|
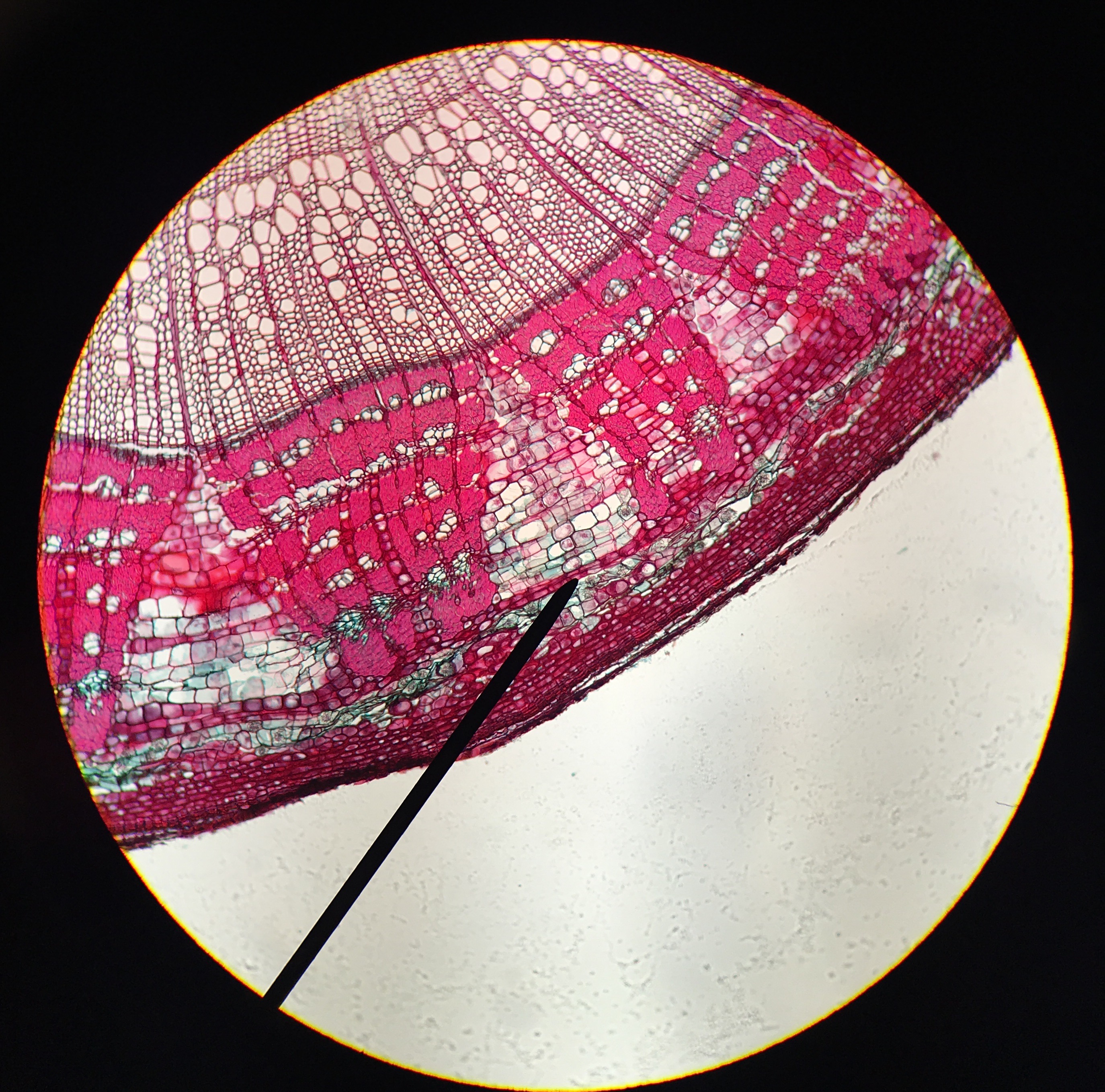
Procambium
In cell biology, the meristem is a structure composed of specialized tissue found in plants, consisting of stem cells, known as meristematic cells, which are undifferentiated cells capable of continuous cellular division. These meristematic cells play a fundamental role in plant growth, regeneration, and acclimatization, as they serve as the source of all differentiated plant tissues and organs. They contribute to the formation of structures such as fruits, leaves, and seeds, as well as supportive tissues like stems and roots. Meristematic cells are totipotent, meaning they have the ability to differentiate into any plant cell type. As they divide, they generate new cells, some of which remain meristematic cells while others differentiate into specialized cells that typically lose the ability to divide or produce new cell types. Due to their active division and undifferentiated nature, meristematic cells form the foundation for the formation of new plant organs and the cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromoplasts
Chromoplasts are plastids, heterogeneous organelles responsible for pigment synthesis and storage in specific photosynthetic eukaryotes. It is thought (according to symbiogenesis) that like all other plastids including chloroplasts and leucoplasts they are descended from symbiotic prokaryotes. Function Chromoplasts are found in fruits, flowers, roots, and stressed and aging leaves, and are responsible for their distinctive colors. This is always associated with a massive increase in the accumulation of carotenoid pigments. The conversion of chloroplasts to chromoplasts in ripening is a classic example. They are generally found in mature tissues and are derived from preexisting mature plastids. Fruits and flowers are the most common structures for the biosynthesis of carotenoids, although other reactions occur there as well including the synthesis of sugars, starches, lipids, aromatic compounds, vitamins, and hormones. The DNA in chloroplasts and chromoplasts is identica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phelloderm
Bark is the outermost layer of stems and roots of woody plants. Plants with bark include trees, woody vines, and shrubs. Bark refers to all the tissues outside the vascular cambium and is a nontechnical term. It overlays the wood and consists of the inner bark and the outer bark. The inner bark, which in older stems is living tissue, includes the innermost layer of the periderm. The outer bark on older stems includes the dead tissue on the surface of the stems, along with parts of the outermost periderm and all the tissues on the outer side of the periderm. The outer bark on trees which lies external to the living periderm is also called the rhytidome. Products derived from bark include bark shingle siding and wall coverings, spices, and other flavorings, tanbark for tannin, resin, latex, medicines, poisons, various hallucinogenic chemicals, and cork. Bark has been used to make cloth, canoes, and ropes and used as a surface for paintings and map making. A number of plants a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cork Cambium
Cork cambium (: cambia or cambiums) is a tissue found in many vascular plants as a part of the epidermis. It is one of the many layers of bark, between the cork and primary phloem. The cork cambium is a lateral meristem and is responsible for secondary growth that replaces the epidermis in roots and stems. It is found in woody and many herbaceous dicots, gymnosperms and some monocots (monocots usually lack secondary growth). It is one of the plant's meristems – the series of tissues consisting of embryonic disk (incompletely differentiated) cells from which the plant grows. The function of cork cambium is to produce the cork, a tough protective material.Junikka, L. (1994) "Macroscopic bark terminology". ''IAWA Journal'' 15(1): 3–45Trockenbrodt, M. (1990) "Survey and discussion of the terminology used in bark anatomy". ''IAWA Bulletin, New Series'' 11: 141–166 Synonyms for cork cambium are bark cambium, peri-cambium and phellogen. Phellogen is defined as the meristematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Cambium
The vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants exhibiting secondary growth, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and oak trees, gymnosperms such as pine trees, as well as in certain other vascular plants. It produces secondary xylem inwards, towards the pith, and secondary phloem outwards, towards the bark. Generally, more secondary xylem is produced than secondary phloem. In herbaceous plants, it occurs in the vascular bundles which are often arranged like beads on a necklace forming an interrupted ring inside the stem. In woody plants, it forms a cylinder of unspecialized meristem cells, as a continuous ring from which the new tissues are grown. Unlike the xylem and phloem, it does not transport water, minerals or food through the plant. Other names for the vascular cambium are the main cambium, wood cambium, or bifacial cambium. Occurrence Vascular cambia are found in all seed plants except for five angiosperm lineages whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phloem
Phloem (, ) is the living tissue in vascular plants that transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis and known as ''photosynthates'', in particular the sugar sucrose, to the rest of the plant. This transport process is called translocation. In trees, the phloem is the innermost layer of the bark, hence the name, derived from the Ancient Greek word (''phloiós''), meaning "bark". The term was introduced by Carl Nägeli in 1858. Different types of phloem can be distinguished. The early phloem formed in the growth apices is called protophloem. Protophloem eventually becomes obliterated once it connects to the durable phloem in mature organs, the metaphloem. Further, secondary phloem is formed during the thickening of stem structures. Structure Phloem tissue consists of conducting cells, generally called sieve elements, parenchyma cells, including both specialized companion cells or albuminous cells and unspecialized cells and supportive cells, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue (biology), tissue in vascular plants, the other being phloem; both of these are part of the vascular bundle. The basic function of the xylem is to transport water upward from the roots to parts of the plants such as stems and leaves, but it also transports plant nutrition, nutrients. The word ''xylem'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning "wood"; the best-known wood organism is plants, though it is found throughout a plant. The term was introduced by Carl Nägeli in 1858. Structure The most distinctive xylem cell (biology), cells are the long tracheary elements that transport water. Tracheids and vessel elements are distinguished by their shape; vessel elements are shorter, and are connected together into long tubes that are called ''vessels''. Wood also contains two other type of cells: Ground tissue#Parenchyma, parenchyma and ground tissue#Fibres, fibers. Xylem can be found: * in vascular bundles, present in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermis (botany)
The epidermis (from the Greek language, Greek ''ἐπιδερμίς'', meaning "over-skin") is a single layer of cells that covers the leaf, leaves, flowers, roots and Plant stem, stems of plants. It forms a boundary between the plant and the external environment. The epidermis serves several functions: it protects against water loss, regulates gas exchange, secretes metabolic compounds, and (especially in roots) absorbs water and mineral nutrients. The epidermis of most leaves shows Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, dorsoventral anatomy: the upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces have somewhat different construction and may serve different functions. Woody stems and some other stem structures such as potato tubers produce a secondary covering called the periderm that replaces the epidermis as the protective covering. Description The epidermis is the outermost cell layer of the primary plant body. In some older works the cells of the leaf epidermis have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Growth
Primary growth in plants is growth that takes place from the tips of roots or shoots. It leads to lengthening of roots and stems and sets the stage for organ formation. It is distinguished from secondary growth that leads to widening. Plant growth takes place in well defined plant locations. Specifically, the cell division and differentiation needed for growth occurs in specialized structures called meristems. These consist of undifferentiated cells (meristematic cells) capable of cell division. Cells in the meristem can develop into all the other tissues and organs that occur in plants. These cells continue to divide until they differentiate and then lose the ability to divide. Thus, the meristems produce all the cells used for plant growth and function. At the tip of each stem and root, an apical meristem adds cells to their length, resulting in the elongation of both. Examples of primary growth are the rapid lengthening growth of seedlings after they emerge from the soil and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Wilhelm Von Nägeli
Carl may refer to: *Carl, Georgia, city in USA *Carl, West Virginia, an unincorporated community *Carl (name), includes info about the name, variations of the name, and a list of people with the name *Carl², a TV series * "Carl", an episode of television series ''Aqua Teen Hunger Force'' * An informal nickname for a student or alum of Carleton College CARL may refer to: *Canadian Association of Research Libraries *Colorado Alliance of Research Libraries See also *Carle (other) *Charles *Carle, a surname *Karl (other) *Karle (other) Karle may refer to: Places * Karle (Svitavy District), a municipality and village in the Czech Republic * Karli, India, a town in Maharashtra, India ** Karla Caves, a complex of Buddhist cave shrines * Karle, Belgaum, a settlement in Belgaum ... {{disambig ja:カール zh:卡尔 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woody Plants
A woody plant is a plant that produces wood as its structural tissue and thus has a hard stem. In cold climates, woody plants further survive winter or dry season above ground, as opposed to herbaceous plants that die back to the ground until spring. Characteristics Woody plants are usually trees, shrubs, or lianas. These are usually perennial plants whose stems and larger roots are reinforced with wood produced from secondary xylem. The main stem, larger branches, and roots of these plants are usually covered by a layer of bark. Wood is a structural tissue that allows woody plants to grow from above ground stems year after year, thus making some woody plants the largest and tallest terrestrial plants. Woody plants, like herbaceous perennials, typically have a dormant period of the year when growth does not take place. This occurs in temperate and continental due to freezing temperatures and lack of daylight during the winter months. Meanwhile, dormancy in subtropical an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Growth
In botany, secondary growth is the growth that results from cell division in the cambia or lateral meristems and that causes the stems and roots to thicken, while primary growth is growth that occurs as a result of cell division at the tips of stems and roots, causing them to elongate, and gives rise to primary tissue. Secondary growth occurs in most seed plants, but monocots usually lack secondary growth. If they do have secondary growth, it differs from the typical pattern of other seed plants. The formation of secondary vascular tissues from the cambium is a characteristic feature of dicotyledons and gymnosperms. In certain monocots, the vascular tissues are also increased after the primary growth is completed but the cambium of these plants is of a different nature. In the living pteridophytes this feature is extremely rare, only occurring in '' Isoetes''. Lateral meristems In many vascular plants, secondary growth is the result of the activity of the two lateral me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |