Cetacea (; , ) is an
infraorder of
aquatic mammals that includes
whales,
dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (t ...
s, and
porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel themselves through the water with powerful up-and-down movement of their tail which ends in a paddle-like fluke, using their flipper-shaped forelimbs to maneuver.
While the majority of cetaceans live in marine environments, a small number exclusively reside in
brackish water or
fresh water. Having a
cosmopolitan distribution, they can be found in some rivers and all of Earth's oceans, and many species inhabit vast ranges where they migrate with the changing of the seasons.
Cetaceans are famous for their high intelligence and complex social behaviour as well as for the enormous size of some of the group's members, such as the
blue whale
The blue whale (''Balaenoptera musculus'') is a marine mammal and a baleen whale. Reaching a maximum confirmed length of and weighing up to , it is the largest animal known to have ever existed. The blue whale's long and slender body can b ...
which reaches a maximum confirmed length of 29.9 meters (98 feet) and a weight of 173 tonnes (190 short tons), making it the largest animal known to have ever existed.
[Wood, Gerald ''The Guinness Book of Animal Facts and Feats'' (1983) ]
There are approximately 89 living species split into two
parvorders:
Odontoceti or toothed whales (containing
porpoises,
dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (t ...
s, other predatory whales like the
beluga and the
sperm whale
The sperm whale or cachalot (''Physeter macrocephalus'') is the largest of the toothed whales and the largest toothed predator. It is the only living member of the genus '' Physeter'' and one of three extant species in the sperm whale famil ...
, and the poorly understood
beaked whale
Beaked whales ( systematic name Ziphiidae) are a family of cetaceans noted as being one of the least known groups of mammals because of their deep-sea habitat and apparent low abundance. Only three or four of the 24 species are reasonably well- ...
s) and the filter feeding
Mysticeti or
baleen whales (which includes species like the
blue whale
The blue whale (''Balaenoptera musculus'') is a marine mammal and a baleen whale. Reaching a maximum confirmed length of and weighing up to , it is the largest animal known to have ever existed. The blue whale's long and slender body can b ...
, the
humpback whale
The humpback whale (''Megaptera novaeangliae'') is a species of baleen whale. It is a rorqual (a member of the family Balaenopteridae) and is the only species in the genus ''Megaptera''. Adults range in length from and weigh up to . The hum ...
and the
bowhead whale
The bowhead whale (''Balaena mysticetus'') is a species of baleen whale belonging to the family Balaenidae and the only living representative of the genus '' Balaena''. They are the only baleen whale endemic to the Arctic and subarctic waters, ...
). Despite their highly modified bodies and carnivorous lifestyle, genetic and fossil evidence places cetaceans as nested within
even-toed ungulate
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing post ...
s, most closely related to
hippopotamus
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two exta ...
within the clade
Whippomorpha.
Cetaceans have been extensively
hunted for their meat,
blubber
Blubber is a thick layer of vascularized adipose tissue under the skin of all cetaceans, pinnipeds, penguins, and sirenians.
Description
Lipid-rich, collagen fiber-laced blubber comprises the hypodermis and covers the whole body, except ...
and oil by commercial operations. Although the
International Whaling Commission
The International Whaling Commission (IWC) is a specialised regional fishery management organisation, established under the terms of the 1946 International Convention for the Regulation of Whaling (ICRW) to "provide for the proper conservation ...
has agreed on putting a halt to commercial whaling, whale hunting is still going on, either under IWC quotas to assist the subsistence of Arctic native people or in the name of scientific research, although a large spectrum of non-lethal methods are now available to study marine mammals in the wild. Cetaceans also face severe environmental hazards from underwater
noise pollution
Noise pollution, also known as environmental noise or sound pollution, is the propagation of noise with ranging impacts on the activity of human or animal life, most of them are harmful to a degree. The source of outdoor noise worldwide is mai ...
, entanglement in abandonned ropes and nets, collisions with ships, plastic and heavy metals build-up, to accelerating climate change,
but how much they are affected varies widely from species to species, from minimally in the case of the
southern bottlenose whale
The southern bottlenose whale (''Hyperoodon planifrons'') is a species of whale, in the Ziphiid family, one of two members of the genus ''Hyperoodon''. Seldom observed, the southern bottlenose whale is resident in Antarctic waters. The species wa ...
to the
baiji (or Chinese river dolphin) which is considered to be functionally extinct due to human activity.
Baleen whales and toothed whales
The two parvorders,
baleen whale
Baleen whales ( systematic name Mysticeti), also known as whalebone whales, are a parvorder of carnivorous marine mammals of the infraorder Cetacea ( whales, dolphins and porpoises) which use keratinaceous baleen plates (or "whalebone") in th ...
s (Mysticeti) and
toothed whale
The toothed whales (also called odontocetes, systematic name Odontoceti) are a parvorder of cetaceans that includes dolphins, porpoises, and all other whales possessing teeth, such as the beaked whales and sperm whales. Seventy-three species ...
s (Odontoceti), are thought to have diverged around thirty-four million years ago.
Baleen whales have bristles made of
keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ...
instead of
teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, te ...
. The bristles filter
krill and other small
invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
s from seawater.
Grey whales feed on bottom-dwelling mollusks.
Rorqual family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
(balaenopterids) use throat pleats to expand their mouths to take in food and sieve out the water.
Balaenids (
right whales and
bowhead whales) have massive heads that can make up 40% of their body mass. Most mysticetes prefer the food-rich colder waters of the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, migrating to the Equator to give birth. During this process, they are capable of fasting for several months, relying on their fat reserves.
The parvorder of Odontocetes – the toothed whales – include sperm whales, beaked whales, orcas, dolphins and porpoises. Generally the teeth are designed for catching fish, squid or other
marine invertebrates, not for chewing them, so prey is swallowed whole. Teeth are shaped like cones (dolphins and sperm whales), spades (
porpoises), pegs (
belugas), tusks (
narwhals) or variable (beaked whale males). Female beaked whales' teeth are hidden in the gums and are not visible, and most male beaked whales have only two short tusks. Narwhals have vestigial teeth other than their tusk, which is present on males and 15% of females and has millions of nerves to sense water temperature, pressure and salinity. A few toothed whales, such as some
orca
The orca or killer whale (''Orcinus orca'') is a toothed whale belonging to the oceanic dolphin family, of which it is the largest member. It is the only extant species in the genus '' Orcinus'' and is recognizable by its black-and-white ...
s, feed on mammals, such as
pinnipeds and other whales.
Toothed whales have well-developed senses – their eyesight and hearing are adapted for both air and water, and they have advanced
sonar capabilities using their
melon
A melon is any of various plants of the family Cucurbitaceae with sweet, edible, and fleshy fruit. The word "melon" can refer to either the plant or specifically to the fruit. Botanically, a melon is a kind of berry, specifically a " pepo". The ...
. Their hearing is so well-adapted for both air and water that some blind specimens can survive. Some species, such as sperm whales, are well adapted for diving to great depths. Several species of toothed whales show
sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most an ...
, in which the males differ from the females, usually for purposes of sexual display or aggression.
Anatomy

Cetacean bodies are generally similar to those of fish, which can be attributed to their lifestyle and the habitat conditions. Their body is well-adapted to their habitat, although they share essential characteristics with other higher mammals (
Eutheria).
[ ]
They have a streamlined shape, and their forelimbs are flippers. Almost all have a
dorsal fin
A dorsal fin is a fin located on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates within various taxa of the animal kingdom. Many species of animals possessing dorsal fins are not particularly closely related to each other, though through c ...
on their backs, but this can take on many forms, depending on the species. A few species, such as the
beluga whale
The beluga whale () (''Delphinapterus leucas'') is an Arctic and sub-Arctic cetacean. It is one of two members of the family Monodontidae, along with the narwhal, and the only member of the genus ''Delphinapterus''. It is also known as the whi ...
, lack them. Both the flipper and the fin are for stabilization and steering in the water.
The male genitals and the mammary glands of females are sunken into the body.
The body is wrapped in a thick layer of fat, known as
blubber
Blubber is a thick layer of vascularized adipose tissue under the skin of all cetaceans, pinnipeds, penguins, and sirenians.
Description
Lipid-rich, collagen fiber-laced blubber comprises the hypodermis and covers the whole body, except ...
. This provides thermal insulation and gives cetaceans their smooth, streamlined body shape. In larger species, it can reach a thickness up to half a meter (1.6 ft).
Sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most an ...
evolved in many toothed whales. Sperm whales,
narwhals, many members of the
beaked whale
Beaked whales ( systematic name Ziphiidae) are a family of cetaceans noted as being one of the least known groups of mammals because of their deep-sea habitat and apparent low abundance. Only three or four of the 24 species are reasonably well- ...
family, several species of the
porpoise family, orcas,
pilot whales, eastern
spinner dolphins and
northern right whale dolphins show this characteristic.
Males in these species developed external features absent in females that are advantageous in combat or display. For example, male sperm whales are up to 63% percent larger than females, and many beaked whales possess tusks used in competition among males.
Hind legs are not present in cetaceans, nor are any other external body attachments such as a
pinna and
hair.
Head
Whales have an elongated head, especially
baleen whales, due to the wide overhanging jaw. Bowhead whale plates can be long. Their nostril(s) make up the
blowhole
Blowhole may refer to:
* Blowhole (anatomy), the hole at the top of a whale's or other cetacean's head
*Blowhole (geology), a hole at the inland end of a sea cave
**Kiama Blowhole in Kiama, Australia
**The Blow Hole, a marine passage between Minst ...
, with one in toothed whales and two in baleen whales.
The nostrils are located on top of the head above the eyes so that the rest of the body can remain submerged while surfacing for air. The back of the skull is significantly shortened and deformed. By shifting the nostrils to the top of the head, the nasal passages extend perpendicularly through the skull.
[ ] The teeth or baleen in the upper jaw sit exclusively on the
maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The ...
. The braincase is concentrated through the nasal passage to the front and is correspondingly higher, with individual cranial bones that overlap.
In toothed whales, connective tissue exists in the
melon
A melon is any of various plants of the family Cucurbitaceae with sweet, edible, and fleshy fruit. The word "melon" can refer to either the plant or specifically to the fruit. Botanically, a melon is a kind of berry, specifically a " pepo". The ...
as a head buckle. This is filled with air sacs and fat that aid in buoyancy and
biosonar
Echolocation, also called bio sonar, is a biological sonar used by several animal species.
Echolocating animals emit calls out to the environment
and listen to the echoes of those calls that return from various objects near them. They use these ...
. The sperm whale has a particularly pronounced melon; this is called the
spermaceti organ
The spermaceti organ is an organ present in the heads of toothed whales of the family Physeteroidea, in particular the sperm whale. This organ contains a waxy liquid called spermaceti and is involved in the generation of sound.
Description
In ...
and contains the eponymous
spermaceti, hence the name "sperm whale". Even the long tusk of the narwhal is a vice-formed tooth. In many toothed whales, the depression in their skull is due to the formation of a large melon and multiple, asymmetric air bags.
River dolphins, unlike most other cetaceans, can turn their head 90°. Most other cetaceans have fused neck vertebrae and are unable to turn their head at all.
The
baleen of baleen whales consists of long, fibrous strands of keratin. Located in place of the teeth, it has the appearance of a huge fringe and is used to sieve the water for
plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a cr ...
and krill.
Brain
The
neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, ...
of many cetaceans is home to elongated
spindle neurons that, prior to 2019, were known only in
hominids. In humans, these cells are thought to be involved in social conduct, emotions, judgment and theory of mind. Cetacean
spindle neurons are found in areas of the brain homologous to where they are found in humans, suggesting they perform a similar function.
Brain size
The size of the brain is a frequent topic of study within the fields of anatomy, biological anthropology, animal science and evolution. Brain size is sometimes measured by weight and sometimes by volume (via MRI scans or by skull volume). ...
was previously considered a major indicator of
intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. It can be described as the ...
. Since most of the brain is used for maintaining bodily functions, greater ratios of brain to body mass may increase the amount of brain mass available for cognitive tasks.
Allometric analysis of the relationship between mammalian brain mass (weight) and body mass for different species of mammals shows that larger species generally have larger brains. However, this increase is not fully proportional. Typically the brain mass only increases in proportion to somewhere between the two-thirds power (or the square of the cube root) and the three-quarters power (or the cube of the fourth root) of the body mass.
''m''''brain'' ∝ (''m''''body'')''k''
where ''k'' is between two-thirds and three-quarters. Thus if Species B is twice the size of Species A, its brain size will typically be somewhere between 60% and 70% higher. Comparison of a particular animal's brain size with the expected brain size based on such an analysis provides an
encephalization quotient that can be used as an indication of animal intelligence. Sperm whales have the largest brain mass of any animal on Earth, averaging and in mature males. The
brain to body mass ratio in some odontocetes, such as belugas and narwhals, is second only to humans. In some whales, however, it is less than half that of humans: 0.9% versus 2.1%.
Skeleton
The cetacean skeleton is largely made up of
cortical bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, a ...
, which stabilizes the animal in the water. For this reason, the usual terrestrial compact bones, which are finely woven
cancellous bone, are replaced with lighter and more elastic material. In many places, bone elements are replaced by cartilage and even fat, thereby improving their
hydrostatic qualities. The ear and the muzzle contain a bone shape that is exclusive to cetaceans with a high density, resembling
porcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises main ...
. This conducts sound better than other bones, thus aiding
biosonar
Echolocation, also called bio sonar, is a biological sonar used by several animal species.
Echolocating animals emit calls out to the environment
and listen to the echoes of those calls that return from various objects near them. They use these ...
.
The number of
vertebrae
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
that make up the spine varies by species, ranging from forty to ninety-three. The
cervical spine, found in all mammals, consists of seven vertebrae which, however, are reduced or fused. This fusion provides stability during swimming at the expense of mobility. The fins are carried by the
thoracic vertebrae, ranging from nine to seventeen individual vertebrae. The
sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. ...
is cartilaginous. The last two to three pairs of ribs are not connected and hang freely in the body wall. The stable lumbar and tail include the other vertebrae. Below the
caudal vertebrae is the
chevron bone.
The front limbs are paddle-shaped with shortened arms and elongated finger bones, to support movement. They are connected by cartilage. The second and third fingers display a proliferation of the finger members, a so-called hyperphalangy. The shoulder joint is the only functional joint in all cetaceans except for the
Amazon river dolphin. The
collarbone is completely absent.
Fluke

Cetaceans have a
cartilaginous fluke at the end of their tails that is used for propulsion. The
fluke is set horizontally on the body, unlike fish, which have vertical tails.
Physiology
Circulation
Cetaceans have powerful hearts. Blood oxygen is distributed effectively throughout the body. They are warm-blooded, i.e., they hold a nearly constant body temperature.
Respiration
Cetaceans have lungs, meaning they breathe air. An individual can last without a breath from a few minutes to over two hours depending on the species. Cetacea are deliberate breathers who must be awake to inhale and exhale. When stale air, warmed from the lungs, is exhaled, it condenses as it meets colder external air. As with a terrestrial mammal breathing out on a cold day, a small cloud of 'steam' appears. This is called the 'spout' and varies across species in shape, angle and height. Species can be identified at a distance using this characteristic.
The structure of the
respiratory and
circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
s is of particular importance for the life of
marine mammals. The oxygen balance is effective. Each breath can replace up to 90% of the total lung volume. For land mammals, in comparison, this value is usually about 15%. During inhalation, about twice as much oxygen is absorbed by the lung tissue as in a land mammal. As with all mammals, the oxygen is stored in the blood and the lungs, but in cetaceans, it is also stored in various tissues, mainly in the muscles. The muscle pigment,
myoglobin
Myoglobin (symbol Mb or MB) is an iron- and oxygen-binding protein found in the cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue of vertebrates in general and in almost all mammals. Myoglobin is distantly related to hemoglobin. Compared to hemoglobin, myoglobi ...
, provides an effective bond. This additional oxygen storage is vital for deep diving, since beyond a depth around , the lung tissue is almost completely compressed by the water pressure.
Abdominal organs
The stomach consists of three chambers. The first region is formed by a loose gland and a muscular forestomach (missing in beaked whales); this is followed by the main stomach and the
pylorus. Both are equipped with glands to help digestion. A bowel adjoins the stomachs, whose individual sections can only be distinguished
histologically. The
liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
is large and separate from the
gall bladder.
The kidneys are long and flattened. The salt concentration in cetacean blood is lower than that in seawater, requiring kidneys to excrete salt. This allows the animals to drink seawater.
Senses
Cetacean
eye
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and conv ...
s are set on the sides rather than the front of the head. This means only species with pointed 'beaks' (such as dolphins) have good
binocular vision
In biology, binocular vision is a type of vision in which an animal has two eyes capable of facing the same direction to perceive a single three-dimensional image of its surroundings. Binocular vision does not typically refer to vision where an ...
forward and downward.
Tear glands secrete greasy tears, which protect the eyes from the salt in the water. The lens is almost spherical, which is most efficient at focusing the minimal light that reaches deep water. Odontocetes have little to no ability to taste or smell, while mysticetes are believed to have some ability to smell because of their reduced, but functional
olfactory system. Cetaceans are known to possess excellent hearing.
At least one species, the
tucuxi or Guiana dolphin, is able to use
electroreception to sense prey.
Ears

The external ear has lost the
pinna (visible ear), but still retains a narrow
external auditory meatus. To register sounds, instead, the posterior part of the
mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bon ...
has a thin lateral wall (the pan bone) fronting a concavity that houses a fat pad. The pad passes anteriorly into the greatly enlarged
mandibular foramen to reach in under the teeth and posteriorly to reach the thin lateral wall of the
ectotympanic. The ectotympanic offers a reduced attachment area for the
tympanic membrane. The connection between this auditory complex and the rest of the skull is reduced—to a single, small cartilage in
oceanic dolphins.
In odontocetes, the complex is surrounded by spongy tissue filled with air spaces, while in mysticetes, it is integrated into the skull as with land mammals. In odontocetes, the tympanic membrane (or ligament) has the shape of a folded-in umbrella that stretches from the ectotympanic ring and narrows off to the
malleus
The malleus, or hammer, is a hammer-shaped small bone or ossicle of the middle ear. It connects with the incus, and is attached to the inner surface of the eardrum. The word is Latin for 'hammer' or 'mallet'. It transmits the sound vibrations ...
(quite unlike the flat, circular membrane found in land mammals.) In mysticetes, it also forms a large protrusion (known as the "glove finger"), which stretches into the external
meatus and the
stapes are larger than in odontocetes. In some
small sperm whales, the malleus is fused with the ectotympanic.
The ear
ossicles are
pachyosteosclerotic (dense and compact) and differently shaped from land mammals (other aquatic mammals, such as
sirenia
The Sirenia (), commonly referred to as sea-cows or sirenians, are an order of fully aquatic, herbivorous mammals that inhabit swamps, rivers, estuaries, marine wetlands, and coastal marine waters. The Sirenia currently comprise two distinct ...
ns and earless seals, have also lost their pinnae). T semicircular canals are much smaller relative to body size than in other mammals.
The
auditory bulla is separated from the skull and composed of two compact and dense bones (the periotic and tympanic) referred to as the tympanoperiotic complex. This complex is located in a cavity in the middle ear, which, in the Mysticeti, is divided by a bony projection and compressed between the exoccipital and squamosal, but in the odontoceti, is large and completely surrounds the bulla (hence called "peribullar"), which is, therefore, not connected to the skull except in
physeterids. In the Odontoceti, the cavity is filled with a dense foam in which the bulla hangs suspended in five or more sets of ligaments. The pterygoid and peribullar
sinuses that form the cavity tend to be more developed in shallow water and riverine species than in
pelagic Mysticeti. In Odontoceti, the composite auditory structure is thought to serve as an acoustic isolator, analogous to the lamellar construction found in the temporal bone in
bats.
Cetaceans use sound to
communicate, using groans, moans, whistles, clicks or the 'singing' of the humpback whale.
Echolocation
Odontoceti are generally capable of
echolocation.
They can discern the size, shape, surface characteristics, distance and movement of an object. They can search for, chase and catch fast-swimming prey in total darkness. Most Odontoceti can distinguish between prey and nonprey (such as humans or boats); captive Odontoceti can be trained to distinguish between, for example, balls of different sizes or shapes. Echolocation clicks also contain characteristic details unique to each animal, which may suggest that toothed whales can discern between their own click and that of others.
Mysticeti have exceptionally thin, wide basilar membranes in their
cochlea
The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the Organ of Corti, the sensory org ...
e without stiffening agents, making their ears adapted for processing low to
infrasonic
Infrasound, sometimes referred to as low status sound, describes sound waves with a frequency below the lower limit of human audibility (generally 20 Hz). Hearing becomes gradually less sensitive as frequency decreases, so for humans to perce ...
frequencies.
Chromosomes
The initial
karyotype
A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of metaphase chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is disce ...
includes a set of
chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
s from 2n = 44. They have four pairs of telocentric chromosomes (whose
centromeres sit at one of the
telomeres), two to four pairs of subtelocentric and one or two large pairs of submetacentric chromosomes. The remaining chromosomes are metacentric—the centromere is approximately in the middle—and are rather small. All cetaceans have chromosomes 2n = 44, except the
sperm whale
The sperm whale or cachalot (''Physeter macrocephalus'') is the largest of the toothed whales and the largest toothed predator. It is the only living member of the genus '' Physeter'' and one of three extant species in the sperm whale famil ...
s and
pygmy sperm whales, which have 2n = 42.
Ecology
Range and habitat
Cetaceans are found in many aquatic habitats. While many marine species, such as the
blue whale
The blue whale (''Balaenoptera musculus'') is a marine mammal and a baleen whale. Reaching a maximum confirmed length of and weighing up to , it is the largest animal known to have ever existed. The blue whale's long and slender body can b ...
, the
humpback whale
The humpback whale (''Megaptera novaeangliae'') is a species of baleen whale. It is a rorqual (a member of the family Balaenopteridae) and is the only species in the genus ''Megaptera''. Adults range in length from and weigh up to . The hum ...
and the
orca
The orca or killer whale (''Orcinus orca'') is a toothed whale belonging to the oceanic dolphin family, of which it is the largest member. It is the only extant species in the genus '' Orcinus'' and is recognizable by its black-and-white ...
, have a distribution area that includes nearly the entire ocean, some species occur only locally or in broken populations. These include the
vaquita, which inhabits a small part of the
Gulf of California and
Hector's dolphin, which lives in some coastal waters in New Zealand.
River dolphin species live exclusively in fresh water.
Many species inhabit specific latitudes, often in tropical or subtropical waters, such as
Bryde's whale or
Risso's dolphin. Others are found only in a specific body of water. The
southern right whale dolphin and the
hourglass dolphin live only in the
Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is regarded as the second-smal ...
. The
narwhal and the
beluga live only in the Arctic Ocean.
Sowerby's beaked whale and the
Clymene dolphin exist only in the Atlantic and the
Pacific white-sided dolphin and the
northern straight dolphin live only in the North Pacific.
Cosmopolitan species may be found in the Pacific, Atlantic and Indian Oceans. However, northern and southern populations become genetically separated over time. In some species, this separation leads eventually to a divergence of the species, such as produced the
southern right whale
The southern right whale (''Eubalaena australis'') is a baleen whale, one of three species classified as right whales belonging to the genus ''Eubalaena''. Southern right whales inhabit oceans south of the Equator, between the latitudes of 20 ...
,
North Pacific right whale and
North Atlantic right whale
The North Atlantic right whale (''Eubalaena glacialis'') is a baleen whale, one of three right whale species belonging to the genus '' Eubalaena'', all of which were formerly classified as a single species. Because of their docile nature, their ...
. Migratory species' reproductive sites often lie in the tropics and their feeding grounds in polar regions.
Thirty-two species are found in European waters, including twenty-five toothed and seven baleen species.
Whale migration
Many species of whales migrate on a latitudinal basis to move between seasonal habitats. For example, the gray whale migrates round trip. The journey begins at winter birthing grounds in warm lagoons along Baja California, and traverses of coastline to summer feeding grounds in the Bering, Chuckchi and Beaufort seas off the coast of Alaska.
Behaviour
Sleep
Conscious breathing cetaceans sleep but cannot afford to be unconscious for long, because they may drown. While knowledge of sleep in wild cetaceans is limited, toothed cetaceans in captivity have been recorded to exhibit
unihemispheric slow-wave sleep (USWS), which means they sleep with one side of their brain at a time, so that they may swim, breathe consciously and avoid both predators and social contact during their period of rest.
A 2008 study found that sperm whales sleep in vertical postures just under the surface in passive shallow 'drift-dives', generally during the day, during which whales do not respond to passing vessels unless they are in contact, leading to the suggestion that whales possibly sleep during such dives.
Diving
While diving, the animals reduce their oxygen consumption by lowering the heart activity and blood circulation; individual organs receive no oxygen during this time. Some
rorquals can dive for up to 40 minutes,
sperm whales between 60 and 90 minutes and
bottlenose whales for two hours. Diving depths average about . Species such as sperm whales can dive to , although more commonly .
Social relations
Most cetaceans are social animals, although a few species live in pairs or are solitary. A group, known as a pod, usually consists of ten to fifty animals, but on occasion, such as mass availability of food or during mating season, groups may encompass more than one thousand individuals. Inter-species socialization can occur.
Pods have a fixed hierarchy, with the priority positions determined by biting, pushing or ramming. The behavior in the group is aggressive only in situations of stress such as lack of food, but usually it is peaceful. Contact swimming, mutual fondling and nudging are common. The playful behavior of the animals, which is manifested in air jumps, somersaults, surfing, or fin hitting, occurs more often than not in smaller cetaceans, such as dolphins and porpoises.
Whale song
Males in some baleen species communicate via
whale song, sequences of high pitched sounds. These "songs" can be heard for hundreds of kilometers. Each population generally shares a distinct song, which evolves over time. Sometimes, an individual can be identified by its distinctive vocals, such as the
52-hertz whale
The 52-hertz whale, colloquially referred to as 52 Blue, is an individual whale of unidentified species that calls at the unusual frequency of 52 hertz. This pitch is at a higher frequency than that of the other whale species with migration ...
that sings at a higher frequency than other whales. Some individuals are capable of generating over 600 distinct sounds.
In baleen species such as humpbacks, blues and fins, male-specific song is believed to be used to attract and display fitness to females.
Hunting
Pod groups also hunt, often with other species. Many species of dolphins accompany large tunas on hunting expeditions, following large schools of fish. The orca hunts in pods and targets belugas and even larger whales. Humpback whales, among others, form in collaboration
bubble carpets to herd krill or plankton into bait balls before lunging at them.
Intelligence

Cetacea are known to teach, learn, cooperate, scheme and grieve.
Smaller cetaceans, such as dolphins and porpoises, engage in complex play behavior, including such things as producing stable underwater
toroidal air-core
vortex
In fluid dynamics, a vortex ( : vortices or vortexes) is a region in a fluid in which the flow revolves around an axis line, which may be straight or curved. Vortices form in stirred fluids, and may be observed in smoke rings, whirlpools in t ...
rings or "
bubble rings". The two main methods of bubble ring production are rapid puffing of air into the water and allowing it to rise to the surface, forming a ring, or swimming repeatedly in a circle and then stopping to inject air into the
helical vortex currents thus formed. They also appear to enjoy biting the vortex rings, so that they burst into many separate bubbles and then rise quickly to the surface. Whales produce bubble nets to aid in herding prey.

Larger whales are also thought to engage in play. The southern right whale elevates its tail fluke above the water, remaining in the same position for a considerable time. This is known as "sailing". It appears to be a form of play and is most commonly seen off the coast of Argentina and South Africa. Humpback whales also display this behaviour.
Self-awareness
In philosophy of self, self-awareness is the experience of one's own personality or individuality. It is not to be confused with consciousness in the sense of qualia. While consciousness is being aware of one's environment and body and life ...
appears to be a sign of abstract thinking. Self-awareness, although not well-defined, is believed to be a precursor to more advanced processes such as
metacognitive reasoning (thinking about thinking) that humans exploit. Dolphins appear to possess self-awareness. The most widely used test for self-awareness in animals is the
mirror test, in which a temporary dye is placed on an animal's body and the animal is then presented with a mirror. Researchers then explore whether the animal shows signs of self-recognition.
Critics claim that the results of these tests are susceptible to the
Clever Hans effect. This test is much less definitive than when used for
primates
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter includin ...
. Primates can touch the mark or the mirror, while dolphins cannot, making their alleged self-recognition behavior less certain. Skeptics argue that behaviors said to identify self-awareness resemble existing social behaviors, so researchers could be misinterpreting self-awareness for social responses. Advocates counter that the behaviors are different from normal responses to another individual. Dolphins show less definitive behavior of self-awareness, because they have no pointing ability.
In 1995, Marten and Psarakos used video to test dolphin self-awareness. They showed dolphins real-time footage of themselves, recorded footage and another dolphin. They concluded that their evidence suggested self-awareness rather than social behavior. While this particular study has not been replicated, dolphins later "passed" the mirror test.
Life history
Reproduction and brooding
Most cetaceans sexually mature at seven to 10 years. An exception to this is the
La Plata dolphin, which is sexually mature at two years, but lives only to about 20. The sperm whale reaches sexual maturity within about 20 years and has a lifespan between 50 and 100 years.
For most species, reproduction is seasonal.
Ovulation
Ovulation is the release of eggs from the ovaries. In women, this event occurs when the ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilize ...
coincides with male
fertility
Fertility is the capability to produce offspring through reproduction following the onset of sexual maturity. The fertility rate is the average number of children born by a female during her lifetime and is quantified demographically. Ferti ...
. This cycle is usually coupled with seasonal movements that can be observed in many species. Most toothed whales have no fixed bonds. In many species, females choose several partners during a season. Baleen whales are largely
monogamous within each reproductive period.
Gestation ranges from 9 to 16 months. Duration is not necessarily a function of size. Porpoises and blue whales gestate for about 11 months. As with all mammals other than marsupials and monotremes, the embryo is fed by the
placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ (anatomy), organ that begins embryonic development, developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation (embryology), implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrien ...
, an organ that draws nutrients from the mother's bloodstream. Mammals without placentas either lay minuscule eggs (monotremes) or bear minuscule offspring (marsupials).
Cetaceans usually bear one calf. In the case of twins, one usually dies, because the mother cannot produce sufficient milk for both. The fetus is positioned for a tail-first delivery, so that the risk of drowning during delivery is minimal. After birth, the mother carries the infant to the surface for its first breath. At birth, they are about one-third of their adult length and tend to be independently active, comparable to terrestrial
mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fu ...
.
Suckling
Like other placental mammals, cetaceans give birth to well-developed calves and nurse them with milk from their
mammary glands
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland in humans and other mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in ...
. When suckling, the mother actively splashes milk into the mouth of the calf, using the muscles of her mammary glands, as the calf has no lips. This milk usually has a high-fat content, ranging from 16 to 46%, causing the calf to increase rapidly in size and weight.
In many small cetaceans, suckling lasts for about four months. In large species, it lasts for over a year and involves a strong bond between mother and offspring.
The mother is solely responsible for brooding. In some species, so-called "aunts" occasionally suckle the young.
This reproductive strategy provides a few offspring that have a high survival rate.
Lifespan
Among cetaceans, whales are distinguished by an unusual longevity compared to other higher mammals. Some species, such as the
bowhead whale
The bowhead whale (''Balaena mysticetus'') is a species of baleen whale belonging to the family Balaenidae and the only living representative of the genus '' Balaena''. They are the only baleen whale endemic to the Arctic and subarctic waters, ...
(''Balaena mysticetus''), can reach over 200 years. Based on the annual rings of the bony
otic capsule
The bony labyrinth (also osseous labyrinth or otic capsule) is the rigid, bony outer wall of the inner ear in the temporal bone. It consists of three parts: the vestibule, semicircular canals, and cochlea. These are cavities hollowed out of the s ...
, the age of the oldest known specimen is a male determined to be 211 years at the time of death.
Death
Upon death, whale carcasses fall to the deep ocean and provide a substantial habitat for marine life. Evidence of whale falls in present-day and fossil records shows that deep-sea whale falls support a rich assemblage of creatures, with a global diversity of 407 species, comparable to other
neritic biodiversity hotspots, such as
cold seep
A cold seep (sometimes called a cold vent) is an area of the ocean floor where hydrogen sulfide, methane and other hydrocarbon-rich fluid seepage occurs, often in the form of a brine pool. ''Cold'' does not mean that the temperature of the see ...
s and
hydrothermal vents.
Deterioration of whale carcasses happens through three stages. Initially, organisms such as
shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachi ...
s and
hagfish scavenge the soft tissues at a rapid rate over a period of months and as long as two years. This is followed by the colonization of bones and surrounding sediments (which contain organic matter) by enrichment opportunists, such as
crustaceans
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean gr ...
and
polychaetes
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are ...
, throughout a period of years. Finally, sulfophilic bacteria reduce the bones releasing
hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The und ...
enabling the growth of
chemoautotrophic
A Chemotroph is an organism that obtains energy by the oxidation of electron donors in their environments. These molecules can be organic ( chemoorganotrophs) or inorganic ( chemolithotrophs). The chemotroph designation is in contrast to phot ...
organisms, which in turn, support organisms such as mussels, clams, limpets and sea snails. This stage may last for decades and supports a rich assemblage of species, averaging 185 per site.
Disease
Brucellosis affects almost all mammals. It is distributed worldwide, while fishing and pollution have caused porpoise population density pockets, which risks further infection and disease spreading. ''
Brucella ceti
''Brucella ceti'' is a gram negative bacterial pathogen of the Brucellaceae family that causes brucellosis in cetaceans. ''Brucella ceti'' has been found in both classes of cetaceans, mysticetes and odontocetes. Brucellosis in some dolphins and ...
'', most prevalent in dolphins, has been shown to cause
chronic disease, increasing the chance of failed birth and
miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion and pregnancy loss, is the death of an embryo or fetus before it is able to survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks of gestation is defined by ESHRE as biochemical ...
s,
male infertility, neurobrucellosis,
cardiopathies, bone and skin
lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
Types
There is no designated classif ...
s,
strandings and death. Until 2008, no case had ever been reported in porpoises, but isolated populations have an increased risk and consequentially a high mortality rate.
Evolution
Phylogenetics

Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and phys ...
and
immunology
Immunology is a branch of medicineImmunology for Medical Students, Roderick Nairn, Matthew Helbert, Mosby, 2007 and biology that covers the medical study of immune systems in humans, animals, plants and sapient species. In such we can see ther ...
show that cetaceans are phylogenetically closely related with the
even-toed ungulate
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing post ...
s (Artiodactyla). Whales' direct lineage began in the early
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " ...
, around 55.8 million years ago, with early artiodactyls.
Fossil discoveries at the beginning of the 21st century confirmed this.
Most molecular biological evidence suggests that
hippos are the closest living relatives. Common anatomical features include similarities in the
morphology of the posterior
molars, and the bony ring on the temporal bone (bulla) and the involucre, a skull feature that was previously associated only with cetaceans.
[
] The fossil record, however, does not support this relationship, because the hippo lineage dates back only about 15 million years.
The most striking common feature is the
talus, a bone in the upper ankle. Early cetaceans,
archaeocetes
Archaeoceti ("ancient whales"), or Zeuglodontes in older literature, is a paraphyletic group of primitive cetaceans that lived from the Early Eocene to the late Oligocene (). Representing the earliest cetacean radiation, they include the initial ...
, show double castors, which occur only in even-toed ungulates. Corresponding findings are from
Tethys Sea deposits in northern India and Pakistan. The Tethys Sea was a shallow sea between the Asian continent and northward-bound Indian plate.

Mysticetes evolved baleen around 25 million years ago and lost their teeth.
Development
Ancestors
The direct ancestors of today's cetaceans are probably found within the
Dorudontidae
Dorudontinae are a group of extinct cetaceans that are related to ''Basilosaurus''.. Retrieved July 2013.
Classification
* Subfamily Dorudontinae
** Genus ''Ancalecetus''
*** ''Ancalecetus simonsi''
** Genus ''Chrysocetus''
*** ''Chrysocetus ...
whose most famous member, ''
Dorudon'', lived at the same time as ''
Basilosaurus''. Both groups had already developed the typical anatomical features of today's whales, such as hearing. Life in the water for a formerly terrestrial creature required significant adjustments such as the fixed bulla, which replaces the mammalian
eardrum, as well as sound-conducting elements for submerged directional hearing. Their wrists were stiffened and probably contributed to the typical build of flippers. The hind legs existed, however, but were significantly reduced in size and with a vestigial pelvis connection.
Transition from land to sea
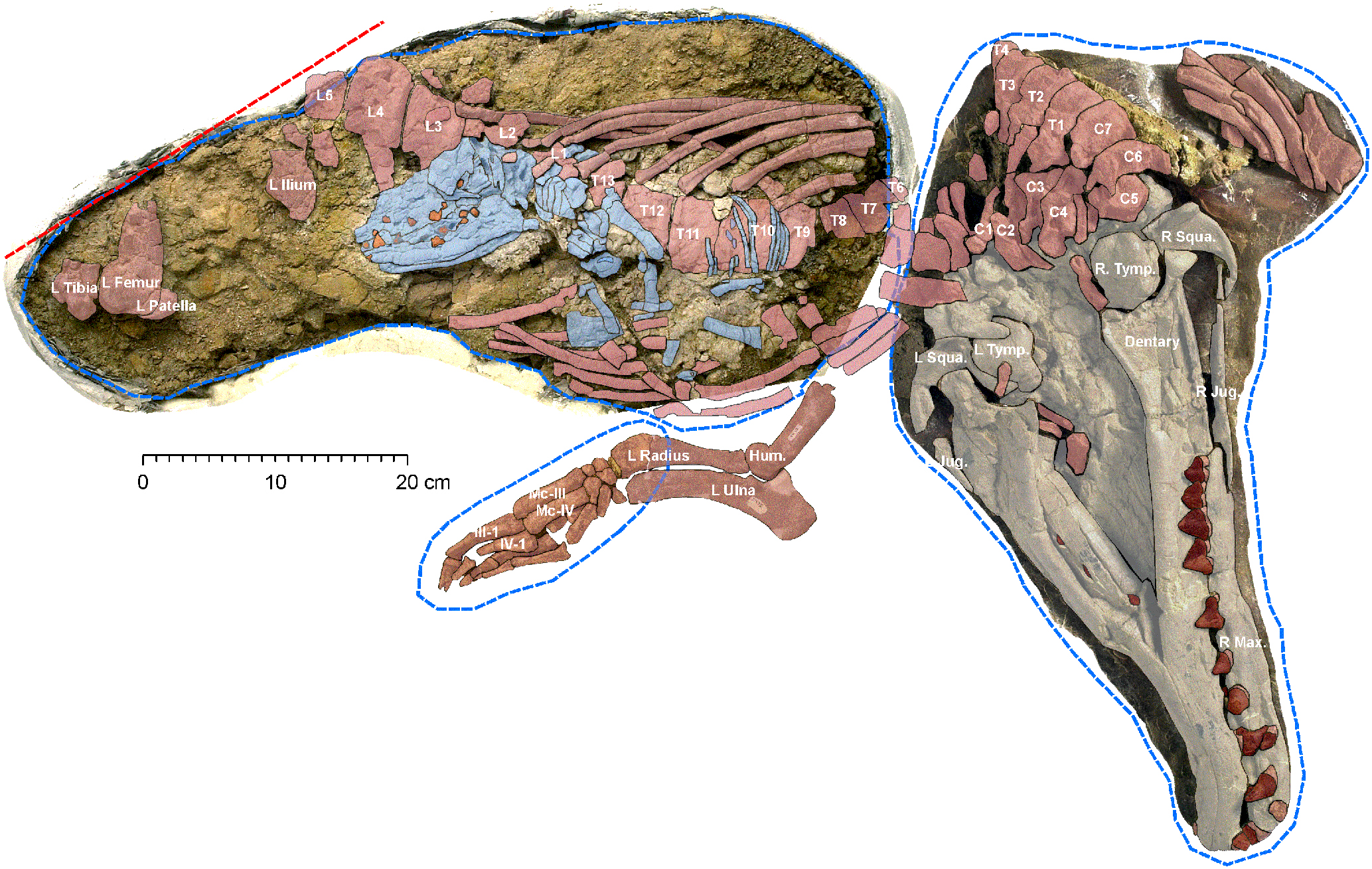
The fossil record traces the gradual transition from terrestrial to aquatic life. The regression of the hind limbs allowed greater flexibility of the spine. This made it possible for whales to move around with the vertical tail hitting the water. The front legs transformed into flippers, costing them their mobility on land.
One of the oldest members of ancient cetaceans (
Archaeoceti) is ''
Pakicetus
''Pakicetus'' is an extinct genus of amphibious cetacean of the family Pakicetidae, which was endemic to Pakistan during the Eocene, about 50 million years ago. It was a wolf-like animal, about to long, and lived in and around water where i ...
'' from the Middle Eocene. This is an animal the size of a wolf, whose skeleton is known only partially. It had functioning legs and lived near the shore. This suggests the animal could still move on land. The long snout had
carnivorous
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other ...
dentition.
The transition from land to sea dates to about 49 million years ago, with the ''
Ambulocetus'' ("running whale"), discovered in Pakistan. It was up to long. The limbs of this archaeocete were leg-like, but it was already fully aquatic, indicating that a switch to a lifestyle independent from land happened extraordinarily quickly. The snout was elongated with overhead nostrils and eyes. The tail was strong and supported movement through water. ''Ambulocetus'' probably lived in mangroves in
brackish water and fed in the
riparian zone
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks ...
as a predator of fish and other vertebrates.
Dating from about 45 million years ago are species such as ''
Indocetus
''Indocetus'' is a protocetid early whale known from the late early Eocene (Lutetian, ) Harudi Formation (, paleocoordinates ) in Kutch, India.
The holotype of is a partial skull in two pieces with the frontal shield and the right occiput an ...
'', ''
Kutchicetus'', ''
Rodhocetus
''Rodhocetus'' (from ''Rodho'', the geological anticline at the type locality, and ''cetus'', Latin for whale) is an extinct genus of protocetid early whale known from the Lutetian of Pakistan. The best-known protocetid, ''Rodhocetus'' is know ...
'' and ''
Andrewsiphius'', all of which were adapted to life in water. The hind limbs of these species were regressed and their body shapes resemble modern whales.
Protocetidae
Protocetidae, the protocetids, form a diverse and heterogeneous group of extinct cetaceans known from Asia, Europe, Africa, South America, and North America.
Description
There were many genera, and some of these are very well known (e.g., '' ...
family member ''Rodhocetus'' is considered the first to be fully aquatic. The body was streamlined and delicate with extended hand and foot bones. The merged pelvic
lumbar spine was present, making it possible to support the floating movement of the tail. It was likely a good swimmer, but could probably move only clumsily on land, much like a modern
seal.
Marine animals
Since the late Eocene, about 40 million years ago, cetaceans populated the subtropical oceans and no longer emerged on land. An example is the 18-m-long ''
Basilosaurus'', sometimes referred to as ''Zeuglodon''. The transition from land to water was completed in about 10 million years. The
Wadi Al-Hitan ("Whale Valley") in Egypt contains numerous skeletons of ''Basilosaurus'', as well as other marine vertebrates.
Taxonomy
Molecular findings and morphological indications suggest that
artiodactyls as traditionally defined are
paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be pa ...
with respect to cetaceans. Cetaceans are deeply nested within the former; the two groups together form a
monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic ...
taxon, for which the name
Cetartiodactyla is sometimes used. Modern nomenclature divides Artiodactyla (or Cetartiodactyla) in four subordinate taxa: camelids (Tylopoda), pigs and peccaries (Suina), ruminants (Ruminantia), and hippos plus whales (Whippomorpha).
Cetacea's presumed location within
Artiodactyla
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing poste ...
can be represented in the following
cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ...
:
[
][
][
][
(see e.g. Fig S10)
]
Within Cetacea, the two
parvorders are
baleen whales (
Mysticeti) which owe their name to their baleen, and
toothed whales (
Odontoceti), which have teeth shaped like cones, spades, pegs, or tusks, and can perceive their environment through
biosonar
Echolocation, also called bio sonar, is a biological sonar used by several animal species.
Echolocating animals emit calls out to the environment
and listen to the echoes of those calls that return from various objects near them. They use these ...
.
The terms ''whale'' and ''dolphin'' are informal:
*
Mysticeti:
:*
Whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
s, with four families:
Balaenidae (right and bowhead whales),
Cetotheriidae (pygmy right whales),
Balaenopteridae (rorquals),
Eschrichtiidae (grey whales)
*
Odontoceti:
:*
Whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
s: with four families:
Monodontidae (belugas and narwhals),
Physeteridae (sperm whales),
Kogiidae (dwarf and pygmy sperm whales), and
Ziphiidae (beaked whales)
:*
Dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (t ...
s, with five families:
Delphinidae (oceanic dolphins),
Platanistidae
Platanistidae is a family of river dolphins containing the extant Ganges river dolphin and Indus river dolphin (both in the genus '' Platanista'') but also extinct relatives from marine deposits in the Neogene.
The Amazon river dolphin, Yangtze ...
(
South Asian river dolphins),
Lipotidae
Lipotidae is a family of river dolphins containing the possibly extinct baiji of China and the fossil genus ''Parapontoporia'' from the Late Miocene and Pliocene of the Pacific coast of North America. The genus '' Prolipotes'', which is based on ...
(old world river dolphins)
Iniidae
Iniidae is a family of river dolphins containing one living genus, ''Inia'', and four extinct genera. The extant genus inhabits the river basins of South America, but the family formerly had a wider presence across the Atlantic Ocean.
Iniidae a ...
(new world river dolphins), and
Pontoporiidae (
La Plata dolphins)
:*
Porpoise
Porpoises are a group of fully aquatic marine mammals, all of which are classified under the family Phocoenidae, parvorder Odontoceti (toothed whales). Although similar in appearance to dolphins, they are more closely related to narwhals ...
s, with one family:
Phocoenidae
The term 'great whales' covers those currently regulated by the
International Whaling Commission
The International Whaling Commission (IWC) is a specialised regional fishery management organisation, established under the terms of the 1946 International Convention for the Regulation of Whaling (ICRW) to "provide for the proper conservation ...
:
[
]
the Odontoceti families Physeteridae (sperm whales), Ziphiidae (beaked whales), and Kogiidae (pygmy and dwarf sperm whales); and all the Mysticeti families Balaenidae (right and bowhead whales), Cetotheriidae (pygmy right whales), Eschrichtiidae (grey whales), and some of the Balaenopteridae (minke, Bryde's, sei, blue and fin; not Eden's and Omura's whales).
[
]
Status
Threats
The primary threats to cetaceans come from people, both directly from whaling or
drive hunting and indirect threats from fishing and pollution.
Whaling

Whaling is the practice of hunting whales, mainly baleen and sperm whales. This activity has gone on since the
Stone Age.
In the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, reasons for whaling included their
meat,
oil usable as fuel and the jawbone, which was used in house construction. At the end of the Middle Ages, early whaling fleets aimed at
baleen whales, such as
bowheads. In the 16th and 17th centuries, the Dutch fleet had about 300 whaling ships with 18,000 crewmen.
In the 18th and 19th centuries, baleen whales especially were hunted for their
baleen, which was used as a replacement for wood, or in products requiring strength and flexibility such as
corsets and
crinoline skirts. In addition, the
spermaceti found in the
sperm whale
The sperm whale or cachalot (''Physeter macrocephalus'') is the largest of the toothed whales and the largest toothed predator. It is the only living member of the genus '' Physeter'' and one of three extant species in the sperm whale famil ...
was used as a machine lubricant and the
ambergris as a material for pharmaceutical and perfume industries. In the second half of the 19th century, the explosive
harpoon
A harpoon is a long spear-like instrument and tool used in fishing, whaling, sealing, and other marine hunting to catch and injure large fish or marine mammals such as seals and whales. It accomplishes this task by impaling the target animal ...
was invented, leading to a massive increase in the catch size.
Large ships were used as "mother" ships for the whale handlers. In the first half of the 20th century, whales were of great importance as a supplier of raw materials. Whales were intensively hunted during this time; in the 1930s, 30,000 whales were killed. This increased to over 40,000 animals per year up to the 1960s, when stocks of large baleen whales collapsed.
Most hunted whales are now threatened, with some great whale populations exploited to the brink of extinction. Atlantic and Korean
gray whale
The gray whale (''Eschrichtius robustus''), also known as the grey whale,Britannica Micro.: v. IV, p. 693. gray back whale, Pacific gray whale, Korean gray whale, or California gray whale, is a baleen whale that migrates between feeding and bre ...
populations were completely eradicated and the
North Atlantic right whale
The North Atlantic right whale (''Eubalaena glacialis'') is a baleen whale, one of three right whale species belonging to the genus '' Eubalaena'', all of which were formerly classified as a single species. Because of their docile nature, their ...
population fell to some 300–600. The
blue whale
The blue whale (''Balaenoptera musculus'') is a marine mammal and a baleen whale. Reaching a maximum confirmed length of and weighing up to , it is the largest animal known to have ever existed. The blue whale's long and slender body can b ...
population is estimated to be around 14,000.
The first efforts to protect whales came in 1931. Some particularly endangered species, such as the
humpback whale
The humpback whale (''Megaptera novaeangliae'') is a species of baleen whale. It is a rorqual (a member of the family Balaenopteridae) and is the only species in the genus ''Megaptera''. Adults range in length from and weigh up to . The hum ...
(which then numbered about 100 animals), were placed under international protection and the first protected areas were established. In 1946, the
International Whaling Commission
The International Whaling Commission (IWC) is a specialised regional fishery management organisation, established under the terms of the 1946 International Convention for the Regulation of Whaling (ICRW) to "provide for the proper conservation ...
(IWC) was established, to monitor and secure whale stocks. Whaling of 14 large species for commercial purposes was prohibited worldwide by this organization from 1985 to 2005, though some countries do not honor the prohibition.
The stocks of species such as humpback and blue whales have recovered, though they are still threatened. The United States Congress passed the
Marine Mammal Protection Act of 1972 sustain the marine mammal population. It prohibits the taking of marine mammals except for several hundred per year taken in Alaska. Japanese whaling ships are allowed to hunt whales of different species for ostensibly scientific purposes.
Aboriginal whaling is still permitted. About 1,200 pilot whales were taken in the
Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic archipelago, island group and an autonomous territory of the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark.
They are located north-northwest of Scotlan ...
in 2017,
and about 900
narwhals and 800
belugas per year are taken in Alaska, Canada, Greenland, and Siberia. About 150 minke are taken in Greenland per year, 120 gray whales in Siberia and 50 bowheads in Alaska, as aboriginal whaling, besides the 600 minke taken commercially by Norway, 300 minke and 100 sei taken by Japan and up to 100 fin whales taken by Iceland.
Iceland and Norway do not recognize the ban and operate commercial whaling. Norway and Japan are committed to ending the ban.
Dolphins and other smaller cetaceans are sometimes hunted in an activity known as dolphin drive hunting. This is accomplished by driving a pod together with boats, usually into a bay or onto a beach. Their escape is prevented by closing off the route to the ocean with other boats or nets. Dolphins are hunted this way in several places around the world, including the
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its ca ...
, the
Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic archipelago, island group and an autonomous territory of the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark.
They are located north-northwest of Scotlan ...
,
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal
, national_motto = "Fi ...
and Japan (the most well-known practitioner). Dolphins are mostly hunted for their
meat, though some end up in
dolphinaria. Despite the controversy thousands of dolphins are caught in drive hunts each year.
Fishing

Dolphin pods often reside near large tuna shoals. This is known to fishermen, who look for dolphins to catch tuna. Dolphins are much easier to spot from a distance than tuna, since they regularly breathe. The fishermen pull their nets hundreds of meters wide in a circle around the dolphin groups, in the expectation that they will net a tuna shoal. When the nets are pulled together, the dolphins become entangled under water and drown. Line fisheries in larger rivers are threats to
river dolphins.
A greater threat than by-catch for small cetaceans is targeted hunting. In Southeast Asia, they are sold as fish-replacement to locals, since the region's edible fish promise higher revenues from exports. In the Mediterranean, small cetaceans are targeted to ease pressure on edible fish.
Strandings
A stranding is when a cetacean leaves the water to lie on a beach. In some cases, groups of whales strand together. The best known are mass strandings of
pilot whales and sperm whales.
Stranded cetaceans usually die, because their as much as body weight compresses their lungs or breaks their ribs. Smaller whales can die of heatstroke because of their thermal insulation.
The causes are not clear. Possible reasons for mass beachings are:
* toxic contaminants
* debilitating parasites (in the respiratory tract, brain or middle ear)
* infections (bacterial or viral)
* flight from predators (including humans)
* social bonds within a group, so that the pod follows a stranded animal
* disturbance of their magnetic senses by natural anomalies in the Earth's magnetic field
* injuries
*
noise pollution
Noise pollution, also known as environmental noise or sound pollution, is the propagation of noise with ranging impacts on the activity of human or animal life, most of them are harmful to a degree. The source of outdoor noise worldwide is mai ...
by shipping traffic, seismic surveys and military sonar experiments
Since 2000, whale strandings frequently occurred following military
sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances ( ranging), communicate with or detect objects on ...
testing. In December 2001, the US Navy admitted partial responsibility for the beaching and the deaths of several marine mammals in March 2000. The coauthor of the interim report stated that animals killed by active sonar of some Navy ships were injured. Generally, underwater noise, which is still on the increase, is increasingly tied to strandings; because it impairs communication and sense of direction.
Climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
influences the major wind systems and ocean currents, which also lead to cetacean strandings. Researchers studying strandings on the Tasmanian coast from 1920 to 2002 found that greater strandings occurred at certain time intervals. Years with increased strandings were associated with severe storms, which initiated cold water flows close to the coast. In nutrient-rich, cold water, cetaceans expect large prey animals, so they follow the cold water currents into shallower waters, where the risk is higher for strandings. Whales and dolphins who live in pods may accompany sick or debilitated pod members into shallow water, stranding them at low tide.
Environmental hazards
Heavy metals, residues of many plant and insect venoms and plastic waste
flotsam are not biodegradable. Sometimes, cetaceans consume these hazardous materials, mistaking them for food items. As a result, the animals are more susceptible to disease and have fewer offspring.
Damage to the
ozone layer
The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of Earth's stratosphere that absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation. It contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) in relation to other parts of the atmosphere, although still small in rel ...
reduces plankton reproduction because of its resulting radiation. This shrinks the food supply for many marine animals, but the filter-feeding baleen whales are most impacted. Even the
Nekton is, in addition to intensive exploitation, damaged by the radiation.
Food supplies are also reduced long-term by
ocean acidification due to increased absorption of increased atmospheric carbon dioxide. The CO
2 reacts with water to form
carbonic acid, which reduces the construction of the
calcium carbonate skeletons of food supplies for zooplankton that baleen whales depend on.
The military and resource extraction industries operate strong
sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances ( ranging), communicate with or detect objects on ...
and blasting operations. Marine seismic surveys use loud, low-frequency sound that show what is lying underneath the Earth's surface.
Vessel traffic also increases noise in the oceans. Such noise can disrupt cetacean behavior such as their use of
biosonar
Echolocation, also called bio sonar, is a biological sonar used by several animal species.
Echolocating animals emit calls out to the environment
and listen to the echoes of those calls that return from various objects near them. They use these ...
for orientation and communication. Severe instances can panic them, driving them to the surface. This leads to bubbles in blood gases and can cause
decompression sickness
Decompression sickness (abbreviated DCS; also called divers' disease, the bends, aerobullosis, and caisson disease) is a medical condition caused by dissolved gases emerging from solution as bubbles inside the body tissues during decompressi ...
. Naval exercises with sonar regularly results in fallen cetaceans that wash up with fatal decompression. Sounds can be disruptive at distances of more than . Damage varies across frequency and species.
Relationship to humans
Research history

In
Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical Greece, Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatet ...
's time, the fourth century BCE, whales were regarded as fish due to their superficial similarity. Aristotle, however, observed many physiological and anatomical similarities with the terrestrial vertebrates, such as blood (circulation), lungs, uterus and fin anatomy. His detailed descriptions were assimilated by the Romans, but mixed with a more accurate knowledge of the dolphins, as mentioned by
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ...
in his ''
Natural history''. In the art of this and subsequent periods, dolphins are portrayed with a high-arched head (typical of porpoises) and a long snout. The
harbour porpoise was one of the most accessible species for early
cetologists
Cetology (from Greek , ''kētos'', " whale"; and , ''-logia'') or whalelore (also known as whaleology) is the branch of marine mammal science that studies the approximately eighty species of whales, dolphins, and porpoises in the scientific o ...
; because it could be seen close to land, inhabiting shallow coastal areas of Europe. Much of the findings that apply to all cetaceans were first discovered in porpoises. One of the first anatomical descriptions of the airways of a harbor porpoise dates from 1671 by John Ray. It nevertheless referred to the porpoise as a fish.
In the
10th edition of Systema Naturae
The 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' is a book written by Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus and published in two volumes in 1758 and 1759, which marks the starting point of zoological nomenclature. In it, Linnaeus introduced binomial nomen ...
(1758), Swedish biologist and taxonomist
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, ...
asserted that cetaceans were mammals and not fish. His groundbreaking binomial system formed the basis of modern whale classification.
Culture
Cetaceans have played a role in human culture through history.
Prehistoric
Stone Age petroglyphs
A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other description ...
, such as those in Roddoy and Reppa (Norway), and the
Bangudae Petroglyphs in South Korea, depict them. Whale bones were used for many purposes. In the
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
settlement of Skara Brae on
Orkney
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) nort ...
sauce pans were made from whale vertebrae.
Antiquity


The whale was first mentioned in
ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
by
Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the '' Iliad'' and the '' Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of ...
. There, it is called Ketos, a term that initially included all large marine animals. From this was derived the Roman word for whale,
Cetus
Cetus () is a constellation, sometimes called 'the whale' in English. The Cetus was a sea monster in Greek mythology which both Perseus and Heracles needed to slay. Cetus is in the region of the sky that contains other water-related conste ...
. Other names were phálaina (
Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical Greece, Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatet ...
,
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
form of ballaena) for the female and, with an ironic characteristic style, musculus (Mouse) for the male.
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
whales were called Physeter, which was meant for the sperm whale ''Physter macrocephalus''. Whales are described in particular by Aristotle,
Pliny and
Ambrose
Ambrose of Milan ( la, Aurelius Ambrosius; ), venerated as Saint Ambrose, ; lmo, Sant Ambroeus . was a theologian and statesman who served as Bishop of Milan from 374 to 397. He expressed himself prominently as a public figure, fiercely promo ...
. All mention both live birth and suckling. Pliny describes the problems associated with the lungs with spray tubes and Ambrose claimed that large whales would take their young into their mouth to protect them.
In the
Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts o ...
especially, the leviathan plays a role as a
sea monster. The essence, which features a giant crocodile or a dragon and a whale, was created according to the Bible by God and should again be destroyed by him. In the
Book of Job
The Book of Job (; hbo, אִיּוֹב, ʾIyyōḇ), or simply Job, is a book found in the Ketuvim ("Writings") section of the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh), and is the first of the Poetic Books in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. Scholars ar ...
, the leviathan is described in more detail.
In Jonah there is a more recognizable description of a whale alongside the prophet
Jonah
Jonah or Jonas, ''Yōnā'', "dove"; gr, Ἰωνᾶς ''Iōnâs''; ar, يونس ' or '; Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spo ...
, who, on his flight from the city of
Nineveh
Nineveh (; akk, ; Biblical Hebrew: '; ar, نَيْنَوَىٰ '; syr, ܢܝܼܢܘܹܐ, Nīnwē) was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul in northern Iraq. It is located on the eastern b ...
is swallowed by a whale.
Dolphins are mentioned far more often than whales. Aristotle discusses the sacred animals of the Greeks in his ''
Historia Animalium'' and gives details of their role as aquatic animals. The Greeks admired the dolphin as a "king of the aquatic animals" and referred to them erroneously as fish. Its intelligence was apparent both in its ability to escape from fishnets and in its collaboration with fishermen.
River dolphins are known from the
Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
and – erroneously – the
Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered ...
. In the latter case it was equated with sharks and catfish. Supposedly they attacked even
crocodile
Crocodiles (family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term crocodile is sometimes used even more loosely to include all extant ...
s.
Dolphins appear in Greek mythology. Because of their intelligence, they rescued multiple people from drowning. They were said to love music – probably not least because of their own song – they saved, in the legends, famous musicians such as
Arion of
Lesbos
Lesbos or Lesvos ( el, Λέσβος, Lésvos ) is a Greek island located in the northeastern Aegean Sea. It has an area of with approximately of coastline, making it the third largest island in Greece. It is separated from Asia Minor by the n ...
from
Methymna or
Kairanos from Miletus. Because of their mental faculties, dolphins were considered to be associated with the god
Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans ...
.

Dolphins belong to the domain of
Poseidon
Poseidon (; grc-gre, Ποσειδῶν) was one of the Twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and myth, god of the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 In pre-Olympian Bronze Age Greece, he was venerated as a ch ...
and led him to his wife Amphitrite. Dolphins are associated with other gods, such as Apollo, Dionysus and Aphrodite. The Greeks paid tribute to both whales and dolphins with their own constellation. The constellation of the Cetus, Whale (Ketos, lat. Cetus) is located south of the Dolphin (Delphi, lat. Delphinus) north of the zodiac.
Ancient art often included dolphin representations, including the Cretan Minoan civilization, Minoans. Later they appeared on reliefs, gems, lamps, coins, mosaics and gravestones. A particularly popular representation is that of Arion or the Taras (mythology) riding on a dolphin. In early Christian art, the dolphin is a popular motif, at times used as a symbol of Christ.
Middle Ages to the 19th century
St. Brendan described in his travel story ''Navigatio Sancti Brendani'' an encounter with a whale, between the years 565–573. He described how he and his companions entered a treeless island, which turned out to be a giant whale, which he called Jasconicus. He met this whale seven years later and rested on his back.
Most descriptions of large whales from this time until the whaling era, beginning in the 17th century, were of beached whales, which resembled no other animal. This was particularly true for the sperm whale, the most frequently stranded in larger groups. Raymond Gilmore documented seventeen sperm whales in the estuary of the Elbe from 1723 to 1959 and thirty-one animals on the coast of Great Britain in 1784. In 1827, a blue whale beached itself off the coast of Ostend. Whales were used as attractions in museums and traveling exhibitions.

Whalers from the 17th to 19th centuries depicted whales in drawings and recounted tales of their occupation. Although they knew that whales were harmless giants, they described battles with harpooned animals. These included descriptions of sea monsters, including huge whales, sharks, sea snakes, giant squid and octopuses.
Among the first whalers who described their experiences on whaling trips was Captain William Scoresby from Great Britain, who published the book ''Northern Whale Fishery'', describing the hunt for northern baleen whales. This was followed by Thomas Beale, a British surgeon, in his book ''Some observations on the natural history of the sperm whale'' in 1835; and Frederick Debell Bennett's ''The tale of a whale hunt'' in 1840. Whales were described in narrative literature and paintings, most famously in the novels ''Moby-Dick, Moby Dick'' by Herman Melville and ''20,000 Leagues Under the Sea'' by Jules Verne.
Baleen was used to make vessel components such as the bottom of a bucket in the Scottish National Museum. The Norsemen crafted ornamented plates from baleen, sometimes interpreted as ironing boards.
In the Canadian Arctic (east coast) in Punuk and Thule culture (1000–1600 C.E.), baleen was used to construct houses in place of wood as roof support for winter houses, with half of the building buried under the ground. The actual roof was probably made of animal skins that were covered with soil and moss.
Modern culture

In the 20th century perceptions of cetaceans changed. They transformed from monsters into creatures of wonder, as science revealed them to be intelligent and peaceful animals. Hunting was replaced by whale and dolphin tourism. This change is reflected in films and novels. For example, the protagonist of the series Flipper (1995 TV series), Flipper was a bottle-nose dolphin. The TV series SeaQuest DSV (1993–1996), the movies Free Willy, Star Trek IV: The Voyage Home and the book series The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy by Douglas Adams are examples.
The study of
whale song also produced a popular album, ''Songs of the Humpback Whale (album), Songs of the Humpback Whale''.
Captivity
Whales and dolphins have been kept in captivity for use in education, research and entertainment since the 19th century.
Belugas
Beluga whales were the first whales to be kept in captivity. Other species were too rare, too shy or too big. The first was shown at Barnum's American Museum, Barnum's Museum in New York City in 1861.
For most of the 20th century, Canada was the predominant source.
They were taken from the Saint Lawrence River, St. Lawrence River estuary until the late 1960s, after which they were predominantly taken from the Churchill River (Hudson Bay), Churchill River estuary until capture was banned in 1992.
Russia then became the largest provider.
Belugas are caught in the Amu Darya, Amur Darya delta and their eastern coast and are transported domestically to aquaria or
dolphinaria in Moscow, St. Petersburg and Sochi, or exported to countries such as Canada.
They have not been domesticated.
As of 2006, 30 belugas lived in Canada and 28 in the United States. 42 deaths in captivity had been reported.
A single specimen can reportedly fetch up to US$100,000 (GB£64,160). The beluga's popularity is due to its unique color and its facial expressions. The latter is possible because while most cetacean "smiles" are fixed, the extra movement afforded by the beluga's unfused cervical vertebrae allows a greater range of apparent expression.
Orcas

The orca's animal intelligence, intelligence, trainability, striking appearance, playfulness in captivity and sheer size have made it a popular exhibit at aquaria and aquatic theme parks. From 1976 to 1997, fifty-five whales were taken from the wild in Iceland, nineteen from Japan and three from Argentina. These figures exclude animals that died during capture. Live captures fell dramatically in the 1990s and by 1999, about 40% of the forty-eight animals on display in the world were captive-born.
Organizations such as World Animal Protection and the Whale and Dolphin Conservation campaign against the practice of keeping them in captivity.
In captivity, they often develop pathologies, such as the
dorsal fin
A dorsal fin is a fin located on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates within various taxa of the animal kingdom. Many species of animals possessing dorsal fins are not particularly closely related to each other, though through c ...
collapse seen in 60–90% of captive males. Captives have reduced life expectancy, on average only living into their 20s, although some live longer, including several over 30 years old and two, Corky II and Lolita, in their mid-40s. In the wild, females who survive infancy live 46 years on average and up to 70–80 years. Wild males who survive infancy live 31 years on average and can reach 50–60 years.
Captivity usually bears little resemblance to wild habitat and captive whales' social groups are foreign to those found in the wild. Critics claim captive life is stressful due to these factors and the requirement to perform circus tricks that are not part of wild orca behavior. Wild orca may travel up to in a day and critics say the animals are too big and intelligent to be suitable for captivity.
Captives occasionally act aggressively towards themselves, their tankmates, or humans, which critics say is a result of stress (medicine), stress.
Orcas are well known for their performances in shows, but the number of orcas kept in captivity is small, especially when compared to the number of bottlenose dolphins, with only forty-four List of captive orcas, captive orcas being held in aquaria as of 2012.
Each country has its own tank requirements; in the US, the minimum enclosure size is set by the Code of Federal Regulations, 9 CFR E § 3.104, under the ''Specifications for the Humane Handling, Care, Treatment and Transportation of Marine Mammals''.

Aggression among captive orcas is common. They attack each other and their trainers as well. In 2013, SeaWorld's treatment of orcas in captivity was the basis of the movie ''Blackfish (film), Blackfish'', which documents the history of Tilikum (orca), Tilikum, an orca at SeaWorld Orlando, who had been involved in the deaths of three people. The film led to proposals by some lawmakers to ban captivity of cetaceans, and led SeaWorld to announce in 2016 that it would phase out its orca program after various unsuccessful attempts to restore its revenues, reputation, and stock price.
Others

Dolphins and porpoises are kept in captivity. Bottlenose dolphins are the most common, as they are relatively easy to train, have a long lifespan in captivity and have a friendly appearance. Bottlenose dolphins live in captivity across the world, though exact numbers are hard to determine. Other species kept in captivity are Atlantic spotted dolphin, spotted dolphins, false killer whales and common dolphins, Commerson's dolphins, as well as rough-toothed dolphins, but all in much lower numbers. There are also fewer than ten
pilot whales,
Amazon river dolphins,
Risso's dolphins,
spinner dolphins, or
tucuxi in captivity. Two unusual and rare hybrid (biology), hybrid dolphins, known as wolphins, are kept at Sea Life Park in Hawaii, which is a cross between a bottlenose dolphin and a false killer whale. Also, two Common dolphin, common/bottlenose hybrids reside in captivity at Discovery Cove and SeaWorld San Diego.
In repeated attempts in the 1960s and 1970s,
narwhals kept in captivity died within months. A breeding pair of pygmy right whales were retained in a netted area. They were eventually released in South Africa. In 1971, SeaWorld captured a California gray whale calf in Mexico at Ojo de Liebre Lagoon, Scammon's Lagoon. The calf, later named Gigi, was separated from her mother using a form of lasso attached to her flukes. Gigi was displayed at SeaWorld San Diego for a year. She was then released with a radio beacon affixed to her back; however, contact was lost after three weeks. Gigi was the first captive baleen whale. JJ, another
gray whale
The gray whale (''Eschrichtius robustus''), also known as the grey whale,Britannica Micro.: v. IV, p. 693. gray back whale, Pacific gray whale, Korean gray whale, or California gray whale, is a baleen whale that migrates between feeding and bre ...
calf, was kept at SeaWorld San Diego. JJ was an orphaned calf that beached itself in April 1997 and was transported two miles to SeaWorld. The calf was a popular attraction and behaved normally, despite separation from his mother. A year later, the then whale though smaller than average, was too big to keep in captivity, and was released on April 1, 1998. A captive
Amazon river dolphin housed at Acuario de Valencia is the only trained river dolphin in captivity.
Here is a list of all the cetaceans that have been taken into captivity for either conservation, research or human entertainment and education purposes currently or in the past, temporarily or permanently.
*Orca
*Vaquita
*False killer whale
*Pygmy killer whale
*Long-finned pilot whale
*Short-finned pilot whale
*Bottlenose dolphin
*Beluga whale
*
Pacific white-sided dolphin
*
Risso's dolphin
*Atlantic white-sided dolphin
*Narwhal
*Spotted dolphin
*Spinner dolphin
*Common dolphin
*Harbour porpoise
*Finless porpoise
*Commerson's dolphin
*Rough-toothed dolphin
*Boto
*Tucuxi
*Wholphin
*Gray whale
*Pygmy sperm whale
*Irrawaddy dolphin
*Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin
*Baiji
*Melon-headed whale
*
South Asian river dolphin
*Minke whale
References
External links
*
*
*
Scottish Cetacean Research & Rescue– see page o
Taxonomy*
*
EIA Cetacean campaign Reports and latest info.
EIA in USA reports etc.
{{Portal bar, Cetaceans, Marine life, Mammals, Animals, Biology, Oceans
Cetaceans,
Extant Ypresian first appearances
Mammal infraorders
Taxa named by Mathurin Jacques Brisson
 Cetaceans have a cartilaginous fluke at the end of their tails that is used for propulsion. The fluke is set horizontally on the body, unlike fish, which have vertical tails.
Cetaceans have a cartilaginous fluke at the end of their tails that is used for propulsion. The fluke is set horizontally on the body, unlike fish, which have vertical tails.
 The external ear has lost the pinna (visible ear), but still retains a narrow external auditory meatus. To register sounds, instead, the posterior part of the
The external ear has lost the pinna (visible ear), but still retains a narrow external auditory meatus. To register sounds, instead, the posterior part of the  Cetacea are known to teach, learn, cooperate, scheme and grieve.
Smaller cetaceans, such as dolphins and porpoises, engage in complex play behavior, including such things as producing stable underwater toroidal air-core
Cetacea are known to teach, learn, cooperate, scheme and grieve.
Smaller cetaceans, such as dolphins and porpoises, engage in complex play behavior, including such things as producing stable underwater toroidal air-core  Larger whales are also thought to engage in play. The southern right whale elevates its tail fluke above the water, remaining in the same position for a considerable time. This is known as "sailing". It appears to be a form of play and is most commonly seen off the coast of Argentina and South Africa. Humpback whales also display this behaviour.
Larger whales are also thought to engage in play. The southern right whale elevates its tail fluke above the water, remaining in the same position for a considerable time. This is known as "sailing". It appears to be a form of play and is most commonly seen off the coast of Argentina and South Africa. Humpback whales also display this behaviour.

 The fossil record traces the gradual transition from terrestrial to aquatic life. The regression of the hind limbs allowed greater flexibility of the spine. This made it possible for whales to move around with the vertical tail hitting the water. The front legs transformed into flippers, costing them their mobility on land.
One of the oldest members of ancient cetaceans ( Archaeoceti) is ''
The fossil record traces the gradual transition from terrestrial to aquatic life. The regression of the hind limbs allowed greater flexibility of the spine. This made it possible for whales to move around with the vertical tail hitting the water. The front legs transformed into flippers, costing them their mobility on land.
One of the oldest members of ancient cetaceans ( Archaeoceti) is '' Whaling is the practice of hunting whales, mainly baleen and sperm whales. This activity has gone on since the Stone Age.
In the
Whaling is the practice of hunting whales, mainly baleen and sperm whales. This activity has gone on since the Stone Age.
In the  Dolphin pods often reside near large tuna shoals. This is known to fishermen, who look for dolphins to catch tuna. Dolphins are much easier to spot from a distance than tuna, since they regularly breathe. The fishermen pull their nets hundreds of meters wide in a circle around the dolphin groups, in the expectation that they will net a tuna shoal. When the nets are pulled together, the dolphins become entangled under water and drown. Line fisheries in larger rivers are threats to river dolphins.
A greater threat than by-catch for small cetaceans is targeted hunting. In Southeast Asia, they are sold as fish-replacement to locals, since the region's edible fish promise higher revenues from exports. In the Mediterranean, small cetaceans are targeted to ease pressure on edible fish.
Dolphin pods often reside near large tuna shoals. This is known to fishermen, who look for dolphins to catch tuna. Dolphins are much easier to spot from a distance than tuna, since they regularly breathe. The fishermen pull their nets hundreds of meters wide in a circle around the dolphin groups, in the expectation that they will net a tuna shoal. When the nets are pulled together, the dolphins become entangled under water and drown. Line fisheries in larger rivers are threats to river dolphins.
A greater threat than by-catch for small cetaceans is targeted hunting. In Southeast Asia, they are sold as fish-replacement to locals, since the region's edible fish promise higher revenues from exports. In the Mediterranean, small cetaceans are targeted to ease pressure on edible fish.
 In
In 
 The whale was first mentioned in
The whale was first mentioned in  Dolphins belong to the domain of
Dolphins belong to the domain of  Whalers from the 17th to 19th centuries depicted whales in drawings and recounted tales of their occupation. Although they knew that whales were harmless giants, they described battles with harpooned animals. These included descriptions of sea monsters, including huge whales, sharks, sea snakes, giant squid and octopuses.
Among the first whalers who described their experiences on whaling trips was Captain William Scoresby from Great Britain, who published the book ''Northern Whale Fishery'', describing the hunt for northern baleen whales. This was followed by Thomas Beale, a British surgeon, in his book ''Some observations on the natural history of the sperm whale'' in 1835; and Frederick Debell Bennett's ''The tale of a whale hunt'' in 1840. Whales were described in narrative literature and paintings, most famously in the novels ''Moby-Dick, Moby Dick'' by Herman Melville and ''20,000 Leagues Under the Sea'' by Jules Verne.
Baleen was used to make vessel components such as the bottom of a bucket in the Scottish National Museum. The Norsemen crafted ornamented plates from baleen, sometimes interpreted as ironing boards.
In the Canadian Arctic (east coast) in Punuk and Thule culture (1000–1600 C.E.), baleen was used to construct houses in place of wood as roof support for winter houses, with half of the building buried under the ground. The actual roof was probably made of animal skins that were covered with soil and moss.
Whalers from the 17th to 19th centuries depicted whales in drawings and recounted tales of their occupation. Although they knew that whales were harmless giants, they described battles with harpooned animals. These included descriptions of sea monsters, including huge whales, sharks, sea snakes, giant squid and octopuses.
Among the first whalers who described their experiences on whaling trips was Captain William Scoresby from Great Britain, who published the book ''Northern Whale Fishery'', describing the hunt for northern baleen whales. This was followed by Thomas Beale, a British surgeon, in his book ''Some observations on the natural history of the sperm whale'' in 1835; and Frederick Debell Bennett's ''The tale of a whale hunt'' in 1840. Whales were described in narrative literature and paintings, most famously in the novels ''Moby-Dick, Moby Dick'' by Herman Melville and ''20,000 Leagues Under the Sea'' by Jules Verne.
Baleen was used to make vessel components such as the bottom of a bucket in the Scottish National Museum. The Norsemen crafted ornamented plates from baleen, sometimes interpreted as ironing boards.
In the Canadian Arctic (east coast) in Punuk and Thule culture (1000–1600 C.E.), baleen was used to construct houses in place of wood as roof support for winter houses, with half of the building buried under the ground. The actual roof was probably made of animal skins that were covered with soil and moss.
 In the 20th century perceptions of cetaceans changed. They transformed from monsters into creatures of wonder, as science revealed them to be intelligent and peaceful animals. Hunting was replaced by whale and dolphin tourism. This change is reflected in films and novels. For example, the protagonist of the series Flipper (1995 TV series), Flipper was a bottle-nose dolphin. The TV series SeaQuest DSV (1993–1996), the movies Free Willy, Star Trek IV: The Voyage Home and the book series The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy by Douglas Adams are examples.
The study of whale song also produced a popular album, ''Songs of the Humpback Whale (album), Songs of the Humpback Whale''.
In the 20th century perceptions of cetaceans changed. They transformed from monsters into creatures of wonder, as science revealed them to be intelligent and peaceful animals. Hunting was replaced by whale and dolphin tourism. This change is reflected in films and novels. For example, the protagonist of the series Flipper (1995 TV series), Flipper was a bottle-nose dolphin. The TV series SeaQuest DSV (1993–1996), the movies Free Willy, Star Trek IV: The Voyage Home and the book series The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy by Douglas Adams are examples.
The study of whale song also produced a popular album, ''Songs of the Humpback Whale (album), Songs of the Humpback Whale''.
 The orca's animal intelligence, intelligence, trainability, striking appearance, playfulness in captivity and sheer size have made it a popular exhibit at aquaria and aquatic theme parks. From 1976 to 1997, fifty-five whales were taken from the wild in Iceland, nineteen from Japan and three from Argentina. These figures exclude animals that died during capture. Live captures fell dramatically in the 1990s and by 1999, about 40% of the forty-eight animals on display in the world were captive-born.
Organizations such as World Animal Protection and the Whale and Dolphin Conservation campaign against the practice of keeping them in captivity.
In captivity, they often develop pathologies, such as the
The orca's animal intelligence, intelligence, trainability, striking appearance, playfulness in captivity and sheer size have made it a popular exhibit at aquaria and aquatic theme parks. From 1976 to 1997, fifty-five whales were taken from the wild in Iceland, nineteen from Japan and three from Argentina. These figures exclude animals that died during capture. Live captures fell dramatically in the 1990s and by 1999, about 40% of the forty-eight animals on display in the world were captive-born.
Organizations such as World Animal Protection and the Whale and Dolphin Conservation campaign against the practice of keeping them in captivity.
In captivity, they often develop pathologies, such as the  Aggression among captive orcas is common. They attack each other and their trainers as well. In 2013, SeaWorld's treatment of orcas in captivity was the basis of the movie ''Blackfish (film), Blackfish'', which documents the history of Tilikum (orca), Tilikum, an orca at SeaWorld Orlando, who had been involved in the deaths of three people. The film led to proposals by some lawmakers to ban captivity of cetaceans, and led SeaWorld to announce in 2016 that it would phase out its orca program after various unsuccessful attempts to restore its revenues, reputation, and stock price.
Aggression among captive orcas is common. They attack each other and their trainers as well. In 2013, SeaWorld's treatment of orcas in captivity was the basis of the movie ''Blackfish (film), Blackfish'', which documents the history of Tilikum (orca), Tilikum, an orca at SeaWorld Orlando, who had been involved in the deaths of three people. The film led to proposals by some lawmakers to ban captivity of cetaceans, and led SeaWorld to announce in 2016 that it would phase out its orca program after various unsuccessful attempts to restore its revenues, reputation, and stock price.
 Dolphins and porpoises are kept in captivity. Bottlenose dolphins are the most common, as they are relatively easy to train, have a long lifespan in captivity and have a friendly appearance. Bottlenose dolphins live in captivity across the world, though exact numbers are hard to determine. Other species kept in captivity are Atlantic spotted dolphin, spotted dolphins, false killer whales and common dolphins, Commerson's dolphins, as well as rough-toothed dolphins, but all in much lower numbers. There are also fewer than ten pilot whales, Amazon river dolphins, Risso's dolphins, spinner dolphins, or tucuxi in captivity. Two unusual and rare hybrid (biology), hybrid dolphins, known as wolphins, are kept at Sea Life Park in Hawaii, which is a cross between a bottlenose dolphin and a false killer whale. Also, two Common dolphin, common/bottlenose hybrids reside in captivity at Discovery Cove and SeaWorld San Diego.
In repeated attempts in the 1960s and 1970s, narwhals kept in captivity died within months. A breeding pair of pygmy right whales were retained in a netted area. They were eventually released in South Africa. In 1971, SeaWorld captured a California gray whale calf in Mexico at Ojo de Liebre Lagoon, Scammon's Lagoon. The calf, later named Gigi, was separated from her mother using a form of lasso attached to her flukes. Gigi was displayed at SeaWorld San Diego for a year. She was then released with a radio beacon affixed to her back; however, contact was lost after three weeks. Gigi was the first captive baleen whale. JJ, another
Dolphins and porpoises are kept in captivity. Bottlenose dolphins are the most common, as they are relatively easy to train, have a long lifespan in captivity and have a friendly appearance. Bottlenose dolphins live in captivity across the world, though exact numbers are hard to determine. Other species kept in captivity are Atlantic spotted dolphin, spotted dolphins, false killer whales and common dolphins, Commerson's dolphins, as well as rough-toothed dolphins, but all in much lower numbers. There are also fewer than ten pilot whales, Amazon river dolphins, Risso's dolphins, spinner dolphins, or tucuxi in captivity. Two unusual and rare hybrid (biology), hybrid dolphins, known as wolphins, are kept at Sea Life Park in Hawaii, which is a cross between a bottlenose dolphin and a false killer whale. Also, two Common dolphin, common/bottlenose hybrids reside in captivity at Discovery Cove and SeaWorld San Diego.
In repeated attempts in the 1960s and 1970s, narwhals kept in captivity died within months. A breeding pair of pygmy right whales were retained in a netted area. They were eventually released in South Africa. In 1971, SeaWorld captured a California gray whale calf in Mexico at Ojo de Liebre Lagoon, Scammon's Lagoon. The calf, later named Gigi, was separated from her mother using a form of lasso attached to her flukes. Gigi was displayed at SeaWorld San Diego for a year. She was then released with a radio beacon affixed to her back; however, contact was lost after three weeks. Gigi was the first captive baleen whale. JJ, another