Carabane on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Carabane, also known as Karabane, is an island and a village located in the extreme south-west of

 A recent geological formation, Brosselard-Faidherbe (1982), p. 10. Carabane consists of a
A recent geological formation, Brosselard-Faidherbe (1982), p. 10. Carabane consists of a  The
The
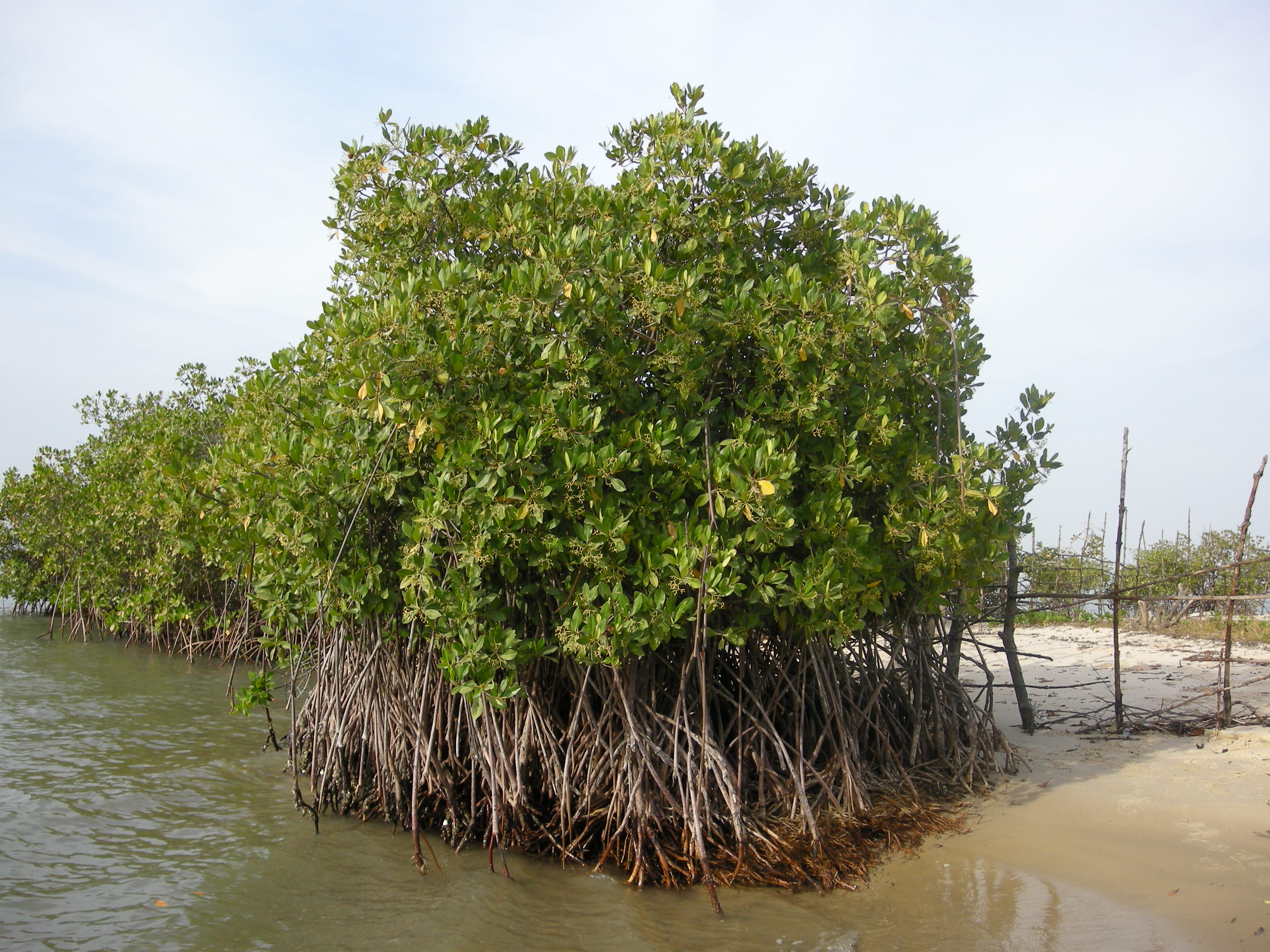 At one time, the island was considered an arid location, where coconuts were the only useful plants likely to flourish and vegetables were difficult to produce. In what has become a tropical climate, vegetation is more abundant than in the north of the country, especially during the wet season. Anxious to attract the attention of the French colonial administration which he judged insufficiently involved in the development of Casamance, administrator Emmanuel Bertrand-Bocandé submitted a report which documented in great detail the plant species then present on the island. Although this report was written in 1849, the information it contains has remained valuable even into the 21st century.
Most of Carabane is covered in mangroves, forming an impassable jungle that can only be crossed in constructed passages. Mangroves are among the few species capable of adapting to the highly saline environment, where the quantity of oxygen in the soil is low. In recent decades there has been concern that the mangroves are less prevalent. There are various reasons for the degradation, including
At one time, the island was considered an arid location, where coconuts were the only useful plants likely to flourish and vegetables were difficult to produce. In what has become a tropical climate, vegetation is more abundant than in the north of the country, especially during the wet season. Anxious to attract the attention of the French colonial administration which he judged insufficiently involved in the development of Casamance, administrator Emmanuel Bertrand-Bocandé submitted a report which documented in great detail the plant species then present on the island. Although this report was written in 1849, the information it contains has remained valuable even into the 21st century.
Most of Carabane is covered in mangroves, forming an impassable jungle that can only be crossed in constructed passages. Mangroves are among the few species capable of adapting to the highly saline environment, where the quantity of oxygen in the soil is low. In recent decades there has been concern that the mangroves are less prevalent. There are various reasons for the degradation, including  Tourists are not as attracted to the island for its mangroves as for the coconut trees which line its beaches, as featured on many of Carabane's postcards. Ropitault (November–December 2007), pp.23–24. These palm trees are a valued resource on the island.
While not as plentiful as in other parts of Basse Casamance such as Mlomp, trees of the ''
Tourists are not as attracted to the island for its mangroves as for the coconut trees which line its beaches, as featured on many of Carabane's postcards. Ropitault (November–December 2007), pp.23–24. These palm trees are a valued resource on the island.
While not as plentiful as in other parts of Basse Casamance such as Mlomp, trees of the ''
 The sandbar of Carabane has very few mammals other than pets, although the French first noted the presence of monkeys in 1835. In 1870, other settlers noted with disgust that the natives often ate monkeys and dogs. In the early 21st century,
The sandbar of Carabane has very few mammals other than pets, although the French first noted the presence of monkeys in 1835. In 1870, other settlers noted with disgust that the natives often ate monkeys and dogs. In the early 21st century,
 When Jean Baudin fell into disgrace due to a serious incident involving an English ship, he was replaced as Resident in October 1849 by Emmanuel Bertrand-Bocandé. This multilingual, enterprising businessman and
When Jean Baudin fell into disgrace due to a serious incident involving an English ship, he was replaced as Resident in October 1849 by Emmanuel Bertrand-Bocandé. This multilingual, enterprising businessman and 
 Meanwhile, the inhabitants of the new French territory did not recognize the authority of the treaties imposed upon them. For this reason, rice farmers in Carabane experienced lootings and abductions by the Karoninka people. Troops led by Émile Pinet-Laprade attacked the Karoninka villages in March 1860, forcing them to submission. A period of calm ensued. While the Mandinka Muslims continued, illegally, to practice slavery and trade, non-Muslim villages tended to come together, accepting the Resident of Carabane as the arbitrator of their disagreements.
In 1869, Carabane became autonomous, but it merged with Sédhiou in 1886. Its garrison of a dozen men was regularly stricken with tropical diseases such as
Meanwhile, the inhabitants of the new French territory did not recognize the authority of the treaties imposed upon them. For this reason, rice farmers in Carabane experienced lootings and abductions by the Karoninka people. Troops led by Émile Pinet-Laprade attacked the Karoninka villages in March 1860, forcing them to submission. A period of calm ensued. While the Mandinka Muslims continued, illegally, to practice slavery and trade, non-Muslim villages tended to come together, accepting the Resident of Carabane as the arbitrator of their disagreements.
In 1869, Carabane became autonomous, but it merged with Sédhiou in 1886. Its garrison of a dozen men was regularly stricken with tropical diseases such as
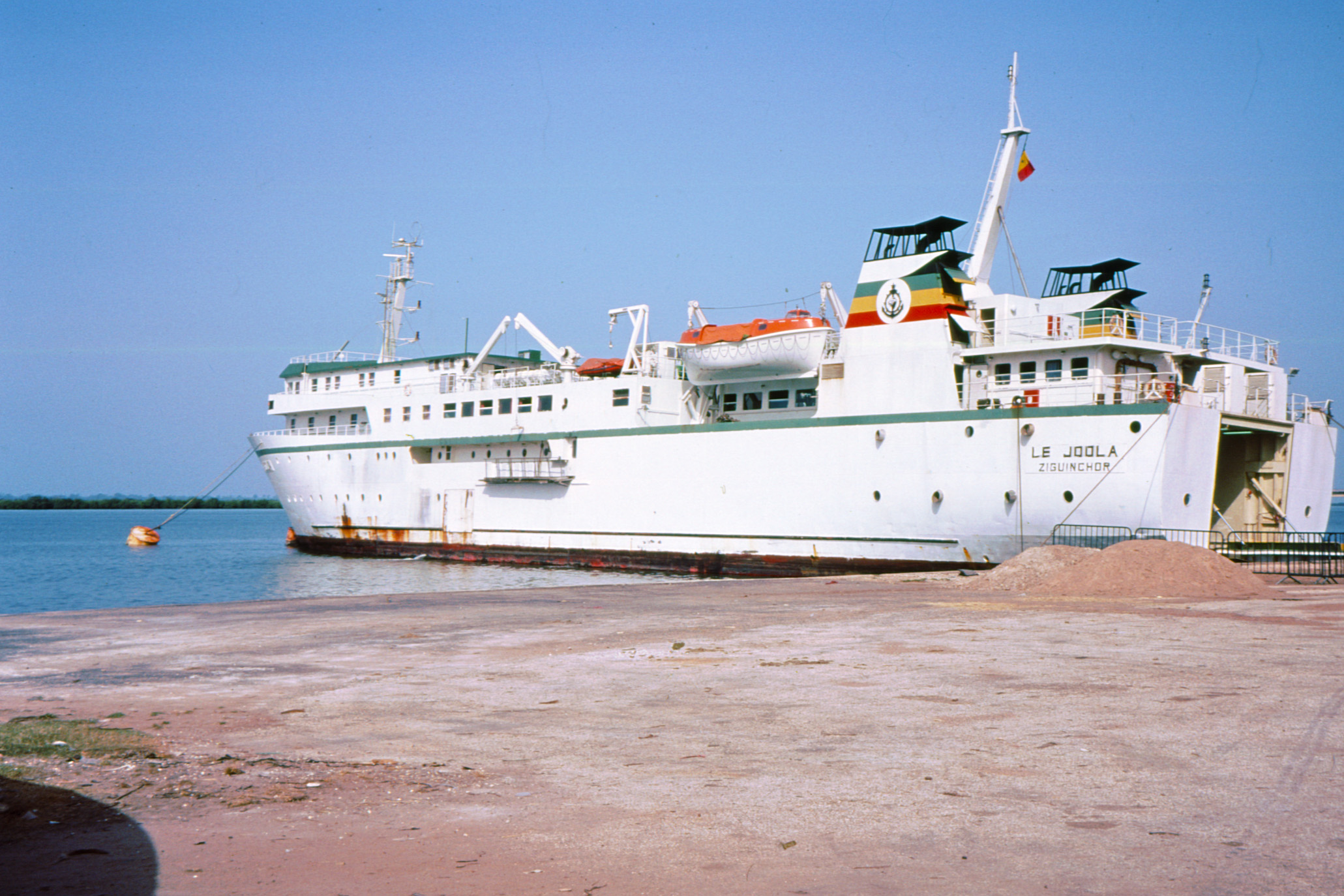 Senegal's independence was declared on August 20, 1960, and after the dissolution of the short-lived
Senegal's independence was declared on August 20, 1960, and after the dissolution of the short-lived
 Formerly an administrative district in its own right,Between 1939 and 1944, the colonial authorities of the AOF were Vichyites and anti- Gaullists, unlike those of the AEF, especially because of the
Formerly an administrative district in its own right,Between 1939 and 1944, the colonial authorities of the AOF were Vichyites and anti- Gaullists, unlike those of the AEF, especially because of the
 Founded in 1892, the Carabane school was one of the first in the region. It began as an all-boys school, but in 1898, three nuns belonging to the indigenous congregation of the Daughters of the Holy Heart of Mary began teaching classes for girls. Soon, there were 60 students. Benoist (2008), p. 253. A school infrastructure description in the region in 1900 reveals that the boys' school in Carabane was open from December to August each year, and that holidays ran from September to November, when parents needed their children in the fields to help cultivate rice. In 1903, when Carabane lost its status as capital, the school was instructing 63 boys and 102 girls. In 1914, it had only 56 boys and 26 girls, a situation similar to that in Bignona.
Founded in 1892, the Carabane school was one of the first in the region. It began as an all-boys school, but in 1898, three nuns belonging to the indigenous congregation of the Daughters of the Holy Heart of Mary began teaching classes for girls. Soon, there were 60 students. Benoist (2008), p. 253. A school infrastructure description in the region in 1900 reveals that the boys' school in Carabane was open from December to August each year, and that holidays ran from September to November, when parents needed their children in the fields to help cultivate rice. In 1903, when Carabane lost its status as capital, the school was instructing 63 boys and 102 girls. In 1914, it had only 56 boys and 26 girls, a situation similar to that in Bignona.
 Carabane has a new primary school, École François Mendy, inaugurated on January 21, 2006, hosting six classes. The literacy rate is approximately 90%. Students may continue their studies at the middle school in Elinkine, the Aline Sitoe Diatta High School in Oussouye, and then a university in either Dakar or Ziguinchor. Carabane's kindergarten is located in a community house, called "House of Women and Children", founded in 1988 under the auspices of Caritas Ziguinchor.
In 1895, the government established a medical post in Carabane, but it closed the following year. In 1898, the Daughters of the Holy Heart of Mary opened a clinic at the same time as the girls' school.
As of 2010, the village has a health facility which is connected to that of Oussouye and Ziguinchor. It provides vaccinations,
Carabane has a new primary school, École François Mendy, inaugurated on January 21, 2006, hosting six classes. The literacy rate is approximately 90%. Students may continue their studies at the middle school in Elinkine, the Aline Sitoe Diatta High School in Oussouye, and then a university in either Dakar or Ziguinchor. Carabane's kindergarten is located in a community house, called "House of Women and Children", founded in 1988 under the auspices of Caritas Ziguinchor.
In 1895, the government established a medical post in Carabane, but it closed the following year. In 1898, the Daughters of the Holy Heart of Mary opened a clinic at the same time as the girls' school.
As of 2010, the village has a health facility which is connected to that of Oussouye and Ziguinchor. It provides vaccinations,
 While a direct route by sea has not been available since the sinking of the ''Joola'', the traveller from Dakar may use various other means of transportation in order to arrive in Basse Casamance. Some national roads connect to Ziguinchor, down the N1 to Kaolack. The N4 and N5 roads cross the Gambia (both the country and the river), the former running through Nioro du Rip to
While a direct route by sea has not been available since the sinking of the ''Joola'', the traveller from Dakar may use various other means of transportation in order to arrive in Basse Casamance. Some national roads connect to Ziguinchor, down the N1 to Kaolack. The N4 and N5 roads cross the Gambia (both the country and the river), the former running through Nioro du Rip to
Web.archive.org
/ref> Significant modifications to the MV ''Aline Sitoe Diatta'', which replaced the ''Wilis'' in March 2008, were considered to allow it to stop safely at the island, and the construction of a berth was announced. Souleymane Ndéné Ndiaye, who later became
 In Basse Casamance, the rice cycle structures the lives of the population and plays a central economic and religious role. The Jola, who constitute 80 to 90% of the population of Basse Casamance, practice a unique form of rice cultivation. Descriptions of the techniques used in the late 15th century, recorded by the first Portuguese
In Basse Casamance, the rice cycle structures the lives of the population and plays a central economic and religious role. The Jola, who constitute 80 to 90% of the population of Basse Casamance, practice a unique form of rice cultivation. Descriptions of the techniques used in the late 15th century, recorded by the first Portuguese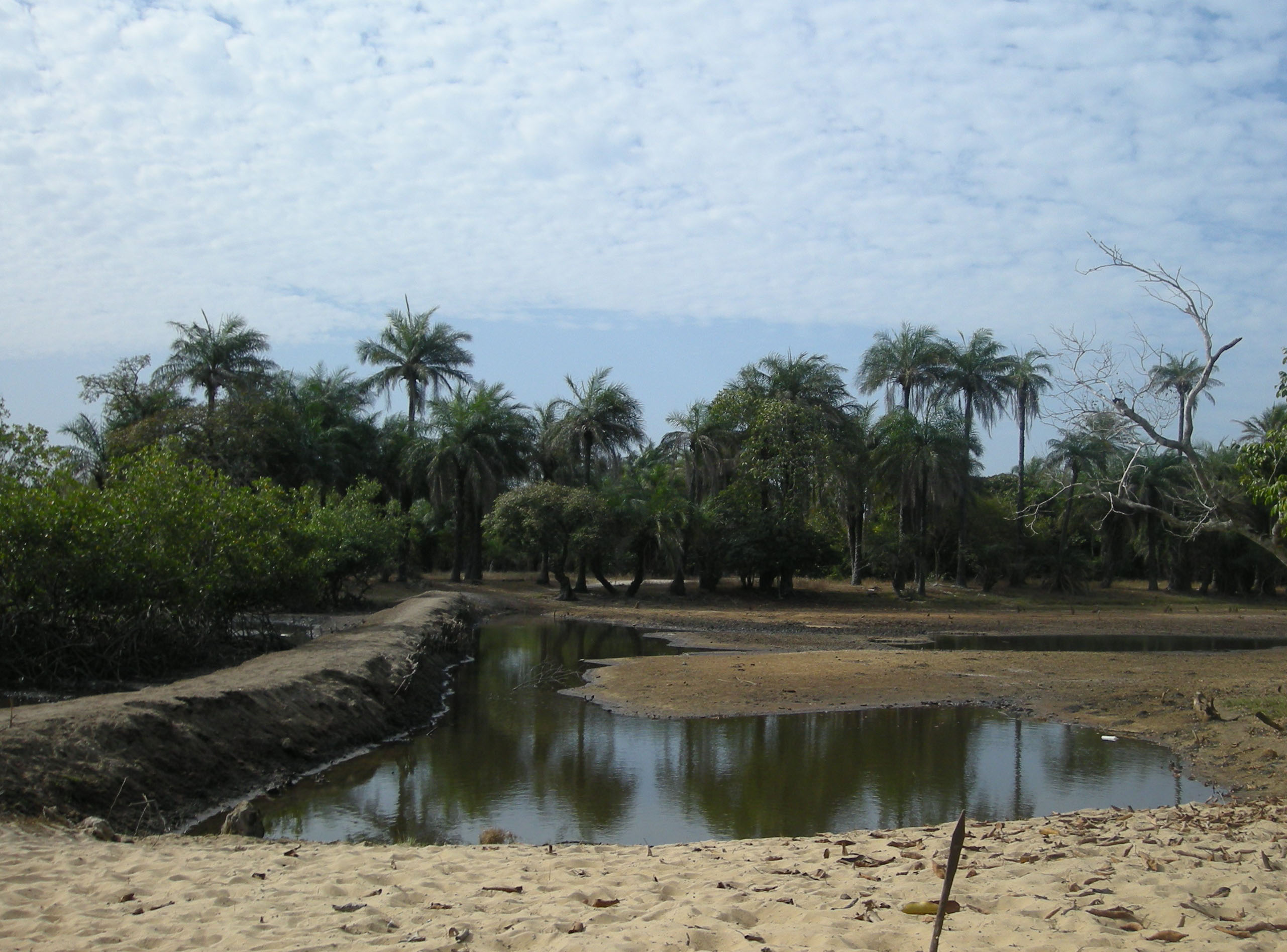  Although practised in Basse Casamance for centuries, rice cultivation has been threatened since the late 1960s. Productivity has declined because many workers have opted for life in the city, even though they continue to support their community. Foucher (2002), pp. 389–390. The drought of the 1970s and 1980s further aggravated the situation.
Although practised in Basse Casamance for centuries, rice cultivation has been threatened since the late 1960s. Productivity has declined because many workers have opted for life in the city, even though they continue to support their community. Foucher (2002), pp. 389–390. The drought of the 1970s and 1980s further aggravated the situation.
 Palm wine (called or in the Jola language) is an alcoholic drink derived from the natural fermentation of palm sap, so is not strictly a wine, which is produced by the fermentation of
Palm wine (called or in the Jola language) is an alcoholic drink derived from the natural fermentation of palm sap, so is not strictly a wine, which is produced by the fermentation of
 Crustaceans, such as sand fiddler crabs and shrimp, among the mangroves also occupy a significant place in the local economy. While a large number of shrimp species inhabit the
Crustaceans, such as sand fiddler crabs and shrimp, among the mangroves also occupy a significant place in the local economy. While a large number of shrimp species inhabit the
 The Republic of Senegal placed an emphasis on
The Republic of Senegal placed an emphasis on
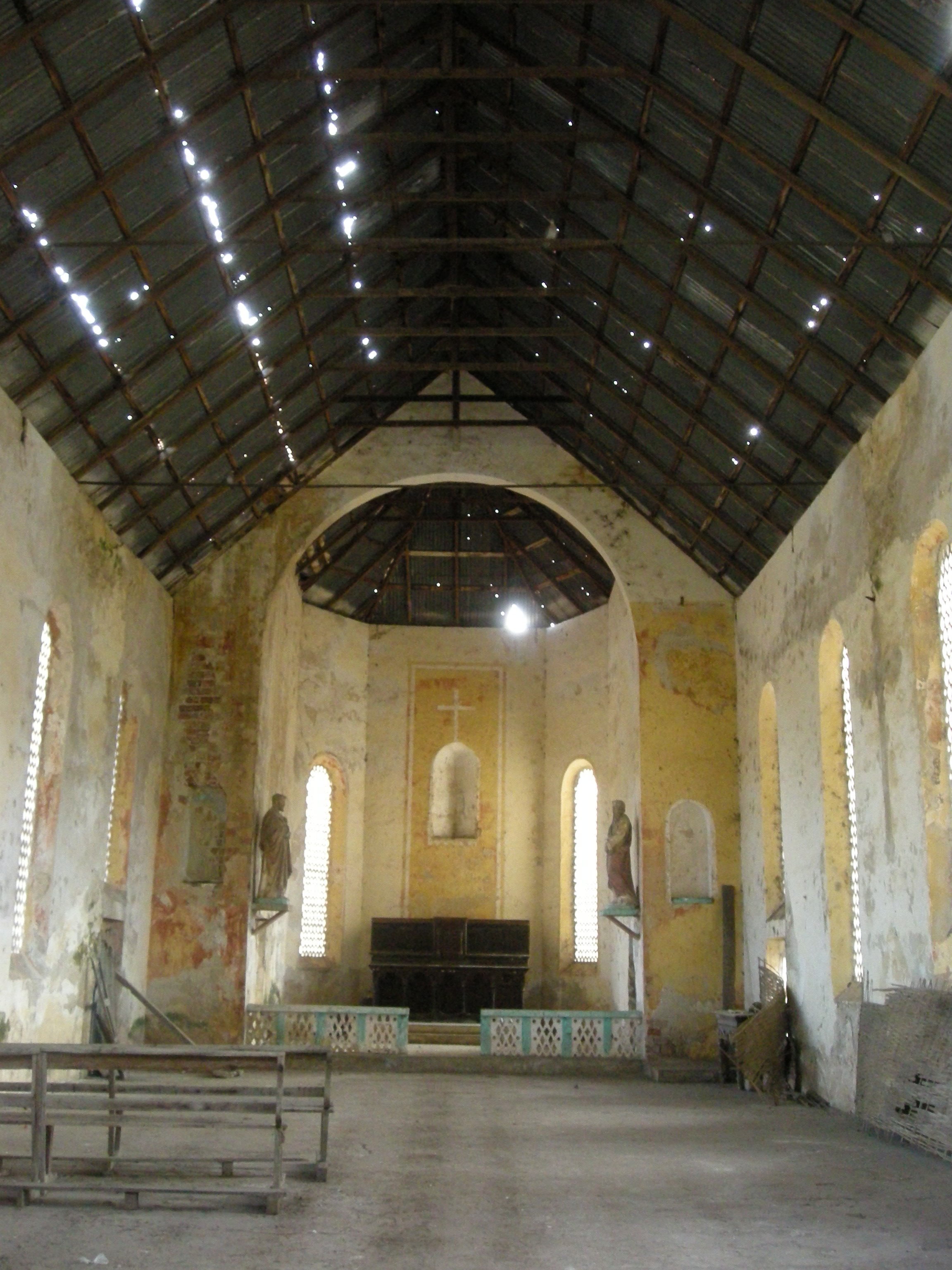


 Carabane has many historic sites, such as the Catholic mission house built in 1880 which has since been turned into a hotel, a
Carabane has many historic sites, such as the Catholic mission house built in 1880 which has since been turned into a hotel, a
Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
, in the mouth of the Casamance River. This relatively recent geological formation consists of a shoal
In oceanography, geomorphology, and Earth science, geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank (geography), bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material, and rises from the bed of a body ...
and alluvium
Alluvium (, ) is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is ...
to which soil is added by accumulation in the branches and roots of the mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have particular adaptations to take in extra oxygen a ...
trees which cover most of the island. Along with the rest of Ziguinchor Region, Carabane has a tropical climate, cycling between a dry season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The t ...
and a wet season
The wet season (sometimes called the rainy season or monsoon season) is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. Generally, the season lasts at least one month. The term ''green season'' is also sometimes used a ...
. The island was once considered an arid location where no useful plants were likely to grow, but it now supports several types of fruit tree, the most common of which are mango
A mango is an edible stone fruit produced by the tropical tree '' Mangifera indica''. It originated from the region between northwestern Myanmar, Bangladesh, and northeastern India. ''M. indica'' has been cultivated in South and Southeast As ...
s and oranges. Although the nearby Basse Casamance National Park and Kalissaye Avifaunal Reserve have been closed for years because of the Casamance Conflict
The Casamance conflict is an ongoing low-level conflict that has been waged between the Politics of Senegal, Government of Senegal and the Movement of Democratic Forces of Casamance (MFDC) since 1982. On May 1, 2014, the leader of the MFDC Suing f ...
, Carabane has continued to attract ornithologists interested in its wide variety of birds. Various species of fish are plentiful around the island, but there are very few mammals.
The earliest known inhabitants of the island were the Jola, the ethnic group which is still the most populous on the island. The Portuguese were active in the region from the 16th century onwards; however, they did not linger on "Mosquito Island", the mosquitoes and black flies convincing them to establish their trading post in the town of Ziguinchor
Ziguinchor (; ; ) is the capital of the Ziguinchor Region, and the chief town of the Casamance area of Senegal, lying at the mouth of the Casamance River. It has a population of 214,874 (2023 census). It is the eighth largest city of Senegal ...
instead in 1645. On January 22, 1836, the island was ceded to France by the village leader of Kagnout
Kagnout (also called Cagnout or Cagnut) is a village in Casamance, Senegal. It is located near the left bank of the estuary of the Casamance River. It is part of the rural community of Mlomp, in the district of Loudia Ouoloff, the department of Ous ...
in return for an annual payment of 196 francs. A series of treaties between the French and the leaders of the local peoples ensued; however, the inhabitants of Carabane did not recognize the authority of the treaties imposed upon them, resulting in lootings and abductions among French rice farmers by the Karoninka people. In 1869, Carabane became autonomous, but it merged with Sédhiou in 1886. Since , the population of the island has gradually declined for a variety of reasons including periods of drought, the Casamance Conflict and, more recently, the sinking of the ferry '' Joola'' in 2002. Much of the village's ability to trade and receive tourists was lost until 2014, when MV ''Aline Sitoe Diatta'' resumed ferry services to the island.
Although Carabane was once a regional capital, the village has since become so politically isolated from the rest of the country that it no longer fits into any category of the administrative structure decreed by the Senegalese government. The Jola account for the majority of the island's population and Jola society has no formal hierarchy. The indigenous population was originally animist
Animism (from meaning 'breath, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct spiritual essence. Animism perceives all things—animals, plants, rocks, rivers, weather systems, human handiwork, and in ...
, but although the sacred groves and fetishes survive as cultural icons of Casamance, the monotheistic
Monotheism is the belief that one God is the only, or at least the dominant deity.F. L. Cross, Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. A ...
belief systems of Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
and Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
have become the most widely held in Carabane. The literacy rate is approximately 90%. Students attend a primary school on the island, but must move at least as far as Elinkine
Elinkine (also called Elinlin or Elinkinde) is a town in Casamance, Senegal, located at the mouth of the Casamance River, from Oussouye.
History
A treaty between France and the leaders of Kagnout took place in Elinkine on March 25, 1851, resu ...
to continue their studies.
The testimonies of explorers and colonial administrators demonstrate that Carabane has participated in rice cultivation, fishery, trade, and palm wine
Palm wine, known by several #Names, local names, is an alcoholic beverage created from the sap of various species of palm trees such as the Borassus, palmyra, date palms, and coconut palms. It is known by various names in different regions and ...
production for a long time. The rice cycle plays a central economic and religious role in the lives of the population. Palm oil
Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil derived from the mesocarp (reddish pulp) of the fruit of oil palms. The oil is used in food manufacturing, in beauty products, and as biofuel. Palm oil accounted for about 36% of global oils produced from o ...
and palm wine are very popular and traditional in the area. The fishery has long been dominated by artisan fishing
Artisanal, subsistence, or traditional fishing consists of various small-scale, low-technology, fishing practices undertaken by individual fishermen (as opposed to commercial fishing). Many of these households are of coastal or island ethnic g ...
, which supplies the daily needs of the island's population; however, broader economic possibilities have been exploited since the early 20th century. Although there have been attempts to cultivate a tourism industry on the island, the inhabitants have been reluctant to participate. Carabane was added to the list of historic sites and monuments of Senegal in 2003.
Toponymy
Theetymology
Etymology ( ) is the study of the origin and evolution of words—including their constituent units of sound and meaning—across time. In the 21st century a subfield within linguistics, etymology has become a more rigorously scientific study. ...
of Carabane remains unclear. It could be connected to the Wolof word ''karabané'', which means "who speaks a lot", or possibly the Portuguese words ''casa'' and ''acaba'', which mean "house" and "finish", respectively. According to this hypothesis, the name means the place "where the houses are finished", a possible allusion to the fact that this village was the first French capital in Basse Casamance. According to other sources, the name comes from ''karam akam'', which means "the other side of the river". These uncertainties are augmented by the instability of the spelling: Karabane with an initial K suggests a Jola or Wolof origin, while Carabane with a C would suggest a Latin derivation, most probably through Portuguese or French.More rarely, one may find the spelling ''Karaban'' (notably in English and German sources) or ''Karabanne'' (particularly in Spanish and Portuguese sources).

Geography
Location
With a total area of , Carabane is the last major island in the mouth of the Casamance River in south-west Senegal. It is situated 12° 32' N latitude and 16° 43' W longitude and is, by way of Elinkine, nearly away fromZiguinchor
Ziguinchor (; ; ) is the capital of the Ziguinchor Region, and the chief town of the Casamance area of Senegal, lying at the mouth of the Casamance River. It has a population of 214,874 (2023 census). It is the eighth largest city of Senegal ...
, the capital of the region of the same name, and a little over from Dakar, the country's capital.
"''Il faut s'armer de patience pour rejoindre l'île de Carabane''" is a common French phrase which means "One must have patience to reach the island of Carabane". While this adage continues to hold true, it was even more appropriate in the 19th century when, according to one traveller, a 26-hour boat trip from Rufisque
Rufisque (; Wolof: Tëngeéj) is a city in the Dakar region of western Senegal, at the base of the Cap-Vert Peninsula east of Dakar, the capital. It has a population of 295,459 (2023 census).
(near Dakar
Dakar ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Senegal, largest city of Senegal. The Departments of Senegal, department of Dakar has a population of 1,278,469, and the population of the Dakar metropolitan area was at 4.0 mill ...
) to Carabane was deemed fairly short, and was credited to a favourable wind.
Despite the seemingly close proximity to its neighbouring communities, a motorized pirogue
A pirogue ( or ), also called a piragua or piraga, is any of various small boats, particularly dugouts and canoes. The word is French and is derived from Spanish ''piragua'' , which comes from the Carib '.
Description
The term 'pirogue' ...
trip to Carabane from Elinkine, the nearest village, takes about thirty minutes; the trip once took an hour and a half by canoe. Carabane may also be accessed by a two- or three-hour boat trip from Ziguinchor. Travelling from Cap Skirring via Cachouane is also possible, but as a detailed map of the region would make clear, the channels of salt water are not easily navigated.
Geology
shoal
In oceanography, geomorphology, and Earth science, geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank (geography), bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material, and rises from the bed of a body ...
and alluvium
Alluvium (, ) is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is ...
. The alluvium has developed because of the saltwater streams that cut across the shoal. As pointed out by early French observers, soils in the region are generally composed of sand and clay, differing in mixture and layer according to natural and human factors. However, Carabane seems to be composed entirely of sand. The lack of clay is the reason that architecture on the island employs straw wrapped around wooden frames more often than banco mud bricks. This type of architecture is also common in the villages of Mlomp
Mlomp is a rural community and village in the Ziguinchor Region of Senegal in the Casamance, situated approximately south-west of Ziguinchor.
As of 2000, it had a population of 7,628, rising to around 8,500 in 2006. Most inhabitants are of Diola ...
and Seleki.
In this flat and marshy area, the branches and roots of mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have particular adaptations to take in extra oxygen a ...
trees form dams where deposits of oyster shells naturally accumulate along with mud and plant detritus. These tangles help retain soil, a process which expands the island where the power of tidal race would normally have the opposite effect.
Rising just over , the southern portion of the island is partially flooded during the rainy season and totally submerged every few years. At low tide, mudflats are exposed so that boats with keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element of a watercraft, important for stability. On some sailboats, it may have a fluid dynamics, hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose as well. The keel laying, laying of the keel is often ...
s are forced to dock a considerable distance from the island. When arriving at Carabane, the ''Joola'' had to stop about north of the village in of water.
 The
The coastal erosion
Coastal erosion is the loss or displacement of land, or the long-term removal of sediment and rocks along the coastline due to the action of Wind wave, waves, Ocean current, currents, tides, wind-driven water, waterborne ice, or other impacts ...
and salinization affecting the west of Senegal are also a source of concern on the island; signs of erosion have been observed in Carabane since 1849. The house of the government representative on the island has burned down twice; each time it was rebuilt, the site of the building had to be moved further and further inland. The island's erosion is evident when one considers that the original location of the house eventually became flooded, even at low tide. During the dry season the river has a tide-dominated delta, with tidewater reaching upstream, while it is being concentrated 50% by evaporation.
Using wells, freshwater is available at a reasonable depth for irrigation and domestic purposes. Until the installation of a pump in 2006, however, drinking water had to be sent by boat from Elinkine.
Climate
The tropical climate of Basse Casamance cycles between adry season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The t ...
and a wet season
The wet season (sometimes called the rainy season or monsoon season) is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. Generally, the season lasts at least one month. The term ''green season'' is also sometimes used a ...
, which usually starts in June and ends in October. Because of the proximity to the ocean, the humidity of the air remains above 40% and contributes to the abundance of vegetation. With the trade wind
The trade winds or easterlies are permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere, ...
s from the Azores High
The Azores High also known as North Atlantic (Subtropical) High/Anticyclone or the Bermuda- High, is a large subtropical semi-permanent centre of high atmospheric pressure typically found south of the Azores in the Atlantic Ocean, at the Horse ...
, the island enjoys a pleasant climate year-round. In the north to north-east, these winds are cool and always wet. Their presence is appreciated by kitesurfers. Agricultural activities, including rice cultivation, depend entirely on rainfall. "''Wah uŋejutumu, emit elaatut''" is a Jola proverb which means "If a project will not be completed, it will be because the rain did not fall." The invocation of fetishes when there is no rain is part of traditional animist rituals. In recent decades, there has been a general decline in rainfall, which threatens rice production, increases soil salinity
Soil salinity is the salt (chemistry), salt content in the soil; the process of increasing the salt content is known as salinization (also called salination in American and British English spelling differences, American English). Salts occur nat ...
, and contributes to the degradation of the mangroves. In May and June, air temperature is around . In January and February, the coldest months, it is around . Temperatures of below are quite rare. In September, the temperature of surface seawater is .
Flora
crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s and the unregulated exploitation of wood. Efforts have been made to safeguard the mangroves and to educate children about their importance.
Bombax
''Bombax'' is a genus of mainly tropical trees in the mallow family. They are native to western Africa, the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian ...
'' genus and Malvaceae
Malvaceae (), or the mallows, is a family of flowering plants estimated to contain 244 genera with 4225 known species. Well-known members of economic importance include Theobroma cacao, cacao, Cola (plant), cola, cotton, okra, Hibiscus sabdariffa, ...
family (all known as 'kapok' in English) are nonetheless present. Their grey wood is very light and easy to work, for which reasons it is used to construct many items, ranging from doors to dugouts. Jola canoes, which range from in length, are carved by adze
An adze () or adz is an ancient and versatile cutting tool similar to an axe but with the cutting edge perpendicular to the handle rather than parallel. Adzes have been used since the Stone Age. They are used for smoothing or carving wood in ha ...
s entirely out of one tree each, unlike the traditional Senegalese pirogue.
As for fruit trees, mango
A mango is an edible stone fruit produced by the tropical tree '' Mangifera indica''. It originated from the region between northwestern Myanmar, Bangladesh, and northeastern India. ''M. indica'' has been cultivated in South and Southeast As ...
s and oranges are the most populous. Prickly pears, flamboyants, and colourful bougainvillea
''Bougainvillea'' ( , ) is a genus of thorny ornamental vines, bushes, and trees belonging to the family, Nyctaginaceae. They are native to Brazil, Bolivia, Paraguay, Peru, and Argentina. There are between 4 and 22 species in the genus. The i ...
s brighten the scenery of hotels and camps on the island. Various organizations have contributed to the deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
of the island.
Fauna
The wide variety of birds in Basse Casamance was noted by early explorers. While Basse Casamance National Park and Kalissaye Avifaunal Reserve have not been open for years due to theCasamance Conflict
The Casamance conflict is an ongoing low-level conflict that has been waged between the Politics of Senegal, Government of Senegal and the Movement of Democratic Forces of Casamance (MFDC) since 1982. On May 1, 2014, the leader of the MFDC Suing f ...
, Carabane has been found to be very conducive to ornithological observation. A study in 1998 discovered the following species on the island: African darter
The African darter (''Anhinga rufa''), sometimes called the snakebird, is a water bird of sub-Saharan Africa and Iraq.
Taxonomy
The African darter is a member of the darter family, Anhingidae, and is closely related to Anhinga, American (''Anhin ...
(''Anhinga rufa''), Goliath heron (''Ardea goliath''), palm-nut vulture (''Gypohierax angolensis''), black-tailed godwit
The black-tailed godwit (''Limosa limosa'') is a large, long-legged, long-billed shorebird first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758. It is a member of the godwit genus, '' Limosa''. There are four subspecies, all with orange head, neck and ches ...
(''Limosa limosa''), whimbrel (''Numenius phaeopus''), Eurasian curlew
The Eurasian curlew or common curlew (''Numenius arquata'') is a very large wader in the family Scolopacidae. It is one of the most widespread of the curlews, breeding across temperate Europe and Asia. In Europe, this species is often referred ...
(''Numenius arquata''), Caspian tern
The Caspian tern (''Hydroprogne caspia'') is a species of tern, with a subcosmopolitan but scattered distribution. Despite its extensive range, it is monotypic of its genus, and has no accepted subspecies. The genus name is from Ancient Greek '' ...
(''Sterna caspia''), blue-spotted wood-dove (''Turtur afer''), red-eyed dove (''Streptopelia semitorquata''), white-rumped swift (''Apus caffer''), woodland kingfisher
The woodland kingfisher (''Halcyon senegalensis'') is a tree kingfisher that is widely distributed in Africa south of the Sahara.
Taxonomy
The Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus included the woodland kingfisher with the binomial nomenclature, ...
(''Halcyon senegalensis''), grey-backed camaroptera (''Camaroptera brachyura''), red-bellied paradise-flycatcher (''Terpsiphone rufiventer''), pied crow
The pied crow (''Corvus albus'') is a widely distributed African bird species in the crow genus of the family Corvidae.
Structurally, the pied crow is better thought of as a small crow-sized raven, especially as it can hybridise with the Somali ...
(''Corvus albus''), black-rumped waxbill (''Estrilda troglodytes'') and yellow-fronted canary (''Serinus mozambicus'').Barlow ''et al''. (1997). Page 3 gives an overview of the birds typical of the coastal and riverine habitats, and the ranges of the listed birds are found under their species' accounts.
Fish are plentiful in the waters surrounding the island, where one may encounter trevallies (''Carangidae''), Giant African threadfins (''Polydactylus quadrifilis''), great barracuda
''Sphyraena barracuda'', commonly known as the great barracuda, is a species of barracuda, a genus of 27 species of large ray-finned fish found in subtropical oceans worldwide. In its natural habitat, the great barracuda is an apex predator.
D ...
s (''Sphyraena barracuda''), or African red snappers (''Lutjanus agennes''). The mangroves are home to many crustaceans such as southern pink shrimp (''Farfantepenaeus notialis''), sand fiddler crabs (''Uca pugilator''), and molluscs
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
. The shellfish population consists mostly of mangrove oyster Mangrove oyster is a common name for several oysters that live on mangrove roots and may refer to:
*'' Crassostrea rhizophorae''
*'' Crassostrea tulipa''
*'
{{Animal common name
Mollusc common names ...
s (''Crassostrea gasar''), which cling to uncovered mangrove roots at low tide. The red-headed agama and monitor lizard
Monitor lizards are lizards in the genus ''Varanus,'' the only extant genus in the family Varanidae. They are native to Africa, Asia, and Oceania, and West African Nile monitor, one species is also found in south America as an invasive species. A ...
make up the reptilian population of the island.
 The sandbar of Carabane has very few mammals other than pets, although the French first noted the presence of monkeys in 1835. In 1870, other settlers noted with disgust that the natives often ate monkeys and dogs. In the early 21st century,
The sandbar of Carabane has very few mammals other than pets, although the French first noted the presence of monkeys in 1835. In 1870, other settlers noted with disgust that the natives often ate monkeys and dogs. In the early 21st century, bottlenose dolphin
The bottlenose dolphin is a toothed whale in the genus ''Tursiops''. They are common, cosmopolitan members of the family Delphinidae, the family of oceanic dolphins. Molecular studies show the genus contains three species: the common bot ...
s (''Tursiops truncatus'') are commonly sighted off the island. The lack of tourism because of the civil unrest has benefited biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
. In this way, the nearby Basse Casamance National Park, which has been closed for years, has seen a remarkable return of Nile crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed in sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the eastern, southern, and ce ...
s (''Crocodylus niloticus
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed in sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the eastern, southern, and ce ...
''), Senegalese manatees ('' Trichechus senegalensis''), and breeding birds.
On an island called ''Ilha dos Mosquitos'' (Portuguese for "Mosquito Island"), the natives and their visitors continue to protect themselves with mosquito net
A mosquito net is a type of meshed curtain or cloth that is circumferentially draped over a bed or a sleeping area to offer the sleeper barrier protection against bites and stings from mosquitos, flies, and other pest insects, and thus a ...
s and Shea butter
Shea butter ( , , or ; ) is a fat (triglyceride; mainly oleic acid and stearic acid) extracted from the nut of the African shea tree ('' Vitellaria paradoxa''). It is ivory in color when raw and commonly dyed yellow with borututu root or ...
. They must also protect themselves from other, smaller insects which are no less troublesome: black flies (''Simulium'').
History
First inhabitants
The traditions of the local peoples are unanimous in affirming that the oldest inhabitants of Casamance are the Bainuk people and that the left bank of the mouth of the river was first populated by the Jola. Portuguese sailors reached the west African coast in the 15th century, and in the 16th century, Portuguese traders became active in the Casamance region, mostly in search of wax,ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and Tooth, teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mamm ...
, and slaves
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
. They did not linger on "Mosquito Island", instead founding their first trading post
A trading post, trading station, or trading house, also known as a factory in European and colonial contexts, is an establishment or settlement where goods and services could be traded.
Typically a trading post allows people from one geogr ...
at Ziguinchor in 1645.
In the late 1820s, a mulatto
( , ) is a Race (human categorization), racial classification that refers to people of mixed Sub-Saharan African, African and Ethnic groups in Europe, European ancestry only. When speaking or writing about a singular woman in English, the ...
trader from Gorée
(; "Gorée Island"; ) is one of the 19 (i.e. districts) of the city of Dakar, Senegal. It is an island located at sea from the main harbour of Dakar (), famous as a destination for people interested in the Atlantic slave trade.
Its populatio ...
, Pierre Baudin, moved to Itou and began planting rice and producing lime by crushing the shells of mangrove oysters and cooking them in lime kiln
A lime kiln is a kiln used for the calcination of limestone (calcium carbonate) to produce the form of lime called ''quicklime'' (calcium oxide). The chemical equation for this reaction is: CaCO3 + heat → CaO + CO2
This reaction can tak ...
s. The French administration treated Baudin as their representative on the island and did not send others because few of the French wanted to live on the island. Being wet and marshy, Carabane had a reputation for its poor sanitation. The local economy was based mainly on weedy rice, which was sold in Ziguinchor or to the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
in The Gambia
The Gambia, officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. Geographically, The Gambia is the List of African countries by area, smallest country in continental Africa; it is surrounded by Senegal on all sides except for ...
. The Baudin family used slaves to produce the rice and, despite the declaration of its official abolition
Abolition refers to the act of putting an end to something by law, and may refer to:
*Abolitionism, abolition of slavery
*Capital punishment#Abolition of capital punishment, Abolition of the death penalty, also called capital punishment
*Abolitio ...
in the French colonial empire
The French colonial empire () comprised the overseas Colony, colonies, protectorates, and League of Nations mandate, mandate territories that came under French rule from the 16th century onward. A distinction is generally made between the "Firs ...
in 1848, slavery continued on the island until the early 20th century.
The colonial administration wanted to expand its influence around the river, particularly because the inhabitants of Gorée were threatened with losing part of their resources with the imminent demise of the slave trade Slave trade may refer to:
* History of slavery - overview of slavery
It may also refer to slave trades in specific countries, areas:
* Al-Andalus slave trade
* Atlantic slave trade
** Brazilian slave trade
** Bristol slave trade
** Danish sl ...
, and also because of their competition with Saint-Louis. On January 9, 1836, Lieutenant Malavois, who was in charge of Gorée, left for Casamance in search of a site for a trading post. The tip of Diogue, on the north shore, was first considered, but at the refusal of the Jola, it was the opposite bank which was eventually accepted.
French colonization
On January 22, 1836, the island was ceded to France by the village leader ofKagnout
Kagnout (also called Cagnout or Cagnut) is a village in Casamance, Senegal. It is located near the left bank of the estuary of the Casamance River. It is part of the rural community of Mlomp, in the district of Loudia Ouoloff, the department of Ous ...
at an annual cost of 196 francs. Still, another treaty made Sédhiou the primary trading post of Casamance, and the exploitation of Carabane was left for some time in the hands of the Baudin family, first Pierre then his brother Jean. Each successively took on the title of Resident. With this official but ambiguous title, they were permitted to continue their trading operation so long as they regularly reported to France.
 When Jean Baudin fell into disgrace due to a serious incident involving an English ship, he was replaced as Resident in October 1849 by Emmanuel Bertrand-Bocandé. This multilingual, enterprising businessman and
When Jean Baudin fell into disgrace due to a serious incident involving an English ship, he was replaced as Resident in October 1849 by Emmanuel Bertrand-Bocandé. This multilingual, enterprising businessman and entomologist
Entomology (from Ancient Greek ἔντομον (''éntomon''), meaning "insect", and -logy from λόγος (''lógos''), meaning "study") is the branch of zoology that focuses on insects. Those who study entomology are known as entomologists. In ...
from Nantes
Nantes (, ; ; or ; ) is a city in the Loire-Atlantique department of France on the Loire, from the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast. The city is the List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, sixth largest in France, with a pop ...
transformed "his" island, sparking a resurgence of commercial and political activity. In 1852, the population surpassed 1,000 inhabitants. A cadastral map
A cadastre or cadaster ( ) is a comprehensive recording of the real estate or real property's metes and bounds, metes-and-bounds of a country.Jo Henssen, ''Basic Principles of the Main Cadastral Systems in the World,'/ref>
Often it is represente ...
assigned tracts of to traders and contractors. Other tracts of were allotted for housing. Provisional concessions were granted to residents of Saint-Louis and Gorée. Other than settlers, the island was mainly inhabited by animist Jola farmers, whose practices were disconcerting to the settlers. Coexistence was not always easy. Christianity was practiced by the Europeans and some of the residents of Gorée, although the island did not yet have a church. Missionaries tried but were not permitted to settle on the island.
The construction of a wharf long allowed the berthing of larger vessels coming in from Casamance. A railed pier was built along the river in order to facilitate the transfer of goods. Carabane exported rice, but also cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
, considered to be of poor quality, Vallon (February–March 1862), p. 465. which was ginned in a factory built by Bertrand-Bocandé in 1840, owned first by Maurel & Prom and then by the Casamance Company. The factory also produced almond
The almond (''Prunus amygdalus'', Synonym (taxonomy)#Botany, syn. ''Prunus dulcis'') is a species of tree from the genus ''Prunus''. Along with the peach, it is classified in the subgenus ''Amygdalus'', distinguished from the other subgenera ...
s and crabwood (''Carapa procera'').
Bertrand-Bocandé became involved in local African politics during his time as Resident. When an intertribal conflict led to an armed raid of Carabane, he mediated the conflict. In 1850, the island's economic growth was disturbed because of an extensive livestock raid
RAID (; redundant array of inexpensive disks or redundant array of independent disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical Computer data storage, data storage components into one or more logical units for th ...
which precipitated further incidents the following year. In response to this conflict with the former owners of Carabane, the residents of Kagnout, Bertrand-Bocandé convinced the governor of Senegal to send a warship to Carabane to frighten off the raiders. This single ship failed to faze the island's opponents, therefore Bertrand-Bocandé requested a detachment of soldiers and several other ships from the governor. When these reinforcements arrived from Gorée, the conflict was successfully ended. A treaty was signed on March 25, establishing the sovereignty of France not only in Casamance, but also in Kagnout and Samatit
Samatit is a village in the rural community of Mlomp, Loudia Ouoloff, Oussouye, Ziguinchor, Casamance.
Geography
The nearest towns are Carabane, Kagnout, Loudia Diola, Elinkine
Elinkine (also called Elinlin or Elinkinde) is a town in Casama ...
. For his involvement in the conflict, Bertrand-Bocandé was accepted into the ''Légion d'honneur
The National Order of the Legion of Honour ( ), formerly the Imperial Order of the Legion of Honour (), is the highest and most prestigious French national order of merit, both military and Civil society, civil. Currently consisting of five cl ...
'' and was given a land concession. Bertrand-Bocandé left the island in 1857 for a leave of absence, but he abandoned his post as Resident in 1860. His tireless activity had a lasting effect on the island.

 Meanwhile, the inhabitants of the new French territory did not recognize the authority of the treaties imposed upon them. For this reason, rice farmers in Carabane experienced lootings and abductions by the Karoninka people. Troops led by Émile Pinet-Laprade attacked the Karoninka villages in March 1860, forcing them to submission. A period of calm ensued. While the Mandinka Muslims continued, illegally, to practice slavery and trade, non-Muslim villages tended to come together, accepting the Resident of Carabane as the arbitrator of their disagreements.
In 1869, Carabane became autonomous, but it merged with Sédhiou in 1886. Its garrison of a dozen men was regularly stricken with tropical diseases such as
Meanwhile, the inhabitants of the new French territory did not recognize the authority of the treaties imposed upon them. For this reason, rice farmers in Carabane experienced lootings and abductions by the Karoninka people. Troops led by Émile Pinet-Laprade attacked the Karoninka villages in March 1860, forcing them to submission. A period of calm ensued. While the Mandinka Muslims continued, illegally, to practice slavery and trade, non-Muslim villages tended to come together, accepting the Resident of Carabane as the arbitrator of their disagreements.
In 1869, Carabane became autonomous, but it merged with Sédhiou in 1886. Its garrison of a dozen men was regularly stricken with tropical diseases such as malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
. In 1877, 527 people were counted on the island, mostly Jola, but also some Wolofs, Muslims, and a few Manjacks from Portuguese Guinea
Portuguese Guinea (), called the Overseas Province of Guinea from 1951 until 1972 and then State of Guinea from 1972 until 1974, was a Portuguese overseas province in West Africa from 1588 until 10 September 1974, when it gained independence as G ...
.
The first Catholic mission in Sédhiou was founded in 1875 and the first baptism
Baptism (from ) is a Christians, Christian sacrament of initiation almost invariably with the use of water. It may be performed by aspersion, sprinkling or affusion, pouring water on the head, or by immersion baptism, immersing in water eit ...
s were celebrated that same year in Carabane. There were 17 people baptised in total, most of whom were residents of the island. The Holy Ghost Fathers' mission in Carabane was founded in 1880 by Father Kieffer. On February 22, he settled on the island, but he served for only two years. The staff of the colonial administration was small: the manager of a customs post with four employees, a gunner, a corporal
Corporal is a military rank in use by the armed forces of many countries. It is also a police rank in some police services. The rank is usually the lowest ranking non-commissioned officer. In some militaries, the rank of corporal nominally corr ...
, and six European tirailleur
A tirailleur (), in the Napoleonic era, was a type of light infantry trained to skirmish ahead of the main columns. Later, the term "''tirailleur''" was used by the French Army as a designation for indigenous infantry recruited in the French c ...
s. There were approximately 250 Christians in Carabane, mostly mulattos. The priest built his house out of Palmyra palm trunks. He visited nearby villages and sometimes went to Sédhiou. The founding of the mission in Carabane was followed by others in Ziguinchor (1888), Elinkine (1891), and several nearby locations in the 20th century. In 1900, a Spiritan missionary, Father Wintz,In 1909, Father Wintz wrote a French—Jola dictionary published by the Elinkine Mission, and reedited in 1968. wrote the first catechism
A catechism (; from , "to teach orally") is a summary or exposition of Catholic theology, doctrine and serves as a learning introduction to the Sacraments traditionally used in catechesis, or Christian religious teaching of children and adult co ...
in the Jola language. Tomàs i Guilera (2005), p. 305.
Temporarily transferred to Ziguinchor, the Carabane mission closed in 1888. Missionaries returned in 1890 and, although they immediately expanded the church building, it was still not large enough to accommodate all those who wished to attend. Thanks to subsidies by the bishop, Magloire-Désiré Barthet, and to donations by the parishioners, a new church was built and inaugurated on the Catholic feast day
The calendar of saints is the traditional Christian method of organizing a liturgical year by associating each day with one or more saints and referring to the day as the feast day or feast of said saint. The word "feast" in this context does n ...
of Saint Anne
According to apocrypha, as well as Christianity, Christian and Islamic tradition, Saint Anne was the mother of Mary, mother of Jesus, Mary, the wife of Joachim and the maternal grandmother of Jesus. Mary's mother is not named in the Bible's Gosp ...
in 1897. The mission also obtained two adjacent properties, lot #73 on the cadastral map. By the following year, the Christian community had performed 1,100 baptisms, as well as many catechumen
Catechesis (; from Greek: , "instruction by word of mouth", generally "instruction") is basic Christian religious education of children and adults, often from a catechism book. It started as education of converts to Christianity, but as the ...
.
Competition between the French and the Portuguese began to show itself in the region during this period. Because the Portuguese-operated trading posts in Cacheu and Farim asked for higher prices than the French-operated trading posts in Carabane and Sédhiou, the Portuguese lost many traders to the French. This trend led to the ceding of Ziguinchor to France, which was negotiated in Carabane in April 1888 between Commissioner Oliveira and Captain Brosselard-Faidherbe.
In 1901, the administrative capital of Casamance was transferred from Carabane to Ziguinchor, a status which was transferred in turn to Oussouye
Oussouye (or Husuy in JolaWilson, William André Auquier. 2007. ''Guinea Languages of the Atlantic group: description and internal classification''. (Schriften zur Afrikanistik, 12.) Frankfurt am Main: Peter Lang.) is a small town and urban commu ...
two years later. By 1904, Carabane had lost several of its amenities, including its customs services, which were centralized. The island's trading houses were abandoned and the number of Christians dwindled from 1,000 to 300 by 1907. Benoist (2008), p. 292
Despite the anti-clerical
Anti-clericalism is opposition to religious authority, typically in social or political matters. Historically, anti-clericalism in Christian traditions has been opposed to the influence of Catholicism. Anti-clericalism is related to secularism, ...
movement's growth in France at the time, education in Carabane continued to be administered by the Holy Ghost Fathers for the boys and by the Sisters of St. Joseph of Cluny for the girls. A chapel also continued to be run on the island.
In 1913, just before the outbreak of , Carabane suffered a fire which caused its business to decline. People gradually left the island in search of work in Ziguinchor and even Dakar
Dakar ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Senegal, largest city of Senegal. The Departments of Senegal, department of Dakar has a population of 1,278,469, and the population of the Dakar metropolitan area was at 4.0 mill ...
. Roche (2000), p. 322. In December 1915, Marcel de Coppet, administrator of Ziguinchor, visited the island in order to recruit tirailleurs
A tirailleur (), in the Napoleonic era, was a type of light infantry trained to skirmish ahead of the main columns. Later, the term "''tirailleur''" was used by the French Army as a designation for indigenous infantry recruited in the French c ...
. Six inhabitants of the island accepted the position: a Christian, a pagan, and four Muslims.
In the aftermath of the Great War, the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
encountered great difficulties in the region. There was insufficient staffing, the cost of living was rising, and the harsh climate began to wear on the buildings. In 1920, the diocese had, in addition to Carabane, thirteen churches and approximately thirty-five chapels. The thirteen churches were located in Dakar, Saint-Louis, Gorée, Rufisque, Thiès
Thiès (; ; Noon language, Noon: ''Chess'') is the third largest city in Senegal with a population of 391,253 in 2023. It lies east of Dakar on the N2 road (Senegal), N2 road and at the junction of railway lines to Dakar, Bamako and Saint-Louis, ...
, Ngazobil, Joal, Fadiouth, Foundiougne, Kaolack, Ziguinchor, Bignona and Banjul
Banjul (, (US) and ), officially the City of Banjul, is the capital city of The Gambia. It is the centre of the eponymous administrative division which is home to an estimated 400,000 residents, making it The Gambia's largest and most densely ...
. In 1922, the Governor decreed which buildings were authorized to practise Catholicism. While the Carabane church was one of the buildings selected, some members blamed the colonial administration for having facilitated the expansion of Islam in the country.
In taking leadership of the diocese
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, prov ...
, Archbishop Le Hunsec noted that the island of Carabane, heavily populated when trading was concentrated there, had lost its influence and now had fewer than 500 inhabitants. He considered transferring the mission to Oussouye, which became a reality in 1927. Starting in 1937, the mission in Oussouye also performed baptisms and funerals in Carabane.
In the same year, a reform school
A reform school was a Prison, penal institution, generally for teenagers, mainly operating between 1830 and 1900. In the United Kingdom and its colonies, reformatory, reformatories (commonly called reform schools) were set up from 1854 onward f ...
was created on the island, operating until 1953, when it was replaced by another in Nianing. A report submitted in 1938 by an educational advisor to Marcel de Coppet, Governor General of French West Africa
French West Africa (, ) was a federation of eight French colonial empires#Second French colonial empire, French colonial territories in West Africa: Colonial Mauritania, Mauritania, French Senegal, Senegal, French Sudan (now Mali), French Guin ...
, detailed the daily life of the prisoners in the school which housed up to 22 boys, mostly convicted for theft but also occasionally for murder.
Recent history
Carabane's population continued to decline gradually after . In 1950, the construction of a seminary was planned in Carabane, but it was transferred to a new building in Nyassia in 1959. The Carabane mission closed its doors during the wet season of 1953, 83 years after its inception. The nuns and their interns moved to Ziguinchor. Thomas (April 1964), pp. 13–46. Senegal's independence was declared on August 20, 1960, and after the dissolution of the short-lived
Senegal's independence was declared on August 20, 1960, and after the dissolution of the short-lived Mali Federation
The Mali Federation () was a federation in West Africa linking the French colonies of Senegal and the Sudanese Republic (or French Sudan) for two months in 1960. It was founded on 4 April 1959 as a territory with self-rule within the French Co ...
, Casamance saw the arrival of officials coming from the north. Although many of them were Wolofs and Muslims, they did not know the Jola country and its traditions. The periods of drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, ...
that ravaged the Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
in the 1970s forced peanut farmers to move to regions where rice was all that grew.
Discontent began to spread among the people, which sometimes escalated to violence. Casamance has since experienced years of conflict which put local initiatives in jeopardy, such as nature reserves and the first network of villages. In 1998, in the middle of the conflict, the French commune of Bon-Encontre committed to providing Carabane with humanitarian aid, both economically and culturally. Carabane has remained one of the calmest areas of Casamance throughout the conflict. Nonetheless, a few small incidents were reported around April 2000. The rebels may have wanted to take advantage of Carabane's reputation to attract media attention.
The ceasefire
A ceasefire (also known as a truce), also spelled cease-fire (the antonym of 'open fire'), is a stoppage of a war in which each side agrees with the other to suspend aggressive actions often due to mediation by a third party. Ceasefires may b ...
of 2004 brought relative peace, but in the meantime, the sinking of the '' Joola'' in 2002 claimed the lives of many inhabitants of Carabane and curtailed much of its ability to engage in trade and accept tourists for several years. Considering the problems brought on by the conflict along with the threat of coastal erosion on the island, some fear the worst. Thus, after years of development and community outreach, Carabane is experiencing difficulties in a number of ways.
Society
Administration
 Formerly an administrative district in its own right,Between 1939 and 1944, the colonial authorities of the AOF were Vichyites and anti- Gaullists, unlike those of the AEF, especially because of the
Formerly an administrative district in its own right,Between 1939 and 1944, the colonial authorities of the AOF were Vichyites and anti- Gaullists, unlike those of the AEF, especially because of the governor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
of Chad
Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North Africa, North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to Chad–Libya border, the north, Sudan to Chad–Sudan border, the east, the Central Afric ...
, Félix Éboué
Adolphe Sylvestre Félix Éboué (; 26 December 1884 – 17 May 1944) was a French Guiana, French French colonial empires, colonial administrator and early adherent to the Free French Forces, Free French Movement. He was the first black Fren ...
. even a regional capital, Carabane is now just one of 23 villages in the rural community of Diembéring, of which Kabrousse, Cap Skirring, and Boucott-Diembéring are the largest centres. This rural community is located in the Kabrousse Arrondissement. It is part of Oussouye Department, the smallest and least central of the three departments in Ziguinchor Region. In a country which includes some 13,000 villages, the village is considered, by a 1972 decree, the elementary entity in the administrative body of the nation. Each is administered by a leader, assisted by a council. After consultation, the nomination of a leader is established by the prefect and approved by the Minister of the Interior
An interior minister (sometimes called a minister of internal affairs or minister of home affairs) is a cabinet official position that is responsible for internal affairs, such as public security, civil registration and identification, emergency ...
. Under Senegalese law, the leader of the village has certain prerogatives, including law enforcement
Law enforcement is the activity of some members of the government or other social institutions who act in an organized manner to enforce the law by investigating, deterring, rehabilitating, or punishing people who violate the rules and norms gove ...
, tax collection, and keeping of vital record
Vital records are records of life events kept under governmental authority, including birth certificates, marriage licenses (or marriage certificates), separation agreements, divorce certificates or divorce party and death certificates. In some ...
s in the village.
While this administrative structure was decreed by a government anxious to deal with interlocutors, such a restructuring has not taken place in Casamance. Berghen and Manga (1999), pp. 21–22. Jola society is devoid of any formal hierarchy. It has no leader with genuine permanent authority. Instead, there are village elders who meet when important decisions need to be made. According to Italian anthropologist
An anthropologist is a scientist engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropologists study aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms, values ...
Paolo Palmeri, the leader of the village has very little power in reality, as he is merely responsible for relations with the national administration. He simply allows the village to continue practicing its traditions. In a society where politics are inextricably linked to religion, the real holders of power are the fetish priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deity, deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in parti ...
s. The very notion of a village is almost inappropriate in this context: it might be more appropriately considered a clan
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship
and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, a clan may claim descent from a founding member or apical ancestor who serves as a symbol of the clan's unity. Many societie ...
or an aggregation of kinship
In anthropology, kinship is the web of social relationships that form an important part of the lives of all humans in all societies, although its exact meanings even within this discipline are often debated. Anthropologist Robin Fox says that ...
. Other specialists, such as Christian Sina Diatta, compare Jola communities to those of mound-building termites
Mound-building termites are a group of termite species that live in mounds which are made of a combination of soil, termite saliva and dung. These termites live in Africa, Australia and South America. The mounds sometimes have a diameter of ...
, in which each member performs a specific function and where the queen is easily replaceable.
Population
In 2003, the village of Carabane's official population count stood at 396 people and 55 households, but it fluctuates with the seasons and sometimes reaches some 1,750 people, according to local sources. Most of the population is Jola. The Jola are very distinct from other majorethnic groups in Senegal
There are various ethnic groups in Senegal. According to "CIA World Factbook: Senegal" (2019 estimates), the ethnic groups are Wolof (39%); Fula (probably including the Halpulaar speaking Toucouleur) (27.5%)); Serer group (probably includin ...
by their language, egalitarian society, freedom from political hierarchy, and lack of slavery. Their traditions have persevered because of their independent spirit as well as their geographical isolation. This ethnic group accounts for 80 to 90% of the residents of Basse Casamance,Linares (2007), p. 5. but only 6 to 8% of the total population of Senegal. They are the largest ethnic group in Carabane, followed by Wolofs, Lebous, and Serers (including Niominka fishermen). Manjacks also live on the island, some of whom came from Saint-Louis and Gorée at the time of the first colonization. Two communities from neighbouring countries, one from Guinea
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Côte d'Ivoire to the southeast, and Sier ...
(the Susu people
The Susu or Soussou people are a Mande-speaking ethnic group living primarily in Guinea and northwestern Sierra Leone, particularly in Kambia District.
) and the other from Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau, officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau, is a country in West Africa that covers with an estimated population of 2,026,778. It borders Senegal to Guinea-Bissau–Senegal border, its north and Guinea to Guinea–Guinea-Bissau b ...
, have settled on the other side of the island at a distance from the village. There are also seasonal workers who come to fish: Ghana
Ghana, officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It is situated along the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, and shares borders with Côte d’Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, and Togo to t ...
ians, Guineans, and Gambians.
The indigenous population was originally animist
Animism (from meaning 'breath, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct spiritual essence. Animism perceives all things—animals, plants, rocks, rivers, weather systems, human handiwork, and in ...
, but while the fetishes and sacred groves dedicated to initiation rites such as boukout survive as cultural icons of Casamance, the monotheistic
Monotheism is the belief that one God is the only, or at least the dominant deity.F. L. Cross, Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. A ...
belief systems of Catholicism and Islam have become the most widely held in Carabane. The 1988 census reported that Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
s account for 94% of the population of Senegal, but only 26.5% of the population of Oussouye Department, where Carabane is located. Still, this department is largely rural, while Carabane has historically supported great ethnic diversity. Islam has not been practiced by Wolof and Serer fishermen since the 19th century, but the colonial administration brought with it many translators, guides, and secretaries from Dakar
Dakar ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Senegal, largest city of Senegal. The Departments of Senegal, department of Dakar has a population of 1,278,469, and the population of the Dakar metropolitan area was at 4.0 mill ...
, many of whom were Muslim.
Education and health
 Carabane has a new primary school, École François Mendy, inaugurated on January 21, 2006, hosting six classes. The literacy rate is approximately 90%. Students may continue their studies at the middle school in Elinkine, the Aline Sitoe Diatta High School in Oussouye, and then a university in either Dakar or Ziguinchor. Carabane's kindergarten is located in a community house, called "House of Women and Children", founded in 1988 under the auspices of Caritas Ziguinchor.
In 1895, the government established a medical post in Carabane, but it closed the following year. In 1898, the Daughters of the Holy Heart of Mary opened a clinic at the same time as the girls' school.
As of 2010, the village has a health facility which is connected to that of Oussouye and Ziguinchor. It provides vaccinations,
Carabane has a new primary school, École François Mendy, inaugurated on January 21, 2006, hosting six classes. The literacy rate is approximately 90%. Students may continue their studies at the middle school in Elinkine, the Aline Sitoe Diatta High School in Oussouye, and then a university in either Dakar or Ziguinchor. Carabane's kindergarten is located in a community house, called "House of Women and Children", founded in 1988 under the auspices of Caritas Ziguinchor.
In 1895, the government established a medical post in Carabane, but it closed the following year. In 1898, the Daughters of the Holy Heart of Mary opened a clinic at the same time as the girls' school.
As of 2010, the village has a health facility which is connected to that of Oussouye and Ziguinchor. It provides vaccinations, family planning
Family planning is the consideration of the number of children a person wishes to have, including the choice to have no children, and the age at which they wish to have them. Things that may play a role on family planning decisions include marit ...
consultations, and prenatal information. A maternity hospital was founded in 1991 which is decorated with a fresco by Malang Badji, one of the most famous artists in the region.
The Ph.D. thesis published in 2003, ''La part de l'autre: une aventure humaine en terre Diola'', meaning "Part of the Other: A Human Adventure in Jola Territory", describes the health challenge present on the island in a more general context.
In particular, the location of the island does not allow easy access to serious or urgent medical assistance. There is a pirogue-ambulance for the transportation of people off the island in the case of medical emergencies.
Economy
The testimonies of explorers and colonial administrators demonstrate that Carabane has participated in rice cultivation, fishery, trade, andpalm wine
Palm wine, known by several #Names, local names, is an alcoholic beverage created from the sap of various species of palm trees such as the Borassus, palmyra, date palms, and coconut palms. It is known by various names in different regions and ...
production for centuries. The island experienced a decline in the 20th century, when Ziguinchor emerged as the regional capital, and more recently because of the negative economic consequences resulting from the Casamance Conflict and the ''Joola'' tragedy.
Transportation and energy
From the colonizers' perspective, Carabane's position at the mouth of the river was an undeniable asset. In the 20th and 21st centuries, in terms of trade and tourism issues, this location is more of a disadvantage because it effectively separates the island from the rest of the country. While a direct route by sea has not been available since the sinking of the ''Joola'', the traveller from Dakar may use various other means of transportation in order to arrive in Basse Casamance. Some national roads connect to Ziguinchor, down the N1 to Kaolack. The N4 and N5 roads cross the Gambia (both the country and the river), the former running through Nioro du Rip to
While a direct route by sea has not been available since the sinking of the ''Joola'', the traveller from Dakar may use various other means of transportation in order to arrive in Basse Casamance. Some national roads connect to Ziguinchor, down the N1 to Kaolack. The N4 and N5 roads cross the Gambia (both the country and the river), the former running through Nioro du Rip to Farafenni
Farafenni or Farafegni sometimes called Chakubanta or Faracity is a town in the Gambia, lying on the Trans-Gambia Highway in the North Bank Division, just south of the border with Senegal. It is an important market town.
The population of F ...
, and the latter crossing the river to Banjul. The two roads merge in Bignona before descending to Ziguinchor. However, traffic is forbidden on both roads between 7 p.m. and 10 a.m., and the routes are subject to frequent accidents and constant demining
Demining or mine clearance is the process of removing land mines from an area. In military operations, the object is to rapidly clear a path through a minefield, and this is often done with devices such as mine plows and blast waves. By cont ...
operations. Alternatively, it is possible to travel by plane to the airport in Ziguinchor or Cap Skirring, or to travel by boat to one of these locations. Reaching Carabane from either town is relatively straightforward.
By boat, the distance between Dakar and Carabane is , although Ziguinchor is only away. Before the launch of the ''Joola'', other boats, mostly well-worn ones, made the connection: first ''Cap Skirring'', then the ''Casamance Express'', and then ''Island Karabane''. In January 1991, a brand new ferry
A ferry is a boat or ship that transports passengers, and occasionally vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A small passenger ferry with multiple stops, like those in Venice, Italy, is sometimes referred to as a water taxi or water bus ...
went into operation. Like its predecessors, it connected Dakar to Ziguinchor, stopping near Carabane where canoes could reach the island. On September 26, 2002, 180 extra passengers boarded the already overloaded ship at this stop,This figure does not take into account the passengers who boarded without a ticket. Members of the military and their families were allowed to ride free of charge. and a few hours later, the ''Joola'' sank. For security reasons, the ''Joolas successor, the ''Wilis'', stopped calling at Carabane, to the great displeasure of the inhabitants. Tourists became rare after that, and from time to time, inhabitants of the island found it necessary to move to Dakar or Ziguinchor.These difficulties were presented in the French documentary ''Un nouveau bateau pour la Casamance'', meaning "A New Boat for Casamance", as part of the ''Thalassa
Thalassa (; ; Attic Greek: , ''thálatta'') was the general word for 'sea' and for its divine female personification in Greek mythology. The word may have been of Pre-Greek origin and connected to the name of the Mesopotamian primordial sea godde ...
'' series on December 1, 2006Web.archive.org
/ref> Significant modifications to the MV ''Aline Sitoe Diatta'', which replaced the ''Wilis'' in March 2008, were considered to allow it to stop safely at the island, and the construction of a berth was announced. Souleymane Ndéné Ndiaye, who later became
Prime Minister of Senegal
The prime minister of Senegal () is the head of government of Senegal. The prime minister is appointed by the president of Senegal, who is directly elected for a five-year term. The prime minister, in turn, appoints the Cabinet of Senegal, afte ...
, laid the first stone of the berth in July 2008, and the entire construction project was financed by the Senegalese government at an estimated cost of 12 billion West African CFA franc
The West African CFA franc ( or simply , ISO 4217 code: XOF; abbreviation: F.CFA) is the currency used by eight independent states in West Africa which make up the West African Economic and Monetary Union (UEMOA): Benin, Burkina Faso, Côte d' ...
s. On April 26, 2014, the MV ''Aline Sitoe Diatta'' stopped at the Carabane berth for the first time, improving transportation for locals and tourists. , the ferry stops at Carabane four times each week in the middle of its trips between Dakar and Ziguinchor.
Agriculture and aquaculture
Rice cultivation
 In Basse Casamance, the rice cycle structures the lives of the population and plays a central economic and religious role. The Jola, who constitute 80 to 90% of the population of Basse Casamance, practice a unique form of rice cultivation. Descriptions of the techniques used in the late 15th century, recorded by the first Portuguese
In Basse Casamance, the rice cycle structures the lives of the population and plays a central economic and religious role. The Jola, who constitute 80 to 90% of the population of Basse Casamance, practice a unique form of rice cultivation. Descriptions of the techniques used in the late 15th century, recorded by the first Portuguese explorers
Exploration is the process of exploring, an activity which has some expectation of discovery. Organised exploration is largely a human activity, but exploratory activity is common to most organisms capable of directed locomotion and the abilit ...
, show them to be similar to those still in use, particularly with respect to flooding and transplanting. Only the varieties of rice have changed, from African rice
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown in West Africa around 3,000 years ago. In agriculture, it has largely been replaced by higher-yielding Asian ric ...
to Asian rice, a separate species.
The basic tool used is the '' kayendo'',Also spelled ''kajandu'', ''kajendo'', ''kadiendo'', or ''kadiandou'' a kind of wooden spade or shovel ranging from , surrounded by a sharp wrought iron blade and attached to a very long, straight, cylindrical neck. The two parts are connected by strips of torn Palmyra palm leaves. The main part is manufactured from a very hard wood measuring in length. The ''kayendo'' is mainly used to plough rice fields, but is also used for other purposes, such as excavation and construction. Men perform the clearing and ploughing while the women take care of the sowing, replanting, and weeding as well as the harvesting between October and January.
An even checkerboard plot model dominates the green landscape during the rainy season, which becomes more austere after harvest. The rice fields differ only in terms of soil type and location. Berghen and Manga (1999), pp. 56–75. Where mangroves are populous, such as in Carabane, the rice paddy fields between them must be protected from the channels of saltwater which overflow during high tide. Rice farmers must therefore build levee
A levee ( or ), dike (American English), dyke (British English; see American and British English spelling differences#Miscellaneous spelling differences, spelling differences), embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is an elevated ridge, natural ...
s, dig ditches, and create ponds. The fish and shrimp
A shrimp (: shrimp (American English, US) or shrimps (British English, UK)) is a crustacean with an elongated body and a primarily Aquatic locomotion, swimming mode of locomotion – typically Decapods belonging to the Caridea or Dendrobranchi ...
which subsequently become trapped are harvested at the end of the rainy season, when the basins are emptied. The plots of land which were safeguarded from flooding are then cleared and ploughed. Several years of drainage are required to desalinate the soil.
 Although practised in Basse Casamance for centuries, rice cultivation has been threatened since the late 1960s. Productivity has declined because many workers have opted for life in the city, even though they continue to support their community. Foucher (2002), pp. 389–390. The drought of the 1970s and 1980s further aggravated the situation.
Although practised in Basse Casamance for centuries, rice cultivation has been threatened since the late 1960s. Productivity has declined because many workers have opted for life in the city, even though they continue to support their community. Foucher (2002), pp. 389–390. The drought of the 1970s and 1980s further aggravated the situation.
Palm oil and palm wine
Among the agricultural activities practised during the dry season, which halts work in the rice fields, the most traditional are those related to the exploitation ofAfrican oil palm
''Elaeis guineensis'' is a species of palm commonly just called oil palm but also sometimes African oil palm or macaw-fat. The first Western person to describe it and bring back seeds was the French naturalist Michel Adanson. Jean-Marie Pelt, « ...
(''Elaeis guineensis''), which provides two products which are very popular in the region: palm oil
Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil derived from the mesocarp (reddish pulp) of the fruit of oil palms. The oil is used in food manufacturing, in beauty products, and as biofuel. Palm oil accounted for about 36% of global oils produced from o ...
and palm wine. Palm oil is an essential ingredient in local cuisine. As a carefully preserved condiment, it is combined with plain rice on holidays. The oil comes from the fruit clusters which are picked by men and then deseeded, allowed to dry, crushed in a mortar, and boiled by women.
grapes
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began approximately 8,0 ...
. The recent partial Islamization
The spread of Islam spans almost 1,400 years. The early Muslim conquests that occurred following the death of Muhammad in 632 CE led to the creation of the caliphates, expanding over a vast geographical area; conversion to Islam was boosted ...
of the region has not challenged its consumption. Fruit clusters are collected exclusively by the men. Supported by a strap, the harvester climbs the tree, cuts the bud, and holds out a funnel which allows the resulting fluid to flow drip by drip into an elongated calabash
Calabash (; ''Lagenaria siceraria''), also known as bottle gourd, white-flowered gourd, long melon, birdhouse gourd, New Guinea bean, New Guinea butter bean, Tasmania bean, and opo squash, is a vine grown for its fruit. It can be either harvest ...
or, more recently, a bottle. The alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
content of palm wine develops throughout the day. The locals consume large quantities on a daily basis, and even more at banquets and ceremonies dedicated to fetishes. Palm wine is often traded for rice or sold in the city. Many Jola proverbs attest the popularity of the drink, such as , which means "With palm wine, one never stands up", or , which means "Sit down, don't spill the palm wine".
Aquaculture
The island's proximity to the river and the ocean suggests that the area is suited to fishing and related activities, yet the indigenous people, mostly land-dwellers, have long been content to practiseartisan fishing
Artisanal, subsistence, or traditional fishing consists of various small-scale, low-technology, fishing practices undertaken by individual fishermen (as opposed to commercial fishing). Many of these households are of coastal or island ethnic g ...
, just to supply their own daily needs. Pirogues cut from the trunks of kapok trees are most often used, along with traps, nets, baskets, and fences. In the early 20th century, experienced fishermen from other parts of Senegal, along with others from Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
, Guinea, and Ghana, developed deep-sea fishing on the island and introduced new equipment.
The collection of shellfish, especially oysters, is another traditional activity which still takes place in Casamance, Cormier-Salem (1989), pp. 91–107. which is one of three oyster-producing regions in Senegal, along with Petite Côte
The Petite Côte is a stretch of coast in Senegal, running south from the Cap-Vert peninsula to the Saloum Delta, near the border with the Gambia.
The northern section near Dakar contains seaside resorts such as Saly Portudal, Rufisque, Nian ...
and Sine-Saloum
Sine-Saloum is a region in Senegal located north of the Gambia and south of the Petite Côte. It encompasses an area of 24,000 square kilometers, about 12% of Senegal, with a population in the 1990s of 1,060,000.
The western portion contains the ...
. Oysters collect on the roots of mangrove trees which are uncovered at low tide. They are harvested during the dry season, mainly by women, who control, from harvest to distribution, an activity that requires little investment and provides them with some financial independence. Oysters are an important component of the family diet. Rich in dietary mineral
In the context of nutrition, a mineral is a chemical element. Some "minerals" are essential for life, but most are not. ''Minerals'' are one of the four groups of essential nutrients; the others are vitamins, essential fatty acids, and essent ...
s and vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription di ...
, they are the second largest source of animal protein among the Jola people after fish, followed by chicken, and pork. Oysters are readily associated with rice, the staple food
A staple food, food staple, or simply staple, is a food that is eaten often and in such quantities that it constitutes a dominant portion of a standard diet for an individual or a population group, supplying a large fraction of energy needs an ...
, and in times of shortage, even replace it. Locally, oysters are boiled or grilled on a wood fire and consumed with a spicy sauce. Those destined for sale or preservation, however, are sun-dried or smoked. In some villages, including Carabane, they are kept alive for several weeks before being transported to market. Oysters are also a source of income, and Carabane is located in the center of the collection zone, which is one of the reasons why boats formerly called at the island. Oysters were once easily transported from Carabane to Dakar, where they were either sold by the pickers themselves or by hawkers.
Senegambian
The Senegambia (other names: Senegambia region or Senegambian zone,Barry, Boubacar, ''Senegambia and the Atlantic Slave Trade'', (Editors: David Anderson, Carolyn Brown; trans. Ayi Kwei Armah; contributors: David Anderson, American Council of Le ...
area, a single family exists in Casamance: Penaeidae
Penaeidae is a family of marine crustaceans in the suborder Dendrobranchiata, which are often referred to as penaeid shrimp or penaeid prawns. The Penaeidae contain many species of economic importance, such as the tiger prawn, whiteleg shrimp, ...
. Southern pink shrimp (''Farfantepenaeus notialis'') are the most commonly collected. They were traditionally caught as part of local artisan fishing by men, women, and children. Shrimp collection in the area experienced significant development in the 1960s, following the establishment of European industrial units. The local fishermen switched to this method, and there was an increased presence of fishermen from other areas. A study in 2005 revealed the extent to which the shrimp population in the region has been depleted, citing multiple causes, including diminishing rainfall, over-salinization of the estuary, and poorly controlled harvesting. Along with the mangrove degradation, the civil unrest, and the inadequate fishery regulation, Casamance has had to deal with the closure in 2003 of a major industrial complex in Ziguinchor which treated and exported shrimp and other crustaceans and employed more than 2,000 people.
Grouped into cooperatives,An example of a cooperative run by women: women play a leading role in the island's economy. Notably through microcredit
Microcredit is the extension of very small loans (microloans) to impoverished borrowers who typically do not have access to traditional banking services due to a lack of collateral (finance), collateral, steady employment, and a verifiable credi ...
, they engage in fishing-related activities, such as smoking fish and processing shrimp, oysters, and shellfish in general. As there is no industrial activity on the island (the closest such activity is in Ziguinchor), the island is experiencing a rural exodus
Rural flight (also known as rural-to-urban migration, rural depopulation, or rural exodus) is the Human migration, migratory pattern of people from rural areas into urban areas. It is urbanization seen from the rural perspective.
In Industriali ...
of young people. They return to help their parents in the rice fields and participate in religious ceremonies during the dry season, but they tend to settle off the island permanently.
Tourism
 The Republic of Senegal placed an emphasis on
The Republic of Senegal placed an emphasis on tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure, and the Commerce, commercial activity of providing and supporting such travel. World Tourism Organization, UN Tourism defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as ...
early in its history. The results were promising, and developing the industry further became a priority in the country's 4th Economic and Social Plan (1973–1977). Casamance subsequently became the main tourist destination in the country. Already having been described in the 19th century by Captain Brosselard-Faidherbe as a kind of Brazil in Africa, Carabane seemed well-placed to attract visitors in search of exoticism
Exoticism (from ''exotic'') is the style or traits considered characteristic of a distant foreign country. In art and design it is a trend where creators become fascinated with ideas and styles from distant regions and draw inspiration from them. ...
as well as vacationers seeking sandy beaches and kite surfing
Kiteboarding or kitesurfing is a sport that involves using wind power with a large power kite to pull a rider across a water, land, snow, sand, or other surface. It combines the aspects of paragliding, surfing, windsurfing, skateboarding, snow ...
.
At the same time, national and even international controversy threatened the industry from the beginning. Those who opposed tourism in Senegal described it as a new form of colonialism while supporters saw it as a panacea that would cure the country of underdevelopment
Underdevelopment, in the context of international development, reflects a broad condition or phenomena defined and critiqued by theorists in fields such as economics, development studies, and postcolonial studies. Used primarily to distinguish s ...
. The idea of alternative tourism was discussed. Several towns in Basse Casamance, including Carabane, were selected to test an integrated agritourism
Agritourism or agrotourism involves any agriculturally based operation or activity that brings visitors to a farm or ranch. It encompasses a wide range of activities, including direct-to-consumer sales such as farm stands and u-pick, agricultu ...
managed by the villagers themselves. In the early 1970s, the agritourism promoter Christian Saglio, a young French sociologist who later became the director of the Leopold Sedar Senghor French Institute in Dakar, believed in Carabane's potential. He stated that he wanted to make the island the "Gorée of Casamance", using it as a hub for other camps. Saglio suggested the restoration of old buildings and canopy beds.
Despite his fervour, Saglio's negotiations with the local people were unsuccessful. Niomoune and Carabane were the first two villages to attempt to apply this innovative approach, but both failed. The inhabitants were reluctant to participate, and the young inexperienced promoter had to abandon some of his ethnographic
Ethnography is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. It explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject of the study. Ethnography is also a type of social research that involves examining ...
theories in favour of being careful to understand the daily realities of villages. The project was eventually abandoned, and the Catholic missions
Missionary work of the Catholic Church has often been undertaken outside the geographically defined parishes and dioceses by religious orders who have people and material resources to spare, and some of which specialized in missions. Eventually, p ...
house was transformed by the nuns themselves into a modern, functional building. Despite the failure of Saglio's initiative in Carabane, agritourist camps were set up over the following decade in a dozen other nearby towns.The camps were set up in Elinkine, Enampore, Baïla, Thionck Essyl
Thionck Essyl (also called Tionk Essil) is a small town and urban commune in Ziguinchor, Senegal, located 65 km north-west of the region capital.
Etymology
The name of the town means "cook remaining crouched."
History
The origins of the t ...
, Coubalan, Affiniam, Abéné, Oussouye
Oussouye (or Husuy in JolaWilson, William André Auquier. 2007. ''Guinea Languages of the Atlantic group: description and internal classification''. (Schriften zur Afrikanistik, 12.) Frankfurt am Main: Peter Lang.) is a small town and urban commu ...
and Palmarin.
While Carabane's tourism sector has suffered because it has not taken part in the network of villages, tourists have avoided travelling to Casamance in general because of the civil unrest. The signing of a ceasefire in 2004 allowed tourism to resume, but not to the extent it had reached before the conflict.
Tour operators continue to advertise the island as a lost paradise surrounded by mangroves where travellers' exotic dreams come to life, Ropitault (November–December 2007), pp. 16–25. but this type of discovery tourism is not as popular as traditional beach-related tourism. Thus, visitors from France, Spain, and Italy often combine tours of the ''cases á impluvium
The ''impluvium'' (: ''impluvia'') is a water-catchment pool system meant to capture rain-water flowing from the ''compluvium'', an area of roof. Often placed in a courtyard, under an opening in the roof, and thus "inside", instead of "outside ...
'' in Enampore or Mlomp with a few days of relaxation in Carabane. The area is also very conducive to the interests of fishing enthusiasts. Along the beach, small stalls offer traditional crafts and clothes at prices lower than those in Cap Skirring or Saly
Saly (also called Sali or Saly Portudal) is a seaside resort and urban commune in Thiès Region on the Petite Côte of Senegal, south of Dakar. It is a major tourist destination in Senegal.
History
Saly was originally a Portuguese trading post kn ...
. Badji Malang, a local painter, potter, sculptor, and poet, has created a camp in the area.
Although remaining separate from the local tourism network, Carabane has demonstrated its support for social solidarity
Solidarity or solidarism is an awareness of shared interests, objectives, standards, and sympathies creating a psychological sense of unity of groups or classes. True solidarity means moving beyond individual identities and single issue politics ...
and holism
Holism is the interdisciplinary idea that systems possess properties as wholes apart from the properties of their component parts. Julian Tudor Hart (2010''The Political Economy of Health Care''pp.106, 258
The aphorism "The whole is greater than t ...
by joining GENSEN (Global Ecovillage Network Senegal), a network of Senegalese ecovillage
An ecovillage is a traditional or intentional community that aims to become more socially, culturally, economically and/or environmentally sustainable. An ecovillage strives to have the least possible negative impact on the natural environment ...
s.
Historic sites

Brittany
Brittany ( ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the north-west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica in Roman Gaul. It became an Kingdom of Brittany, independent kingdom and then a Duch ...
-style church building
A church, church building, church house, or chapel is a building used for Christian worship services and Christian activities. The earliest identified Christian church is a house church founded between 233 AD and 256 AD.
''Church'' is also ...
which is no longer in use, and a former slave-trade building. There is also a French cemetery where a Troupes de marine-Captain with the name Aristide Protet was shot with a poisoned arrow
Arrow poisons are used to poison arrow heads or darts for the purposes of hunting and warfare. They have been used by indigenous peoples worldwide and are still in use in areas of South America, Africa and Asia. Notable examples are the poisons se ...
and buried standing up in front of the sea, according to his last wishes. Some tour guides falsely claim that this was Auguste Léopold Protet
Auguste Léopold Protet (; 1808 – 1862) was a French Navy admiral. He fought in the Second Opium War, and was killed in the Taiping Rebellion at the Fengxian District of Shanghai on the afternoon of 17 May 1862.
He was born at Saint-Servan, Fr ...
, the founder of the city of Dakar, but the name Aristide Protet is clearly shown on the tomb's plaque.
Near the beach are ruins of buildings, pontoons, and wells, with a large tree in the center. A huge piece of metal in its midst bears the inscription ''CEO Forrester & Co. Vauxhall Foundry. 18 Liverpool S3''.
Carabane was added to the list of historic sites and monuments of Senegal in 2003. An application for Carabane to become a World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
was filed with UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
on November 18, 2005.
Inspired by Gorée's example, Carabane is attempting to pay homage to victims of slavery
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
by starting a small museum like the House of Slaves
The House of Slaves (''Maison des Esclaves'') and its Door of No Return is a museum and memorial to the victims of the Atlantic slave trade on Gorée Island, 3 km off the coast of the city of Dakar, Dakar, Senegal. Its museum, which was opened in ...
. Like Gorée and Saint-Louis, Carabane places great importance on its cultural heritage
Cultural heritage is the heritage of tangible and intangible heritage assets of a group or society that is inherited from past generations. Not all heritages of past generations are "heritage"; rather, heritage is a product of selection by socie ...
. The architectural reminders of this heritage require significant restoration as they have experienced considerable degradation. In 1964, French anthropologist Louis-Vincent Thomas posed the question of whether Carabane should be preserved, and this question continues to be relevant. The local people suggest that the entire Diogue– Nikine–Carabane area needs saving.
See also
*Geography of Senegal
Senegal is a coastal West African nation located 14th parallel north, 14 degrees north of the equator and 14th meridian west, 14 degrees west of the Prime Meridian. The country's total area is 196,190 km2 of which 192,000 km2 is la ...
* History of Senegal
The history of Senegal is commonly divided into a number of periods, encompassing the prehistoric era, the precolonial period, colonialism, and the contemporary era.
Paleolithic
The earliest evidence of human life is found in the valley of the ...
* List of islands of Senegal
This is a list of islands of Senegal.
Islands
References
{{Authority control
*
Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
;Cartography * ''Entrée de la Casamance et mouillage de Carabane'',nautical chart
A nautical chart or hydrographic chart is a graphic representation of a sea region or water body and adjacent coasts or river bank, banks. Depending on the scale (map), scale of the chart, it may show depths of water (bathymetry) and heights of ...
drawn up by Aristide Vallon in 1862, corrected in 1869 and edited in 1871
*''Africa. West Coast. Senegal. Entrance to the River Kasamanze (Karabane Anchorage)'', map drawn up in 1909 and edited in 1921
;Filmography
* ''Casamance: l'autre Sénégal'', documentary film
A documentary film (often described simply as a documentary) is a nonfiction Film, motion picture intended to "document reality, primarily for instruction, education or maintaining a Recorded history, historical record". The American author and ...
by Virginie Berda, 2006
* ''Un nouveau bateau pour la Casamance'', news report by Anne Gouraud and Olivier Bonnet produced by France 3
France 3 () is a French free-to-air Public broadcasting, public television network. The second flagship network of France Télévisions, it broadcasts a wide range of general and specialized programming.
France 3 is structured as a Region ...
for the television series ''Thalassa
Thalassa (; ; Attic Greek: , ''thálatta'') was the general word for 'sea' and for its divine female personification in Greek mythology. The word may have been of Pre-Greek origin and connected to the name of the Mesopotamian primordial sea godde ...
'', 2006
External links
* * * * {{Coord, 12.5378, -16.7008, type:city, format=dms, display=title Populated places in Ziguinchor region Atlantic islands of Senegal