of the other lipids. Through the interaction with the phospholipid fatty-acid chains, cholesterol increases membrane packing, which both alters membrane fluidity and maintains membrane integrity so that animal cells do not need to build cell walls (like plants and most bacteria). The membrane remains stable and durable without being rigid, allowing animal cells to change shape and animals to move.
The structure of the tetracyclic
Tetracyclics are cyclic compound, cyclic chemical compounds that contain four fused ring (chemistry), rings of atoms, for example, Tröger's base.
Some tricyclic compounds having three fused and one tethered ring (connected to main nucleus by ...
ring of cholesterol contributes to the fluidity of the cell membrane, as the molecule is in a ''trans'' conformation making all but the side chain of cholesterol rigid and planar. In this structural role, cholesterol also reduces the permeability of the plasma membrane to neutral solutes, hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
ions, and sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
ions.
Substrate presentation
Cholesterol regulates the biological process ofsubstrate presentation
In molecular biology, substrate presentation is a biological process that activates a protein. The protein is sequestered away from its substrate and then activated by release and exposure to its substrate. A ''substrate'' is typically the subst ...
and the enzymes that use substrate presentation as a mechanism of their activation. Phospholipase D2 (PLD2
Phospholipase D2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PLD2'' gene.
Function
Phosphatidylcholine (PC)-specific phospholipase D, phospholipases D (PLDs) catalyze the hydrolysis of PC to produce phosphatidic acid and choline. Activati ...
) is a well-defined example of an enzyme activated by substrate presentation. The enzyme is palmitoylated causing the enzyme to traffic to cholesterol dependent lipid domains sometimes called " lipid rafts". The substrate of phospholipase D
Phospholipase D (PLD) (EC 3.1.4.4; also known as lipophosphodiesterase II, lecithinase D, choline phosphatase; systematic name: phosphatidylcholine phosphatidohydrolase) is an anesthetic-sensitive and mechanosensitive enzyme of the phospholipa ...
is phosphatidylcholine
Phosphatidylcholines (PC) are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.
They are a major component of biological membranes and can easily be obtained from a variety of readily available sources, such as egg yolk or soyb ...
(PC) which is unsaturated and is of low abundance in lipid rafts. PC localizes to the disordered region of the cell along with the polyunsaturated lipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdIns(4,5)''P''2, also known simply as PIP2 or PI(4,5)P2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes. PtdIns(4,5)''P''2 is enriched at the plasma membrane where it is a substrate for a number of ...
(PIP2). PLD2 has a PIP2 binding domain
In molecular biology, binding domain is a protein domain which binds to a specific atom or molecule, such as calcium or DNA. A protein domain is a part of a protein sequence and a tertiary structure that can change or evolve, function, and live ...
. When PIP2 concentration in the membrane increases, PLD2 leaves the cholesterol-dependent domains and binds to PIP2 where it then gains access to its substrate PC and commences catalysis based on substrate presentation.

Signaling
Cholesterol is also implicated in cell signaling processes, assisting in the formation oflipid raft
The cell membrane, plasma membranes of cells contain combinations of glycosphingolipids, cholesterol and protein Receptor (biochemistry), receptors organized in glycolipoprotein lipid microdomains termed lipid rafts. Their existence in cellular me ...
s in the plasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
, which brings receptor proteins in close proximity with high concentrations of second messenger molecules.
In multiple layers, cholesterol and phospholipids, both electrical insulators, can facilitate speed of transmission of electrical impulses along nerve tissue. For many neuron fibers, a myelin
Myelin Sheath ( ) is a lipid-rich material that in most vertebrates surrounds the axons of neurons to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) pass along the axon. The myelinated axon can be lik ...
sheath, rich in cholesterol since it is derived from compacted layers of Schwann cell
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes (named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann) are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Glial cells function to support neurons and in the PNS, also include Satellite glial cell, satellite ...
or oligodendrocyte membranes, provides insulation for more efficient conduction of impulses. Demyelination (loss of myelin) is believed to be part of the basis for multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
.
Cholesterol binds to and affects the gating of a number of ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by Gating (electrophysiol ...
s such as the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are Receptor (biochemistry), receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the c ...
, GABAA receptor, and the inward-rectifier potassium channel
Inward-rectifier potassium channels (Kir, IRK) are a specific Lipid-gated_ion_channels, lipid-gated subset of potassium channels. To date, seven subfamilies have been identified in various mammalian cell types, plants, and bacteria. They are acti ...
. Cholesterol also activates the estrogen-related receptor alpha
Estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRα), also known as NR3B1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group B, member 1), is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''ESRRA'' (Estrogen Related Receptor Alpha) gene. ERRα was originally cloned ...
(ERRα), and may be the endogenous
Endogeny, in biology, refers to the property of originating or developing from within an organism, tissue, or cell.
For example, ''endogenous substances'', and ''endogenous processes'' are those that originate within a living system (e.g. an ...
ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's el ...
for the receptor
Receptor may refer to:
* Sensory receptor, in physiology, any neurite structure that, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and respond ...
. The constitutively active nature of the receptor may be explained by the fact that cholesterol is ubiquitous in the body. Inhibition of ERRα signaling by reduction of cholesterol production has been identified as a key mediator of the effects of statin
Statins (or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) are a class of medications that lower cholesterol. They are prescribed typically to people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease.
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play ...
s and bisphosphonate
Bisphosphonates are a class of drugs that prevent the loss of bone density, used to treat osteoporosis and similar diseases. They are the most commonly prescribed to treat osteoporosis.
Evidence shows that they reduce the risk of fracture in ...
s on bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
, muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
, and macrophage
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that ...
s. On the basis of these findings, it has been suggested that the ERRα should be de-orphanized and classified as a receptor for cholesterol.
As a chemical precursor
Within cells, cholesterol is also a precursor molecule for severalbiochemical pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical ...
s. For example, it is the precursor molecule for the synthesis of vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
in the calcium metabolism
Calcium metabolism is the movement and regulation of calcium ions (Ca2+) ''in'' (via the gut) and ''out'' (via the gut and kidneys) of the body, and ''between'' body compartments: the blood plasma, the extracellular and intracellular fluids, an ...
and all steroid hormones
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids (typically made in the adrenal cortex, hence ''cortico-'') and sex steroids (typically made in the gonads or placenta). Withi ...
, including the adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer adrenal corte ...
hormones cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone in the glucocorticoid class of hormones and a stress hormone. When used as medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
Cortisol is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal corte ...
and aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays ...
, as well as the sex hormones progesterone
Progesterone (; P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the ma ...
, estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
s, and testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
, and their derivatives.
Epidermis
The stratum corneum is the outermost layer of the epidermis. It is composed of terminally differentiated and enucleatedcorneocyte
Corneocytes are terminally differentiated keratinocytes and compose most of the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the epidermis. They are regularly replaced through desquamation and renewal from lower epidermal layers and are essential fo ...
s that reside within a lipid matrix, like "bricks and mortar." Together with ceramide
Ceramides are a family of waxy lipid molecules. A ceramide is composed of sphingosine and a fatty acid joined by an amide bond. Ceramides are found in high concentrations within the cell membrane of Eukaryote, eukaryotic cells, since they are co ...
s and free fatty acids, cholesterol forms the lipid mortar, a water-impermeable barrier that prevents evaporative water loss. As a rule of thumb, the epidermal lipid matrix is composed of an equimolar mixture of ceramides (≈50% by weight), cholesterol (≈25% by weight), and free fatty acids (≈15% by weight), with smaller quantities of other lipids also being present. Cholesterol sulfate reaches its highest concentration in the granular layer of the epidermis. Steroid sulfate sulfatase then decreases its concentration in the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the epidermis. The relative abundance of cholesterol sulfate in the epidermis varies across different body sites with the heel of the foot having the lowest concentration.
Metabolism
Cholesterol isrecycled
Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new materials and objects. This concept often includes the recovery of energy from waste materials. The recyclability of a material depends on its ability to reacquire the propert ...
in the body. The liver excretes cholesterol into biliary
A bile duct is any of a number of long tube-like structures that carry bile, and is present in most vertebrates. The bile duct is separated into three main parts: the fundus (superior), the body (middle), and the neck (inferior).
Bile is requ ...
fluids, which are then stored in the gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow Organ (anatomy), organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath t ...
, which then excretes them in a non-ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
ified form (via bile) into the digestive tract. Typically, about 50% of the excreted cholesterol is reabsorbed by the small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ (anatomy), organ in the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract where most of the #Absorption, absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intes ...
back into the bloodstream.
Biosynthesis and regulation
Biosynthesis
Almost all animal tissues synthesize cholesterol fromacetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidation, o ...
. All animal cells (exceptions exist within the invertebrates) manufacture cholesterol, for both membrane structure and other uses, with relative production rates varying by cell type and organ function. About 80% of total daily cholesterol production occurs in the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
and the intestines
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. ...
; other sites of higher synthesis
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to:
Science Chemistry and biochemistry
*Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors
**Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organi ...
rates include the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
, the adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer adrenal corte ...
s, and the reproductive organ
A sex organ, also known as a reproductive organ, is a part of an organism that is involved in sexual reproduction. Sex organs constitute the primary sex characteristics of an organism. Sex organs are responsible for producing and transporting ...
s.
Synthesis within the body starts with the mevalonate pathway
The mevalonate pathway, also known as the isoprenoid pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway is an essential metabolic pathway present in eukaryotes, archaea, and some bacteria. The pathway produces two five-carbon building blocks called isopentenyl ...
where two molecules of acetyl CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized fo ...
condense to form acetoacetyl-CoA
Acetoacetyl CoA is the precursor of HMG-CoA in the mevalonate pathway, which is essential for cholesterol biosynthesis. It also takes a similar role in the ketone bodies synthesis ( ketogenesis) pathway of the liver. In the ketone bodies digestion ...
. This is followed by a second condensation between acetyl CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized fo ...
and acetoacetyl-CoA
Acetoacetyl CoA is the precursor of HMG-CoA in the mevalonate pathway, which is essential for cholesterol biosynthesis. It also takes a similar role in the ketone bodies synthesis ( ketogenesis) pathway of the liver. In the ketone bodies digestion ...
to form 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA
β-Hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), also known as 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A, is an intermediate in the mevalonate pathway, mevalonate and ketogenesis pathways. It is formed from acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA by HMG-CoA synthase ...
(HMG-CoA
β-Hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), also known as 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A, is an intermediate in the mevalonate pathway, mevalonate and ketogenesis pathways. It is formed from acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA by HMG-CoA synthase ...
).
 This molecule is then reduced to mevalonate by the enzyme
This molecule is then reduced to mevalonate by the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase
HMG-CoA reductase (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, official symbol HMGCR) is the rate-limiting enzyme (NADH-dependent, ; NADPH-dependent, ) of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other ...
. Production of mevalonate is the rate-limiting and irreversible step in cholesterol synthesis and is the site of action for statin
Statins (or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) are a class of medications that lower cholesterol. They are prescribed typically to people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease.
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play ...
s (a class of cholesterol-lowering drugs).
 Mevalonate is finally converted to
Mevalonate is finally converted to isopentenyl pyrophosphate
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate, or IDP) is an isoprenoid precursor. IPP is an intermediate in the classical, HMG-CoA reductase pathway (commonly called the mevalonate pathway) and in the ''non-mevalonate'' MEP pathway of i ...
(IPP) through two phosphorylation steps and one decarboxylation step that requires ATP.
 Three molecules of isopentenyl pyrophosphate condense to form
Three molecules of isopentenyl pyrophosphate condense to form farnesyl pyrophosphate
Farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP), also known as farnesyl diphosphate (FDP), is the precursor to all sesquiterpenes, which comprises thousands of compounds. These include all sesquiterpenes as well as sterols and carotenoids. It is also used in the syn ...
through the action of geranyl transferase.
 Two molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate then condense to form
Two molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate then condense to form squalene
Squalene is an organic compound. It is a triterpene with the formula C30H50. It is a colourless oil, although impure samples appear yellow. It was originally obtained from shark liver oil (hence its name, as '' Squalus'' is a genus of sharks). ...
by the action of squalene synthase
Squalene synthase (SQS) or farnesyl-diphosphate:farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyl transferase is an enzyme localized to the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. SQS participates in the terpenoid, isoprenoid biosynthetic pathway, catalyzing a two-s ...
in the endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a part of a transportation system of the eukaryote, eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. The word endoplasmic means "within the cytoplasm", and reticulum is Latin for ...
.


Oxidosqualene cyclase Oxidosqualene cyclases (OSC) are enzymes involved in cyclization reactions of 2,3-oxidosqualene to form sterols or triterpenes.
There are two major groups of sterol-producing OSC enzymes:
* Cycloartenol synthase (CAS), found in all plants, which ...
then cyclizes squalene to form lanosterol
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast, plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol. In the eyes of vertebrates, lanosterol is a natural constituent, havin ...
.


 Finally,
Finally, lanosterol
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast, plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol. In the eyes of vertebrates, lanosterol is a natural constituent, havin ...
is converted to cholesterol via either of two pathways, the Bloch pathway, or the Kandutsch-Russell pathway.
The final 19 steps to cholesterol contain NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require N ...
and oxygen to help oxidize methyl group
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula (whereas normal methane has the formula ). In formulas, the group is often abbreviated a ...
s for removal of carbons, mutase
A mutase is an enzyme of the isomerase class that catalyzes the movement of a functional group from one position to another within the same molecule. In other words, mutases catalyze intramolecular group transfers. Examples of mutases include '' b ...
s to move alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or at the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as Alpha-olefin, α-olefins.
The Internationa ...
groups, and NADH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an ade ...
to help reduce ketones
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone ( ...
.


Konrad Bloch
Konrad Emil Bloch (; 21 January 1912 – 15 October 2000) was a German Americans, German-American biochemist. Bloch received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1964 (joint with Feodor Lynen) for discoveries concerning the mechanism and ...
and Feodor Lynen
Feodor Felix Konrad Lynen (; 6 April 1911 – 6 August 1979) was a German biochemist. In 1964 he won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine together with Konrad Bloch for their discoveries concerning the mechanism and regulation of cholestero ...
shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine () is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, acco ...
in 1964 for their discoveries concerning some of the mechanisms and methods of regulation of cholesterol and fatty acid metabolism
Fatty acid metabolism consists of various metabolic processes involving or closely related to fatty acids, a family of molecules classified within the lipid macronutrient category. These processes can mainly be divided into (1) catabolic processe ...
.
Regulation of cholesterol synthesis
Biosynthesis of cholesterol is directly regulated by the cholesterol levels present, though thehomeostatic
In biology, homeostasis (British also homoeostasis; ) is the state of steady internal physical and chemical conditions maintained by living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and includes many variables, su ...
mechanisms involved are only partly understood. A higher intake of food leads to a net decrease in endogenous production, whereas a lower intake of food has the opposite effect. The main regulatory mechanism is the sensing of intracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions ...
cholesterol in the endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a part of a transportation system of the eukaryote, eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. The word endoplasmic means "within the cytoplasm", and reticulum is Latin for ...
by the protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
SREBP
Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) are transcription factors that bind to the sterol regulatory element DNA sequence TCACNCCAC. Mammalian SREBPs are encoded by the genes '' SREBF1'' and '' SREBF2''. SREBPs belong to the basic- ...
(sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 and 2). In the presence of cholesterol, SREBP is bound to two other proteins: SCAP (SREBP cleavage-activating protein) and INSIG-1
Insulin induced gene 1, also known as INSIG1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''INSIG1'' gene.
''INSIG1'' is short for insulin-induced gene 1; it is located on chromosome 7 (7q36). This human gene encodes for a transmembrane prote ...
. When cholesterol levels fall, INSIG-1 dissociates from the SREBP-SCAP complex, which allows the complex to migrate to the Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic Cell (biology), cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it protein targeting, packages proteins ...
. Here SREBP is cleaved by S1P and S2P (site-1 protease and site-2 protease), two enzymes that are activated by SCAP when cholesterol levels are low.
The cleaved SREBP then migrates to the nucleus and acts as a transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
to bind to the sterol regulatory element (SRE), which stimulates the transcription of many genes. Among these are the low-density lipoprotein (LDL
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons (aka ULDL by the overall densit ...
) receptor and HMG-CoA reductase
HMG-CoA reductase (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, official symbol HMGCR) is the rate-limiting enzyme (NADH-dependent, ; NADPH-dependent, ) of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other ...
. The LDL receptor scavenges circulating LDL from the bloodstream, whereas HMG-CoA reductase leads to an increase in endogenous production of cholesterol. A large part of this signaling pathway was clarified by Dr. Michael S. Brown and Dr. Joseph L. Goldstein
Joseph Leonard Goldstein ForMemRS (born April 18, 1940) is an American biochemist. He received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1985, along with fellow University of Texas Southwestern researcher, Michael Brown, for their studies r ...
in the 1970s. In 1985, they received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine () is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, acco ...
for their work. Their subsequent work shows how the SREBP pathway regulates the expression of many genes that control lipid formation and metabolism and body fuel allocation.
Cholesterol synthesis can also be turned off when cholesterol levels are high. HMG-CoA reductase contains both a cytosolic domain (responsible for its catalytic function) and a membrane domain. The membrane domain senses signals for its degradation. Increasing concentrations of cholesterol (and other sterols) cause a change in this domain's oligomerization state, which makes it more susceptible to destruction by the proteasome
Proteasomes are essential protein complexes responsible for the degradation of proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are found inside all e ...
. This enzyme's activity can also be reduced by phosphorylation by an AMP-activated protein kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
. Because this kinase is activated by AMP, which is produced when ATP is hydrolyzed, it follows that cholesterol synthesis is halted when ATP levels are low.
Plasma transport and regulation of absorption
 As an isolated molecule, cholesterol is only minimally soluble in
As an isolated molecule, cholesterol is only minimally soluble in water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
, or hydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
In contrast, hydrophobes are n ...
. Because of this, it dissolves in blood at exceedingly small concentrations. To be transported effectively, cholesterol is instead packaged within lipoprotein
A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly whose primary function is to transport hydrophobic lipid (also known as fat) molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids. They consist of a triglyceride and cholesterol center, sur ...
s, complex discoidal particles with exterior amphiphilic
In chemistry, an amphiphile (), or amphipath, is a chemical compound possessing both hydrophilic (''water-loving'', polar) and lipophilic (''fat-loving'', nonpolar) properties. Such a compound is called amphiphilic or amphipathic. Amphiphilic c ...
proteins and lipids, whose outward-facing surfaces are water-soluble and inward-facing surfaces are lipid-soluble. This allows it to travel through the blood via emulsification
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Although ...
. Unbound cholesterol, being amphipathic, is transported in the monolayer surface of the lipoprotein particle along with phospholipids and proteins. Cholesterol esters bound to fatty acid, on the other hand, are transported within the fatty hydrophobic core of the lipoprotein, along with triglyceride.
There are several types of lipoproteins in the blood. In order of increasing density, they are chylomicron
Chylomicrons (from the Greek χυλός, chylos, meaning ''juice'' (of plants or animals), and micron, meaning ''small''), also known as ultra low-density lipoproteins (ULDL), are lipoprotein particles that consist of triglycerides (85–92%), ...
s, very-low-density lipoprotein
Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), density relative to extracellular water, is a type of lipoprotein made by the liver. VLDL is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins (chylomicrons, VLDL, intermediate-density lipoprotein, low-density lip ...
(VLDL), intermediate-density lipoprotein
Intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDLs) belong to the lipoprotein particle family and are formed from the degradation of very low-density lipoproteins as well as high-density lipoproteins. IDL is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins (chylo ...
(IDL), low-density lipoprotein
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons (aka ULDL by the overall density ...
(LDL), and high-density lipoprotein
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins which transport all fat molecules (lipids) around the body within the water outside cells. They are t ...
(HDL). Lower protein/lipid ratios make for less dense lipoproteins. Cholesterol within different lipoproteins is identical, although some are carried as their native "free" alcohol form (the cholesterol-OH group facing the water surrounding the particles), while others as fatty acyl esters, known also as cholesterol esters, within the particles.
Lipoprotein particles are organized by complex apolipoproteins, typically 80–100 different proteins per particle, which can be recognized and bound by specific receptors on cell membranes, directing their lipid payload into specific cells and tissues currently ingesting these fat transport particles. These surface receptors serve as unique molecular signatures, which then help determine fat distribution delivery throughout the body.
Chylomicrons, the least dense cholesterol transport particles, contain apolipoprotein B-48
Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the gene. Its measurement is commonly used to detect the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Isoforms
The protein occurs in the plasma in two main isoforms, Apo ...
, apolipoprotein C
In the field of molecular biology, apolipoprotein C is a family of four low molecular weight apolipoproteins, designated as C-I, C-II, C-III, and C-IV. These are surface components of chylomicrons, VLDL, and HDL. When an organism is in the fas ...
, and apolipoprotein E
Apolipoprotein E (Apo-E) is a protein involved in the metabolism of fats in the body of mammals. A subtype is implicated in Alzheimer's disease and cardiovascular diseases. It is encoded in humans by the gene ''APOE''.
Apo-E belongs to a family ...
(the principal cholesterol carrier in the brain) in their shells. Chylomicrons carry fats from the intestine to muscle and other tissues in need of fatty acids for energy or fat production. Unused cholesterol remains in more cholesterol-rich chylomicron remnants and is taken up from here to the bloodstream by the liver.
VLDL particles are produced by the liver from triacylglycerol
A triglyceride (from ''tri-'' and '' glyceride''; also TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids.
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates as ...
and cholesterol which was not used in the synthesis of bile acids. These particles contain apolipoprotein B100
Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the gene. Its measurement is commonly used to detect the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Isoforms
The protein occurs in the plasma in two main isoforms, Apo ...
and apolipoprotein E
Apolipoprotein E (Apo-E) is a protein involved in the metabolism of fats in the body of mammals. A subtype is implicated in Alzheimer's disease and cardiovascular diseases. It is encoded in humans by the gene ''APOE''.
Apo-E belongs to a family ...
in their shells and can be degraded by lipoprotein lipase
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) (EC 3.1.1.34, systematic name triacylglycerol acylhydrolase (lipoprotein-dependent)) is a member of the lipase gene family, which includes pancreatic lipase, hepatic lipase, and endothelial lipase. It is a water-solubl ...
on the artery wall to IDL. This arterial wall cleavage allows absorption of triacylglycerol
A triglyceride (from ''tri-'' and '' glyceride''; also TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids.
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates as ...
and increases the concentration of circulating cholesterol. IDL particles are then consumed in two processes: half is metabolized by HTGL and taken up by the LDL receptor on the liver cell surfaces, while the other half continues to lose triacylglycerols in the bloodstream until they become cholesterol-laden LDL particles.
LDL particles are the major blood cholesterol carriers. Each one contains approximately 1,500 molecules of cholesterol ester. LDL particle shells contain just one molecule of apolipoprotein B100
Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the gene. Its measurement is commonly used to detect the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Isoforms
The protein occurs in the plasma in two main isoforms, Apo ...
, recognized by LDL receptor
The low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDL-R) is a mosaic protein of 839 amino acids (after removal of 21-amino acid signal peptide) that mediates the endocytosis of cholesterol-rich low-density lipoprotein (LDL). It is a cell-surface receptor ...
s in peripheral tissues. Upon binding of apolipoprotein B100
Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the gene. Its measurement is commonly used to detect the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Isoforms
The protein occurs in the plasma in two main isoforms, Apo ...
, many LDL receptors concentrate in clathrin
Clathrin is a protein that plays a role in the formation of coated vesicles. Clathrin was first isolated by Barbara Pearse in 1976. It forms a triskelion shape composed of three clathrin heavy chains and three light chains. When the triskel ...
-coated pits. Both LDL and its receptor form vesicles within a cell via endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which Chemical substance, substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a Vesicle (biology and chem ...
. These vesicles then fuse with a lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle that is found in all mammalian cells, with the exception of red blood cells (erythrocytes). There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation cent ...
, where the lysosomal acid lipase enzyme hydrolyzes the cholesterol esters. The cholesterol can then be used for membrane biosynthesis or esterified and stored within the cell, so as to not interfere with the cell membranes.
LDL receptors are used up during cholesterol absorption, and its synthesis is regulated by SREBP
Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) are transcription factors that bind to the sterol regulatory element DNA sequence TCACNCCAC. Mammalian SREBPs are encoded by the genes '' SREBF1'' and '' SREBF2''. SREBPs belong to the basic- ...
, the same protein that controls the synthesis of cholesterol ''de novo'', according to its presence inside the cell. A cell with abundant cholesterol will have its LDL receptor synthesis blocked, to prevent new cholesterol in LDL particles from being taken up. Conversely, LDL receptor synthesis proceeds when a cell is deficient in cholesterol.
When this process becomes unregulated, LDL particles without receptors begin to appear in the blood. These LDL particles are oxidized and taken up by macrophages
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that ...
, which become engorged and form foam cells. These foam cells often become trapped in the walls of blood vessels and contribute to atherosclerotic plaque
An atheroma, or atheromatous plaque, is an abnormal accumulation of material in the inner layer of an arterial wall.
The material consists of mostly macrophage cells, or debris, containing lipids, calcium and a variable amount of fibrous conne ...
formation. Differences in cholesterol homeostasis affect the development of early atherosclerosis (carotid intima-media thickness). These plaques are the main causes of heart attacks, strokes, and other serious medical problems, leading to the association of so-called LDL cholesterol (actually a lipoprotein
A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly whose primary function is to transport hydrophobic lipid (also known as fat) molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids. They consist of a triglyceride and cholesterol center, sur ...
) with "bad" cholesterol.
HDL particles are thought to transport cholesterol back to the liver, either for excretion or for other tissues that synthesize hormones, in a process known as reverse cholesterol transport Reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) is a multistep process comprising removal of excess cholesterol from cells in the body and delivery to the liver for excretion into the small intestine.
Enhancing reverse cholesterol transport is considered a po ...
(RCT). Large numbers of HDL particles correlates with better health outcomes, whereas low numbers of HDL particles is associated with atheroma
An atheroma, or atheromatous plaque, is an abnormal accumulation of material in the tunica intima, inner layer of an arterial wall.
The material consists of mostly macrophage, macrophage cells, or debris, containing lipids, calcium and a variabl ...
tous disease progression in the arteries.
Metabolism, recycling and excretion
Cholesterol is susceptible to oxidation and easily forms oxygenated derivatives calledoxysterol
An oxysterol is a derivative of cholesterol obtained by Redox, oxidation involving enzymes and / or pro-oxidants. Such compounds play important roles in various biological processes such as cholesterol homeostasis, lipid metabolism (sphingolipids, ...
s. Three different mechanisms can form these: autoxidation, secondary oxidation to lipid peroxidation, and cholesterol-metabolizing enzyme oxidation. A great interest in oxysterols arose when they were shown to exert inhibitory actions on cholesterol biosynthesis. This finding became known as the "oxysterol hypothesis". Additional roles for oxysterols in human physiology include their participation in bile acid biosynthesis, function as transport forms of cholesterol, and regulation of gene transcription.
In biochemical experiments, radiolabelled forms of cholesterol, such as tritiated-cholesterol, are used. These derivatives undergo degradation upon storage, and it is essential to purify cholesterol prior to use. Cholesterol can be purified using small Sephadex LH-20 columns.
Cholesterol is oxidized by the liver into a variety of bile acids
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver in peroxisomes. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine residues to give anions called bile ...
. These, in turn, are conjugated with glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (G ...
, taurine
Taurine (), or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is a naturally occurring amino sulfonic acid that is widely distributed in animal tissues. It is a major constituent of bile and can be found in the large intestine. It is named after Latin (cogna ...
, glucuronic acid
Glucuronic acid (GCA, from ) is a uronic acid that was first isolated from urine (hence the name "uronic acid"). It is found in many natural gum, gums such as gum arabic ( 18%), xanthan, and kombucha tea and is important for the metabolism of ...
, or sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
. A mixture of conjugated and nonconjugated bile acids, along with cholesterol itself, is excreted from the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
into the bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), also known as gall, is a yellow-green/misty green fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is primarily composed of water, is pro ...
. Approximately 95% of the bile acids are reabsorbed from the intestines, and the remainder are lost in the feces. The excretion and reabsorption of bile acids forms the basis of the enterohepatic circulation
Enterohepatic circulation is the circulation of biliary acids, bilirubin, drugs or other substances from the liver to the bile, followed by entry into the small intestine, absorption by the enterocyte and transport back to the liver. Enterohepa ...
, which is essential for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. Under certain circumstances, when more concentrated, as in the gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow Organ (anatomy), organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath t ...
, cholesterol crystallises and is the major constituent of most gallstone
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of ...
s (lecithin
Lecithin ( ; from the Ancient Greek "yolk") is a generic term to designate any group of yellow-brownish fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues which are amphiphilic – they attract both water and fatty substances (and so ar ...
and bilirubin
Bilirubin (BR) (adopted from German, originally bili—bile—plus ruber—red—from Latin) is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normcomponent of the straw-yellow color in urine. Another breakdown product, stercobilin, causes the brown ...
gallstones also occur, but less frequently). Every day, up to 1 g of cholesterol enters the colon. This cholesterol originates from the diet, bile, and desquamated intestinal cells, and it can be metabolized by the colonic bacteria. Cholesterol is converted mainly into coprostanol
5β-Coprostanol (5β-cholestan-3β-ol) is a 27-carbon stanol formed from the net reductive metabolism of cholesterol (cholest-5en-3β-ol) in the Gut (zoology), gut of most higher animals and birds. This compound has frequently been used as a bi ...
, a nonabsorbable sterol that is excreted in the feces.
Although cholesterol is a steroid generally associated with mammals, the human pathogen ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb), also known as Koch's bacillus, is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis.
First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' ha ...
'' is able to completely degrade this molecule and contains a large number of genes that are regulated by its presence. Many of these cholesterol-regulated genes are homologues of fatty acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an ...
β-oxidation
In biochemistry and metabolism, beta oxidation (also β-oxidation) is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA enters ...
genes, but have evolved in such a way as to bind large steroid substrates like cholesterol.
Dietary sources
Animal fat
Animal fats are lipids derived from animals which are used by the animal for a multitude of functions, or can be used by humans for dietary, sanitary, and cosmetic purposes. Depending on the temperature of the fat, it can change between a solid s ...
s are complex mixtures of triglyceride
A triglyceride (from '' tri-'' and '' glyceride''; also TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids.
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates ...
s, with lesser amounts of both the phospholipid
Phospholipids are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typ ...
s and cholesterol molecules from which all animal (and human) cell membranes are constructed. Since all animal cells manufacture cholesterol, all animal-based foods contain cholesterol in varying amounts. Major dietary sources of cholesterol include red meat
In gastronomy, red meat is commonly red when raw (and a dark color after it is cooked), in contrast to white meat, which is pale in color before (and after) cooking. In culinary terms, only flesh from mammals or fowl (not fish) is classified ...
, egg yolks and whole egg
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the ...
s, liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
, kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
, giblets
Giblets is a culinary term for the edible offal of a fowl, typically including the Heart#Food, heart, gizzard, Liver (food), liver, and other organs.
A whole bird from a butcher is often packaged with the giblets, sometimes sealed in a bag wi ...
, fish oil
Fish oil is oil derived from the tissues of oily fish. Fish oils contain the omega−3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), precursors of certain eicosanoids that are known to reduce inflammation in the bod ...
, shellfish, and butter
Butter is a dairy product made from the fat and protein components of Churning (butter), churned cream. It is a semi-solid emulsion at room temperature, consisting of approximately 81% butterfat. It is used at room temperature as a spread (food ...
. Human breast milk
Breast milk (sometimes spelled as breastmilk) or mother's milk is milk produced by the mammary glands in the breasts of women. Breast milk is the primary source of nutrition for newborn infants, comprising fats, proteins, carbohydrates, and a var ...
also contains significant quantities of cholesterol.
Plant cells synthesize cholesterol as a precursor for other compounds, such as phytosterols
Phytosterols are phytosteroids, similar to cholesterol, that serve as structural components of biological membranes of plants. They encompass plant sterols and stanols. More than 250 sterols and related compounds have been identified. Free phyto ...
and steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes t ...
al glycoalkaloid
Glycoalkaloids are a family of chemical compounds derived from alkaloids to which sugar groups are appended. Several are potentially toxic, most notably the poisons commonly found in the plant species '' Solanum dulcamara'' (bittersweet nightshad ...
s, with cholesterol remaining in plant foods only in minor amounts or absent. Some plant foods, such as avocado
The avocado, alligator pear or avocado pear (''Persea americana'') is an evergreen tree in the laurel family (Lauraceae). It is native to Americas, the Americas and was first domesticated in Mesoamerica more than 5,000 years ago. It was priz ...
, flax seed
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. In 2022, France produced 75% of the ...
s and peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), goober pea, pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics by small and large ...
s, contain phytosterols, which compete with cholesterol for absorption in the intestines and reduce the absorption of both dietary and bile cholesterol. A typical diet contributes on the order of 0.2 gram of phytosterols, which is not enough to have a significant impact on blocking cholesterol absorption. Phytosterols intake can be supplemented through the use of phytosterol-containing functional foods
A functional food is a food claimed to have an additional benefit beyond just nutrition (often one related to health promotion or disease prevention) by modifying the cultivation of the native food or by adding ingredients during manufacturin ...
or dietary supplement
A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement a person's diet by taking a pill (pharmacy), pill, capsule (pharmacy), capsule, tablet (pharmacy), tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients eithe ...
s that are recognized as having potential to reduce levels of LDL
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons (aka ULDL by the overall densit ...
-cholesterol.
Medical guidelines and recommendations
In 2015, the scientific advisory panel ofU.S. Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the US federal government created to protect the health of the US people and providing essential human services. Its motto is "Im ...
and U.S. Department of Agriculture for the 2015 iteration of the Dietary Guidelines for Americans dropped the previously recommended limit of consumption of dietary cholesterol to 300 mg per day with a new recommendation to "eat as little dietary cholesterol as possible", thereby acknowledging an association between a diet low in cholesterol and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease.
A 2013 report by the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology recommended focusing on healthy dietary patterns rather than specific cholesterol limits, as they are hard for clinicians and consumers to implement. They recommend the DASH
The dash is a punctuation mark consisting of a long horizontal line. It is similar in appearance to the hyphen but is longer and sometimes higher from the baseline. The most common versions are the endash , generally longer than the hyphen ...
and Mediterranean diet
The Mediterranean diet is a concept first proposed in 1975 by the American biologist Ancel Keys and chemist Margaret Keys. The diet took inspiration from the eating habits and traditional food typical of Crete, much of the rest of Greece, and s ...
, which are low in cholesterol. A 2017 review by the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate Heart, cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability ...
recommends switching saturated fats
A saturated fat is a type of fat in which the fatty acid chains have all single bonds between the carbon atoms. A fat known as a glyceride is made of two kinds of smaller molecules: a short glycerol backbone, and fatty acids that each contai ...
for polyunsaturated fats
In biochemistry and nutrition, a polyunsaturated fat is a fat that contains a polyunsaturated fatty acid (abbreviated PUFA), which is a subclass of fatty acid characterized by a backbone with two or more carbon–carbon double bonds.
Some polyunsa ...
to reduce cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
risk.
Some supplemental guidelines have recommended doses of phytosterols in the 1.6–3.0 grams per day range (Health Canada, EFSA, ATP III, FDA). A meta-analysis demonstrated a 12% reduction in LDL-cholesterol at a mean dose of 2.1 grams per day. The benefits of a diet supplemented with phytosterols have also been questioned.
Clinical significance
Hypercholesterolemia
 According to the
According to the lipid hypothesis
The lipid hypothesis (also known as the cholesterol hypothesis) is a medical theory postulating a link between blood cholesterol levels and the occurrence of cardiovascular disease. A summary from 1976 described it as: "measures used to lower t ...
, elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood lead to atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. This is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and is driven by eleva ...
which may increase the risk of heart attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
, stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
, and peripheral artery disease
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a vascular disorder that causes abnormal narrowing of arteries other than those that supply the heart or brain. PAD can happen in any blood vessel, but it is more common in the legs than the arms.
When narr ...
. Since higher blood LDL – especially higher LDL concentrations and smaller LDL particle size – contributes to this process more than the cholesterol content of the HDL particles, LDL particles are often termed "bad cholesterol". High concentrations of functional HDL, which can remove cholesterol from cells and atheromas, offer protection and are commonly referred to as "good cholesterol". These balances are mostly genetically determined, but can be changed by body composition, medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to medical diagnosis, diagnose, cure, treat, or preventive medicine, prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmaco ...
s, diet, and other factors. A 2007 study demonstrated that blood total cholesterol levels have an exponential effect on cardiovascular and total mortality, with the association more pronounced in younger subjects. Because cardiovascular disease is relatively rare in the younger population, the impact of high cholesterol on health is larger in older people.
Elevated levels of the lipoprotein fractions, LDL, IDL and VLDL, rather than the total cholesterol level, correlate with the extent and progress of atherosclerosis. Conversely, the total cholesterol can be within normal limits, yet be made up primarily of small LDL and small HDL particles, under which conditions atheroma growth rates are high. A ''post hoc'' analysis of the IDEAL and the EPIC prospective studies found an association between high levels of HDL cholesterol (adjusted for apolipoprotein A-I and apolipoprotein B) and increased risk of cardiovascular disease, casting doubt on the cardioprotective role of "good cholesterol".
About one in 250 individuals can have a genetic mutation for the LDL cholesterol receptor that causes them to have familial hypercholesterolemia. Inherited high cholesterol can also include genetic mutations in the PCSK9 gene and the gene for apolipoprotein B.
Elevated cholesterol levels are treatable by a diet that reduces or eliminates saturated fat, and trans fats, often followed by one of various hypolipidemic agents, such as statin
Statins (or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) are a class of medications that lower cholesterol. They are prescribed typically to people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease.
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play ...
s, fibrate
In pharmacology, the fibrates are a class of amphipathic carboxylic acids and esters. They are derivatives of fibric acid (phenoxyisobutyric acid). They are used for a range of metabolic disorders, mainly hypercholesterolemia (high choles ...
s, cholesterol absorption inhibitors, monoclonal antibody therapy
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have varied therapeutic uses. It is possible to create a mAb that binds specifically to almost any extracellular target, such as cell surface proteins and cytokines. They can be used to render their target ineffectiv ...
(PCSK9
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) is an enzyme encoded by the ''PCSK9'' gene in humans on chromosome 1. It is the 9th member of the proprotein convertase family of proteins that activate other proteins. Similar genes ( orth ...
inhibitors), nicotinic acid derivatives or bile acid sequestrants. There are several international guidelines on the treatment of hypercholesterolemia.
Human trials using HMG-CoA reductase
HMG-CoA reductase (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, official symbol HMGCR) is the rate-limiting enzyme (NADH-dependent, ; NADPH-dependent, ) of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other ...
inhibitors, known as statin
Statins (or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) are a class of medications that lower cholesterol. They are prescribed typically to people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease.
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play ...
s, have repeatedly confirmed that changing lipoprotein transport patterns from unhealthy to healthier patterns significantly lowers cardiovascular disease event rates, even for people with cholesterol values currently considered low for adults. Studies have shown that reducing LDL cholesterol levels by about 38.7 mg/dL with the use of statins can reduce cardiovascular disease and stroke risk by about 21%. Studies have also found that statins reduce atheroma progression. As a result, people with a history of cardiovascular disease may derive benefit from statins irrespective of their cholesterol levels (total cholesterol below 5.0 mmol/L 93 mg/dL, and in men without cardiovascular disease, there is benefit from lowering abnormally high cholesterol levels ("primary prevention"). Primary prevention in women was originally practiced only by extension of the findings in studies on men, since, in women, none of the large statin trials conducted prior to 2007 demonstrated a significant reduction in overall mortality or in cardiovascular endpoints. Meta-analyses have demonstrated significant reductions in all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, without significant heterogeneity by sex.
The 1987 report of National Cholesterol Education Program {{Primary sources, article, date=May 2011The National Cholesterol Education Program is a program managed by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, a division of the National Institutes of Health. Its goal is to reduce increased cardiovascula ...
, Adult Treatment Panels suggests the total blood cholesterol level should be: < 200 mg/dL normal blood cholesterol, 200–239 mg/dL borderline-high, > 240 mg/dL high cholesterol. The American Heart Association
The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate Heart, cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability ...
provides a similar set of guidelines for total (fasting) blood cholesterol levels and risk for heart disease: Statins are effective in lowering LDL cholesterol and widely used for primary prevention
Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, is the application of healthcare measures to prevent diseases.Hugh R. Leavell and E. Gurney Clark as "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting physical and mental health a ...
in people at high risk of cardiovascular disease, as well as in secondary prevention
Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, is the application of healthcare measures to prevent diseases.Hugh R. Leavell and E. Gurney Clark as "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting physical and mental health a ...
for those who have developed cardiovascular disease. The average global mean total Cholesterol for humans has remained at about 4.6 mmol/L (178 mg/dL) for men and women, both crude and age standardized, for nearly 40 years from 1980 to 2018, with some regional variations and reduction of total Cholesterol in Western nations.
More current testing methods determine LDL ("bad") and HDL ("good") cholesterol separately, allowing cholesterol analysis to be more nuanced. The desirable LDL level is considered to be less than 100 mg/dL (2.6 mmol/L).
 Total cholesterol is defined as the sum of HDL, LDL, and VLDL. Usually, only the total, HDL, and triglycerides are measured. For cost reasons, the VLDL is usually estimated as one-fifth of the triglycerides and the LDL is estimated using the Friedewald formula (or a variant): estimated LDL = otal cholesterol− otal HDL− stimated VLDL Direct LDL measures are used when triglycerides exceed 400 mg/dL. The estimated VLDL and LDL have more error when triglycerides are above 400 mg/dL.
In the
Total cholesterol is defined as the sum of HDL, LDL, and VLDL. Usually, only the total, HDL, and triglycerides are measured. For cost reasons, the VLDL is usually estimated as one-fifth of the triglycerides and the LDL is estimated using the Friedewald formula (or a variant): estimated LDL = otal cholesterol− otal HDL− stimated VLDL Direct LDL measures are used when triglycerides exceed 400 mg/dL. The estimated VLDL and LDL have more error when triglycerides are above 400 mg/dL.
In the Framingham Heart Study
The Framingham Heart Study is a long-term, ongoing cardiovascular cohort study of residents of the city of Framingham, Massachusetts. The study began in 1948 with 5,209 adult subjects from Framingham, and is now on its third generation of partic ...
, each 10 mg/dL (0.6 mmol/L) increase in total cholesterol levels increased 30-year overall mortality by 5% and CVD mortality by 9%. While subjects over the age of 50 had an 11% increase in overall mortality, and a 14% increase in cardiovascular disease mortality per 1 mg/dL (0.06 mmol/L) year drop in total cholesterol levels. The researchers attributed this phenomenon to a different correlation, whereby the disease itself increases risk of death, as well as changes a myriad of factors, such as weight loss and the inability to eat, which lower serum cholesterol. This effect was also shown in men of all ages and women over 50 in the Vorarlberg Health Monitoring and Promotion Programme. These groups were more likely to die of cancer, liver diseases, and mental diseases with very low total cholesterol, of 186 mg/dL (10.3 mmol/L) and lower. This result indicates the low-cholesterol effect occurs even among younger respondents, contradicting the previous assessment among cohorts of older people that this is a marker for frailty occurring with age.
Hypocholesterolemia
Abnormally low levels of cholesterol are termed ''hypocholesterolemia
Hypocholesterolemia is the presence of abnormally low (''hypo-'') levels of cholesterol in the blood (''-emia''). A defect in the body's production of cholesterol can lead to adverse consequences as well. Cholesterol is an essential component of ma ...
''. Research into the causes of this state is relatively limited, but some studies suggest a link with depression, cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, and cerebral hemorrhage
Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), also known as hemorrhagic stroke, is a sudden bleeding into the tissues of the brain (i.e. the parenchyma), into its ventricles, or into both. An ICH is a type of bleeding within the skull and one kind of stro ...
. In general, the low cholesterol levels seem to be a consequence, rather than a cause, of an underlying illness. A genetic defect in cholesterol synthesis causes Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome
Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome is an inborn error of metabolism, inborn error of cholesterol synthesis. It is an autosome, autosomal recessive (genetics), recessive, multiple malformation syndrome caused by a mutation in the enzyme 7-Dehydrochole ...
, which is often associated with low plasma cholesterol levels. Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. Thyrotoxicosis is a condition that occurs due to elevated levels of thyroid hormones of any cause and therefore includes hyperth ...
, or any other endocrine disturbance which causes upregulation of the LDL receptor
The low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDL-R) is a mosaic protein of 839 amino acids (after removal of 21-amino acid signal peptide) that mediates the endocytosis of cholesterol-rich low-density lipoprotein (LDL). It is a cell-surface receptor ...
, may result in hypocholesterolemia.
Testing
TheAmerican Heart Association
The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate Heart, cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability ...
recommends testing cholesterol every 4–6 years for people aged 20 years or older. A separate set of American Heart Association
The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate Heart, cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability ...
guidelines issued in 2013 indicates that people taking statin
Statins (or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) are a class of medications that lower cholesterol. They are prescribed typically to people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease.
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play ...
medications should have their cholesterol tested 4–12 weeks after their first dose and then every 3–12 months thereafter. For men ages 45 to 65 and women ages 55 to 65, a cholesterol test should occur every 1–2 years, and for seniors over age 65, an annual test should be performed.
A blood sample after 12-hours of fasting
Fasting is the act of refraining from eating, and sometimes drinking. However, from a purely physiological context, "fasting" may refer to the metabolic status of a person who has not eaten overnight (before "breakfast"), or to the metabolic sta ...
is taken by a healthcare professional
A health professional, healthcare professional (HCP), or healthcare worker (sometimes abbreviated as HCW) is a provider of health care treatment and advice based on formal training and experience. The field includes those who work as a nurse, physi ...
from an arm vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and feta ...
to measure a lipid profile
A lipid profile or lipid panel is a Test panel, panel of blood tests used to find abnormalities in blood lipid ( such as cholesterol and triglycerides) concentrations. The results of this test can identify certain Inborn error of lipid metabolis ...
for a) total cholesterol, b) HDL cholesterol, c) LDL cholesterol, and d) triglyceride
A triglyceride (from '' tri-'' and '' glyceride''; also TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids.
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates ...
s. Results may be expressed as "calculated", indicating a calculation of total cholesterol, HDL, and triglycerides.
Cholesterol is tested to determine for "normal" or "desirable" levels if a person has a total cholesterol of 5.2 mmol/L or less (200 mg/dL), an HDL value of more than 1 mmol/L (40 mg/dL, "the higher, the better"), an LDL value of less than 2.6 mmol/L (100 mg/dL), and a triglycerides level of less than 1.7 mmol/L (150 mg/dL). Blood cholesterol in people with lifestyle, aging, or cardiovascular risk factors, such as diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or th ...
, hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
, family history of coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of cardiovascular disease, heart disease involving Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up ...
, or angina
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina is typically the result of parti ...
, are evaluated at different levels.
Interactive pathway map
Cholesteric liquid crystals
Some cholesterol derivatives (among other simple cholesteric lipids) are known to generate the cholestericliquid crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal can flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a common direction as i ...
line phase. The cholesteric phase is, in fact, a chiral
Chirality () is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek language, Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object.
An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is dist ...
nematic phase, and it changes colour when its temperature changes. This makes cholesterol derivatives useful for indicating temperature in liquid-crystal display
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other Electro-optic modulator, electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers to display information. Liq ...
thermometer
A thermometer is a device that measures temperature (the hotness or coldness of an object) or temperature gradient (the rates of change of temperature in space). A thermometer has two important elements: (1) a temperature sensor (e.g. the bulb ...
s and in temperature-sensitive paints.
Stereoisomers
stereoisomer
In stereochemistry, stereoisomerism, or spatial isomerism, is a form of isomerism in which molecules have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in ...
s that arise from its eight stereocenters, although only two of the stereoisomers have biochemical significance (''nat''-cholesterol and ''ent''-cholesterol, for ''natural'' and ''enantiomer'', respectively), and only one occurs naturally (''nat''-cholesterol).
Additional images
Steroidogenesis
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter memb ...
, using cholesterol as building material
File:Cholesterol Spacefill.jpeg, Space-filling model
In chemistry, a space-filling model, also known as a ''calotte model'', is a type of three-dimensional (3D) molecular model where the atoms are represented by spheres whose radii are proportional to the radii of the atoms and whose center-to- ...
of the Cholesterol molecule
File:Steroid numbering.svg, Numbering of the steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes t ...
nuclei
See also
*Arcus senilis
Arcus senilis (AS), also known as gerontoxon, arcus lipoides, arcus corneae, corneal arcus, arcus adiposus, or arcus cornealis, are rings in the peripheral cornea. It is usually caused by cholesterol deposits, so it may be a sign of high cholester ...
"Cholesterol ring" in the eyes
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
References
External links
* {{Authority control Cholestanes GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators Lipid disorders Neurosteroids Nutrition Receptor agonists Sterols