Chalcis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Chalcis (;
 The earliest recorded mention of Chalcis is in the
The earliest recorded mention of Chalcis is in the
 It is recorded as a city in the 6th-century ''
It is recorded as a city in the 6th-century ''
p. 6:390
footnote 69 to
 The Byzantine diocese of Chalkis was initially a
The Byzantine diocese of Chalkis was initially a
 * GR-44
* GR-77
* GR-1/ E75 is south and west about from Chalcis in
* GR-44
* GR-77
* GR-1/ E75 is south and west about from Chalcis in


 *
*
GCatholic - (former and titular) Latin see
Photos from Chalcis, Evoia
; Bibliography - ecclesiastical history * Pius Bonifacius Gams, ''Series episcoporum Ecclesiae Catholicae'', Leipzig 1931, pp. 430–431 * Michel Lequien, ''Oriens christianus in quatuor Patriarchatus digestus'', Paris 1740, Vol. II, coll. 212-215 * Gaetano Moroni, ''Dizionario di erudizione storico-ecclesiastica'', vol. 47, pp. 262–263 * Konrad Eubel, Hierarchia Catholica Medii Aevi, vol. 1, p. 367; vol. 2, p. 203; vol. 3, p. 259 * Raymond Janin, v. 2. 'Chalcis', in ''Dictionnaire d'Histoire et de Géographie ecclésiastiques'', vol. XII, Paris 1953, coll. 278-279 {{Authority control Ancient Euboea Cities in ancient Greece Greek prefectural capitals Mediterranean port cities and towns in Greece Populated places in Euboea Members of the Delian League Ancient Greek cities Populated places in ancient Euboea Greek city-states
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
and Katharevousa
Katharevousa (, , literally "purifying anguage) is a conservative form of the Modern Greek language conceived in the late 18th century as both a literary language and a compromise between Ancient Greek and the contemporary vernacular, Demotic ...
: , ), also called Chalkida or Halkida (Modern Greek
Modern Greek (, or , ), generally referred to by speakers simply as Greek (, ), refers collectively to the dialects of the Greek language spoken in the modern era, including the official standardized form of the language sometimes referred to ...
: , ), is the chief city of the island of Euboea
Euboea ( ; , ), also known by its modern spelling Evia ( ; , ), is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete, and the sixth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by ...
or Evia in Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
, situated on the Euripus Strait
The Euripus Strait ( ) is a narrow channel of water separating the Greek island of Euboea in the Aegean Sea from Boeotia in mainland Greece. The strait's principal port is Chalcis on Euboea, located at the strait's narrowest point.
The strait is ...
at its narrowest point. The name is preserved from antiquity and is derived from the Greek χαλκός (copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
), though there is no trace of any mines in the area. In the Late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the Periodization, period of History of Europe, European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period ( ...
, it was known as Negropont(e), an Italian name that has also been applied to the entire island of Euboea.
History
Ancient Greece
 The earliest recorded mention of Chalcis is in the
The earliest recorded mention of Chalcis is in the Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; , ; ) is one of two major Ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odyssey'', the poem is divided into 24 books and ...
, where it is mentioned in the same line as its rival Eretria
Eretria (; , , , , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers ...
. It is also documented that the ships set for the Trojan War
The Trojan War was a legendary conflict in Greek mythology that took place around the twelfth or thirteenth century BC. The war was waged by the Achaeans (Homer), Achaeans (Ancient Greece, Greeks) against the city of Troy after Paris (mytho ...
gathered at Aulis, the south bank of the strait near the city. Chamber tombs at Trypa and Vromousa dated to the Mycenaean period
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainla ...
were excavated by Papavasiliou in 1910. In the 8th and 7th centuries BC, colonists from Chalcis founded thirty townships on the peninsula of Chalcidice
Chalkidiki (; , alternatively Halkidiki), also known as Chalcidice, is a peninsula and regional units of Greece, regional unit of Greece, part of the region of Central Macedonia, in the Geographic regions of Greece, geographic region of Macedon ...
and several important cities in Magna Graecia
Magna Graecia refers to the Greek-speaking areas of southern Italy, encompassing the modern Regions of Italy, Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania, and Sicily. These regions were Greek colonisation, extensively settled by G ...
and Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
, such as Naxos
Naxos (; , ) is a Greek island belonging to the Cyclades island group. It is the largest island in the group. It was an important centre during the Bronze Age Cycladic Culture and in the Ancient Greek Archaic Period. The island is famous as ...
, Rhegion, Zankle and Cumae
Cumae ( or or ; ) was the first ancient Greek colony of Magna Graecia on the mainland of Italy and was founded by settlers from Euboea in the 8th century BCE. It became a rich Roman city, the remains of which lie near the modern village of ...
. Its mineral produces, metal-work, purple
Purple is a color similar in appearance to violet light. In the RYB color model historically used in the arts, purple is a secondary color created by combining red and blue pigments. In the CMYK color model used in modern printing, purple is ...
, and pottery not only found markets among these settlements but were distributed over the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
in the ships of Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
and Samos
Samos (, also ; , ) is a Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese archipelago, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the Mycale Strait. It is also a separate reg ...
. The development of the city led consequently to the increase of the population and finally to the colonization with the establishment of many important cities in the West, but also in the Greek area. The first recorded settlement in the West, which paved the way for the 2nd Greek colonization, is Pithecusae on the island of Ischia, in front of Naples, from Chalcidians and Eretrians around 770 BC. The etymology of the toponym "Pithikousa" comes from the pithos (pitharia) that the first settlers had with them to transport their products. Because of the first Chalcidian settlers, the Romans initially called all Greeks "Chalcidians", as they were the first Greeks they came into contact with.A few years later, the Chalcidian Antimnestos founds Rigio in 730-720 BC. and Crataimenis' fellow-citizen Zagli (later Messina) in 730 BC, thus wanting to control the sea strait between Sicily and Italy, just as the Metropolis of Chalkida controlled the Euboean gulfs. In the 8th century BC the increase in trade between the Chalkidian colonies in lower Italy and Sicily with the local populations resulted in the spread of the Chalkidic alphabet among the most ancient inhabitants of the peninsula. The Etruscans took this alphabet and appropriated it so that they too could express themselves in writing. Over the centuries the Romans renamed it 'Latin'.So today, at least eight letters of all Latin-derived languages are the same as their ancient Euboic counterparts. They are C, D, F, P, R, S and X (pronounced ks). The transmission of the Chalkidic alphabet to the west is the most important cultural contribution of ancient Chalkida to the world culture.
The Lelantine War
The Lelantine War was a military conflict between the two ancient Greek city states Chalcis and Eretria in Euboea which took place in the early Archaic period, between c. 710 and 650 BC. The reason for war was, according to tradition, the strugg ...
was a war fought in the late 8th century BC. between the two powerful ancient states of Evia, Chalkida and Eretria, which at that time were at the height of their prosperity. This war was one of the first known major wars between ancient Greek cities and took pan-Hellenic dimensions as the warring Chalcidians and Eretrians allied themselves with other Greek cities.
As Herodotus mentions, the Samians allied with the Chalcidians, while the Milesians allied with the Eretrians. The Thessalians also allied with the Chalcidians, a fact mentioned by Plutarch. The historical sources provide evidence for only one battle of the war, undoubtedly the last, with the reference point being the death of the Thessalian Amphidamandas, who was praised by Hesiod. In this battle the help from the Thessalian cavalry resulted in victory for Chalkida, by which it acquired the best agricultural district of Euboea and became the chief city of the island. Late in the 6th century BC, its prosperity was broken by a disastrous war with the Athenians
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
, who expelled the ruling aristocracy and settled a cleruchy
A cleruchy (, ''klēroukhia''; also klerouchy and kleruchy) in Classical Greece, was a specialized type of colony established by Athens. The term comes from the Greek word , ''klēroukhos'', literally "lot-holder".
History
Normally, Greek colon ...
on the site. Chalcis subsequently became a member of both the Delian League
The Delian League was a confederacy of Polis, Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, founded in 478 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Classical Athens, Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Achaemenid Empire, Persian ...
s.
Chalkis has had a Greco-Jewish presence since antiquity, which is sometimes claimed to have been continuous and to thus form Europe's oldest Jewish community, although there is no evidence of it through the early Middle Ages.
In the Hellenistic period, it gained importance as a fortress by which the Macedonian rulers controlled central Greece. It was used by kings Antiochus III of Syria (192 BC) and Mithradates VI of Pontus (88 BC) as a base for invading Greece. Characteristic is the fact that in 323 BC the Stagerite philosopher Aristotle comes to Chalkida to die the following year at his mother's house. Then during the Hellenistic era, settlers from Chalkida founded Chalkida in Syria, by order of Seleucus I, from which settlers founded another Chalkida in the Lebanon Valley, as well as another Chalkida in Arabia.
Under Roman rule, Chalcis retained a measure of commercial prosperity within the province of Achaea
Achaea () or Achaia (), sometimes transliterated from Greek language, Greek as Akhaia (, ''Akhaḯa'', ), is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Western Greece and is situated in the northwest ...
(southern Greece).
Middle Ages and early Modern period

Synecdemus
The ''Synecdemus'' or ''Synekdemos'' () is a geographic text, attributed to Hierocles, which contains a table of administrative divisions of the Byzantine Empire and lists of their cities. The work is dated to the reign of Justinian
Justinia ...
'' and mentioned by the contemporary historian Procopius of Caesarea
Procopius of Caesarea (; ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; ; – 565) was a prominent late antique Greek scholar and historian from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman general Belisarius in Emperor Justinian's wars, Procopius became the pr ...
, who recorded that a movable bridge linked the two shores of the strait. In Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
times, Chalcis was usually called Euripos, a name also applied to the entire island of Euboea, although the ancient name survived in administrative and ecclesiastical usage until the 9th century; alternatively, it is possible that the name was given anew to a settlement that was founded in the 9th century in the location of the ancient city, after the latter had been abandoned in the early Middle Ages. The town survived an Arab naval raid in the 880s and its bishop is attested in the 869–70 Church council held at Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
.
By the 12th century, the town featured a Venetian trading station, being attacked by the Venetian fleet in 1171 and eventually seized by Venice in 1209, in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
.
For Westerners, its common name was Negropont or Negroponte. This name comes indirectly from the Greek name of the Euripus Strait
The Euripus Strait ( ) is a narrow channel of water separating the Greek island of Euboea in the Aegean Sea from Boeotia in mainland Greece. The strait's principal port is Chalcis on Euboea, located at the strait's narrowest point.
The strait is ...
: the phrase στὸν Εὔριπον 'to Evripos', was rebracketed as στὸ Νεὔριπον 'to Nevripos', and became Negroponte in Italian by folk etymology
Folk etymology – also known as (generative) popular etymology, analogical reformation, (morphological) reanalysis and etymological reinterpretation – is a change in a word or phrase resulting from the replacement of an unfamiliar form by a mo ...
, the ''ponte'' 'bridge' being interpreted as the bridge of ChalcisEdward Gibbon, '' The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'', J.B. Bury, ed., Methuen, 189p. 6:390
footnote 69 to
Boeotia
Boeotia ( ), sometimes Latinisation of names, Latinized as Boiotia or Beotia (; modern Greek, modern: ; ancient Greek, ancient: ), is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Central Greece (adm ...
.
The town was a condominium between Venice and the Veronese
Veronese is the Italian word denoting someone or something from Verona, Italy and may refer to:
* Veronese Riddle, a popular riddle in the Middle Ages
* Veronese (moth), ''Veronese'' (moth), a moth genus in the family Crambidae
* Monte Veronese, ...
barons of the rest of Euboea, known as the " triarchs", who resided there. Chalcis or Negroponte became a Latin Church
The Latin Church () is the largest autonomous () particular church within the Catholic Church, whose members constitute the vast majority of the 1.3 billion Catholics. The Latin Church is one of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical ...
diocese
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, prov ...
, see below.
A large hoard of late medieval jewellery dating from Venetian times was found in Chalcis Castle in the nineteenth century and is now in the British Museum
The British Museum is a Museum, public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is the largest in the world. It documents the story of human cu ...
. The synagogue dated to around 1400.
Negroponte played a significant role in the history of Frankish Greece
The Frankish Occupation (; anglicized as ), also known as the Latin Occupation () and, for the Venetian domains, Venetian Occupation (), was the period in Greek history after the Fourth Crusade (1204), when a number of primarily French ...
, and was attacked by the Principality of Achaea
The Principality of Achaea () or Principality of Morea was one of the vassal states of the Latin Empire, which replaced the Byzantine Empire after the capture of Constantinople during the Fourth Crusade. It became a vassal of the Kingdom of Thes ...
in the War of the Euboeote Succession (1257/8), the Catalan Company
The Catalan Company or the Great Catalan Company (; , , , or ) was a company of mercenaries led by Roger de Flor in the early 14th century and hired by Byzantine Emperor Andronikos II Palaiologos to combat the increasing power of the Anatolian b ...
in 1317, the Turks in 1350/1, until it was finally captured by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
after a long siege in 1470. That siege is the subject of the Rossini
Gioachino Antonio Rossini (29 February 1792 – 13 November 1868) was an Italian composer of the late Classical and early Romantic eras. He gained fame for his 39 operas, although he also wrote many songs, some chamber music and piano p ...
opera'' Maometto II''. The Ottomans made it the seat of the Admiral of the Archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands. An archipelago may be in an ocean, a sea, or a smaller body of water. Example archipelagos include the Aegean Islands (the o ...
(the Aegean Islands). In 1688, it was successfully held by the Ottomans against a strong Venetian attack.
The modern town
Chalkida became part of the newborn Greek state after theGreek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. In 1826, the Greeks were assisted ...
. The modern town received an impetus in its export trade from the establishment of railway connection with Athens and its port Piraeus in 1904. In the early 20th century it was composed of two parts—the old walled town at the bridge over the Euripus, where a number of Turkish families continued to live until the late 19th century, and a sizeable Jewish community lived until World War II, and the more modern suburb that lies outside it, chiefly occupied by Greeks.
The old town, called the Castro (citadel), was surrounded by a full circuit of defense walls until they were completely razed for urban development around the start of the 20th century.
The city is served by a railway station and is the terminus for the Athens Suburban Railway to Athens.
There is a Holocaust memorial honoring the Jewish lives lost during World War II outside of the Chalkis Jewish cemetery.
Ecclesiastical history
Greek bishopric
 The Byzantine diocese of Chalkis was initially a
The Byzantine diocese of Chalkis was initially a suffragan
A suffragan bishop is a type of bishop in some Christian denominations.
In the Catholic Church, a suffragan bishop leads a diocese within an ecclesiastical province other than the principal diocese, the metropolitan archdiocese; the diocese led ...
of the Archdiocese of Corinth, but in the 9th century was transferred to the Metropolitan of Athens, remaining in the sway of the Patriarchate of Constantinople
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople (, ; ; , "Roman Orthodox Patriarchate, Ecumenical Patriarchate of Istanbul") is one of the fifteen to seventeen autocephalous churches that together compose the Eastern Orthodox Church. It is headed ...
. It was also known as Euripo, like it is mentioned in the Byzantine imperial Notitia Episcopatuum The ''Notitiae Episcopatuum'' (singular: ''Notitia Episcopatuum'') were official documents that furnished for Eastern countries the list and hierarchical rank of the metropolitan and suffragan bishoprics of a church.
In the Roman Church (the mos ...
since emperor Leo VI the Wise
Leo VI, also known as Leo the Wise (; 19 September 866 – 11 May 912), was Byzantine Emperor from 886 to 912. The second ruler of the Macedonian dynasty (although his parentage is unclear), he was very well read, leading to his epithet. During ...
(886-912).
Several of its Greek bishops are recorded, but some are disputed :
* Constantinus, signed in 458 a letter by the bishops of Greece to Byzantine emperor
The foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, which Fall of Constantinople, fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised s ...
Leo I the Thracian
Leo I (; 401 – 18 January 474), also known as "the Thracian" (; ), was Eastern Roman emperor from 457 to 474. He was a native of Dacia Aureliana near historic Thrace. He is sometimes surnamed with the epithet "the Great" (; ), probably to ...
after the murder by Coptic mobs of patriarch Proterius of Alexandria
Pope Proterius of Alexandria (died 457) was Patriarch of Alexandria from 451 to 457. He had been appointed by the Council of Chalcedon to replace the deposed Dioscorus. He regarded as hieromartyr by the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic ...
.
** Lequien list before him Anatolius (in 363), but he was probably bishop of Beroea
Beroea (or Berea, ) was an ancient city of the Hellenistic period and Roman Empire now known as Veria (or Veroia) in Macedonia, Northern Greece. It is a small city on the eastern side of the Vermio Mountains north of Mount Olympus. The town is m ...
in Syria Prima (now Aleppo
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and ...
).
** next Lequien inserts, by benefit of doubt, Iohannes Damasceno, whom he also lists as bishop of Euroea (in Phoenicia) alias Evaria, in Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
.
* Teodorus and Teofilattus, successive (?) bishops of Euripus, participated in the 869–70 Church council held at Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
. viz. the Council of Constantinople of 879–880, both treating the fate of Patriarch Photios I of Constantinople
Photius I of Constantinople (, ''Phōtios''; 815 – 6 February 893), also spelled ''Photius''Fr. Justin Taylor, essay "Canon Law in the Age of the Fathers" (published in Jordan Hite, T.O.R., and Daniel J. Ward, O.S.B., "Readings, Cases, Mate ...
.
Latin crusader bishopric
At the establishment of thecrusader state
The Crusader states, or Outremer, were four Catholic polities established in the Levant region and southeastern Anatolia from 1098 to 1291. Following the principles of feudalism, the foundation for these polities was laid by the First Crusade ...
Lordship of Negroponte, Chalcis or Negroponte (seat of the central one of its three 'triarchies' constituent baronies) became a Latin Church
The Latin Church () is the largest autonomous () particular church within the Catholic Church, whose members constitute the vast majority of the 1.3 billion Catholics. The Latin Church is one of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical ...
diocese
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, prov ...
, the first bishop being Theodorus, the Greek bishop of the see, who entered communion with the see of Rome
See or SEE may refer to:
* Visual perception
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Music:
** ''See'' (album), studio album by rock band The Rascals
*** "See", song by The Rascals, on the album ''See''
** "See" (Tycho song), song by Tycho
* Televisio ...
, installed by papal legate
300px, A woodcut showing Henry II of England greeting the Pope's legate.
A papal legate or apostolic legate (from the ancient Roman title '' legatus'') is a personal representative of the Pope to foreign nations, to some other part of the Catho ...
.
On 8 February 1314, the Latin see was united ''in commendam
In canon law, commenda (or ''in commendam'') was a form of transferring an ecclesiastical benefice ''in trust'' to the ''custody'' of a patron. The phrase ''in commendam'' was originally applied to the provisional occupation of an ecclesiastica ...
'' (as an 'additional benefice') with the Latin Patriarchate of Constantinople, so that the exiled Patriarch, excluded from Constantinople itself since the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
reconquest of the city, could have actual jurisdiction on Greek soil and exercise a direct role as head of the Latin clergy in what remained of Latin Greece
The Frankish Occupation (; Anglicization, anglicized as ), also known as the Latin Occupation () and, for the Republic of Venice, Venetian domains, Venetian Occupation (), was the period in Greek history after the Fourth Crusade (1204), w ...
.
Main sights
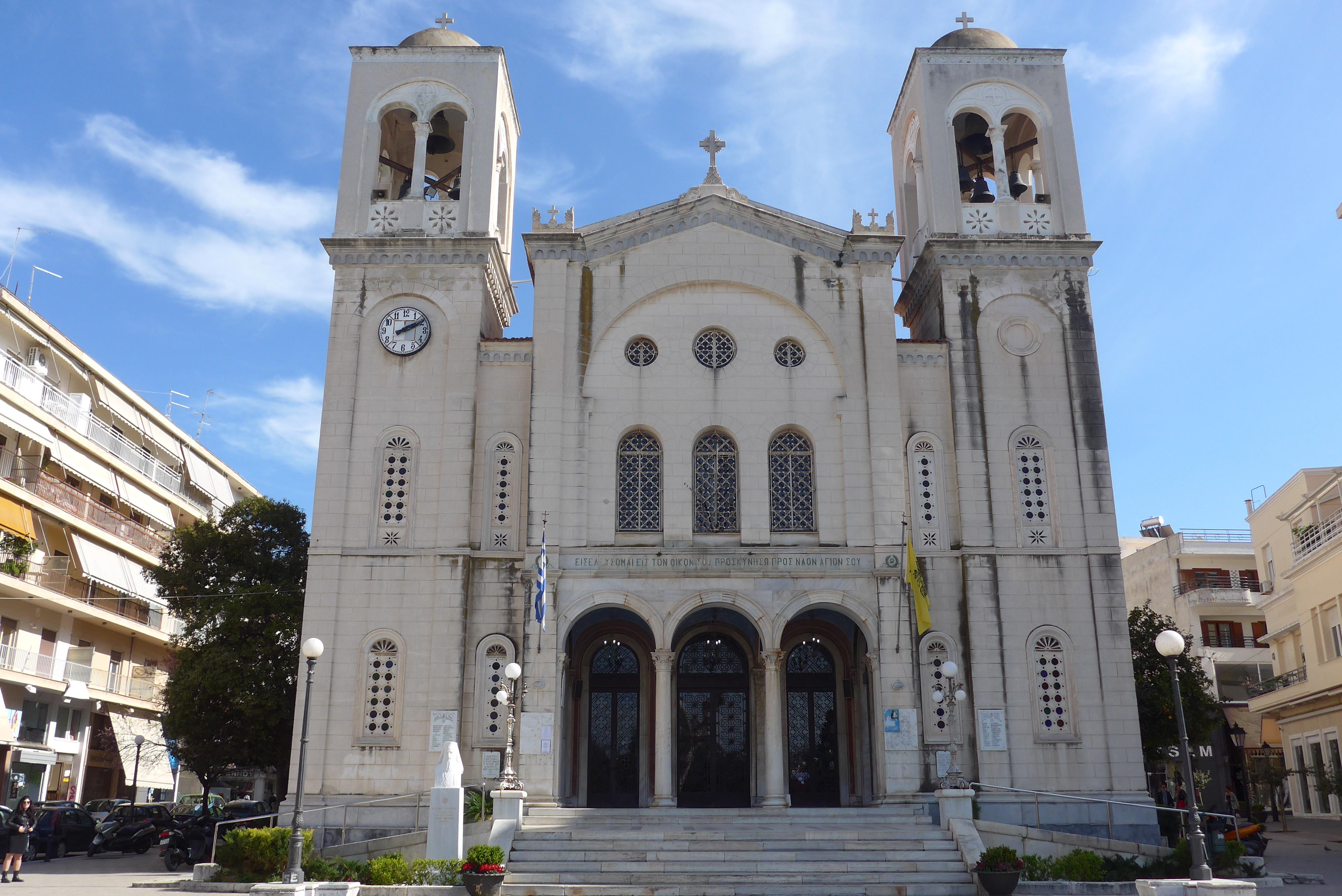
The church of Saint Paraskevi (thepatron saint
A patron saint, patroness saint, patron hallow or heavenly protector is a saint who in Catholicism, Anglicanism, Eastern Orthodoxy or Oriental Orthodoxy is regarded as the heavenly advocate of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, fa ...
of the island) was the church of the Dominican Priory of Negroponte, one of the first two houses authorized for the Order of Preachers' Province of Greece in 1249. Started about 1250, this is among the oldest examples of early Dominican architecture surviving, and is one of the only early Dominican churches to retain its original form until the present. The central arch over the iconostasis and the ceiling and walls of the south chapel are the best examples of Italian Gothic stone-carving in Greece. Images of the Dominican saints, Dominic and Peter Martyr, stand at the base of the central arch. The north chapel holds the tomb of the founder of the senatorial Lippamano family of Venice. Some of the column capitals are Byzantine.
The bridges
The town is now connected to mainland Greece by two bridges, the "Sliding Bridge" in the west at the narrowest point of theEuripus Strait
The Euripus Strait ( ) is a narrow channel of water separating the Greek island of Euboea in the Aegean Sea from Boeotia in mainland Greece. The strait's principal port is Chalcis on Euboea, located at the strait's narrowest point.
The strait is ...
and a suspension bridge.
The Euripus Strait
The Euripus Strait ( ) is a narrow channel of water separating the Greek island of Euboea in the Aegean Sea from Boeotia in mainland Greece. The strait's principal port is Chalcis on Euboea, located at the strait's narrowest point.
The strait is ...
which separates the city and the island from the mainland was bridged in 411 BC with a wooden bridge. In the time of Justinian
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
the fixed bridge was replaced with a movable structure. The Turks replaced this once again with a fixed bridge. In 1856, a wooden swing bridge was built; in 1896, an iron swing bridge, and in 1962, the existing "sliding bridge"; the construction works of the 19th century destroyed the most part of the medieval castle built across the bridge. The Euripus Bridge or Chalcis Bridge, a cable-stayed suspension bridge opened in 1993, joins Chalcis to the mainland to the south.
A special tidal phenomenon takes place in the strait, as strong tidal currents reverse direction once every six hours, creating strong currents and maelstroms. See also the commentary about this explanation in
Municipality
The municipality Chalcis was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of Chalcis city itself with four former municipalities, which also became municipal units: * Anthidona * Avlida * Lilantia * Nea Artaki The municipality has an area of 424.766 km2, the municipal unit 30.804 km2.Transportation
 * GR-44
* GR-77
* GR-1/ E75 is south and west about from Chalcis in
* GR-44
* GR-77
* GR-1/ E75 is south and west about from Chalcis in Boeotia
Boeotia ( ), sometimes Latinisation of names, Latinized as Boiotia or Beotia (; modern Greek, modern: ; ancient Greek, ancient: ), is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Central Greece (adm ...
.
In 2003, a bypass of Chalcis was opened from the southern part of the bridge to connect with GR-77, also with access to GR-44.
Chalcis station is the northern terminus of the Oinoi–Chalcis railway, and is served by Line 3 of the Athens Suburban Railway.
Historical population
Notable residents


 *
* Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
(384–322 BC, ancient philosopher, lived in Chalcis the last year of his life (323–322 BC))
* Giovanni Maria Angiolello from Vicenza, Italy, 15th century.
* Yiannis Anastasopoulos (1931–present), author
* Eva Asderaki Professional Tennis Umpire, first woman to umpire the US Open tennis final
* Sotiria Bellou (1921–1997), singer
* Angelos Basinas (1976–present), professional footballer
* Nikolaos Christodoulou, military officer
* Mordehai Frizis (1893–1940), military officer
* Dimitrios Katheniotis, military officer
* Nikolaos Kalogeropoulos, PM of Greece
* Konstantinos Kallias (1901–2004), politician
* Orestis Makris (1898–1975), actor and tenor
* Dimitris Mytaras (1934–2017), painter
* Georgios Papanikolaou (1883–1962), physician, Pap smear
The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, also known as Pap smear (AE), cervical smear (BE), cervical screening (BE), or smear test (BE)) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes in ...
test founder
* Nikos Skalkottas (1901–1949), composer
* Giannis Skarimpas ( Agia Efthymia, 1893–1984), author
* Telémachos Alexiou, Greek-German filmmaker and visual artist
* Georgios Papachatzis (1905–1991), jurist
Sports teams
Chalcis also has awater polo
Water polo is a competitive sport, competitive team sport played in water between two teams of seven players each. The game consists of four quarters in which the teams attempt to score goals by throwing the water polo ball, ball into the oppo ...
team named NC Chalkida, a football (soccer) team named Chalkida F.C., as well as a junior football team named Evoikos Chalkida.
The Chalkida football team merged with Lilas Vasilikou for a period of two years (2004–2006). The team was finally dissolved because of financial difficulties. Although there was a team created with the same name (AOX) it does not represent the glorious team of the past.
Chalcis also has a basketball team ( AGEX), which previously played in the Greek A2 Basketball League. For a while, Chalkida hosts the basketball team Ikaros Chalkidas that played in the top Greek Basket League
The Greek Basketball League (GBL), and also known as the Stoiximan Greek Basketball League (GBL) for sponsorship reasons, is the Greek basketball league system, first tier level professional basketball league in Greece. It is run by the ...
.
Twin towns
Chalcis is twinned with: *Wuhan
Wuhan; is the capital of Hubei, China. With a population of over eleven million, it is the most populous city in Hubei and the List of cities in China by population, eighth-most-populous city in China. It is also one of the nine National cent ...
Geography
Climate
Chalcis has amediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate ( ), also called a dry summer climate, described by Köppen and Trewartha as ''Cs'', is a temperate climate type that occurs in the lower mid-latitudes (normally 30 to 44 north and south latitude). Such climates typic ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
: ''Csa''), closely bordering a semi-arid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a aridity, dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below Evapotranspiration#Potential evapotranspiration, potential evapotranspiration, but not as l ...
climate with hot, dry summers and mild, rainy winters.
See also
* List of Catholic dioceses in Greece * Licodia Eubea, Catania, Sicily Italy - The name ''Eubea'' was given to the place in 1872, to identify with Chalcis, because it is believed to be the colony of Leontini.References
Sources and external links
* *GCatholic - (former and titular) Latin see
Photos from Chalcis, Evoia
; Bibliography - ecclesiastical history * Pius Bonifacius Gams, ''Series episcoporum Ecclesiae Catholicae'', Leipzig 1931, pp. 430–431 * Michel Lequien, ''Oriens christianus in quatuor Patriarchatus digestus'', Paris 1740, Vol. II, coll. 212-215 * Gaetano Moroni, ''Dizionario di erudizione storico-ecclesiastica'', vol. 47, pp. 262–263 * Konrad Eubel, Hierarchia Catholica Medii Aevi, vol. 1, p. 367; vol. 2, p. 203; vol. 3, p. 259 * Raymond Janin, v. 2. 'Chalcis', in ''Dictionnaire d'Histoire et de Géographie ecclésiastiques'', vol. XII, Paris 1953, coll. 278-279 {{Authority control Ancient Euboea Cities in ancient Greece Greek prefectural capitals Mediterranean port cities and towns in Greece Populated places in Euboea Members of the Delian League Ancient Greek cities Populated places in ancient Euboea Greek city-states