Chihuahua (state) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Chihuahua, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chihuahua, is one of the 31 states which, along with
 The earliest evidence of human inhabitants of modern-day Chihuahua was discovered in the area of Samalayuca and Rancho Colorado. Clovis points have been found in northeastern Chihuahua that have been dated from 12,000 BC to 7000 BC. It is thought that these inhabitants were hunter gatherers.
Inhabitants of the state later developed farming with the domestication of corn. An archeological site in northern Chihuahua known as ''Cerro Juanaqueña'' revealed squash cultivation, irrigation techniques, and
The earliest evidence of human inhabitants of modern-day Chihuahua was discovered in the area of Samalayuca and Rancho Colorado. Clovis points have been found in northeastern Chihuahua that have been dated from 12,000 BC to 7000 BC. It is thought that these inhabitants were hunter gatherers.
Inhabitants of the state later developed farming with the domestication of corn. An archeological site in northern Chihuahua known as ''Cerro Juanaqueña'' revealed squash cultivation, irrigation techniques, and  Between AD 300 and 1300 in the northern part of the state along the wide, fertile valley on the San Miguel River the
Between AD 300 and 1300 in the northern part of the state along the wide, fertile valley on the San Miguel River the
 In 1562,
In 1562,  In 1631, Juan Rangel de Biezma discovered a rich vein of silver and subsequently established San José del Parral near the site. Parral remained an important economic and cultural center for the next 300 years. On December 8, 1659, Fray García de San Francisco founded the mission of Nuestra Señora de Guadalupe de Mansos del Paso del Río del Norte and founded the town El Paso del Norte (present day
In 1631, Juan Rangel de Biezma discovered a rich vein of silver and subsequently established San José del Parral near the site. Parral remained an important economic and cultural center for the next 300 years. On December 8, 1659, Fray García de San Francisco founded the mission of Nuestra Señora de Guadalupe de Mansos del Paso del Río del Norte and founded the town El Paso del Norte (present day
 During the Napoleonic Occupation of Spain,
During the Napoleonic Occupation of Spain,  Hidalgo's death resulted in a political vacuum on the insurgent side until 1812. The royalist military commander, General Felix Calleja, continued to pursue rebel troops. Insurgent fighting evolved into guerrilla warfare, and eventually the next major insurgent leader, José María Morelos y Pavón, who had led rebel movements with Hidalgo, became head of the insurgents.
Hidalgo is hailed as the ''Father of the Nation'' even though it was
Hidalgo's death resulted in a political vacuum on the insurgent side until 1812. The royalist military commander, General Felix Calleja, continued to pursue rebel troops. Insurgent fighting evolved into guerrilla warfare, and eventually the next major insurgent leader, José María Morelos y Pavón, who had led rebel movements with Hidalgo, became head of the insurgents.
Hidalgo is hailed as the ''Father of the Nation'' even though it was
 Because of the general instability of the federal government during 1828, the installation of the new legislature did not take place until the middle of the following year. It was quickly dissolved by Governor Santiago de Baca Ortiz, who replaced it with a more pronounced Yorkino type. When Guerrero's liberal administration was overthrown in December, Gaspar de Ochoa aligned with
Because of the general instability of the federal government during 1828, the installation of the new legislature did not take place until the middle of the following year. It was quickly dissolved by Governor Santiago de Baca Ortiz, who replaced it with a more pronounced Yorkino type. When Guerrero's liberal administration was overthrown in December, Gaspar de Ochoa aligned with
 Bishop José Antonio Laureano de Zubiría of Durango was banished for resisting the law relating to priests and other encroachments on the church; another joined the western states in a short lived coalition for sustaining the federal system. Chihuahua adopted the
Bishop José Antonio Laureano de Zubiría of Durango was banished for resisting the law relating to priests and other encroachments on the church; another joined the western states in a short lived coalition for sustaining the federal system. Chihuahua adopted the
 The state seemed at relative calm compared to the rest of the country due to its close ties to the United States until 1841. In 1843 the possibility of war was anticipated by the state government and it began to reinforce the defense lines along the political boundary with Texas. Supplies of weapons were sent to fully equip the military and steps were taken to improve efficiency at the presidios. Later, the Regimen for the Defenders of the Border were organized by the state which were made up of: light cavalry, four squads of two brigades, and a small force of 14 men and 42 officials at the price of 160,603 pesos per year. During the beginning of the 1840s, private citizens took it upon themselves to stop the commercial caravans of supplies from the United States, but being so far away from the large suppliers in central Mexico the caravan was allowed to continue in March 1844. Continuing to anticipate a war, the state legislature on July 11, 1846 by decree enlisted 6,000 men to serve along the border; during that time Ángel Trías quickly rose to power by portraying zealous anti-American rhetoric. Trías took the opportunity to dedicate important state resources to gain economic concessions from the people and loans from many municipalities in preparation to defend the state; he used all the money he received to equip and organize a large volunteer militia. Ángel Trías took measures for state self-dependence in regards to state militia due to the diminishing financial support from the federal government.
The United States Congress declared war on Mexico on May 13, 1846 after only having a few hours to debate. Although President José Mariano Paredes' issuance of a manifesto on May 23 is sometimes considered the declaration of war, Mexico officially declared war by Congress on July 7. After the American invasion of New Mexico, Chihuahua sent 12,000 men led by Colonel Vidal to the border to stop the American military advance into the state. The Mexican forces being impatient to confront the American forces passed beyond El Paso del Norte about north along the Rio Grande. The first battle that Chihuahua fought was the battle of El Bracito; the Mexican forces consisting of 500 cavalry and 70 infantry confronted a force of 1,100–1,200 Americans on December 25, 1846. The battle ended badly by the Mexican forces that were then forced to retreat back into the state of Chihuahua. By December 27, 1846, the American forces occupied El Paso del Norte. General Doniphan maintained camp in El Paso del Norte awaiting supplies and artillery which he received in February 1847.
On February 8, 1847, Doniphan continued his march with 924 men mostly from Missouri; he accompanied a train of 315 wagons of a large commercial caravan heading to the state capital. Meanwhile, the Mexican forces in the state had time to prepare a defense against the Americans. About north of the capital where two mountain ranges join from east to west is the only pass into the capital; known as Sacramento Pass, this point is now part of present-day
The state seemed at relative calm compared to the rest of the country due to its close ties to the United States until 1841. In 1843 the possibility of war was anticipated by the state government and it began to reinforce the defense lines along the political boundary with Texas. Supplies of weapons were sent to fully equip the military and steps were taken to improve efficiency at the presidios. Later, the Regimen for the Defenders of the Border were organized by the state which were made up of: light cavalry, four squads of two brigades, and a small force of 14 men and 42 officials at the price of 160,603 pesos per year. During the beginning of the 1840s, private citizens took it upon themselves to stop the commercial caravans of supplies from the United States, but being so far away from the large suppliers in central Mexico the caravan was allowed to continue in March 1844. Continuing to anticipate a war, the state legislature on July 11, 1846 by decree enlisted 6,000 men to serve along the border; during that time Ángel Trías quickly rose to power by portraying zealous anti-American rhetoric. Trías took the opportunity to dedicate important state resources to gain economic concessions from the people and loans from many municipalities in preparation to defend the state; he used all the money he received to equip and organize a large volunteer militia. Ángel Trías took measures for state self-dependence in regards to state militia due to the diminishing financial support from the federal government.
The United States Congress declared war on Mexico on May 13, 1846 after only having a few hours to debate. Although President José Mariano Paredes' issuance of a manifesto on May 23 is sometimes considered the declaration of war, Mexico officially declared war by Congress on July 7. After the American invasion of New Mexico, Chihuahua sent 12,000 men led by Colonel Vidal to the border to stop the American military advance into the state. The Mexican forces being impatient to confront the American forces passed beyond El Paso del Norte about north along the Rio Grande. The first battle that Chihuahua fought was the battle of El Bracito; the Mexican forces consisting of 500 cavalry and 70 infantry confronted a force of 1,100–1,200 Americans on December 25, 1846. The battle ended badly by the Mexican forces that were then forced to retreat back into the state of Chihuahua. By December 27, 1846, the American forces occupied El Paso del Norte. General Doniphan maintained camp in El Paso del Norte awaiting supplies and artillery which he received in February 1847.
On February 8, 1847, Doniphan continued his march with 924 men mostly from Missouri; he accompanied a train of 315 wagons of a large commercial caravan heading to the state capital. Meanwhile, the Mexican forces in the state had time to prepare a defense against the Americans. About north of the capital where two mountain ranges join from east to west is the only pass into the capital; known as Sacramento Pass, this point is now part of present-day  The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, signed on February 2, 1848, by American diplomat Nicholas Trist and Mexican plenipotentiary representatives Luis G. Cuevas, Bernardo Couto, and Miguel Atristain, ended the war, gave the U.S. undisputed control of Texas, and established the U.S.–Mexican border of the Rio Grande. As news of peace negotiations reached the state, new call to arms began to flare among the people of the state. But as the Mexican officials in Chihuahua heard that General Price was heading back to Mexico with a large force comprising several companies of infantry and three companies of cavalry and one division of light artillery from Santa Fe on February 8, 1848, Ángel Trías sent a message to Sacramento Pass to ask for succession of the area as they understood the war had concluded. General Price, misunderstanding this as a deception by the Mexican forces, continued to advance towards the state capital. On March 16, 1848 Price began negotiations with Ángel Trías, but the Mexican leader responded with an ultimatum to General Price. The American forces engaged with the Mexican forces near Santa Cruz de los Rosales on March 16, 1848. The Battle of Santa Cruz de los Rosales was the last battle of the Mexican–American War and it occurred after the peace treaty was signed. The American forces maintained control over the state capital for three months after the confirmation of the peace treaty. The American presence served to delay the possible succession of the state which had been discussed at the end of 1847, and the state remained under United States occupation until May 22, 1848.
During the American occupation of the state, the number of Indian attacks was drastically reduced, but in 1848 the attacks resumed to such a degree that the Mexican officials had no choice but to resume military projects to protect Mexican settlements in the state. Through the next three decades the state faced constant attacks from the indigenous on Mexican settlements. After the occupation the people of the state were worried about the potential attack from the hostile indigenous tribes north of the Rio Grande; as a result a decree on July 19, 1848, the state established 18 military colonies along the Rio Grande. The new military colonies were to replace the presidios as population centers to prevent future invasions by indigenous tribes; these policies remained prominent in the state until 1883. Eventually the state replaced the old state security with a state policy to form militias organized with every Mexican in the state capable to serve between the ages of 18 and 55 to fulfill the mandate of having six men defending for every 1000 residents.
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, signed on February 2, 1848, by American diplomat Nicholas Trist and Mexican plenipotentiary representatives Luis G. Cuevas, Bernardo Couto, and Miguel Atristain, ended the war, gave the U.S. undisputed control of Texas, and established the U.S.–Mexican border of the Rio Grande. As news of peace negotiations reached the state, new call to arms began to flare among the people of the state. But as the Mexican officials in Chihuahua heard that General Price was heading back to Mexico with a large force comprising several companies of infantry and three companies of cavalry and one division of light artillery from Santa Fe on February 8, 1848, Ángel Trías sent a message to Sacramento Pass to ask for succession of the area as they understood the war had concluded. General Price, misunderstanding this as a deception by the Mexican forces, continued to advance towards the state capital. On March 16, 1848 Price began negotiations with Ángel Trías, but the Mexican leader responded with an ultimatum to General Price. The American forces engaged with the Mexican forces near Santa Cruz de los Rosales on March 16, 1848. The Battle of Santa Cruz de los Rosales was the last battle of the Mexican–American War and it occurred after the peace treaty was signed. The American forces maintained control over the state capital for three months after the confirmation of the peace treaty. The American presence served to delay the possible succession of the state which had been discussed at the end of 1847, and the state remained under United States occupation until May 22, 1848.
During the American occupation of the state, the number of Indian attacks was drastically reduced, but in 1848 the attacks resumed to such a degree that the Mexican officials had no choice but to resume military projects to protect Mexican settlements in the state. Through the next three decades the state faced constant attacks from the indigenous on Mexican settlements. After the occupation the people of the state were worried about the potential attack from the hostile indigenous tribes north of the Rio Grande; as a result a decree on July 19, 1848, the state established 18 military colonies along the Rio Grande. The new military colonies were to replace the presidios as population centers to prevent future invasions by indigenous tribes; these policies remained prominent in the state until 1883. Eventually the state replaced the old state security with a state policy to form militias organized with every Mexican in the state capable to serve between the ages of 18 and 55 to fulfill the mandate of having six men defending for every 1000 residents.

 The state united behind the
The state united behind the  The French forces tried to subdue and capture the liberal government based in
The French forces tried to subdue and capture the liberal government based in  President Juárez once again based his government in the state of Chihuahua and it served as the center for the resistance against the French invasion throughout Mexico. On March 25, 1866, a battle ensued in the Plaza de Armas in the center of Chihuahua City between the French imperial forces that were guarding the plaza and the Republican forces led by General Terrazas. Being completely caught off guard, the French imperial forces sought refuge by bunkering themselves in the Cathedral of the Holy Cross, Our Lady of Regla, and St Francis of Assisi and made it almost impossible to penetrate their defenses. General Terrazas then decided to fire a heavy artillery barrage with 8 kg cannonballs. The first cannon fired hit a bell in the tower of the church, instantly breaking it in half; soon after, 200 men of the imperial army forces surrendered. The republican forces had recovered control over the state capital. The bell in the church was declared a historical monument and can be seen today in the Cathedral. By April 1866, the state government had established a vital trading route from Chihuahua City to San Antonio, Texas; the government began to replenish their supplies and reinforce their fight against the Imperial forces.
General Aguirre moved to the deserts of the southeastern portion of the state and defeated the French forces in Parral, led by Colonel Cottret. By the middle of 1866, the state of Chihuahua was declared free of enemy control; Parral was the last French stronghold within the state. On June 17, 1866, President Juárez arrived in Chihuahua City and remained in the capital until December 10, 1866. During his two years in the state of Chihuahua, President Juárez passed ordinances regarding the rights of adjudication of property and nationalized the property of the clergy. The distance of the French forces and their allies allowed the Ministry of War, led by General Negrete, to reorganize the state's national guard into the Patriotic Battalion of Chihuahua, which was deployed to fight in the battle of
President Juárez once again based his government in the state of Chihuahua and it served as the center for the resistance against the French invasion throughout Mexico. On March 25, 1866, a battle ensued in the Plaza de Armas in the center of Chihuahua City between the French imperial forces that were guarding the plaza and the Republican forces led by General Terrazas. Being completely caught off guard, the French imperial forces sought refuge by bunkering themselves in the Cathedral of the Holy Cross, Our Lady of Regla, and St Francis of Assisi and made it almost impossible to penetrate their defenses. General Terrazas then decided to fire a heavy artillery barrage with 8 kg cannonballs. The first cannon fired hit a bell in the tower of the church, instantly breaking it in half; soon after, 200 men of the imperial army forces surrendered. The republican forces had recovered control over the state capital. The bell in the church was declared a historical monument and can be seen today in the Cathedral. By April 1866, the state government had established a vital trading route from Chihuahua City to San Antonio, Texas; the government began to replenish their supplies and reinforce their fight against the Imperial forces.
General Aguirre moved to the deserts of the southeastern portion of the state and defeated the French forces in Parral, led by Colonel Cottret. By the middle of 1866, the state of Chihuahua was declared free of enemy control; Parral was the last French stronghold within the state. On June 17, 1866, President Juárez arrived in Chihuahua City and remained in the capital until December 10, 1866. During his two years in the state of Chihuahua, President Juárez passed ordinances regarding the rights of adjudication of property and nationalized the property of the clergy. The distance of the French forces and their allies allowed the Ministry of War, led by General Negrete, to reorganize the state's national guard into the Patriotic Battalion of Chihuahua, which was deployed to fight in the battle of
 President Benito Juárez was re-elected in the general election of 1867 in which he received strong liberal support, especially in Chihuahua. Luis Terrazas was confirmed by the people of Chihuahua to be governor of the state. But soon after the election, President Juárez had another crisis on his hands; the Juárez administration was suspected to be involved in the assassination of the military chief José María Patoni executed by General Canto in August 1868. General Canto turned himself over to Donato Guerra. Canto was sentenced to death, but later his sentence changed to 10 years imprisonment. The sense of injustice gave rise to a new rebellion in 1869 that threatened the federal government. In response, the Juárez administration took drastic measures by temporarily suspending constitutional rights, but the governor of Chihuahua did not support this action. Hostilities continued to increase especially after the election of 1871 which was perceived to be fraudulent. A new popular leader arose among the rebels, Porfirio Díaz. The federal government was successful in quelling rebellions in Durango and Chihuahua. On July 18, 1872, President Juárez died from a heart attack; soon after, many of his supporters ceased the fighting. Peace returned to Chihuahua and the new government was led by Governor Antonio Ochoa (formerly a co-owner of the Batopilas silver mines) in 1873 after Luis Terrazas finished his term in 1872.
But the peace in the state did not last long, the elections of 1875 caused new hostilities. Ángel Trías led a new movement against the government in June 1875 and maintained control over the government until September 18, 1875 when Donato Guerra the orchestrator of the Revolution of the North was captured. Donato Guerra was assassinated in a suburb of Chihuahua City where he was incarcerated for conspiring with Ángel Trías. During October 1875 several locations were controlled by rebel forces, but the government finally regained control on November 25, 1875.
President Benito Juárez was re-elected in the general election of 1867 in which he received strong liberal support, especially in Chihuahua. Luis Terrazas was confirmed by the people of Chihuahua to be governor of the state. But soon after the election, President Juárez had another crisis on his hands; the Juárez administration was suspected to be involved in the assassination of the military chief José María Patoni executed by General Canto in August 1868. General Canto turned himself over to Donato Guerra. Canto was sentenced to death, but later his sentence changed to 10 years imprisonment. The sense of injustice gave rise to a new rebellion in 1869 that threatened the federal government. In response, the Juárez administration took drastic measures by temporarily suspending constitutional rights, but the governor of Chihuahua did not support this action. Hostilities continued to increase especially after the election of 1871 which was perceived to be fraudulent. A new popular leader arose among the rebels, Porfirio Díaz. The federal government was successful in quelling rebellions in Durango and Chihuahua. On July 18, 1872, President Juárez died from a heart attack; soon after, many of his supporters ceased the fighting. Peace returned to Chihuahua and the new government was led by Governor Antonio Ochoa (formerly a co-owner of the Batopilas silver mines) in 1873 after Luis Terrazas finished his term in 1872.
But the peace in the state did not last long, the elections of 1875 caused new hostilities. Ángel Trías led a new movement against the government in June 1875 and maintained control over the government until September 18, 1875 when Donato Guerra the orchestrator of the Revolution of the North was captured. Donato Guerra was assassinated in a suburb of Chihuahua City where he was incarcerated for conspiring with Ángel Trías. During October 1875 several locations were controlled by rebel forces, but the government finally regained control on November 25, 1875.
 After the death of the president Benito Juárez in 1872, the first magistracy of the country was occupied by the vice-president Sebastián Lerdo de Tejada, who called for new elections. Two candidates were registered; Lerdo de Tejada and General
After the death of the president Benito Juárez in 1872, the first magistracy of the country was occupied by the vice-president Sebastián Lerdo de Tejada, who called for new elections. Two candidates were registered; Lerdo de Tejada and General  The officials in Mexico City reduced the price of corn from six cents to two cents a pound. The northern portion of the state continued to decline economically which led to another revolt led by G. Casavantes in August 1879; Governor Trías was accused of misappropriation of funds and inefficient administration of the state. Casavantes took the state capital and occupied it briefly; he was also successful in forcing Governor Trías to exile. Shortly afterwards, the federal government sent an entourage led by Treviño; Casavantes was immediately ordered to resign his position. Casavantes declared political victory as he was able to publicly accuse and depose Governor Trías. At the same time the states of Durango and Coahuila had a military confrontation over territorial claims and water rights; this altercation between the state required additional federal troops to stabilize the area. Later a dispute ensued again among the states of Coahuila, Durango, and Chihuahua over the mountain range area known as Sierra Mojada, when large deposits of gold ore was discovered. The state of Chihuahua officially submitted a declaration of protest in May 1880 that shortly after was amicably settled. Despite the difficulties at the beginning, Díaz was able to secure and stabilize the state, which earned the confidence and support of the people.
During the 1880s, the Díaz administration consolidated several government agencies throughout Mexico to control credit and currency by the creation of the Institution of Credit and Currency. Because Díaz had created such an effective centralized government, he was able to concentrate decision making and maintain control over the economic instability.
The officials in Mexico City reduced the price of corn from six cents to two cents a pound. The northern portion of the state continued to decline economically which led to another revolt led by G. Casavantes in August 1879; Governor Trías was accused of misappropriation of funds and inefficient administration of the state. Casavantes took the state capital and occupied it briefly; he was also successful in forcing Governor Trías to exile. Shortly afterwards, the federal government sent an entourage led by Treviño; Casavantes was immediately ordered to resign his position. Casavantes declared political victory as he was able to publicly accuse and depose Governor Trías. At the same time the states of Durango and Coahuila had a military confrontation over territorial claims and water rights; this altercation between the state required additional federal troops to stabilize the area. Later a dispute ensued again among the states of Coahuila, Durango, and Chihuahua over the mountain range area known as Sierra Mojada, when large deposits of gold ore was discovered. The state of Chihuahua officially submitted a declaration of protest in May 1880 that shortly after was amicably settled. Despite the difficulties at the beginning, Díaz was able to secure and stabilize the state, which earned the confidence and support of the people.
During the 1880s, the Díaz administration consolidated several government agencies throughout Mexico to control credit and currency by the creation of the Institution of Credit and Currency. Because Díaz had created such an effective centralized government, he was able to concentrate decision making and maintain control over the economic instability.
 The Díaz administration made political decisions and took legal measures that allowed the elite throughout Mexico to concentrate the nation's wealth by favoring monopolies. During this time, two-fifths of the state's territory was divided among 17 rich families which owned practically all of the arable land in Chihuahua. The state economy grew at a rapid pace during the Porfiriato; the economy in Chihuahua was dominated by agriculture and mining. The Díaz administration helped Governor
The Díaz administration made political decisions and took legal measures that allowed the elite throughout Mexico to concentrate the nation's wealth by favoring monopolies. During this time, two-fifths of the state's territory was divided among 17 rich families which owned practically all of the arable land in Chihuahua. The state economy grew at a rapid pace during the Porfiriato; the economy in Chihuahua was dominated by agriculture and mining. The Díaz administration helped Governor
 Díaz created an effective centralized government that helped concentrate wealth and political power among the elite upper class, mostly
Díaz created an effective centralized government that helped concentrate wealth and political power among the elite upper class, mostly  A handful of families owned large estates (known as
A handful of families owned large estates (known as  In response to Madero's letter to action,
In response to Madero's letter to action,
. On March 26, 1913, The uneasy alliance of Carranza, Obregón, Villa, and Zapata eventually led the rebels to victory. The fight against Huerta formally ended on August 15, 1914, when Álvaro Obregón signed a number of treaties in Teoloyucan in which the last of Huerta's forces surrendered to him and recognized the constitutional government. On August 20, 1914, Carranza made a triumphal entry into
The uneasy alliance of Carranza, Obregón, Villa, and Zapata eventually led the rebels to victory. The fight against Huerta formally ended on August 15, 1914, when Álvaro Obregón signed a number of treaties in Teoloyucan in which the last of Huerta's forces surrendered to him and recognized the constitutional government. On August 20, 1914, Carranza made a triumphal entry into
 The main mountain range in the state is the
The main mountain range in the state is the  The plains at the foot of the Sierra Madre Occidental is an elongated mesa known as Altiplanicie Mexicana that exhibits a steppe climate and serves as a transition zone from the mountain climate in the western part of the state to the desert climate in the eastern side of the state. The steppe zone accounts for a third of the state's area, and it experiences pronounced dry and wet seasons. The pronounced rainy season in the steppe is usually observed in the months of July, August, and September. The steppe also encounters extreme temperatures that often reach over in the summer and drop below in the winter. The steppe zone is an important agriculture zone due to an extensive development of canals exploiting several rivers that flow down from the mountains. The steppe zone is the most populated area of the state.
The most important river in the state is Río Conchos which is the largest tributary to the Río Grande from the Mexican side; the river descends from the zenith of the Sierra Madre Occidental in the southwest part of the state and winds through the center of the state where the water is exploited in the steppe zone and it eventually empties into the Río Grande in the small desert town of Ojinaga.
The desert zone also accounts for about a third of the state's surface area. The Chihuahuan Desert is an international biome that also extends into the neighboring Mexican state of
The plains at the foot of the Sierra Madre Occidental is an elongated mesa known as Altiplanicie Mexicana that exhibits a steppe climate and serves as a transition zone from the mountain climate in the western part of the state to the desert climate in the eastern side of the state. The steppe zone accounts for a third of the state's area, and it experiences pronounced dry and wet seasons. The pronounced rainy season in the steppe is usually observed in the months of July, August, and September. The steppe also encounters extreme temperatures that often reach over in the summer and drop below in the winter. The steppe zone is an important agriculture zone due to an extensive development of canals exploiting several rivers that flow down from the mountains. The steppe zone is the most populated area of the state.
The most important river in the state is Río Conchos which is the largest tributary to the Río Grande from the Mexican side; the river descends from the zenith of the Sierra Madre Occidental in the southwest part of the state and winds through the center of the state where the water is exploited in the steppe zone and it eventually empties into the Río Grande in the small desert town of Ojinaga.
The desert zone also accounts for about a third of the state's surface area. The Chihuahuan Desert is an international biome that also extends into the neighboring Mexican state of
 The climate in the state depends mainly in the elevation of the terrain. According to
The climate in the state depends mainly in the elevation of the terrain. According to 


 *Subtropical Highland ( Cfb) most common at elevations above above sea level; this climate zone has warm summers reaching a maximum temperature of and summer lows of . Heavy rainstorms are observed from July to September. Winters are cold reaching a maximum low of and a maximum high of . During the winter months many snowstorms are observed with typically of snow per season.
*Humid Subtropical ( Cwa) climate is most common at elevations between above sea level; this climate zone has warm humid summers and an average summer temperature of . The summer average precipitation is , mostly in the months of: July, August, and September. From November to March there are many rainstorms and snowstorms caused by high elevation and prominent cold fronts. Winter temperatures can reach a low of .
*Semi-arid climate or Steppe ( BSk) is most common at elevations between above sea level; this climate zone has an annual average of and maximum temperatures above and lows reaching slightly below , with a wet season in the late summer and fall. Snowfall is rare but possible in the winter and frost is common from December to March. The annual average rainfall in the steppe climate zone is about .
*Hot Desert ( BWh) is most common at elevations below above sea level; this climate zone tends to have a hot summer at temperatures that often reach . Winter is warm, rarely dropping below . Precipitation averages 6–10 in. per year; most of the moisture falls during the monsoon of late summer.
*Cool Desert ( BWk) is most common at elevations above above sea level; this climate zone tends to have a mild summer, rarely reaching temperatures over . Winter weather varies from mild to cold depending on northern fronts, often dropping below . Precipitation averages 10–16 in. per year; most of the moisture falls during the monsoon of late summer.
*Subtropical Highland ( Cfb) most common at elevations above above sea level; this climate zone has warm summers reaching a maximum temperature of and summer lows of . Heavy rainstorms are observed from July to September. Winters are cold reaching a maximum low of and a maximum high of . During the winter months many snowstorms are observed with typically of snow per season.
*Humid Subtropical ( Cwa) climate is most common at elevations between above sea level; this climate zone has warm humid summers and an average summer temperature of . The summer average precipitation is , mostly in the months of: July, August, and September. From November to March there are many rainstorms and snowstorms caused by high elevation and prominent cold fronts. Winter temperatures can reach a low of .
*Semi-arid climate or Steppe ( BSk) is most common at elevations between above sea level; this climate zone has an annual average of and maximum temperatures above and lows reaching slightly below , with a wet season in the late summer and fall. Snowfall is rare but possible in the winter and frost is common from December to March. The annual average rainfall in the steppe climate zone is about .
*Hot Desert ( BWh) is most common at elevations below above sea level; this climate zone tends to have a hot summer at temperatures that often reach . Winter is warm, rarely dropping below . Precipitation averages 6–10 in. per year; most of the moisture falls during the monsoon of late summer.
*Cool Desert ( BWk) is most common at elevations above above sea level; this climate zone tends to have a mild summer, rarely reaching temperatures over . Winter weather varies from mild to cold depending on northern fronts, often dropping below . Precipitation averages 10–16 in. per year; most of the moisture falls during the monsoon of late summer.
 The state has a great diversity due to the large number of microclimates found and dramatic varying terrain. The flora throughout the
The state has a great diversity due to the large number of microclimates found and dramatic varying terrain. The flora throughout the  The fauna in the state is just as diverse as the flora and varies greatly due to the large contrast in climates. In the mountain zone of the state the most observed mammals are: Mexican fox squirrel ('' Sciurus nayaritensis''), antelope jackrabbit ('' Lepus alleni''), raccoon ('' Procyon lotor''), hooded skunk ('' Mephitis macroura''), collared peccary ('' Dicotyles tajacu''), white-tailed deer ('' Odocoileus virginianus''), mule deer ('' Odocoileus hemionus''), American bison ('' Bison bison''), cougar (''
The fauna in the state is just as diverse as the flora and varies greatly due to the large contrast in climates. In the mountain zone of the state the most observed mammals are: Mexican fox squirrel ('' Sciurus nayaritensis''), antelope jackrabbit ('' Lepus alleni''), raccoon ('' Procyon lotor''), hooded skunk ('' Mephitis macroura''), collared peccary ('' Dicotyles tajacu''), white-tailed deer ('' Odocoileus virginianus''), mule deer ('' Odocoileus hemionus''), American bison ('' Bison bison''), cougar (''
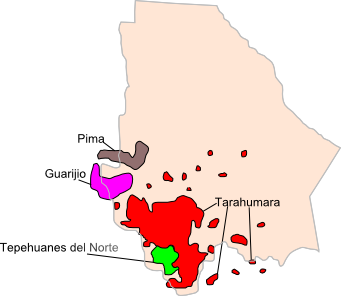

 The last census in Mexico that asked for an individual's race, which was taken in 1921, indicated that 50.09% of the population identified as Mestizo (mixed Amerindian and European descent). The second-largest group was whites at 36.33% of the population. The third-largest group was the "pure indigenous" population, constituting 12.76% of the population. The remaining 0.82% of the population of Chihuahua was considered "other", i.e. neither Mestizo, indigenous, nor white. The most important indigenous tribes of the state of Chihuahua are:
* Tarahumara: The largest ethnic group of indigenous people in the state. They call themselves ''Rarámuri'', which means "Barefoot Runner". They are famous for their endurance in running long distances. They live in large areas of the
The last census in Mexico that asked for an individual's race, which was taken in 1921, indicated that 50.09% of the population identified as Mestizo (mixed Amerindian and European descent). The second-largest group was whites at 36.33% of the population. The third-largest group was the "pure indigenous" population, constituting 12.76% of the population. The remaining 0.82% of the population of Chihuahua was considered "other", i.e. neither Mestizo, indigenous, nor white. The most important indigenous tribes of the state of Chihuahua are:
* Tarahumara: The largest ethnic group of indigenous people in the state. They call themselves ''Rarámuri'', which means "Barefoot Runner". They are famous for their endurance in running long distances. They live in large areas of the

 The state has the 9th-largest state economy in Mexico, accounting for 3.69% of the country's GDP. Chihuahua has the fifth highest manufacturing GDP in Mexico and ranks second for the most factories funded by foreign investment in the country. As of 2022, the state had an estimated 1.050 trillion pesos (52.2 billion dollars) of annual GDP. According to official federal statistical studies, the service sector accounted for the largest portion of the state economy at 59.28%; the manufacturing and industrial sector is estimated to account for 34.36% of the state's GDP, with the agricultural sector accounting for 6.36% of the state's GDP. Manufacturing sector was the principal foreign investment in the state followed by the mining sector. In 2011, the state received approximately 884 million dollars in
The state has the 9th-largest state economy in Mexico, accounting for 3.69% of the country's GDP. Chihuahua has the fifth highest manufacturing GDP in Mexico and ranks second for the most factories funded by foreign investment in the country. As of 2022, the state had an estimated 1.050 trillion pesos (52.2 billion dollars) of annual GDP. According to official federal statistical studies, the service sector accounted for the largest portion of the state economy at 59.28%; the manufacturing and industrial sector is estimated to account for 34.36% of the state's GDP, with the agricultural sector accounting for 6.36% of the state's GDP. Manufacturing sector was the principal foreign investment in the state followed by the mining sector. In 2011, the state received approximately 884 million dollars in  During the 1990s after
During the 1990s after
Chihuahua state government
Secretariat of Industrial Development of Chihuahua State Government
Chihuahua's municipal governments
Chihuahua photos
Encyclopædia Britannica, Chihuahua
Chihuahuan Frontier
{{Authority control States of Mexico Mexican Plateau states * States and territories established in 1824
Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city of Mexico, as well as the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North America. It is one of the most important cultural and finan ...
, comprise the 32 federal entities of Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
. It is located in the northwestern part of Mexico and is bordered by the states of Sonora
Sonora (), officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Sonora (), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. The state is divided into Municipalities of Sonora, 72 ...
to the west, Sinaloa
Sinaloa (), officially the (), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, compose the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 18 municipalities, and its capital city is Culiacán Rosales.
It is located in northwest Mexic ...
to the southwest, Durango
Durango, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Durango, is one of the 31 states which make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico, situated in the northwest portion of the country. With a population of 1,832,650 ...
to the south, and Coahuila
Coahuila, formally Coahuila de Zaragoza, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Coahuila de Zaragoza, is one of the 31 states of Mexico. The largest city and State Capital is the city of Saltillo; the second largest is Torreón and the thi ...
to the east. To the north and northeast, it shares an extensive border with the U.S. adjacent to the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its so ...
s of New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ...
and Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
. The state was named after its capital city, Chihuahua City
The city of Chihuahua or Chihuahua City ( ; Lipan language, Lipan: ) is the state capital of the Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. , the city of Chihuahua had a population of 925,762 inhabitants. while the metropolitan area had a popu ...
; the largest city is Ciudad Juárez
Ciudad Juárez ( , ; "Juárez City"), commonly referred to as just Juárez (Lipan language, Lipan: ''Tsé Táhú'ayá''), is the most populous city in the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. It was k ...
. In 1864 the city of Chihuahua was declared capital of Mexico by Benito Juarez Benito may refer to:
Places
* Benito, Kentucky, United States
* Benito, Manitoba, Canada
* Benito River, a river in Equatorial Guinea
Other uses
* Benito (name)
** Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (29 July 188328 April 1 ...
during the Reform War and French intervention. The city of Parral was the largest producer of silver in the world in 1640. During the Mexican War of Independence
The Mexican War of Independence (, 16 September 1810 – 27 September 1821) was an armed conflict and political process resulting in Mexico's independence from the Spanish Empire. It was not a single, coherent event, but local and regional ...
, Miguel Hidalgo
Don Miguel Gregorio Antonio Ignacio Hidalgo y Costilla Gallaga Mandarte y Villaseñor (8 May 1753 – 30 July 1811), commonly known as Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla or simply Miguel Hidalgo (), was a Catholic priest, leader of the Mexican Wa ...
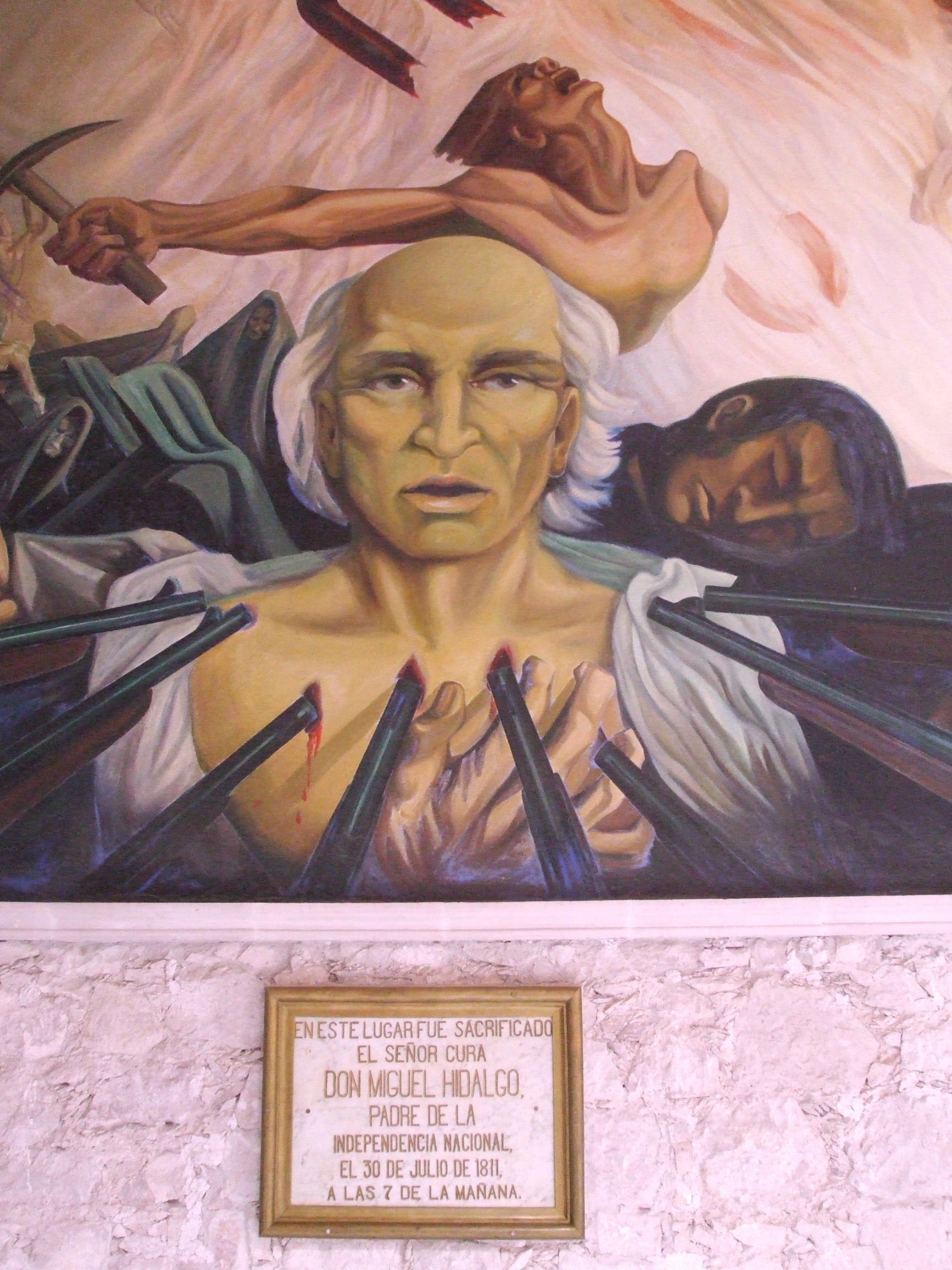
was executed on July 30, 1811, in Chihuahua city.
Although Chihuahua is primarily identified with its namesake, the Chihuahuan Desert, it has more forests than any other state in Mexico, aside from Durango
Durango, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Durango, is one of the 31 states which make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico, situated in the northwest portion of the country. With a population of 1,832,650 ...
. Due to its varied climate, the state has a large variety of fauna and flora. The state is mostly characterized by rugged mountainous terrain and wide river valleys. The Sierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American C ...
mountain range, part of the continental spine that also includes the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
, dominates the state's terrain, and is home to the state's greatest attraction, , or Copper Canyon, a canyon system larger and deeper than the Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon is a steep-sided canyon carved by the Colorado River in Arizona, United States. The Grand Canyon is long, up to wide and attains a depth of over a mile ().
The canyon and adjacent rim are contained within Grand Canyon Nati ...
. The state also has the largest crystal cave in Mexico known as the Naica cave discovered in 2001. Chihuahua is also home to the archaeological site of Paquimé
Casas Grandes (Spanish for ''Great Houses''; also known as Paquimé) is a prehistoric archaeological site in the northern Mexican state of Chihuahua. Construction of the site is attributed to the Mogollon culture. Casas Grandes has been desig ...
in Casas Grandes that was created by the people of the Mogollon civilization of Northern Mexico and is recognized as an UNESCO World Heritage site. Chihuahua is the largest state in Mexico by area, with an area of , it is slightly larger than the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, and slightly smaller than Wyoming
Wyoming ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States, Western United States. It borders Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho t ...
, the tenth largest US state by area. The state is consequently known under the nickname ('The Great State' or 'The Big State').
The famous Mexican train Ch-P, a.k.a. " Chepe" starts from Chihuahua, calle Mendez, and reaches the Pacific Ocean, through the Sierra Madre and the Copper Canyon.
On the slope of the Sierra Madre Occidental mountains (around the regions of Casas Grandes
Casas Grandes (Spanish for ''Great Houses''; also known as Paquimé) is a prehistoric archaeological site in the northern Mexico, Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. Construction of the site is attributed to the Mogollon culture. Casa ...
, Cuauhtémoc
Cuauhtémoc (, ), also known as Cuauhtemotzín, Guatimozín, or Guatémoc, was the Aztec ruler ('' tlatoani'') of Tenochtitlan from 1520 to 1521, and the last Aztec Emperor. The name Cuauhtemōc means "one who has descended like an eagle", an ...
and Parral), there are vast prairies of short yellow grass, the source of the bulk of the state's agricultural production. Most of the inhabitants live along the Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( or ) in the United States or the Río Bravo (del Norte) in Mexico (), also known as Tó Ba'áadi in Navajo language, Navajo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the Southwestern United States a ...
Valley, and the Conchos River Valley. The etymology
Etymology ( ) is the study of the origin and evolution of words—including their constituent units of sound and meaning—across time. In the 21st century a subfield within linguistics, etymology has become a more rigorously scientific study. ...
of the name Chihuahua has long been disputed by historians and linguists. The most accepted theory explains that the name was derived from the Nahuatl language
Nahuatl ( ; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahuas, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller popul ...
meaning "the place where the water of the rivers meet" (i.e. "confluence", cf. Koblenz
Koblenz ( , , ; Moselle Franconian language, Moselle Franconian: ''Kowelenz'') is a German city on the banks of the Rhine (Middle Rhine) and the Moselle, a multinational tributary.
Koblenz was established as a Roman Empire, Roman military p ...
).
Chihuahua has a diversified state economy. The three most important economic centers in the state are: Ciudad Juárez
Ciudad Juárez ( , ; "Juárez City"), commonly referred to as just Juárez (Lipan language, Lipan: ''Tsé Táhú'ayá''), is the most populous city in the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. It was k ...
, an international manufacturing center; Chihuahua, the state capital; and Cuauhtémoc
Cuauhtémoc (, ), also known as Cuauhtemotzín, Guatimozín, or Guatémoc, was the Aztec ruler ('' tlatoani'') of Tenochtitlan from 1520 to 1521, and the last Aztec Emperor. The name Cuauhtemōc means "one who has descended like an eagle", an ...
, the state's main agriculture hub and an internationally recognized center for apple production. Today, Chihuahua serves as an important commercial route prospering from billions of dollars from international trade as a result of NAFTA
The North American Free Trade Agreement (, TLCAN; , ALÉNA), referred to colloquially in the Anglosphere as NAFTA, ( ) was an agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States that created a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The ...
. The state also suffers the fallout of illicit trade and activities from drug cartels, especially at the border. The state is also home to inventors; Victor Leaton Ochoa, Rafael Mendoza Blanco and Luis T. Hernandez Terrazas.
History
Prehistory
 The earliest evidence of human inhabitants of modern-day Chihuahua was discovered in the area of Samalayuca and Rancho Colorado. Clovis points have been found in northeastern Chihuahua that have been dated from 12,000 BC to 7000 BC. It is thought that these inhabitants were hunter gatherers.
Inhabitants of the state later developed farming with the domestication of corn. An archeological site in northern Chihuahua known as ''Cerro Juanaqueña'' revealed squash cultivation, irrigation techniques, and
The earliest evidence of human inhabitants of modern-day Chihuahua was discovered in the area of Samalayuca and Rancho Colorado. Clovis points have been found in northeastern Chihuahua that have been dated from 12,000 BC to 7000 BC. It is thought that these inhabitants were hunter gatherers.
Inhabitants of the state later developed farming with the domestication of corn. An archeological site in northern Chihuahua known as ''Cerro Juanaqueña'' revealed squash cultivation, irrigation techniques, and ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcela ...
artifacts dating to around 2000 BC.
 Between AD 300 and 1300 in the northern part of the state along the wide, fertile valley on the San Miguel River the
Between AD 300 and 1300 in the northern part of the state along the wide, fertile valley on the San Miguel River the Casas Grandes
Casas Grandes (Spanish for ''Great Houses''; also known as Paquimé) is a prehistoric archaeological site in the northern Mexico, Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. Construction of the site is attributed to the Mogollon culture. Casa ...
(''Big Houses'') culture developed into an advanced civilization. The Casas Grandes civilization is part of a major prehistoric archaeological culture known as Mogollon which is related to the Ancestral Pueblo culture. Paquimé
Casas Grandes (Spanish for ''Great Houses''; also known as Paquimé) is a prehistoric archaeological site in the northern Mexican state of Chihuahua. Construction of the site is attributed to the Mogollon culture. Casas Grandes has been desig ...
was the center of the Casas Grandes civilization. Extensive archaeological evidence shows commerce, agriculture, and hunting at Paquimé and Cuarenta Casas (''Forty Houses'').
La Cueva de las Ventanas (''The Cave of Windows''), a series of cliff dwellings along an important trade route, and Las Jarillas Cave scrambled along the canyons of the Sierra Madre in Northwestern Chihuahua date between AD 1205 and 1260 and belong to the Paquimé
Casas Grandes (Spanish for ''Great Houses''; also known as Paquimé) is a prehistoric archaeological site in the northern Mexican state of Chihuahua. Construction of the site is attributed to the Mogollon culture. Casas Grandes has been desig ...
culture. Cuarenta Casas is thought to have been a branch settlement from Paquimé to protect the trade route from attack. Archaeologists believe the civilization began to decline during the 13th century and by the 15th century the inhabitants of Paquimé sought refuge in the Sierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American C ...
while others are thought to have emigrated north and joined the Ancestral Pueblo peoples. According to anthropologist current natives tribes (Yaqui
The Yaqui, Hiaki, or Yoeme, are an Indigenous people of Mexico and Native Americans in the United States, Native American tribe, who speak the Yaqui language, a Uto-Aztecan language.
Their primary homelands are in Río Yaqui valley in the no ...
, Mayo, Opata, and Tarahumara) are descendants of the Casas Grandes culture.
During the 14th century in the northeastern part of the state nomad tribes by the name of Jornado hunted bison
A bison (: bison) is a large bovine in the genus ''Bison'' (from Greek, meaning 'wild ox') within the tribe Bovini. Two extant taxon, extant and numerous extinction, extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American ...
along the Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( or ) in the United States or the Río Bravo (del Norte) in Mexico (), also known as Tó Ba'áadi in Navajo language, Navajo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the Southwestern United States a ...
; they left numerous rock paintings throughout the northeastern part of the state. When the Spanish explorers reached this area they found their descendants, the Suma and Manso tribes. In the southern part of the state, in a region known as Aridoamerica
Aridoamerica is a cultural and ecological region spanning Northern Mexico and the Southwestern United States, defined by the presence of the drought-resistant, culturally significant staple food, the tepary bean ('' Phaseolus acutifolius'').P ...
, Chichimeca
Chichimeca () is the name that the Nahua peoples of Mexico generically applied to nomadic and semi-nomadic peoples who were established in present-day Bajío region of Mexico. Chichimeca carried the same meaning as the Roman term "barbarian" tha ...
people survived by hunting, gathering, and farming between AD 300 and 1300. The Chichimeca are the ancestors of the Tepehuán people.
Colonial era
Nueva Vizcaya (New Biscay) was the first province of northernNew Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
to be explored and settled by the Spanish. Around 1528, a group of Spaniard explorers, led by Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca
Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca (; 1488/90/92"Cabeza de Vaca, Alvar Núñez (1492?-1559?)." American Eras. Vol. 1: Early American Civilizations and Exploration to 1600. Detroit: Gale, 1997. 50-51. Gale Virtual Reference Library. Web. 10 December ...
, first entered the territory of what is now Chihuahua. The conquest of the territory lasted nearly one century and encountered fierce resistance from the Conchos tribe, but the desire of the Spanish Crown
The monarchy of Spain or Spanish monarchy () is the constitutional form of government of Spain. It consists of a Hereditary monarchy, hereditary monarch who reigns as the head of state, being the highest office of the country.
The Spanish ...
to transform the region into a bustling mining center led to a strong strategy to control the area.
 In 1562,
In 1562, Francisco de Ibarra
Francisco de Ibarra (1539 –June 3, 1575) was a Spanish-Basque explorer, founder of the city of Durango, and governor of the Spanish province of Nueva Vizcaya, in present-day Durango and Chihuahua.
Biography
Francisco de Ibarra was born a ...
headed a personal expedition in search of the mythical cities of Cíbola and Quivira
Quivira was a province of the ancestral Wichita people, located near the Great Bend of the Arkansas River in central Kansas, The exact site may be near present-day Lyons extending northeast to Salina.
The Wichita city of Etzanoa, which flouris ...
; he traveled through the present-day state of Chihuahua. Francisco de Ibarra
Francisco de Ibarra (1539 –June 3, 1575) was a Spanish-Basque explorer, founder of the city of Durango, and governor of the Spanish province of Nueva Vizcaya, in present-day Durango and Chihuahua.
Biography
Francisco de Ibarra was born a ...
is thought to have been the first European to see the ruins of Paquimé. In 1564, Rodrigo de Río de Loza, a lieutenant under Francisco de Ibarra, stayed behind after the expedition and found gold at the foot of the mountains of the Sierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American C ...
; he founded the first Spanish city in the region, Santa Bárbara in 1567 by bringing 400 European families to the settlement. A few years later, in 1569, Franciscan missionaries led by Fray Agustín Rodríguez from the coast of Sinaloa and the state of Durango founded the first mission in the state in Valle de San Bartolomé (present-day Valle de Allende). Fray Agustín Rodríguez evangelized the native population until 1581. Between 1586 and 1588, an epidemic caused a temporary exodus of the small population in the territory of Nueva Vizcaya.
Santa Bárbara became the launching place for expeditions into New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ...
by Spanish conquistadors like Antonio de Espejo
Antonio de Espejo (c. 1540–1585) was a Spanish explorer who led an expedition, accompanied by Diego Perez de Luxan, into what is now New Mexico and Arizona in 1582–83.pg 189 - The expedition created interest in establishing a Spanish col ...
, Gaspar Castaño, Antonio Gutiérrez de Umaña, Francisco Leyba de Bonilla, and Vicente de Zaldívar. Several expeditions were led to find a shorter route from Santa Bárbara to New Mexico. In April 1598, Juan de Oñate
Juan de Oñate y Salazar (; 1550–1626) was a Spanish conquistador, explorer and viceroy of the province of Santa Fe de Nuevo México in the viceroyalty of New Spain, in the present-day U.S. state of New Mexico. He led early Spanish expedition ...
found a short route from Santa Bárbara to New Mexico which came to be called El Paso del Norte (The Northern Pass). The discovery of El Paso del Norte was important for the expansion of El Camino Real de Tierra Adentro (The Inner Land Royal Road) to link Spanish settlements in New Mexico to Mexico City; El Camino Real de Tierra Adentro facilitated transport of settlers and supplies to New Mexico and Camargo.
Ciudad Juárez
Ciudad Juárez ( , ; "Juárez City"), commonly referred to as just Juárez (Lipan language, Lipan: ''Tsé Táhú'ayá''), is the most populous city in the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. It was k ...
) in 1667.
The Spanish society that developed in the region replaced the sparse population of indigenous peoples. The absence of servants and workers forged the spirit of northern people as self-dependent, creative people that defended their European heritage. In 1680, settlers from Santa Fe, New Mexico sought refuge in El Paso del Norte for twelve years after fleeing the attacks from Pueblo tribes, but returned to Santa Fe in 1692 after Diego de Vargas recaptured the city and vicinity. In 1709, Antonio de Deza y Ulloa founded the state capital Chihuahua City
The city of Chihuahua or Chihuahua City ( ; Lipan language, Lipan: ) is the state capital of the Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. , the city of Chihuahua had a population of 925,762 inhabitants. while the metropolitan area had a popu ...
; shortly after, the city became the headquarters for the regional mining offices of the Spanish crown known as 'Real de Minas de San Francisco de Cuéllar' in honor of the Viceroy of New Spain, Francisco Fernández de la Cueva Enríquez, Duke of Alburquerque and the Marquee of Cuéllar.
Mexican War of Independence
 During the Napoleonic Occupation of Spain,
During the Napoleonic Occupation of Spain, Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla
Don Miguel Gregorio Antonio Ignacio Hidalgo y Costilla Gallaga Mandarte y Villaseñor (8 May 1753 – 30 July 1811), commonly known as Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla or simply Miguel Hidalgo (), was a Catholic priest, leader of the Mexican War ...
, a Catholic priest of progressive ideas, declared Mexican independence in the small town of Dolores, Guanajuato
Guanajuato, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guanajuato, is one of the 32 states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Guanajuato, 46 municipalities and its cap ...
on September 16, 1810, with a proclamation known as the "Grito de Dolores". Hidalgo built a large support among intellectuals, liberal priests and many poor people. Hidalgo fought to protect the rights of the poor and indigenous population. He started on a march to the capital, Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city of Mexico, as well as the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North America. It is one of the most important cultural and finan ...
, but retreated back north when faced with the elite of the royal forces at the outskirts of the capital. He established a liberal government from Guadalajara, Jalisco
Guadalajara ( ; ) is the capital and the most populous city in the western Mexican List of states of Mexico, state of Jalisco, as well as the most densely populated municipality in Jalisco. According to the 2020 census, the city has a population ...
but was soon forced to flee north by the royal forces that recaptured the city. Hidalgo attempted to reach the United States and gain American support for Mexican independence. Hidalgo reached Saltillo
Saltillo () is the capital and largest city of the northeastern Mexican state of Coahuila and is also the municipal seat of the municipality of the same name. Mexico City, Monterrey, and Saltillo are all connected by a major railroad and high ...
, Coahuila
Coahuila, formally Coahuila de Zaragoza, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Coahuila de Zaragoza, is one of the 31 states of Mexico. The largest city and State Capital is the city of Saltillo; the second largest is Torreón and the thi ...
where he publicly resigned his military post and rejected a pardon offered by Viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory.
The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the Anglo-Norman ''roy'' (Old Frenc ...
Francisco Venegas in return for Hidalgo's surrender. A short time later, he and his supporters were captured by royalist Ignacio Elizondo
Francisco Ignacio de Elizondo Villarreal, (born Salinas Valley, New Kingdom of León, New Spain, March 9, 1766 - died San Marcos, Texas, New Spain, c. September 12, 1813), was a royalist military officer during the Mexican war of independence ag ...
at the Wells of Baján
Wells most commonly refers to:
* Wells, Somerset, a cathedral city in Somerset, England
* Well, an excavation or structure created in the ground
* Wells (name)
Wells may also refer to:
Places Canada
*Wells, British Columbia
England
* Wells ...
(Norias de Baján) on March 21, 1811 and taken to the city of Chihuahua. Hidalgo forced the Bishop of Valladolid, Manuel Abad y Queipo, to rescind the excommunication
Excommunication is an institutional act of religious censure used to deprive, suspend, or limit membership in a religious community or to restrict certain rights within it, in particular those of being in Koinonia, communion with other members o ...
order he had circulated against him on September 24, 1810. Later, the Inquisition issued an excommunication edict on October 13, 1810, condemning Miguel Hidalgo as a seditionary, apostate
Apostasy (; ) is the formal disaffiliation from, abandonment of, or renunciation of a religion by a person. It can also be defined within the broader context of embracing an opinion that is contrary to one's previous religious beliefs. One who ...
, and heretic
Heresy is any belief or theory that is strongly at variance with established beliefs or customs, particularly the accepted beliefs or religious law of a religious organization. A heretic is a proponent of heresy.
Heresy in Christianity, Judai ...
.
Hidalgo was turned over to the Bishop of Durango
Durango, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Durango, is one of the 31 states which make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico, situated in the northwest portion of the country. With a population of 1,832,650 ...
, Francisco Gabriel de Olivares, for an official defrocking
Defrocking, unfrocking, degradation, or laicization of clergy is the removal of their rights to exercise the functions of the ordained ministry. It may be grounded on criminal convictions, disciplinary problems, or disagreements over doctrine or ...
and excommunication on July 27, 1811. He was then found guilty of treason by a military court and executed by firing squad
Firing may refer to:
* Dismissal (employment), sudden loss of employment by termination
* Firemaking, the act of starting a fire
* Burning; see combustion
* Shooting, specifically the discharge of firearms
* Execution by firing squad, a method of ...
on July 30 at 7 in the morning. Before his execution, he thanked his jailers, Private Soldiers Ortega and Melchor, in letters for their humane treatment. At his execution, Hidalgo placed his right hand over his heart to show the riflemen where they should aim. He also refused the use of a blindfold. His body, along with the bodies of Allende, Aldama and José Mariano Jiménez were decapitated, and the heads were put on display on the four corners of the Alhóndiga de Granaditas
Alhóndiga is a municipality located in the province of Guadalajara, Castilla–La Mancha, Spain. As of 1 January 2022 it had a registered population of 158. The municipality spans across a total area of 19.26 km2.
The locality was an early in ...
in Guanajuato
Guanajuato, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guanajuato, is one of the 32 states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Guanajuato, 46 municipalities and its cap ...
. The heads remained there for ten years until the end of the Mexican War of Independence
The Mexican War of Independence (, 16 September 1810 – 27 September 1821) was an armed conflict and political process resulting in Mexico's independence from the Spanish Empire. It was not a single, coherent event, but local and regional ...
to serve as a warning to other insurgents. Hidalgo's headless body was first displayed outside the prison but then buried in the Church of St Francis in Chihuahua. Those remains would later be transferred, in 1824, to Mexico City.
 Hidalgo's death resulted in a political vacuum on the insurgent side until 1812. The royalist military commander, General Felix Calleja, continued to pursue rebel troops. Insurgent fighting evolved into guerrilla warfare, and eventually the next major insurgent leader, José María Morelos y Pavón, who had led rebel movements with Hidalgo, became head of the insurgents.
Hidalgo is hailed as the ''Father of the Nation'' even though it was
Hidalgo's death resulted in a political vacuum on the insurgent side until 1812. The royalist military commander, General Felix Calleja, continued to pursue rebel troops. Insurgent fighting evolved into guerrilla warfare, and eventually the next major insurgent leader, José María Morelos y Pavón, who had led rebel movements with Hidalgo, became head of the insurgents.
Hidalgo is hailed as the ''Father of the Nation'' even though it was Agustín de Iturbide
Agustín Cosme Damián de Iturbide y Arámburu (; 27 September 178319 July 1824), commonly known as Agustín de Iturbide and later by his regnal name Agustín I, was the first Emperor of Mexico from 1822 until his abdication in 1823. An offi ...
and not Hidalgo who achieved Mexican Independence in 1821. Shortly after gaining independence, the day to celebrate it varied between September 16, the day of Hidalgo's Grito, and September 27, the day Iturbide rode into Mexico City to end the war. Later, political movements would favor the more liberal Hidalgo over the conservative Iturbide, so that eventually September 16, 1810 became the officially recognized day of Mexican independence. The reason for this is that Hidalgo is considered to be "precursor and creator of the rest of the heroes of the (Mexican War of) Independence." Hidalgo has become an icon for Mexicans who resist tyranny in the country. Diego Rivera
Diego Rivera (; December 8, 1886 – November 24, 1957) was a Mexican painter. His large frescoes helped establish the Mexican muralism, mural movement in Mexican art, Mexican and international art.
Between 1922 and 1953, Rivera painted mural ...
painted Hidalgo's image in half a dozen murals. José Clemente Orozco
José Clemente Orozco (November 23, 1883 – September 7, 1949) was a Mexican caricaturist and painter, who specialized in political murals that established the Mexican Mural Renaissance together with murals by Diego Rivera, David Alfaro Siquei ...
depicted him with a flaming torch of liberty and considered the painting among his best work. David Alfaro Siqueiros
David Alfaro Siqueiros (born José de Jesús Alfaro Siqueiros; December 29, 1896 – January 6, 1974) was a Mexican social realist painter, best known for his large public murals using the latest in equipment, materials and technique. Along with ...
was commissioned by San Nicolás University in Morelia to paint a mural for a celebration commemorating the 200th anniversary of Hidalgo's birth. The town of his parish was renamed Dolores Hidalgo in his honor and the state of Hidalgo was created in 1869. Every year on the night of September 15–16, the president of Mexico re-enacts the Grito from the balcony of the National Palace Buildings called National Palace include:
*National Palace (Dominican Republic), in Santo Domingo
* National Palace (El Salvador), in San Salvador
* National Palace (Ethiopia), in Addis Ababa; also known as the Jubilee Palace
* National Palace (Guat ...
. This scene is repeated by the heads of cities and towns all over Mexico. The remains of Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla lie in the column of the Angel of Independence in Mexico City. Next to it is a lamp lit to represent the sacrifice of those who gave their lives for Mexican Independence.
Constituent legislatures
In the constituent legislature or convention, theconservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, customs, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civiliza ...
and liberal elements formed using the nicknames of ''Chirrines'' and ''Cuchas''. The military entered as a third party. The elections for the first regular legislature were disputed, and it was not until May 1, 1826, that the body was installed. The liberals gained control and the opposition responded by fomenting a conspiracy. This was promptly stopped with the aid of informers, and more strenuous measures were taken against the conservatives. Extra powers were conferred on the Durango governor, Santiago Baca Ortiz, deputy to the first national congress, and leader of the liberal party.History Of The North Mexican States And Texas, Vol. II 1801–1889, San Francisco, The History Company, Publishers, 1889, Chapter 24
González's rebellion
Opponents continued to plot against the new government. In March 1827, Lieutenant J.M. González proclaimed himself comandante general, arrested the governor, and dissolved the legislature. General Parras was sent to suppress the movement. Comandante general J. J. Ayestarán was replaced by José Figueroa. When elections failed, the government intervened in favor of the Yorkino party, which had electedVicente Guerrero
Vicente Ramón Guerrero Saldaña (; baptized 10 August 1782 – 14 February 1831) was a Mexican military officer from 1810–1821 and a statesman who became the nation's second president in 1829. He was one of the leading generals who fought ag ...
to the presidency.
 Because of the general instability of the federal government during 1828, the installation of the new legislature did not take place until the middle of the following year. It was quickly dissolved by Governor Santiago de Baca Ortiz, who replaced it with a more pronounced Yorkino type. When Guerrero's liberal administration was overthrown in December, Gaspar de Ochoa aligned with
Because of the general instability of the federal government during 1828, the installation of the new legislature did not take place until the middle of the following year. It was quickly dissolved by Governor Santiago de Baca Ortiz, who replaced it with a more pronounced Yorkino type. When Guerrero's liberal administration was overthrown in December, Gaspar de Ochoa aligned with Anastasio Bustamante
Trinidad Anastasio de Sales Ruiz Bustamante y Oseguera (; 27 July 1780 – 6 February 1853) was a Mexican physician, general, and politician who served as the 4th President of Mexico three times from 1830 to 1832, 1837 to 1839, and 1839 to 1841. ...
, and in February 1830, organized an opposition group that arrested the new governor, F. Elorriaga, along with other prominent Yorkinos. He then summoned the legislature, which had been dissolved by Baca. The civil and military authorities were now headed by J. A. Pescador and Simón Ochoa.
Vicente Guerrero
The general features of the preceding occurrence applied also to Chihuahua, although in a modified form. The first person elected under the new constitution of 1825 was Simón Elías González, who being inSonora
Sonora (), officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Sonora (), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. The state is divided into Municipalities of Sonora, 72 ...
, was induced to remain there. José Antonio Arcé took his place as ruler in Chihuahua. In 1829, González became general commander of Chihuahua, when his term of office on the west coast expired. Arcé was less of a yorkino than his confrère of Durango. Although unable to resist the popular demand for the expulsion of the Spaniards, he soon quarreled with the legislature, which declared itself firmly for Guerrero
Guerrero, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guerrero, is one of the 32 states that compose the administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Guerrero, 85 municipalities. The stat ...
, and announcing his support of Bustamante's revolution, he suspended, in March 1830, eight members of that body, the vice-governor, and several other officials, and expelled them from the state. The course thus outlined was followed by Governor José Isidro Madero, who succeeded in 1830, associated with J. J. Calvo as general commander, stringent laws being issued against secret societies
A secret society is an organization about which the activities, events, inner functioning, or membership are concealed. The society may or may not attempt to conceal its existence. The term usually excludes covert groups, such as intelligence a ...
, which were supposed to be the main spring to the anti-clerical feeling among liberals.
Durango and Bustamante
The anti-clerical feeling was widespread, andDurango
Durango, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Durango, is one of the 31 states which make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico, situated in the northwest portion of the country. With a population of 1,832,650 ...
supported the initial reaction against the government at Mexico. In May 1832, José Urrea, a rising officer, supported the restoration of President Pedraza. On July 20, Governor Elorriaga was reinstated, and Baca along with the legislative minority were brought back to form a new legislature, which met on September 1. Chihuahua showed no desire to imitate the revolutionary movement and Urrea prepared to invade the state. Comandante-general J.J.Calvo threatened to retaliate, and a conflict seemed imminent. The entry of General Santa Anna into Mexico brought calm, as the leaders waited for clarity.
Santa Anna
Plan of Cuernavaca
A plan is typically any diagram or list of steps with details of timing and resources, used to achieve an objective to do something. It is commonly understood as a temporal set of intended actions through which one expects to achieve a goal.
...
in July 1834 while President Valentín Gómez Farías
Valentín Gómez Farías (; 14 February 1781 – 5 July 1858) was a Mexican physician and liberal politician who became president of Mexico twice, first from 1833 to 1834, during the period of the First Mexican Republic, and again from 1846 ...
was in power. Because the plan was not enforced, commanding officer, Colonel J.I. Gutiérrez, declared the term of the legislature and governor expired on September 3.
At a convention of citizens called to select a new provisional ruler, Gutiérrez obtained the vote, with P. J. Escalante for his deputy, and a council to guide the administration. Santa Anna ordered the reinstatement of Mendarozqueta as comandante general. Gutiérrez yielded, but Escalante refused to surrender office, demonstrations of support ensued, but Escalante yielded when troops were summoned from Zacatecas
Zacatecas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Zacatecas, is one of the Political divisions of Mexico, 31 states of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Zacatecas, 58 municipalities and its capital city is Zacatecas City, Zacatec ...
. A new election brought a new legislature, and conforming governors. In September 1835 José Urrea a federalist army officer came into power.
Comandante general Simón Elías González, was nominated governor and military command was given to Colonel J.J. Calvo, whose firmness had earned well-merited praise. The state was in the midst of a war with the Apache
The Apache ( ) are several Southern Athabaskan language-speaking peoples of the Southwestern United States, Southwest, the Southern Plains and Northern Mexico. They are linguistically related to the Navajo. They migrated from the Athabascan ho ...
s, which became the focus of all their energy and resources. After a review of the situation, Simón Elías González declared that the interests of the territory would be best served by uniting the civil and military power, at least while the campaign lasted. He resigned under opposition, but was renominated in 1837.
Mexican–American War
Chihuahua City
The city of Chihuahua or Chihuahua City ( ; Lipan language, Lipan: ) is the state capital of the Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. , the city of Chihuahua had a population of 925,762 inhabitants. while the metropolitan area had a popu ...
. The Battle of Sacramento was the most important battle fought in the state of Chihuahua because it was the sole defense for the state capital. The battle ended quickly because of some devastating defensive errors from the Mexican forces and the ingenious strategic moves by the American forces. After their loss at the Battle of Sacramento, the remaining Mexican soldiers retreated south, leaving the city to American occupation. Almost 300 Mexicans were killed in the battle, as well as almost 300 wounded. The Americans also confiscated large amounts of Mexican supplies and took 400 Mexican soldiers prisoners of war. American forces maintained an occupation of the state capital for the rest of the Mexican–American War.
 The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, signed on February 2, 1848, by American diplomat Nicholas Trist and Mexican plenipotentiary representatives Luis G. Cuevas, Bernardo Couto, and Miguel Atristain, ended the war, gave the U.S. undisputed control of Texas, and established the U.S.–Mexican border of the Rio Grande. As news of peace negotiations reached the state, new call to arms began to flare among the people of the state. But as the Mexican officials in Chihuahua heard that General Price was heading back to Mexico with a large force comprising several companies of infantry and three companies of cavalry and one division of light artillery from Santa Fe on February 8, 1848, Ángel Trías sent a message to Sacramento Pass to ask for succession of the area as they understood the war had concluded. General Price, misunderstanding this as a deception by the Mexican forces, continued to advance towards the state capital. On March 16, 1848 Price began negotiations with Ángel Trías, but the Mexican leader responded with an ultimatum to General Price. The American forces engaged with the Mexican forces near Santa Cruz de los Rosales on March 16, 1848. The Battle of Santa Cruz de los Rosales was the last battle of the Mexican–American War and it occurred after the peace treaty was signed. The American forces maintained control over the state capital for three months after the confirmation of the peace treaty. The American presence served to delay the possible succession of the state which had been discussed at the end of 1847, and the state remained under United States occupation until May 22, 1848.
During the American occupation of the state, the number of Indian attacks was drastically reduced, but in 1848 the attacks resumed to such a degree that the Mexican officials had no choice but to resume military projects to protect Mexican settlements in the state. Through the next three decades the state faced constant attacks from the indigenous on Mexican settlements. After the occupation the people of the state were worried about the potential attack from the hostile indigenous tribes north of the Rio Grande; as a result a decree on July 19, 1848, the state established 18 military colonies along the Rio Grande. The new military colonies were to replace the presidios as population centers to prevent future invasions by indigenous tribes; these policies remained prominent in the state until 1883. Eventually the state replaced the old state security with a state policy to form militias organized with every Mexican in the state capable to serve between the ages of 18 and 55 to fulfill the mandate of having six men defending for every 1000 residents.
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, signed on February 2, 1848, by American diplomat Nicholas Trist and Mexican plenipotentiary representatives Luis G. Cuevas, Bernardo Couto, and Miguel Atristain, ended the war, gave the U.S. undisputed control of Texas, and established the U.S.–Mexican border of the Rio Grande. As news of peace negotiations reached the state, new call to arms began to flare among the people of the state. But as the Mexican officials in Chihuahua heard that General Price was heading back to Mexico with a large force comprising several companies of infantry and three companies of cavalry and one division of light artillery from Santa Fe on February 8, 1848, Ángel Trías sent a message to Sacramento Pass to ask for succession of the area as they understood the war had concluded. General Price, misunderstanding this as a deception by the Mexican forces, continued to advance towards the state capital. On March 16, 1848 Price began negotiations with Ángel Trías, but the Mexican leader responded with an ultimatum to General Price. The American forces engaged with the Mexican forces near Santa Cruz de los Rosales on March 16, 1848. The Battle of Santa Cruz de los Rosales was the last battle of the Mexican–American War and it occurred after the peace treaty was signed. The American forces maintained control over the state capital for three months after the confirmation of the peace treaty. The American presence served to delay the possible succession of the state which had been discussed at the end of 1847, and the state remained under United States occupation until May 22, 1848.
During the American occupation of the state, the number of Indian attacks was drastically reduced, but in 1848 the attacks resumed to such a degree that the Mexican officials had no choice but to resume military projects to protect Mexican settlements in the state. Through the next three decades the state faced constant attacks from the indigenous on Mexican settlements. After the occupation the people of the state were worried about the potential attack from the hostile indigenous tribes north of the Rio Grande; as a result a decree on July 19, 1848, the state established 18 military colonies along the Rio Grande. The new military colonies were to replace the presidios as population centers to prevent future invasions by indigenous tribes; these policies remained prominent in the state until 1883. Eventually the state replaced the old state security with a state policy to form militias organized with every Mexican in the state capable to serve between the ages of 18 and 55 to fulfill the mandate of having six men defending for every 1000 residents.

La Mesilla
The frontier counties of the state along the border with the United States expected federal protection from the federal government under Herrera and Arista, but were soon disappointed by the federal government's decision to deploy military forces to other areas of the country due to internal challenges in the state ofJalisco
Jalisco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Jalisco, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is located in western Mexico and is bordered by s ...
. Ángel Trías led a rebellion to successfully depose the unpopular conservative Governor Cordero at the end of 1852.
Despite the efforts of strong political forces led by Ángel Trías in the state could not stop President Santa Anna from selling La Mesilla as part of the Gadsden Purchase
The Gadsden Purchase ( "La Mesilla sale") is a region of present-day southern Arizona and southwestern New Mexico that the United States acquired from Mexico by the Treaty of Mesilla, which took effect on June 8, 1854. The purchase included lan ...
on December 30, 1853 for 15 million USD. It was then ratified in the United States on April 25, 1854 and signed by President Franklin Pierce
Franklin Pierce (November 23, 1804October 8, 1869) was the 14th president of the United States, serving from 1853 to 1857. A northern Democratic Party (United States), Democrat who believed that the Abolitionism in the United States, abolitio ...
, with final approval action taken by Mexico on June 8, 1854. The citizens of the area held strong anti-American sentiments and raided American settlers and travelers across the area.
The Reform War and the French Intervention
 The state united behind the
The state united behind the Plan of Ayutla
The Plan of Ayutla was the 1854 written plan aimed at removing conservative, centralist President Antonio López de Santa Anna from control of Mexico during the Second Federal Republic of Mexico period. Initially, it seemed little different from ...
and ratified the new constitution in 1855. The state was able to survive through the Reform War
The Reform War (17 December 185711 January 1861) or War of Reform (), also known as the Three Years' War (), and the Mexican Civil War, was a complex civil conflict in Mexico fought between Mexican liberals and conservatives with regional var ...
with minimal damage due to the large number of liberal political figures. The 1858 conservative movement did not succeed in the state even after the successful military campaign of the conservative Zuloaga with 1,000 men occupied the cities of Chihuahua and Parral. In August 1859, Zuloaga and his forces were defeated by the liberal Orozco and his forces; Orozco soon after deposed the state governor, but had to flee to Durango two months later. In the late 1860s the conservative General Cajen briefly entered the state after his campaign through the state of Jalisco and helped establish conservative politicians and ran out the liberal leaders Jesús González Ortega and José María Patoni. Cajen took possession of the state capital and established himself as governor; he brooked no delay in uniting a large force to combat the liberal forces which he defeated in ''La Batalla del Gallo''. Cajen attained several advantages over the liberals within the state, but soon lost his standing due to a strong resurgence of the liberal forces within the state. The successful liberal leaders José María Patoni of Durango and J.E. Muñoz of Chihuahua quickly strengthened their standing by limiting the political rights of the clergy implementing the presidential decree. The state elected General Luis Terrazas
Luis Terrazas (20 July 1829 in Chihuahua, Mexico – 18 June 1923 in Chihuahua) was a Mexican politician, businessman, rancher, and soldier.
Career
Terrazas was a pivotal figure in the history of the state of Chihuahua from the middle ...
, a liberal leader, as governor; he would continue to fight small battles within the state to suppress conservative uprisings during 1861.
In consequence to the Reform War, the federal government was bankrupt and could not pay its foreign debts to Spain, England, and France. On July 17, 1861, President Juárez decreed a moratorium on payment to foreign debtors for a period of two years. Spain, England, and France did not accept the moratorium by Mexico; they united at the Convention of the Triple Alliance on October 31, 1861 in which they agreed to take possession of several custom stations within Mexico as payment. A delegation of the Triple Alliance arrived in Veracruz in December 1861. President Juárez immediately sent his Foreign Affairs Minister, Manuel Doblado, who is able to reduce the debts through the Pacto de Soledad (Soledad Pact). General Juan Prim
Juan Prim y Prats, 1st Count of Reus, 1st Marquis of los Castillejos, 1st Viscount of Bruch (; ; 6 December 1814 – 30 December 1870) was a Spanish general and statesman who was briefly Prime Minister of Spain until his assassination.
Bio ...
of Spain persuaded the English delegation to accept the terms of the Pacto de Soledad, but the French delegation refused.
The liberal political forces maintained strong control over the state government until shortly after the French Intervention which turned the tables in favor to the conservative forces once again. The intervention had serious repercussions for the state of Chihuahua. President Juárez, in an effort to organize a strong defense against the French, decreed a list of national guard units that every state had to contribute to the Ministry of War and the Navy; Chihuahua was responsible for inducting 2,000 men. Regaining power, Governor Luis Terrazas
Luis Terrazas (20 July 1829 in Chihuahua, Mexico – 18 June 1923 in Chihuahua) was a Mexican politician, businessman, rancher, and soldier.
Career
Terrazas was a pivotal figure in the history of the state of Chihuahua from the middle ...
assigned the First Battalion of Chihuahua for integration into the national army led by General Jesús González Ortega; the battalion was deployed to Puebla. After the defeat of the army in Puebla, the Juárez administration was forced to abandon Mexico City; the president retreated further north seeking refuge in the state of Chihuahua.
Under threat from the conservative forces, Governor Terrazas was deposed, and the state legislature proclaimed martial law in the state in April 1864 and established Jesús José Casavantes as the new governor. In response, José María Patoni decided to march to Chihuahua with presidential support. Meanwhile, Maximilian von Habsburg, a younger brother of the Emperor of Austria, was proclaimed Emperor Maximilian I of Mexico on April 10, 1864 with the backing of Napoleon III and a group of Mexican conservatives. Before President Benito Juárez
Benito Pablo Juárez García (; 21 March 1806 – 18 July 1872) was a Mexican politician, military commander, and lawyer who served as the 26th president of Mexico from 1858 until his death in office in 1872. A Zapotec peoples, Zapotec, he w ...
was forced to flee, Congress granted him an emergency extension of his presidency, which would go into effect in 1865 when his term expired, and last until 1867. At the same time, the state liberals and conservatives compromised to allow the popular Ángel Trías take the governorship; by this time the French forces had taken control over the central portions of the country and were making preparations to invade the northern states.
Saltillo
Saltillo () is the capital and largest city of the northeastern Mexican state of Coahuila and is also the municipal seat of the municipality of the same name. Mexico City, Monterrey, and Saltillo are all connected by a major railroad and high ...
. On September 21, 1864, José María Patoni and Jesús González Ortega lost against the French forces at the Battle of Estanzuelas; the supreme government led by President Juárez was forced to evacuate the city of Saltillo
Saltillo () is the capital and largest city of the northeastern Mexican state of Coahuila and is also the municipal seat of the municipality of the same name. Mexico City, Monterrey, and Saltillo are all connected by a major railroad and high ...
and relocate to Chihuahua. Juárez stopped in Ciudad Jiménez, Valle de Allende, and Hidalgo de Parral, in turn. He decreed Parral the capital of Mexico from October 2–5, 1864. Perceiving the threat from the advancing French forces, the president continued his evacuation through Santa Rosalía de Camargo, Santa Cruz de Rosales, and finally Chihuahua, Chihuahua
The city of Chihuahua or Chihuahua City ( ; Lipan language, Lipan: ) is the state capital of the Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. , the city of Chihuahua had a population of 925,762 inhabitants. while the metropolitan area had a popu ...
. On October 12, 1864, the people of the state gave President Juárez an overwhelmingly supportive reception, led by Governor Ángel Trías. On October 15, 1864 the city of Chihuahua was declared the temporary capital of Mexico.
After running imperial military affairs in the states of Coahuila and Durango, General Agustín Enrique Brincourt made preparations to invade the state of Chihuahua. On July 8, 1865 Brincourt crossed the Nazas River in northern Durango, heading toward Chihuahua. On July 22 Brincourt crossed the banks of Río Florido into Ciudad Jiménez; one day later he arrived at Valle de Allende where he sent Colonel Pyot with a garrison to take control of Hidalgo del Parral. Brincourt continued through Santa Rosalía de Camargo and Santa Cruz de Rosales. President Juárez remained in the state capital until August 5, 1865 when he left for El Paso del Norte (present-day Ciudad Juárez
Ciudad Juárez ( , ; "Juárez City"), commonly referred to as just Juárez (Lipan language, Lipan: ''Tsé Táhú'ayá''), is the most populous city in the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. It was k ...
) due to evidence that the French were to attack the city. On the same day, the President named General Manuel Ojinaga the new governor and placed him in charge of all the republican forces. Meanwhile, General Villagran surprised the imperial forces in control of Hidalgo de Parral; after a short two-hour battle, Colonel Pyot was defeated and forced to retreat. At the Battle of Parral, the French lost 55 men to the Republican forces. On August 13, 1865, the French forces with an estimated 2,500 men arrived at the outskirts of Chihuahua City, and on August 15, 1865, General Brincourt defeated the republican forces, taking control of the state capital. Brincourt designated Tomás Zuloaga as Prefect of Chihuahua. Fearing the French would continue their campaign to El Paso del Norte, President Juárez relocated to El Carrizal, a secluded place in the mountains near El Paso del Norte, in August 1865, . It would have been easy for the French forces to continue in pursuit of President Juárez across the border, but they feared altercations with American forces. General François Achille Bazaine
François Achille Bazaine (13 February 181123 September 1888) was an officer of the French army. Rising from the ranks, during four decades of distinguished service (including 35 years on campaign) under Louis-Philippe I, Louis-Philippe and then ...
ordered the French troops to retreat back to the state of Durango after only reaching a point one days travel north of Chihuahua City. General Brincourt asked for 1,000 men to be left behind to help maintain control over the state, but his request was denied. After the death of General Ojinaga, the Republican government declared General Villagran in charge of the fight against the Imperial forces. The French left the state on October 29, 1865. President Juárez returned to Chihuahua City on November 20, 1865 and remained in the city until December 9, 1865 when he returned to El Paso del Norte. Shortly after the president left Chihuahua City, Terrazas was restored as governor of the state on December 11, 1865.
Maximilian was deeply dissatisfied with General Bazaine's decision to abandon the state capital of Chihuahua and immediately ordered Agustín B. Billaut to recapture the city. On December 11, 1865, Billaut with a force of 500 men took control of the city. By January 31, 1866 Billaut was ordered to leave Chihuahua, but he left behind 500 men to maintain control. At the zenith of their power, the imperialist forces controlled all but four states in Mexico; the only states to maintain strong opposition to the French were: Guerrero, Chihuahua, Sonora, and Baja California.
 President Juárez once again based his government in the state of Chihuahua and it served as the center for the resistance against the French invasion throughout Mexico. On March 25, 1866, a battle ensued in the Plaza de Armas in the center of Chihuahua City between the French imperial forces that were guarding the plaza and the Republican forces led by General Terrazas. Being completely caught off guard, the French imperial forces sought refuge by bunkering themselves in the Cathedral of the Holy Cross, Our Lady of Regla, and St Francis of Assisi and made it almost impossible to penetrate their defenses. General Terrazas then decided to fire a heavy artillery barrage with 8 kg cannonballs. The first cannon fired hit a bell in the tower of the church, instantly breaking it in half; soon after, 200 men of the imperial army forces surrendered. The republican forces had recovered control over the state capital. The bell in the church was declared a historical monument and can be seen today in the Cathedral. By April 1866, the state government had established a vital trading route from Chihuahua City to San Antonio, Texas; the government began to replenish their supplies and reinforce their fight against the Imperial forces.
General Aguirre moved to the deserts of the southeastern portion of the state and defeated the French forces in Parral, led by Colonel Cottret. By the middle of 1866, the state of Chihuahua was declared free of enemy control; Parral was the last French stronghold within the state. On June 17, 1866, President Juárez arrived in Chihuahua City and remained in the capital until December 10, 1866. During his two years in the state of Chihuahua, President Juárez passed ordinances regarding the rights of adjudication of property and nationalized the property of the clergy. The distance of the French forces and their allies allowed the Ministry of War, led by General Negrete, to reorganize the state's national guard into the Patriotic Battalion of Chihuahua, which was deployed to fight in the battle of
President Juárez once again based his government in the state of Chihuahua and it served as the center for the resistance against the French invasion throughout Mexico. On March 25, 1866, a battle ensued in the Plaza de Armas in the center of Chihuahua City between the French imperial forces that were guarding the plaza and the Republican forces led by General Terrazas. Being completely caught off guard, the French imperial forces sought refuge by bunkering themselves in the Cathedral of the Holy Cross, Our Lady of Regla, and St Francis of Assisi and made it almost impossible to penetrate their defenses. General Terrazas then decided to fire a heavy artillery barrage with 8 kg cannonballs. The first cannon fired hit a bell in the tower of the church, instantly breaking it in half; soon after, 200 men of the imperial army forces surrendered. The republican forces had recovered control over the state capital. The bell in the church was declared a historical monument and can be seen today in the Cathedral. By April 1866, the state government had established a vital trading route from Chihuahua City to San Antonio, Texas; the government began to replenish their supplies and reinforce their fight against the Imperial forces.
General Aguirre moved to the deserts of the southeastern portion of the state and defeated the French forces in Parral, led by Colonel Cottret. By the middle of 1866, the state of Chihuahua was declared free of enemy control; Parral was the last French stronghold within the state. On June 17, 1866, President Juárez arrived in Chihuahua City and remained in the capital until December 10, 1866. During his two years in the state of Chihuahua, President Juárez passed ordinances regarding the rights of adjudication of property and nationalized the property of the clergy. The distance of the French forces and their allies allowed the Ministry of War, led by General Negrete, to reorganize the state's national guard into the Patriotic Battalion of Chihuahua, which was deployed to fight in the battle of Matamoros, Tamaulipas
Matamoros, officially known as Heroica Matamoros, is a city in the northeastern Mexican state of Tamaulipas, and the municipal seat of the homonymous municipality. It is on the southern bank of the Rio Grande, directly across the border from Bro ...
against the French. After a series of major defeats and an escalating threat from Prussia, France began pulling troops out of Mexico in late 1866. Disillusioned with the liberal political views of Maximilian, the Mexican conservatives abandoned him, and in 1867 the last of the Emperor's forces were defeated. Maximilian was sentenced to death by a military court; despite national and international pleas for amnesty, Juárez refused to commute the sentence. Maximilian was executed by firing squad on June 19, 1867.
Juárez Government
 President Benito Juárez was re-elected in the general election of 1867 in which he received strong liberal support, especially in Chihuahua. Luis Terrazas was confirmed by the people of Chihuahua to be governor of the state. But soon after the election, President Juárez had another crisis on his hands; the Juárez administration was suspected to be involved in the assassination of the military chief José María Patoni executed by General Canto in August 1868. General Canto turned himself over to Donato Guerra. Canto was sentenced to death, but later his sentence changed to 10 years imprisonment. The sense of injustice gave rise to a new rebellion in 1869 that threatened the federal government. In response, the Juárez administration took drastic measures by temporarily suspending constitutional rights, but the governor of Chihuahua did not support this action. Hostilities continued to increase especially after the election of 1871 which was perceived to be fraudulent. A new popular leader arose among the rebels, Porfirio Díaz. The federal government was successful in quelling rebellions in Durango and Chihuahua. On July 18, 1872, President Juárez died from a heart attack; soon after, many of his supporters ceased the fighting. Peace returned to Chihuahua and the new government was led by Governor Antonio Ochoa (formerly a co-owner of the Batopilas silver mines) in 1873 after Luis Terrazas finished his term in 1872.
But the peace in the state did not last long, the elections of 1875 caused new hostilities. Ángel Trías led a new movement against the government in June 1875 and maintained control over the government until September 18, 1875 when Donato Guerra the orchestrator of the Revolution of the North was captured. Donato Guerra was assassinated in a suburb of Chihuahua City where he was incarcerated for conspiring with Ángel Trías. During October 1875 several locations were controlled by rebel forces, but the government finally regained control on November 25, 1875.
President Benito Juárez was re-elected in the general election of 1867 in which he received strong liberal support, especially in Chihuahua. Luis Terrazas was confirmed by the people of Chihuahua to be governor of the state. But soon after the election, President Juárez had another crisis on his hands; the Juárez administration was suspected to be involved in the assassination of the military chief José María Patoni executed by General Canto in August 1868. General Canto turned himself over to Donato Guerra. Canto was sentenced to death, but later his sentence changed to 10 years imprisonment. The sense of injustice gave rise to a new rebellion in 1869 that threatened the federal government. In response, the Juárez administration took drastic measures by temporarily suspending constitutional rights, but the governor of Chihuahua did not support this action. Hostilities continued to increase especially after the election of 1871 which was perceived to be fraudulent. A new popular leader arose among the rebels, Porfirio Díaz. The federal government was successful in quelling rebellions in Durango and Chihuahua. On July 18, 1872, President Juárez died from a heart attack; soon after, many of his supporters ceased the fighting. Peace returned to Chihuahua and the new government was led by Governor Antonio Ochoa (formerly a co-owner of the Batopilas silver mines) in 1873 after Luis Terrazas finished his term in 1872.
But the peace in the state did not last long, the elections of 1875 caused new hostilities. Ángel Trías led a new movement against the government in June 1875 and maintained control over the government until September 18, 1875 when Donato Guerra the orchestrator of the Revolution of the North was captured. Donato Guerra was assassinated in a suburb of Chihuahua City where he was incarcerated for conspiring with Ángel Trías. During October 1875 several locations were controlled by rebel forces, but the government finally regained control on November 25, 1875.
Porfiriato
 After the death of the president Benito Juárez in 1872, the first magistracy of the country was occupied by the vice-president Sebastián Lerdo de Tejada, who called for new elections. Two candidates were registered; Lerdo de Tejada and General
After the death of the president Benito Juárez in 1872, the first magistracy of the country was occupied by the vice-president Sebastián Lerdo de Tejada, who called for new elections. Two candidates were registered; Lerdo de Tejada and General Porfirio Díaz
José de la Cruz Porfirio Díaz Mori (; ; 15 September 1830 – 2 July 1915) was a General (Mexico), Mexican general and politician who was the dictator of Mexico from 1876 until Mexican Revolution, his overthrow in 1911 seizing power in a Plan ...
, one of the heroes of the Battle of Puebla
The Battle of Puebla (; ), also known as the Battle of May 5 () took place on 5 May 1862, near Puebla de los Ángeles, during the second French intervention in Mexico. French troops under the command of Charles de Lorencez repeatedly failed to s ...
which had taken place on May 5, 1862. Lerdeo de Tejada won the election, but lost popularity after he announced his intent to run for re-election. On March 21, 1876, Don Porfirio Díaz rebelled against President Sebastián Lerdo de Tejada. The Plan of Tuxtepec defended the "No Re-election" principle. On June 2, 1876 the garrisons in the state of Chihuahua surrendered to the authority of General Porfirio Díaz; Governor Antonio Ochoa was arrested until all the Lerdista forces were suppressed throughout the state. Porfirio Díaz then helped Trías regain the governorship of the state of Chihuahua allowing for the Plan of Tuxtepec to be implemented. The victory of the Plan of Tuxtepec, gave the interim presidency to José María Iglesias and later, as the only candidate, the General Porfirio Díaz assumed the presidency on May 5, 1877.
During the first years of the Porfiriato
The Porfiriato or Porfirismo (, ), coined by Mexican historian Daniel Cosío Villegas, is a term given to the period when General Porfirio Díaz ruled Mexico under an Authoritarianism, authoritarian military dictatorship in the late 19th and e ...
(Porfirio Díaz Era), the Díaz administration had to combat several attacks from the Lerdista forces and the Apache. A new rebellion led by the Lerdista party was orchestrated from exile in the United States. The Lerdista forces were able to temporarily occupy the city of El Paso del Norte until mid-1877. During 1877 the northern parts of the state suffered through a spell of extreme drought which were responsible for many deaths in El Paso del Norte.
 The officials in Mexico City reduced the price of corn from six cents to two cents a pound. The northern portion of the state continued to decline economically which led to another revolt led by G. Casavantes in August 1879; Governor Trías was accused of misappropriation of funds and inefficient administration of the state. Casavantes took the state capital and occupied it briefly; he was also successful in forcing Governor Trías to exile. Shortly afterwards, the federal government sent an entourage led by Treviño; Casavantes was immediately ordered to resign his position. Casavantes declared political victory as he was able to publicly accuse and depose Governor Trías. At the same time the states of Durango and Coahuila had a military confrontation over territorial claims and water rights; this altercation between the state required additional federal troops to stabilize the area. Later a dispute ensued again among the states of Coahuila, Durango, and Chihuahua over the mountain range area known as Sierra Mojada, when large deposits of gold ore was discovered. The state of Chihuahua officially submitted a declaration of protest in May 1880 that shortly after was amicably settled. Despite the difficulties at the beginning, Díaz was able to secure and stabilize the state, which earned the confidence and support of the people.
During the 1880s, the Díaz administration consolidated several government agencies throughout Mexico to control credit and currency by the creation of the Institution of Credit and Currency. Because Díaz had created such an effective centralized government, he was able to concentrate decision making and maintain control over the economic instability.
The officials in Mexico City reduced the price of corn from six cents to two cents a pound. The northern portion of the state continued to decline economically which led to another revolt led by G. Casavantes in August 1879; Governor Trías was accused of misappropriation of funds and inefficient administration of the state. Casavantes took the state capital and occupied it briefly; he was also successful in forcing Governor Trías to exile. Shortly afterwards, the federal government sent an entourage led by Treviño; Casavantes was immediately ordered to resign his position. Casavantes declared political victory as he was able to publicly accuse and depose Governor Trías. At the same time the states of Durango and Coahuila had a military confrontation over territorial claims and water rights; this altercation between the state required additional federal troops to stabilize the area. Later a dispute ensued again among the states of Coahuila, Durango, and Chihuahua over the mountain range area known as Sierra Mojada, when large deposits of gold ore was discovered. The state of Chihuahua officially submitted a declaration of protest in May 1880 that shortly after was amicably settled. Despite the difficulties at the beginning, Díaz was able to secure and stabilize the state, which earned the confidence and support of the people.
During the 1880s, the Díaz administration consolidated several government agencies throughout Mexico to control credit and currency by the creation of the Institution of Credit and Currency. Because Díaz had created such an effective centralized government, he was able to concentrate decision making and maintain control over the economic instability.
 The Díaz administration made political decisions and took legal measures that allowed the elite throughout Mexico to concentrate the nation's wealth by favoring monopolies. During this time, two-fifths of the state's territory was divided among 17 rich families which owned practically all of the arable land in Chihuahua. The state economy grew at a rapid pace during the Porfiriato; the economy in Chihuahua was dominated by agriculture and mining. The Díaz administration helped Governor
The Díaz administration made political decisions and took legal measures that allowed the elite throughout Mexico to concentrate the nation's wealth by favoring monopolies. During this time, two-fifths of the state's territory was divided among 17 rich families which owned practically all of the arable land in Chihuahua. The state economy grew at a rapid pace during the Porfiriato; the economy in Chihuahua was dominated by agriculture and mining. The Díaz administration helped Governor Luis Terrazas
Luis Terrazas (20 July 1829 in Chihuahua, Mexico – 18 June 1923 in Chihuahua) was a Mexican politician, businessman, rancher, and soldier.
Career
Terrazas was a pivotal figure in the history of the state of Chihuahua from the middle ...
by funding the Municipal Public Library in Chihuahua City and passing a federal initiative for the construction of the railroad from Chihuahua City to Ciudad Júarez. By 1881, the Central Mexican Railroad was completed which connected Mexico City to Ciudad Juárez. In 1883 telephone lines were installed throughout the state, allowing communication between Chihuahua City and Aldama. By 1888 the telephone services were extended from the capital to the cities of Julimes, Meoqui, and Hidalgo del Parral; the telecommunication network in the state covered an estimated 3,500 kilometers. The need of laborers to construct the extensive infrastructure projects resulted in a significant Asian immigration, mostly from China. Asian immigrants soon become integral to the state economy by opening restaurants, small grocery stores, and hotels. By the end of the Terrazas term, the state experienced an increase in commerce, mining, and banking. When the banks were nationalized, Chihuahua became the most important banking state in Mexico.
Under Governor Miguel Ahumada, the education system in the state was unified and brought under tighter control by the state government, and the metric system was standardized throughout the state to replace the colonial system of weights and measures. On September 16, 1897, the Civilian Hospital of Chihuahua was inaugurated in Chihuahua City and became known among the best in the country. In 1901 the Heroes Theater (Teatro de los Héroes) opened in Chihuahua City. On August 18, 1904, Governor Terrazas was replaced by Governor Enrique C. Creel. From 1907 to 1911, the Creel administration succeeded in advancing the state's legal system, modernizing the mining industry, and raising public education standards. In 1908 the Chihuahuan State Penitentiary was built, and the construction on the first large scale dam project was initiated on the Chuviscar River. During the same time, the streets of Chihuahua City were paved and numerous monuments were built in Chihuahua City and Ciudad Juárez.
Mexican Revolution
 Díaz created an effective centralized government that helped concentrate wealth and political power among the elite upper class, mostly
Díaz created an effective centralized government that helped concentrate wealth and political power among the elite upper class, mostly criollo
Criollo or criolla (Spanish for creole) may refer to:
People
* Criollo people, a social class in the Spanish colonial system.
Animals
* Criollo duck, a species of duck native to Central and South America.
* Criollo cattle, a group of cattle bre ...
. The economy was characterized by the construction of factories, roads, dams, and better farms. The Díaz administration passed new land laws that virtually unraveled all the rights previously recognized and the land reforms passed by President Benito Juárez. No peasant or farmer could claim the land he occupied without formal legal title.
 A handful of families owned large estates (known as
A handful of families owned large estates (known as hacienda
A ''hacienda'' ( or ; or ) is an estate (or '' finca''), similar to a Roman '' latifundium'', in Spain and the former Spanish Empire. With origins in Andalusia, ''haciendas'' were variously plantations (perhaps including animals or orchards ...
s) and controlled the greater part of the land across the state while the vast majority of Chihuahuans were landless. The state economy was largely defined by ranching and mining. At the expense of the working class
The working class is a subset of employees who are compensated with wage or salary-based contracts, whose exact membership varies from definition to definition. Members of the working class rely primarily upon earnings from wage labour. Most c ...
, the Díaz administration promoted economic growth by encouraging investment from foreign companies from the United Kingdom, France, Imperial Germany
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
and the United States. The proletariat
The proletariat (; ) is the social class of wage-earners, those members of a society whose possession of significant economic value is their labour power (their capacity to work). A member of such a class is a proletarian or a . Marxist ph ...
was often exploited, and found no legal protection or political recourse to redress injustices.
Despite the internal stability (known as the ''paz porfiriana''), modernization, and economic growth in Mexico during the Porfiriato from 1876 to 1910, many across the state became deeply dissatisfied with the political system. When Díaz first ran for office, he committed to a strict "No Re-election" policy in which he disqualified himself to serve consecutive terms. Eventually backtracking on many of his initial political positions Díaz became a de facto dictator. Díaz became increasingly unpopular due to brutal suppression of political dissidents by using the Rurales
In Mexico, the term ''Rurales'' ( Spanish) is used to refer to two armed government forces. The historic Guardia Rural ('Rural Guard') was a rural mounted police force, founded by President Benito Juárez in 1861 and expanded by President Porf ...
and manipulating the elections to solidify his political machine. The working class was frustrated with the Díaz regime due to the corruption of the political system that had increased the inequality between the rich and poor. The peasants felt disenfranchised by the policies that promoted the unfair distribution of land where 95% of the land was owned by the top 5%.
The end of the ''Porfiriato'' came in 1910 with the beginning of the Mexican Revolution. Díaz had stated that Mexico was ready for democracy and he would step down to allow other candidates to compete for the presidency, but Díaz decided to run again in 1910 for the last time against Francisco I. Madero. During the campaign Díaz incarcerated Madero on election day in 1910. Díaz was announced the winner of the election by a landslide, triggering the revolution. Madero supporter Toribio Ortega took up arms with a group of followers at Cuchillo Parado, Chihuahua on November 10, 1910.
 In response to Madero's letter to action,
In response to Madero's letter to action, Pascual Orozco
Pascual Orozco Vázquez, Jr. (in contemporary documents, sometimes spelled "Oroszco") (28 January 1882 – 30 August 1915) was a Mexican revolutionary leader who rose up to support Francisco I. Madero in late 1910 to depose long-time presid ...
(a wealthy mining baron) and Chihuahua Governor Abraham González formed a powerful military union in the north, taking military control of several northern Mexican cities with other revolutionary leaders, including Pancho Villa
Francisco "Pancho" Villa ( , , ; born José Doroteo Arango Arámbula; 5 June 1878 – 20 July 1923) was a Mexican revolutionary and prominent figure in the Mexican Revolution. He was a key figure in the revolutionary movement that forced ...
. Against Madero's wishes, Orozco and Villa fought for and won Ciudad Juárez. After militias loyal to Madero defeated the Mexican federal army, on May 21, 1911, Madero signed the Treaty of Ciudad Juárez with Díaz. It required that Díaz abdicate his rule and be replaced by Madero. Insisting on a new election, Madero won overwhelmingly in late 1911, and he established a liberal democracy and received support from the United States and popular leaders such as Orozco and Villa. Orozco eventually became disappointed with the Madero's government and led a rebellion against him. He organized his own army, called "Orozquistas"—also called the Colorados ("Red Flaggers")—after Madero refused to agree to social reforms calling for better working hours, pay and conditions. The rural working class, which had supported Madero, now took up arms against him in support of Orozco.
In March 1912, in Chihuahua, Gen. Pascual Orozco revolted. Immediately President Francisco Madero commanded Gen. Victoriano Huerta of the Federal Army, to put down the Orozco revolt. The governor of Chihuahua mobilized the state militia led by Colonel Pancho Villa to supplement General Huerta. By June, Villa notified Huerta that the Orozco revolt had been put down and that the militia would consider themselves no longer under Huerta's command and would depart. Huerta became furious and ordered that Villa be executed. Raúl Madero, Madero's brother, intervened to save Villa's life. Jailed in Mexico City, Villa fled to the United States. Madero's time as leader was short-lived, ended by a coup d'état in 1913 led by Gen. Victoriano Huerta
José Victoriano Huerta Márquez (; 23 December 1850 – 13 January 1916) was a Mexican general, politician, engineer and dictator who was the 39th President of Mexico, who came to power by coup against the democratically elected government of ...
; Orozco sided with Huerta, and Huerta made him one of his generals.Pascual Orozco : Faces of the Revolution : The Storm That Swept Mexico : PBS. On March 26, 1913,
Venustiano Carranza
José Venustiano Carranza de la Garza (; 29 December 1859 – 21 May 1920), known as Venustiano Carranza, was a Mexican land owner and politician who served as President of Mexico from 1917 until his assassination in 1920, during the Mexican Re ...
issued the Plan de Guadalupe, which refused to recognize Huerta as president and called for war between the two factions. Soon after the assassination of President Madero, Carranza returned to Mexico to fight Huerta, but with only a handful of comrades. However, by 1913 his forces had swelled into an army of thousands, called the División del Norte (Northern Division). Villa and his army, along with Emiliano Zapata
Emiliano Zapata Salazar (; 8 August 1879 – 10 April 1919) was a Mexican revolutionary. He was a leading figure in the Mexican Revolution of 1910–1920, the main leader of the people's revolution in the Mexican state of Morelos, and the insp ...
and Álvaro Obregón
Álvaro Obregón Salido (; 19 February 1880 – 17 July 1928) was a Mexican general, inventor and politician who served as the 46th President of Mexico from 1920 to 1924. Obregón was re-elected to the presidency in 1928 but was assassinated b ...
, united with Carranza to fight against Huerta. In March 1914 Carranza traveled to Ciudad Juárez, which served as rebellion's capital for the remainder of the struggle with Huerta. In April 1914 U.S. opposition to Huerta had reached its peak, blockading the regime's ability to resupply from abroad. Carranza trying to keep his nationalistic credentials threatened war with the United States. In his spontaneous response to U.S. President Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was the 28th president of the United States, serving from 1913 to 1921. He was the only History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democrat to serve as president during the Prog ...
Carranza asked "that the president withdraw American troops from Mexico."Carothers to Secretary of State, April 22, 1914, Wilson Papers, Ser. 2, as quoted in
The situation became so tense that war with the United States seemed imminent. On April 22, 1914, on the initiative of Felix A. Sommerfeld and Sherburne Hopkins, Pancho Villa traveled to Juárez to calm fears along the border and asked President Wilson's emissary George Carothers to tell "Señor Wilson" that he had no problems with the American occupation of Veracruz. Carothers wrote to Secretary William Jennings Bryan
William Jennings Bryan (March 19, 1860 – July 26, 1925) was an American lawyer, orator, and politician. He was a dominant force in the History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, running three times as the party' ...
: "As far as he was concerned we could keep Vera Cruz 'sic''and hold it so tight that not even water could get in to Huerta and . . . he could not feel any resentment". Whether trying to please the U.S. government or through the diplomatic efforts of Sommerfeld and Carothers, or maybe as a result of both, Villa stepped out from under Carranza's stated foreign policy.
 The uneasy alliance of Carranza, Obregón, Villa, and Zapata eventually led the rebels to victory. The fight against Huerta formally ended on August 15, 1914, when Álvaro Obregón signed a number of treaties in Teoloyucan in which the last of Huerta's forces surrendered to him and recognized the constitutional government. On August 20, 1914, Carranza made a triumphal entry into
The uneasy alliance of Carranza, Obregón, Villa, and Zapata eventually led the rebels to victory. The fight against Huerta formally ended on August 15, 1914, when Álvaro Obregón signed a number of treaties in Teoloyucan in which the last of Huerta's forces surrendered to him and recognized the constitutional government. On August 20, 1914, Carranza made a triumphal entry into Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city of Mexico, as well as the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North America. It is one of the most important cultural and finan ...
. Carranza (supported by Obregón) was now the strongest candidate to fill the power vacuum and set himself up as head of the new government. This government successfully printed money, passed laws, etc.
Villa and Carranza had different political goals causing Villa to become an enemy of Carranza. After Carranza took control in 1914, Villa and other revolutionaries who opposed him met at what was called the Convention of Aguascalientes
The Convention of Aguascalientes was a major meeting that took place during the Mexican Revolution between the factions in the Mexican Revolution that had defeated Victoriano Huerta's Federal Army and forced his resignation and exile in July 1914 ...
. The convention deposed Carranza in favor of Eulalio Gutiérrez. In the winter of 1914 Villa's and Zapata's troops entered and occupied Mexico City. Villa was forced from the city in early 1915 and attacked the forces of Gen. Obregón at the Battle of Celaya and was badly defeated in the bloodiest battle of the revolution, with thousands dead. With the defeat of Villa, Carranza seized power. A short time later the United States recognized Carranza as president of Mexico. Even though Villa's forces were badly depleted by his loss at Celaya, he continued his fight against the Carranza government. Finally, in 1920, Obregón—who had defeated him at Celaya—finally reached an agreement with Villa end his rebellion.
Public opinion pressured the U.S. government to bring Villa to justice for the raid on Columbus, New Mexico
Columbus is an incorporated village in Luna County, New Mexico, United States, about north of the Mexican border. It is considered a place of historical interest, as the scene of a 1916 attack by Mexican general Francisco "Pancho" Villa that ...
; U.S. President Wilson sent Gen. John J. Pershing and some 5,000 troops into Mexico in an unsuccessful attempt to capture Villa. It was known as the Punitive Expedition
A punitive expedition is a military journey undertaken to punish a political entity or any group of people outside the borders of the punishing state or union. It is usually undertaken in response to perceived disobedient or morally wrong beha ...
. After nearly a year of pursuing Villa, American forces returned to the United States. The American intervention had been limited to the western sierras of Chihuahua. Villa had the advantage of intimately knowing the inhospitable terrain of the Sonoran Desert and the almost impassable Sierra Madre mountains and always managed to stay one step ahead of his pursuers. In 1923 Villa was assassinated by a group of seven gunmen who ambushed him while he was sitting in the back seat of his car in Parral.
Modern
On February 6, 2010, formerGovernor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
José Reyes Baeza proposed to move the three State Powers (Executive, Legislative, and Judicial) from Chihuahua to Ciudad Juárez
Ciudad Juárez ( , ; "Juárez City"), commonly referred to as just Juárez (Lipan language, Lipan: ''Tsé Táhú'ayá''), is the most populous city in the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. It was k ...
in order to face the insecurity problems in Ciudad Juárez, but that request was rejected by the State Legislature on February 12.
Geography
The state of Chihuahua is the largest state in the country and is known as El Estado Grande (The Big State); it accounts for 12.6% of the land of Mexico and is slightly larger than theUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. The area is landlocked by the states of Sonora
Sonora (), officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Sonora (), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. The state is divided into Municipalities of Sonora, 72 ...
to the west, Sinaloa
Sinaloa (), officially the (), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, compose the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 18 municipalities, and its capital city is Culiacán Rosales.
It is located in northwest Mexic ...
to the south-west, Durango
Durango, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Durango, is one of the 31 states which make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico, situated in the northwest portion of the country. With a population of 1,832,650 ...
to the south, and Coahuila
Coahuila, formally Coahuila de Zaragoza, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Coahuila de Zaragoza, is one of the 31 states of Mexico. The largest city and State Capital is the city of Saltillo; the second largest is Torreón and the thi ...
to the east, and by the U.S. states of Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
to the northeast and New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ...
to the north. The state is made up of three geologic regions: Mountains, Plains-Valleys, and Desert, which occur in large bands from west to east. Because of the different geologic regions there are contrasting climates and ecosystems.
 The main mountain range in the state is the
The main mountain range in the state is the Sierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American C ...
reaching a maximum altitude of 10,826 ft (3,300 m) known as Cerro Mohinora. Mountains account for one third of the state's surface area which include large coniferous forests. The climate in the mountainous regions varies. Chihuahua has more forests than any other state in Mexico making the area a bountiful source of wood; the mountainous areas are rich in minerals important to Mexico's mining industry. Precipitation and temperature in the mountainous areas depends on the elevation. Between the months of November and March snow storms are possible in the lower elevations and are frequent in the higher elevations. There are several watersheds located in the Sierra Madre Occidental all of the water that flows through the state; most of the rivers finally empty into the Río Grande. Temperatures in some canyons in the state reach over in the summer while the same areas rarely drop below in the winter. Microclimates found in the heart of the Sierra Madre Occidental in the state could be considered tropical, and wild tropical plants have been found in some canyons. ''La Barranca del Cobre'', or Copper Canyon, a spectacular canyon system larger and deeper than the Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon is a steep-sided canyon carved by the Colorado River in Arizona, United States. The Grand Canyon is long, up to wide and attains a depth of over a mile ().
The canyon and adjacent rim are contained within Grand Canyon Nati ...
; the canyon also contains Mexico's two tallest waterfalls: Basaseachic Falls and Piedra Volada. There are two national parks found in the mountainous area of the state: Cumbres de Majalca National Park and Basaseachic Falls National Park.
 The plains at the foot of the Sierra Madre Occidental is an elongated mesa known as Altiplanicie Mexicana that exhibits a steppe climate and serves as a transition zone from the mountain climate in the western part of the state to the desert climate in the eastern side of the state. The steppe zone accounts for a third of the state's area, and it experiences pronounced dry and wet seasons. The pronounced rainy season in the steppe is usually observed in the months of July, August, and September. The steppe also encounters extreme temperatures that often reach over in the summer and drop below in the winter. The steppe zone is an important agriculture zone due to an extensive development of canals exploiting several rivers that flow down from the mountains. The steppe zone is the most populated area of the state.
The most important river in the state is Río Conchos which is the largest tributary to the Río Grande from the Mexican side; the river descends from the zenith of the Sierra Madre Occidental in the southwest part of the state and winds through the center of the state where the water is exploited in the steppe zone and it eventually empties into the Río Grande in the small desert town of Ojinaga.
The desert zone also accounts for about a third of the state's surface area. The Chihuahuan Desert is an international biome that also extends into the neighboring Mexican state of
The plains at the foot of the Sierra Madre Occidental is an elongated mesa known as Altiplanicie Mexicana that exhibits a steppe climate and serves as a transition zone from the mountain climate in the western part of the state to the desert climate in the eastern side of the state. The steppe zone accounts for a third of the state's area, and it experiences pronounced dry and wet seasons. The pronounced rainy season in the steppe is usually observed in the months of July, August, and September. The steppe also encounters extreme temperatures that often reach over in the summer and drop below in the winter. The steppe zone is an important agriculture zone due to an extensive development of canals exploiting several rivers that flow down from the mountains. The steppe zone is the most populated area of the state.
The most important river in the state is Río Conchos which is the largest tributary to the Río Grande from the Mexican side; the river descends from the zenith of the Sierra Madre Occidental in the southwest part of the state and winds through the center of the state where the water is exploited in the steppe zone and it eventually empties into the Río Grande in the small desert town of Ojinaga.
The desert zone also accounts for about a third of the state's surface area. The Chihuahuan Desert is an international biome that also extends into the neighboring Mexican state of Coahuila
Coahuila, formally Coahuila de Zaragoza, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Coahuila de Zaragoza, is one of the 31 states of Mexico. The largest city and State Capital is the city of Saltillo; the second largest is Torreón and the thi ...
and into the U.S. states of Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
and New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ...
. The desert zone is mainly of flat topography with some small mountain ranges that run north to south. The desert in the state varies slightly with a small variant in climate. The lower elevations of the desert zone are found in the north along the Rio Grande which experience hotter temperatures in the summer and winter while the southern portion of the desert zone experiences cooler temperatures due to its higher elevation. The Samalayuca dunes cover an area of about 150 km2; it is an impressive site of the Chihuahuan Desert and is a protected area by the state due to unique species of plants and animals.
Climate
Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
the state has five major climate zones. The Sierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American C ...
dominates the western part of the state; there are two main climates in this area: Subtropical Highland (Cfb) and Humid Subtropical
A humid subtropical climate is a subtropical -temperate climate type, characterized by long and hot summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between la ...
(Cwa). There are some microclimates in the state due to the varying topology mostly found in the western side of the state. The two best known microclimates are: Tropical savanna climate
Tropical savanna climate or tropical wet and dry climate is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification categories ''Aw'' (for a dry "winter") and ''As'' (for a dry "summer"). The driest month has less than ...
(Aw) in deep canyons located in the extreme southern part of the state; Continental Mediterranean climate (Dsb) in the extremely high elevations of the Sierra Madre Occidental. Satellite image to the right shows the vegetation is much greener in the west because of the cooler temperatures and larger amounts of precipitation as compared to the rest of the state.
In the far eastern part of the state the Chihuahuan Desert dominates due to low precipitation and extremely high temperatures; some areas of the eastern part of the state are so dry no vegetation is found like the Sand Dunes of Samalayuca. There are two distinctive climate zones found in the eastern part of the state: Hot Desert (BWh) and Cool Desert (BWk) which are differentiated by average annual temperature due to differences in elevation. There is a transition zone in the middle of the state between the two extremely different climates from the east and west; this zone is the Steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without closed forests except near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the tropical and subtropica ...
characterized by a compromise between juxtaposed climate zones.

 *Subtropical Highland ( Cfb) most common at elevations above above sea level; this climate zone has warm summers reaching a maximum temperature of and summer lows of . Heavy rainstorms are observed from July to September. Winters are cold reaching a maximum low of and a maximum high of . During the winter months many snowstorms are observed with typically of snow per season.
*Humid Subtropical ( Cwa) climate is most common at elevations between above sea level; this climate zone has warm humid summers and an average summer temperature of . The summer average precipitation is , mostly in the months of: July, August, and September. From November to March there are many rainstorms and snowstorms caused by high elevation and prominent cold fronts. Winter temperatures can reach a low of .
*Semi-arid climate or Steppe ( BSk) is most common at elevations between above sea level; this climate zone has an annual average of and maximum temperatures above and lows reaching slightly below , with a wet season in the late summer and fall. Snowfall is rare but possible in the winter and frost is common from December to March. The annual average rainfall in the steppe climate zone is about .
*Hot Desert ( BWh) is most common at elevations below above sea level; this climate zone tends to have a hot summer at temperatures that often reach . Winter is warm, rarely dropping below . Precipitation averages 6–10 in. per year; most of the moisture falls during the monsoon of late summer.
*Cool Desert ( BWk) is most common at elevations above above sea level; this climate zone tends to have a mild summer, rarely reaching temperatures over . Winter weather varies from mild to cold depending on northern fronts, often dropping below . Precipitation averages 10–16 in. per year; most of the moisture falls during the monsoon of late summer.
*Subtropical Highland ( Cfb) most common at elevations above above sea level; this climate zone has warm summers reaching a maximum temperature of and summer lows of . Heavy rainstorms are observed from July to September. Winters are cold reaching a maximum low of and a maximum high of . During the winter months many snowstorms are observed with typically of snow per season.
*Humid Subtropical ( Cwa) climate is most common at elevations between above sea level; this climate zone has warm humid summers and an average summer temperature of . The summer average precipitation is , mostly in the months of: July, August, and September. From November to March there are many rainstorms and snowstorms caused by high elevation and prominent cold fronts. Winter temperatures can reach a low of .
*Semi-arid climate or Steppe ( BSk) is most common at elevations between above sea level; this climate zone has an annual average of and maximum temperatures above and lows reaching slightly below , with a wet season in the late summer and fall. Snowfall is rare but possible in the winter and frost is common from December to March. The annual average rainfall in the steppe climate zone is about .
*Hot Desert ( BWh) is most common at elevations below above sea level; this climate zone tends to have a hot summer at temperatures that often reach . Winter is warm, rarely dropping below . Precipitation averages 6–10 in. per year; most of the moisture falls during the monsoon of late summer.
*Cool Desert ( BWk) is most common at elevations above above sea level; this climate zone tends to have a mild summer, rarely reaching temperatures over . Winter weather varies from mild to cold depending on northern fronts, often dropping below . Precipitation averages 10–16 in. per year; most of the moisture falls during the monsoon of late summer.
Flora and fauna
 The state has a great diversity due to the large number of microclimates found and dramatic varying terrain. The flora throughout the
The state has a great diversity due to the large number of microclimates found and dramatic varying terrain. The flora throughout the Sierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American C ...
mountain range varies with elevation. Pine (''Pinus
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae.
''World Flora Online'' accepts 134 species-rank taxa (119 species and 15 nothospecies) of pines as c ...
'') and oak (''Quercus
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
'') species are usually found at an elevation of 2,000 m (6,560 ft) above sea level. The most common species of flora found in the mountains are: ''Pinus
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae.
''World Flora Online'' accepts 134 species-rank taxa (119 species and 15 nothospecies) of pines as c ...
'', ''Quercus
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
'', ''Abies
Firs are evergreen coniferous trees belonging to the genus ''Abies'' () in the family Pinaceae. There are approximately 48–65 extant species, found on mountains throughout much of North and Central America, Eurasia, and North Africa. The genu ...
'', ''Ficus
''Ficus'' ( or ) is a genus of about 850 species of woody trees, shrubs, vines, epiphytes and hemiepiphytes in the family (biology), family Moraceae. Collectively known as fig trees or figs, they are native throughout the tropics with a few spe ...
'', ''Vachellia
''Vachellia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae, commonly known as thorn trees or acacias. It belongs to the subfamily Mimosoideae. Its species were considered members of genus '' Acacia'' until 2009. ''Vachellia'' ...
'', Ipomoea
''Ipomoea'' () is the largest genus in the plant family Convolvulaceae, with over 600 species. It is a large and diverse group, with common names including morning glory, Ipomoea aquatica, water convolvulus or water spinach, sweet potato, ...
, ''Acacia
''Acacia'', commonly known as wattles or acacias, is a genus of about of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa, South America, and Austral ...
'', ''Lysiloma
''Lysiloma'' is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Fabaceae.
The genus is native to the Americas, and species range from Arizona and New Mexico through Mexico and Central America to Costa Rica, and in Florida, Cuba, Hispaniola, ...
'', ''Bursera
''Bursera'' is a genus with about 100 described species of flowering shrubs and trees varying in size up to high. It is the type genus for Burseraceae. The trees are native (often for many species endemic) to the Americas, from the southern Uni ...
'', ''Vitex
''Vitex'' is a genus of flowering plants in the sage family Lamiaceae. It has about 250 species.Raymond M. Harley, Sandy Atkins, Andrey L. Budantsev, Philip D. Cantino, Barry J. Conn, Renée J. Grayer, Madeline M. Harley, Rogier P.J. de Kok, Tat ...
'', ''Tabebuia
''Tabebuia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the Family (biology), family Bignoniaceae.Eberhard Fischer, Inge Theisen, and Lúcia G. Lohmann. 2004. "Bignoniaceae". pages 9-38. In: Klaus Kubitzki (editor) and Joachim W. Kadereit (volume editor) ...
'', '' Sideroxylon'', ''Cordia
''Cordia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the borage family, Boraginaceae. It contains 228 species of shrubs and trees, that are found in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide. Many of the species are commonly called manjack, while may ...
'', ''Fouquieria
''Fouquieria'' is a genus of 11 species of desert Flowering plant, flowering plants, the sole genus in the Family (biology), family Fouquieriaceae. The genus is native to North America and includes the ocotillo (''Fouquieria splendens, F. splende ...
'', '' Pithecellobium''. The state is home to one of the largest variation species of the genus ''Pinus
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae.
''World Flora Online'' accepts 134 species-rank taxa (119 species and 15 nothospecies) of pines as c ...
'' in the world. The lower elevations have a steppe vegetation with a variety of grasses and small bushes. Several species of ''Juniperus
Junipers are coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Juniperus'' ( ) of the cypress family Cupressaceae. Depending on the taxonomy, between 50 and 67 species of junipers are widely distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere as far south ...
'' dot the steppe and the transition zone.
According to the World Wide Fund for Nature
The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) is a Swiss-based international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named th ...
, the Chihuahuan Desert may be the most biologically diverse desert in the world, whether measured on species richness or endemism, although the region has been heavily degraded over time. Many native species have been replaced with creosote shrubs. The most common desert flora in the state includes: ''Agave
''Agave'' (; ; ) is a genus of monocots native to the arid regions of the Americas. The genus is primarily known for its succulent and xerophytic species that typically form large Rosette (botany), rosettes of strong, fleshy leaves.
Many plan ...
'', ''Larrea
''Larrea'' is a genus of flowering plants in the caltrop family, Zygophyllaceae. It contains five species of evergreen shrubs that are native to the Americas. The generic name honours Bishop Juan Antonio Hernández Pérez de Larrea, a patron of ...
'', '' Prosopis'', ''Fouquieria
''Fouquieria'' is a genus of 11 species of desert Flowering plant, flowering plants, the sole genus in the Family (biology), family Fouquieriaceae. The genus is native to North America and includes the ocotillo (''Fouquieria splendens, F. splende ...
'', ''Dasylirion
''Dasylirion'' is a genus of succulent, rosette-forming plants in the Asparagaceae family (where it is included in the Nolinoideae subfamily). Most species are native to mountainous arid regions of Mexico, with some species also native to the Sou ...
'', ''Yucca
''Yucca'' ( , YUCK-uh) is both the scientific name and common name for a genus native to North America from Panama to southern Canada. It contains 50 accepted species. In addition to yucca, they are also known as Adam's needle or Spanish-bayon ...
'', ''Poaceae
Poaceae ( ), also called Gramineae ( ), is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos, the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivate ...
'', '' Lophophora'', ''Opuntia
''Opuntia'', commonly called the prickly pear cactus, is a genus of flowering plants in the cactus family Cactaceae, many known for their flavorful fruit and showy flowers. Cacti are native to the Americas, and are well adapted to arid clima ...
'', '' Echinocereus'', '' Baileya'', '' Chilopsis'', '' Eucnide'', and '' Hylocereus''.
 The fauna in the state is just as diverse as the flora and varies greatly due to the large contrast in climates. In the mountain zone of the state the most observed mammals are: Mexican fox squirrel ('' Sciurus nayaritensis''), antelope jackrabbit ('' Lepus alleni''), raccoon ('' Procyon lotor''), hooded skunk ('' Mephitis macroura''), collared peccary ('' Dicotyles tajacu''), white-tailed deer ('' Odocoileus virginianus''), mule deer ('' Odocoileus hemionus''), American bison ('' Bison bison''), cougar (''
The fauna in the state is just as diverse as the flora and varies greatly due to the large contrast in climates. In the mountain zone of the state the most observed mammals are: Mexican fox squirrel ('' Sciurus nayaritensis''), antelope jackrabbit ('' Lepus alleni''), raccoon ('' Procyon lotor''), hooded skunk ('' Mephitis macroura''), collared peccary ('' Dicotyles tajacu''), white-tailed deer ('' Odocoileus virginianus''), mule deer ('' Odocoileus hemionus''), American bison ('' Bison bison''), cougar (''Puma concolor
The cougar (''Puma concolor'') (, '' KOO-gər''), also called puma, mountain lion, catamount and panther is a large small cat native to the Americas. It inhabits North, Central and South America, making it the most widely distributed wil ...
''), jaguar (''Panthera onca
The jaguar (''Panthera onca'') is a large cat species and the only living member of the genus ''Panthera'' that is native to the Americas. With a body length of up to and a weight of up to , it is the biggest cat species in the Americas a ...
''), eastern cottontail (''Sylvilagus floridanus
The eastern cottontail (''Sylvilagus floridanus'') is a New World cottontail rabbit, a member of the family Leporidae. It is the most common rabbit species in North America.
Distribution
The eastern cottontail can be found in meadows and shrubby ...
''), North American porcupine ('' Erethizon dorsatum''), bobcat ('' Lynx rufus''), Mexican wolf ('' Canis lupus baileyi''), and coyote (''Canis latrans
The coyote (''Canis latrans''), also known as the American jackal, prairie wolf, or brush wolf, is a species of canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the gray wolf, and slightly smaller than the closely relat ...
''). The American black bear (''Ursus americanus
The American black bear (''Ursus americanus''), or simply black bear, is a species of medium-sized bear which is endemic to North America. It is the continent's smallest and most widely distributed bear species. It is an omnivore, with a diet v ...
'') is also found but in very small numbers. The main cause of degradation has been grazing. Although there are many reptilian species in the mountains the most observed species include: Northern Mexican pine snake, '' Pituophis deppei jani'', Texas horned lizard ''( Phrynosoma cornutum)'', rock rattlesnake ''( Crotalus lepidus)'', black-tailed rattlesnake ''( Crotalus molossus)'', and plateau tiger salamander '' Ambystoma velasci'', one of possibly many amphibians to be found in the mountains.
The Chihuahuan Desert is home to a diverse ecosystem which is home to a large variety of mammals. The most common mammals in the desert include: desert cottontail ''Sylvilagus audubonii
The desert cottontail (''Sylvilagus audubonii''), also known as Audubon's cottontail, is a New World cottontail rabbit, and a member of the family Leporidae. Unlike the European rabbit (''Oryctolagus cuniculus''), they do not form social burrow s ...
'', black-tailed jackrabbit '' Lepus californicus'', hooded skunk, cactus mouse '' Peromyscus eremicus'', white-throated woodrat '' Neotoma albigula'', pallid bat '' Antrozous pallidus'', and coyote. The most observed reptiles in the desert include: Mohave rattlesnake '' Crotalus scutulatus'', twin-spotted rattlesnake ''Crotalus pricei
:''Common names: twin-spotted rattlesnake,Campbell JA, Lamar WW (2004). ''The Venomous Reptiles of the Western Hemisphere''. Ithaca and London: Comstock Publishing Associates. 870 pp., 1500 plates. . western twin-spotted rattlesnake, Klauber LM ...
'', prairie rattlesnake '' Crotalus viridis'', ridge-nosed rattlesnake '' Crotalus willardi'', whip snake '' Masticophis flagellum'', New Mexico whiptail '' Aspidoscelis neomexicanus'', and red-spotted toad '' Bufo punctatus''.
The state is also a host to a large population of birds which include endemic species and migratory species: greater roadrunner ''Geococcyx californianus
The greater roadrunner (''Geococcyx californianus'') is a long-legged bird in the cuckoo family, Cuculidae, from the Aridoamerica region in the Southwestern United States and Mexico. The scientific name means "Californian earth-cuckoo". Along with ...
'', cactus wren '' Campylorhynchus brunneicapillus'', Mexican jay '' Aphelocoma ultramarina'', Steller's jay '' Cyanocitta stelleri'', acorn woodpecker '' Melanerpes formicivorus'', canyon towhee '' Pipilo fuscus'', mourning dove '' Zenaida macroura'', broad-billed hummingbird '' Cynanthus latirostris'', Montezuma quail '' Cyrtonyx montezumae'', mountain trogon '' Trogon mexicanus'', turkey vulture '' Cathartes aura'', and golden eagle ''Aquila chrysaetos
The golden eagle (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known birds of p ...
''. '' Trogon mexicanus'' is an endemic species found in the mountains in Mexico and has symbolic significance to Mexicans.
Demography
According to the census by the (INEGI) in 2005, the state population is 3,241,444 making the state the 11th most populated state in Mexico. Census recorded 1,610,275 men and 1,631,169 women. The median age of the population is 25 years. The northern state is placed seventh in the nation regarding quality of life and sixth in terms of life expectancy at 75.2 years of age. During the period from 2000–2005 it is estimated that 49,722 people left the state for the United States. Some 82,000 people are thought to have immigrated to the state from 2000–2005 mainly coming fromVeracruz
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entit ...
(17.6%), United States (16.2%), Durango
Durango, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Durango, is one of the 31 states which make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico, situated in the northwest portion of the country. With a population of 1,832,650 ...
(13.2%), Coahuila
Coahuila, formally Coahuila de Zaragoza, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Coahuila de Zaragoza, is one of the 31 states of Mexico. The largest city and State Capital is the city of Saltillo; the second largest is Torreón and the thi ...
(8.0%) and Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and large ...
(4.5%). It is believed that there is a large number of undocumented immigrants in that state the come from Central and South America which mainly settle in Ciudad Juárez
Ciudad Juárez ( , ; "Juárez City"), commonly referred to as just Juárez (Lipan language, Lipan: ''Tsé Táhú'ayá''), is the most populous city in the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. It was k ...
. According to the 2005 census, the population grew 1.06% from 2000 to 2005. The state has an uneven settlement of people and the lowest population density of any Mexican state; according to the 2005 census there were 12 people per km2. Of all the 3,241,444 people in the state, two-thirds (2,072,129) live in the cities of Ciudad Juárez
Ciudad Juárez ( , ; "Juárez City"), commonly referred to as just Juárez (Lipan language, Lipan: ''Tsé Táhú'ayá''), is the most populous city in the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. It was k ...
and Chihuahua. Only three other cities have populations over 100,000: Parral 101,147, Cuauhtémoc
Cuauhtémoc (, ), also known as Cuauhtemotzín, Guatimozín, or Guatémoc, was the Aztec ruler ('' tlatoani'') of Tenochtitlan from 1520 to 1521, and the last Aztec Emperor. The name Cuauhtemōc means "one who has descended like an eagle", an ...
105,725, and Delicias 108,187.
Ethnic groups


Sierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American C ...
. Many have migrated to the large cities of the state mainly for economic incentives.
* Tepehuan Del Norte: A tribe linguistically differentiated from the Tepehuan in the state of Durango. The tribe lives near the small towns of Guadalupe y Calvo and Baborigame.
* Guarijío: A small tribe linguistically differentiated from the other tribes of the state. Little is known about these indigenous tribes except that they live near the small villages of Chínipas and Uruachi.
* Pima: A large ethnic group that lives across extensive areas of northwestern Mexico and southwestern United States. The population of the tribe in the state is small, mostly around the town of Temósachi. Although all the tribe speaks the same language, variant dialects have been discovered between different settlements.
According to the 2020 Census, 1.63% of Chihuahua's population identified as Black, Afro-Mexican, or of African descent.
Religion
Although the great majority of residents of the state of Chihuahua are Catholics, there is a large diversity of religions within the state. There are many apostolic churches,Mormon
Mormons are a religious and cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's death in 1844, the movement split into several ...
wards, and large Mennonite
Mennonites are a group of Anabaptism, Anabaptist Christianity, Christian communities tracing their roots to the epoch of the Radical Reformation. The name ''Mennonites'' is derived from the cleric Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland, part of ...
communities. Those aged 5 years and older claim to be the following religious beliefs: 84.6% are Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
; 7.1% are Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
; 2.0% are Nondenominational
A non-denominational person or organization is one that does not follow (or is not restricted to) any particular or specific religious denomination.
The term has been used in the context of various faiths, including Jainism, Baháʼí Faith, Zoro ...
; 5.1% are Atheist
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
. Compared to most of Mexico, the state has a higher percentage of Protestants.
During the Mexican Revolution, Álvaro Obregón invited a group of Canadian German-speaking Mennonites to resettle in Mexico. By the late 1920s, some 7,000 had immigrated to Chihuahua State and Durango State, almost all from Canada, only a few from the U.S. and Russia. Today, Mexico accounts for about 42% of all Mennonites in Latin America. They are a largely insular community that speaks a form of German and wear traditional clothing. They own their own businesses in various communities in Chihuahua, and account for about half of the state's farm economy, excelling in cheese production.
Main cities
The state has one city with a population exceeding one million: Ciudad Juárez. Ciudad Juárez is ranked eighth most populous city in the country, and Chihuahua City was ranked 16th most populous in Mexico. Chihuahua (along with Baja California) is the only state in Mexico to have two cities ranked in the top 20 most populated. El Paso and Ciudad Juárez comprise one of the largest binational metropolitan areas in the world, with a combined population of 2.4 million. In fact, Ciudad Juárez is one of the fastest-growing cities in the world, in spite of the fact that it is "the most violent zone in the world outside of declared war zones". For instance, a few years ago theFederal Reserve Bank of Dallas
The Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas (informally referred to as the Dallas Fed) is one of 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks that, along with the Federal Reserve Board of Governors in Washington, D.C., make up the Federal Reserve System, the centra ...
published that in Ciudad Juárez "the average annual growth over the 10-year period 1990–2000 was 5.3 percent. Juárez experienced much higher population growth than the state of Chihuahua and than Mexico as a whole".
Chihuahua City has one of the highest literacy rates in the country, at 98%; 35% of the population is aged 14 or below, 60% 15-65, and 5% over 65. The growth rate is 2.4%.
The 76.5% of the population of the state of Chihuahua live in cities which makes the state one of the most urbanized in Mexico.

Education
According to the Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Geografía e Informática (INEGI), 95.6% of the population over the age of 15 could read and write Spanish, and 97.3% of children of ages 8–14 could read and write Spanish. An estimated 93.5% of the population ages 6–14 attend an institution of education. Estimated 12.8% of residents of the state have obtained a college degree., "Perfil Sociodemográfico de Chihuahua" ''Conteo de Población y Vivienda 2005'' Insitutio Nacional de Estadística, Geografía e Informática p 32-43 Average schooling is 8.5 years, which means that in general the average citizen over 15 years of age has gone as far as a second year in secondary education. Institutions of higher education include: * Instituto Tecnológico de Chihuahua * Instituto Tecnológico de Chihuahua II * Universidad Autónoma de Ciudad Juárez * Universidad Autónoma de Chihuahua * Instituto Tecnólogico y de Estudios Superiores de Monterrey Campus Chihuahua *Universidad La Salle
Universidad (Spanish for "university") may refer to:
Places
* Universidad, San Juan, Puerto Rico
* Universidad (Madrid)
Football clubs
* Universidad SC, a Guatemalan football club that represents the Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala
...
* Universidad Tecnológica de Chihuahua
Government
The current government of the state was established officially by the Political Constitution of the United Mexican States in 1917. The state government is divided into three branches: the legislative branch, the judicial branch, and the executive branch. The government is centrally located in the state capitalChihuahua City
The city of Chihuahua or Chihuahua City ( ; Lipan language, Lipan: ) is the state capital of the Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. , the city of Chihuahua had a population of 925,762 inhabitants. while the metropolitan area had a popu ...
.
The legislative branch consists of an elected assembly of representatives to form the state congress. The congress is composed of 33 deputies, of which 22 are directly elected to represent each of the 22 districts in the state. In addition 11 deputies are elected by system of proportional representation through a list of registered political party members. Deputies are elected every three years and cannot be reelected consecutively.
The judicial branch is led by the Supreme Tribunal of Justice which is constituted of 15 magistrate judges. The judges are appointed by the governor and approved by the state congress. The executive branch is headed by the governor of the state, who is elected for one term of six years on the fourth day of October every election year. Governors are not eligible to be reelected due to constitutional one-term limitation.
The state is represented at the federal level in the Congress of the Union
The Congress of the Union (, ), formally known as the General Congress of the United Mexican States (''Congreso General de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos''), is the legislature of the federal government of Mexico. It consists of two chambers: t ...
by three senators and nine deputies (representatives). The deputies serve three-year terms and are elected in federal elections. The senators serve six-year terms and are elected in federal elections.
Administrative divisions
Chihuahua is subdivided into 67 '' municipios'' (municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
).
Economy
 The state has the 9th-largest state economy in Mexico, accounting for 3.69% of the country's GDP. Chihuahua has the fifth highest manufacturing GDP in Mexico and ranks second for the most factories funded by foreign investment in the country. As of 2022, the state had an estimated 1.050 trillion pesos (52.2 billion dollars) of annual GDP. According to official federal statistical studies, the service sector accounted for the largest portion of the state economy at 59.28%; the manufacturing and industrial sector is estimated to account for 34.36% of the state's GDP, with the agricultural sector accounting for 6.36% of the state's GDP. Manufacturing sector was the principal foreign investment in the state followed by the mining sector. In 2011, the state received approximately 884 million dollars in
The state has the 9th-largest state economy in Mexico, accounting for 3.69% of the country's GDP. Chihuahua has the fifth highest manufacturing GDP in Mexico and ranks second for the most factories funded by foreign investment in the country. As of 2022, the state had an estimated 1.050 trillion pesos (52.2 billion dollars) of annual GDP. According to official federal statistical studies, the service sector accounted for the largest portion of the state economy at 59.28%; the manufacturing and industrial sector is estimated to account for 34.36% of the state's GDP, with the agricultural sector accounting for 6.36% of the state's GDP. Manufacturing sector was the principal foreign investment in the state followed by the mining sector. In 2011, the state received approximately 884 million dollars in remittance
A remittance is a non-commercial transfer of money by a foreign worker, a member of a diaspora community, or a citizen with familial ties abroad, for household income in their home country or homeland.
Money sent home by migrants competes ...
s from the United States, which was 4.5% of all remittances from the United States to Mexico.
NAFTA
The North American Free Trade Agreement (, TLCAN; , ALÉNA), referred to colloquially in the Anglosphere as NAFTA, ( ) was an agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States that created a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The ...
was signed, industrial development grew rapidly with foreign investment. Large factories known as ''maquiladoras'' were built to export manufactured goods to the United States and Canada. Today, most of the maquiladoras produce electronics, automobile, and aerospace components. There are more than 406 companies operating under the federal IMMEX or Prosec program in Chihuahua. The large portion of the manufacturing sector of the state is 425 factories divided into 25 industrial parks accounting for 12.47% of the ''maquiladoras'' in Mexico, which employ 294,026 people in the state. While export-driven manufacturing is one of the most important components of the state's economy, the industrial sector is quite diverse and can be broken down into several sectors, which are: electronics, agro-industrial, wood base manufacturing, mineral, and biotech. Similar to the rest of the country, small businesses continue to be the foundation of the state's economy. Small business employs the largest portion of the population.
, the state's economy employed 786,758 people, which accounted for 3.9% of the country's workforce with annual GDP per capita of 136,417 pesos (12,338 dollars). The average employee wage in Chihuahua is approximately 193 pesos per day. The minimum wage
A minimum wage is the lowest remuneration that employers can legally pay their employees—the price floor below which employees may not sell their labor. List of countries by minimum wage, Most countries had introduced minimum wage legislation b ...
in the state is 61.38 pesos (4.66 dollars) per day except for the municipalities of Guadalupe, Ciudad Juárez
Ciudad Juárez ( , ; "Juárez City"), commonly referred to as just Juárez (Lipan language, Lipan: ''Tsé Táhú'ayá''), is the most populous city in the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. It was k ...
, and Praxedis G. Guerrero, which have a minimum wage of 64.76 Mexican pesos (4.92 dollars).
Agriculture is a relatively small component of the state's economy and varies greatly due to the varying climate across the state. The state ranked first in Mexico for the production of the following crops: oat
The oat (''Avena sativa''), sometimes called the common oat, is a species of cereal grain grown for its seed, which is known by the same name (usually in the plural). Oats appear to have been domesticated as a secondary crop, as their seeds ...
s, chile verde, cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
, apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
s, pecan
The pecan ( , , ; ''Carya illinoinensis'') is a species of hickory native to the Southern United States and northern Mexico in the region of the Mississippi River.
The tree is cultivated for its seed primarily in the U.S. states of Georgia ( ...
s, and quince
The quince (; ''Cydonia oblonga'') is the sole member of the genus ''Cydonia'' in the Malinae subtribe (which contains apples, pears, and other fruits) of the Rosaceae family. It is a deciduous tree that bears hard, aromatic bright golden-yel ...
. The state has an important dairy industry with large milk processors throughout the state. Delicias is home to Alpura, the second-largest dairy company in Mexico. The state has a large logging industry ranking second in oak and third in pine in Mexico. The mining industry is a small but continues to produce large amounts of minerals. The state ranked first place in the country for the production of lead with 53,169 metric tons. Chihuahua ranked second in Mexico for zinc at 150,211 metric tons, silver at 580,271 kg, and gold at 15,221.8 kg.
Notable People
: People from Chihuahua (state)Media
Newspapers
A newspaper is a Periodical literature, periodical publication containing written News, information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background. Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as poli ...
of Chihuahua include: ''El Diario (Juárez)'', ''El Diario de Chihuahua'', ''El Heraldo de Chihuahua'', ''El Heraldo de la Tarde'', ''El Mexicano'', ''El Sol de Parral'', and ''Norte de Ciudad Juárez.''
See also
*Chihuahua (dog)
The Chihuahua (or ) is a Mexican list of dog breeds, breed of toy dog. It is named for the Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua and is one of the smallest dog breeds in the world. It is usually kept as a companion animal.
History
...
, a dog breed named after the state
*Geography of Mexico
The geography of Mexico describes the geographic features of Mexico, a country in the Americas. Mexico is located at about 23° N and 102° W in the southern portion of North America. From its farthest land points, Mexico is a little over in l ...
*Indigenous peoples of Mexico
Indigenous peoples of Mexico (), Native Mexicans () or Mexican Native Americans (), are those who are part of communities that trace their roots back to populations and communities that existed in what is now Mexico before the arrival of Europe ...
* Los Medanos, the Samalayuca Dune Fields
* Glanton's gang, a band of mercenaries
Notes
References
External links
*Chihuahua state government
Secretariat of Industrial Development of Chihuahua State Government
Chihuahua's municipal governments
Chihuahua photos
Encyclopædia Britannica, Chihuahua
Chihuahuan Frontier
{{Authority control States of Mexico Mexican Plateau states * States and territories established in 1824