cataracts on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A cataract is a cloudy area in the
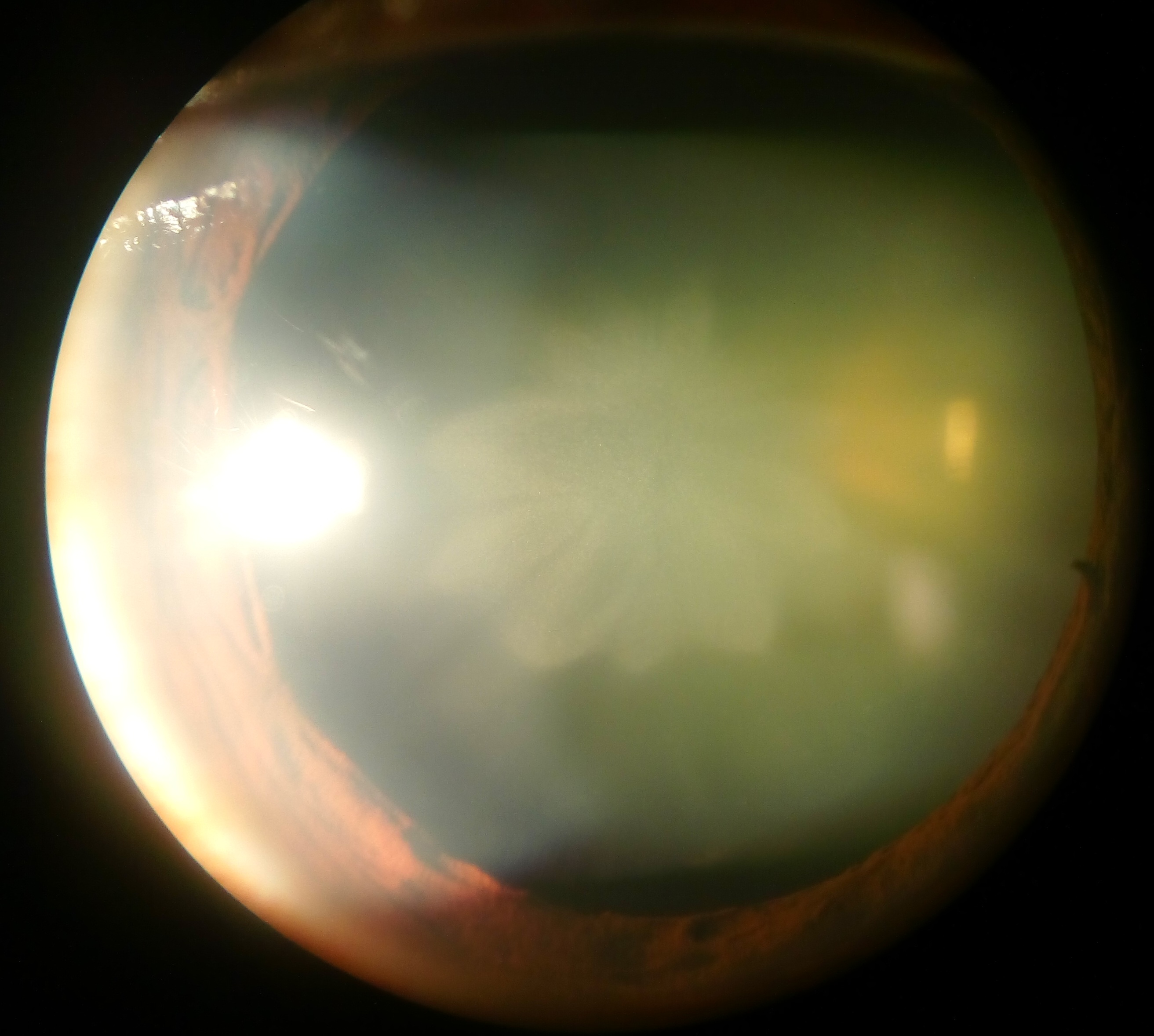 Blunt trauma causes swelling, thickening, and whitening of the lens fibers. While the swelling normally resolves with time, the white color may remain. In severe blunt trauma, or in injuries that penetrate the eye, the capsule in which the lens sits can be damaged. This damage allows fluid from other parts of the eye to rapidly enter the lens leading to swelling and then whitening, obstructing light from reaching the retina at the back of the eye. Cataracts may develop in 0.7 to 8.0% of cases following electrical injuries. Blunt trauma can also result in star- (stellate) or petal-shaped cataracts.
Blunt trauma causes swelling, thickening, and whitening of the lens fibers. While the swelling normally resolves with time, the white color may remain. In severe blunt trauma, or in injuries that penetrate the eye, the capsule in which the lens sits can be damaged. This damage allows fluid from other parts of the eye to rapidly enter the lens leading to swelling and then whitening, obstructing light from reaching the retina at the back of the eye. Cataracts may develop in 0.7 to 8.0% of cases following electrical injuries. Blunt trauma can also result in star- (stellate) or petal-shaped cataracts.
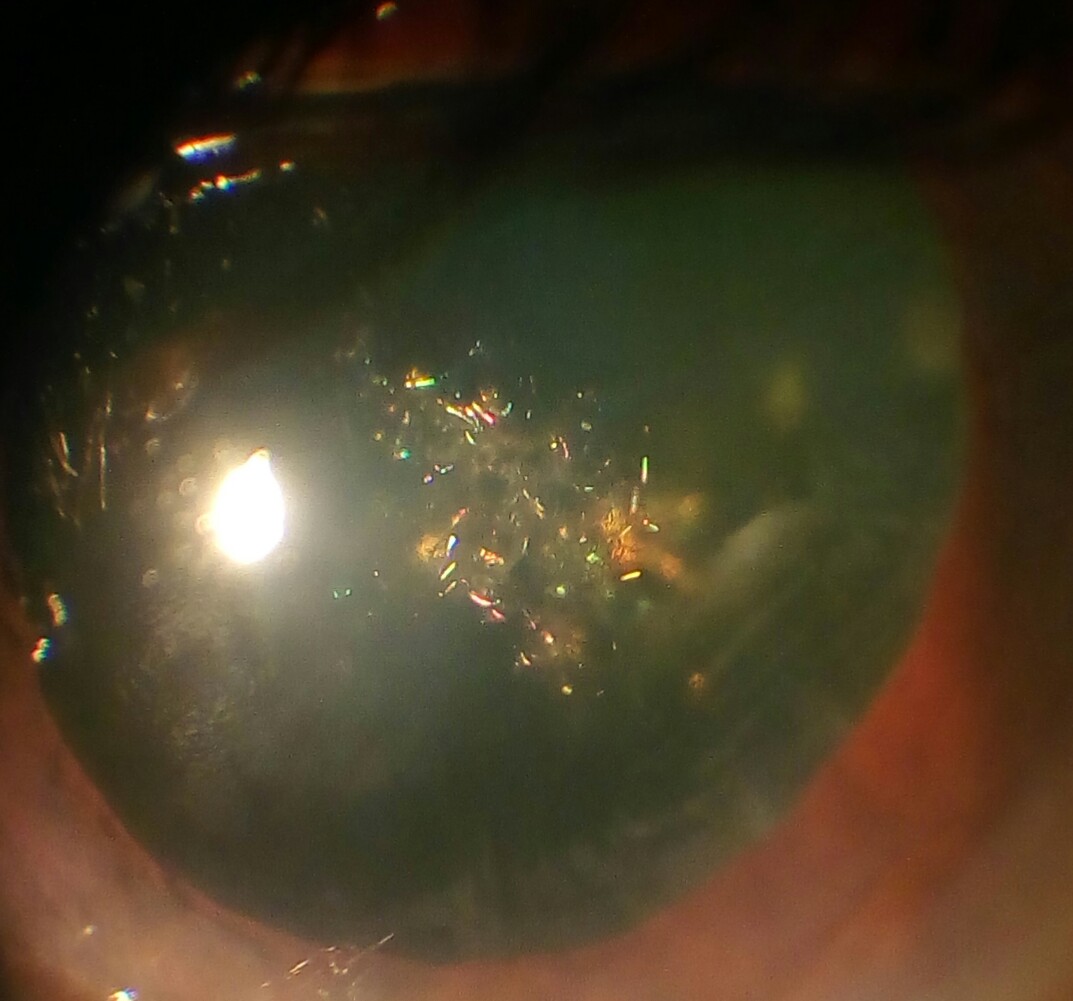 The genetic component is strong in the development of cataracts, most commonly through mechanisms that protect and maintain the lens. The presence of cataracts in childhood or early life can occasionally be due to a particular syndrome. Examples of chromosome abnormalities associated with cataracts include 1q21.1 deletion syndrome, cri-du-chat syndrome, Down syndrome, Patau's syndrome, trisomy 18 ( Edward's syndrome), and Turner's syndrome, and in the case of neurofibromatosis type 2, juvenile cataract on one or both sides may be noted. Examples of single-gene disorder include Alport's syndrome, Conradi's syndrome, cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis, myotonic dystrophy, and oculocerebrorenal syndrome or Lowe syndrome.
The genetic component is strong in the development of cataracts, most commonly through mechanisms that protect and maintain the lens. The presence of cataracts in childhood or early life can occasionally be due to a particular syndrome. Examples of chromosome abnormalities associated with cataracts include 1q21.1 deletion syndrome, cri-du-chat syndrome, Down syndrome, Patau's syndrome, trisomy 18 ( Edward's syndrome), and Turner's syndrome, and in the case of neurofibromatosis type 2, juvenile cataract on one or both sides may be noted. Examples of single-gene disorder include Alport's syndrome, Conradi's syndrome, cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis, myotonic dystrophy, and oculocerebrorenal syndrome or Lowe syndrome.

 Cataracts may be partial or complete, stationary or progressive, hard or soft. Histologically, the main types of age-related cataracts are nuclear sclerosis, cortical, and posterior subcapsular.
is the most common type of cataract, and involves the central or 'nuclear' part of the lens. This eventually becomes hard, or 'sclerotic', due to condensation on the lens nucleus and the deposition of brown pigment within the lens. In its advanced stages, it is called a brunescent cataract. In early stages, an increase in sclerosis may cause an increase in refractive index of the lens. This causes a myopic shift (lenticular shift) that decreases hyperopia and enables presbyopic patients to see at near without reading glasses. This is only temporary and is called second sight.
are due to the lens cortex (outer layer) becoming opaque. They occur when changes in the fluid contained in the periphery of the lens cause fissuring. When these cataracts are viewed through an
Cataracts may be partial or complete, stationary or progressive, hard or soft. Histologically, the main types of age-related cataracts are nuclear sclerosis, cortical, and posterior subcapsular.
is the most common type of cataract, and involves the central or 'nuclear' part of the lens. This eventually becomes hard, or 'sclerotic', due to condensation on the lens nucleus and the deposition of brown pigment within the lens. In its advanced stages, it is called a brunescent cataract. In early stages, an increase in sclerosis may cause an increase in refractive index of the lens. This causes a myopic shift (lenticular shift) that decreases hyperopia and enables presbyopic patients to see at near without reading glasses. This is only temporary and is called second sight.
are due to the lens cortex (outer layer) becoming opaque. They occur when changes in the fluid contained in the periphery of the lens cause fissuring. When these cataracts are viewed through an
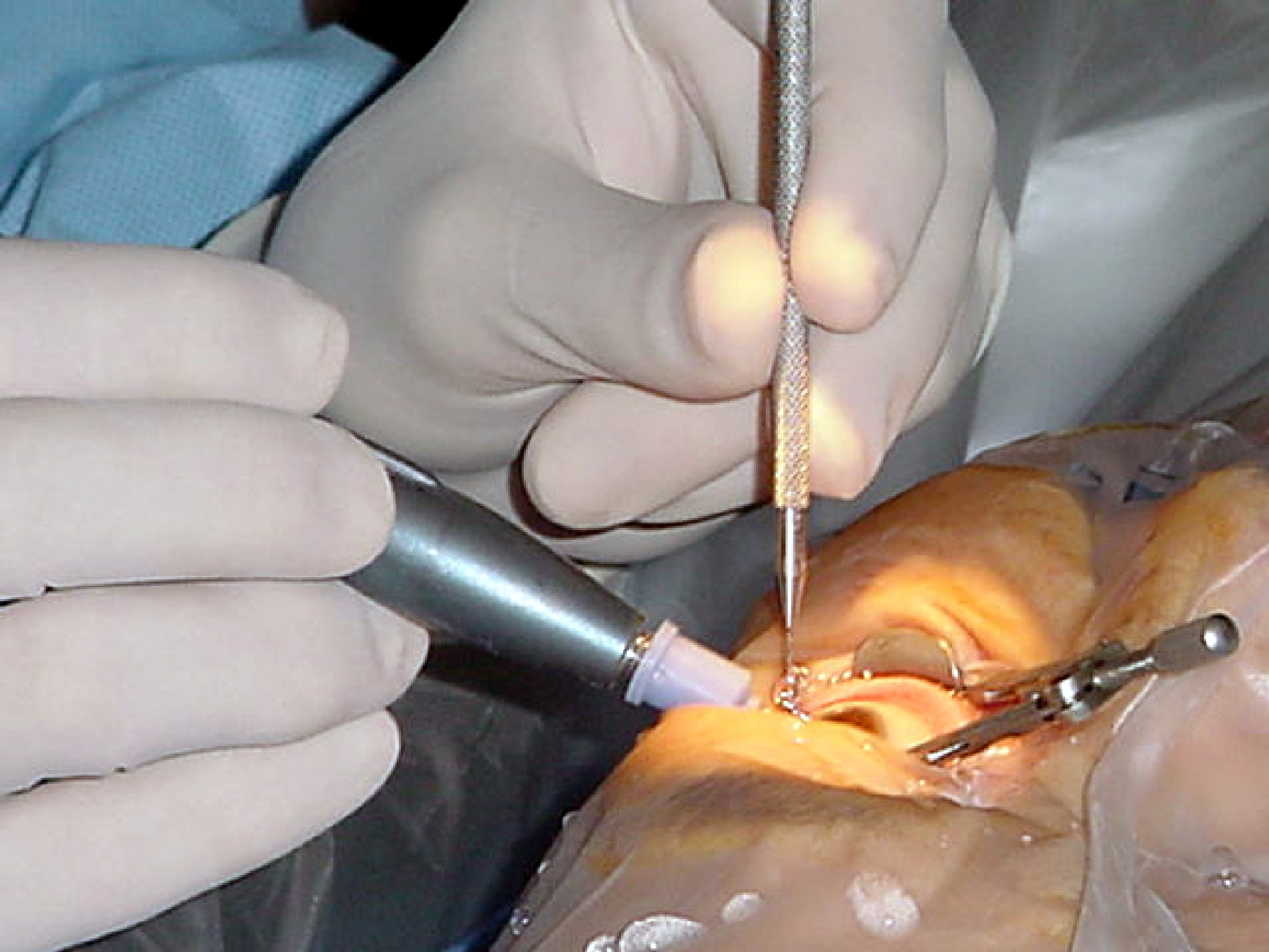 The appropriateness of surgery depends on a person's particular functional and visual needs and other risk factors. Cataract removal can be performed at any stage and no longer requires ripening of the lens. Surgery is usually
The appropriateness of surgery depends on a person's particular functional and visual needs and other risk factors. Cataract removal can be performed at any stage and no longer requires ripening of the lens. Surgery is usually
 The postoperative recovery period (after removing the cataract) is usually short. The patient is usually ambulatory on the day of surgery, but is advised to move cautiously and avoid straining or heavy lifting for about a month. The eye is usually patched on the day of surgery and use of an eye shield at night is often suggested for several days after surgery.
In all types of surgery, the cataractous lens is removed and replaced with an artificial lens, known as an
The postoperative recovery period (after removing the cataract) is usually short. The patient is usually ambulatory on the day of surgery, but is advised to move cautiously and avoid straining or heavy lifting for about a month. The eye is usually patched on the day of surgery and use of an eye shield at night is often suggested for several days after surgery.
In all types of surgery, the cataractous lens is removed and replaced with an artificial lens, known as an
 Age-related cataracts are responsible for 51% of world blindness, about 20 million people. Globally, cataracts cause moderate to severe disability in 53.8 million (2004), 52.2 million of whom are in low and middle income countries.
In many countries, surgical services are inadequate, and cataracts remain the leading cause of blindness. Even where surgical services are available, low vision associated with cataracts may still be prevalent as a result of long waits for, and barriers to, surgery, such as cost, lack of information and transportation problems.
In the United States, age-related lens changes have been reported in 42% between the ages of 52 and 64, 60% between the ages 65 and 74, and 91% between the ages of 75 and 85. Cataracts affect nearly 22 million Americans age 40 and older. By age 80, more than half of all Americans have cataracts. Direct medical costs for cataract treatment are estimated at $6.8 billion annually.
In the eastern Mediterranean region, cataracts are responsible for over 51% of blindness. Access to eye care in many countries in this region is limited. Childhood-related cataracts are responsible for 5–20% of world childhood blindness.
Vision loss due to cataracts increases the risk of dementia in the elderly population, increases the likelihood of falls and road traffic accidents, and by detrimental effects on the quality of life increases mortality.
Age-related cataracts are responsible for 51% of world blindness, about 20 million people. Globally, cataracts cause moderate to severe disability in 53.8 million (2004), 52.2 million of whom are in low and middle income countries.
In many countries, surgical services are inadequate, and cataracts remain the leading cause of blindness. Even where surgical services are available, low vision associated with cataracts may still be prevalent as a result of long waits for, and barriers to, surgery, such as cost, lack of information and transportation problems.
In the United States, age-related lens changes have been reported in 42% between the ages of 52 and 64, 60% between the ages 65 and 74, and 91% between the ages of 75 and 85. Cataracts affect nearly 22 million Americans age 40 and older. By age 80, more than half of all Americans have cataracts. Direct medical costs for cataract treatment are estimated at $6.8 billion annually.
In the eastern Mediterranean region, cataracts are responsible for over 51% of blindness. Access to eye care in many countries in this region is limited. Childhood-related cataracts are responsible for 5–20% of world childhood blindness.
Vision loss due to cataracts increases the risk of dementia in the elderly population, increases the likelihood of falls and road traffic accidents, and by detrimental effects on the quality of life increases mortality.
as PDF
The authors declare a financial interest in a company producing femtosecond laser equipment.
Pictures of different types of cataracts
{{Authority control Aging-associated diseases Blindness Eye diseases Disorders of lens Eye Ophthalmology Vision Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate
lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements'') ...
of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision of the eye. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and difficulty seeing at night. This may result in trouble driving, reading, or recognizing faces. Poor vision caused by cataracts may also result in an increased risk of falling and depression. Cataracts cause 51% of all cases of blindness
Visual or vision impairment (VI or VIP) is the partial or total inability of visual perception. In the absence of treatment such as corrective eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment, visual impairment may cause the individual difficul ...
and 33% of visual impairment
Visual or vision impairment (VI or VIP) is the partial or total inability of visual perception. In the absence of treatment such as corrective eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment, visual impairment may cause the individual difficul ...
worldwide.
Cataracts are most commonly due to aging
Ageing (or aging in American English) is the process of becoming Old age, older until death. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi; whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentiall ...
but may also occur due to trauma or radiation exposure, be present from birth, or occur following eye surgery for other problems. Risk factors include diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
, longstanding use of corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
medication, smoking tobacco, prolonged exposure to sunlight
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible spectrum, visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrare ...
, and alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
. In addition to these, poor nutrition, obesity, chronic kidney disease, and autoimmune diseases have been recognized in various studies as contributing to the development of cataracts. Cataract formation is primarily driven by oxidative stress, which damages lens proteins, leading to their aggregation and the accumulation of clumps of protein or yellow-brown pigment in the lens. This reduces the transmission of light to the retina at the back of the eye, impairing vision. Additionally, alterations in the lens’s metabolic processes, including imbalances in calcium and other ions, contribute to cataract development. Diagnosis is typically through an eye examination
An eye examination, commonly known as an eye test, is a series of tests performed to assess Visual acuity, vision and ability to Focus (optics), focus on and discern objects. It also includes other tests and examinations of the human eye, eyes. ...
, with ophthalmoscopy and slit-lamp examination being the most effective methods. During ophthalmoscopy, the pupil is dilated, and the red reflex is examined for any opacities in the lens. Slit-lamp examination provides further details on the characteristics, location, and extent of the cataract.
Wearing sunglasses
Sunglasses or sun glasses (informally called shades or sunnies; more names Sunglasses#Other names, below) are a form of Eye protection, protective eyewear designed primarily to prevent bright sunlight and high-energy visible light from damagin ...
with UV protection and a wide brimmed hat, eating leafy vegetables and fruits, and avoiding smoking may reduce the risk of developing cataracts, or slow the process. Early on, the symptoms may be improved with glasses
Glasses, also known as eyeglasses (American English), spectacles (Commonwealth English), or colloquially as specs, are vision eyewear with clear or tinted lenses mounted in a frame that holds them in front of a person's eyes, typically u ...
. If this does not help, surgery to remove the cloudy lens and replace it with an artificial lens is the only effective treatment. Cataract surgery is not readily available in many countries, and surgery is needed only if the cataracts are causing problems and generally results in an improved quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
.
About 20 million people worldwide are blind due to cataracts. It is the cause of approximately 5% of blindness in the United States and nearly 60% of blindness in parts of Africa and South America. Blindness from cataracts occurs in about 10 to 40 per 100,000 children in the developing world
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreeme ...
, and 1 to 4 per 100,000 children in the developed world
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for eval ...
. Cataracts become more common with age. In the United States, cataracts occur in 68% of those over the age of 80 years. Additionally they are more common in women, and less common in Hispanic and Black people.
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms vary depending on the type of cataract, though considerable overlap occurs. People with nuclear sclerotic or brunescent cataracts often notice a reduction of vision. Nuclear cataracts typically cause greater impairment of distance vision than of near vision. Those with posterior subcapsular cataracts usually complain of glare as their major symptom. The severity of cataract formation, assuming no other ocular disease is present, is primarily assessed using a visual acuity test. Additional symptoms may include frequent changes in glasses prescription and the appearance of colored halos around lights, which can be attributed to the hydration of the lens.Congenital cataract
Congenital cataracts are a lens opacity that is present at birth. Congenital cataracts occur in a broad range of severity. Some lens opacities do not progress and are visually insignificant, others can produce profound visual impairment.
Cong ...
s can result in amblyopia if not treated in a timely manner.
Causes
Age
Age is the most common cause of cataracts. Lens proteins denature and degrade over time, and this process is accelerated by diseases such asdiabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or th ...
and hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
. Environmental factors, including toxins, radiation, and ultraviolet light
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of th ...
have cumulative effects which are worsened by the loss of protective and restorative mechanisms due to alterations in gene expression and chemical processes within the eye.
Oxidative stress
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal ...
associated with lipid peroxidation is an important pathogenic mechanism in cataract formation. Senile cataracts are associated with a decrease in antioxidant
Antioxidants are Chemical compound, compounds that inhibit Redox, oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce Radical (chemistry), free radicals. Autoxidation leads to degradation of organic compounds, including living matter. Antioxidants ...
capacity in the lens. An increase in oxidative stress in the lens or a decrease in the ability to remove reactive oxygen species
In chemistry and biology, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (), water, and hydrogen peroxide. Some prominent ROS are hydroperoxide (H2O2), superoxide (O2−), hydroxyl ...
can lead to the lens becoming more opaque.
Trauma
 Blunt trauma causes swelling, thickening, and whitening of the lens fibers. While the swelling normally resolves with time, the white color may remain. In severe blunt trauma, or in injuries that penetrate the eye, the capsule in which the lens sits can be damaged. This damage allows fluid from other parts of the eye to rapidly enter the lens leading to swelling and then whitening, obstructing light from reaching the retina at the back of the eye. Cataracts may develop in 0.7 to 8.0% of cases following electrical injuries. Blunt trauma can also result in star- (stellate) or petal-shaped cataracts.
Blunt trauma causes swelling, thickening, and whitening of the lens fibers. While the swelling normally resolves with time, the white color may remain. In severe blunt trauma, or in injuries that penetrate the eye, the capsule in which the lens sits can be damaged. This damage allows fluid from other parts of the eye to rapidly enter the lens leading to swelling and then whitening, obstructing light from reaching the retina at the back of the eye. Cataracts may develop in 0.7 to 8.0% of cases following electrical injuries. Blunt trauma can also result in star- (stellate) or petal-shaped cataracts.
Radiation
Cataracts can arise as an effect of exposure to various types of radiation. X-rays, one form ofionizing radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching ...
, may damage the DNA of lens cells. Ultraviolet light, specifically UVB, has also been shown to cause cataracts, and some evidence indicates sunglasses worn at an early age can slow its development in later life. Microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
s, a type of nonionizing radiation, may cause harm by denaturing protective enzymes (e.g., glutathione peroxidase), by oxidizing protein thiol groups (causing protein aggregation
In molecular biology, protein aggregation is a phenomenon in which intrinsically disordered proteins, intrinsically-disordered or mis-folded proteins aggregate (i.e., accumulate and clump together) either intra- or extracellularly. Protein aggre ...
), or by damaging lens cells via thermoelastic expansion. The protein coagulation caused by electric and heat injuries whitens the lens. This same process is what makes the clear albumen of an egg become white and opaque during cooking.
Genetics
 The genetic component is strong in the development of cataracts, most commonly through mechanisms that protect and maintain the lens. The presence of cataracts in childhood or early life can occasionally be due to a particular syndrome. Examples of chromosome abnormalities associated with cataracts include 1q21.1 deletion syndrome, cri-du-chat syndrome, Down syndrome, Patau's syndrome, trisomy 18 ( Edward's syndrome), and Turner's syndrome, and in the case of neurofibromatosis type 2, juvenile cataract on one or both sides may be noted. Examples of single-gene disorder include Alport's syndrome, Conradi's syndrome, cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis, myotonic dystrophy, and oculocerebrorenal syndrome or Lowe syndrome.
The genetic component is strong in the development of cataracts, most commonly through mechanisms that protect and maintain the lens. The presence of cataracts in childhood or early life can occasionally be due to a particular syndrome. Examples of chromosome abnormalities associated with cataracts include 1q21.1 deletion syndrome, cri-du-chat syndrome, Down syndrome, Patau's syndrome, trisomy 18 ( Edward's syndrome), and Turner's syndrome, and in the case of neurofibromatosis type 2, juvenile cataract on one or both sides may be noted. Examples of single-gene disorder include Alport's syndrome, Conradi's syndrome, cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis, myotonic dystrophy, and oculocerebrorenal syndrome or Lowe syndrome.
Skin diseases
The skin and the lens have the same embryological origin and so can be affected by similar diseases. Those withatopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema, is a long-term type of inflammation of the skin. Atopic dermatitis is also often called simply eczema but the same term is also used to refer to dermatitis, the larger group of skin conditi ...
and eczema
Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened ...
occasionally develop shield ulcer cataracts. Ichthyosis is an autosomal recessive disorder associated with cuneiform cataracts and nuclear sclerosis. Basal-cell nevus and pemphigus
Pemphigus ( or ) is a rare group of blistering autoimmune diseases that affect the skin and mucous membranes.
The name is derived from the Greek root ''pemphix'', meaning "blister".
In pemphigus, autoantibody, autoantibodies form against de ...
have similar associations.
Smoking and alcohol
Cigarette smoking
Tobacco smoking is the practice of burning tobacco and ingesting the resulting smoke. The smoke may be inhaled, as is done with cigarettes, or released from the mouth, as is generally done with pipes and cigars. The practice is believed to hav ...
has been shown to increase the risk of age-related cataract and nuclear cataract. Evidence is conflicting over the effect of alcohol. Some surveys have shown a link, but others that followed people over longer terms have not.
Inadequate vitamin C
Lowvitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription di ...
intake and serum levels have been associated with greater cataract rates. However, use of supplements of vitamin C has not demonstrated benefit.
Medications
Some medications, such as systemic, topical, or inhaledcorticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s, may increase the risk of cataract development. Corticosteroids most commonly cause posterior subcapsular cataracts. People with schizophrenia
Schizophrenia () is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations (typically, Auditory hallucination#Schizophrenia, hearing voices), delusions, thought disorder, disorganized thinking and behavior, and Reduced affect display, f ...
often have risk factors for lens opacities (such as diabetes, hypertension, and poor nutrition). Second-generation antipsychotic
Antipsychotics, previously known as neuroleptics and major tranquilizers, are a class of Psychiatric medication, psychotropic medication primarily used to manage psychosis (including delusions, hallucinations, paranoia or disordered thought), p ...
medications are unlikely to contribute to cataract formation. Miotics and triparanol may increase the risk.
Post-operative
Nearly every person who undergoes a vitrectomy—without ever having had cataract surgery—will experience progression of nuclear sclerosis after the operation. This may be because the native vitreous humor is different from the solutions used to replace the vitreous (vitreous substitutes), such as BSS Plus. This may also be because the native vitreous humour containsascorbic acid
Ascorbic acid is an organic compound with formula , originally called hexuronic acid. It is a white solid, but impure samples can appear yellowish. It dissolves freely in water to give mildly acidic solutions. It is a mild reducing agent.
Asco ...
which helps neutralize oxidative damage to the lens and because conventional vitreous substitutes do not contain ascorbic acid. Accordingly, for phakic patients requiring a vitrectomy it is becoming increasingly common for ophthalmologists to offer the vitrectomy combined with prophylactic cataract surgery
Cataract surgery, also called lens replacement surgery, is the removal of the natural lens (anatomy), lens of the human eye, eye that has developed a cataract, an opaque or cloudy area. The eye's natural lens is usually replaced with an artific ...
to prevent cataract formation.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is the administration of 100% oxygen at pressures greater than one-atmosphere absolute pressure (1 ATA) for a therapeutic purpose. HBOT can have several side effects, including the long-term development of cataracts. This is rare and generally associated with multiple HBOT exposures over a long period. As it does not usually become symptomatic during HBOT, it may often go unrecognised and is probably under-reported. Evidence is emerging that lifetime dosage of oxygen may be a precipitating factor in the development of age-related cataracts. Nuclear cataracts have been hypothesized to be the end stage of the far better known phenomenon of hyperbaric myopic shift.Other diseases
*Metabolic
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the ...
and nutritional diseases
** Aminoaciduria or Lowe's syndrome
** Cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis
** Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or th ...
** Fabry's disease
** Galactosemia
Galactosemia (British galactosaemia, from Greek γαλακτόζη + αίμα, meaning galactose + blood, accumulation of galactose in blood) is a rare genetics, genetic Metabolism, metabolic Disease, disorder that affects an individual's ability t ...
/ galactosemic cataract
** Homocystinuria
** Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is an increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels in the blood. This occurs from a disorder either within the parathyroid glands ( primary hyperparathyroidism) or as response to external stimuli ( secondary hyperparathyroi ...
** Hypoparathyroidism
** Hypervitaminosis D
** Hypothyroidism
** Hypocalcaemia
** Mucopolysaccharidoses
** Wilson's disease
* Congenital
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at childbirth, birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disability, disabilities that may be physical disability, physical, intellectual disability, intellectual, or dev ...
** Congenital syphilis
Congenital syphilis is syphilis that occurs when a mother with untreated syphilis passes the infection to her baby during pregnancy or at childbirth, birth. It may present in the fetus, infant, or later. Clinical features vary and differ between ...
** Cytomegalic inclusion disease
** Rubella
Rubella, also known as German measles or three-day measles, is an infection caused by the rubella virus. This disease is often mild, with half of people not realizing that they are infected. A rash may start around two weeks after exposure and ...
** Cockayne syndrome
Cockayne syndrome (CS), also called Neill-Dingwall syndrome, is a rare and fatal autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by growth failure, impaired development of the nervous system, abnormal sensitivity to sunlight ( photo ...
* Genetic syndromes
** Down syndrome
** Patau syndrome
** Edwards syndrome
* Infections:
** Cysticercosis
** Leprosy
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease (HD), is a Chronic condition, long-term infection by the bacteria ''Mycobacterium leprae'' or ''Mycobacterium lepromatosis''. Infection can lead to damage of the Peripheral nervous system, nerves, respir ...
** Onchocerciasis
Onchocerciasis, also known as river blindness, is a disease caused by infection with the parasitic worm ''Onchocerca volvulus''. Symptoms include severe itching, bumps under the skin, and blindness. It is the second-most common cause of blindne ...
** Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by ''Toxoplasma gondii'', an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis are associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric and behavioral conditions. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or month ...
** Varicella
* Secondary to other eye diseases:
** Retinopathy of prematurity
** Aniridia
Aniridia is a condition characterized by the absence or near absence of the iris, the colored, muscular ring in the eye that controls the size of the pupil and regulates the amount of light entering the eye. This absence results in a primarily b ...
** Uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and ...
** Retinal detachment
** Retinitis pigmentosa

Diagnosis
Classification
 Cataracts may be partial or complete, stationary or progressive, hard or soft. Histologically, the main types of age-related cataracts are nuclear sclerosis, cortical, and posterior subcapsular.
is the most common type of cataract, and involves the central or 'nuclear' part of the lens. This eventually becomes hard, or 'sclerotic', due to condensation on the lens nucleus and the deposition of brown pigment within the lens. In its advanced stages, it is called a brunescent cataract. In early stages, an increase in sclerosis may cause an increase in refractive index of the lens. This causes a myopic shift (lenticular shift) that decreases hyperopia and enables presbyopic patients to see at near without reading glasses. This is only temporary and is called second sight.
are due to the lens cortex (outer layer) becoming opaque. They occur when changes in the fluid contained in the periphery of the lens cause fissuring. When these cataracts are viewed through an
Cataracts may be partial or complete, stationary or progressive, hard or soft. Histologically, the main types of age-related cataracts are nuclear sclerosis, cortical, and posterior subcapsular.
is the most common type of cataract, and involves the central or 'nuclear' part of the lens. This eventually becomes hard, or 'sclerotic', due to condensation on the lens nucleus and the deposition of brown pigment within the lens. In its advanced stages, it is called a brunescent cataract. In early stages, an increase in sclerosis may cause an increase in refractive index of the lens. This causes a myopic shift (lenticular shift) that decreases hyperopia and enables presbyopic patients to see at near without reading glasses. This is only temporary and is called second sight.
are due to the lens cortex (outer layer) becoming opaque. They occur when changes in the fluid contained in the periphery of the lens cause fissuring. When these cataracts are viewed through an ophthalmoscope
Ophthalmoscopy, also called funduscopy, is a test that allows a health professional to see inside the fundus of the eye and other structures using an ophthalmoscope (or funduscope). It is done as part of an eye examination and may be done as part ...
, or other magnification system, the appearance is similar to white spokes of a wheel. Symptoms often include problems with glare and light scatter at night.
are cloudy at the back of the lens adjacent to the capsule (or bag) in which the lens sits. Because light becomes more focused toward the back of the lens, they can cause disproportionate symptoms for their size.
An immature cataract has some transparent protein, but with a mature cataract, all the lens protein is opaque. In a hypermature or Morgagnian cataract, the lens proteins have become liquid. Congenital cataract, which may be detected in adulthood, has a different classification and includes lamellar, polar, and sutural cataracts.
Cataracts can be classified by using the lens opacities classification system LOCS III. In this system, cataracts are classified based on type as nuclear, cortical, or posterior. The cataracts are further classified based on severity on a scale from 1 to 5. The LOCS III system is highly reproducible.
Prevention
Risk factors such as UVB exposure and smoking can be addressed. Although no means of preventing cataracts has been scientifically proven, wearingsunglasses
Sunglasses or sun glasses (informally called shades or sunnies; more names Sunglasses#Other names, below) are a form of Eye protection, protective eyewear designed primarily to prevent bright sunlight and high-energy visible light from damagin ...
that block ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
light may slow their development. While adequate intake of vitamins A, C, and E may protect against the risk of cataracts, clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel v ...
s have shown no benefit from supplements, although the evidence is mixed, but weakly positive, for a potential protective effect of the carotenoid
Carotenoids () are yellow, orange, and red organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, archaea, and fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, corn, tomatoes, cana ...
s, lutein and zeaxanthin.
Treatment
Surgical
 The appropriateness of surgery depends on a person's particular functional and visual needs and other risk factors. Cataract removal can be performed at any stage and no longer requires ripening of the lens. Surgery is usually
The appropriateness of surgery depends on a person's particular functional and visual needs and other risk factors. Cataract removal can be performed at any stage and no longer requires ripening of the lens. Surgery is usually outpatient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by healthcare professionals. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other healt ...
and usually performed using local anesthesia
Local anesthesia is any technique to induce the absence of sense, sensation in a specific part of the body, generally for the aim of inducing local analgesia, i.e. local insensitivity to pain, although other local senses may be affected as well. ...
. About 9 of 10 patients can achieve a corrected vision of 20/40 or better after surgery.
Several recent evaluations found that cataract surgery can meet expectations only when significant functional impairment due to cataracts exists before surgery. Visual function estimates such as VF-14 have been found to give more realistic estimates than visual acuity testing alone. In some developed countries, a trend to overuse cataract surgery has been noted, which may lead to disappointing results.
Phacoemulsification is the most widely used cataract surgery in the developed world. This procedure uses ultrasonic energy to emulsify the cataract lens. Phacoemulsification typically comprises six steps:
* Anaesthetic – The eye is numbed with either a subtenon injection around the eye (see: retrobulbar block) or topical anesthetic eye drops. The former also provides paralysis of the eye muscles.
* Corneal incision – Two cuts are made at the margin of the clear cornea to allow insertion of instruments into the eye.
* Capsulorhexis – A needle or small pair of forceps is used to create a circular hole in the capsule in which the lens sits.
* Phacoemulsification – A handheld ultrasonic probe is used to break up and emulsify the lens into liquid using the energy of ultrasound waves. The resulting 'emulsion' is sucked away.
* Irrigation and aspiration – The cortex, which is the soft outer layer of the cataract, is aspirated or sucked away. Fluid removed is continually replaced with a saline solution to prevent collapse of the structure of the anterior chamber (the front part of the eye).
* Lens insertion – A plastic, foldable lens is inserted into the capsular bag that formerly contained the natural lens. Some surgeons also inject an antibiotic into the eye to reduce the risk of infection. The final step is to inject salt water into the corneal wounds to cause the area to swell and seal the incision.
A Cochrane review found little to no difference in visual acuity as a function of the size of incisions made for phacoemulsification in the range from ≤ 1.5 mm to 3.0 mm. Extracapsular cataract extraction (ECCE) consists of removing the lens manually, but leaving the majority of the capsule intact. The lens is expressed through a 10- to 12-mm incision which is closed with sutures at the end of surgery. ECCE is less frequently performed than phacoemulsification, but can be useful when dealing with very hard cataracts or other situations where emulsification is problematic. Manual small incision cataract surgery (MSICS) has evolved from ECCE. In MSICS, the lens is removed through a self-sealing scleral tunnel wound in the sclera
The sclera, also known as the white of the eye or, in older literature, as the tunica albuginea oculi, is the opaque, fibrous, protective outer layer of the eye containing mainly collagen and some crucial elastic fiber.
In the development of t ...
which, ideally, is watertight and does not require suturing. Although "small", the incision is still markedly larger than the portal in phacoemulsification. This surgery is increasingly popular in the developing world where access to phacoemulsification is still limited.
Intracapsular cataract extraction (ICCE) is rarely performed. The lens and surrounding capsule are removed in one piece through a large incision while pressure is applied to the vitreous membrane. The surgery has a high rate of complications.
Prognosis
Postoperative care
 The postoperative recovery period (after removing the cataract) is usually short. The patient is usually ambulatory on the day of surgery, but is advised to move cautiously and avoid straining or heavy lifting for about a month. The eye is usually patched on the day of surgery and use of an eye shield at night is often suggested for several days after surgery.
In all types of surgery, the cataractous lens is removed and replaced with an artificial lens, known as an
The postoperative recovery period (after removing the cataract) is usually short. The patient is usually ambulatory on the day of surgery, but is advised to move cautiously and avoid straining or heavy lifting for about a month. The eye is usually patched on the day of surgery and use of an eye shield at night is often suggested for several days after surgery.
In all types of surgery, the cataractous lens is removed and replaced with an artificial lens, known as an intraocular lens
An intraocular lens (IOL) is a lens (optics), lens implanted in the human eye, eye usually as part of a treatment for cataracts or for correcting other vision problems such as myopia, near-sightedness (myopia) and farsightedness, far-sightednes ...
, which stays in the eye permanently. Intraocular lenses are usually monofocal, correcting for either distance or near vision. Multifocal lenses may be implanted to improve near and distance vision simultaneously, but these lenses may increase the chance of unsatisfactory vision.
Complications
Serious complications of cataract surgery include retinal detachment and endophthalmitis. In both cases, patients notice a sudden decrease in vision. In endophthalmitis, patients often describe pain. Retinal detachment frequently presents with unilateralvisual field
The visual field is "that portion of space in which objects are visible at the same moment during steady fixation of the gaze in one direction"; in ophthalmology and neurology the emphasis is mostly on the structure inside the visual field and it i ...
defects, blurring of vision, flashes of light, or floating spots.
The risk of retinal detachment was estimated as about 0.4% within 5.5 years, corresponding to a 2.3-fold risk increase compared to naturally expected incidence, with older studies reporting a substantially higher risk. The incidence is increasing over time in a somewhat linear manner, and the risk increase lasts for at least 20 years after the procedure. Particular risk factors are younger age, male sex, longer axial length, and complications during surgery. In the highest risk group of patients, the incidence of pseudophakic retinal detachment may be as high as 20%.
The risk of endophthalmitis occurring after surgery is less than one in 1000.
Corneal edema
Edema (American English), also spelled oedema (British English), and also known as fluid retention, swelling, dropsy and hydropsy, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. S ...
and cystoid macular edema are less serious but more common, and occur because of persistent swelling at the front of the eye in corneal edema or back of the eye in cystoid macular edema. They are normally the result of excessive inflammation following surgery, and in both cases, patients may notice blurred, foggy vision. They normally improve with time and with application of anti-inflammatory drops. The risk of either occurring is around one in 100. It is unclear whether NSAIDs or corticosteroids are superior at reducing postoperative inflammation.
Posterior capsular opacification, also known as after-cataract, is a condition in which months or years after successful cataract surgery, vision deteriorates or problems with glare and light scattering recur, usually due to thickening of the back or posterior capsule surrounding the implanted lens, so-called 'posterior lens capsule opacification'. Growth of natural lens cells remaining after the natural lens was removed may be the cause, and the younger the patient, the greater the chance of this occurring. Management involves cutting a small, circular area in the posterior capsule with targeted beams of energy from a laser, called Nd:YAG laser capsulotomy, after the type of laser used. The laser can be aimed very accurately, and the small part of the capsule which is cut falls harmlessly to the bottom of the inside of the eye. This procedure leaves sufficient capsule to hold the lens in place, but removes enough to allow light to pass directly through to the retina. Serious side effects are rare. Posterior capsular opacification is common and occurs following up to one in four operations, but these rates are decreasing following the introduction of modern intraocular lenses together with a better understanding of the causes.
Vitreous touch syndrome is a possible complication of intracapsular cataract extraction.
Epidemiology
History
Cataract surgery was first described by the Ayurvedic physician, Suśruta (about 5th century BCE) in '' Sushruta Samhita'' inancient India
Anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. The earliest known human remains in South Asia date to 30,000 years ago. Sedentism, Sedentariness began in South Asia around 7000 BCE; ...
. Most of the methods focused on hygiene. Follow-up treatments include bandaging of the eye and covering the eye with warm butter
Butter is a dairy product made from the fat and protein components of Churning (butter), churned cream. It is a semi-solid emulsion at room temperature, consisting of approximately 81% butterfat. It is used at room temperature as a spread (food ...
. Cataracts and their treatment in Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Em ...
are discussed in '' De Medicinae'' (29 CE) by the Latin encyclopedist Aulus Cornelius Celsus. Archaeological evidence of eye surgery in the Roman era also exists.
Galen of Pergamon (2nd century CE), the Greek physician, described an operation similar to modern cataract surgery. Using a needle-shaped instrument, Galen attempted to remove the cataract-affected lens of the eye.
The Ophthalmology in medieval Islam, Arab ophthalmologist Ammar Al-Mawsili, in his ''The Book of Choice in Ophthalmology'', written ''circa'' 1000 CE, wrote of his invention of a syringe
A syringe is a simple reciprocating pump consisting of a plunger (though in modern syringes, it is actually a piston) that fits tightly within a cylindrical tube called a barrel. The plunger can be linearly pulled and pushed along the inside ...
and the technique of cataract extraction while experiment
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs whe ...
ing with it on a patient.
In 1468 Abiathar Crescas, a Jewish physician and astrologer of the Crown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon (, ) ;, ; ; . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of Barcelona (later Principality of Catalonia) and ended as a consequence of the War of the Sp ...
, famously removed the cataracts of King John II of Aragon
John II (Spanish language, Spanish: ''Juan II'', Catalan language, Catalan: ''Joan II'', Aragonese language, Aragonese: ''Chuan II'' and ; 29 June 1398 – 20 January 1479), called the Great (''el Gran'') or the Faithless (''el Sense Fe''), was ...
, restoring his eyesight.
Etymology
"Cataract" is derived from theLatin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
', itself from the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
(') 'waterfall'. As rapidly running water turns white, so the term may have been used metaphorically to describe the similar appearance of mature ocular opacities. In Latin, ''cataracta'' had the alternative meaning "portcullis
A portcullis () is a heavy, vertically closing gate typically found in medieval fortifications. It consists of a latticed Grille (architecture), grille made of wood and/or metal, which slides down grooves inset within each jamb of the gateway.
...
" and the name possibly passed through French to form the English meaning "eye disease" (early 15th century), on the notion of "obstruction". Early Persian physicians called the term ''nazul-i-ah'', or "descent of the water"—vulgarised into waterfall disease or cataract—believing such blindness to be caused by an outpouring of corrupt humour
Humour (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English) or humor (American English) is the tendency of experiences to provoke laughter and provide amusement. The term derives from the humorism, humoral medicine of the ancient Gre ...
into the eye.
Research
N-Acetylcarnosine drops have been investigated as a medical treatment for cataracts. The drops are believed to work by reducingoxidation
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
and glycation
Glycation (non-enzymatic glycosylation) is the covalent bond, covalent attachment of a sugar to a protein, lipid or nucleic acid molecule. Typical sugars that participate in glycation are glucose, fructose, and their derivatives. Glycation is th ...
damage in the lens, particularly reducing crystallin crosslinking. Some benefit has been shown in small manufacturer-sponsored randomized controlled trials but further independent corroboration is still required.
Femtosecond laser mode-locking, used during cataract surgery, was originally used to cut accurate and predictable flaps in LASIK
LASIK or Lasik (; "laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis"), commonly referred to as laser eye surgery or laser vision correction, is a type of refractive surgery for the correction of myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism. LASIK surgery is p ...
surgery, and has been introduced to cataract surgery. The incision at the junction of the sclera and cornea and the hole in capsule during capsulorhexis, traditionally made with a handheld blade, needle, and forceps, are dependent on skill and experience of the surgeon. Sophisticated three-dimensional images of the eyes can be used to guide lasers to make these incisions. A Nd:YAG laser can also then break up the cataract as in phacoemulsification.The authors declare a financial interest in a company producing femtosecond laser equipment.
Stem cells
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can change into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell ...
have been used in a clinical trial, with results submitted in 2014 and published in March 2016, for lens regeneration in twelve children under the age of two with cataracts present at birth. The children were followed for six months, so it is unknown what the long-term results have been, and it is unknown if this procedure would work in adults.
See also
* *References
Further reading
*External links
Pictures of different types of cataracts
{{Authority control Aging-associated diseases Blindness Eye diseases Disorders of lens Eye Ophthalmology Vision Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate