Child Abuse on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Child abuse (also called child endangerment or child maltreatment) is physical, sexual, emotional and/or
Child abuse (also called child endangerment or child maltreatment) is physical, sexual, emotional and/or
 The immediate physical effects of abuse or neglect can be relatively minor (bruises or cuts) or severe (broken bones, hemorrhage, death). Certain injuries, such as rib fractures or femoral fractures in infants that are not yet walking, may increase suspicion of child physical abuse, although such injuries are only seen in a fraction of children suffering physical abuse. Cigarette burns or scald injuries may also prompt evaluation for child physical abuse.
The long-term impact of child abuse and neglect on physical health and development can be:
* Shaken baby syndrome. Shaking a baby is a common form of child abuse that often results in permanent neurological damage (80% of cases) or death (30% of cases). Damage results from intracranial hypertension (increased pressure in the skull) after bleeding in the brain, damage to the spinal cord and neck, and rib or bone fractures.
* Impaired brain development. Child abuse and neglect have been shown, in some cases, to cause important regions of the brain to fail to form or grow properly, resulting in impaired development. Structural brain changes as a result of child abuse or neglect include overall smaller brain volume, hippocampal atrophy, prefrontal cortex dysfunction, decreased corpus callosum density, and delays in the myelination of synapses. These alterations in brain maturation have long-term consequences for cognitive, language, and academic abilities. In addition, these neurological changes impact the amygdala and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis which are involved in stress response and may cause PTSD symptoms.
* Poor physical health. In addition to possible immediate adverse physical effects, household dysfunction and childhood maltreatment are strongly associated with many chronic physical and psychological effects, including subsequent ill-health in childhood, adolescence and adulthood, with higher rates of chronic conditions, high-risk health behaviors and shortened lifespan. Adults who experienced abuse or neglect during childhood are more likely to have physical ailments such as allergies, arthritis, asthma, bronchitis, high blood pressure, and ulcers. There may be a higher risk of developing cancer later in life, as well as possible immune dysfunction.
* Data from a recent study supports previous findings that specific neurobiochemical changes are linked to exposure to violence and abuse, several biological pathways can possibly lead to the development of illness, and certain physiological mechanisms can moderate how severe illnesses become in patients with past experience with violence or abuse.
* Recent studies give evidence of a link between stress occurring early in life and epigenetic modifications that last into adulthood.
The immediate physical effects of abuse or neglect can be relatively minor (bruises or cuts) or severe (broken bones, hemorrhage, death). Certain injuries, such as rib fractures or femoral fractures in infants that are not yet walking, may increase suspicion of child physical abuse, although such injuries are only seen in a fraction of children suffering physical abuse. Cigarette burns or scald injuries may also prompt evaluation for child physical abuse.
The long-term impact of child abuse and neglect on physical health and development can be:
* Shaken baby syndrome. Shaking a baby is a common form of child abuse that often results in permanent neurological damage (80% of cases) or death (30% of cases). Damage results from intracranial hypertension (increased pressure in the skull) after bleeding in the brain, damage to the spinal cord and neck, and rib or bone fractures.
* Impaired brain development. Child abuse and neglect have been shown, in some cases, to cause important regions of the brain to fail to form or grow properly, resulting in impaired development. Structural brain changes as a result of child abuse or neglect include overall smaller brain volume, hippocampal atrophy, prefrontal cortex dysfunction, decreased corpus callosum density, and delays in the myelination of synapses. These alterations in brain maturation have long-term consequences for cognitive, language, and academic abilities. In addition, these neurological changes impact the amygdala and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis which are involved in stress response and may cause PTSD symptoms.
* Poor physical health. In addition to possible immediate adverse physical effects, household dysfunction and childhood maltreatment are strongly associated with many chronic physical and psychological effects, including subsequent ill-health in childhood, adolescence and adulthood, with higher rates of chronic conditions, high-risk health behaviors and shortened lifespan. Adults who experienced abuse or neglect during childhood are more likely to have physical ailments such as allergies, arthritis, asthma, bronchitis, high blood pressure, and ulcers. There may be a higher risk of developing cancer later in life, as well as possible immune dysfunction.
* Data from a recent study supports previous findings that specific neurobiochemical changes are linked to exposure to violence and abuse, several biological pathways can possibly lead to the development of illness, and certain physiological mechanisms can moderate how severe illnesses become in patients with past experience with violence or abuse.
* Recent studies give evidence of a link between stress occurring early in life and epigenetic modifications that last into adulthood.
 The Adverse Childhood Experiences Study is a long-running investigation into the relationship between childhood adversity, including various forms of abuse and neglect, and health problems in later life. The initial phase of the study was conducted in
The Adverse Childhood Experiences Study is a long-running investigation into the relationship between childhood adversity, including various forms of abuse and neglect, and health problems in later life. The initial phase of the study was conducted in
 Most acts of physical violence against children are undertaken with the intent to punish. In the United States, interviews with parents reveal that as many as two thirds of documented instances of physical abuse begin as acts of corporal punishment meant to correct a child's behavior, while a large-scale Canadian study found that three quarters of substantiated cases of physical abuse of children have occurred within the context of
Most acts of physical violence against children are undertaken with the intent to punish. In the United States, interviews with parents reveal that as many as two thirds of documented instances of physical abuse begin as acts of corporal punishment meant to correct a child's behavior, while a large-scale Canadian study found that three quarters of substantiated cases of physical abuse of children have occurred within the context of
''International Encyclopedia of the Social Sciences''. 2008. Children resulting from unintended pregnancies are more likely to be abused or neglected. In addition, unintended pregnancies are more likely than intended pregnancies to be associated with abusive relationships, and there is an increased risk of physical violence during pregnancy. Which cites: * * * * They also result in poorer maternal mental health, and lower mother-child relationship quality. There is some limited evidence that children with moderate or severe disabilities are more likely to be victims of abuse than non-disabled children. A study on child abuse sought to determine: the forms of child abuse perpetrated on children with disabilities; the extent of child abuse; and the causes of child abuse of children with disabilities. A questionnaire on child abuse was adapted and used to collect data in this study. Participants comprised a sample of 31 pupils with disabilities (15 children with vision impairment and 16 children with hearing impairment) selected from special schools in Botswana. The study found that the majority of participants were involved in doing domestic chores. They were also sexually, physically and emotionally abused by their teachers. This study showed that children with disabilities were vulnerable to child abuse in their schools.
 Female genital mutilation (FGM) is defined by the
Female genital mutilation (FGM) is defined by the
, World Health Organization, 2011, p. 2: "Most women who have experienced FGM live in one of the 28 countries in Africa and the Middle East – nearly half of them in just two countries: Egypt and Ethiopia. Countries in which FGM has been documented include: Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Cote d'Ivoire, Djibouti, Egypt, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, Sudan, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania and Yemen. The prevalence of FGM ranges from 0.6% to 98% of the female population." * Rahman, Anika and Toubia, Nahid. ''Female Genital Mutilation: A Guide to Laws and Policies Worldwide''. Zed Books, 2000 (hereafter Rahman and Toubia 2000), p. 7: "Currently, FC/FGM is practiced in 28 African countries in the sub-Saharan and Northeastern regions." * Also se
"Eliminating Female Genital Mutilation"
, World Health Organization, 2008, p. 4: "Types I, II and III female genital mutilation have been documented in 28 countries in Africa and in a few countries in Asia and the Middle East." FGM is mostly found in a geographical area ranging across Africa, from east to west – from Somalia to Senegal, and from north to south – from Egypt to Tanzania. FGM is most often carried out on young girls aged between infancy and 15 years. FGM is classified into four types, of which type 3 – infibulation – is the most extreme form. The consequences of FGM include physical, emotional and sexual problems, and include serious risks during
 In some parts of the world, girls are strongly discouraged from attending school. They are sometimes attacked by members of the community if they do so. In parts of South Asia, girls schools are set on fire by vigilante groups. Such attacks are common in
In some parts of the world, girls are strongly discouraged from attending school. They are sometimes attacked by members of the community if they do so. In parts of South Asia, girls schools are set on fire by vigilante groups. Such attacks are common in
Glass children: The lived experiences of siblings of people with a disability or chronic illness.
Journal of Community & Applied Social Psychology. 32 (5), pp. 936–948.
WHO fact sheet on child maltreatment
World Report on Violence Against Children
, Secretary-General of the United Nations
Prevent Child Abuse America
"Cold-nosed Comfort"
(using a service dog to aid child abuse victims), ''Maryland Lawyer'' {{Authority control Paraphilias
 Child abuse (also called child endangerment or child maltreatment) is physical, sexual, emotional and/or
Child abuse (also called child endangerment or child maltreatment) is physical, sexual, emotional and/or psychological
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ...
maltreatment or neglect
In the context of caregiving, neglect is a form of abuse where the perpetrator, who is responsible for caring for someone who is unable to care for themselves, fails to do so. It can be a result of carelessness, indifference, or unwillingness and ...
of a child, especially by a parent or a caregiver. Child abuse may include any act or failure to act by a parent or a caregiver that results in actual or potential wrongful harm to a child and can occur in a child's home, or in organizations, schools, or communities the child interacts with.
Different jurisdictions have different requirements for mandatory reporting and have developed different definitions of what constitutes child abuse, and therefore have different criteria to remove children from their families or to prosecute a criminal charge.
History
As late as the 19th century, cruelty to children, perpetrated by employers and teachers, was commonplace and widespread, and corporal punishment was customary in many countries, but in the first half of the 19th century, pathologists studying filicide (the parental killing of children) reported cases of death from paternal rage, recurrent physical maltreatment, starvation, and sexual abuse. In an 1860 paper, French forensic medical expert Auguste Ambroise Tardieu gathered together a series of 32 such cases, of which 18 were fatal, the children dying from starvation and/or recurrent physical abuse; it included the case of Adeline Defert, who was returned by her grandparents at the age of 8, and for 9 years tortured by her parents – whipped every day, hung up by her thumbs and beaten with a nailed plank, burnt with hot coals and her wounds bathed in nitric acid, and deflorated with a baton. Tardieu made home visits and observed the effect on the children; he noticed that the sadness and fear on their faces disappeared when they were placed under protection. He commented, "When we consider the tender age of these poor defenceless beings, subjected daily and almost hourly to savage atrocities, unimaginable tortures and harsh privation, their lives one long martyrdom – and when we face the fact that their tormentors are the very mothers who gave them life, we are confronted with one of the most appalling problems that can disturb the soul of a moralist, or the conscience of justice". His observations were echoed by Boileau de Castélnau (who introduced the term misopédie – hatred of children), and confirmed by Aubry and severaltheses
A thesis (: theses), or dissertation (abbreviated diss.), is a document submitted in support of candidature for an academic degree or professional qualification presenting the author's research and findings.International Standard ISO 7144: D ...
.
These early French observations failed to cross the language barrier, and other nations remained ignorant of the cause of many traumatic lesions in infants and toddlers; almost one hundred years would pass before humankind began to systematically confront Tardieu's "appalling problem". In the 20th century, evidence began to accumulate from pathology
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatme ...
and paediatric radiology, particularly in relation to chronic subdural haematoma and limb fractures: subdural haematoma had a curious bimodal distribution, idiopathic in infants and traumatic in adults, while unexplained ossifying periostitis of the long bones was similar to that occurring after breech extractions. In 1946, John Caffey, the American founder of paediatric radiology, drew attention to the association of long bone fractures and chronic subdural haematoma, and, in 1955, it was noticed that infants removed from the care of aggressive, immature and emotionally ill parents developed no new lesions.
As a result, professional inquiry into the topic began again in the 1960s. The July 1962 publication of the paper "The Battered Child-Syndrome" authored principally by pediatrician C. Henry Kempe and published in '' The Journal of the American Medical Association'' represents the moment that child maltreatment entered mainstream awareness. Before the article's publication, injuries to children—even repeated bone fractures—were not commonly recognized as the results of intentional trauma. Instead, physicians often looked for undiagnosed bone disease
Bone disease refers to the medical conditions which affect the bone.
Terminology
A bone disease is also called an "osteopathy", but because the term osteopathy is often used to refer to an alternative health-care philosophy, use of the term can ...
s or accepted parents' accounts of accidental mishaps such as falls or assaults by neighborhood bullies.
The study of child abuse emerged as an academic discipline
An academic discipline or academic field is a subdivision of knowledge that is taught and researched at the college or university level. Disciplines are defined (in part) and recognized by the academic journals in which research is published, a ...
in the early 1970s in the United States. Elisabeth Young-Bruehl maintained that despite the growing numbers of child advocates and interest in protecting children which took place, the grouping of children into "the abused" and the "non-abused" created an artificial distinction that narrowed the concept of children's rights
Children's rights or the rights of children are a subset of human rights with particular attention to the rights of special protection and care afforded to minors.
to simply protection from maltreatment, and blocked investigation of how children are discriminated against in society generally. Another effect of the way child abuse and neglect have been studied, according to Young-Bruehl, was to close off consideration of how children themselves perceive maltreatment and the importance they place on adults' attitudes toward them. Young-Bruehl wrote that when the belief in children's inherent inferiority to adults is present in society, all children suffer whether or not their treatment is labeled as "abuse".
Definitions
Definitions of what constitutes child abuse vary among professionals, between social and cultural groups, and across time. The terms ''abuse'' and ''maltreatment'' are often used interchangeably in the literature. ''Child maltreatment'' can also be anumbrella term
Hypernymy and hyponymy are the wikt:Wiktionary:Semantic relations, semantic relations between a generic term (''hypernym'') and a more specific term (''hyponym''). The hypernym is also called a ''supertype'', ''umbrella term'', or ''blanket term ...
covering all forms of child abuse and child neglect
Child neglect is an act of caregivers (e.g., parents) that results in depriving a child of their basic needs, such as the failure to provide adequate supervision, health care, clothing, or housing, as well as other physical, emotional, social, ...
. Defining child maltreatment depends on prevailing cultural values as they relate to children, child development
Child development involves the Human development (biology), biological, psychological and emotional changes that occur in human beings between birth and the conclusion of adolescence. It is—particularly from birth to five years— a foundation ...
, and parenting
Parenting or child rearing promotes and supports the physical, cognitive, social, emotional, and educational development from infancy to adulthood. Parenting refers to the intricacies of raising a child and not exclusively for a biologica ...
. Definitions of child maltreatment can vary across the sectors of society which deal with the issue, such as child protection
Child protection (also called child welfare) is the safeguarding of children from violence, exploitation, abuse, abandonment, and neglect. It involves identifying signs of potential harm. This includes responding to allegations or suspicions ...
agencies, legal and medical communities, public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the de ...
officials, researchers, practitioners, and child advocates. Since members of these various fields tend to use their own definitions, communication across disciplines can be limited, hampering efforts to identify, assess, track, treat, and prevent child maltreatment.
In general, ''abuse'' refers to (usually deliberate) acts of commission while ''neglect'' refers to acts of omission. ''Child maltreatment'' includes both acts of commission and acts of omission on the part of parents or caregivers that cause actual or threatened harm to a child. Some health professionals and authors consider neglect as part of the definition of ''abuse'', while others do not; this is because the harm may have been unintentional, or because the caregivers did not understand the severity of the problem, which may have been the result of cultural beliefs about how to raise a child. Delayed effects of child abuse and neglect, especially emotional neglect, and the diversity of acts that qualify as child abuse, are also factors.
The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO) defines ''child abuse'' and ''child maltreatment'' as "all forms of physical and/or emotional ill-treatment, sexual abuse, neglect or negligent treatment or commercial or other exploitation, resulting in actual or potential harm to the child's health, survival, development or dignity in the context of a relationship of responsibility, trust or power." The WHO also says, "Violence against children includes all forms of violence against people under 18 years old, whether perpetrated by parents or other caregivers, peers, romantic partners, or strangers." In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
(CDC) uses the term ''child maltreatment'' to refer to both acts of commission (abuse), which include "words or overt actions that cause harm, potential harm, or threat of harm to a child", and acts of omission (neglect), meaning "the failure to provide for a child's basic physical, emotional, or educational needs or to protect a child from harm or potential harm". The United States federal Child Abuse Prevention and Treatment Act defines ''child abuse and neglect'' as, at minimum, "any recent act or failure to act on the part of a parent or caretaker which results in death, serious physical or emotional harm, sexual abuse or exploitation" or "an act or failure to act which presents an imminent risk of serious harm".
Forms of abuse
, the World Health Organization distinguishes four types of child maltreatment:physical abuse
Physical abuse is any intentional act causing injury or trauma to another person or animal by way of bodily contact. In most cases, children are the victims of physical abuse, but adults can also be victims, as in cases of domestic violence or ...
; sexual abuse
Sexual abuse or sex abuse is abusive sexual behavior by one person upon another. It is often perpetrated using physical force, or by taking advantage of another. It often consists of a persistent pattern of sexual assaults. The offender is re ...
; emotional (or psychological) abuse; and neglect
In the context of caregiving, neglect is a form of abuse where the perpetrator, who is responsible for caring for someone who is unable to care for themselves, fails to do so. It can be a result of carelessness, indifference, or unwillingness and ...
.
Physical abuse
Among professionals and the general public, there is disagreement as to what behaviors constitutephysical abuse
Physical abuse is any intentional act causing injury or trauma to another person or animal by way of bodily contact. In most cases, children are the victims of physical abuse, but adults can also be victims, as in cases of domestic violence or ...
of a child.Noh Anh, Helen (1994). "Cultural Diversity and the Definition of Child Abuse", in Barth, R.P. et al., ''Child Welfare Research Review'', Columbia University Press, 1994, p. 28. Physical abuse often does not occur in isolation but as part of a pattern of behaviors including authoritarian control, anxiety-provoking behavior, and a lack of parental warmth. The WHO defines physical abuse as:
Overlapping definitions of physical abuse and physical punishment
A corporal punishment or a physical punishment is a punishment which is intended to cause physical pain to a person. When it is inflicted on minors, especially in home and school settings, its methods may include spanking or paddling. When ...
of children highlight a subtle or non-existent distinction between abuse and punishment, but most physical abuse is physical punishment "in intent, form, and effect". As of 2006, for instance, Paulo Sergio Pinheiro wrote in the UN Secretary-General's Study on Violence Against Children:
Most nations with child abuse laws deem the deliberate infliction of serious injuries, or actions that place the child at obvious risk of serious injury or death, to be illegal. Bruises, scratches, burns, broken bones, lacerations—as well as repeated "mishaps", and rough treatment that could cause physical injuries—can be physical abuse. Multiple injuries or fractures at different stages of healing can raise suspicion of abuse.
The psychologist Alice Miller, noted for her books on child abuse, took the view that humiliations, spankings, and beatings, slaps in the face, etc. are all forms of abuse, because they injure the integrity and dignity of a child, even if their consequences are not visible right away.
Physical abuse as a child can lead to physical and mental difficulties in the future, including re-victimization, personality disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental disorder that develops from experiencing a Psychological trauma, traumatic event, such as sexual assault, domestic violence, child abuse, warfare and its associated traumas, natural disaster ...
(PTSD), dissociative disorders, depression, anxiety, suicidal ideation, eating disorders, substance use disorders, and aggression. Physical abuse in childhood has also been linked to homelessness in adulthood.
Battered-child syndrome
C. Henry Kempe and his colleagues were the first to describe the battered-child syndrome in 1962. The battered-child syndrome is a term used to describe a collection of injuries that young children sustain as a result of repeated physical abuse or neglect. These symptoms may include: fractures of bones, multiple soft tissue injuries, subdural hematoma (bleeding in the brain),malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
, and poor skin hygiene.
Children suffering from battered-child syndrome may come to the doctor's attention for a problem unrelated to abuse or after experiencing an acute injury, but when examined, they show signs of long-term abuse. In most cases, the caretakers try to justify the visible injuries by blaming them on minor accidents. When asked, parents may attribute the injuries to a child's behaviour or habits, such as being fussy or clumsy. Despite the abuse, the child may show attachment to the parent.
Sexual abuse
Child sexual abuse (CSA) is a form of child abuse in which an adult or older adolescent abuses a child for sexual stimulation. Sexual abuse refers to the participation of a child in a sexual act aimed toward the physical gratification or the financial profit of the person committing the act. Forms of CSA include asking or pressuring a child to engage in sexual activities (regardless of the outcome),indecent exposure
Indecent exposure is the deliberate public exposure by a person of a portion of their body in a manner contrary to local standards of appropriate behavior. Laws and social attitudes regarding indecent exposure vary significantly in different ...
of the genitals to a child, displaying pornography to a child, actual sexual contact with a child, physical contact with the child's genitals, viewing of the child's genitalia without physical contact, or using a child to produce child pornography
Child pornography (also abbreviated as CP, also called child porn or kiddie porn, and child sexual abuse material, known by the acronym CSAM (underscoring that children can not be deemed willing participants under law)), is Eroticism, erotic ma ...
. Selling the sexual services of children is also a type of child abuse.
Effects of child sexual abuse on the victim(s) include guilt and self-blame, flashbacks, nightmares, insomnia
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder where people have difficulty sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep for as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low ene ...
, fear of things associated with the abuse (including objects, smells, places, doctor's visits, etc.), self-esteem
Self-esteem is confidence in one's own worth, abilities, or morals. Self-esteem encompasses beliefs about oneself (for example, "I am loved", "I am worthy") as well as emotional states, such as triumph, despair, pride, and shame. Smith and Macki ...
difficulties, sexual dysfunction
Sexual dysfunction is difficulty experienced by an individual or partners during any stage of normal sexual activity, including physical pleasure, desire, preference, arousal, or orgasm. The World Health Organization defines sexual dysfunction ...
, chronic pain
Chronic pain is pain that persists or recurs for longer than 3 months.https://icd.who.int/browse/2025-01/mms/en#1581976053 It is also known as gradual burning pain, electrical pain, throbbing pain, and nauseating pain. This type of pain is in cont ...
, addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to use a drug or engage in a behavior that produces natural reward, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use can ...
, self-injury
Self-harm refers to intentional behaviors that cause harm to oneself. This is most commonly regarded as direct injury of one's own skin tissues, usually without suicidal intention. Other terms such as cutting, self-abuse, self-injury, and s ...
, suicidal ideation, somatic complaints, depression, PTSD, anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response ...
, other mental illnesses including borderline personality disorder
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a personality disorder characterized by a pervasive, long-term pattern of significant interpersonal relationship instability, an acute fear of Abandonment (emotional), abandonment, and intense emotiona ...
, propensity to re-victimization in adulthood, bulimia nervosa
Bulimia nervosa, also known simply as bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating (eating large quantities of food in a short period of time, often feeling out of control) followed by compensatory behaviors, such as self-indu ...
, and physical injury to the child, among other problems. Children who are the victims are also at an increased risk of sexually transmitted infections due to their immature immune systems and a high potential for mucosal tears during forced sexual contact. Sexual victimization at a young age has been correlated with several risk factors for contracting HIV including decreased knowledge of sexual topics, increased prevalence of HIV, engagement in risky sexual practices, condom avoidance, lower knowledge of safe sex practices, frequent changing of sexual partners, and more years of sexual activity.
, in the United States, about 15% to 25% of women and 5% to 15% of men were sexually abused when they were children. Most sexual abuse offenders are acquainted with their victims; approximately 30% are relatives of the child, most often brothers, sisters, fathers, mothers, uncles or cousins; around 60% are other acquaintances such as friends of the family, babysitters, or neighbours; strangers are the offenders in approximately 10% of child sexual abuse cases. In over one-third of cases, the perpetrator is also a minor.
In 1999 the BBC reported on the RAHI Foundation's survey of sexual abuse in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, in which 76% of respondents said they had been abused as children, 40% of those stating the perpetrator was a family member.
Psychological abuse
There are multiple definitions of child psychological abuse: * In 1995, The American Professional Society on the Abuse of Children (APSAC) defined it as: spurning, terrorizing, isolating, exploiting, corrupting, denying emotional responsiveness, or neglect" or "A repeated pattern of caregiver behavior or extreme incident(s) that convey to children that they are worthless, flawed, unloved, unwanted, endangered, or only of value in meeting another's needs" * In 2013, theAmerican Psychiatric Association
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) is the main professional organization of psychiatrists and trainee psychiatrists in the United States, and the largest psychiatric organization in the world. It has more than 39,200 members who are in ...
(APA) added Child Psychological Abuse to the DSM-5
The ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition'' (DSM-5), is the 2013 update to the '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'', the taxonomic and diagnostic tool published by the American Psychiat ...
, describing it as "nonaccidental verbal or symbolic acts by a child's parent or caregiver that result, or have reasonable potential to result, in significant psychological harm to the child."
* In the United States, states' laws vary, but most have laws against "mental injury" against minors.
* Some have defined it as the production of psychological and social defects in the growth of a minor as a result of behavior such as loud yelling, coarse and rude attitude, inattention, harsh criticism, and denigration of the child's personality. Other examples include name-calling, ridicule, degradation, destruction of personal belongings, torture or killing of a pet, excessive or extreme unconstructive criticism
Criticism is the construction of a judgement about the negative or positive qualities of someone or something. Criticism can range from impromptu comments to a written detailed response. , ''the act of giving your opinion or judgment about the ...
, inappropriate or excessive demands, withholding communication, and routine labeling or humiliation
Humiliation is the abasement of pride, which creates mortification or leads to a state of being Humility, humbled or reduced to lowliness or submission. It is an emotion felt by a person whose social status, either by force or willingly, has ...
.
* Many psychological abuse that happens to adults are harder to change to improve and turn back due to fixed habits and living style after abuse. Child abuse can create a big toll on psychological behavior that put many risk to unhealthy thoughts. In order to minimize these negative outcomes, many need to seek help to spread awareness to those around them for preventative measures.
In 2014, the APA found that child ''psychological'' abuse is the most prevalent form of childhood abuse in the United States, affecting nearly 3 million children annually. Research has suggested that the consequences of child psychological abuse may be equally as harmful as those of sexual or physical abuse.
Victims of emotional abuse may react by distancing themselves from the abuser, internalizing the abusive words, or fighting back by insult
An insult is an expression, statement, or behavior that is often deliberately disrespectful, offensive, scornful, or derogatory towards an individual or a group.
Insults can be intentional or unintentional, and they often aim to belittle, of ...
ing the abuser. Emotional abuse can result in abnormal or disrupted attachment development, a tendency for victims to blame themselves ( self-blame) for the abuse, learned helplessness
Learned helplessness is the behavior exhibited by a subject after enduring repeated aversive stimuli beyond their control. It was initially thought to be caused by the subject's acceptance of their powerlessness, by way of their discontinuing att ...
, and overly passive behavior in order to avoid such a situation again.
Neglect
Child neglect is the ''failure'' of a parent or other person with responsibility for the child, to provide needed food, clothing, shelter, medical care, or supervision to the degree that the child's health, safety or well-being may be threatened with harm. Neglect is also a lack of attention from the people surrounding a child, and the non-provision of the relevant and adequate necessities for the child's survival, which would be a ''lack'' of attention, love, and nurturing. Some observable signs of child neglect include: the child is frequently absent from school, begs or steals food or money, lacks needed medical and dental care, is consistently dirty, or lacks appropriate clothing for the weather. The 2010 Child Maltreatment Report ( NCANDS), a yearly United States federal government report based on data supplied by state Child Protective Services (CPS) Agencies in the U.S., found that neglect/neglectful behavior was the "most common form of child maltreatment". Neglectful acts can be divided into six sub-categories: * Supervisory neglect: characterized by the absence of a parent or guardian which can lead to physical harm, sexual abuse, or criminal behavior; * Physical neglect: characterized by the failure to provide the basic physical necessities, such as a safe and clean home; * Medical neglect: characterized by the lack of providing medical care; * Emotional neglect: characterized by a lack of nurturance, encouragement, and support; * Educational neglect: characterized by the caregivers lack to provide an education and additional resources to actively participate in the school system; and * Abandonment: when the parent or guardian leaves a child alone for a long period of time without a babysitter or caretaker. Neglected children may experience delays in physical and psychosocial development, possibly resulting inpsychopathology
Psychopathology is the study of mental illness. It includes the signs and symptoms of all mental disorders. The field includes Abnormal psychology, abnormal cognition, maladaptive behavior, and experiences which differ according to social norms ...
and impaired neuropsychological
Neuropsychology is a branch of psychology concerned with how a person's cognition and behavior are related to the brain and the rest of the nervous system. Professionals in this branch of psychology focus on how injuries or illnesses of the brai ...
functions including executive function
In cognitive science and neuropsychology, executive functions (collectively referred to as executive function and cognitive control) are a set of cognitive processes that support goal-directed behavior, by regulating thoughts and actions thro ...
, attention
Attention or focus, is the concentration of awareness on some phenomenon to the exclusion of other stimuli. It is the selective concentration on discrete information, either subjectively or objectively. William James (1890) wrote that "Atte ...
, processing speed, language, memory and social skills. Researchers investigating maltreated children have repeatedly found that neglected children in the foster and adoptive populations manifest different emotional and behavioral reactions to regain lost or secure relationships and are frequently reported to have disorganized attachments and a need to control their environment. Such children are not likely to view caregivers as being a source of safety, and instead typically show an increase in aggressive and hyperactive behaviors which may disrupt healthy or secure attachment with their adopted parents. These children seem to have learned to adapt to an abusive and inconsistent caregiver by becoming cautiously self-reliant, and are often described as glib, manipulative and disingenuous in their interactions with others as they move through childhood. Children who are victims of neglect can have a more difficult time forming and maintaining relationships, such as romantic or friendship, later in life due to the lack of attachment they had in their earlier stages of life.
Effects
Child abuse can result in immediate adverse physical effects but it is also strongly associated with developmental problems and with many chronic physical and psychological effects, including subsequent ill-health, including higher rates of chronic conditions, high-risk health behaviors and shortened lifespan. Child abuse has also been linked tosuicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death.
Risk factors for suicide include mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse. Some suicides are impulsive acts driven by stress (such as from financial or ac ...
, according to a May 2019 study, published in the Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 Unit ...
University Press.
Maltreated children may be at risk to become maltreating adults.
Emotional
Physical and emotional abuse have comparable effects on a child's emotional state and have been linked to childhood depression, low self-compassion, and negative automatic thoughts. Some research suggests that high stress levels from child abuse may cause structural and functional changes within the brain, and therefore cause emotional and social disruptions. Abused children can grow up experiencing insecurities, low self-esteem, and lack of development. Many abused children experience ongoing difficulties with trust, social withdrawal, trouble in school, and forming relationships. Babies and other young children can be affected differently by abuse than their older counterparts. Babies and pre-school children who are being emotionally abused or neglected may be overly affectionate towards strangers or people they have not known for very long. They can lack confidence or become anxious, appear to not have a close relationship with their parent, exhibit aggressive behavior or act nasty towards other children and animals. Older children may use foul language or act in a markedly different way to other children at the same age, struggle to control strong emotions, seem isolated from their parents, lack social skills or have few, if any, friends. Children can also experience reactive attachment disorder (RAD). RAD is defined as markedly disturbed and developmentally inappropriate social relatedness, that usually begins before the age of 5 years. RAD can present as a persistent failure to start or respond in a developmentally appropriate fashion to most social situations. The long-term impact of emotional abuse has not been studied widely, but recent studies have begun to document its long-term consequences. Emotional abuse has been linked to increased depression, anxiety, and difficulties in interpersonal relationships (Spertus, Wong, Halligan, & Seremetis, 2003). Victims of child abuse and neglect are more likely to commit crimes as juveniles and adults. Domestic violence also takes its toll on children; although the child is not the one being abused, the child witnessing the domestic violence is greatly influenced as well. Research studies conducted such as the "Longitudinal Study on the Effects of Child Abuse and Children's Exposure to Domestic Violence", show that 36.8% of children engage in felony assault compared to the 47.5% of abused/assaulted children. Research has shown that children exposed to domestic violence increases the chances of experienced behavioral and emotional problems (depression, irritability, anxiety, academic problems, and problems in language development).Physical
 The immediate physical effects of abuse or neglect can be relatively minor (bruises or cuts) or severe (broken bones, hemorrhage, death). Certain injuries, such as rib fractures or femoral fractures in infants that are not yet walking, may increase suspicion of child physical abuse, although such injuries are only seen in a fraction of children suffering physical abuse. Cigarette burns or scald injuries may also prompt evaluation for child physical abuse.
The long-term impact of child abuse and neglect on physical health and development can be:
* Shaken baby syndrome. Shaking a baby is a common form of child abuse that often results in permanent neurological damage (80% of cases) or death (30% of cases). Damage results from intracranial hypertension (increased pressure in the skull) after bleeding in the brain, damage to the spinal cord and neck, and rib or bone fractures.
* Impaired brain development. Child abuse and neglect have been shown, in some cases, to cause important regions of the brain to fail to form or grow properly, resulting in impaired development. Structural brain changes as a result of child abuse or neglect include overall smaller brain volume, hippocampal atrophy, prefrontal cortex dysfunction, decreased corpus callosum density, and delays in the myelination of synapses. These alterations in brain maturation have long-term consequences for cognitive, language, and academic abilities. In addition, these neurological changes impact the amygdala and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis which are involved in stress response and may cause PTSD symptoms.
* Poor physical health. In addition to possible immediate adverse physical effects, household dysfunction and childhood maltreatment are strongly associated with many chronic physical and psychological effects, including subsequent ill-health in childhood, adolescence and adulthood, with higher rates of chronic conditions, high-risk health behaviors and shortened lifespan. Adults who experienced abuse or neglect during childhood are more likely to have physical ailments such as allergies, arthritis, asthma, bronchitis, high blood pressure, and ulcers. There may be a higher risk of developing cancer later in life, as well as possible immune dysfunction.
* Data from a recent study supports previous findings that specific neurobiochemical changes are linked to exposure to violence and abuse, several biological pathways can possibly lead to the development of illness, and certain physiological mechanisms can moderate how severe illnesses become in patients with past experience with violence or abuse.
* Recent studies give evidence of a link between stress occurring early in life and epigenetic modifications that last into adulthood.
The immediate physical effects of abuse or neglect can be relatively minor (bruises or cuts) or severe (broken bones, hemorrhage, death). Certain injuries, such as rib fractures or femoral fractures in infants that are not yet walking, may increase suspicion of child physical abuse, although such injuries are only seen in a fraction of children suffering physical abuse. Cigarette burns or scald injuries may also prompt evaluation for child physical abuse.
The long-term impact of child abuse and neglect on physical health and development can be:
* Shaken baby syndrome. Shaking a baby is a common form of child abuse that often results in permanent neurological damage (80% of cases) or death (30% of cases). Damage results from intracranial hypertension (increased pressure in the skull) after bleeding in the brain, damage to the spinal cord and neck, and rib or bone fractures.
* Impaired brain development. Child abuse and neglect have been shown, in some cases, to cause important regions of the brain to fail to form or grow properly, resulting in impaired development. Structural brain changes as a result of child abuse or neglect include overall smaller brain volume, hippocampal atrophy, prefrontal cortex dysfunction, decreased corpus callosum density, and delays in the myelination of synapses. These alterations in brain maturation have long-term consequences for cognitive, language, and academic abilities. In addition, these neurological changes impact the amygdala and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis which are involved in stress response and may cause PTSD symptoms.
* Poor physical health. In addition to possible immediate adverse physical effects, household dysfunction and childhood maltreatment are strongly associated with many chronic physical and psychological effects, including subsequent ill-health in childhood, adolescence and adulthood, with higher rates of chronic conditions, high-risk health behaviors and shortened lifespan. Adults who experienced abuse or neglect during childhood are more likely to have physical ailments such as allergies, arthritis, asthma, bronchitis, high blood pressure, and ulcers. There may be a higher risk of developing cancer later in life, as well as possible immune dysfunction.
* Data from a recent study supports previous findings that specific neurobiochemical changes are linked to exposure to violence and abuse, several biological pathways can possibly lead to the development of illness, and certain physiological mechanisms can moderate how severe illnesses become in patients with past experience with violence or abuse.
* Recent studies give evidence of a link between stress occurring early in life and epigenetic modifications that last into adulthood.
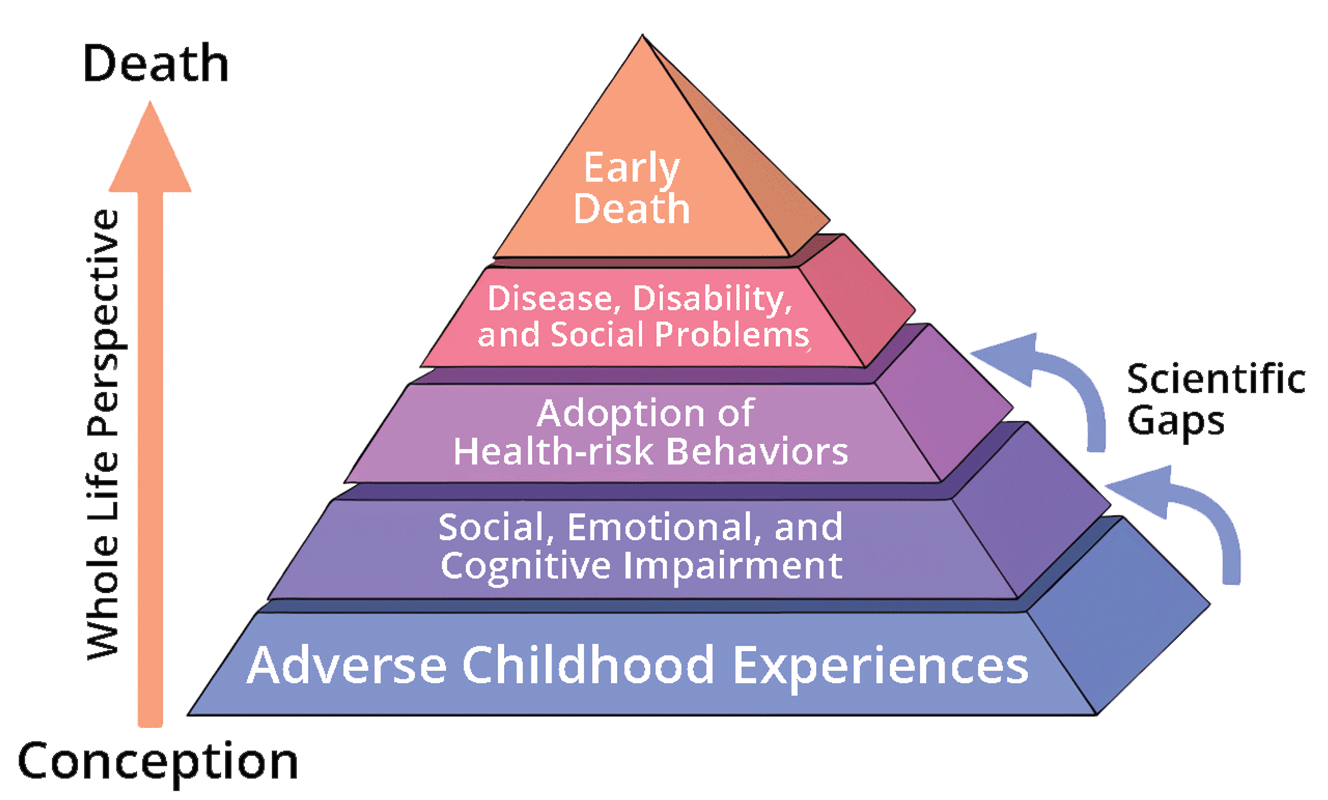
Adverse Childhood Experiences Study
 The Adverse Childhood Experiences Study is a long-running investigation into the relationship between childhood adversity, including various forms of abuse and neglect, and health problems in later life. The initial phase of the study was conducted in
The Adverse Childhood Experiences Study is a long-running investigation into the relationship between childhood adversity, including various forms of abuse and neglect, and health problems in later life. The initial phase of the study was conducted in San Diego, California
San Diego ( , ) is a city on the Pacific coast of Southern California, adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a population of over 1.4 million, it is the List of United States cities by population, eighth-most populous city in t ...
from 1995 to 1997. The World Health Organization summarizes the study as:childhood maltreatment and household dysfunction contribute to the development – decades later – of the chronic diseases that are the most common causes of death and disability in the United States... A strong relationship was seen between the number of adverse experiences (including physical and sexual abuse in childhood) and self-reports of cigarette smoking, obesity, physical inactivity, alcoholism, drug abuse, depression, attempted suicide, sexual promiscuity and sexually transmitted diseases in later life.A long-term study of adults retrospectively reporting adverse childhood experiences including verbal, physical and sexual abuse, as well as other forms of childhood trauma found 25.9% of adults reported verbal abuse as children, 14.8% reported physical abuse, and 12.2% reported sexual abuse. Data from the
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
(CDC) and Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System corroborate these high rates. There is a high correlation between the number of different adverse childhood experiences (A.C.E.s) and risk for poor health outcomes in adults including cancer, heart attack, mental illness, reduced longevity, and drug and alcohol abuse. An anonymous self-reporting survey of Washington State students finds 6–7% of 8th, 10th and 12th grade students actually attempt suicide. Rates of depression are twice as high. Other risk behaviors are even higher. There is a relationship between child physical and sexual abuse and suicide. For legal and cultural reasons as well as fears by children of being taken away from their parents most childhood abuse goes unreported and unsubstantiated.
It has been discovered that childhood abuse can lead to the addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to use a drug or engage in a behavior that produces natural reward, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use can ...
of drugs and alcohol in adolescence and adult life. Studies show that any type of abuse experienced in childhood can cause neurological changes making an individual more prone to addictive tendencies. A significant study examined 900 court cases of children who had experienced sexual and physical abuse along with neglect. The study found that a large sum of the children who were abused are now currently addicted to alcohol. This case study outlines how addiction is a significant effect of childhood abuse.
Psychological
Children who have a history of neglect or physical abuse are at risk of developing psychiatric problems, or a disorganized attachment style. In addition, children who experience child abuse or neglect are 59% more likely to be arrested as juveniles, 28% more likely to be arrested as adults, and 30% more likely to commit violent crime. Disorganized attachment is associated with a number of developmental problems, including dissociative symptoms, as well as anxiety, depressive, and acting out symptoms. When some of these children become parents, especially if they have PTSD, dissociative symptoms, and other sequelae of child abuse, they may encounter difficulty when faced with their infant and young children's needs and normative distress, which may in turn lead to adverse consequences for their child's social-emotional development. Additionally, children may find it difficult to feel empathy towards themselves or others, which may cause them to feel alone and unable to make friends. Despite these potential difficulties, psychosocial intervention can be effective, at least in some cases, in changing the ways maltreated parents think about their young children. Victims of childhood abuse also have different types of physical health problems later in life. Some reportedly have some type of chronic head, abdominal, pelvic, or muscular pain with no identifiable reason.Takele Hamnasu, MBA. ''Impact of Childhood Abuse on Adult Health''. Amberton University. Even though the majority of childhood abuse victims know or believe that their abuse is, or can be, the cause of different health problems in their adult life, for the great majority their abuse was not directly associated with those problems, indicating that they were most likely diagnosed with other possible causes for their health problems, instead of their childhood abuse. On the other hand, there are some children who are raised in child abuse, but who manage to do unexpectedly well later in life regarding the preconditions. Such children have been termed ', as inspired from the way that dandelions seem to prosper irrespective of soil, sun, drought, or rain. Such children (or currently grown-ups) are of high interest in finding factors that mitigate the effects of child abuse.Causes
Child abuse is a complex phenomenon with multiple causes. No single factor can be identified as to why some adults behave abusively or neglectfully toward children. The World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Society for Prevention of Child Abuse and Neglect (ISPCAN) identify multiple factors at the level of the individual, their relationships, their local community, and their society at large, that combine to influence the occurrence of child maltreatment. At the individual level, studies have shown that age, mental health, and substance use, and a personal history of abuse may serve as risk factors of child abuse. At the level of society, factors contributing to child maltreatment include cultural norms that encourage harsh physical punishment of children, economic inequality, and the lack ofsocial safety net
A social safety net (SSN) consists of non-contributory assistance existing to improve lives of vulnerable families and individuals experiencing poverty and destitution. Examples of SSNs are previously-contributory social pensions, in-kind and foo ...
s. WHO and ISPCAN state that understanding the complex interplay of various risk factors is vital for dealing with the problem of child maltreatment.
Factors related to relationships include marital strife and tension. Parents who physically abuse their spouses are more likely than others to physically abuse their children. However, it is impossible to know whether marital strife is a cause of child abuse, or if both the marital strife and the abuse are caused by tendencies in the abuser. Parents may also set expectations for their child that are clearly beyond the child's capability (e.g., preschool children who are expected to be totally responsible for self-care or provision of nurturance to parents), and the resulting frustration caused by the child's non-compliance may function as a contributory factor of the occurrence of child abuse.
 Most acts of physical violence against children are undertaken with the intent to punish. In the United States, interviews with parents reveal that as many as two thirds of documented instances of physical abuse begin as acts of corporal punishment meant to correct a child's behavior, while a large-scale Canadian study found that three quarters of substantiated cases of physical abuse of children have occurred within the context of
Most acts of physical violence against children are undertaken with the intent to punish. In the United States, interviews with parents reveal that as many as two thirds of documented instances of physical abuse begin as acts of corporal punishment meant to correct a child's behavior, while a large-scale Canadian study found that three quarters of substantiated cases of physical abuse of children have occurred within the context of physical punishment
A corporal punishment or a physical punishment is a punishment which is intended to cause physical pain to a person. When it is inflicted on minors, especially in home and school settings, its methods may include spanking or paddling. When ...
. Other studies have shown that children and infants who are spanked by parents are several times more likely to be severely assaulted by their parents or suffer an injury requiring medical attention. Studies indicate that such abusive treatment often involves parents attributing conflict to their child's willfulness or rejection, as well as "coercive family dynamics and conditioned emotional responses". Factors involved in the escalation of ordinary physical punishment by parents into confirmed child abuse may be the punishing parent's inability to control their anger or judge their own strength, and the parent being unaware of the child's physical vulnerabilities."Corporal Punishment"''International Encyclopedia of the Social Sciences''. 2008. Children resulting from unintended pregnancies are more likely to be abused or neglected. In addition, unintended pregnancies are more likely than intended pregnancies to be associated with abusive relationships, and there is an increased risk of physical violence during pregnancy. Which cites: * * * * They also result in poorer maternal mental health, and lower mother-child relationship quality. There is some limited evidence that children with moderate or severe disabilities are more likely to be victims of abuse than non-disabled children. A study on child abuse sought to determine: the forms of child abuse perpetrated on children with disabilities; the extent of child abuse; and the causes of child abuse of children with disabilities. A questionnaire on child abuse was adapted and used to collect data in this study. Participants comprised a sample of 31 pupils with disabilities (15 children with vision impairment and 16 children with hearing impairment) selected from special schools in Botswana. The study found that the majority of participants were involved in doing domestic chores. They were also sexually, physically and emotionally abused by their teachers. This study showed that children with disabilities were vulnerable to child abuse in their schools.
Substance use disorder
Substance use disorder (SUD) is the persistent use of drugs despite substantial harm and adverse consequences to self and others. Related terms include ''substance use problems'' and ''problematic drug or alcohol use''. Along with substance-ind ...
can be a major contributing factor to child abuse. One U.S. study found that parents with documented substance use, most commonly alcohol, cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
, and heroin, were much more likely to mistreat their children, and were also much more likely to reject court-ordered services and treatments. Another study found that over two-thirds of cases of child maltreatment involved parents with substance use disorders. This study specifically found relationships between alcohol and physical abuse, and between cocaine and sexual abuse. Also, parental stress caused by substance increases the likelihood of the minor exhibiting internalizing and externalizing behaviors. Although the abuse victim does not always realize the abuse is wrong, the internal confusion can lead to chaos. Inner anger turns to outer frustration. Once aged 17/18, drink and drugs are used to numb the hurt feelings, nightmares, and daytime flashbacks. Acquisitive crimes to pay for the chemicals are inevitable if the victim is unable to find employment.
Unemployment and financial difficulties are associated with increased rates of child abuse. In 2009 CBS News reported that child abuse in the United States had increased during the economic recession
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
. It gave the example of a father who had never been the primary care-taker of the children. Now that the father was in that role, the children began to come in with injuries. Parental mental health has also been seen as a factor towards child maltreatment. According to a recent Children's HealthWatch study, mothers with positive symptoms of depression display a greater rate of food insecurity, poor health care for their children, and greater number of hospitalizations.
The American psychoanalyst Elisabeth Young-Bruehl maintains that harm to children is justified and made acceptable by widely held beliefs in children's inherent subservience to adults, resulting in a largely unacknowledged prejudice against children she terms ''childism''. She contends that such prejudice, while not the immediate cause of child maltreatment, must be investigated in order to understand the motivations behind a given act of abuse, as well as to shed light on societal failures to support children's needs and development in general. Founding editor of the ''International Journal of Children's Rights'', Michael Freeman, also argues that the ultimate causes of child abuse lie in prejudice against children, especially the view that human rights do not apply equally to adults and children. He writes, "the roots of child abuse lie not in parental psycho-pathology or in socio-environmental stress (though their influences cannot be discounted) but in a sick culture which denigrates and depersonalizes, which reduces children to property, to sexual objects so that they become the legitimate victims of both adult violence and lust".
Worldwide
Child abuse is an international public health crisis.Poverty
Poverty is a state or condition in which an individual lacks the financial resources and essentials for a basic standard of living. Poverty can have diverse Biophysical environmen ...
and substance use disorder
Substance use disorder (SUD) is the persistent use of drugs despite substantial harm and adverse consequences to self and others. Related terms include ''substance use problems'' and ''problematic drug or alcohol use''. Along with substance-ind ...
s are common social problems worldwide, and no matter the location, show a similar trend in the correlation to child abuse. Differences in cultural perspectives play a significant role in how children are treated. Laws reflect the population's views on what is acceptable – for example whether child corporal punishment
A corporal punishment or a physical punishment is a punishment which is intended to cause physical pain to a person. When it is inflicted on Minor (law), minors, especially in home and school settings, its methods may include spanking or Padd ...
is legal or not.
A study conducted by members from several Baltic and Eastern European countries, together with specialists from the United States, examined the causes of child abuse in the countries of Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
, Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
, Macedonia and Moldova
Moldova, officially the Republic of Moldova, is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe, with an area of and population of 2.42 million. Moldova is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. ...
. In these countries, respectively, 33%, 42%, 18% and 43% of children reported at least one type of child abuse. According to their findings, there was a series of correlations between the potential risk factors of parental employment status, alcohol abuse
Alcohol abuse encompasses a spectrum of alcohol-related substance abuse. This spectrum can range from being mild, moderate, or severe. This can look like consumption of more than 2 drinks per day on average for men, or more than 1 drink per ...
, and family size within the abuse ratings. In three of the four countries, parental substance use was considerably correlated with the presence of child abuse, and although it was a lower percentage, still showed a relationship in the fourth country (Moldova). Each country also showed a connection between the father not working outside of the home and either emotional or physical child abuse. After the fall of the communism regime, some positive changes have followed with regard to tackling child abuse. While there is a new openness and acceptance regarding parenting styles and close relationships with children, child abuse has certainly not ceased to exist. While controlling parenting may be less of a concern, financial difficulty, unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work du ...
, and substance use remain dominating factors in child abuse throughout Eastern Europe.
There is some evidence that countries in conflict or transitioning out of conflict have increased rates of child abuse. This increasing prevalence may be secondary to displacement and family disruption, as well as trauma.
Asian parenting perspectives hold different ideals from American culture
The culture of the United States encompasses various social behaviors, institutions, and Social norm, norms, including forms of Languages of the United States, speech, American literature, literature, Music of the United States, music, Visual a ...
. Many have described their traditions as including physical and emotional closeness that ensures a lifelong bond between parent and child, as well as establishing parental authority and child obedience through harsh discipline
Discipline is the self-control that is gained by requiring that rules or orders be obeyed, and the ability to keep working at something that is difficult. Disciplinarians believe that such self-control is of the utmost importance and enforce a ...
.Lau, A. S., Takeuchi, D. T., & Alegría, M. (2006). Parent-to-child aggression among Asian American parents: Culture, context, and vulnerability. ''Journal of Marriage and Family'', 68(5), 1261–1275. Retrieved Balancing disciplinary responsibilities within parenting is common in many Asian cultures, including China, Japan, Singapore, Vietnam and Korea. To some cultures, forceful parenting may be seen as abuse, but in other societies such as these, the use of force is looked at as a reflection of parental devotion.
These cultural differences can be studied from many perspectives. Most importantly, overall parental behavior is genuinely different in various countries. Each culture has their own "range of acceptability", and what one may view as offensive, others may seem as tolerable. Behaviors that are normal to some may be viewed as abusive to others, all depending on the societal norms
A social norm is a shared standard of acceptable behavior by a group. Social norms can both be informal understandings that govern the behavior of members of a society, as well as be codified into rules and laws. Social normative influences or s ...
of that particular country. The differences in these cultural beliefs demonstrate the importance of examining all cross-cultural
Cross-cultural may refer to:
*cross-cultural studies, a comparative tendency in various fields of cultural analysis
*cross-cultural communication, a field of study that looks at how people from differing culture, cultural backgrounds communicate
* ...
perspectives when studying the concept of child abuse. Some professionals argue that cultural norms that sanction physical punishment are one of the causes of child abuse, and have undertaken campaigns to redefine such norms.
In April 2015, public broadcasting reported that the rate of child abuse in South Korea had increased to 13% compared with the previous year, and 75% of attackers were the children's own parents.
Possible link to animal abuse
A large national survey by the Norwegian Centre for Violence and Traumatic Stress Studies found a "substantial overlap between companion animal abuse and child abuse" and that cruelty to animals "most frequently co-occurred with psychological abuse and less severe forms of physical child abuse," which "resonates with conceptualizations of domestic abuse as an ongoing pattern of psychological abuse and coercive control."Investigation
Suspicion for physical abuse is recommended when injuries occur in a child who is not yet able to walk independently. Additionally, having multiple injuries that are in different stages of healing and having injuries in unusual location, such as the torso, ears, face, or neck, may prompt evaluation for child abuse. Medical professionals may also become suspicious of child abuse when a caregiver is not able to provide an explanation for an injury that is consistent with the type or severity of the injury. In many jurisdictions, suspected abuse, even if not necessarily proven, requires reporting tochild protection
Child protection (also called child welfare) is the safeguarding of children from violence, exploitation, abuse, abandonment, and neglect. It involves identifying signs of potential harm. This includes responding to allegations or suspicions ...
agencies, such as the Child Protection Services in the United States. Recommendations for healthcare workers, such as primary care providers and nurse
Nursing is a health care profession that "integrates the art and science of caring and focuses on the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and human functioning; prevention of illness and injury; facilitation of healing; and alle ...
s, who are often suited to encounter suspected abuse are advised to firstly determine the child's immediate need for safety. A private environment away from suspected abusers is desired for interviewing and examining. Leading statements that can distort the story are avoided. As disclosing abuse can be distressing and sometimes even shameful, reassuring the child that he or she has done the right thing by telling and that they are not bad or that the abuse was not their fault helps in disclosing more information. Dolls are sometimes used to help explain what happened. In Mexico, psychologists trial using cartoons to speak to children who may be more likely to disclose information than to an adult stranger. For the suspected abusers, it is also recommended to use a nonjudgmental, nonthreatening attitude towards them and to withhold expressing shock, in order to help disclose information.
A key part of child abuse work is assessment. A few methods of assessment include Projective tests, clinical interviews, and behavioral observations.
* Projective tests allow for the child to express themselves through drawings, stories, or even descriptions in order to get help establish an initial understanding of the abuse that took place
* Clinical interviews are comprehensive interviews performed by professionals to analyze the mental state of the one being interviewed
* Behavioral observation gives an insight into things that trigger a child's memory of the abuse through observation of the child's behavior when interacting with other adults or children
A particular challenge arises where child protection professionals are assessing families where neglect is occurring. Neglect is a complex phenomenon without a universally-accepted definition and professionals cite difficulty in knowing which questions to ask to identify neglect. Younger children, children living in poverty, and children with more siblings are at increased risk of neglect.
Prevention
A support-group structure is needed to reinforce parenting skills and closely monitor the child's well-being. Visiting home nurse or social-worker visits are also required to observe and evaluate the progress of the child and the caretaking situation. The support-group structure and visiting home nurse or social-worker visits are not mutually exclusive. Many studies have demonstrated that the two measures must be coupled together for the best possible outcome. Studies show that if health and medical care personnel in a structured way ask parents about important psychosocial risk factors in connection with visiting pediatric primary care and, if necessary, offering the parent help may help prevent child maltreatment. Children's school programs regarding "good touch ... bad touch" can provide children with a forum in which to role-play and learn to avoid potentially harmful scenarios. Pediatricians can help identify children at risk of maltreatment and intervene with the aid of a social worker or provide access to treatment that addresses potential risk factors such as maternal depression. Videoconferencing has also been used to diagnose child abuse in remote emergency departments and clinics. Unintended conception increases the risk of subsequent child abuse, and large family size increases the risk of child neglect. Thus, a comprehensive study for the National Academy of Sciences concluded that affordable contraceptive services should form the basis for child abuse prevention. "The starting point for effective child abuse programming is pregnancy planning," according to an analysis for US Surgeon GeneralC. Everett Koop
Charles Everett Koop (October 14, 1916 – February 25, 2013) was an American pediatric surgeon and public health administrator who served as the 13th surgeon general of the United States under President Ronald Reagan from 1982 to 1989. According ...
.
Findings from research published in 2016 support the importance of family relationships in the trajectory of a child's life: family-targeted interventions are important for improving long-term health, particularly in communities that are socioeconomically disadvantaged.
Resources for child-protection services are sometimes limited. According to Hosin (2007), "a considerable number of traumatized abused children do not gain access to protective child-protection strategies." Briere (1992) argues that only when "lower-level violence" of children ceases to be culturally tolerated will there be changes in the victimization and police protection of children.
United States
Child sexual abuse prevention programs were developed in the United States of America during the 1970s and originally delivered to children. Programmes delivered to parents were developed in the 1980s and took the form of one-off meetings, two to three hours long. In the last 15 years, web-based programmes have been developed. Since 1983, April has been designated Child Abuse Prevention Month in the United States. U.S. PresidentBarack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
continued that tradition by declaring April 2009 Child Abuse Prevention Month. One way the Federal government of the United States
The Federal Government of the United States of America (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the Federation#Federal governments, national government of the United States.
The U.S. federal government is composed of three distinct ...
provides funding for child-abuse prevention is through Community-Based Grants for the Prevention of Child Abuse and Neglect (CBCAP).
An investigation by ''The Boston Globe
''The Boston Globe,'' also known locally as ''the Globe'', is an American daily newspaper founded and based in Boston, Massachusetts. The newspaper has won a total of 27 Pulitzer Prizes. ''The Boston Globe'' is the oldest and largest daily new ...
'' and ProPublica
ProPublica (), legally Pro Publica, Inc., is a nonprofit investigative journalism organization based in New York City. ProPublica's investigations are conducted by its staff of full-time reporters, and the resulting stories are distributed to ne ...
published in 2019 found that the 50 states, the District of Columbia
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and Federal district of the United States, federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from ...
, and Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territo ...
were all out of compliance with the requirements of the Child Abuse Prevention and Treatment Act, and that underfunding of child welfare agencies and substandard procedures in some states caused failures to prevent avoidable child injuries and deaths.
A number of policies and programs have been put in place in the U.S. to try to better understand and to prevent child abuse fatalities, including: safe-haven laws, child fatality review teams, training for investigators, shaken baby syndrome prevention programs, and child abuse death laws which mandate harsher sentencing for taking the life of a child.Douglas, E.M., 2005, ''Child maltreatment fatalities: What do we know, what have we learned, and where do we go from here?,''pp 4.1–4.18, in Child Victimization, edited by K. Kendall-Tackett & S. Giacomoni, published by Civic Research Institute, Kingston, N.J.
Treatments
A number of treatments are available to victims of child abuse. However, children who experience childhood trauma do not heal from abuse easily. Trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy, first developed to treat sexually abused children, is now used for victims of any kind of trauma. It targets trauma-related symptoms in children including PTSD,clinical depression
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Intro ...
and anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response ...
. It also includes a component for non-offending parents. Several studies have found that sexually abused children undergoing TF-CBT improved more than children undergoing certain other therapies. Data on the effects of TF-CBT for children who experienced non-sexual abuse was not available . The purpose of dealing with the thoughts and feelings associated with the trauma is to deal with nightmares, flashbacks and other intrusive experiences that might be spontaneously brought on by any number of discriminative stimuli in the environment or in the individual's brain. This would aid the individual in becoming less fearful of specific stimuli that would arouse debilitating fear, anger, sadness or other negative emotion. In other words, the individual would have some control or mastery over those emotions.
Rational Cognitive Emotive Behavior Therapy is another available treatment and is intended to provide abused children and their adoptive parents with positive behavior change, corrective interpersonal skills, and greater control over themselves and their relationships.
Parent–child interaction therapy was designed to improve the child-parent relationship following the experience of domestic violence. It targets trauma-related symptoms in infants, toddlers, and preschoolers, including PTSD, aggression, defiance, and anxiety. It is supported by two studies of one sample.
School-based programs have also been developed to treat children who are survivors of abuse. This approach teaches children, parents, teachers, and other school staff how to identify the signs of child maltreatment as well as skills that can be helpful in preventing child maltreatment.
Other forms of treatment include group therapy, play therapy, and art therapy. Each of these types of treatment can be used to better assist the client, depending on the form of abuse they have experienced. Play therapy and art therapy are ways to get children more comfortable with therapy by working on something that they enjoy (coloring, drawing, painting, etc.). The design of a child's artwork can be a symbolic representation of what they are feeling, relationships with friends or family, and more. Being able to discuss and analyze a child's artwork can allow a professional to get a better insight of the child.
Interventions targeting the offending parents are rare. Parenting training can prevent child abuse in the short term, and help children with a range of emotional, conduct and behavioral challenges, but there is insufficient evidence about whether it has impact on parents who already abuse their children. Abuse-focused cognitive behavioral therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions, primarily depression, PTSD, and anxiety disorders.
Cognitive behavioral therapy focuses on challenging and chang ...
may target offending parents, but most interventions exclusively target victims and non-offending parents.
Prevalence
Child abuse is complex and difficult to study. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), estimates of the rates of child maltreatment vary widely by country, depending on how child maltreatment is defined, the type of maltreatment studied, the scope and quality of data gathered, and the scope and quality of surveys that ask for self-reports from victims, parents, and caregivers. Despite these limitations, international studies show that a quarter of all adults report experiencing physical abuse as children, and that 1 in 5 women and 1 in 13 men report experiencing childhood sexual abuse. Emotional abuse and neglect are also common childhood experiences. , an estimated 41,000 children under 15 are victims ofhomicide
Homicide is an act in which a person causes the death of another person. A homicide requires only a Volition (psychology), volitional act, or an omission, that causes the death of another, and thus a homicide may result from Accident, accidenta ...
each year. The WHO states that this number underestimates the true extent of child homicide; a significant proportion of child deaths caused by maltreatment are incorrectly attributed to unrelated factors such as falls, burns, and drowning. Also, girls are particularly vulnerable to sexual violence, exploitation and abuse in situations of armed conflict
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or between such organi ...
and refugee
A refugee, according to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), is a person "forced to flee their own country and seek safety in another country. They are unable to return to their own country because of feared persecution as ...
settings, whether by combatants, security forces, community members, aid workers, or others.
United States
The National Research Council wrote in 1993 that "...the available evidence suggests that child abuse and neglect is an important, prevalent problem in the United States ..Child abuse and neglect are particularly important compared with other critical childhood problems because they are often directly associated with adverse physical and mental health consequences in children and families". In 1995, a one-off judicial decision found that parents failing to sufficiently speak the national standard language at home to their children was a form of child abuse by a judge in a child custody matter. In 1998, Douglas Besharov, the first Director of the U.S. Center on Child Abuse and Neglect, stated "the existing laws are often vague and overly broad" and there was a "lack of consensus among professionals and Child Protective Services (CPS), personnel about what the terms abuse and neglect mean". In 2012, Child Protective Services (CPS) agencies estimated that about 9 out of 1000 children in the United States were victims of child maltreatment. Most (78%) were victims of neglect. Physical abuse, sexual abuse, and other types of maltreatment, were less common, making up 18%, 9%, and 11% of cases, respectively ("other types" included emotional abuse, parental substance use, and inadequate supervision). According to data reported by the Children's Bureau of the US Department of Health and Human Services, more than 3.5 million allegations of child abuse were looked into by child protective services who in turn confirmed 674,000 of those cases in 2017. However, CPS reports may underestimate the true scope of child maltreatment. A non-CPS study estimated that one in four children experience some form of maltreatment in their lifetimes, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). In February 2017, the American Public Health Association published a Washington University study estimating 37% of American children experienced a child protective services investigation by age 18 (or 53% if African American). According to David Finkelhor who tracked Child Maltreatment Report (NCANDS) data from 1990 to 2010, sexual abuse had declined 62% from 1992 to 2009 and the long-term trend for physical abuse was also down by 56% since 1992. He stated: "It is unfortunate that information about the trends in child maltreatment are not better publicized and more widely known. The long-term decline in sexual and physical abuse may have important implications for public policy." A child abuse fatality occurs when a child's death is the result of abuse or neglect, or when abuse or neglect are contributing factors to a child's death. In 2008, 1,730 children died in the United States due to factors related to abuse; this is a rate of 2 per 100,000 U.S. children. Family situations which place children at risk include moving, unemployment, and having non-family members living in the household. A number of policies and programs have been put in place in the U.S. to try to better understand and to prevent child abuse fatalities, including: safe-haven laws, child fatality review teams, training for investigators, shaken baby syndrome prevention programs, and child abuse death laws which mandate harsher sentencing for taking the life of a child. In a year-long period between 2019 and 2020, approximately 8.4 out of every 1,000 children were abused or neglected, a number equating to 618,000 children. 77.2% of the perpetrators were parents, the majority of which were one parent acting alone. 37.6% of child abuse was perpetrated by mothers acting alone, and 23.6% was perpetrated by fathers acting alone. 20.7% of child abuse was committed by both parents.Examples
Child labor
Child trafficking is the recruitment, transportation, transfer, harbouring or receipt of children for the purpose of exploitation. Children are trafficked for purposes such as of commercial sexual exploitation, bonded labour, camel jockeying, child domestic labour, drug couriering, child soldiering, illegal adoptions, and begging. It is difficult to obtain reliable estimates concerning the number of children trafficked each year, primarily due to the covert and criminal nature of the practice. TheInternational Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is one of the firs ...
estimates that 1.2 million children are trafficked each year.
Child labor refers to the employment of children in any work that deprives children of their childhood, interferes with their ability to attend regular school, or is mentally, physically, socially or morally dangerous and harmful. The International Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is one of the firs ...
considers such labor to be a form of exploitation and abuse of children. Child labor refers to those occupations which infringe the development of children (due to the nature of the job or lack of appropriate regulation) and does not include age appropriate and properly supervised jobs in which minors may participate. According to ILO, globally, around 215 million children work, many full-time. Many of these children do not go to school, do not receive proper nutrition or care, and have little or no time to play. More than half of them are exposed to the worst forms of child labor, such as child prostitution
Child prostitution is prostitution involving a child, and it is a form of commercial sexual exploitation of children. The term normally refers to prostitution of a minor, or person under the legal age of consent.
In most jurisdictions, child ...
, drug trafficking, armed conflicts and other hazardous environments. There exist several international instruments protecting children from child labor, including the Minimum Age Convention, 1973 and the Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention.
More girls under 16 work as domestic worker
A domestic worker is a person who works within a residence and performs a variety of household services for an individual, from providing cleaning and household maintenance, or cooking, laundry and ironing, or care for children and elderly ...
s than any other category of child labor, often sent to cities by parents living in rural poverty such as in restaveks in Haiti.
Forced adoption
Children in poverty have been removed from their families with their welfare being used an argument to do so. The European Court of Human Rights ruled that Norway, which disproportionately removes children of immigrant background and argues it gives them a better future, was mistaking poverty for neglect and that there are other ways to help destitute children. InSwitzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
, between the 1850s and the mid-20th century, hundreds of thousands of children mostly from poor or single parents were forcefully removed from their parents by the authorities, and sent to work on farms, living with new families. They were known as ''contract children'' or '' Verdingkinder''.
Removing children of ethnic minorities from their families to be adopted by those of the dominant ethnic group has been used as a method of forced assimilation. The Stolen Generations in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
involved Australian Aboriginal
Aboriginal Australians are the various indigenous peoples of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland and many of its islands, excluding the ethnically distinct people of the Torres Strait Islands.
Humans first migrated to Australia (co ...
and Torres Strait Islander
Torres Strait Islanders ( ) are the Indigenous Melanesians, Melanesian people of the Torres Strait Islands, which are part of the state of Queensland, Australia. Ethnically distinct from the Aboriginal Australians, Aboriginal peoples of the res ...
children. In Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, the Canadian Indian residential school system involved First Nations
First nations are indigenous settlers or bands.
First Nations, first nations, or first peoples may also refer to:
Indigenous groups
*List of Indigenous peoples
*First Nations in Canada, Indigenous peoples of Canada who are neither Inuit nor Mé ...
, Métis
The Métis ( , , , ) are a mixed-race Indigenous people whose historical homelands include Canada's three Prairie Provinces extending into parts of Ontario, British Columbia, the Northwest Territories and the northwest United States. They ha ...
and Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwe ...
children, who often suffered severe abuse. As part of the persecution of Uyghurs in China, in 2017 alone at least half a million children were also forcefully separated from their families, and placed in pre-school camps with prison-style surveillance systems and 10,000 volt electric fences.
Child harvesting
It is speculated that, for-profitorphanage
An orphanage is a residential institution, total institution or group home, devoted to the care of orphans and children who, for various reasons, cannot be cared by their biological families. The parents may be deceased, absent, or abusi ...
s are increasing and push for children to join even though demographic data show that even the poorest extended families usually take in children whose parents have died and it would be cheaper to aid close relatives who want to take in the orphans. Experts maintain that separating children from their families often harm children's development. Adoption fees result in such orphanages and similar networks such as "baby factories" in Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
coercing or abducting and raping women to sell their babies for adoption. During the One Child Policy in China, when women were only allowed to have one child, local governments would often allow the woman to give birth and then they would take the baby away. Child traffickers, often paid by the government, would sell the children to orphanages that would arrange international adoptions worth tens of thousands of dollars, turning a profit for the government.
Infanticide
Under natural conditions, mortality rates for girls under five are slightly lower than boys for biological reasons. However, after birth, neglect and diverting resources to male children can lead to some countries having a skewed ratio with more boys than girls, with such practices killing an approximate 230,000 girls under five in India each year. While sex-selective abortion is more common among the higher income population, who can access medical technology, abuse after birth, such as infanticide and abandonment, is more common among the lower income population. Baby farming is practice of accepting custody of a child in exchange for payment. As it became profitable, baby 'farmers' would neglect or murder the babies to keep costs down. Illegitimacy and its attendantsocial stigma
Stigma, originally referring to the visible marking of people considered inferior, has evolved to mean a negative perception or sense of disapproval that a society places on a group or individual based on certain characteristics such as their ...
were usually the impetus for a mother's decision to give her child to a baby farmer. Methods proposed to deal with the issue are baby hatches to drop off unwanted babies and safe-haven laws, which decriminalize abandoning babies unharmed.
Body modification
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO) as "all procedures that involve partial or total removal of the external female genitalia, or other injury to the female genital organs for non-medical reasons." It is practiced mainly in 28 countries in Africa, and in parts of Asia and the Middle East."An update on WHO's work on female genital mutilation (FGM)", World Health Organization, 2011, p. 2: "Most women who have experienced FGM live in one of the 28 countries in Africa and the Middle East – nearly half of them in just two countries: Egypt and Ethiopia. Countries in which FGM has been documented include: Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Cote d'Ivoire, Djibouti, Egypt, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, Sudan, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania and Yemen. The prevalence of FGM ranges from 0.6% to 98% of the female population." * Rahman, Anika and Toubia, Nahid. ''Female Genital Mutilation: A Guide to Laws and Policies Worldwide''. Zed Books, 2000 (hereafter Rahman and Toubia 2000), p. 7: "Currently, FC/FGM is practiced in 28 African countries in the sub-Saharan and Northeastern regions." * Also se
"Eliminating Female Genital Mutilation"
, World Health Organization, 2008, p. 4: "Types I, II and III female genital mutilation have been documented in 28 countries in Africa and in a few countries in Asia and the Middle East." FGM is mostly found in a geographical area ranging across Africa, from east to west – from Somalia to Senegal, and from north to south – from Egypt to Tanzania. FGM is most often carried out on young girls aged between infancy and 15 years. FGM is classified into four types, of which type 3 – infibulation – is the most extreme form. The consequences of FGM include physical, emotional and sexual problems, and include serious risks during
childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour, parturition and delivery, is the completion of pregnancy, where one or more Fetus, fetuses exits the Womb, internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section and becomes a newborn to ...
. The countries which choose to ratify the Istanbul Convention
The Council of Europe Convention on Preventing and Combating Violence Against Women and Domestic Violence, better known as the Istanbul Convention, is a International human rights instruments, human rights treaty of the Council of Europe oppos ...
, the first legally binding instrument in Europe in the field of violence against women and domestic violence, are bound by its provisions to ensure that FGM is criminalized. Labia stretching is the act of lengthening the labia minora and may be initiated in girls from ages 8 to 14 years.
The practice of using hot stones or other implements to flatten the breast tissue of pubescent girls is widespread in Cameroon and exists elsewhere in West Africa as well. It is believed to have come with that diaspora to Britain, where the government declared it a form of child abuse and said that it could be prosecuted under existing assault laws.
Sexual rites of passage
A tradition often performed in some regions in Africa involves a man initiating a girl into womanhood by having sex with her, usually after her first period, in a practice known as "sexual cleansing". The rite can last for three days and there is an increased risk of contractingsexually transmitted infection
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, e ...
s as the ritual requires condoms not be worn.
Violence against girl students
 In some parts of the world, girls are strongly discouraged from attending school. They are sometimes attacked by members of the community if they do so. In parts of South Asia, girls schools are set on fire by vigilante groups. Such attacks are common in
In some parts of the world, girls are strongly discouraged from attending school. They are sometimes attacked by members of the community if they do so. In parts of South Asia, girls schools are set on fire by vigilante groups. Such attacks are common in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
and Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
. Notable examples include the kidnapping of hundreds of female students in Chibok in 2014 and Dapchi in 2018.
Child marriage
A child marriage is a marriage in which one or both participants are minors, often before the age ofpuberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
. Child marriages are common in many parts of the world, especially in parts of Asia and Africa. The United Nations considers those below the age of 18 years to be incapable of giving valid consent to marriage and therefore regards such marriages as a form of forced marriage
Forced marriage is a marriage in which one or more of the parties is married without their consent or against their will. A marriage can also become a forced marriage even if both parties enter with full consent if one or both are later force ...
; and that marriages under the age of majority have significant potential to constitute a form of child abuse. In many countries, such practices are lawful or – even where laws prohibit child marriage – often unenforced. India has more child brides than any other nation, with 40% of the world total. The countries with the highest rates of child marriage are: Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
(75%), Central African Republic
The Central African Republic (CAR) is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Chad to Central African Republic–Chad border, the north, Sudan to Central African Republic–Sudan border, the northeast, South Sudan to Central ...
and Chad
Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North Africa, North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to Chad–Libya border, the north, Sudan to Chad–Sudan border, the east, the Central Afric ...
(68%), and Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
(66%).
Bride kidnapping, also known as marriage by abduction or marriage by capture, has been practiced around the world and throughout history, and sometimes involves minors. It is still practiced in parts of Central Asia, the Caucasus region, and some African countries. In Ethiopia, marriage by abduction is widespread, and many young girls are kidnapped this way. In most countries, bride kidnapping is considered a criminal offense rather than a valid form of marriage. In many cases, the groom also rape
Rape is a type of sexual assault involving sexual intercourse, or other forms of sexual penetration, carried out against a person without consent. The act may be carried out by physical force, coercion, abuse of authority, or against a person ...
s his kidnapped bride, in order to prevent her from returning to her family due to shame.
Money marriage refers to a marriage where a girl, usually, is married off to a man to settle debts owed by her parents. The female is referred to as a "money wife".
Sacred prostitution
Sacred prostitution, temple prostitution, cult prostitution, and religious prostitution are purported Ritual, rites consisting of Prostitution, paid intercourse performed in the context of religious worship, possibly as a form of fertility rite o ...
often involves girls being pledged to priests or those of higher castes, such as fetish slaves in West Africa.
Violence against children with superstitious accusations
Customary beliefs in witchcraft are common in many parts of the world, even among the educated. Anthropologists have argued that those with disabilities are often viewed as bad omens as raising a child with a disability in such communities are an insurmountable hurdle. For example, in southern Ethiopia, children with physical abnormalities are considered to be ritually impure or mingi, the latter are believed to exert an evil influence upon others, so disabled infants have traditionally been disposed of without a proper burial. A 2010UNICEF
UNICEF ( ), originally the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, officially United Nations Children's Fund since 1953, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing Humanitarianism, humanitarian and Development a ...
report notes that accusations against children are a recent phenomenon with women and the elderly usually being accused 10–20 years ago. Greater urbanization and the growing economic burden of raising children is attributed as a factor."Rise in African children accused of witchcraft".BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broad ...
, 17 July 2010. , between 25,000 and 50,000 children in Kinshasa
Kinshasa (; ; ), formerly named Léopoldville from 1881–1966 (), is the Capital city, capital and Cities of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, largest city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Kinshasa is one of the world's fastest-grow ...
, Democratic Republic of the Congo, had been accused of witchcraft
Witchcraft is the use of Magic (supernatural), magic by a person called a witch. Traditionally, "witchcraft" means the use of magic to inflict supernatural harm or misfortune on others, and this remains the most common and widespread meanin ...
and abandoned. In Malawi
Malawi, officially the Republic of Malawi, is a landlocked country in Southeastern Africa. It is bordered by Zambia to the west, Tanzania to the north and northeast, and Mozambique to the east, south, and southwest. Malawi spans over and ...
it is common practice to accuse children of witchcraft and many children have been abandoned, abused and even killed as a result. In the Nigerian, Akwa Ibom State
Akwa Ibom is a States of Nigeria, state in the South South, South-South geopolitical zone of Nigeria. It borders Cross River State to the east, Rivers State and Abia State to the west and north-west, and the Atlantic Ocean to the south. The state ...
and Cross River State about 15,000 children were branded as witches. This practice is also found in communities in the Amazon. Children who are specifically at risk include orphans, street-children, albinos, disabled children, children who are unusually gifted, children who were born prematurely or in unusual positions, twins, children of single mothers and children who express gender identity issues and can involve children as young as eight. Consequently, those accused of being a witch are ostracized and subjected to punishment, torture and even murdered, often by being buried alive or left to starve. Reports by UNICEF, UNHCR
The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) is a United Nations agency mandated to aid and Humanitarian protection, protect refugees, Internally displaced person, forcibly displaced communities, and Statelessness, s ...
, Save The Children
The Save the Children Fund, commonly known as Save the Children, is an international non-governmental organization. It was founded in the UK in 1919; its goal is to improve the lives of children worldwide.
The organization raises money to imp ...
and Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. Headquartered in New York City, the group investigates and reports on issues including War crime, war crimes, crim ...
have highlighted the violence and abuse towards children accused of witchcraft in Africa.
Ethics
One of the most challenging ethical dilemmas arising from child abuse relates to the parental rights of abusive parents or caretakers with regard to their children, particularly in medical settings. In the United States, the 2008 New Hampshire case of Andrew Bedner drew attention to this legal and moral conundrum. Bedner, accused of severely injuring his infant daughter, sued for the right to determine whether or not she remain on life support; keeping her alive, which would have prevented a murder charge, created a motive for Bedner to act that conflicted with the apparent interests of his child. Bioethicists Jacob M. Appel and Thaddeus Mason Pope recently argued, in separate articles, that such cases justify the replacement of the accused parent with an alternative decision-maker. Child abuse also poses ethical concerns related toconfidentiality
Confidentiality involves a set of rules or a promise sometimes executed through confidentiality agreements that limits the access to or places restrictions on the distribution of certain types of information.
Legal confidentiality
By law, la ...
, as victims may be physically or psychologically unable to report abuse to authorities. Accordingly, many jurisdictions and professional bodies have made exceptions to standard requirements for confidentiality and legal privileges in instances of child abuse. Medical professionals, including doctors, therapists, and other mental health workers typically owe a duty of confidentiality to their patients and clients, either by law or the standards of professional ethics
Professional ethics encompass the personal and corporate standards of behavior expected of professionals.
The word professionalism originally applied to vows of a religious order. By no later than the year 1675, the term had seen secular appli ...
, and cannot disclose personal information without the consent
Consent occurs when one person voluntarily agrees to the proposal or desires of another. It is a term of common speech, with specific definitions used in such fields as the law, medicine, research, and sexual consent. Consent as understood i ...
of the individual concerned. This duty conflicts with an ethical obligation to protect children from preventable harm. Accordingly, confidentiality is often waived when these professionals have a good faith suspicion that child abuse or neglect has occurred or is likely to occur and make a report to local child protection
Child protection (also called child welfare) is the safeguarding of children from violence, exploitation, abuse, abandonment, and neglect. It involves identifying signs of potential harm. This includes responding to allegations or suspicions ...
authorities. This exception allows professionals to breach confidentiality and make a report even when children or their parents or guardians have specifically instructed to the contrary. Child abuse is also a common exception to physician–patient privilege: a medical professional may be called upon to testify in court as to otherwise privileged evidence about suspected child abuse despite the wishes of children or their families. Some child abuse policies in Western countries have been criticized both by some conservatives, who claim such policies unduly interfere in the privacy of the family, and by some feminists of the left wing, who claim such policies disproportionally target and punish disadvantaged women who are often themselves in vulnerable positions. There has also been concern that ethnic minority families are disproportionally targeted.
Legislation
Canada
Laws and legislation against child abuse are enacted on the provincial and Federal Territories level. Investigations into child abuse are handled by Provincial and Territorial Authorities through government social service departments and enforcement is through local police and courts.Germany
In Germany, the abuse of vulnerable persons (including children) is punishable according to the German Criminal code § 225 with a from 6 months to 10 years, in aggravated cases at least 1 year (to 15 years pursuant to § 38). If the case is only an attempt, the penalty can be lower (§ 23). However, crimes against children must be prosecuted within 10 years (in aggravated cases 20 years) of the victims reaching 30 years of age (§ 78b and § 78). As of 2020, Germany and the Netherlands are 2 out of all 27 EU countries that do not have any reporting obligations for civilians or professionals. There is no mandatory reporting law, which would grant reporters of child abuse anonymity and immunity.United States
In the 1960s, mandatory reporting in the United States was introduced and had been adopted in some form by all 50 states by 1970. In 1974, the Child Abuse Prevention and Treatment Act (CAPTA) was introduced and began an upswing in reported child sexual abuse cases which lasted until the 1990s. The Child Abuse Victims Rights Act of 1986 gave victims of child abuse the ability to file lawsuits against abuse perpetrators and their employers after the statute of limitations had expired. The Victims of Child Abuse Act of 1990 further gave victims of abuse capacity to press charges by permitting the court to assign lawyers to advise, act in the best interest of, and elevate the voices of child victims of abuse. The Adoption and Safe Families Act (1997) followed, shifting emphasis away from court-sanctioned reunification of families to giving parents or guardians time-bound opportunities for rehabilitation prior to making long term plans for children. Child Abuse Reform and Enforcement Act was enacted in 2000 to further reduce the incidence of child abuse and neglect. Shifting legislative focus more heavily towards sexual abuse and exploitation of children, Adam Walsh Child Protection and Safety Act was passed in 2006 to increase penalties and registration for child sexual abuse, exploitation, and transportation crimes. top Exploitation Through Trafficking Act passed in 2013 aimed at preventing the prosecution of sexually exploited youth being sex trafficked, redirecting abused and exploited youth from the criminal justice system to the child welfare system. This and other laws redirecting victims of child sex trafficking to the child welfare system are known as "Safe Harbor" laws. , 18 states had legislation requiring that mandated reporters report based on suspicion of child abuse of neglect.Advocacy organizations
United States
There are organizations at national, state, and county levels in the United States that provide community leadership in preventing child abuse and neglect. Mary Ellen Wilson, also called Mary Ellen McCormack, was an American whose case of child abuse, the first documented case of child abuse in the United States, led to the creation of the New York Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Children, which was incorporated in 1875. It was the world's first child protective agency. Prevent Child Abuse America, founded in 1976, operates in 46 states to provide child abuse and neglect protection. Founded in 1985, the National Children's Advocacy Center, along with National Children's Alliance, coordinates efforts and sets standards and policy for child advocacy centers across the US and abroad. The Children's Trust Fund Alliance, established in 1989, provides funding support to state level child abuse organisations. Many investigations into child abuse in the US are handled on the local level by 924 child advocacy centers, some of which are distributed among 34 other countries. Other organizations focus on specific prevention strategies. The National Center on Shaken Baby Syndrome focuses its efforts on the specific issue of preventing child abuse that is manifested as shaken baby syndrome. NICHD, also known as the National Institute of Child Health & Human Development is an organization that helps victims of child abuse through one of its branches. Through the Child Development and Behavior (CDB) Branch, NICHD raises awareness efforts by supporting research projects to better understand the short- and long-term impacts of child abuse and neglect. They provide programs and observe National Child Abuse Prevention Month every April since 1984. TheUnited States Children's Bureau
The United States Children's Bureau is a federal agency founded in 1912, organized under the United States Department of Health and Human Services' Administration for Children and Families. Today, the bureau's operations involve improving child a ...
, a federal agency tasked to improve child abuse protection leads activities for the Month, including the release of updated statistics about child abuse and neglect, candlelight vigils, and fundraisers to support prevention activities and treatment for victims. The Bureau also sponsors a "Blue Ribbon Campaign", in which people wear blue ribbons in memory of children who have died from abuse, or in honor of individuals and organizations that have taken important steps to prevent child abuse and neglect.
Canada
Charitable organizations exist in each province to assist children and families with abuse. Organizations such as the Canadian Red Cross, Kids Help Phone, and Guardians of the Children Canada, are able to direct people to locally available resources.See also
*Abuse
Abuse is the act of improper usage or treatment of a person or thing, often to unfairly or improperly gain benefit. Abuse can come in many forms, such as: physical or verbal maltreatment, injury, assault, violation, rape, unjust practices, ...
* Abusive power and control
* Adverse Childhood Experiences
* AMBER Alert
* Bullying
Bullying is the use of force, coercion, Suffering, hurtful teasing, comments, or threats, in order to abuse, aggression, aggressively wikt:domination, dominate, or intimidate one or more others. The behavior is often repeated and habitual. On ...
* Child abuse in association football
* Child and family services
* Child sexual abuse
Child sexual abuse (CSA), also called child molestation, is a form of child abuse in which an adult or older adolescent uses a child for sexual stimulation. Forms of child sexual abuse include engaging in Human sexual activity, sexual activit ...
* Child murder
Pedicide, also known as child murder, child manslaughter or child homicide, is the homicide of an individual who is a Age of majority, minor. In many legal jurisdictions, it is considered an Aggravation (law), aggravated form of homicide. The a ...
* Child protection
Child protection (also called child welfare) is the safeguarding of children from violence, exploitation, abuse, abandonment, and neglect. It involves identifying signs of potential harm. This includes responding to allegations or suspicions ...
* Cinderella effect
* Complex post-traumatic stress disorder
* Corporal punishment in the home
* Dysfunctional family
In psychology, abnormality (also dysfunctional behavior, maladaptive behavior, or deviant behavior) is a behavioral characteristic assigned to those with conditions that are regarded as dysfunctional. Behavior is considered to be abnormal when i ...
* Emotional dysregulation
* Foster Care
Foster care is a system in which a minor has been placed into a ward, group home ( residential child care community or treatment centre), or private home of a state- certified caregiver, referred to as a "foster parent", or with a family mem ...
* Influence of childhood trauma in psychopathy
* Isolation to facilitate abuse
* Karly's Law
* List of global issues
* National Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Children
The National Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Children (NSPCC) is a British child protection charity founded as the Liverpool Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Children (LSPCC) by Thomas Agnew on 19 April 1883. The NSPCC lobbies t ...
* Narcissistic parent
* Outcry witness
* Parental bullying of children
* Parental narcissistic abuse
* Residential Child Care Community
Residential child care communities or children's homes are a type of residential care, which refers to long-term care given to children who cannot stay in their birth family home. There are two different approaches towards residential care: The fa ...
* School corporal punishment
Corporal punishment in schools is the deliberate infliction of physical pain as a response to undesired behavior by students. The term corporal punishment derives from , the Latin word for the body. In schools it may involve striking the student o ...
* Songs about child abuse
References
Further reading
* * * * * * Miller, Alice (1990). ''"Thou Shalt Not Be Aware": Society's Betrayal of the Child'', in series, ''Meridian Book '. Trans. by Heildegarde and Hunter Hannum. New York: Penguin. x, 329 p. Trans. from the German, titled . pbk * * * Hanvey, I., Malovic, A. and Ntontis, E. 2022Glass children: The lived experiences of siblings of people with a disability or chronic illness.
Journal of Community & Applied Social Psychology. 32 (5), pp. 936–948.
External links
WHO fact sheet on child maltreatment
World Report on Violence Against Children
, Secretary-General of the United Nations
Prevent Child Abuse America
"Cold-nosed Comfort"
(using a service dog to aid child abuse victims), ''Maryland Lawyer'' {{Authority control Paraphilias
Abuse
Abuse is the act of improper usage or treatment of a person or thing, often to unfairly or improperly gain benefit. Abuse can come in many forms, such as: physical or verbal maltreatment, injury, assault, violation, rape, unjust practices, ...
Family therapy
Child welfare
Crimes
Adverse childhood experiences