|
Segontium
Segontium () is a Roman fort on the outskirts of Caernarfon in Gwynedd, North Wales. Etymology The fort probably takes its name either directly from the Afon Seiont or from a pre-existing British settlement itself named for the river. The name is a Latinised form of the Brythonic language *seg-ontio, which may be translated as "strong place". There is no evidence that the fort is connected to the Segontiaci, a British tribe noted by Julius Caesar. History Roman Segontium was founded by Agricola in AD 77 or 78 after he had conquered the Ordovices in North Wales. It was the main Roman fort in the north of Roman Wales and was designed to hold about a thousand auxiliary infantry. It was connected by a Roman road to the Roman legionary base at Chester, Deva Victrix. Unlike the medieval Caernarfon Castle that was built alongside the Seiont estuary more than a thousand years later, Segontium was situated on higher ground to the east giving a good view of the Menai Straits. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caernarfon
Caernarfon (; ) is a List of place names with royal patronage in the United Kingdom, royal town, Community (Wales), community and port in Gwynedd, Wales. It has a population of 9,852 (with Caeathro). It lies along the A487 road, on the eastern shore of the Menai Strait, opposite the island of Anglesey. The city of Bangor, Gwynedd, Bangor is to the north-east, while Snowdonia (Eryri) fringes Caernarfon to the east and south-east. Abundant natural resources in and around the Menai Strait enabled human habitation in prehistoric Britain. The Ordovices, a list of Celtic tribes, Celtic tribe, lived in the region during the period known as Roman Britain. The castra, Roman fort Segontium was established around AD 80 to subjugate the Ordovices during the Roman conquest of Britain. The Romans occupied the region until the end of Roman rule in Britain in 382, after which Caernarfon became part of the Kingdom of Gwynedd. In the late 11th century, William the Conqueror ordered the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caernarfon Castle
Caernarfon Castle (; ) is a medieval fortress in Gwynedd, north-west Wales. The first fortification on the site was a motte-and-bailey castle built in the late 11th century, which King Edward I of England began to replace with the current stone structure in 1283. The castle and town established by Edward acted as the administrative centre of north Wales, and as a result the defences were built on a grand scale. There was a deliberate link with Caernarfon's Roman past—nearby is the Castra, Roman fort of Segontium—and the castle's walls are reminiscent of the Walls of Constantinople. While the castle was under construction, Caernarfon town walls, town walls were built around Caernarfon. The work cost between £20,000 and £25,000 from the start until the work ended in 1330. Although the castle appears mostly complete from the outside, the interior buildings no longer survive and many parts of the structure were never finished. In 1294 the town and castle were sacked and ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segontiaci
The Segontiaci were a tribe of Iron Age Britain in the first century BCE. They are known only from a brief mention in the writings of Julius Caesar. They may have been one of the four tribes of Kent, represented in Caesar by references to the "four kings of that region" and in the archaeological record by distinct pottery assemblages. During Julius Caesar's second invasion of Britain in 54 BCE, following Caesar's military success and restoration of King Mandubracius to power over the Trinovantes, opposition to the Romans coalesced around the figure of Cassivellaunus which led to divided loyalties among the Britons, as Caesar records. Emissaries of five British tribes, including the Segontiaci (the others being the Ancalites, the Bibroci, the Cenimagni and the Cassi), arrived at the Roman camp to treat for peace, and agreed to reveal details of Cassivellaunus' stronghold. Caesar besieged him there and brought him to terms. When Caesar left Britain he took hostages from the Briton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the territory that became the Roman province of ''Britannia'' after the Roman conquest of Britain, consisting of a large part of the island of Great Britain. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. Julius Caesar invaded Britain in 55 and 54 BC as part of his Gallic Wars. According to Caesar, the Britons had been overrun or culturally assimilated by the Belgae during the British Iron Age and had been aiding Caesar's enemies. The Belgae were the only Celtic tribe to cross the sea into Britain, for to all other Celtic tribes this land was unknown. He received tribute, installed the friendly king Mandubracius over the Trinovantes, and returned to Gaul. Planned invasions under Augustus were called off in 34, 27, and 25 BC. In 40 AD, Caligula assembled 200,000 men at the Channel on the continent, only to have them gather seashells () according to Suetonius, perhaps as a symbolic gesture to proclaim Caligula's victory over th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
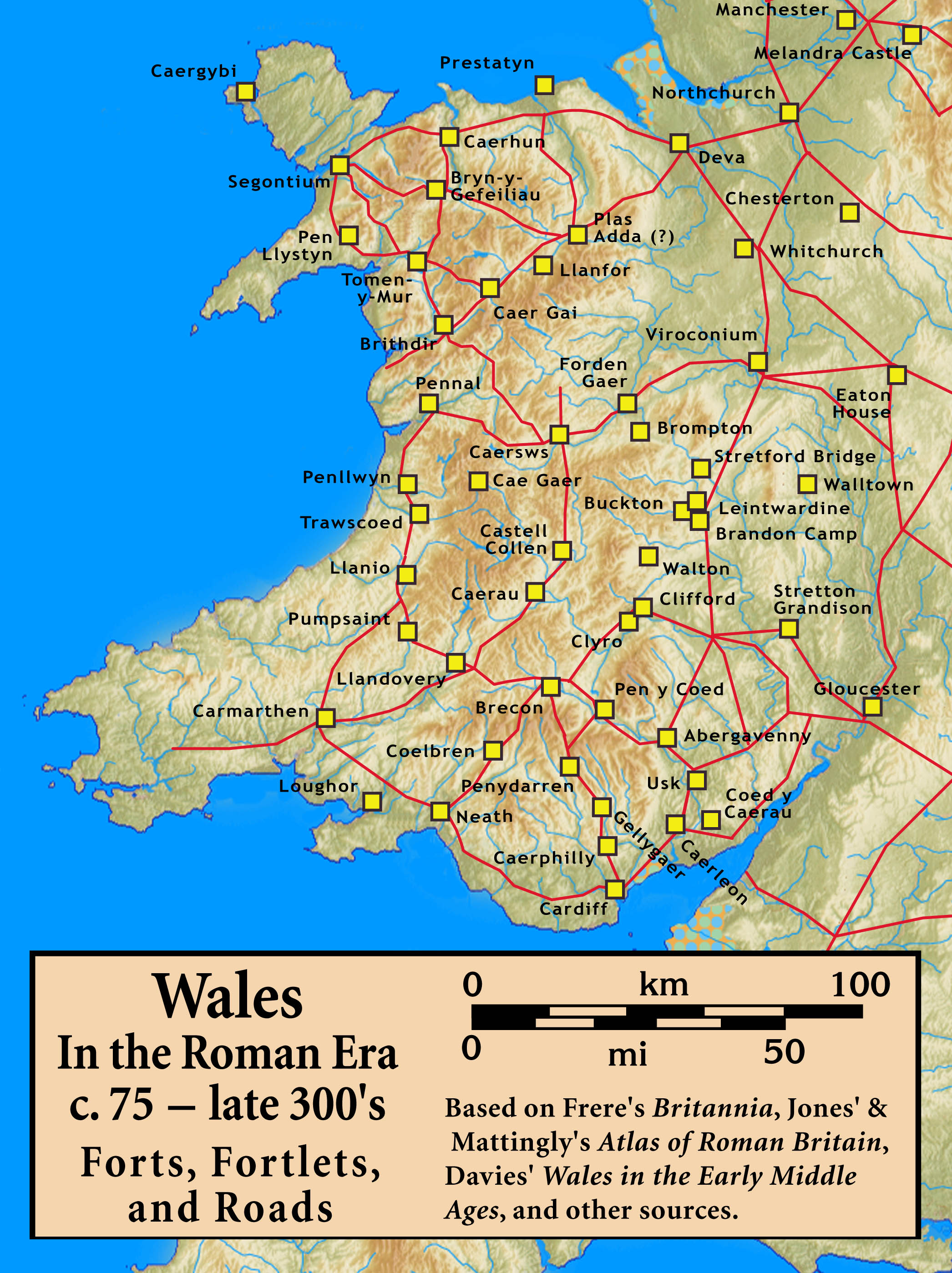
Wales In The Roman Era
The Roman era in the area of modern Wales began in 48 AD, with a military invasion by the Roman governor, imperial governor of Roman Britain. The conquest was completed by 78 AD, and Roman rule endured until the End of Roman rule in Britain, region was abandoned in 383 AD. The Roman Empire held a military occupation in most of Wales, except for the southern coastal region of South Wales, east of the Gower Peninsula, where there is a legacy of Romanization (cultural), Romanisation #Romanisation, in the region, and some southern sites such as Carmarthen, which was the civitas capital of the Demetae, Demetae tribe. The only town in Wales founded by the Romans, Caerwent, is in South Wales. Wales was a rich source of #Mining, mineral wealth, and the Romans used Roman engineering, their engineering Roman technology, technology to extract large amounts of gold, copper, and lead, as well as modest amounts of some other metals such as zinc and silver. The Roman #Roman invasion and conq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Seiont
Afon Seiont ( Welsh, meaning 'River Seiont' in English) is a river in Gwynedd, Wales which runs into the Menai Strait. Its source is the outflow of Llyn Padarn near Llanberis, and it flows out in a generally northwest direction. Between the outflow and the village of Llanrug it is known as the Afon Rhythallt, changing its name just after the village. Its mouth is in the town of Caernarfon, forming a natural harbour as it flows out into the Menai Strait. The Afon Nant Peris provides the main inflow into Llyn Peris which then drains into Llyn Padarn with the addition of the waters of the Afon Arddu which drains the northern slopes of Snowdon. The name of the Roman fort of Segontium, near Caernarfon, is based on the Latinised form of the name 'Seiont'. In the Brythonic language translates as 'strong place'. See also * Aber Afon Seiont - Site of Special Scientific Interest at mouth of river * List of rivers of Wales This is a list of rivers of Wales, organised geographi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brittonic Languages
The Brittonic languages (also Brythonic or British Celtic; ; ; and ) form one of the two branches of the Insular Celtic languages; the other is Goidelic. It comprises the extant languages Breton, Cornish, and Welsh. The name ''Brythonic'' was derived by Welsh Celticist John Rhys from the Welsh word , meaning Ancient Britons as opposed to an Anglo-Saxon or Gael. The Brittonic languages derive from the Common Brittonic language, spoken throughout Great Britain during the Iron Age and Roman period. In the 5th and 6th centuries emigrating Britons also took Brittonic speech to the continent, most significantly in Brittany and Britonia. During the next few centuries, in Celtic language decline in England, much of Britain the language was replaced by Old English and Scottish Gaelic, with the remaining Common Brittonic language splitting into regional dialects, eventually evolving into Welsh, Cornish, Breton, Cumbric, and probably Pictish. Welsh and Breton continue to be s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallia Belgica
Gallia Belgica ("Belgic Gaul") was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and Germany. Before the Roman province came into existence in about 50 BC, the region was conquered by Julius Caesar during his Gallic Wars. His report, the ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'', described Belgic Gaul as one of the three parts of Gaul (Tres Galliæ), the other two being Gallia Aquitania and Gallia Lugdunensis. Belgica stretched from the Marne River, Marne and Seine rivers, which Caesar described as a cultural boundary between the Belgae and the Celts, Celtic Gauls. In the north and east it stretched all the way to the Rhine. The official Roman province of this name was later created by emperor Augustus in 22 BC, and named after the Belgae, as the largest tribal confederation in the area. However, it also included the territories of the T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; ; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through cursus honorum, the customary succession of offices under the reigns of Marcus Aurelius and Commodus. Severus was the final contender to seize power after the death of the emperor Pertinax in 193 during the Year of the Five Emperors. After deposing and killing the incumbent emperor Didius Julianus, Severus fought his rival claimants, the Roman generals Pescennius Niger and Clodius Albinus. Niger was defeated in 194 at the Battle of Issus (194), Battle of Issus in Cilicia (Roman province), Cilicia. Later that year Severus waged a short punitive campaign beyond the eastern frontier, annexing the Osroene, Kingdom of Osroene as a new province. Severus defeated Albinus three years later at the Battle of Lugdunum in Roman Gaul, Gaul. Following the consolidation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chester
Chester is a cathedral city in Cheshire, England, on the River Dee, Wales, River Dee, close to the England–Wales border. With a built-up area population of 92,760 in 2021, it is the most populous settlement in the borough of Cheshire West and Chester. It is also the historic county town of Cheshire and the List of Cheshire settlements by population, second-largest settlement in Cheshire after Warrington. Chester was founded in 79 AD as a "Castra, castrum" or Roman Empire, Roman fort with the name Deva Victrix during the reign of Emperor Vespasian. One of the main army camps in Roman Britain, Deva later became a major civilian settlement. In 689, Æthelred of Mercia, King Æthelred of Mercia founded the Minster Church of West Mercia, which later became Chester's first cathedral, and the Angles (tribe), Angles extended and strengthened the walls to protect the city against the Danes (Germanic tribe), Danes. Chester was one of the last cities in England to Norman conquest of Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Invasions Of Wales
Invasions of the British Isles have occurred several times throughout their history. The British Isles have been subject to several waves of invasion and settlement since humans began inhabiting the region approximately 900,000 years ago during the Paleolithic. Notable invasions of the British Isles including the Roman conquest of Britain, Viking expansion, the Norman Conquest, the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland and the Glorious Revolution. Prehistory and antiquity Neolithic transition By around 12,000 BC, during the Mesolithic, Western Hunter Gatherers had started to repopulate Britain at the end of the Younger Dryas. A study by Brace et al. (2019) found evidence of a substantial replacement of this population ca. 4,000 BC, with the introduction of agriculture by Early European Farmers from continental Europe. According to the authors, "the transition to farming in Britain occurred with little introgression from resident foragers – either during initial colonization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqueduct (Roman)
The Romans constructed aqueducts throughout their Republic and later Empire, to bring water from outside sources into cities and towns. Aqueduct water supplied public baths, latrines, fountains, and private households; it also supported mining operations, milling, farms, and gardens. Aqueducts moved water through gravity alone, along a slight overall downward gradient within conduits of stone, brick, concrete or lead; the steeper the gradient, the faster the flow. Most conduits were buried beneath the ground and followed the contours of the terrain; obstructing peaks were circumvented or, less often, tunneled through. Where valleys or lowlands intervened, the conduit was carried on bridgework, or its contents fed into high-pressure lead, ceramic, or stone pipes and siphoned across. Most aqueduct systems included sedimentation tanks, which helped to reduce any water-borne debris. Sluices, ''castella aquae'' (distribution tanks) and stopcocks regulated the supply to individu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |