Capture Fishery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A wild

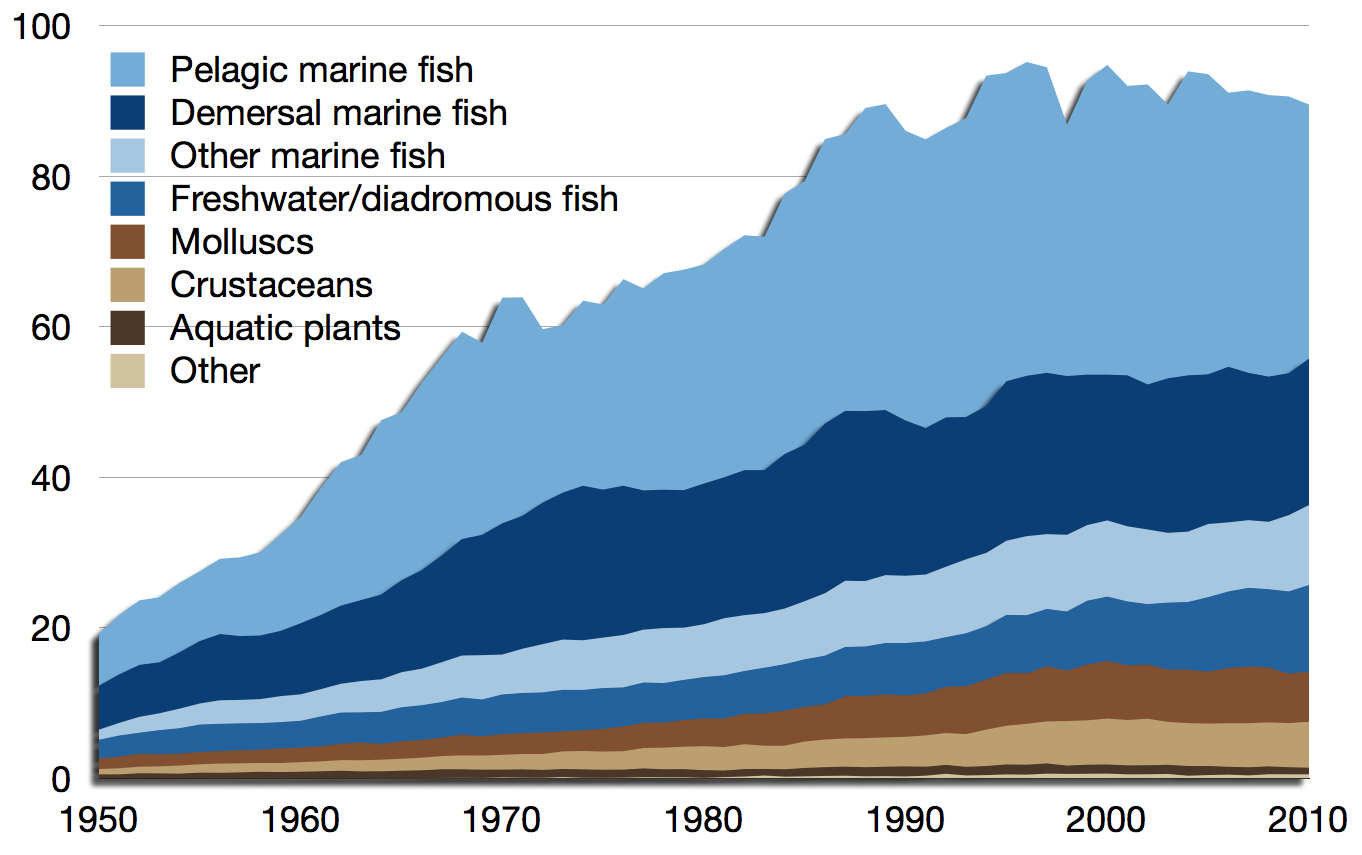 According to the
According to the

 Apart from plastics, there are particular problems with other toxins which do not disintegrate rapidly in the marine environment. Heavy metals are metallic chemical elements that have a relatively high density and are toxic or poisonous at low concentrations. Examples are mercury,
Apart from plastics, there are particular problems with other toxins which do not disintegrate rapidly in the marine environment. Heavy metals are metallic chemical elements that have a relatively high density and are toxic or poisonous at low concentrations. Examples are mercury,

''Historical overfishing and the recent collapse of coastal ecosystems''
Science 293:629-638. Our World in Data provides a figure showing the trend in global fishing exploitation over a few decades to reveal the intensifying circumstances at hand: Overfishing presents many threats to fish population densities, obviously. However, as these populations plummet below the maximum sustainable yield (MSY) value for the specific population, you are now risking the loss of biodiversity and possibility for extinction due to less diversity. This loss in diversity is especially concerning as we deal with environmental changes from climate change since less diversity decreases a populations ability to adapt and survive the alterations of the habitat.
File:Maximum-sustainable-yield-of-fish-with-addition.png, This graph demonstrates the importance of following a specific quota of exploitation to sustain a resource such as a fish population.
Status of the world's marine species
/ref> * Sharks, rays, and chimaeras: are deep water
''Ecological extinction and evolution in the brave new ocean''
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA.
''World ocean database.''
Retrieved 19 April 2008. * The Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia (2007
Retrieved 19 April 2008. * Jacques, Peter (2006
''Globalization and the world ocean''
Rowman Altamira. * Pauly, Daniel; Watson, Reg and Alder, Jackie (2005
''Global trends in world fisheries: impacts on marine ecosystems and food security''
Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society, Volume 360, Number 1453. * De Young, Cassandra (2007
''
Web site
Population Distribution within 100 km of Coastlines
(2000)
''Carbon cycle science''
{{Fishing industry topics Fishing industry
fishery
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life or, more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a., fishing grounds). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish far ...
is a natural
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the laws, elements and phenomena of the physical world, including life. Although humans are part ...
body of water
A body of water or waterbody is any significant accumulation of water on the surface of Earth or another planet. The term most often refers to oceans, seas, and lakes, but it includes smaller pools of water such as ponds, wetlands, or more rare ...
with a sizeable free-ranging fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
or other aquatic animal
An aquatic animal is any animal, whether vertebrate or invertebrate, that lives in a body of water for all or most of its lifetime. Aquatic animals generally conduct gas exchange in water by extracting dissolved oxygen via specialised respirato ...
(crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s and mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s) population that can be harvested for its commercial value. Wild fisheries
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life or, more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a., fishing grounds). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farm ...
can be marine (saltwater
Saline water (more commonly known as salt water) is water that contains a high concentration of dissolved salts (mainly sodium chloride). On the United States Geological Survey (USGS) salinity scale, saline water is saltier than brackish wat ...
) or lacustrine
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from t ...
/riverine
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it run ...
(freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mi ...
), and rely heavily on the carrying capacity
The carrying capacity of an ecosystem is the maximum population size of a biological species that can be sustained by that specific environment, given the food, habitat, water, and other resources available. The carrying capacity is defined as the ...
of the local aquatic ecosystem
An aquatic ecosystem is an ecosystem found in and around a body of water, in contrast to land-based terrestrial ecosystems. Aquatic ecosystems contain communities of organisms—aquatic life—that are dependent on each other and on their environ ...
.
Wild fisheries are sometimes called capture fisheries. The aquatic life they support is not artificially controlled in any meaningful way and needs to be "captured" or fished. Wild fisheries exist primarily in the oceans, and particularly around coast
A coast (coastline, shoreline, seashore) is the land next to the sea or the line that forms the boundary between the land and the ocean or a lake. Coasts are influenced by the topography of the surrounding landscape and by aquatic erosion, su ...
s and continental shelves
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
, but also exist in lake
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from ...
s and river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
s. Issues with wild fisheries are overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing Fish stocks, fish stock), resu ...
and pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause harm. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the component ...
. Significant wild fisheries have collapsed or are in danger of collapsing, due to overfishing and pollution. Overall, production from the world's wild fisheries has levelled out, and may be starting to decline.
As a contrast to wild fisheries, farmed fisheries can operate in sheltered coastal waters, in rivers, lakes and pond
A pond is a small, still, land-based body of water formed by pooling inside a depression (geology), depression, either naturally or artificiality, artificially. A pond is smaller than a lake and there are no official criteria distinguishing ...
s, or in enclosed bodies of water such as pools or fish tank
An aquarium (: aquariums or aquaria) is a vivarium of any size having at least one transparent side in which aquatic plants or animals are kept and displayed. fishkeeping, Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, aquati ...
s. Farmed fisheries are technological in nature, and revolve around developments in aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. Nelu ...
. Farmed fisheries are expanding, and Chinese
Chinese may refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people identified with China, through nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**Han Chinese, East Asian ethnic group native to China.
**'' Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic ...
aquaculture in particular is making many advances. Nevertheless, the majority of fish consumed by humans continues to be sourced from wild fisheries. As of the early 21st century, fish is humanity's only significant wild food source
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin and contains essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is inges ...
.
Marine and inland production

 According to the
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, , translates ...
(FAO), the world harvest by commercial fisheries
Commercial fishing is the activity of catching fish and other seafood for commercial profit, mostly from wild fisheries. It provides a large quantity of food to many countries around the world, but those who practice it as an industry must often p ...
in 2010 consisted of 88.6 million tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the s ...
s of aquatic animal
An aquatic animal is any animal, whether vertebrate or invertebrate, that lives in a body of water for all or most of its lifetime. Aquatic animals generally conduct gas exchange in water by extracting dissolved oxygen via specialised respirato ...
s captured in wild fisheries, plus another 0.9 million tons of aquatic plants
Aquatic plants, also referred to as hydrophytes, are vascular plants and non-vascular plants that have adapted to live in aquatic environments ( saltwater or freshwater). In lakes, rivers and wetlands, aquatic vegetations provide cover for aquat ...
(seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of ''Rhodophyta'' (red), '' Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
etc.). This can be contrasted with 59.9 million tonnes produced in fish farm
Fish farming or pisciculture involves commercial breeding of fish, most often for food, in fish tanks or artificial enclosures such as fish ponds. It is a particular type of aquaculture, which is the controlled cultivation and harvesting of aq ...
s, plus another 19.0 million tons of aquatic plants harvested in aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. Nelu ...
.
Marine fisheries
Topography
Ocean currents
Gyres and upwelling
Biomass
Habitats
Coastal waters
Continental shelves
Coral reefs
Open sea
Seamounts
Maritime species
Freshwater fisheries
Lakes
Worldwide, freshwater lakes have an area of 1.5 million square kilometres. Saline inland seas add another 1.0 million square kilometres. There are 28 freshwater lakes with an area greater than 5,000 square kilometres, totalling 1.18 million square kilometres or 79 percent of the total. Freshwater fisheries are essential to supporting human life around the globe whether they are used for recreation or commercial use. Climate change presents several challenges in sustaining these fisheries as waters become warmer resulting in decreased dissolved oxygen, as the toxicity of pollutants increases, and as the physiological changes in fishes and changes in their habitat systems alter what we are used to. Deoxygenation and eutrophication are two major effects that are detrimental to fish and ecosystem health and the problem is more prevalent as the size of the body of water decreases. Details on the changes occurring in fish physiology and their habitats can be found at the respective citation. Increased management and surveillance on freshwater fisheries will be vital to the longevity, sustainability, and productivity of the fisheries and essential to maintaining our food production from that source.Rivers
Pollution
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause harm. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the component ...
is the introduction of contaminants into an environment. Wild fisheries flourish in oceans, lakes, and rivers, and the introduction of contaminants is an issue of concern, especially as regards plastics, pesticides, heavy metals, and other industrial and agricultural pollutants which do not disintegrate rapidly in the environment. Land run-off and industrial, agricultural, and domestic waste enter rivers and are discharged into the sea. Pollution from ships is also a problem.
Plastic waste
Marine debris
Marine debris, also known as marine litter, is human-created solid material that has deliberately or accidentally been released in seas or the ocean. Floating oceanic debris tends to accumulate at the center of gyres and on coastlines, freque ...
is human-created waste that ends up floating in the sea. Oceanic debris tends to accumulate at the centre of gyres and coastlines, frequently washing aground where it is known as beach litter. Eighty percent of all known marine debris is plastic - a component that has been rapidly accumulating since the end of World War II. Plastics accumulate because they don't biodegrade
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradati ...
as many other substances do; while they will photodegrade on exposure to the sun, they do so only under dry conditions, as water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
inhibits this process.
Discarded plastic bag
A plastic bag, poly bag, or pouch is a type of container made of thin, flexible, plastic film, nonwoven fabric, or plastic textile. Plastic bags are used for containing and transporting goods such as foods, produce, Powder (substance), powders, ...
s, six-pack rings
Six-pack rings or six-pack yokes are a set of connected plastic rings that are used in multi-packs of beverage, particularly six-packs of beverage cans. The rings have gained notoriety because of concerns for marine debris entangling wildlife.
...
and other forms of plastic waste
Plastic pollution is the accumulation of plastic objects and particles (e.g. plastic bottles, bags and microbeads) in the Earth's environment that adversely affects humans, wildlife and their habitat. Plastics that act as pollutants are cate ...
which finish up in the ocean present dangers to wildlife and fisheries. Aquatic life can be threatened through entanglement, suffocation, and ingestion.
Nurdles, also known as mermaids' tears, are plastic pellets typically under five millimetres in diameter, and are a major contributor to marine debris. They are used as a raw material in plastics manufacturing, and are thought to enter the natural environment
The natural environment or natural world encompasses all life, biotic and abiotic component, abiotic things occurring nature, naturally, meaning in this case not artificiality, artificial. The term is most often applied to Earth or some parts ...
after accidental spillages. Nurdles are also created through the physical weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals (as well as wood and artificial materials) through contact with water, atmospheric gases, sunlight, and biological organisms. It occurs '' in situ'' (on-site, with little or no move ...
of larger plastic debris. They strongly resemble fish eggs
Roe, ( ) or hard roe, is the fully ripe internal egg masses in the ovaries, or the released external egg masses, of fish and certain marine animals such as shrimp, scallop, sea urchins and squid. As a seafood, roe is used both as a cooked in ...
, only instead of finding a nutritious meal, any marine wildlife that ingests them will likely starve, be poisoned and die.
Many animals that live on or in the sea consume flotsam by mistake, as it often looks similar to their natural prey. Plastic debris, when bulky or tangled, is difficult to pass, and may become permanently lodged in the digestive tracts of these animals, blocking the passage of food and causing death through starvation or infection. Tiny floating particles also resemble zooplankton
Zooplankton are the heterotrophic component of the planktonic community (the " zoo-" prefix comes from ), having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequent ...
, which can lead filter feeders
Filter feeders are aquatic animals that acquire nutrients by feeding on organic matters, food particles or smaller organisms (bacteria, microalgae and zooplanktons) suspended in water, typically by having the water pass over or through a spec ...
to consume them and cause them to enter the ocean food chain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web, often starting with an autotroph (such as grass or algae), also called a producer, and typically ending at an apex predator (such as grizzly bears or killer whales), detritivore (such as ...
. In samples taken from the North Pacific Gyre
The North Pacific Gyre (NPG) or North Pacific Subtropical Gyre (NPSG), located in the northern Pacific Ocean, is one of the five major oceanic gyres. This gyre covers most of the northern Pacific Ocean. It is the largest ecosystem on Earth, loca ...
in 1999 by the Algalita Marine Research Foundation, the mass of plastic exceeded that of zooplankton by a factor of six. More recently, reports have surfaced that there may now be 30 times more plastic than plankton, the most abundant form of life in the ocean.
Toxic additives
Additive may refer to:
Mathematics
* Additive function, a function in number theory
* Additive map, a function that preserves the addition operation
* Additive set-function see Sigma additivity
* Additive category, a preadditive category with fin ...
used in the manufacture of plastic materials can leach out into their surroundings when exposed to water. Waterborne hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thu ...
pollutants collect and magnify on the surface of plastic debris, thus making plastic far more deadly in the ocean than it would be on land. Hydrophobic contaminants are also known to bioaccumulate
Bioaccumulation is the gradual accumulation of substances, such as pesticides or other chemicals, in an organism. Bioaccumulation occurs when an organism absorbs a substance faster than it can be lost or eliminated by catabolism and excretion. Th ...
in fatty tissues, biomagnifying up the food chain and putting great pressure on apex predator
An apex predator, also known as a top predator or superpredator, is a predator at the top of a food chain, without natural predators of its own.
Apex predators are usually defined in terms of trophic dynamics, meaning that they occupy the hig ...
s. Some plastic additives are known to disrupt the endocrine system
The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant Organ (biology), organs. In vertebrat ...
when consumed, others can suppress the immune system or decrease reproductive rates.
Toxins
lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
, nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
, arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
and cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12 element, group 12, zinc and mercury (element), mercury. Like z ...
. Other persistent toxins are PCBs
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are organochlorine compounds with the formula C12 H10−''x'' Cl''x''; they were once widely used in the manufacture of carbonless copy paper, as heat transfer fluids, and as dielectric and coolant fluids f ...
, DDT
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, commonly known as DDT, is a colorless, tasteless, and almost odorless crystalline chemical compound, an organochloride. Originally developed as an insecticide, it became infamous for its environmental impacts. ...
, pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s, furan
Furan is a Heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic Ring (chemistry), ring with four carbon Atom, atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as f ...
s, dioxin
Dioxin may refer to a number of different substances. Most notably:
* 1,2-Dioxin or 1,4-dioxin, two unsaturated heterocyclic 6-membered rings in which two carbon atoms have been replaced by oxygen atoms, which gives the molecular formula C4H4O2 ...
s and phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (− O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, . Phenolic compounds ar ...
.
Such toxins can accumulate in the tissues of many species of aquatic life in a process called bioaccumulation
Bioaccumulation is the gradual accumulation of substances, such as pesticides or other chemicals, in an organism. Bioaccumulation occurs when an organism absorbs a substance faster than it can be lost or eliminated by catabolism and excretion. T ...
. They are also known to accumulate in benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning "the depths". ...
environments, such as estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
and bay mud
Bay mud consists of thick deposits of soft, unconsolidated silty clay, which is saturated with water; these soil layers are situated at the bottom of certain estuary, estuaries, which are normally in temperate regions that have experienced cyclic ...
s: a geological record of human activities of the last century.
Some specific examples are
* Chinese and Russian industrial pollution such as phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (− O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, . Phenolic compounds ar ...
and heavy metals in the Amur River
The Amur River () or Heilong River ( zh, s=黑龙江) is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China (historically the Outer and Inner Manchuria). The Amur ''proper'' is ...
have devastated fish stocks and damaged its estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime enviro ...
soil.
* Wabamun Lake
Wabamun Lake (sometimes spelled Wabumun) is one of the most heavily used lakes in Alberta, Canada. It lies west of Edmonton. It is long and wide, covers and is at its deepest, with somewhat clear water.
Its name derives from the Cree langu ...
in Alberta
Alberta is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Canada. It is a part of Western Canada and is one of the three Canadian Prairies, prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to its west, Saskatchewan to its east, t ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, once the best whitefish lake in the area, now has unacceptable levels of heavy metals in its sediment and fish.
* Acute and chronic pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause harm. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the component ...
events have been shown to impact southern California kelp forest
Kelp forests are underwater areas with a high density of kelp, which covers a large part of the world's coastlines. Smaller areas of anchored kelp are called kelp beds. They are recognized as one of the most productive and dynamic ecosystems on E ...
s, though the intensity of the impact seems to depend on both the nature of the contaminants and duration of exposure.
* Due to their high position in the food chain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web, often starting with an autotroph (such as grass or algae), also called a producer, and typically ending at an apex predator (such as grizzly bears or killer whales), detritivore (such as ...
and the subsequent accumulation of heavy metals
upright=1.2, Crystals of lead.html" ;"title="osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead
Heavy metals is a controversial and ambiguous term for metallic elements with relatively h ...
from their diet, mercury levels can be high in larger species such as bluefin and albacore
The albacore (''Thunnus alalunga''), known also as the longfin tuna, is a species of tuna of the order Scombriformes. It is found in temperate and tropical waters across the globe in the epipelagic and mesopelagic zones. There are six distinct ...
. As a result, in March 2004 the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
issued guidelines recommending that pregnant women, nursing mothers and children limit their intake of tuna and other types of predatory fish.
* Some shellfish and crabs can survive polluted environments, accumulating heavy metals or toxins in their tissues. For example, mitten crab
The Chinese mitten crab (''Eriocheir sinensis''; ; Jyutping: daai6 zaap6 haai5; Shanghainese: ''du6-zaq8-ha5'', "big sluice crab"), also known as the Shanghai hairy crab (, p ''Shànghǎi máoxiè''), is a medium-sized burrowing cr ...
s have a remarkable ability to survive in highly modified aquatic habitats, including polluted waters. The farming and harvesting of such species needs careful management if they are to be used as a food.
* Mining
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasib ...
has a poor environmental track record. For example, according to the United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent agency of the United States government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it began operation on De ...
, mining has contaminated portions of the headwaters of over 40% of watersheds in the western continental US. Much of this pollution finishes up in the sea.
* Heavy metals enter the environment through oil spill
An oil spill is the release of a liquid petroleum hydrocarbon into the environment, especially the marine ecosystem, due to human activity, and is a form of pollution. The term is usually given to marine oil spills, where oil is released into th ...
s - such as the Prestige oil spill
The ''Prestige'' oil spill occurred off the coast of Galicia, Spain in November 2002, caused by the sinking of the 26-year-old, structurally deficient oil tanker , carrying 77,000 tonnes of heavy fuel oil. During a storm, it burst a tank on 1 ...
on the Galician coast - or from other natural or anthropogenic sources.
Eutrophication
Eutrophication
Eutrophication is a general term describing a process in which nutrients accumulate in a body of water, resulting in an increased growth of organisms that may deplete the oxygen in the water; ie. the process of too many plants growing on the s ...
is an increase in chemical nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s, typically compounds containing nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
or phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared ar ...
, in an ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
. It can result in an increase in the ecosystem's primary productivity
Primary or primaries may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels
* Primary (band), from Australia
* Primary (musician), hip hop musician and record producer from South Korea
* Primary Music, Israeli record label
Works
* ...
(excessive plant growth and decay), and further effects including lack of oxygen and severe reductions in water quality, fish, and other animal populations.
The biggest culprit are rivers that empty into the ocean, and with it the many chemicals used as fertilizers
A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrition, plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from Liming (soil), liming materials or other non- ...
in agriculture as well as waste from livestock
Livestock are the Domestication, domesticated animals that are raised in an Agriculture, agricultural setting to provide labour and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, Egg as food, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The t ...
and humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
. An excess of oxygen depleting chemicals in the water can lead to hypoxia and the creation of a dead zone
Dead zone may refer to:
Science and technology
* Dead zone (cell phone), an area where cell phones cannot transmit to a nearby cell site
* Dead zone (ecology), low-oxygen areas in the world's oceans
* Dead band, the region of insensitivity of a ...
.
Surveys have shown that 54% of lakes in Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
are eutrophic
Eutrophication is a general term describing a process in which nutrients accumulate in a body of water, resulting in an increased growth of organisms that may deplete the oxygen in the water; ie. the process of too many plants growing on the s ...
; in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, 53%; in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
, 48%; in South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
, 41%; and in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
, 28%.ILEC/Lake Biwa Research Institute ds 1988–1993 Survey of the State of the World's Lakes. Volumes I-IV. International Lake Environment Committee, Otsu and United Nations Environment Programme, Nairobi. Estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
also tend to be naturally eutrophic because land-derived nutrients are concentrated where run-off enters the marine environment in a confined channel. The World Resources Institute
The World Resources Institute (WRI) is a global research non-profit organization established in 1982 with funding from the MacArthur Foundation under the leadership of James Gustave Speth. Subsequent presidents include Jonathan Lash (1993– ...
has identified 375 hypoxic coastal zones around the world, concentrated in coastal areas in Western Europe, the Eastern and Southern coasts of the US, and East Asia, particularly in Japan. In the ocean, there are frequent red tide
A harmful algal bloom (HAB), or excessive algae growth, sometimes called a red tide in marine environments, is an algal bloom that causes negative impacts to other organisms by production of natural algae-produced toxins, water deoxygenation, ...
algae blooms that kill fish and marine mammals and cause respiratory problems in humans and some domestic animals when the blooms reach close to shore.
In addition to land runoff
Surface runoff (also known as overland flow or terrestrial runoff) is the unconfined flow of water over the ground surface, in contrast to '' channel runoff'' (or ''stream flow''). It occurs when excess rainwater, stormwater, meltwater, or other ...
, atmospheric anthropogenic
Anthropogenic ("human" + "generating") is an adjective that may refer to:
* Anthropogeny, the study of the origins of humanity
Anthropogenic may also refer to things that have been generated by humans, as follows:
* Human impact on the enviro ...
fixed nitrogen
Nitrogen fixation is a chemical process by which molecular dinitrogen () is converted into ammonia (). It occurs both biologically and abiologically in chemical industries. Biological nitrogen fixation or ''diazotrophy'' is catalyzed by enz ...
can enter the open ocean. A study in 2008 found that this could account for around one third of the ocean's external (non-recycled) nitrogen supply and up to three per cent of the annual new marine biological production. It has been suggested that accumulating reactive nitrogen in the environment may have consequences as serious as putting carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Acidification
The oceans are normally a naturalcarbon sink
A carbon sink is a natural or artificial carbon sequestration process that "removes a greenhouse gas, an aerosol or a precursor of a greenhouse gas from the atmosphere". These sinks form an important part of the natural carbon cycle. An overar ...
, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Because the levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide are increasing, the oceans are becoming more acidic.
The potential consequences of ocean acidification are not fully understood, but there are concerns that structures made of calcium carbonate may become vulnerable to dissolution, affecting corals and the ability of shellfish to form shells.
A report from NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charting the seas, conducting deep-sea exploratio ...
scientists published in the journal Science in May 2008 found that large amounts of relatively acidified water are upwelling to within four miles of the Pacific continental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an islan ...
area of North America. This area is a critical zone where most local marine life lives or is born. While the paper dealt only with areas from Vancouver
Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the cit ...
to northern California, other continental shelf areas may be experiencing similar effects.
Effects of fishing
Habitat destruction
Fishing net
A fishing net or fish net is a net (device), net used for fishing. Fishing nets work by serving as an improvised fish trap, and some are indeed rigged as traps (e.g. #Fyke nets, fyke nets). They are usually wide open when deployed (e.g. by cast ...
s that have been left or lost in the ocean by fishermen are called ghost net
Ghost nets are fishing nets that have been abandoned, lost, or otherwise discarded in the ocean, lakes, and rivers. These nets, often nearly invisible in the dim light, can be left tangled on a rocky reef or drifting in the open sea. They can ...
s, and can entangle fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
, dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal in the cetacean clade Odontoceti (toothed whale). Dolphins belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontopori ...
s, sea turtle
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerh ...
s, shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the ...
s, dugong
The dugong (; ''Dugong dugon'') is a marine mammal. It is one of four living species of the order Sirenia, which also includes three species of manatees. It is the only living representative of the once-diverse family Dugongidae; its closest ...
s, crocodile
Crocodiles (family (biology), family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large, semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term "crocodile" is sometimes used more loosely to include ...
s, seabird
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adaptation, adapted to life within the marine ecosystem, marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent ...
s, crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura (meaning "short tailed" in Greek language, Greek), which typically have a very short projecting tail-like abdomen#Arthropoda, abdomen, usually hidden entirely under the Thorax (arthropo ...
s, and other creatures. Acting as designed, these nets restrict movement, causing starvation, laceration and infection, and—in those that need to return to the surface to breathe—suffocation.
Fishing operations often use trawl netting dragging and dredging them across the ocean bottom. Numerous habitats and ecosystems are disturbed and destroyed by trawling including coral reefs, sediments, and grasses that provide feeding and breeding grounds for a plethora of marine organisms. Coastal habitats such as mangroves are often sites of aquaculture farming practices in which the mangroves are either destroyed for easier use of the land or experience harmful conditions due to the farm being abandoned once the area becomes too polluted with excess nutrients.
Overfishing
Some specific examples of overfishing. * On the east coast of theUnited States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, the availability of bay scallops has been greatly diminished by the overfishing of sharks in the area. A variety of sharks have, until recently, fed on rays
Ray or RAY may refer to:
Fish
* Ray (fish), any cartilaginous fish of the superorder Batoidea
* Ray (fish fin anatomy), the bony or horny spine on ray-finned fish
Science and mathematics
* Half-line (geometry) or ray, half of a line split at an ...
, which are a main predator of bay scallops. With the shark population reduced, in some places almost totally, the rays have been free to dine on scallops to the point of greatly decreasing their numbers.
* Chesapeake Bay's once-flourishing oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but no ...
populations historically filtered the estuary's entire water volume of excess nutrients every three or four days. Today that process takes almost a year, and sediment, nutrients, and algae can cause problems in local waters. Oysters filter these pollutants, and either eat them or shape them into small packets that are deposited on the bottom where they are harmless.
* The Australian government alleged in 2006 that Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
illegally overfished southern bluefin tuna
The southern bluefin tuna (''Thunnus maccoyii'') is a tuna of the family Scombridae found in open southern Hemisphere waters of all the world's oceans mainly between 30°S and 50°S, to nearly 60°S. At up to and weighing up to , it is amon ...
by taking 12,000 to 20,000 tonnes per year instead of their agreed 6,000 tonnes; the value of such overfishing would be as much as US$2 billion. Such overfishing has resulted in severe damage to stocks. "Japan's huge appetite for tuna will take the most sought-after stocks to the brink of commercial extinction unless fisheries agree on more rigid quotas" stated the WWF. Japan disputes this figure, but acknowledges that some overfishing has occurred in the past.
* Jackson, Jeremy B C et al. (2001''Historical overfishing and the recent collapse of coastal ecosystems''
Science 293:629-638. Our World in Data provides a figure showing the trend in global fishing exploitation over a few decades to reveal the intensifying circumstances at hand: Overfishing presents many threats to fish population densities, obviously. However, as these populations plummet below the maximum sustainable yield (MSY) value for the specific population, you are now risking the loss of biodiversity and possibility for extinction due to less diversity. This loss in diversity is especially concerning as we deal with environmental changes from climate change since less diversity decreases a populations ability to adapt and survive the alterations of the habitat.
Loss of biodiversity
Eachspecies
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
in an ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
is affected by the other species in that ecosystem. There are very few single prey-single predator relationships. Most prey are consumed by more than one predator, and most predators have more than one prey. Their relationships are also influenced by other environmental factors. In most cases, if one species is removed from an ecosystem, other species will most likely be affected, up to the point of extinction.
Species biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
is a major contributor to the stability of ecosystems. When an organism exploits a wide range of resources, a decrease in biodiversity is less likely to have an impact. However, for an organism which exploit only limited resources, a decrease in biodiversity is more likely to have a strong effect.
Reduction of habitat, hunting and fishing of some species to extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
or near extinction, and pollution tend to tip the balance of biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
. For a systematic treatment of biodiversity within a trophic level
The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. Within a food web, a food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may, in turn, be eaten themselves. The trophic level of an organism is the ...
, see unified neutral theory of biodiversity
The unified neutral theory of biodiversity and biogeography (here "Unified Theory" or "UNTB") is a theory and the title of a monograph by ecologist Stephen P. Hubbell. It aims to explain the diversity and relative abundance of species in ecolo ...
.
Threatened species
The global standard for recordingthreatened
A threatened species is any species (including animals, plants and fungi) which is vulnerable to extinction in the near future. Species that are threatened are sometimes characterised by the population dynamics measure of ''critical depensatio ...
marine species is the IUCN
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the status ...
Red List of Threatened Species. This list is the foundation for marine conservation priorities worldwide. A species is listed in the threatened category if it is considered to be critically endangered
An IUCN Red List critically endangered (CR or sometimes CE) species is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as facing an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. As of December 2023, of t ...
, endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
, or vulnerable. Other categories are near threatened
A near-threatened species is a species which has been Conservation status, categorized as "Near Threatened" (NT) by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as that may be vulnerable to Endangered species, endangerment in the ne ...
and data deficient
A data deficient (DD) species is one which has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as offering insufficient information for a proper assessment of conservation status to be made. This does not necessaril ...
.
Marine
Many marine species are under increasing risk of extinction and marinebiodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
is undergoing potentially irreversible loss due to threats such as overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing Fish stocks, fish stock), resu ...
, bycatch
Bycatch (or by-catch), in the fishing industry, is a fish or other marine species that is caught unintentionally while fishing for specific species or sizes of wildlife. Bycatch is either the wrong species, the wrong sex, or is undersized or juve ...
, climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
, invasive species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native spec ...
and coastal development.
By 2008, the IUCN
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the status ...
had assessed about 3,000 marine species. This includes assessments of known species of shark, ray, chimaera, reef-building coral, grouper, marine turtle, seabird, and marine mammal. Almost one-quarter (22%) of these groups have been listed as threatened.IUCN
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the status ...
Status of the world's marine species
/ref> * Sharks, rays, and chimaeras: are deep water
pelagic
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean and can be further divided into regions by depth. The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the sur ...
species, which makes them difficult to study in the wild. Not a lot is known about their ecology and population status. Much of what is currently known is from their capture in nets from both targeted and accidental catch. Many of these slow growing species are not recovering from overfishing by shark fisheries around the world.
* Groupers: Major threats are overfishing, particularly the uncontrolled fishing of small juveniles and spawning adults.
* Coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in group ...
s: The primary threats to coral
Corals are colonial marine invertebrates within the subphylum Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact Colony (biology), colonies of many identical individual polyp (zoology), polyps. Coral species include the important Coral ...
s are bleaching and disease which has been linked to an increase in sea temperatures. Other threats include coastal development, coral extraction, sedimentation and pollution. The coral triangle
The Coral Triangle (CT) is a roughly triangular area in the tropical waters around Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, Solomon Islands, and Timor-Leste. This area contains at least 500 species of reef-building corals in each ...
(Indo-Malay-Philippine archipelago) region has the highest number of reef-building coral species in threatened category as well as the highest coral species diversity. The loss of coral reef ecosystems will have devastating effects on many marine species, as well as on people that depend on reef resources for their livelihoods.
* Marine mammals: include whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully Aquatic animal, aquatic placental mammal, placental marine mammals. As an informal and Colloquialism, colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea ...
s, dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal in the cetacean clade Odontoceti (toothed whale). Dolphins belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontopori ...
s, porpoise
Porpoises () are small Oceanic dolphin, dolphin-like cetaceans classified under the family Phocoenidae. Although similar in appearance to dolphins, they are more closely related to narwhals and Beluga whale, belugas than to the Oceanic dolphi ...
s, seal
Seal may refer to any of the following:
Common uses
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, also called "true seal"
** Fur seal
** Eared seal
* Seal ( ...
s, sea lion
Sea lions are pinnipeds characterized by external ear flaps, long foreflippers, the ability to walk on all fours, short and thick hair, and a big chest and belly. Together with the fur seals, they make up the family Otariidae, eared seals. ...
s, walrus
The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large pinniped marine mammal with discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. It is the only extant species in the family Odobeni ...
es, sea otter
The sea otter (''Enhydra lutris'') is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern Pacific Ocean, North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between , making them the heaviest members of ...
, marine otter
The marine otter (''Lontra felina'') is a rare and relatively unknown South American mammal of the weasel family (Mustelidae). The scientific name means "feline otter", and in Spanish, the marine otter is also often referred to as : "marine c ...
, manatee
Manatees (, family (biology), family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivory, herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing t ...
s, dugong
The dugong (; ''Dugong dugon'') is a marine mammal. It is one of four living species of the order Sirenia, which also includes three species of manatees. It is the only living representative of the once-diverse family Dugongidae; its closest ...
and the polar bear
The polar bear (''Ursus maritimus'') is a large bear native to the Arctic and nearby areas. It is closely related to the brown bear, and the two species can Hybrid (biology), interbreed. The polar bear is the largest extant species of bear ...
. Major threats include entanglement in ghost net
Ghost nets are fishing nets that have been abandoned, lost, or otherwise discarded in the ocean, lakes, and rivers. These nets, often nearly invisible in the dim light, can be left tangled on a rocky reef or drifting in the open sea. They can ...
s, targeted harvesting, noise pollution from military and seismic sonar, and boat strikes. Other threats are water pollution, habitat loss from coastal development, loss of food sources due to the collapse of fisheries, and climate change.
* Seabirds: Major threats include longline fisheries and gillnet
Gillnetting is a fishing method that uses gillnets: vertical panels of netting that hang from a line with regularly spaced floaters that hold the line on the surface of the water. The floats are sometimes called "corks" and the line with corks is ...
s, oil spill
An oil spill is the release of a liquid petroleum hydrocarbon into the environment, especially the marine ecosystem, due to human activity, and is a form of pollution. The term is usually given to marine oil spills, where oil is released into th ...
s, and predation by rodents and cats in their breeding grounds. Other threats are habitat loss and degradation from coastal development, logging and pollution.
* Marine turtles: Marine turtles lay their eggs on beaches, and are subject to threats such as coastal development, sand mining, and predators, including humans who collect their eggs for food in many parts of the world. At sea, marine turtles can be targeted by small scale subsistence fisheries, or become bycatch
Bycatch (or by-catch), in the fishing industry, is a fish or other marine species that is caught unintentionally while fishing for specific species or sizes of wildlife. Bycatch is either the wrong species, the wrong sex, or is undersized or juve ...
during longline and trawling
Trawling is an industrial method of fishing that involves pulling a fishing net through the water behind one or more boats. The net used for trawling is called a trawl. This principle requires netting bags which are towed through water to catch di ...
activities, or become entangled in ghost net
Ghost nets are fishing nets that have been abandoned, lost, or otherwise discarded in the ocean, lakes, and rivers. These nets, often nearly invisible in the dim light, can be left tangled on a rocky reef or drifting in the open sea. They can ...
s or struck by boats.
An ambitious project, called the Global Marine Species Assessment, is under way to make IUCN Red List assessments for another 17,000 marine species by 2012. Groups targeted include the approximately 15,000 known marine fishes, and important habitat-forming primary producer
Primary or primaries may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels
* Primary (band), from Australia
* Primary (musician), hip hop musician and record producer from South Korea
* Primary Music, Israeli record label
Work ...
s such mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have particular adaptations to take in extra oxygen a ...
s, seagrass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine (ocean), marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four Family (biology), families (Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and ...
es, certain seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of ''Rhodophyta'' (red), '' Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
s and the remaining coral
Corals are colonial marine invertebrates within the subphylum Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact Colony (biology), colonies of many identical individual polyp (zoology), polyps. Coral species include the important Coral ...
s; and important invertebrate groups including mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s and
echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any animal of the phylum Echinodermata (), which includes starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars and sea cucumbers, as well as the sessile sea lilies or "stone lilies". While bilaterally symmetrical as ...
s.
Freshwater
Freshwater fisheries have a disproportionately high diversity of species compared to other ecosystems. Although freshwater habitats cover less than 1% of the world's surface, they provide a home for over 25% of known vertebrates, more than 126,000 known animal species, about 24,800 species offreshwater fish
Freshwater fish are fish species that spend some or all of their lives in bodies of fresh water such as rivers, lakes, ponds and inland wetlands, where the salinity is less than 1.05%. These environments differ from marine habitats in many wa ...
, molluscs
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
, crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura (meaning "short tailed" in Greek language, Greek), which typically have a very short projecting tail-like abdomen#Arthropoda, abdomen, usually hidden entirely under the Thorax (arthropo ...
s and dragonflies
A dragonfly is a flying insect belonging to the infraorder Anisoptera below the order Odonata. About 3,000 extant species of dragonflies are known. Most are tropical, with fewer species in temperate regions. Loss of wetland habitat threate ...
, and about 2,600 macrophyte
Aquatic plants, also referred to as hydrophytes, are vascular plants and non-vascular plants that have adapted to live in aquatic environments ( saltwater or freshwater). In lakes, rivers and wetlands, aquatic vegetations provide cover for aquat ...
s.
Continuing industrial and agricultural developments place huge strain on these freshwater systems. Waters are polluted or extracted at high levels, wetlands are drained, rivers channelled, forests deforestated leading to sedimentation, invasive species are introduced, and over-harvesting occurs.
In the 2008 IUCN
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the status ...
Red List, about 6,000 or 22% of the known freshwater species have been assessed at a global scale, leaving about 21,000 species still to be assessed. This makes clear that, worldwide, freshwater species are highly threatened, possibly more so than species in marine fisheries. However, a significant proportion of freshwater species are listed as data deficient
A data deficient (DD) species is one which has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as offering insufficient information for a proper assessment of conservation status to be made. This does not necessaril ...
, and more field surveys are needed.
Fisheries management
A recent paper published by theNational Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, NGO, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the ...
of the USA warns that: "Synergistic effects of habitat destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease ...
, overfishing, introduced species, warming, acidification, toxins, and massive runoff of nutrients are transforming once complex ecosystems like coral reefs and kelp forests into monotonous level bottoms, transforming clear and productive coastal seas into anoxic dead zones, and transforming complex food webs topped by big animals into simplified, microbially dominated ecosystems with boom and bust cycles of toxic dinoflagellate blooms, jellyfish, and disease".Jackson, Jeremy B C (2008''Ecological extinction and evolution in the brave new ocean''
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA.
See also
*Fishing by country
This page lists the world fisheries' production. The tonnage from capture and aquaculture is listed by country.
Fish, crustaceans, molluscs, etc.
Following is a sortable table of the world fisheries' harvest in 2022. The tonnage from capture and ...
* List of countries by seafood consumption
This list of countries by seafood consumption gives a comprehensive overview that ranks nations worldwide based on their annual seafood consumption per capita. Seafood includes fish and other important marine animals. While national meat consump ...
* List of harvested aquatic animals by weight
This is a list of aquatic animals that are harvested commercially in the greatest amounts, listed in order of tonnage per year (2012) by the Food and Agriculture Organization. Species listed here have an annual tonnage in excess of 160,000 tonnes ...
* Ocean fisheries A fishery is an area with an associated fish or aquatic population which is harvested for its commercial value. Fisheries can be wild or farmed. Most of the world's wild fisheries are in the ocean. This article is an overview of ocean fisheries.
...
* Population dynamics of fisheries
A fishery is an area with an associated fish or aquatic population which is harvested for its commercial or recreational value. Fisheries can be wild or farmed. Population dynamics describes the ways in which a given population grows and shr ...
* World fish production
The global commercial production for human use of fish and other aquatic organisms occurs in two ways: they are either captured wild by commercial fishing or they are cultivated and harvested using aquacultural and farming techniques.
According ...
References
* World Ocean Atlas (2005''World ocean database.''
Retrieved 19 April 2008. * The Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia (2007
Retrieved 19 April 2008. * Jacques, Peter (2006
''Globalization and the world ocean''
Rowman Altamira. * Pauly, Daniel; Watson, Reg and Alder, Jackie (2005
''Global trends in world fisheries: impacts on marine ecosystems and food security''
Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society, Volume 360, Number 1453. * De Young, Cassandra (2007
''
FAO
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition ...
'', Fisheries Technical Paper 488, Rome. .
External links
* International Nitrogen InitiativeWeb site
Population Distribution within 100 km of Coastlines
(2000)
World Resources Institute
The World Resources Institute (WRI) is a global research non-profit organization established in 1982 with funding from the MacArthur Foundation under the leadership of James Gustave Speth. Subsequent presidents include Jonathan Lash (1993– ...
.
* NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charting the seas, conducting deep-sea exploratio ...
''Carbon cycle science''
{{Fishing industry topics Fishing industry