Celtiberia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
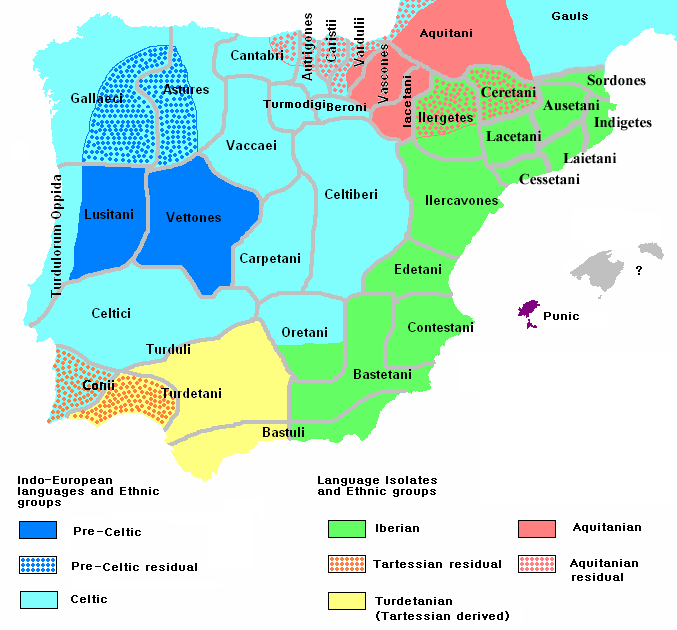 The Celtiberians were a group of
The Celtiberians were a group of
 The cultural stronghold of Celtiberians was the northern area of the central '' meseta'' in the upper valleys of the
The cultural stronghold of Celtiberians was the northern area of the central '' meseta'' in the upper valleys of the
 After Numantia was finally taken and destroyed, Roman cultural influences increased; this is the period of the earliest Botorrita inscribed plaque; later plaques, significantly, are inscribed in
After Numantia was finally taken and destroyed, Roman cultural influences increased; this is the period of the earliest Botorrita inscribed plaque; later plaques, significantly, are inscribed in
''e-Keltoi'' 6
*J. P. Mallory, ''In Search of the Indo-Europeans'', Thames & Hudson, London (1989) * *J. Alberto Arenas Esteban, & Mª Victoria Palacios Tamayo, ''El origen del mundo celtibérico'', Excmº Ayuntamiento de Molina de Aragón (1999) *
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20081006160601/http://www.arqueotavira.com/Mapas/Iberia/Populi.htm Detailed map of the Pre-Roman Peoples of Iberia (around 200 BC)* {{Authority control Celtic tribes of the Iberian Peninsula Ancient peoples of Spain Ancient peoples of Portugal Transhumant ethnic groups
Celts
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apoge ...
and Celticized peoples inhabiting an area in the central-northeastern Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
during the final centuries BC. They were explicitly mentioned as being Celts
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apoge ...
by several classic authors (e.g. Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
). These tribes spoke the Celtiberian language
Celtiberian or Northeastern Hispano-Celtic is an extinct Indo-European language of the Celtic branch spoken by the Celtiberians in an area of the Iberian Peninsula between the headwaters of the Douro, Tagus, Júcar and Turia rivers and the ...
and wrote it by adapting the Iberian alphabet, in the form of the Celtiberian script. The numerous inscriptions that have been discovered, some of them extensive, have enabled scholars to classify the Celtiberian language
Celtiberian or Northeastern Hispano-Celtic is an extinct Indo-European language of the Celtic branch spoken by the Celtiberians in an area of the Iberian Peninsula between the headwaters of the Douro, Tagus, Júcar and Turia rivers and the ...
as a Celtic language, one of the Hispano-Celtic
Hispano-Celtic is a term for all forms of Celtic spoken in the Iberian Peninsula before the arrival of the Romans (c. 218 BC, during the Second Punic War). In particular, it includes:
* A northeastern inland language attested at a relati ...
(also known as Iberian Celtic) languages that were spoken in pre-Roman and early Roman Iberia. Archaeologically, many elements link Celtiberians with Celts
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apoge ...
in Central Europe, but also show large differences with both the Hallstatt culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western Europe, Western and Central European archaeological culture of the Late Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe (Hallst ...
and La Tène culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a Iron Age Europe, European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman Republic, Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age ...
.
There is no complete agreement on the exact definition of Celtiberians among classical authors, nor modern scholars. The Ebro river clearly divides the Celtiberian areas from non-Indo-European speaking peoples. In other directions, the demarcation is less clear. Most scholars include the Arevaci, Pellendones, Belli, Titti and Lusones as Celtiberian tribes, and occasionally the Berones, Vaccaei
The Vaccaei or Vaccei were a pre- Roman Celtic people of Spain, who inhabited the sedimentary plains of the central Duero valley, in the Meseta Central of northern Hispania (specifically in Castile and León).
Origins
Also designated Vaccaena ...
, Carpetani
The Carpetani ( Greek: ''Karpetanoi''), also named ''Karpesioi'' by Polybius, were one of the Celtic peoples inhabiting the Iberian Peninsula prior to the Roman conquest. Their core domain was constituted by the lands between the Tagus and the ...
, Olcades or Lobetani.
In 195 BC, part of Celtiberia was conquered by the Romans, and by 72 BC the entire region had become part of the Roman province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman g ...
of Hispania Citerior
Hispania Citerior (English: "Hither Iberia", or "Nearer Iberia") was a Roman province in Hispania during the Roman Republic. It was on the eastern coast of Iberia down to the town of Cartago Nova, today's Cartagena in the autonomous community of ...
. The subjugated Celtiberians waged a protracted struggle against the Roman conquerors, staging uprisings in 195–193 BC, 181–179 BC, 153–151 BC, and 143–133 BC. In 105 BC, Celtiberian warriors drove the Germanic Cimbri
The Cimbri (, ; ) were an ancient tribe in Europe. Ancient authors described them variously as a Celtic, Gaulish, Germanic, or even Cimmerian people. Several ancient sources indicate that they lived in Jutland, which in some classical texts was ...
from Spain in the Cimbrian War
The Cimbrian or Cimbric War (113–101 BC) was fought between the Roman Republic and the Germanic peoples, Germanic and Celts, Celtic tribes of the Cimbri and the Teutons, Ambrones and Tigurini, who migrated from the Jutland peninsula into Roma ...
(113–101 BC) and also played an important role in the Sertorian War
The Sertorian War was a civil war in the Roman Republic fought from 80 to 72 BC between two Roman factions, one led by Quintus Sertorius and another led by the senate as constituted in the aftermath of Sulla's civil war. The war was fough ...
(80–72 BC).
Etymology
The term ''Celtiberi'' appears in accounts byDiodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus or Diodorus of Sicily (; 1st century BC) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek historian from Sicily. He is known for writing the monumental Universal history (genre), universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty ...
, Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; ; ; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who prospered during the reigns of the Roman Emperors Trajan, Hadrian, and Antoninus Pius.
He was born c. 95 in Alexandria. After holding the senior offices in the pr ...
and Martial
Marcus Valerius Martialis (known in English as Martial ; March, between 38 and 41 AD – between 102 and 104 AD) was a Roman and Celtiberian poet born in Bilbilis, Hispania (modern Spain) best known for his twelve books of '' Epigrams'', pu ...
who recognized intermarriage between Celts and Iberians
The Iberians (, from , ''Iberes'') were an ancient people settled in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian Peninsula, at least from the 6th century BC. They are described in Greek and Roman sources (among others, by Hecataeus of Mil ...
after a period of continuous warfare, though Barry Cunliffe
Sir Barrington Windsor Cunliffe (born 10 December 1939), usually known as Sir Barry Cunliffe, is a British archaeologist and academic. He was Professor of European Archaeology at the University of Oxford from 1972 to 2007. Since 2007, he has been ...
says "this has the ring of guesswork about it." Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
just saw the Celtiberians as a branch of the ''Celti''. Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
thought that the original home of the Celts in Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, compri ...
was the territory of the Celtici in the south-west, on the grounds of an identity of sacred rites, language, and the names of cities.
History
Early history
Strabo cites Ephorus's belief that there were Celts in the Iberian peninsula as far asCádiz
Cádiz ( , , ) is a city in Spain and the capital of the Province of Cádiz in the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia. It is located in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula off the Atlantic Ocean separated fr ...
.
Celtic presence in Iberia likely dates to as early as the 6th century BC, when the ''castros'' evinced a new permanence with stone walls and protective ditches. Archaeologists Martín Almagro Gorbea and Alberto José Lorrio Alvarado recognize the distinguishing iron tools and extended family social structure of developed Celtiberian culture as evolving from the archaic ''castro'' culture which they consider "proto-Celtic".
Archaeological finds identify the culture as continuous with the culture reported by Classical writers from the late 3rd century onwards (Almagro-Gorbea and Lorrio). The ethnic map of Celtiberia was highly localized however, composed of different tribes and ''nations'' from the 3rd century centered upon fortified ''oppida
An ''oppidum'' (: ''oppida'') is a large fortified Iron Age Europe, Iron Age settlement or town. ''Oppida'' are primarily associated with the Celts, Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread acros ...
'' and representing a wide-ranging degree of local assimilation with the autochthonous cultures in a mixed Celtic and Iberian stock.
 The cultural stronghold of Celtiberians was the northern area of the central '' meseta'' in the upper valleys of the
The cultural stronghold of Celtiberians was the northern area of the central '' meseta'' in the upper valleys of the Tagus
The Tagus ( ; ; ) is the longest river in the Iberian Peninsula. The river rises in the Montes Universales between Cuenca and Teruel, in mid-eastern Spain, flows , generally westward, and empties into the Atlantic Ocean in Lisbon.
Name
T ...
and Douro
The Douro (, , , ; ; ) is the largest river of the Iberian Peninsula by discharge. It rises near Duruelo de la Sierra in the Spanish Soria Province, province of Soria, meanders briefly south, then flows generally west through the northern par ...
east to the ''Iberus'' (Ebro
The Ebro (Spanish and Basque ; , , ) is a river of the north and northeast of the Iberian Peninsula, in Spain. It rises in Cantabria and flows , almost entirely in an east-southeast direction. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea, forming a de ...
) river, in the modern provinces of Soria, Guadalajara
Guadalajara ( ; ) is the capital and the most populous city in the western Mexican List of states of Mexico, state of Jalisco, as well as the most densely populated municipality in Jalisco. According to the 2020 census, the city has a population ...
, Zaragoza
Zaragoza (), traditionally known in English as Saragossa ( ), is the capital city of the province of Zaragoza and of the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Aragon, Spain. It lies by the Ebro river and its tributaries, the ...
and Teruel
Teruel () is a city in Aragon, located in eastern Spain, and is also the capital of Teruel (province), Teruel Province. It had a population of 35,900 as of 2022, making it the least populated provincial capital in Spain. It is noted for its har ...
. There, when Greek and Roman geographers and historians encountered them, the established Celtiberians were controlled by a military aristocracy that had become a hereditary elite. The dominant tribe were the Arevaci, who dominated their neighbors from powerful strongholds at Okilis (Medinaceli
Medinaceli () is a municipality and town in the province of Soria, in Castile and León, Spain. Built on a hilltop at about 1210 metres above sea level, the town oversees the Jalón valley. The municipality includes other villages like Torralba ...
) and who rallied the long Celtiberian resistance to Rome. Other Celtiberians were the Belli and Titti in the Jalón valley, and the Lusones to the east.
Excavations at the Celtiberian strongholds ''Kontebakom-Bel'' Botorrita, ''Sekaisa'' Segeda, Termantia complement the grave goods found in Celtiberian cemeteries, where aristocratic tombs of the 6th to 5th centuries BC give way to warrior tombs with a tendency from the 3rd century BC for weapons to disappear from grave goods, either indicating an increased urgency for their distribution among living fighters or, as Almagro-Gorbea and Lorrio think, the increased urbanization of Celtiberian society. Many late Celtiberian ''oppida'' are still occupied by modern towns, inhibiting archaeology.
Metalwork stands out in Celtiberian archaeological finds, partly from its indestructible nature, emphasizing Celtiberian articles of warlike uses, horse trappings and prestige weapons. The two-edged sword adopted by the Romans was previously in use among the Celtiberians, and Latin ''lancea'', a thrown spear, was a Hispanic word, according to Varro
Marcus Terentius Varro (116–27 BCE) was a Roman polymath and a prolific author. He is regarded as ancient Rome's greatest scholar, and was described by Petrarch as "the third great light of Rome" (after Virgil and Cicero). He is sometimes call ...
. Celtiberian culture was increasingly influenced by Rome in the two final centuries BC.
From the 3rd century, the clan
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship
and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, a clan may claim descent from a founding member or apical ancestor who serves as a symbol of the clan's unity. Many societie ...
was superseded as the basic Celtiberian political unit by the ''oppidum
An ''oppidum'' (: ''oppida'') is a large fortified Iron Age Europe, Iron Age settlement or town. ''Oppida'' are primarily associated with the Celts, Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread acros ...
'', a fortified organized city with a defined territory that included the ''castros'' as subsidiary settlements. These ''civitates'' as the Roman historians called them, could make and break alliances, as surviving inscribed hospitality pacts attest, and minted coinage. The old clan structures lasted in the formation of the Celtiberian armies, organized along clan-structure lines, with consequent losses of strategic and tactical control.
Late period
The Celtiberians were the most influential ethnic group in Iberia when the Mediterranean powers (Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
and Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
) started their conquests. In 220 BC, the Punic army was attacked when preparing to cross the Tagus river by a coalition of Vaccei, Carpetani
The Carpetani ( Greek: ''Karpetanoi''), also named ''Karpesioi'' by Polybius, were one of the Celtic peoples inhabiting the Iberian Peninsula prior to the Roman conquest. Their core domain was constituted by the lands between the Tagus and the ...
and Olcades. Despite these clashes, during the Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of Punic Wars, three wars fought between Ancient Carthage, Carthage and Roman Republic, Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For ...
the Celtiberians served most often as allies or mercenaries of Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
in its conflict with Rome, and crossed the Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
in the mixed forces under Hannibal
Hannibal (; ; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Punic people, Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Ancient Carthage, Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War.
Hannibal's fat ...
's command. Under Scipio Africanus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus (, , ; 236/235–) was a Roman general and statesman who was one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Ancient Carthage, Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the greatest milit ...
, the Romans were able to secure alliances and change the allegiances of many Celtiberian tribes, using these allied warriors against the Carthaginian forces and allies in Spain. After the conflict, Rome took possession of the Punic empire in Spain, and some Celtiberians soon challenged the new dominant power that loomed in the borders of its territory. Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus spent the years 182 to 179 pacifying the Celtiberians. Gracchus boasted of destroying over 300 Celtiberian settlements.
In 155 BC, a raid into Hispania Ulterior
Hispania Ulterior (English: "Further Hispania", or occasionally "Thither Hispania") was a Roman province located in Hispania (on the Iberian Peninsula) during the Roman Republic, roughly located in Baetica and in the Guadalquivir valley of moder ...
(Farther Spain) by the Lusitani
The Lusitanians were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking people living in the far west of the Iberian Peninsula, in present-day central Portugal and Extremadura and Castilla y Leon of Spain. It is uncertain whether the Lusitanians ...
and the defeat of two successive Roman praetors encouraged the town of Segeda in Hispania Citerior
Hispania Citerior (English: "Hither Iberia", or "Nearer Iberia") was a Roman province in Hispania during the Roman Republic. It was on the eastern coast of Iberia down to the town of Cartago Nova, today's Cartagena in the autonomous community of ...
(Nearer Spain) to rebel. The following year, it refused to pay tribute or provide a military contingent to Rome but formed instead a confederacy with neighboring towns and began the construction of a defensive wall. Quintus Fulvius Nobilior was sent against the Celtiberians in 153 BC, with nearly 30,000 men. But the consul was late in arriving and ambushed soon after, with 6,000 Romans slain. A siege of Numantia several days later, where the Segedans had taken refuge, was no more successful. Three elephants were brought up against the town walls but became frightened and turned on the Romans, who retreated in confusion. There were other setbacks, and the hapless Nobilior was obliged to withdraw to camp, where more men suffered frostbite and died of the winter cold. Nobilior lost over 10,000 men in his campaign. In 137 BC, the Celtiberians forced the surrender of a 20,000-man Roman consular army led by Gaius Hostilius Mancinus. In 134 BC, the consul Scipio Aemilianus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus Aemilianus (185 BC – 129 BC), known as Scipio Aemilianus or Scipio Africanus the Younger, was a Roman general and statesman noted for his military exploits in the Third Punic War against Carthage and durin ...
took charge of the demoralized Roman troops in Spain and laid siege to Numantia.
Nearby fields were laid waste and what was not used burned. The stronghold of Numantia then was circumvallated with a ditch and palisade, behind which was a wall ten feet high. Towers were placed every hundred feet and mounted with catapult
A catapult is a ballistics, ballistic device used to launch a projectile at a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden rel ...
s and ballistae. To blockade the nearby river, logs were placed in the water, moored by ropes on the shore. Knives and spear heads were embedded in the wood, which rotated in the strong current. Allied tribes were ordered to send reinforcements. Even Jugurtha
Jugurtha or Jugurthen (c. 160 – 104 BC) was a king of Numidia, the ancient kingdom of the Numidians in northwest Africa. When the Numidian king Micipsa, who had adopted Jugurtha, died in 118 BC, Micipsa's two sons, Hiempsal and Adherbal ...
, who later would revolt from Rome, himself, was sent from Numidia
Numidia was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia and Libya. The polity was originally divided between ...
with twelve war elephants. The Roman forces now numbered 60,000 men and were arrayed around the besieged town in seven camps. The Numantines, "ready though they were to die, no opportunity was given them of fighting".
There were several desperate attempts to break out but they were repulsed. Nor could there be any help from neighboring towns. Eventually, as their hunger increased, envoys were sent to Scipio, asking if they would be treated with moderation if they surrendered, pleading that they had fought for their women and children, and the freedom of their country. But Scipio would accept only '' deditio'' (surrender). Hearing this demand for absolute submission, the Numantines, "who were previously savage in temper because of their absolute freedom and quite unaccustomed to obey the orders of others, and were now wilder than ever and beside themselves by reason of their hardships," slew their own ambassadors.
After eight months, the starving population was reduced to cannibalism and, filthy and foul smelling, compelled to surrender. But, "such was the love of liberty and of valour which existed in this small barbarian town," relates Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; ; ; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who prospered during the reigns of the Roman Emperors Trajan, Hadrian, and Antoninus Pius.
He was born c. 95 in Alexandria. After holding the senior offices in the pr ...
, that many chose to kill themselves rather than capitulate. Families poisoned themselves, weapons were burned, and the beleaguered town set ablaze. There had been only about 8,000 fighting men when the war began; half that number survived to garrison Numantia. Only a pitiable few survived to walk in Scipio's triumph. The others were sold as slaves and the town razed to the ground, the territory divided among its neighbors.
 After Numantia was finally taken and destroyed, Roman cultural influences increased; this is the period of the earliest Botorrita inscribed plaque; later plaques, significantly, are inscribed in
After Numantia was finally taken and destroyed, Roman cultural influences increased; this is the period of the earliest Botorrita inscribed plaque; later plaques, significantly, are inscribed in Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
. The Sertorian War
The Sertorian War was a civil war in the Roman Republic fought from 80 to 72 BC between two Roman factions, one led by Quintus Sertorius and another led by the senate as constituted in the aftermath of Sulla's civil war. The war was fough ...
(80–72 BC) marked the last formal resistance of the Celtiberian cities to Roman domination, which submerged the Celtiberian culture.
The Celtiberian presence remains on the map of Spain in hundreds of Celtic place-names. The archaeological recovery of Celtiberian culture commenced with the excavations of Numantia, published between 1914 and 1931.
A Roman army auxiliary unit, the Cohors I Celtiberorum, is known from Britain, attested by 2nd century AD discharge diplomas
A diploma is a document awarded by an educational institution (such as a college or university) testifying the recipient has graduated by successfully completing their courses of studies. Historically, it has also referred to a charter or offi ...
. Guy de la Bédoyère ''Eagles over Britannia: the Roman Army in Britain''. Stroud: Tempus, 2001 ; p. 241.
Genetics
In a March 2019 genetic study published in ''Science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
'', three Celtiberians buried at La Hoya, Alava (in Beron territory) between 400 BC and 195 BC were examined. They had high levels of north
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
-central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
an ancestry compared to non-Celtic populations of Iberia. One of the males examined was found to be a carrier of the paternal haplogroup I2a1a1a.
See also
*Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula
This is a list of the pre- Roman people of the Iberian Peninsula (the Roman Hispania, i.e., modern Portugal, Spain and Andorra). Some closely fit the concept of a people, ethnic group or tribe. Others are confederations or even unions of tribe ...
*Gallaeci
The Gallaeci (also Callaeci or Callaici; ) were a Celtic tribal complex who inhabited Gallaecia, the north-western corner of Iberia, a region roughly corresponding to what is now the Norte Region in northern Portugal, and the Spanish regions ...
Notes
References
*Ángel Montenegro ''et alii'', ''Historia de España 2 – colonizaciones y formación de los pueblos prerromanos (1200–218 a.C)'', Editorial Gredos, Madrid (1989) *Antonio Arribas, ''The Iberians'', Thames & Hudson, London (1964) *Francisco Burillo Mozota, ''Los Celtíberos, etnias y estados'', Crítica, Barcelona (1998, revised edition 2007) *Barry Cunliffe
Sir Barrington Windsor Cunliffe (born 10 December 1939), usually known as Sir Barry Cunliffe, is a British archaeologist and academic. He was Professor of European Archaeology at the University of Oxford from 1972 to 2007. Since 2007, he has been ...
, "Iberia and the Celtiberians" in ''The Ancient Celts'', Penguin Books, London (1997)
*Alberto J. Lorrio Alvarado, ''Los Celtíberos'', Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Murcia (1997)
*Alberto J. Lorrio Alvarado and Gonzalo Ruiz Zapatero, "The Celts in Iberia: an Overview" i''e-Keltoi'' 6
*J. P. Mallory, ''In Search of the Indo-Europeans'', Thames & Hudson, London (1989) * *J. Alberto Arenas Esteban, & Mª Victoria Palacios Tamayo, ''El origen del mundo celtibérico'', Excmº Ayuntamiento de Molina de Aragón (1999) *
External links
* * * * ** ttps://web.archive.org/web/20081006160601/http://www.arqueotavira.com/Mapas/Iberia/Populi.htm Detailed map of the Pre-Roman Peoples of Iberia (around 200 BC)* {{Authority control Celtic tribes of the Iberian Peninsula Ancient peoples of Spain Ancient peoples of Portugal Transhumant ethnic groups