Carnarvon Castle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Caernarfon Castle (; ) is a medieval fortress in
 War broke out again between England and Wales on 22 March 1282. The Welsh leader, Llywelyn ap Gruffudd, died later that year on 11 December. His brother
War broke out again between England and Wales on 22 March 1282. The Welsh leader, Llywelyn ap Gruffudd, died later that year on 11 December. His brother 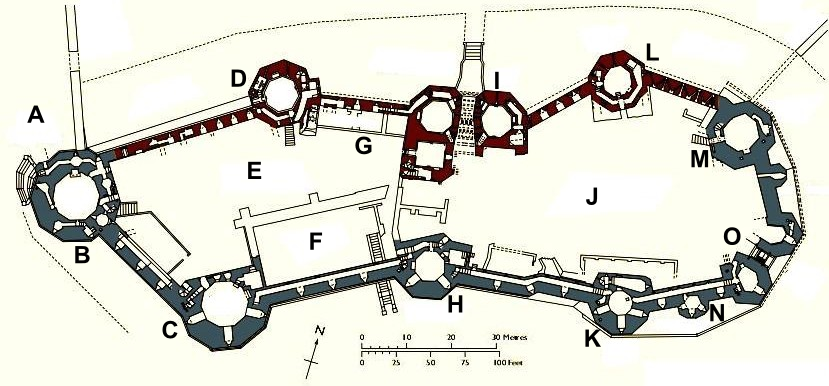 Construction at Caernarfon Castle continued over the winter of 1283–84. The extent of completion is uncertain, although architectural historian Arnold Taylor speculated that when Edward and Eleanor visited again in Easter 1284 the Eagle Tower may have been complete. The
Construction at Caernarfon Castle continued over the winter of 1283–84. The extent of completion is uncertain, although architectural historian Arnold Taylor speculated that when Edward and Eleanor visited again in Easter 1284 the Eagle Tower may have been complete. The
 The architect, Master
The architect, Master  Studded along the curtain wall are several polygonal towers from which flanking fire could be deployed. There were
Studded along the curtain wall are several polygonal towers from which flanking fire could be deployed. There were
Cadw owner of Caernarfon CastleCaernarfon Castle - World History Encyclopedia
{{Authority control Buildings and structures completed in 1330 Cadw Caernarfon Castles in Gwynedd Grade I listed buildings in Gwynedd Grade I listed castles in Wales Historic house museums in Wales Museums in Gwynedd Tourist attractions in Gwynedd World Heritage Sites in Wales Castles and Town Walls of King Edward in Gwynedd
Gwynedd
Gwynedd () is a county in the north-west of Wales. It borders Anglesey across the Menai Strait to the north, Conwy, Denbighshire, and Powys to the east, Ceredigion over the Dyfi estuary to the south, and the Irish Sea to the west. The ci ...
, north-west Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
. The first fortification on the site was a motte-and-bailey castle
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy ...
built in the late 11th century, which King Edward I of England
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots (Latin: Malleus Scotorum), was King of England from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he was Lord of Ireland, and from 1254 ...
began to replace with the current stone structure in 1283. The castle and town established by Edward acted as the administrative centre of north Wales, and as a result the defences were built on a grand scale. There was a deliberate link with Caernarfon's Roman past—nearby is the Roman fort
''Castra'' () is a Latin term used during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire for a military 'camp', and ''castrum'' () for a 'fort'. Either could refer to a building or plot of land, used as a fortified military base.. Included is a discuss ...
of Segontium
Segontium () is a Roman fort on the outskirts of Caernarfon in Gwynedd, North Wales.
Etymology
The fort probably takes its name either directly from the Afon Seiont or from a pre-existing British settlement itself named for the river. The name ...
—and the castle's walls are reminiscent of the Walls of Constantinople
The Walls of Constantinople (; ) are a series of defensive wall, defensive stone walls that have surrounded and protected the city of Constantinople (modern Fatih district of Istanbul) since its founding as the new capital of the Roman Empire b ...
.
While the castle was under construction, town walls
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or Earthworks (military), earthworks to extensive military fortifications such as ...
were built around Caernarfon. The work cost between £20,000 and £25,000 from the start until the work ended in 1330. Although the castle appears mostly complete from the outside, the interior buildings no longer survive and many parts of the structure were never finished. In 1294 the town and castle were sacked and captured by Madog ap Llywelyn
Madog ap Llywelyn (died after 1312) was the leader of the Welsh revolt of 1294–95 against English rule in Wales. The revolt was surpassed in longevity only by the revolt of Owain Glyndŵr in the 15th century. Madog belonged to a junior branch ...
during his rebellion against the English, but were recaptured the following year. The castle was unsuccessfully besieged during the Glyndŵr Rising Glyndŵr, also spelled Glyndwr, may refer to:
* Owain Glyndŵr – Medieval Welsh prince and leader
** Glyndŵr rebellion – 15th century Welsh uprising
* Glyndŵr (district) – District of Wales (1974–1996)
** Montgomeryshire and Glyndŵr ( ...
of 1400–1415. When the Tudor dynasty
The House of Tudor ( ) was an English and Welsh dynasty that held the throne of England from 1485 to 1603. They descended from the Tudors of Penmynydd, a Welsh noble family, and Catherine of Valois. The Tudor monarchs ruled the Kingdom of Eng ...
ascended to the English throne in 1485, tensions between the Welsh and English began to diminish and castles were considered less important. As a result, Caernarfon Castle was allowed to fall into a state of disrepair.
Despite its dilapidated condition, during the English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
Caernarfon Castle was held by Royalists
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of gover ...
and besieged three times by Parliamentarian forces. This was the last time the castle was used in war. The castle was neglected until the 19th century when the state funded repairs. The castle was used for the investiture of the Prince of Wales in 1911 and again in 1969. The castle is managed by Cadw
(, a Welsh verbal noun meaning "keeping/preserving") is the historic environment service of the Welsh Government and part of the Tourism and Culture group. works to protect the historic buildings and structures, the landscapes and heritage ...
, the Welsh Government
The Welsh Government ( ) is the Executive (government), executive arm of the Welsh devolution, devolved government of Wales. The government consists of Cabinet secretary, cabinet secretaries and Minister of State, ministers. It is led by the F ...
's historic environment service. It is part of the World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
"Castles and Town Walls of King Edward in Gwynedd
The Castles and Town Walls of King Edward in Gwynedd is a UNESCO-designated World Heritage Site located in Gwynedd, Wales. It includes the castles of Beaumaris and Harlech and the castles and town walls of Caernarfon and Conwy. UNESCO considers ...
".
Background
The first fortifications at Caernarfon were built by the Romans. Theirfort
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from La ...
, which they named , is on the outskirts of the modern town. The fort sat near the bank of the River Seiont; the fort was probably built here due to the sheltered position and because it could be resupplied via the river Seiont. Caernarfon derives its name from the Roman fortifications. In Welsh, the place was called (lenition
In linguistics, lenition is a sound change that alters consonants, making them "weaker" in some way. The word ''lenition'' itself means "softening" or "weakening" (from Latin 'weak'). Lenition can happen both synchronically (within a language ...
of ) , meaning 'the stronghold in the land over against '; is the Welsh name for Anglesey
Anglesey ( ; ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms the bulk of the Principal areas of Wales, county known as the Isle of Anglesey, which also includes Holy Island, Anglesey, Holy Island () and some islets and Skerry, sker ...
. Little is known about the fate of Segontium and its associated civilian settlement after the Romans departed from Britain in the early 5th century.
Early castle
Following theNorman Conquest of England
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, French people, French, Flemish people, Flemish, and Bretons, Breton troops, all led by the Du ...
, William the Conqueror
William the Conqueror (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), sometimes called William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England (as William I), reigning from 1066 until his death. A descendant of Rollo, he was D ...
turned his attention to Wales. According to the Domesday Survey
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by ...
of 1086, the Norman Robert of Rhuddlan
Robert of Rhuddlan (died 3 July 1093) was a Norman adventurer who became lord of much of north-east Wales and for a period lord of all North Wales.
Robert was the son of Humphrey de Tillieul (or Bigod) and Adeliza de Grentemesnil, brother of Ar ...
was nominally in command of the whole of northern Wales. He was killed by the Welsh in 1088. His cousin Hugh d'Avranches, Earl of Chester
Hugh d'Avranches ( 1047 – 27 July 1101), nicknamed ''le Gros'' (the Large) or ''Lupus'' (the Wolf), was from 1071 the second Norman Earl of Chester and one of the great magnates of early Norman England.
Early life and career
Hugh d'Avra ...
, reasserted Norman control of north Wales by building three castles: one at an unknown location somewhere in Meirionnydd
is a coastal and mountainous region of Wales. It has been a kingdom, a , a district and, as Merionethshire, a county. It is currently a committee area within the county Gwynedd.
Kingdom
(Meirion, with as a Welsh suffix of land, literally 'La ...
, one at Aberlleiniog on Anglesey, and another at Caernarfon. This early castle was built on a peninsula, bounded by the River Seiont and the Menai Strait
The Menai Strait () is a strait which separates the island of Anglesey from Gwynedd, on the mainland of Wales. It is situated between Caernarfon Bay in the south-west and Conwy Bay in the north-east, which are both inlets of the Irish Sea. The s ...
; it would have been a motte and bailey
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy ...
, defended by a timber palisade
A palisade, sometimes called a stakewall or a paling, is typically a row of closely placed, high vertical standing tree trunks or wooden or iron stakes used as a fence for enclosure or as a defensive wall. Palisades can form a stockade.
Etymo ...
and earthworks. The motte, or mound, was integrated into the later Edwardian castle, but the location of the original bailey is uncertain, although it may have been to the north-east of the motte. Excavations on top of the motte in 1969 revealed no traces of medieval occupation, suggesting any evidence had been removed. It is likely that the motte was surmounted by a wooden tower known as a keep
A keep is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in castles that were fortified residen ...
. The Welsh recaptured Gwynedd in 1115, and Caernarfon Castle came into the possession of the Welsh princes. From contemporary documents written at the castle, it is known that Llywelyn the Great
Llywelyn ab Iorwerth (, – 11 April 1240), also known as Llywelyn the Great (, ; ), was a medieval Welsh ruler. He succeeded his uncle, Dafydd ab Owain Gwynedd, as King of Gwynedd in 1195. By a combination of war and diplomacy, he dominate ...
and later Llywelyn ap Gruffudd
Llywelyn ap Gruffudd ( – 11 December 1282), also known as Llywelyn II and Llywelyn the Last (), was List of rulers of Gwynedd, Prince of Gwynedd, and later was recognised as the Prince of Wales (; ) from 1258 until his death at Cilmeri in 128 ...
occasionally stayed at Caernarfon.
Edwardian castle
 War broke out again between England and Wales on 22 March 1282. The Welsh leader, Llywelyn ap Gruffudd, died later that year on 11 December. His brother
War broke out again between England and Wales on 22 March 1282. The Welsh leader, Llywelyn ap Gruffudd, died later that year on 11 December. His brother Dafydd ap Gruffydd
Dafydd ap Gruffudd, also known as ''Dafydd III'' (11 July 1238 – 3 October 1283), was a Prince of Gwynedd until after the death of his brother, Llywelyn ap Gruffudd, when he proclaimed himself as the Prince of Wales from 11 December 1282. H ...
continued to fight against the English, but in 1283 Edward I was victorious. Edward marched through northern Wales, capturing castles such as that at Dolwyddelan
Dolwyddelan ( ; ; ) is a village and Community (Wales), community in Conwy County Borough, Wales. The community occupies most of the valley of the Afon Lledr, and contains the settlements of Dolwyddelan, Pentre Bont, Blaenau Dolwyddelan, and Po ...
, and establishing his own at Conwy
Conwy (, ), previously known in English as Conway, is a walled market town, community and the administrative centre of Conwy County Borough in North Wales. The walled town and castle stand on the west bank of the River Conwy, facing Deganwy ...
. War finally drew to a close in May 1283 when Dolbadarn Castle
Dolbadarn Castle ( ; ; ) is a fortification built by the Welsh prince Llywelyn the Great during the early 13th century, at the base of the Llanberis Pass, in northern Wales. The castle was important both militarily and as a symbol of Llywelyn's ...
, Dafydd ap Gruffudd's last castle, was captured. Shortly afterwards, Edward began building castles at Harlech
Harlech () is a seaside resort and community (Wales), community in Gwynedd, North Wales, and formerly in the Historic counties of Wales, historic county of Merionethshire. It lies on Tremadog Bay in the Snowdonia National Park. Before 1966, it ...
and Caernarfon. The castles of Caernarfon, Conwy and Harlech were the most impressive of their time in Wales, and their construction—along with other Edwardian castles in the country—helped establish English rule. The master mason responsible for the design and construction of the castle was probably James of Saint George
Master James of Saint George (–1309; French: , Old French: Mestre Jaks, Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ...: Mestre Jaks, Latin: Magister Jaco ...
, an experienced architect and military engineer who played an important role in building the Edwardian castles in Wales. According to the ''Flores Historiarum
The ''Flores Historiarum'' (Flowers of History) is the name of two different (though related) Latin chronicles by medieval English historians that were created in the 13th century, associated originally with the Abbey of St Albans.
Wendover's ...
'', during the construction of the castle and planned town, the body of the Roman emperor Magnus Maximus
Magnus Maximus (; died 28 August 388) was Roman emperor in the West from 383 to 388. He usurped the throne from emperor Gratian.
Born in Gallaecia, he served as an officer in Britain under Theodosius the Elder during the Great Conspiracy ...
was discovered, and Edward I ordered its reburial in a local church.
The construction of the new stone castle was part of a programme of building which transformed Caernarfon; town walls were added, connected to the castle, and a new quay was built. The earliest reference to building at Caernarfon dates from 24 June 1283, when a ditch had been dug separating the site of the castle from the town to the north. A ''bretagium'', a type of stockade
A stockade is an enclosure of palisades and tall walls, made of logs placed side by side vertically, with the tops sharpened as a defensive wall.
Etymology
''Stockade'' is derived from the French word ''estocade''. The French word was derived f ...
, was created around the site to protect it while the permanent defences were under construction. Timber was shipped from as far away as Liverpool. Stone was quarried from nearby places, such as from Anglesey and around the town. A force of hundreds worked on the excavation of the moat and digging the foundations for the castle. As the site expanded, it began to encroach on the town; houses were cleared to allow the construction. Residents were not paid compensation until three years later. While the foundations for the stone walls were being created, timber-framed
Timber framing () and "post-and-beam" construction are traditional methods of building with heavy Beam (structure), timbers, creating structures using squared-off and carefully fitted and Woodworking joints, joined timbers with joints secure ...
apartments were built for Edward I and Eleanor of Castile
Eleanor of Castile (1241 – 28 November 1290) was Queen of England as the first wife of Edward I. She was educated at the Castilian court and also ruled as Countess of Ponthieu in her own right () from 1279. After diplomatic efforts to s ...
, his queen. They arrived at Caernarfon on either 11 or 12 July 1283 and stayed for over a month.
 Construction at Caernarfon Castle continued over the winter of 1283–84. The extent of completion is uncertain, although architectural historian Arnold Taylor speculated that when Edward and Eleanor visited again in Easter 1284 the Eagle Tower may have been complete. The
Construction at Caernarfon Castle continued over the winter of 1283–84. The extent of completion is uncertain, although architectural historian Arnold Taylor speculated that when Edward and Eleanor visited again in Easter 1284 the Eagle Tower may have been complete. The Statute of Rhuddlan
The Statute of Rhuddlan (), also known as the Statutes of Wales ( or ''Valliae'') or as the Statute of Wales ( or ''Valliae''), was a royal ordinance by Edward I of England, which gave the constitutional basis for the government of the Principal ...
, enacted on 3 March 1284, made Caernarfon a borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English language, English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
...
and the administrative centre of the county of Gwynedd. According to tradition, Edward II was born at Caernarfon on 25 April 1284. Edward was created Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales (, ; ) is a title traditionally given to the male heir apparent to the History of the English monarchy, English, and later, the British throne. The title originated with the Welsh rulers of Kingdom of Gwynedd, Gwynedd who, from ...
in 1301, with control over Wales and its incomes. Since then the title has traditionally been held by the eldest son of the monarch. According to a famous legend, the king had promised the Welsh that he would name "a prince born in Wales, who did not speak a word of English" and then produced his infant son to their surprise; but the story may well be apocryphal, as it can only be traced to the 16th century. In 1284, Caernarfon was defended by a garrison of forty men, more than the thirty-strong garrisons at Conwy and Harlech. Even in peace time, when most castles would have a guard of only a few men, Caernarfon was defended by between twenty and forty people due to its importance.
By 1285, Caernarfon's town walls
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or Earthworks (military), earthworks to extensive military fortifications such as ...
were mostly complete. At the same time work continued on the castle. Spending on construction was negligible from 1289 and accounts end in 1292. Edward I's campaign of castle-building in Wales cost £80,000 between 1277 and 1304, and £95,000 between 1277 and 1329; by 1292 £12,000 had been spent on the construction of Caernarfon's castle—of which the southern façade was furthest along—and town walls. As the southern wall and town walls completed a defensive circuit around Caernarfon, the plan was to build the castle's northern façade last.
In 1294, Wales broke out in rebellion led by Madog ap Llywelyn
Madog ap Llywelyn (died after 1312) was the leader of the Welsh revolt of 1294–95 against English rule in Wales. The revolt was surpassed in longevity only by the revolt of Owain Glyndŵr in the 15th century. Madog belonged to a junior branch ...
, Prince of Wales. As Caernarfon was the centre of administration in Gwynedd and a symbol of English power, it was targeted by the Welsh. Madog's forces captured the town in September, and in the process heavily damaged the town walls. The castle was defended by just a ditch and a temporary barricade. It was quickly taken and anything flammable was set alight. Fire raged across Caernarfon, leaving destruction in its wake. In the summer of 1295, the English moved to retake Caernarfon. By November the same year, the English began refortifying the town. Rebuilding the town walls was a high priority, and £1,195 (nearly half the sum initially spent on the walls) was spent on completing the job two months ahead of schedule. Attention then shifted to the castle and on finishing the work that had halted in 1292. Once the rebellion was put down, Edward began building Beaumaris Castle
Beaumaris Castle ( ; , ), in Beaumaris, Anglesey, Wales, was built as part of Edward I of England, Edward I's Conquest of Wales by Edward I of England, campaign to conquer north Wales after 1282. Plans were probably first made to construct t ...
on the Isle of Anglesey. The work was overseen by James of Saint George; as a result, Walter of Hereford
Walter of Hereford was a holder of the feudalism, feudal title Baron Bergavenny or Lord Abergavenny in the Welsh Marches in the mid twelfth century.
Lineage
Walter of Hereford was a son of Miles of Gloucester, 1st Earl of Hereford, and Sibyl of ...
took over as master mason for the new phase of construction. By the end of 1301, a further £4,500 had been spent on the work; the focus of the work was on the northern wall and towers. The accounts between November 1301 and September 1304 are missing, possibly because there was a hiatus in work while labour moved north to help out with England's war against Scotland. Records show that Walter of Hereford had left Caernarfon and was in Carlisle in October 1300; he remained occupied with the Scottish wars until the autumn of 1304 when building at Caernarfon resumed. Walter died in 1309 and his immediate subordinate, Henry of Ellerton, took over the position of master mason. Construction continued at a steady rate until 1330.
From 1284 to 1330, when accounts end, between £20,000 and £25,000 was spent on Caernarfon's castle and town walls. Such a sum was enormous and dwarfed the spending on castles such as Dover
Dover ( ) is a town and major ferry port in Kent, southeast England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies southeast of Canterbury and east of Maidstone. ...
and Château Gaillard
Château Gaillard () is a medieval castle ruin overlooking the River Seine above the commune of Les Andelys, in the French department of Eure, in Normandy. It is located some north-west of Paris and from Rouen. Construction began in 1196 u ...
, which were amongst the most expensive and impressive fortifications of the later 12th and early 13th centuries. Subsequent additions to Caernarfon were not major, and what remains of the castle is substantially from the Edwardian period. Despite the expense, much of what was planned for the castle was never carried out. The rears of the King's Gate (the entrance from the town) and the Queen's Gate (the entrance from the south-east) were left unfinished, and foundations in the castle's interior mark where buildings would have stood had work continued.
Later history
For around two centuries after the conquest of Wales, the arrangements established by Edward I for the governance of the country remained in place. During this time the castle was constantly garrisoned, and Caernarfon was effectively the capital of north Wales. There was a degree of discrimination, with the most important administrative jobs in Wales usually closed to Welsh people. Tension between the Welsh and their English conquerors spilled over at the start of the 15th century with the outbreak of theGlyndŵr Rising Glyndŵr, also spelled Glyndwr, may refer to:
* Owain Glyndŵr – Medieval Welsh prince and leader
** Glyndŵr rebellion – 15th century Welsh uprising
* Glyndŵr (district) – District of Wales (1974–1996)
** Montgomeryshire and Glyndŵr ( ...
(1400–1415). During the revolt, Caernarfon was one of the targets of Owain Glyndŵr
Owain ap Gruffydd (28 May 135420 September 1415), commonly known as Owain Glyndŵr (Glyn Dŵr, , anglicised as Owen Glendower) was a Welsh people, Welsh leader, soldier and military commander in the Wales in the late Middle Ages, late Middle ...
's army. The town and castle were besieged in 1401, and in November that year the Battle of Tuthill was fought nearby between Caernarfon's defenders and the besieging force. In 1403 and 1404, Caernarfon was besieged by Welsh troops with support from French forces; the garrison at the time was around thirty. The accession of the Tudor dynasty
The House of Tudor ( ) was an English and Welsh dynasty that held the throne of England from 1485 to 1603. They descended from the Tudors of Penmynydd, a Welsh noble family, and Catherine of Valois. The Tudor monarchs ruled the Kingdom of Eng ...
to the English throne in 1485 heralded a change in the way Wales was administered. The Tudors were Welsh in origin, and their rule eased hostilities between the Welsh and English. As a result, castles such as Caernarfon, which provided secure centres from which the country could be administered, became less important. They were neglected, and in 1538 it was reported that many castles in Wales were "moche ruynous and ferre in decaye for lakke of tymely reparations".
In Caernarfon's case the walls of the town and castle remained in good condition, while features which required maintenance—such as roofs—were in a state of decay and much timber was rotten. Conditions were so poor that of the castle's seven towers and two gatehouses, only the Eagle Tower and the King's Gate had roofs by 1620. The domestic buildings inside the castle had been stripped of anything valuable, such as glass and iron. Despite the disrepair of the domestic buildings, the castle's defences were in a good enough state that during the English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
in the mid-17th century it was garrisoned by Royalists
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of gover ...
. Caernarfon Castle was besieged three times during the war. The constable
A constable is a person holding a particular office, most commonly in law enforcement. The office of constable can vary significantly in different jurisdictions. ''Constable'' is commonly the rank of an officer within a police service. Other peo ...
was John Byron, 1st Baron Byron
John Byron, 1st Baron Byron (1599 – 23 August 1652) was an English nobleman, Royalist, politician, peer, knight, and supporter of Charles I during the English Civil War.
Life
Byron was the son of Sir John Byron of Newstead Abbey, Nottingh ...
, who surrendered Caernarfon to Parliamentarian forces in 1646. It was the last time Caernarfon Castle saw fighting. Although it was ordered in 1660 that the castle and town walls should be dismantled, the work was aborted early on and may never have started.
Despite avoiding slighting
Slighting is the deliberate damage of high-status buildings to reduce their value as military, administrative, or social structures. This destruction of property is sometimes extended to the contents of buildings and the surrounding landscape. It ...
, the castle was neglected until the late 19th century. From the 1870s onwards, the government funded repairs to Caernarfon Castle. The deputy-constable Llewellyn Turner oversaw the work, in many cases controversially restoring and rebuilding the castle, rather than simply conserving the existing stonework. Steps, battlement
A battlement, in defensive architecture, such as that of city walls or castles, comprises a parapet (a defensive low wall between chest-height and head-height), in which gaps or indentations, which are often rectangular, occur at intervals ...
s, and roofs were repaired, and the moat to the north of the castle was cleared of post-medieval buildings that were considered to spoil the view, despite the protest of locals. Under the auspices of the Office of Works
The Office of Works was an organisation responsible for structures and exterior spaces, first established as part of the English royal household in 1378 to oversee the building and maintenance of the royal castles and residences.
In 1832 it be ...
and its successors since 1908, the castle was preserved due to its historic significance. In 1911, Caernarfon was used for the investiture of the Prince of Wales, for the investiture of Edward, Prince of Wales (later Edward VIII
Edward VIII (Edward Albert Christian George Andrew Patrick David; 23 June 1894 – 28 May 1972), later known as the Duke of Windsor, was King of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Empire, and Emperor of India, from 20 January ...
), eldest son of the newly crowned King George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until Death and state funeral of George V, his death in 1936.
George w ...
; the ceremony was held there at the insistence of the Chancellor of the Exchequer David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George, 1st Earl Lloyd-George of Dwyfor (17 January 1863 – 26 March 1945) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1922. A Liberal Party (United Kingdom), Liberal Party politician from Wales, he was known for leadi ...
, a Welshman raised in Caernarfonshire. In 1969, the precedent was repeated with the Investiture of Charles, Prince of Wales
The investiture of the Prince of Wales, investiture of Charles, Prince of Wales (later King Charles III), took place in Caernarfon Castle, north Wales, on 1 July 1969. The ceremony formally presented the title of Prince of Wales to the 20-year ...
, (who acceded as Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms.
Charles was born at Buckingham Palace during the reign of his maternal grandfather, King George VI, and ...
in 2022). Although Caernarfon Castle has been the property of the Crown
The Crown is a political concept used in Commonwealth realms. Depending on the context used, it generally refers to the entirety of the State (polity), state (or in federal realms, the relevant level of government in that state), the executive ...
since it was built, it is currently cared for by ''Cadw
(, a Welsh verbal noun meaning "keeping/preserving") is the historic environment service of the Welsh Government and part of the Tourism and Culture group. works to protect the historic buildings and structures, the landscapes and heritage ...
'' (), the Welsh Government
The Welsh Government ( ) is the Executive (government), executive arm of the Welsh devolution, devolved government of Wales. The government consists of Cabinet secretary, cabinet secretaries and Minister of State, ministers. It is led by the F ...
's historic environment division, responsible for the maintenance and care of Wales' historic buildings. In 1986, Caernarfon was added to the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
list of World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
s as part of the "Castles and Town Walls of King Edward in Gwynedd
The Castles and Town Walls of King Edward in Gwynedd is a UNESCO-designated World Heritage Site located in Gwynedd, Wales. It includes the castles of Beaumaris and Harlech and the castles and town walls of Caernarfon and Conwy. UNESCO considers ...
" in recognition of its global importance and to help conserve and protect the site. The castle houses the Royal Welch Fusiliers Museum
The Royal Welch Fusiliers Museum is a museum dedicated to the history of the Royal Welch Fusiliers, a historic regiment of the British Army. The museum is located within Caernarfon Castle in Caernarfon, Gwynedd, North Wales. Admission is included ...
. During 2015 a new "entrance pavilion" was built, designed by architects Donald Insall Associates.
Caernarfon Castle is now a major tourist attraction, with over 205,000 people visiting the attraction in 2018. A three-year restoration project, costing £5M and concluding in April 2023, has opened up previously-closed areas of the castle, and enabled wheelchair access to the battlements.
Architecture
 The architect, Master
The architect, Master James of Saint George
Master James of Saint George (–1309; French: , Old French: Mestre Jaks, Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ...: Mestre Jaks, Latin: Magister Jaco ...
, was partly influenced by a desire to make the structure impressive as a symbol of the new English rule in Wales. This was particularly acute as Caernarfon was made the centre of government in the northern part of the country. The Edwardian castle's layout was mostly dictated by the lie of the land, although the inclusion of the previous castle's motte played a part. It is a narrow enclosure, roughly in the shape of a figure eight. It was divided into two enclosures, upper and lower "wards", in the east and west respectively, with the eastern containing royal accommodation, although this was never completed. The divide was supposed to be established by a range of fortified buildings, however these too were never built.
 Studded along the curtain wall are several polygonal towers from which flanking fire could be deployed. There were
Studded along the curtain wall are several polygonal towers from which flanking fire could be deployed. There were battlement
A battlement, in defensive architecture, such as that of city walls or castles, comprises a parapet (a defensive low wall between chest-height and head-height), in which gaps or indentations, which are often rectangular, occur at intervals ...
s on the tops of walls and towers, and along the southern face were firing galleries; it was intended to include galleries along the northern face but they were never built. In the opinion of military historian Allen Brown, this combined to make Caernarfon Castle "one of the most formidable concentrations of fire-power to be found in the Middle Ages".
Most of the northern towers had four storeys including a basement. The Eagle Tower at the western corner of the castle was the grandest. It has three turrets which were once surmounted by statues of eagles. The tower contained grand lodgings, and was probably built for Sir Otton de Grandson
Otto de Grandson (–1328), sometimes numbered Otto I to distinguish him from later members of his family with the same name, was the most prominent of the Savoyard knights in the service of Edward I, Savoyard knights in the service of King ...
, the first justiciar
Justiciar is the English form of the medieval Latin term or (meaning "judge" or "justice"). The Chief Justiciar was the king's chief minister, roughly equivalent to a modern Prime Minister of the United Kingdom.
The Justiciar of Ireland was ...
of Wales. A basement level contained a water gate, through which visitors travelling up the River Seiont could enter the castle. Water was drawn from a well in the eponymous Well Tower.
Caernarfon's appearance differs from that of other Edwardian castles through the use of banded coloured stone in the walls and in its polygonal, rather than round, towers. There has been extensive academic debate over the interpretation of these features. Historian Arnold Taylor argued that the design of the castle was a representation of the Walls of Constantinople
The Walls of Constantinople (; ) are a series of defensive wall, defensive stone walls that have surrounded and protected the city of Constantinople (modern Fatih district of Istanbul) since its founding as the new capital of the Roman Empire b ...
. The conscious use of imagery from the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
was therefore an assertion of authority by Edward I, and influenced by ''Breudwyt Macsen Wledig'', the legendary dream of Magnus Maximus
Magnus Maximus (; died 28 August 388) was Roman emperor in the West from 383 to 388. He usurped the throne from emperor Gratian.
Born in Gallaecia, he served as an officer in Britain under Theodosius the Elder during the Great Conspiracy ...
, a Roman emperor. In his dream Maximus had seen a fort, "the fairest that man ever saw", within a city at the mouth of a river in a mountainous country and opposite an island. Edward interpreted this to mean Segontium was the city of Maximus' dream and drew on the imperial link when building Caernarfon Castle. The purported discovery of Magnus's remains and the addition of carved imperial eagle
The eagle is used in heraldry as a charge, as a supporter, and as a crest. Heraldic eagles can be found throughout world history like in the Achaemenid Empire or in the present Republic of Indonesia. The European post-classical symbolism of ...
s to one of the towers may have been intended to reinforce this narrative. Recent work by historian Abigail Wheatley suggests that the design of Caernarfon was indeed an assertion of Edward's authority, but that it drew on imagery from Roman sites in Britain with the intent of creating an allusion to Arthurian
According to legends, King Arthur (; ; ; ) was a king of Britain. He is a folk hero and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain.
In Welsh sources, Arthur is portrayed as a leader of the post-Ro ...
legitimacy for the king.
There were two main entrances, one leading from the town (the King's Gate) and one allowing direct access to the castle without having to proceed through the town (the Queen's Gate). Their form was typical of the time: a passage between two flanking towers. If the King's Gate had been completed, a visitor would have crossed two drawbridge
A drawbridge or draw-bridge is a type of moveable bridge typically at the entrance to a castle or tower surrounded by a moat. In some forms of English, including American English, the word ''drawbridge'' commonly refers to all types of moveable b ...
s, passed through five doors and under six portcullis
A portcullis () is a heavy, vertically closing gate typically found in medieval fortifications. It consists of a latticed Grille (architecture), grille made of wood and/or metal, which slides down grooves inset within each jamb of the gateway.
...
es, and negotiated a right-angle turn before emerging into the lower enclosure. The route was overlooked by numerous arrow loops and murder holes
A murder hole or meurtrière is a hole in the ceiling of a gateway or passageway in a fortification through which the defenders could shoot, throw or pour harmful substances or objects such as rocks, arrows, scalding water, hot sand, quicklime, ...
. A statue of Edward II was erected in a niche overlooking the town, above the entrance to the King's Gate. In the opinion of architectural historian Arnold Taylor, "No building in Britain demonstrates more strikingly the immense strength of medieval fortifications than the great twin-towered gateway to Caernarfon Castle." The Queen's Gate is unusual in that its entrance is above ground level; this was due to the integration of the earlier motte, raising the ground level of the interior. Externally, the gate would have been approached by a stone ramp which is no longer present.
While the curtain wall and its towers survive largely intact, all that remains of the buildings contained within the castle are the foundations. While royal lodgings were in the upper ward, the lower ward contained buildings such as the kitchens. The kitchens were located immediately west of the King's Gate. On the basis of their insubstantial foundations, Taylor suggests that the kitchens were not strongly built. The other key feature of the castle's domestic side was the Great Hall
A great hall is the main room of a royal palace, castle or a large manor house or hall house in the Middle Ages. It continued to be built in the country houses of the 16th and early 17th centuries, although by then the family used the great cha ...
. This abutted the south side of the lower ward and was . Though only the foundations survive, the Great Hall would have been an impressive building, featuring fine architecture, and used to host royal entertainment. Had Caernarfon been completed as intended, it could have contained a royal household of several hundred people.
Constables of Caernarfon Castle
Before 1835 the Constable of the castle served as mayor of Caernarfon. A list of the constables from 1284 to 1835 is thus available at the Caernarfon Royal Town Council site, below. * 1890–1908:John Henry Puleston
Sir John Henry Puleston (2 June 1830 – 19 October 1908) was a Welsh journalist and entrepreneur in the United States and later a Conservative Party (UK), Conservative politician who represented Devonport (UK Parliament constituency), Devonpor ...
* 1908–1945: David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George, 1st Earl Lloyd-George of Dwyfor (17 January 1863 – 26 March 1945) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1922. A Liberal Party (United Kingdom), Liberal Party politician from Wales, he was known for leadi ...
, OM, PC
* 1945–1963: Hon. William Ormsby-Gore
* 1963–2017: The Earl of Snowdon, GCVO
The Royal Victorian Order () is a dynastic order of knighthood established in 1896 by Queen Victoria. It recognises distinguished personal service to the monarch, members of the royal family, or to any viceroy or senior representative of the m ...
* 2018–present: Edmund Seymour Bailey
Edmund is a masculine given name in the English language. The name is derived from the Old English elements ''ēad'', meaning "prosperity" or "riches", and ''mund'', meaning "protector".
Persons named Edmund include:
People Kings and nobles
*Ed ...
, Lord Lieutenant of Gwynedd
See also
*Castles in Great Britain and Ireland
Castles have played an important military, economic and social role in Great Britain and Ireland since their introduction following the Norman invasion of England in 1066. Although a small number of castles had been built in England in the 105 ...
*List of castles in Wales
Wales is sometimes called the "castle capital of the world" because of the large number of castles in a relatively small area. Wales had about 600 castles, of which over 100 are still standing, either as ruins or as restored buildings. The ...
References
;Notes ;Bibliography * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * *External links
Cadw owner of Caernarfon Castle
{{Authority control Buildings and structures completed in 1330 Cadw Caernarfon Castles in Gwynedd Grade I listed buildings in Gwynedd Grade I listed castles in Wales Historic house museums in Wales Museums in Gwynedd Tourist attractions in Gwynedd World Heritage Sites in Wales Castles and Town Walls of King Edward in Gwynedd