chlorenchyma on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The ground tissue of plants includes all tissues that are neither
The ground tissue of plants includes all tissues that are neither
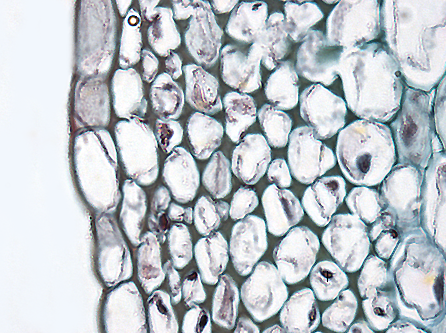 Collenchyma tissue is composed of elongated cells with irregularly thickened walls. They provide structural support, particularly in growing shoots and
Collenchyma tissue is composed of elongated cells with irregularly thickened walls. They provide structural support, particularly in growing shoots and
 Fibers or bast are generally long, slender, so-called prosenchymatous cells, usually occurring in strands or bundles. Such bundles or the totality of a stem's bundles are colloquially called fibers. Their high load-bearing capacity and the ease with which they can be processed has since antiquity made them the source material for a number of things, like
Fibers or bast are generally long, slender, so-called prosenchymatous cells, usually occurring in strands or bundles. Such bundles or the totality of a stem's bundles are colloquially called fibers. Their high load-bearing capacity and the ease with which they can be processed has since antiquity made them the source material for a number of things, like
link
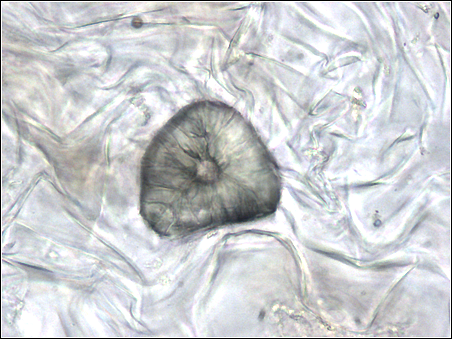 Sclereids are the reduced form of sclerenchyma cells with highly thickened, lignified walls.
They are small bundles of sclerenchyma tissue in
Sclereids are the reduced form of sclerenchyma cells with highly thickened, lignified walls.
They are small bundles of sclerenchyma tissue in
dermal
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided i ...
nor vascular Vascular can refer to:
* blood vessels, the vascular system in animals
* vascular tissue
Vascular tissue is a complex transporting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. The primary components of vascular tissue ...
. It can be divided into three types based on the nature of the cell walls. This tissue system is present between the dermal tissue and forms the main bulk of the plant body.
# Parenchyma cells have thin primary walls and usually remain alive after they become mature. Parenchyma forms the "filler" tissue in the soft parts of plants, and is usually present in cortex
Cortex or cortical may refer to:
Biology
* Cortex (anatomy), the outermost layer of an organ
** Cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the vertebrate cerebrum, part of which is the ''forebrain''
*** Motor cortex, the regions of the cerebral cortex i ...
, pericycle, pith
Pith, or medulla, is a tissue in the stems of vascular plants. Pith is composed of soft, spongy parenchyma cells, which in some cases can store starch. In eudicotyledons, pith is located in the center of the stem. In monocotyledons, it ex ...
, and medullary rays in primary stem
Stem or STEM most commonly refers to:
* Plant stem, a structural axis of a vascular plant
* Stem group
* Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics
Stem or STEM can also refer to:
Language and writing
* Word stem, part of a word respon ...
and root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
.
# Collenchyma cells have thin primary walls with some areas of secondary thickening. Collenchyma provides extra mechanical and structural support, particularly in regions of new growth.
# Sclerenchyma cells have thick lignified secondary walls and often die when mature. Sclerenchyma provides the main structural support to the plant.
#Aerenchyma
Aerenchyma or aeriferous parenchyma or lacunae, is a modification of the parenchyma to form a spongy tissue that creates spaces or air channels in the leaves, stems and roots of some plants, which allows exchange of gases between the shoot and ...
cells are found in aquatic plants. They are also known to be parenchyma cells with large air cavities surrounded by irregular cells which form columns called trabeculae.
Parenchyma
Parenchyma is a versatile ground tissue that generally constitutes the "filler" tissue in soft parts of plants. It forms, among other things, thecortex
Cortex or cortical may refer to:
Biology
* Cortex (anatomy), the outermost layer of an organ
** Cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the vertebrate cerebrum, part of which is the ''forebrain''
*** Motor cortex, the regions of the cerebral cortex i ...
(outer region) and pith
Pith, or medulla, is a tissue in the stems of vascular plants. Pith is composed of soft, spongy parenchyma cells, which in some cases can store starch. In eudicotyledons, pith is located in the center of the stem. In monocotyledons, it ex ...
(central region) of stems, the cortex of roots, the mesophyll of leaves, the pulp of fruits, and the endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the Embryo#Pla ...
of seeds. Parenchyma cells are often living cells and may remain meristematic, meaning that they are capable of cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell (biology), cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukar ...
if stimulated. They have thin and flexible cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of glycosidic bond, β(1→4) linked glucose, D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important s ...
cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer that surrounds some Cell type, cell types, found immediately outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. Primarily, it provides the cell with structural support, shape, protection, ...
s and are generally polyhedral when close-packed, but can be roughly spherical when isolated from their neighbors. Parenchyma cells are generally large. They have large central vacuoles, which allow the cells to store and regulate ions
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
, waste products, and water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
. Tissue specialised for food storage is commonly formed of parenchyma cells.
Parenchyma cells have a variety of functions:
* In leaves
A leaf (: leaves) is a principal appendage of the stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, ...
, they form two layers of mesophyll cells immediately beneath the epidermis of the leaf, that are responsible for photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
and the exchange of gases. These layers are called the palisade parenchyma and spongy mesophyll. Palisade parenchyma cells can be either cuboidal or elongated. Parenchyma cells in the mesophyll of leaves are specialised parenchyma cells called chlorenchyma cells (parenchyma cells with chloroplasts). Parenchyma cells are also found in other parts of the plant.
* Storage of starch, protein, fats, oils and water in roots, tubers (e.g. potatoes
The potato () is a starchy tuberous vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are underground stem tubers of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'', a perennial in the nightshade famil ...
), seed endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the Embryo#Pla ...
(e.g. cereal
A cereal is a grass cultivated for its edible grain. Cereals are the world's largest crops, and are therefore staple foods. They include rice, wheat, rye, oats, barley, millet, and maize ( Corn). Edible grains from other plant families, ...
s) and cotyledon
A cotyledon ( ; ; "a cavity, small cup, any cup-shaped hollow",
gen. (), ) is a "seed leaf" – a significant part of the embryo within the seed of a plant – and is formally defined as "the embryonic leaf in seed-bearing plants, one or mor ...
s (e.g. pulses and peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), goober pea, pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics by small and large ...
s)
* Secretion
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mec ...
(e.g. the parenchyma cells lining the inside of resin ducts)
* Wound repair and the potential for renewed meristematic activity
* Other specialised functions such as aeration
Aeration (also called aerification or aeriation) is the process by which air is circulated through, mixed with or dissolved in a liquid or other substances that act as a fluid (such as soil). Aeration processes create additional surface area in t ...
(aerenchyma
Aerenchyma or aeriferous parenchyma or lacunae, is a modification of the parenchyma to form a spongy tissue that creates spaces or air channels in the leaves, stems and roots of some plants, which allows exchange of gases between the shoot and ...
) provides buoyancy and helps aquatic plants float.
* Chlorenchyma cells carry out photosynthesis and manufacture food.
The shape of parenchyma cells varies with their function. In the spongy mesophyll of a leaf, parenchyma cells range from near-spherical and loosely arranged with large intercellular spaces, to branched or stellate, mutually interconnected with their neighbours at the ends of their arms to form a three-dimensional network, like in the red kidney bean ''Phaseolus vulgaris
''Phaseolus vulgaris'', the common bean,, is a herbaceous annual plant grown worldwide for its edible dry seeds or green, unripe pods. Its leaf is also occasionally used as a vegetable and the straw as fodder. Its botanical classification, alo ...
'' and other mesophytes.Jeffree CE, Read N, Smith JAC and Dale JE (1987). Water droplets and ice deposits in leaf intercellular spaces: redistribution of water during cryofixation for scanning electron microscopy. Planta 172, 20-37 These cells, along with the epidermal guard cell
Guard cells are specialized cells in the epidermis of leaves, stems and other organs of land plants that are used to control gas exchange. They are produced in pairs with a gap between them that forms a stomatal pore. The stomatal pores are lar ...
s of the stoma
In botany, a stoma (: stomata, from Greek language, Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth"), also called a stomate (: stomates), is a pore found in the Epidermis (botany), epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exc ...
, form a system of air spaces and chambers that regulate the exchange of gases. In some works, the cells of the leaf epidermis are regarded as specialised parenchymal cells,Hill, J. Ben; Overholts, Lee O; Popp, Henry W. Grove Jr., Alvin R. Botany. A textbook for colleges. Publisher: MacGraw-Hill 1960 but the modern preference has long been to classify the epidermis as plant dermal tissue, and parenchyma as ground tissue.Evert, Ray F; Eichhorn, Susan E. Esau's Plant Anatomy: Meristems, Cells, and Tissues of the Plant Body: Their Structure, Function, and Development. Publisher: Wiley-Liss 2006.
Shapes of parenchyma:
* Polyhedral (found in pallisade tissue of the leaf)
* Spherical
* Stellate (found in stem of plants and have well-developed air spaces between them)
* Elongated (also found in pallisade tissue of leaf)
* Lobed (found in spongy and pallisade mesophyll tissue of some plants)
Collenchyma
 Collenchyma tissue is composed of elongated cells with irregularly thickened walls. They provide structural support, particularly in growing shoots and
Collenchyma tissue is composed of elongated cells with irregularly thickened walls. They provide structural support, particularly in growing shoots and leaves
A leaf (: leaves) is a principal appendage of the stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, ...
(as seen, for example, the resilient strands in stalks of celery
Celery (''Apium graveolens'' Dulce Group or ''Apium graveolens'' var. ''dulce'') is a cultivated plant belonging to the species ''Apium graveolens'' in the family Apiaceae that has been used as a vegetable since ancient times.
The original wild ...
). Collenchyma cells are usually living, and have only a thick primary cell wall made up of cellulose and pectin. Cell wall thickness is strongly affected by mechanical stress upon the plant. The walls of collenchyma in shaken plants (to mimic the effects of wind etc.), may be 40–100% thicker than those not shaken.
There are four main types of collenchyma:
* Angular collenchyma (thickened at intercellular contact points)
* Tangential collenchyma (cells arranged into ordered rows and thickened at the tangential face of the cell wall)
* Annular collenchyma (uniformly thickened cell walls)
* Lacunar collenchyma (collenchyma with intercellular spaces)
Collenchyma cells are most often found adjacent to outer growing tissues such as the vascular cambium
The vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants exhibiting secondary growth, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and oak trees, gymnosperms such as pine trees, as well as in certain other vascular ...
and are known for increasing structural support and integrity.
The first use of "collenchyma" () was by Link (1837) who used it to describe the sticky substance on ''Bletia
''Bletia'' is a genus of about 30 species of orchids (family Orchidaceae), almost all of which are terrestrial; some are occasionally lithophytic or epiphytic. It is named after Spanish botanist and pharmacist Don Luis Blet. The genus is wides ...
'' (Orchidaceae) pollen. Complaining about Link's excessive nomenclature, Schleiden (1839) stated mockingly that the term "collenchyma" could have more easily been used to describe elongated sub-epidermal cells with unevenly thickened cell walls.
Sclerenchyma
Sclerenchyma is the tissue which makes the plant hard and stiff. Sclerenchyma is the supporting tissue inplant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s. Two types of sclerenchyma cells exist: fibers cellular and sclereids. Their cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer that surrounds some Cell type, cell types, found immediately outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. Primarily, it provides the cell with structural support, shape, protection, ...
s consist of cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of glycosidic bond, β(1→4) linked glucose, D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important s ...
, hemicellulose
A hemicellulose (also known as polyose) is one of a number of heteropolymers (matrix polysaccharides), such as arabinoxylans, present along with cellulose in almost all embryophyte, terrestrial plant cell walls. Cellulose is crystalline, strong, an ...
, and lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidit ...
. Sclerenchyma cells are the principal supporting cells in plant tissues that have ceased elongation. Sclerenchyma fibers are of great economic importance, since they constitute the source material for many fabrics (e.g. flax
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. In 2022, France produced 75% of t ...
, hemp
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a plant in the botanical class of ''Cannabis sativa'' cultivars grown specifically for industrial and consumable use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest ...
, jute
Jute ( ) is a long, rough, shiny bast fibre that can be Spinning (textiles), spun into coarse, strong threads. It is produced from flowering plants in the genus ''Corchorus'', of the mallow family Malvaceae. The primary source of the fiber is ...
, and ramie
Ramie (pronounced: , ; from Malay ), ''Boehmeria nivea'', is a flowering plant in the nettle family Urticaceae, native to eastern Asia. It is an herbaceous perennial growing to tall;
).
Unlike the collenchyma, mature sclerenchyma is composed of dead cells with extremely thick cell walls ( secondary walls) that make up to 90% of the whole cell volume. The term ''sclerenchyma'' is derived from the Greek σκληρός (''sklērós''), meaning "hard." It is the hard, thick walls that make sclerenchyma cells important strengthening and supporting elements in plant parts that have ceased elongation. The difference between sclereids is not always clear: transitions do exist, sometimes even within the same plant.
Fibers
 Fibers or bast are generally long, slender, so-called prosenchymatous cells, usually occurring in strands or bundles. Such bundles or the totality of a stem's bundles are colloquially called fibers. Their high load-bearing capacity and the ease with which they can be processed has since antiquity made them the source material for a number of things, like
Fibers or bast are generally long, slender, so-called prosenchymatous cells, usually occurring in strands or bundles. Such bundles or the totality of a stem's bundles are colloquially called fibers. Their high load-bearing capacity and the ease with which they can be processed has since antiquity made them the source material for a number of things, like rope
A rope is a group of yarns, Plying, plies, fibres, or strands that are plying, twisted or braided together into a larger and stronger form. Ropes have high tensile strength and can be used for dragging and lifting. Rope is thicker and stronger ...
s, fabrics and mattress
A mattress is a large, usually rectangular pad for supporting a person Lying (position), lying down, especially for sleeping. It is designed to be used as a bed, or on a bed frame as part of a bed. Mattresses may consist of a Quilting, quilted o ...
es. The fibers of flax
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. In 2022, France produced 75% of t ...
(''Linum usitatissimum'') have been known in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
and Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
for more than 3,000 years, those of hemp
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a plant in the botanical class of ''Cannabis sativa'' cultivars grown specifically for industrial and consumable use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest ...
(''Cannabis sativa'') in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
for just as long. These fibers, and those of jute
Jute ( ) is a long, rough, shiny bast fibre that can be Spinning (textiles), spun into coarse, strong threads. It is produced from flowering plants in the genus ''Corchorus'', of the mallow family Malvaceae. The primary source of the fiber is ...
(''Corchorus capsularis'') and ramie
Ramie (pronounced: , ; from Malay ), ''Boehmeria nivea'', is a flowering plant in the nettle family Urticaceae, native to eastern Asia. It is an herbaceous perennial growing to tall;
(''Boehmeria nivea'', a nettle
Nettle refers to plants with stinging hairs, particularly those of the genus '' Urtica''. It can also refer to plants which resemble ''Urtica'' species in appearance but do not have stinging hairs. Plants called "nettle" include:
* ball nettle ...
), are extremely soft and elastic and are especially well suited for the processing to textile
Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, and different types of #Fabric, fabric. ...
s. Their principal cell wall material is cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of glycosidic bond, β(1→4) linked glucose, D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important s ...
.
Contrasting are hard fibers that are mostly found in monocot
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are flowering plants whose seeds contain only one Embryo#Plant embryos, embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. A monocot taxon has been in use for several decades, but ...
s. Typical examples are the fiber of many grasses, ''Agave sisalana'' (sisal
Sisal (, ; ''Agave sisalana'') is a species of flowering plant native to southern Mexico, but widely cultivated and naturalized in many other countries. It yields a stiff fibre used in making rope and various other products. The sisal fiber is ...
), ''Yucca
''Yucca'' ( , YUCK-uh) is both the scientific name and common name for a genus native to North America from Panama to southern Canada. It contains 50 accepted species. In addition to yucca, they are also known as Adam's needle or Spanish-bayon ...
'' or ''Phormium tenax
''Phormium tenax'' (called flax in New Zealand English; in Māori language, Māori; New Zealand flax outside New Zealand; and New Zealand hemp in historical nautical contexts) is an evergreen perennial plant native to New Zealand and Norfolk I ...
'', '' Musa textilis'' and others. Their cell walls contain, besides cellulose, a high proportion of lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidit ...
. The load-bearing capacity of ''Phormium tenax'' is as high as 20–25 kg/mm², the same as that of good steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
wire (25 kg/ mm²), but the fibre tears as soon as too great a strain is placed upon it, while the wire distorts and does not tear before a strain of 80 kg/mm². The thickening of a cell wall has been studied in ''Linum
''Linum'' (flax) is a genus of approximately 200 species''Linum''.
The Jepson Manual. ...
''. Starting at the centre of the fiber, the thickening layers of the secondary wall are deposited one after the other. Growth at both tips of the cell leads to simultaneous elongation. During development the layers of secondary material seem like tubes, of which the outer one is always longer and older than the next. After completion of growth, the missing parts are supplemented, so that the wall is evenly thickened up to the tips of the fibers.
Fibers usually originate from meristematic tissues. The Jepson Manual. ...
Cambium
A cambium (: cambiums or cambia), in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth. It is found in the area between xylem and phloem. A cambium can also be defined as a cellular plant tissue from whic ...
and procambium
In cell biology, the meristem is a structure composed of specialized tissue found in plants, consisting of stem cells, known as meristematic cells, which are undifferentiated cells capable of continuous cellular division. These meristematic ce ...
are their main centers of production. They are usually associated with the xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue (biology), tissue in vascular plants, the other being phloem; both of these are part of the vascular bundle. The basic function of the xylem is to transport water upward from the roots to parts o ...
and phloem
Phloem (, ) is the living tissue in vascular plants that transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis and known as ''photosynthates'', in particular the sugar sucrose, to the rest of the plant. This transport process is ...
of the vascular bundles. The fibers of the xylem are always lignified, while those of the phloem are cellulosic. Reliable evidence for the fibre cells' evolutionary origin from tracheid
A tracheid is a long and tapered Lignin, lignified cell in the xylem of Tracheophyta, vascular plants. It is a type of conductive cell called a tracheary element. Angiosperms also use another type of conductive cell, called vessel elements, to t ...
s exists. During evolution the strength of the tracheid cell walls was enhanced, the ability to conduct water was lost and the size of the pits was reduced. Fibers that do not belong to the xylem are bast (outside the ring of cambium) and such fibers that are arranged in characteristic patterns at different sites of the shoot.
The term "sclerenchyma" (originally ''Sclerenchyma'') was introduced by Mettenius in 1865.Mettenius, G. 1865. Über die Hymenophyllaceae. ''Abhandlungen der Mathematisch-Physischen Klasse der Königlich-Sächsischen Gesellschaft der Wissenschaften'' 11: 403-504, pl. 1-5link
Sclereids
 Sclereids are the reduced form of sclerenchyma cells with highly thickened, lignified walls.
They are small bundles of sclerenchyma tissue in
Sclereids are the reduced form of sclerenchyma cells with highly thickened, lignified walls.
They are small bundles of sclerenchyma tissue in plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s that form durable layers, such as the cores of apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
s and the gritty texture of pear
Pears are fruits produced and consumed around the world, growing on a tree and harvested in late summer into mid-autumn. The pear tree and shrub are a species of genus ''Pyrus'' , in the Family (biology), family Rosaceae, bearing the Pome, po ...
s (''Pyrus communis''). Sclereids are variable in shape. The cells can be isodiametric, prosenchymatic, forked or elaborately branched. They can be grouped into bundles, can form complete tubes located at the periphery or can occur as single cells or small groups of cells within parenchyma
upright=1.6, Lung parenchyma showing damage due to large subpleural bullae.
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ such as the brain or lungs, or a structure such as a tumour. In zoology, it is the tissue that ...
tissues. But compared with most fibres, sclereids are relatively short. Characteristic examples are brachysclereids or the stone cells (called stone cells because of their hardness) of pears and quince
The quince (; ''Cydonia oblonga'') is the sole member of the genus ''Cydonia'' in the Malinae subtribe (which contains apples, pears, and other fruits) of the Rosaceae family. It is a deciduous tree that bears hard, aromatic bright golden-yel ...
s (''Cydonia oblonga'') and those of the shoot of the wax plant (''Hoya carnosa''). The cell walls fill nearly all the cell's volume. A layering of the walls and the existence of branched pits is clearly visible. Branched pits such as these are called ramiform pits. The shell of many seeds like those of nuts as well as the stones of drupe
In botany, a drupe (or stone fruit) is a type of fruit in which an outer fleshy part (exocarp, or skin, and mesocarp, or flesh) surrounds a single shell (the ''pip'' (UK), ''pit'' (US), ''stone'', or ''pyrena'') of hardened endocarp with a seed ...
s like cherries
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus ''Prunus'', and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit).
Commercial cherries are obtained from cultivars of several species, such as the sweet ''Prunus avium'' and the sour ''Prunus cerasus''. The name ...
and plum
A plum is a fruit of some species in Prunus subg. Prunus, ''Prunus'' subg. ''Prunus'.'' Dried plums are often called prunes, though in the United States they may be labeled as 'dried plums', especially during the 21st century.
Plums are ...
s are made up from sclereids.
These structures are used to protect other cells.
References
Further reading
* * Moore, Randy; Clark, W. Dennis; and Vodopich, Darrell S. (1998). ''Botany'' (3rd ed.). McGraw-Hill. . * Chrispeels MJ, Sadava DE. (2002) Plants, Genes and Crop Biotechnology. Jones and Bartlett Inc., {{Biological tissue Plant anatomy Plant cells Tissues (biology)