The Canal du Midi (; ) is a long canal in
Southern France
Southern France, also known as the south of France or colloquially in French as , is a geographical area consisting of the regions of France that border the Atlantic Ocean south of the Marais Poitevin,Louis Papy, ''Le midi atlantique'', Atlas e ...
(). Originally named the ''Canal Royal en Languedoc'' (Royal Canal in Languedoc) and renamed by
French revolutionaries to ''Canal du Midi'' in 1789, the canal is considered one of the greatest construction works of the 17th century.
The canal connects the
Garonne to the
Étang de Thau on the
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
and, along with the long
Canal de Garonne, forms the
Canal des Deux Mers, joining the Atlantic to the Mediterranean.
Strictly speaking, ''"Canal du Midi"'' refers to the portion initially constructed from
Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
to the Mediterranean – the Deux-Mers canal project aimed to link together several sections of navigable waterways to join the Mediterranean and the Atlantic: first the Canal du Midi, then the
Garonne which was more or less navigable between Toulouse and
Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( ; ; Gascon language, Gascon ; ) is a city on the river Garonne in the Gironde Departments of France, department, southwestern France. A port city, it is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the Prefectures in F ...
, then the
Garonne Lateral Canal built later, and finally the
Gironde estuary after Bordeaux.
Jean-Baptiste Colbert authorized the start of work by royal edict in October 1666, with the aim of developing the
wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
trade, under the supervision of
Pierre-Paul Riquet, and construction lasted from 1666 to 1681, during the reign of
Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
. The Canal du Midi is one of the oldest canals of Europe still in operation (the prototype being the
Briare Canal). The challenges in these works are closely related to the challenges of inland water transport today. The key challenge, raised by Pierre-Paul Riquet, was to convey water from the
Montagne Noire (Black Mountains) to the
Seuil de Naurouze, the highest point of the canal.
The Canal du Midi was inscribed as a
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
in 1996, because of its outstanding engineering and artistic design, and it was designated as an
International Historic Civil Engineering Landmark in 2016.
Introduction
Location and profile of the canal

The Canal du Midi is located in the south of France, in the departments of
HĂ©rault
HĂ©rault (; , ) is a departments of France, department of the Regions of France, region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania, Southern France. Named after the HĂ©rault (river), HĂ©rault River, its Prefectures in France, prefecture is M ...
,
Aude
Aude ( ; ) is a Departments of France, department in Southern France, located in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region and named after the river Aude (river), Aude. The departmental council also calls it " ...
, and
Haute-Garonne
Haute-Garonne (; , ; ''Upper Garonne'') is a department in the southwestern French region of Occitanie. Named after the river Garonne, which flows through the department. Its prefecture and main city is Toulouse, the country's fourth-largest. ...
. It is long, starting in the west at
Port de l'Embouchure,
Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
and terminating in the east at ''Les Onglous'',
Marseillan, where the canal opens into the
Ă©tang de Thau (between
Agde and
Sète).
The Canal du Midi is a
summit-level canal, climbing from Toulouse on the Atlantic side over a distance of to the
Seuil de Naurouze or summit level, where the feeder canal enters. The total rise is , and the summit level is at an altitude of . This difference in level down to the sea is covered over the remaining distance of from Naurouze to Les Onglous on the Étang de Thau.
The design canal depth is with a minimum of . The
draft
Draft, the draft, or draught may refer to:
Watercraft dimensions
* Draft (hull), the distance from waterline to keel of a vessel
* Draft (sail), degree of curvature in a sail
* Air draft, distance from waterline to the highest point on a v ...
allowed is although regular users advise that even with boats will occasionally touch the bottom because of silt deposits in many places. The width on the surface is on average with variations between and . Finally, the width of the canal bed is .
This longitudinal profile of the Canal du Midi shows it rising from
Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
(1) to the
Seuil de Naurouze (2), then dropping down to
Castelnaudary (3),
Carcassonne
Carcassonne is a French defensive wall, fortified city in the Departments of France, department of Aude, Regions of France, region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania. It is the prefectures in France, prefecture of the department.
...
(4) and
Trèbes (5). The canal continues to
BĂ©ziers after passing through the
Fonserannes Locks (6), then
Agde (7), to finish at
Sète on the
Ă©tang de Thau (8).
The longest
canal pound
A canal pound (from impound), reach, or level (American usage), is the stretch of level water impounded between two canal locks. Canal pounds can vary in length from the non-existent, where two or more immediately adjacent locks form a canal lock# ...
is between
Argens Lock and the
Fonserannes Locks, while the shortest canal pound is between the two
Fresquel locks.
[René Gast, ''The Canal du Midi and the Canals from the Atlantic to the Mediterranean'', éditions Ouest-France, 2000, , p. 22 ]
Legal status
For historical reasons, the Canal du Midi has a unique legal status, which was
codified in 1956
[A. Homont, noted by the ]Conseil d'État
In France, the (; Council of State) is a governmental body that acts both as legal adviser to the executive branch and as the supreme court for administrative justice, which is one of the two branches of the French judiciary system. Establ ...
, ''Ministry of Public Works and Transport c. Dame Boudet'', 3 May 1963, ''Judicial Topics: administrative right'', 1963, pp. 489-490. in the ''Public Code of waterways and inland navigation'', then in the ''General code of the property of public persons''. Under Article L. 2111-11 of the Code, public domain of the canal is determined by reference to the
fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
once granted to
Pierre-Paul Riquet and limits were set by an official report in 1772. The staff quarters and warehouses, as well as the
Lampy reservoir, were also added. Articles L. 2124-20 to L. 2124-25 set rules for maintenance of the canal, which is generally the responsibility of the public entity that owns it, with the participation of
communes and, in some cases, waterside residents.
Under the Act of 27 November 1897,
the State of France owns the Canal du Midi and its management is delegated to the public body
Voies Navigables de France, attached to the Ministry of Transport.
History
Abandoned projects

The building of a
canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface ...
was an old idea. Numerous and sometimes utopian projects were devised to build a canal between the
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
and the
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
. Leaders such as
Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
,
Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68) was a Roman emperor and the final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 until his ...
,
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
,
François I,
Charles IX and
Henry IV had dreamed of it, as it is a true political and economic issue. King
François I brought
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 1452 - 2 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested o ...
to France in 1516 and commissioned a survey of a route from the Garonne at Toulouse to the
Aude
Aude ( ; ) is a Departments of France, department in Southern France, located in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region and named after the river Aude (river), Aude. The departmental council also calls it " ...
at
Carcassonne
Carcassonne is a French defensive wall, fortified city in the Departments of France, department of Aude, Regions of France, region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania. It is the prefectures in France, prefecture of the department.
...
.
The construction of such a structure would save vessels (of trade but also the
king's galleys) and goods from sailing around the
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
which could take a month to complete. At that time shipping was fraught with dangers such as
piracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and valuable goods, or taking hostages. Those who conduct acts of piracy are call ...
and the
Barbary pirates
The Barbary corsairs, Barbary pirates, Ottoman corsairs, or naval mujahideen (in Muslim sources) were mainly Muslim corsairs and privateers who operated from the largely independent Barbary states. This area was known in Europe as the Barba ...
.
[Franck Ferrand, ''The Great adventure of the Canal du Midi'', transmitted in ''Au cœur de l'histoire'' on Europe 1, 29 May 2013 ]
The most realistic projects were presented to the King in the 16th century. A first draft was presented by
Nicolas Bachelier in 1539 to the
Estates of Languedoc[''Canal du Midi''](_blank)
Structurae, consulted on 20 August 2007. then a second in 1598 by Pierre Reneau and finally a third project was proposed by Bernard Aribat de BĂ©ziers in 1617. These projects were abandoned because they did not give enough thought to the water supply for the canal and provided a system of diversion of water from
Pyrénées
The Pyrenees are a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. They extend nearly from their union with the Cantabrian Mountains to Cap de Creus on the Mediterranean coast, reaching a maximum elevation of at the peak of Aneto.
F ...
rivers too complex or impossible to implement. In 1650 another engineer also proposed to divert water from the
Ariège to
Cintegabelle
Cintegabelle (; ) is a commune in the Haute-Garonne department in southwestern France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include ...
to bring a non-navigable canal to Pech-David near
Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
. Again, the question arose of how to carry water to the
Seuil de Naurouze at a greater height than that of Toulouse.
The projects were not launched for fear of losing too much money and conviction of the human impossibility to dig such a canal. The major problem was how to supply the summit sections with enough water.
[Chandra Mukerji, ''Impossible Engineering'' Princeton: Princeton University Press, 304 pages, ][Jean-Denis Bergasse ''Le Canal du Midi'' Cessenon: J-D Bergasse 1982-1984, .]
Nevertheless,
Pierre-Paul Riquet, a wealthy collector of
salt tax
A salt tax refers to the direct taxation of salt, usually levied proportionately to the volume of salt purchased. The taxation of salt dates as far back as 300 BC, as salt has been a valuable good used for gifts and religious offerings since 605 ...
in
Languedoc
The Province of Languedoc (, , ; ) is a former province of France.
Most of its territory is now contained in the modern-day region of Occitanie in Southern France. Its capital city was Toulouse. It had an area of approximately .
History
...
proposed a more convincing project than his predecessors. When
Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
received his proposal through the
Archbishop of Toulouse (Charles-François Anglure of Bourlemont) in 1662 he saw the opportunity to deprive
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
of part of its resources, and the opportunity to mark his reign with an imperishable work.

English translation:
Study of the project
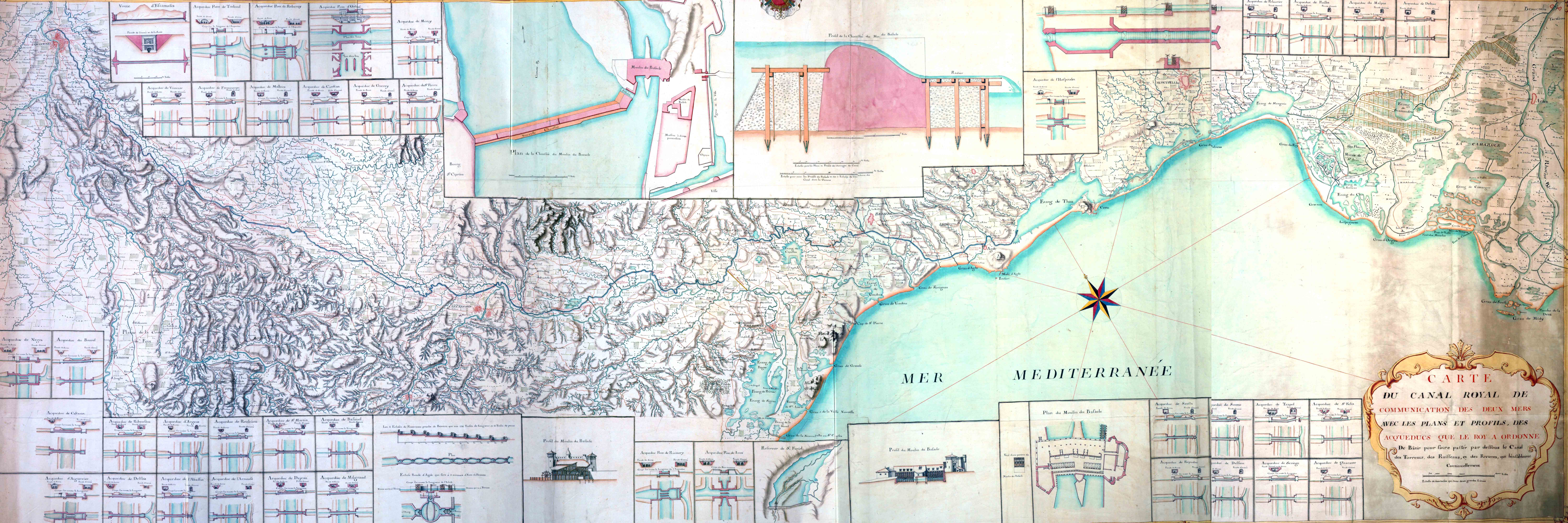
Compared to canals, managing rivers is difficult but only one canal is required between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. Unlike a river, it is easier to manage the flow of a canal to ensure a constant flow of traffic throughout the year.
The Canal du Midi is a
summit-level canal because it must pass over a height between two valleys. The construction of this canal required passage through the
Seuil de Naurouze or the Seuil de Graissens.
Thirty years passed from the start of planning to the commencement of work: a similar project was also studied by a committee of which Riquet's father was a member.
Highlights
In 1660, Riquet found the solution to the main problem: the water supply to the summit point to feed both sides of the canal. His idea was to get water flowing from the
Montagne Noire. His important knowledge of the
hydrography of the Montagne Noire and Sor allowed him to imagine an ingenious irrigation system. He was inspired by the French engineer
Adam de Craponne who had implemented the same system for the
Craponne Canal.

For this, he planned to recover the mountain waters in dams and reservoirs and then forward them to the
Seuil de Naurouze through channels crossing the Seuil de Graissens. The water from the Sor passing near
Revel was the main supply envisaged by Riquet. Other rivers from the Montagne Noire were also part of the system such as the Alzeau, the Laudot, the Rieutort, the Bernassonne, and the . The Montagne Noire is a region with twice the rainfall of the plain of
Lauragais with 1400 millimetres per year at around above sea level. To store the river water he planned to create three basins: the Reservoir of Lampy-Vieux, a hexagonal harbour basin at Naurouze, and the
Bassin de Saint-Ferréol with a large earth dam across the mouth of the valley of the Laudot stream.
In 1664, during the study of the project, the
Estates of Languedoc asked Riquet to put into practice his idea experimentally. He then built a test channel diverting water from the Sor to the
Seuil de Naurouze. It was the
Rigole de la plaine which he completed in 1665 and used to prove that it is possible to bring water to the highest points of the course of the canal.
[Michel Cotte, ''Canal du Midi, marvel of Europe'', Paris: Belin, 2003, 191 pages, , p. 26. ] This was the event that reassured the Committee of Experts that the king had set up on site to inspect the choices and plans prepared by Riquet. From that moment
Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
knew that the canal was technically feasible.
Inaccuracies by Pierre-Paul Riquet

Riquet studied in depth the supply of water to the canal at the Seuil de Naurouze. His study appeared rigorous and included a pilot phase with the construction of the
Rigole de la plaine to substantiate his claim. The project still remained unclear in many respects especially the route of the canal. This route was not final and was not precise as it would be today for a highway project or
high-speed railway. Only the directions of the route were known and plotted on a map. Changes in the route could be made by the Contractor depending on the difficulties he encountered on the ground.
On the Atlantic side, he proposed several layouts: one to pass by
Castres
Castres (; ''Castras'' in the Languedocian dialect, Languedocian dialect of Occitan language, Occitan) is the sole Subprefectures in France, subprefecture of the Tarn (department), Tarn Departments of France, department in the Occitania (adminis ...
and
Revel through the Seuil de Graissens and
Agout. In fact, this river was already under development for navigation. Another route would pass by the Girou river and avoid
Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
as in the preceding route. On the Mediterranean side, the route was not set. He would use the Fresquel until the
Aude
Aude ( ; ) is a Departments of France, department in Southern France, located in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region and named after the river Aude (river), Aude. The departmental council also calls it " ...
but the arrival on the coast was first intended to be at
Narbonne
Narbonne ( , , ; ; ; Late Latin:) is a commune in Southern France in the Occitanie region. It lies from Paris in the Aude department, of which it is a sub-prefecture. It is located about from the shores of the Mediterranean Sea and was ...
then at
Sète.
In 1663 Riquet conducted field studies to finally fix the path on the Atlantic side by the seuil de Naurouze along the valley of the
Hers-Vif to
Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
downstream of the
Garonne. The navigable part of the river is downstream of
Bazacle which was a ford in the centre of Toulouse, blocking navigation. The canal could not consider not going through the economic heart of the region so therefore the final route was via Castres and the Girou.
Study techniques
Pierre-Paul Riquet had no technical training and learnt on the job. He regularly practised experiments and field observations. His technique remained highly empirical because at that time applied science and hydraulic techniques through laws or concepts had not been mastered. Even so, Riquet had a scientific approach as he systematically took measurements of
flow and made calculations of volumes. In addition, to overcome his technical shortcomings, he was surrounded by many technicians such as Hector BoutheroĂĽe,
François Andreossy surveyor and cartographer, and
Pierre Campmas an expert in water flows.
He set up experiments to prove that it was possible to bring the water to the
Seuil de Naurouze from the river Sor in the
Montagne Noire.
At his own expense, of 200,000 livres, he built a test canal, only two feet wide, and on the 9 November 1665 he opened the flow successfully. When the canal was authorized the next year, this test rigole would become the
Rigole de la plaine. He also built on his property in
Bonrepos a model of the canal with
locks,
tunnel
A tunnel is an underground or undersea passageway. It is dug through surrounding soil, earth or rock, or laid under water, and is usually completely enclosed except for the two portals common at each end, though there may be access and ve ...
s, and ''Ă©panchoirs'' (spillways) reproducing the slopes and feeding all with water.
Political and economic context
The economic situation of the country was quite difficult at the time. When
Colbert became minister he believed that domestic and international trade was not in favour of the
Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from th ...
. The
Dutch could take better advantage of trade and economic activity in the country. The prices of
grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached husk, hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and ...
dropped a lot and wine production fell in 1660. This crisis caused depreciation of land values and small farms were going bankrupt. In addition, the region of
Languedoc
The Province of Languedoc (, , ; ) is a former province of France.
Most of its territory is now contained in the modern-day region of Occitanie in Southern France. Its capital city was Toulouse. It had an area of approximately .
History
...
experienced religious conflict during the
Fronde. It was difficult to implement a policy in this area and in particular to introduce taxes such as the
salt tax
A salt tax refers to the direct taxation of salt, usually levied proportionately to the volume of salt purchased. The taxation of salt dates as far back as 300 BC, as salt has been a valuable good used for gifts and religious offerings since 605 ...
.
Colbert then saw Pierre-Paul Riquet and his project as a way to pursue a policy of economic expansion in the service of
absolutism in Languedoc. In fact, Riquet proposed himself to implement the salt tax and to build the Canal du Midi. Thus, the construction of the canal would permit the creation of a direct passage between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic without passing through the
Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Europe from Africa.
The two continents are separated by 7.7 nautical miles (14.2 kilometers, 8.9 miles) at its narrowest point. Fe ...
controlled by the Spaniards, the aim being to destroy the Spanish trade and establish a commercial flow through Languedoc. The Languedoc region had many resources such as
wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
,
wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented fruit. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the fruit and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Wine is most often made f ...
from
Minervois,
woollen cloth,
silk
Silk is a natural fiber, natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be weaving, woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is most commonly produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoon (silk), c ...
, and
salt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as r ...
which producers were struggling to export due to lack of trade. By passing through the Canal du Midi, Colbert hoped to distribute goods in the different regions of ''
le Midi'' to strengthen royal power and open up Toulouse and its region.
The edict of Louis XIV and the financing of the project
Despite a project that seemed precarious, Colbert authorized commencement of work by a royal edict in October 1666 after the approval of a committee of experts that looked at the route of the canal for several months. The project benefited significantly from the appointment of an engineer for fortifications and hydraulics –
Louis Nicolas de Clerville – who used his influence with Colbert to start the project. The decree specified the authorization of the construction of the canal, its issuing of
invitations to tender, and its awarding to the designer, Pierre-Paul Riquet, and his descendants. It also gave rights of expropriation to Riquet and describes the possibility of creating mills, warehouses and housing for the operation of the canal. The project formed a tax-exempt "fief" whose owner had the rights of
fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
and
hunting
Hunting is the Human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, and killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to obtain the animal's body for meat and useful animal products (fur/hide (sk ...
. Finally, it describes the operating procedures including the introduction of tolls, traffic organization, and ownership of vessels. The king decided to cede the ownership and operation of the facility in a particular order to overcome the potential drawbacks of a work so great. This system ensured the continued maintenance and operation of the canal even if the state's finances are at their lowest.
The work was launched in two phases each called an "enterprise". The first enterprise of connecting Toulouse to
Trèbes was estimated at 3.6 million
livres. The finances of the State, however, were not very sound and the
Estates of Languedoc were not willing to fund such a project for fear that their funds would be used for unexpected expenses. So, in exchange for the ownership and operation of the canal, Pierre-Paul Riquet proposed to finance part of the works from his own funds. The rest was to be paid by the State in exchange for profits that Riquet earned from the salt tax. The second enterprise of works between Trèbes and the
Ă©tang de Thau in December 1668 cost 5.832 million
livres plus a million more livres for the resumption of work on the port of Sète.
Ultimately, while the initial budget was six million livres, all the work together would cost between 17 and 18 million livres of the time, 40% was advanced by the King, 40% by the province, and 20% by Riquet himself, who became the owner. His descendants continued to pay two million livres for over 50 years.
Construction of the canal

At the age of 63, Riquet started his great enterprise, sending his personal engineer,
François Andreossy, and a local water expert, Pierre Roux, to the
Montagne Noire to work on the water supply. This supply system successfully fed the canal with water where it crossed the continental divide, replacing water that drained toward the two seas. The system was a masterpiece of both
hydraulic and
structural engineering
Structural engineering is a sub-discipline of civil engineering in which structural engineers are trained to design the 'bones and joints' that create the form and shape of human-made Structure#Load-bearing, structures. Structural engineers also ...
, and served as an early ratification of Riquet's vision. It was also a major part of the massive undertaking.
Work began on the first "enterprise" on 1 January 1667 with the construction of the trough of the
Rigole de la plaine then continued on 15 April 1667 with the laying of the first stone of the
Lac de Saint-Ferréol.
[René Gast, ''The Canal du Midi and the Navigable waterways from the Atlantic to the Mediterranean'', Rennes: Ed. Ouest-France, 2000, 125 pages, , p. 18. ] Originally Riquet wanted to build a dozen reservoirs but the Commissioner General of fortifications,
Louis Nicolas de Clerville, asked him to replace them with a single reservoir. This was a great novelty at the time – no reservoir-lake of this magnitude had ever been built before.
Some of
Clerville's men with experience in military engineering came, to build the huge dam for the single reservoir, the
Bassin de St. Ferréol, on the river Laudot. The Laudot is a tributary of the
Tarn in the Montagne Noire some from the summit of the proposed canal at
Seuil de Naurouze. This massive dam, long, above the riverbed and thick at its base was the largest work of
civil engineering
Civil engineering is a regulation and licensure in engineering, professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads ...
in Europe and only the second major dam to be built in Europe, after one in
Alicante
Alicante (, , ; ; ; officially: ''/'' ) is a city and municipalities of Spain, municipality in the Valencian Community, Spain. It is the capital of the province of Alicante and a historic Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean port. The population ...
in Spain. It was connected to the Canal du Midi by a contoured channel over long, wide with a base width of . It was eventually equipped with 14 locks in order to bring building materials for the canal down from the mountains and to create a new port for the mountain town of
Revel.

In November 1667 an official ceremony laid the foundation stone of the Garonne lock in Toulouse in the presence of representatives of the
Parlement of Toulouse
The Parlement of Toulouse () was one of the '' parlements'' of the Kingdom of France, established in the city of Toulouse and responsible for a territory roughly similar to the modern administrative region of Occitania. It was modelled on the ...
, the ''
Capitouls'' (sheriffs), and the
Archbishop of Toulouse, Charles-François d'Anglure de Bourlemont. A first filling of water was made between the seuil de Naurouze and Toulouse during the winter of 1671–1672 and the first boat traffic could begin. In 1673 the section from Naurouze to Trèbes was completed marking the end of the first "enterprise".
From 1671 the second enterprise began linking
Trèbes to the
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
and to build the port of
Sète (then called ''Cette'', the location was chosen and the port constructed by Clerville). This part of the canal posed problems at the junction between the
étang de Thau and Trèbes because the canal must cross the course of the
HĂ©rault
HĂ©rault (; , ) is a departments of France, department of the Regions of France, region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania, Southern France. Named after the HĂ©rault (river), HĂ©rault River, its Prefectures in France, prefecture is M ...
and the Libron. To work around the problem, Riquet set up a system of valves and chambers for Libron and a round lock with three doors for the
Ă©tang de Thau and the
HĂ©rault
HĂ©rault (; , ) is a departments of France, department of the Regions of France, region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania, Southern France. Named after the HĂ©rault (river), HĂ©rault River, its Prefectures in France, prefecture is M ...
. The round lock at
Agde could switch between a reach of the Canal du Midi and the Hérault. This part of the canal was also a problem at the level of the seuil of Ensérune and the descent to
Beziers in the valley of the
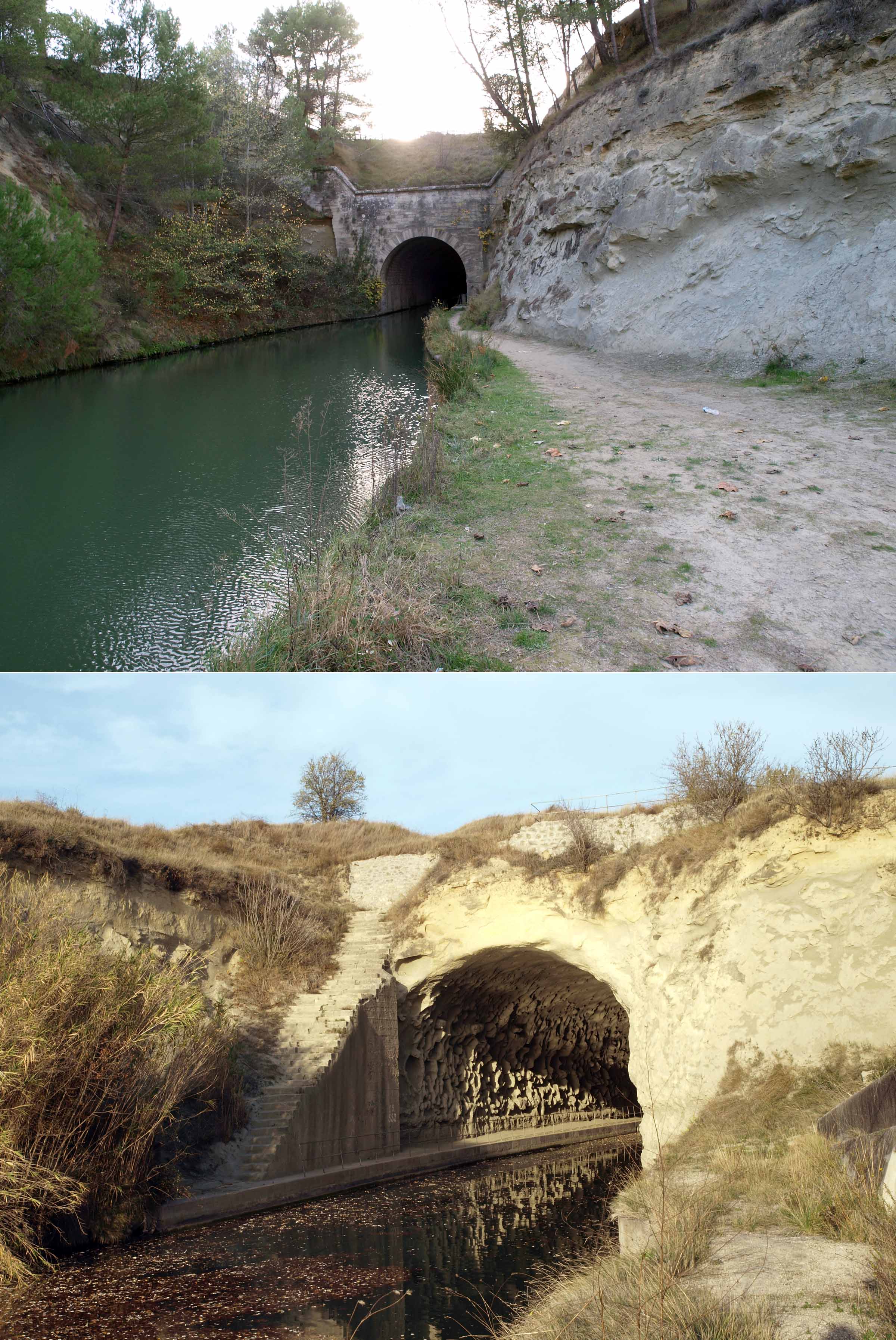
Orb. Riquet solved these problems on the one hand by digging the
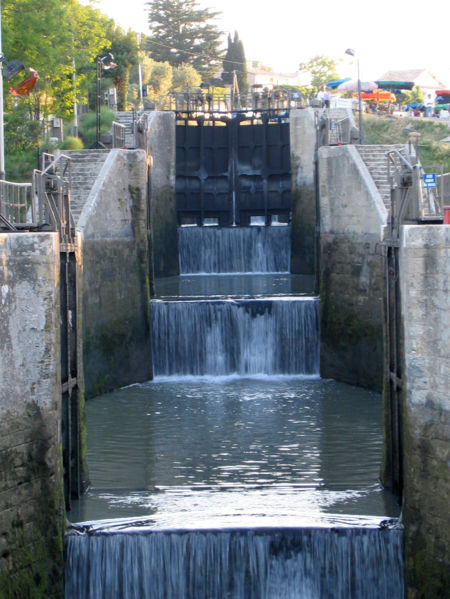
Malpas Tunnel and secondly by building at Fonserannes a row of
eight lock chambers to the Orb. The
Malpas Tunnel was the first canal passage ever built through a tunnel. The Canal du Midi passes through a tunnel through a hill at the
Oppidum d'Ensérune.
In 1681 work on the canal ended at BĂ©ziers. However, in October 1680, Riquet died during construction. He did not see the end of the project. It was the king's engineer, ''La Feuille'', who took over.
His sons inherited the canal, but the family's investments were not recovered and debts not fully paid until over 100 years later. The canal was well managed and run as a paternalistic enterprise until the
revolution
In political science, a revolution (, 'a turn around') is a rapid, fundamental transformation of a society's class, state, ethnic or religious structures. According to sociologist Jack Goldstone, all revolutions contain "a common set of elements ...
.
The canal was built on a grand scale, with oval shaped locks long, wide at the gates and wide in the middle. This design was intended to resist the collapse of the walls that happened early in the project. The oval locks used the strength of the arch against the inward pressure of the surrounding soil that had destabilized the early locks with straight walls.
Such arches had been used by the Romans for retaining walls in
Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
, so this technique was not new, but its application to locks was revolutionary and was imitated in early American canals.
Many of the structures were designed with neoclassical elements to further echo the king's ambitions to make France a New Rome. The Canal du Midi as a grand piece of infrastructural engineering in itself was promoted as worthy of Rome and the political dreams behind it were clarified with plaques in Latin, and walls built with Roman features.
In May 1681 the channel was thoroughly inspected by order of the king to check the work and the water-tightness of the canal. It was then officially opened to navigation on 15 May 1681. At the inauguration of the canal at Toulouse on 15 May, the King's steward and the president of the
Estates of Languedoc travelled first on the canal followed by many other boats carrying particularly
wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
. After the maiden voyage, the canal was drained as the work was not complete; it would not be reopened until December 1682. The canal was opened to traffic in May 1683 and stopped receiving public works in March 1685.
Work organization and social conditions
For fifteen years nearly 12,000 workers worked on the construction of the canal. Riquet hired men and women between 20 and 50 years old whom he organized in sections forming workshops led by a controller-general. This
rationalization of work permitted the optimisation of tasks and allowed several projects to be performed at the same time. All of the work was manual and the digging of the canal was with
shovel
A shovel is a tool used for digging, lifting, and moving bulk materials, such as soil, coal, gravel, snow, sand, or ore. Most shovels are hand tools consisting of a broad blade fixed to a medium-length handle. Shovel blades are usually made ...
s and
pickaxe
A pickaxe, pick-axe, or pick is a generally T-shaped hand tool used for Leverage (mechanics), prying. Its head is typically metal, attached perpendicularly to a longer handle, traditionally made of wood, occasionally metal, and increasingly ...
s. The workforce was made up of farmers and local workers whose number varied from one period to another during the year. Pierre-Paul Riquet appealed to the military to compensate for this fluctuation. He also set up monthly payments of workers for their loyalty.
He also offered accommodation for two
deniers per day.
The women labourers were surprisingly important to the canal's engineering. Many came from former
Roman bath colonies in the
Pyrenees
The Pyrenees are a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. They extend nearly from their union with the Cantabrian Mountains to Cap de Creus on the Mediterranean coast, reaching a maximum elevation of at the peak of Aneto. ...
, where elements of classical hydraulics had been maintained as a living tradition. They were employed at first to move earth to the dam at Saint Ferréol, but their supervisors, who were struggling to design the channels from the dam to the canal, recognized their expertise. Engineering in this period was mainly focused on fortress construction, and hydraulics was concerned mostly with mining and problems of drainage. Building a navigational canal across the continent was well beyond the formal knowledge of the military engineers expected to supervise it, but the peasant women who were carriers of classical hydraulic methods added to the repertoire of available techniques. They not only perfected the water supply system for the canal but also threaded the waterway through the mountains near Béziers, using few locks, and built the eight-lock staircase at Fonserannes.
The financial and social conditions of employment of the workers were very favourable and unusual for the time. To retain his workforce, Riquet paid his workers well enough. More importantly, he gave benefits never before seen such as non-working rain days, Sundays and public holidays, and finally paid sick leave. The
employment contract
An employment contract or contract of employment is a kind of contract used in labour law to attribute rights and responsibilities between parties to a bargain.
The contract is between an "employee" and an "employer". It has arisen out of the old m ...
was individual and done by free recruitment. Pay was, at the beginning, 20
sols (1
livre
Livre may refer to:
Currency
* French livre, one of a number of obsolete units of currency of France
* Livre tournois, one particular obsolete unit of currency of France
* Livre parisis, another particular obsolete unit of currency of France
* Fre ...
) per day, double the agricultural wage. Discontent from farm owners, however, forced Riquet to reduce pay to 15, then 12 sols per day. In 1668 he established the monthly payment of 10
livres.
Trades and work measures implemented
Many trades were found on the work sites of the canal in addition to the seasonal workers who were most often farmers. The
masons and
stonecutters were responsible for the construction of structures such as
bridge
A bridge is a structure built to Span (engineering), span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or railway) without blocking the path underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, whi ...
s,
locks, and
spillway
A spillway is a structure used to provide the controlled release of water downstream from a dam or levee, typically into the riverbed of the dammed river itself. In the United Kingdom, they may be known as overflow channels. Spillways ensure tha ...
s. The
blacksmith
A blacksmith is a metalsmith who creates objects primarily from wrought iron or steel, but sometimes from #Other metals, other metals, by forging the metal, using tools to hammer, bend, and cut (cf. tinsmith). Blacksmiths produce objects such ...
s and levellers were responsible for the maintenance of the tools and equipment. Carters and carriers, the
Farrier
A farrier is a specialist in equine hoof care, including the trimming and balancing of horses' hooves and the placing of shoes on their hooves, if necessary. A farrier combines some blacksmith's skills (fabricating, adapting, and adju ...
s and owners of
sawmill
A sawmill (saw mill, saw-mill) or lumber mill is a facility where logging, logs are cut into lumber. Modern sawmills use a motorized saw to cut logs lengthwise to make long pieces, and crosswise to length depending on standard or custom sizes ...
s were also requisitioned for the works.
Workers were organized into sections controlled by captains and sergeants. Finally, Pierre-Paul Riquet was surrounded by aides as well as auditor-generals and inspector-generals of the canal.
The workers' tools were very limited: picks, hoes and shovels to dig, baskets and stretchers to transport materials. They were provided to workers who must maintain them themselves.
Gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, charcoal (which is mostly carbon), and potassium nitrate, potassium ni ...
was used to blast the rocks.
Inauguration
In 1681 the first inspection took place "dry". The king appointed a commission composed of Henri d'Aguessau, steward of Languedoc, Mr de la Feuille, Father Mourgues a Jesuit professor of
rhetoric
Rhetoric is the art of persuasion. It is one of the three ancient arts of discourse ( trivium) along with grammar and logic/ dialectic. As an academic discipline within the humanities, rhetoric aims to study the techniques that speakers or w ...
and mathematics at the
University of Toulouse, two sons and two in-laws of Pierre-Paul Riquet, as well as Messrs.
Andréossy, Gilade, and Contigny. This commission embarked for Beziers on 2 May 1681 and went up the canal back to Toulouse over six days. The filling with water had been done showing a measure of the progress of checks to Castelnaudary (the section Toulouse-Castelnaudary had water since 1672).
The inauguration itself took place just after the first inspection. The same people re-embarked at Toulouse on 15 May 1681 on a flagship boat followed by dozens of other boats. The
Cardinal de Bonzi, Archbishop of Narbonne and President-born of the
Estates of Languedoc joined the procession which arrived at Castelnaudary on 17 May. A great religious ceremony took place on 18 May at the Church of Saint-Roch followed by a procession to the canal to bless the work, the convoy, and the people present.
The convoy resumed its progress on 20 May with stops in the evening at Villepinte, on the 21st at Penautier, the 22nd at Puicheric, and the 23rd at Roubia. On 24 May it was the passage through the
Malpas Tunnel then crossing the locks of Fonsérannes. The cardinal and the bishops went down to Beziers on the same day.
Supplementary works
In 1686,
Vauban was made responsible for inspecting the channel which he quickly found was in a dilapidated state. He then ordered Antoine Niquet, the engineer of fortifications for Languedoc, to carry out new work at the
Montagne Noire level to drill the Cammazes Tunnel to extend the
Rigole de la montagne and strengthen the
Bassin de Saint-Ferréol. In his haste, Riquet had underestimated the number of rivers that in case of a flood would silt up and swell the canal. The barrage of Saint-Ferréol was too small and its supply system was inefficient.
Vauban also built many masonry structures to isolate the many rivers that flow into the canal and spillways to regulate the water level. He built 49 culverts and aqueducts, including the
Cesse aqueduct, the
Orbiel aqueduct and the Pechlaurier culvert. Finally, he reinforced a lot of works and dams originally built by Riquet. This series of works, which lasted until 1694, greatly improved the supply and management of water. Antoine Niquet was responsible for monitoring the canal until 1726.
The Canal du Midi still had shortcomings because it did not pass through
Carcassonne
Carcassonne is a French defensive wall, fortified city in the Departments of France, department of Aude, Regions of France, region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania. It is the prefectures in France, prefecture of the department.
...
nor
Narbonne
Narbonne ( , , ; ; ; Late Latin:) is a commune in Southern France in the Occitanie region. It lies from Paris in the Aude department, of which it is a sub-prefecture. It is located about from the shores of the Mediterranean Sea and was ...
and did not join the
RhĂ´ne
The Rhône ( , ; Occitan language, Occitan: ''Ròse''; Franco-Provençal, Arpitan: ''Rôno'') is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and Southeastern France before dischargi ...
. In addition, to reach
Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( ; ; Gascon language, Gascon ; ) is a city on the river Garonne in the Gironde Departments of France, department, southwestern France. A port city, it is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the Prefectures in F ...
, it was necessary to take the
Garonne which has variable flow rates and violent floods. The ''Canal de Jonction'' or 'junction canal', built in 1776, gave access to Narbonne via the
Canal de la Robine de Narbonne. The same year the
Canal de Brienne allowed the bypass of
Bazacle - the ford on the Garonne in Toulouse which blocked the river. The connection between the
Ă©tang de Thau and the
Rhone was also completed in 1808. In 1810 a diversion canal allowed Carcassonne to be connected. Finally, in 1857 the
Canal latéral à la Garonne was opened between
Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
and
Castets-en-Dorthe, completing the link between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea that Riquet had dreamt of.
Management

Channel management was ensured primarily by the descendants of Riquet. This was through the elder son Jean-Mathias who took control of the fief until 1714, then Victor-Pierre-François until 1760, then Victor-Maurice, and finally Jean-Gabriel. The Riquet family quickly put up a pyramidal organisation structure with a "Director-General of the Canal" who governs a board of directors responsible for specific geographic areas of the channel. Seven zones were defined in the west and the east: Toulouse, Naurouze, Castelnaudary, Trèbes
Le Somail, Beziers, and
Agde. Each Director is responsible for maintenance of his zone and is supported by a receiver and a controller. Hundreds of lock-keepers are responsible for the locks. This organization facilitates the control and hiring of employees.
In Toulouse, a group of three people form a steering committee: the director general of works, the Receiver General who sets the fees, and the Comptroller General in charge of accounting. Canal management ensures the supply of money to pay for various works and staff hired for the canal. In the 1770s a tax report showed an income of 640,000
livres, half of which went to maintenance and salaries, and half the profits and funds were exceptional works. In 1785 this benefit increased to 950,000 livres which was a very large sum for the time.
Maintenance
The maintenance of the canal was a real problem for the descendants of Riquet. Despite many precautions, the canal silts up with silt from the water supply. In addition, it fills with the branches and leaves of trees. Every winter, a period of closure allows the cleaning of the canal. It is necessary to re-dig the canal bed every year for two months. These works are expensive and two months is not always sufficient. Another problem is the invasion of the canal by weeds in the levels and spillways. There is no way to eradicate this scourge. In 1820 dredging was set up to pull up the weeds and the mud layer.
Finally,
rain
Rain is a form of precipitation where water drop (liquid), droplets that have condensation, condensed from Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is res ...
,
frost, and
drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, ...
forces managers to keep an eye all along the canal to repair leaks and cracks that might open. Today, the channel is subject to the same constraints and managers must perform the same work. They are now mechanized. Approximately 350 employees are made available to the Waterways of France manager by the
Ministry of Ecology, Sustainable Development and Energy
Ministry may refer to:
Government
* Ministry (collective executive), the complete body of government ministers under the leadership of a prime minister
* Ministry (government department), a department of a government
Religion
* Christian mi ...
to maintain the canal.
Operational history of the canal
Once used to transport goods and people, the Canal du Midi is now mainly used by boaters and other tourists.
Initially, the canal appears to have been mainly used by small sailing barges with easily lowered masts, bow-hauled by gangs of men. By the middle of the 18th century, horse towing had largely taken over and steam tugs came in 1834 to cross the Étang. By 1838 273 vessels were regularly working the canal and passenger and packet boats for mail continued a brisk trade until the coming of the railways in 1857.
A "malle-poste" postal service was set up on boats along the canal. As for the
Stagecoach
A stagecoach (also: stage coach, stage, road coach, ) is a four-wheeled public transport coach used to carry paying passengers and light packages on journeys long enough to need a change of horses. It is strongly sprung and generally drawn by ...
for the mail, the boats were pulled by horses on
towpaths. This type of transport was considered revolutionary thanks to its regularity, comfort, safety, and speed that were an improvement over the road. In addition, the canal could be travelled throughout the year. The journey takes four days from
Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
to
Sète.
This time was reduced to 32 hours in 1855 which corresponds to a speed of thanks to the replacement of horses every
[According to the exposition ''Evocation of the canal du Midi'' in the area of the autoroute of Port-Lauragais in the commune of Avignonet-Lauragais.] pulling boats. In addition rather than cross multiple locks travellers were transferred from one vessel to another which saved time and saved water used for the opening of the locks. Finally, the journeys also took place at night to save even more time. In 1684, travel from Toulouse to Agde cost one livre and a half. The rate was set per
league with the rates displayed on a sign. Thus, a
bourgeois
The bourgeoisie ( , ) are a class of business owners, merchants and wealthy people, in general, which emerged in the Late Middle Ages, originally as a "middle class" between the peasantry and Aristocracy (class), aristocracy. They are tradition ...
paid three
sols per league while a
valet or a
sailor
A sailor, seaman, mariner, or seafarer is a person who works aboard a watercraft as part of its crew, and may work in any one of a number of different fields that are related to the operation and maintenance of a ship. While the term ''sailor'' ...
paid one and a half sols per league. Payment offices were located along the route. Each office indicated the rate and provided the distances between each office.
The Canal relied on wheat and wine traffic in Languedoc which was its main purpose. This commercial traffic had the effect of enriching the descendants of Riquet very quickly. The
wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
,
wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented fruit. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the fruit and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Wine is most often made f ...
, and
alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
could be exported from
Lauragais to
Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
,
Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( ; ; Gascon language, Gascon ; ) is a city on the river Garonne in the Gironde Departments of France, department, southwestern France. A port city, it is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the Prefectures in F ...
, and
Marseille
Marseille (; ; see #Name, below) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Departments of France, department of Bouches-du-RhĂ´ne and of the Provence-Alpes-CĂ´te d'Azur Regions of France, region. Situated in the ...
. The canal had the effect of broadening the sales area of the producers of Languedoc. In the 1730s commerce thrived and greatly improved agricultural businesses. The canal also allowed the import to Languedoc of products from other regions such as
Marseille soap,
rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
,
starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
,
dried fish
Fresh fish rapidly deteriorates unless some way can be found to preserve it. Drying (food), Drying is a method of food preservation that works by removing water from the food, which inhibits the growth of microorganisms. Open air drying using sun ...
, and
spices
In the culinary arts, a spice is any seed, fruit, root, Bark (botany), bark, or other plant substance in a form primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of pl ...
and
dye
Juan de Guillebon, better known by his stage name DyE, is a French musician. He is known for the music video of the single "Fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction that involves supernatural or Magic (supernatural), magical ele ...
s. However, it was never the grand international route envisaged by the kings of France as its traffic was limited to local and national trade.
Freight rates depend on the cargo. Thus in the 17th century, the transportation of wheat cost 12
deniers per
quintal and that of oats 6 deniers per quintal.
The boats
At its opening the canal was used by a majority of boats for the transport of goods. These vessels were twenty metres long and were hauled by horses or men.
[René Gast, ''The Canal du Midi and the Navigable waterways from the Atlantic to the Mediterranean'', Rennes : Ed. Ouest-France, 2000, 125 pages, , p. 25. ] The tonnage of vessels increased over the centuries, from 60 tonnes at the beginning to 120 tonnes at the start of the 19th century. The proper Canal
Barge
A barge is typically a flat-bottomed boat, flat-bottomed vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. Original use was on inland waterways, while modern use is on both inland and ocean, marine water environments. The firs ...
s were called "owned barge" or "canal barge" and also plied the route. In 1778 there were about 250 barges. In 1914, there were 126 "owned boats", 70 rented boats, 300 horses, and 75 mules. In the year 1930 motor barges had completely replaced animal traction. They relaunched in part the merchant traffic on the canal but commercial and merchant inland water shipping finally disappeared around the late 1980s. The year 1856 was a record year for merchant activity with more than 110 million tonnes-kilometres of cargo and nearly 100,000 passengers carried.
For 250 years, horses have pulled many boats such as fast barges or long commercial boats. A horse can tow up to 120 times its weight when the load is on the water. Animal traction was then a strategic element in the operation of a canal.
The mail-barges or "post vehicles" which transported passengers were boats many metres long with a simple shelter on the deck. These boats evolved to become faster and more luxurious with lounges and were very large since the largest could reach long. Services inside these vessels also evolved with first class in private salons and second class in a common room. During the heyday of the canal some boats included first class lounges where dinner was served.
Rail competition

Curiously, the canal did not really serve its purpose. The economic and political context hindered the economic development that had been expected. After two hundred years of operation, the canal began to suffer from competition from rail and road. It reached its peak in the middle of the 19th century. In 1858
Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles-Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was President of France from 1848 to 1852 and then Emperor of the French from 1852 until his deposition in 1870. He was the first president, second emperor, and last ...
signed a decree entrusting the canal for a period of 40 years to the
Chemins de fer du Midi railway company, the owner of the Bordeaux-Narbonne railway line. This act had the effect of amplifying the decline in boat traffic on the canal. The company primarily promoted the railway and placed higher freight rates on commercial traffic in the canal. The Canal du Midi had the highest rates of any of France's waterway. In addition, the railway became smoother and faster than the waterway especially as the Canal du Midi suffered from its limited tonnage.
The period before 1859 corresponded to the canal operating without competition while from 1859 the installation of railways in the south of France began. The effect of rail competition is clearly visible in the table with the halving of freight traffic between 1856 and 1879. The traffic then continued to decline gradually. As for the railway, the
Bordeaux–Sète railway carried almost 200 million tonne-kilometres in 1860. Management of the canal was taken over by the State in 1898 who made successive investments to maintain its competitiveness. The state removed taxes and tolls which had the effect of reviving traffic on the canal to which reached 80 million tonne-kilometres in 1909.
The end of merchant traffic

The government tried to revive the renovation of the canal by enacting a legal program to lift the channel to the standards of the
Freycinet gauge. The canals of northern France were already at this level and had traffic well above the Canal du Midi. However, the law remained unimplemented due to lack of funds.
At the end of the
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
traffic was completely disorganized. In 1920 freight traffic recovered rapidly with the arrival of motorised barges. The HPLM company (Le Havre-Paris-Lyon-Marseille) operated 30 boats on the Canal du Midi. The
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
saw a slowdown in traffic due to the shortage of
oil but recovery was rapid after the conflict and the traffic reached 110 million km. However, the canal suffered from a size too small for later barges with high tonnage. Rail became more and more competitive and road transport also became a second competitor. The Canal du Midi became the third means of transport. Freight traffic ceased in the 1970s. In 1980 there were only two barges (the ''Bacchus'', a wine carrier and the ''Espérance'', a grain carrier) carrying regular traffic between
Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
and
Sète: they definitively ceased their activities in 1989 following the cessation of navigation pronounced by the Prefect of the Region due to
drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, ...
. In 1991 operation of the canal was assigned to the administration of ''
Voies navigables de France'' who remain managers today.
The canal in the 21st century
From the end of the 20th century, the canal has offered many activities. It can again play its original role in allowing the transit of boats between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
A canal for tourism and recreation

The Canal du Midi is now used primarily by tourists, recreation, and housing.
It attracts more and more
river tourism, including sailing on chartered boats, restaurant-boats, or
hotel barges such as the
Anjodi. Tourism has grown from the 1960s, most significantly from Britain, and then exploded in the 1980s. The canal was featured prominently in the
BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
television series ''
Rick Stein's French Odyssey'' (2005), further publicising the canal to a British audience. Busier than the
Seine
The Seine ( , ) is a river in northern France. Its drainage basin is in the Paris Basin (a geological relative lowland) covering most of northern France. It rises at Source-Seine, northwest of Dijon in northeastern France in the Langres plat ...
, the canal alone accounts for one-fifth of French river tourism and 80% of passengers are foreigners, primarily Germans, Swiss and British. There are approximately 10,000 boat passages per year through the
Fonséranes locks,
with the most traffic at the Argens lock with 11,000 boats carrying an average of five passengers. The canal directly employs about 1,900 people, and the annual economic impact due to the activity of the canal is about 122 million euros.
Navigation of the channel is open from the third Saturday in March to the first week of November. Outside of this period, navigation can be authorized for individuals who have requested it. The winter period is called the "period of unemployment" and allows the completion of all maintenance work.
The Canal du Midi also allows other sports, mainly in urban areas, such as
rowing,
canoeing
Canoeing is an activity which involves paddling a canoe with a single-bladed paddle. In some parts of Europe, canoeing refers to both canoeing and kayaking, with a canoe being called an 'open canoe' or Canadian.
A few of the recreational ...
,
fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
,
cycling
Cycling, also known as bicycling or biking, is the activity of riding a bicycle or other types of pedal-driven human-powered vehicles such as balance bikes, unicycles, tricycles, and quadricycles. Cycling is practised around the world fo ...
,
roller-skating, and
hiking
A hike is a long, vigorous walk, usually on trails or footpaths in the countryside. Walking for pleasure developed in Europe during the eighteenth century. Long hikes as part of a religious pilgrimage have existed for a much longer time.
"Hi ...
along the banks. A paved stretch of from
Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
to
Avignonet-Lauragais and another of between
BĂ©ziers and
Portiragnes are particularly suited to cycling and
rollerblading. It is possible to cycle the entire Canal des Deux Mers from Sète to Bordeaux. In addition, many barges have been converted to family housing, theatres, exhibition spaces, and restaurants.
A canal for water

During the dry season, the canal serves as a reservoir for
agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
. Nearly 700
irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
pumps are installed along the canal. This is one of the fundamental roles of the canal and one of the reasons for its maintenance by the State since the end of commercial traffic. The canal can irrigate up to of agricultural land.
The
Rigole de la plaine carries water from the Sor tapped from an offtake at Pont Crouzet for irrigation before emptying into the Canal du Midi. In addition, individual samples are collected from the water on the area between
Revel and the
seuil de Naurouze. In 1980 the
Lac de la Ganguise was built near
Castelnaudary providing a water reserve of 22 million cubic metres. In 2005 the
dam was raised to reach a capacity of 44 million cubic metres. Near the old basin of Naurouze the Naurouze pumping station helps to regulate the water in the Canal du Midi and the lake. An underground pipe, the gallery of Mandore, provides the Naurouze with additional water from the
Rigole de la plaine to Lake Ganguise. Conversely, during the dry season, Lake Ganguise can supply the Canal du Midi if the water supply of the Rigole de la plaine is not enough.
The canal has also provided a supply of drinking water through the water treatment plants at Picotalen (Picotalen I and Picotalen II) since 1973. They are part of the installations installed by the Institution for Interdepartmental Hydraulic Planning of Montagne Noire (IIAHMN) since its inception in 1948 to meet the water needs of
Lauragais. The plant supplies water from the Cammazes channel to nearly 185 communes.
The Canal as heritage

While the canal was once seen as a tool of production, trade, and commerce it is now considered to be architectural and technical heritage as evidenced by the refusal of the mayor of Toulouse, Pierre Baudis, to allow space on the Canal du Midi to be used for an urban expressway. It has not been downgraded and remains open for navigation. On 7 December 1996 the channel and a buffer zone of 2,000 km were included in the list of
World Heritage Sites
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritag ...
by
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
. In the same year, it was classified under French law as a ''Grand Site of France''. This classification was extended to the canals of the plain and the mountain in 1996 and 2001. It caused a very rapid increase in tourist numbers.
Nevertheless, maintenance has not been carried out completely because many players are involved: two
Regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
, six
Departments
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
* Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
, and local collective authorities. None wish to bear the cost of restoration and do not always dare to launch development programs. ''
Platanus
''Platanus'' ( ) is a genus consisting of a small number of tree species native to the Northern Hemisphere. They are the sole living members of the family Platanaceae.
All mature members of ''Platanus'' are tall, reaching in height. The type ...
'' (plane trees) is a particular source of problems because their roots destroy the banks and the paved cycle paths and their leaves invade the canal. In addition they are weakened by disease (
canker of ''Platanus''). The canal is a heavy heritage to maintain and enhance as the manager of French canals,
Voies navigables de France (VNF), specializes in the management and maintenance of
French canals in a market and commercial economy and not in the tourism market where the Canal du Midi is located. In addition maintenance costs are higher than in a traditional network because of the age of the canal. Also, the operation of the channel generates low levels of earnings. VNF must try to establish local partnerships to develop and maintain the canal
[''Report of the Inspector-General of Architecture and Heritage 2003''](_blank)
p. 11. since its budget does not allow it to provide the care and supervision of of canals.
The classification as a World Heritage Site creates an additional level of oversight by the State who must ensure that any changes along the canal and its structures are compatible with the strategic issues of
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
. However, a report of the General Inspectorate of Architecture and Heritage in 2003 showed that the channel was in very poor condition with many works and infrastructure devaluing its surroundings and suffering from significant housing pressure evidenced by uncontrolled construction, poorly designed facilities that misrepresent the site, and the construction of
marina
A marina (from Spanish , Portuguese and Italian : "related to the sea") is a dock or basin with moorings and supplies for yachts and small boats.
A marina differs from a port in that a marina does not handle large passenger ships or cargo ...
s in the ports on the canal. Nevertheless, to respect the uniformity of the canal development and support efforts for improvement, the Canal du Midi remains under the management of VNF under the tutelage of the State who want to create a monitoring mission like the
Loire
The Loire ( , , ; ; ; ; ) is the longest river in France and the 171st longest in the world. With a length of , it drains , more than a fifth of France's land, while its average discharge is only half that of the RhĂ´ne.
It rises in the so ...
and
Mont-Saint-Michel.
The structures
The Canal du Midi is long with a total of 328 structures including 63
locks,
[The number here is the number of separate locations of locks. The numbers given in Locks on the Canal du Midi count the number of individual lock chambers hence the discrepancy] 126
bridge
A bridge is a structure built to Span (engineering), span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or railway) without blocking the path underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, whi ...
s, 55
aqueducts, 7 aqueducts, 6
dams,
1
spillway
A spillway is a structure used to provide the controlled release of water downstream from a dam or levee, typically into the riverbed of the dammed river itself. In the United Kingdom, they may be known as overflow channels. Spillways ensure tha ...
, and 1
tunnel
A tunnel is an underground or undersea passageway. It is dug through surrounding soil, earth or rock, or laid under water, and is usually completely enclosed except for the two portals common at each end, though there may be access and ve ...
.
Water supply for the canal


It takes 90 million cubic metres of water to feed the canal for one year. To do this, Riquet set up a complex system of water supply to the canal. The idea was to capture the waters of the
Montagne Noire located several tens of kilometres away and bring it to the
Seuil de Naurouze, the highest point of the future canal, through channels.
These channels, called "
Rigole de la montagne" (Channel of the Mountain) and "
Rigole de la plaine" (Channel of the Plain) connected the upper three reservoirs (Lampy, Cammazes, and Saint-Ferréol) at the seuil de Naurouze. The Rigole de la Montagne measured long and has 22 structures between the outlet at Alzeau and the falls of Cammazes. The Rigole de la Plaine measured long at altitude and included 68 structures between the Crouzet bridge and the seuil de Naurouze.
Initially, two
reservoir
A reservoir (; ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam, usually built to water storage, store fresh water, often doubling for hydroelectric power generation.
Reservoirs are created by controlling a watercourse that drains an existing body of wa ...
s fed the highest point of the canal at the seuil de Naurouze: the
Bassin de Saint-Ferréol had a capacity of 6.3 million cubic metres and was built between 1667 and 1672. The other reservoir was much smaller - the
Bassin de Lampy. Called "Lampy-Vieux", it was quickly replaced by the "Lampy-Neuf" with a capacity of 1,672,000 cubic metres built over a hundred years later between 1777 and 1782.
The
Bassin de Saint-Ferréol was and remains the main water reservoir for the canal with a surface of . It receives the waters of the Montagne Noire via the Channel of the Mountain which is itself supplied by the basin of Lampy. The lake waters are retained by a
dam long and wide consisting of three parallel walls. The channel surrounds the basin and can evacuate any excess water. A museum is located near the outlets and has displays on the history of the construction of the Lake.
Originally the engineer planned and built a third reservoir, the Naurouze, but it was abandoned in 1680 due to its excessive silting. Pierre-Paul Riquet had dreamed of the construction of a new city around this basin that never saw the day. A floodway was quickly dug to drain the Naurouze basin from the south.
Other reservoirs were also built at Carcassonne to supply the lower part of the canal to the Mediterranean. So the waters of the Fresquel, the Cesse, and the Orbiel augmented those of the canal. On the other hand, the waters of the
Orb at
BĂ©ziers provided additional flow to part of the canal. In 1957 the Cammazes dam with a capacity of 20 million cubic metres of water was filled on the Sor which completed and finalized the supply network. This lake provides drinking water to more than 200 communes in the region. Of the 20 million cubic metres, 4 million are reserved for feeding the Canal du Midi.
The locks
The first
locks built on the Toulouse plain by
Pierre-Paul Riquet were experimental and were not satisfactory. They consisted of rectangular locks with wooden stilts as foundations for the side walls. This form did not properly restrain the lateral material when the lock was empty. They then collapsed on themselves. He redefined the shape of his locks to rounded side walls,
[Protective walls in the chamber of the lock] thicker, and more resistant to the lateral pressure of the earth. The dimensions of the locks were then large enough for the time. Because of these rounded forms, the architecture of the locks in the Canal du Midi is called
Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
style.
The locks were built in stone and sealed with
lime. They are closed by two double leaf doors. The doors, originally timber with the fewest possible metal parts, are subject to severe moisture stress and pressure. They had a "vantelle" (valve) controlled by a
rack and pinion that allowed the draining of water from the lock chamber.
The nominal size of the locks built by Pierre-Paul Riquet was long, wide at the door, wide in the centre of the lock and an average of in height. In the 20th century, many locks were changed and therefore no longer have the original features.
At the town of
BĂ©ziers there is a staircase of eight locks at
Fonsérannes to bring it to the river
Orb. The locks had to be cut from solid rock, and descended a hillside whose gradient varied. All the locks had to contain the same volume of water, but could not have precisely the same shape. Nonetheless, they were built successfully without a need for repair. This amazing piece of engineering was subcontracted out to two illiterate brothers, the Medhailes, and was built by a workforce composed mainly of women.
Some of the locks on the canal are architectural gems. For instance, the
Agde Round Lock has three doors: two doors provide access to each side of the channel and the third provides access to the
HĂ©rault
HĂ©rault (; , ) is a departments of France, department of the Regions of France, region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania, Southern France. Named after the HĂ©rault (river), HĂ©rault River, its Prefectures in France, prefecture is M ...
going to the Mediterranean. This system allows triple access while protecting the canal from river flooding. Similarly, the canal has several multiple locks – i.e. with multiple locks attached to one another. This system saves doors and foundations in areas where the slope is greatest. The best known of these locks is
Fonserannes Lock which has eight chambers.
Today most of the locks are electrified which replaced the manual opening of the sluices and lock gates.
The ports

Several ports were built at regular intervals along the route of the canal in order to load and unload goods and also to provide stopping-places for travellers. Toulouse has two ports: the
port de l'Embouchure is located at the junction of the Canal du Midi, the
Canal de Brienne, and the
Lateral canal of the Garonne while
Port Saint-Sauveur is located in the centre of town near the ''Hall of Grains''. There were two other ports in Toulouse but they were destroyed for urban development. So the ''Port des Minimes'' and the ''Port Saint-Etienne'' were replaced by
towpaths.
Castelnaudary has a port of called ''Grand Basin'' built between 1666 and 1671. It served as a stopover halfway between Toulouse and Sète. Cybelle island in the middle of the basin was used to protect the barges from the wind. Carcassonne is today a major tourist stop on the canal and has a port built in 1810 at the time when the city was connected to the canal. The port of Trèbes is a major port which has numerous moorings for boats. There are also the ports of
Homps which was one of the most important on the canal and
Le Somail which was a popular place for rest and recreation. Finally, just before its arrival at the Mediterranean Sea, the canal has two ports: the port of
Agde where there is the old hotel of the "Administration of the Canal", and the port of Onglous at
Marseillan which is the last port before
Sète and its royal canal giving access to the sea.
Newer ports were built such as
Ramonville-Saint-Agne, called Port-Sud, which has many residential barges and is set directly overlooking the harbour, and Port-Lauragais located near
Avignonet-Lauragais on a service area of the
A61 autoroute.
The aqueducts
Related article:
Aqueducts on the Canal du Midi
Several aqueducts
[An aqueduct is a 'canal bridge' (''pont-canal'' in French) carrying a canal over a river or valley, or any depression in the terrain. The same word in English is used for any overhead structure carrying water, while the French equivalent ''aqueduc'' refers to a water conveyance structure or (as in the case of the Canal du Mid) a siphon or culvert under the canal. This chapter refers only to the actual aqueducts carrying the canal itself, and not the secondary hydraulic structures.] were built along the route of the Canal du Midi. They allow the canal to cross rivers that could disrupt the water flow in the canal. In fact, the rivers flowing into the canal cause an overflow of water during flooding and fill the canal with silt. Some aqueducts date from the time of Pierre-Paul Riquet, but most were built after the completion of the canal in particular due to improvements recommended by
Vauban. The canal has the following aqueducts (in order from Agde to Toulouse):
*
Orb aqueduct (PK 208) which was inaugurated in 1857, eliminating the difficult crossing of the river Orb
*
Cesse aqueduct (PK 168)
*
RĂ©pudre aqueduct (PK 159) was built between 1667 and 1676 to span the RĂ©pudre near the village of
Paraza. The RĂ©pudre is a small tributary of the
Aude
Aude ( ; ) is a Departments of France, department in Southern France, located in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region and named after the river Aude (river), Aude. The departmental council also calls it " ...
in which the flow is too variable especially in winter (bridge length: ). It was also the first aqueduct built by Pierre-Paul Riquet
*
Orbiel aqueduct at
Trèbes (PK 117)
*
Fresquel aqueduct (PK 109) was built beginning in 1800 and opened on 31 May 1810, as a result of the realignment of the route to pass through the centre of the city of
Carcassonne
Carcassonne is a French defensive wall, fortified city in the Departments of France, department of Aude, Regions of France, region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania. It is the prefectures in France, prefecture of the department.
...
, a city that refused to pay a share of the cost when the canal was first built
*
Herbettes aqueduct, (PK 8), a new aqueduct at Toulouse completed in 1983, long, to cross a four-lane motorway.
Other structures
Pierre-Paul Riquet and the engineers who followed him over three centuries built many other structures on the Canal du Midi, of which the most important are listed here:

*the
Malpas Tunnel long southeast of the
Oppidum d'Ensérune which passes through a hill above sea level and was a technical challenge for the time
*the Argent-Double spillway located in
La Redorte near the
Argent-Double Aqueduct: this work incorporates eleven successive stone arches contemporary to
Vauban, its designer; it was built by Antoine de Niquet and allows for the overflow water from the canal to be discharged into the stream
*the
Fonserannes water slope, which bypasses the 6-lock staircase at
Fonserannes, was built at the time when the canal was to be upgraded to
Freycinet gauge to save time and allow larger vessels to work on. It has a unique machinery whose maintenance is expensive, but for several years, VNF has attempted to rehabilitate it to reduce waiting times at the Fonséranes locks
*the
Ouvrages du Libron (the works of Libron), a unique achievement of its kind which allows the canal to cross the course of the Libron near
Agde
*the
watermill
A watermill or water mill is a mill that uses hydropower. It is a structure that uses a water wheel or water turbine to drive a mechanical process such as mill (grinding), milling (grinding), rolling, or hammering. Such processes are needed in ...
s of the Canal du Midi are located in derivation of the number of
locks (e.g. Naurouze, Gay, Trèbes, Matabiau, Minimes, Castelnaudary, Castanet, Beziers, etc.) and used the water height differences to power
Quern-stones to grind grain from the commissioning of the canal. Thereafter, they become real
Gristmill
A gristmill (also: grist mill, corn mill, flour mill, feed mill or feedmill) grinds cereal grain into flour and Wheat middlings, middlings. The term can refer to either the grinding mechanism or the building that holds it. Grist is grain that h ...
s during the 18th century.
Flora and fauna

The canal is a long ribbon of water stretching through the landscape and attracts many animal species. Several species of fish such as
bream breed in the canal, and others reproduce in its feeding rivers and spend part of their life in the canal.
Mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s such as
anadontes, a kind of freshwater mussel, and
corbicules, a kind of freshwater
clam
Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve mollusc. The word is often applied only to those that are deemed edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the sea floor or riverbeds. Clams h ...
, occur in the canal.
Invasive Coypu (River rat or nutria) and
Muskrat
The muskrat or common muskrat (''Ondatra zibethicus'') is a medium-sized semiaquatic rodent native to North America and an introduced species in parts of Europe, Asia, and South America.
The muskrat is found in wetlands over various climates ...
s introduced from the Americas burrow into the banks, which they damage. Finally, many animals and birds come to drink water from the canal.
The canal is also a very vegetated place. In the beginning, Pierre-Paul Riquet planted trees to stabilize the
banks of the canal especially where it overlooked the surrounding lands. The
willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, of the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 350 species (plus numerous hybrids) of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions.
Most species are known ...
was widely used for its rapid growth. The engineer also planted
irises on the side of the canal to reduce subsidence of its banks. In the 18th century, the trees planted along the canal become a source of income. So
mulberries were planted for rearing
silkworms. Then, with the end of the silk culture in 1772, the mulberry trees were replaced by the
poplar from Italy which was the most productive wood. Structures and lock-keepers' houses were decorated with
fruit tree
A fruit tree is a tree which bears fruit that is consumed or used by animals and humans. All trees that are flowering plants produce fruit, which are the ripened ovaries of flowers containing one or more seeds. In horticultural usage, the te ...
s. At the time of the
French Revolution plantations around the canal had approximately 60,000 trees when there were only 45,000 at the beginning. It was under the
First Empire that
plane trees
''Platanus'' ( ) is a genus consisting of a small number of tree species native to the Northern Hemisphere. They are the sole living members of the family Platanaceae.
All mature members of ''Platanus'' are tall, reaching in height. The type ...
began to be planted to replace the cut trees, which are today the dominant variety along the canal.
However, for several years, plane trees have been infected with canker stain, a disease caused by a microscopic fungus called ''
Ceratocystis platani''. The first outbreaks were detected in 2006 with the number of infected plane trees reaching 83 in 2008 and 153 in 2009. Selective tree-felling campaigns have been conducted to try to stop the spread but with no effect. In addition, there is no effective treatment against the disease. In 2011, 211 places and 1,338 diseased trees have been identified. In 15 to 20 years all 42,000 plane trees of the Canal du Midi will have to be felled and replaced mainly by other species (
ash,
lime), after initial experiments with a variety of plane-tree resisting the parasite.
The Canal du Midi as a model

The Canal du Midi was one of the great achievements of the late 17th century.
Riquet understood the hydraulic system of the Montagne Noire and had controlled it to serve the Canal du Midi. King
Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
, who was the sponsor, also left it as a mark of his commitment to grandeur.
The canal was also magnified by the ''
Encyclopedia or Reasoned Dictionary of Science, Arts, and Crafts'' by
Diderot
Denis Diderot (; ; 5 October 171331 July 1784) was a French philosopher, art critic, and writer, best known for serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. He was a prominent figure during t ...
and
D'Alembert
Jean-Baptiste le Rond d'Alembert ( ; ; 16 November 1717 – 29 October 1783) was a French mathematician, mechanics, mechanician, physicist, philosopher, and music theorist. Until 1759 he was, together with Denis Diderot, a co-editor of the ''E ...
in 1765 who highlighted its value and greatness. They compare it to Roman constructions. Another encyclopedia writer,
Joseph Jerome Lefrancois Lalande lauded the architectural and hydraulic achievement in his work ''The navigation canals and especially the Canal de Languedoc'' in 1778. Similarly,
Bernard Forest de BĂ©lidor
Bernard Forest de Bélidor (1698, Catalonia, Spain – 8 September 1761, Paris, France) was a French engineer, significant to the development of the science of hydraulics and ballistics.
He was the son of Jean Baptiste Foret de Belidor, an offic ...
congratulated the designer in ''Hydraulic Architecture''. The canal became an example in Europe as throughout the
Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment (also the Age of Reason and the Enlightenment) was a Europe, European Intellect, intellectual and Philosophy, philosophical movement active from the late 17th to early 19th century. Chiefly valuing knowledge gained th ...
it was the only canal of this size in Europe.
The American
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
, politician, architect, and future president of the
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, came to study the Canal du Midi in 1787.
As the United States Ambassador to France he envisaged the construction of a similar work to link the
Potomac River
The Potomac River () is in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography D ...
to
Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( ) is the fourth-largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and also has the shortest avera ...
.
In the 1820s the
Hungarian reformer
István Széchenyi
Count István Széchenyi de Sárvár-Felsővidék (, ; archaically English: Stephen Széchenyi; 21 September 1791 – 8 April 1860) was a Hungarian politician, political theorist, and writer. Widely considered one of the greatest statesme ...
visited France and was greatly impressed with the Canal du Midi in France. It inspired him to envision ways to improve navigation on the lower
Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
and
Tisza, which he implemented later in his career.
People linked to the canal
*
Pierre-Paul Riquet, designer of the Canal du Midi. He obtained from the king the ownership and operation of the Canal du Midi for life for himself and his descendants. He died in October 1680 shortly before its completion.
*
Jean-Baptiste Colbert,
Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
's
Controller-General of Finances
The Controller-General or Comptroller-General of Finances () was the name of the minister in charge of finances in France from 1661 to 1791. It replaced the former position of Superintendent of Finances (''Surintendant des finances''), which was ab ...
who was commissioned by the king to assess the cost and feasibility of the project.
*
Sebastien Le Prestre de Vauban, the royal architect and engineer who made many improvements to the canal between 1685 and 1686
*
François Andreossy, a close associate and deputy of Pierre-Paul Riquet who continued the work after the Riquet's death.
*
Louis Nicolas de Clerville an engineer who controlled and oversaw the works and advised Riquet.
See also
*
Aqueducts on the Canal du Midi
*
Canal de Garonne
*
Épanchoir de Foucaud
*
Fonsérannes Locks
*
Fonserannes water slope
*
Galaube Lake
*
La Nouvelle branch
*
Le Somail
*
Locks on the Canal du Midi
*
Pont Marengo, in
Carcassonne
Carcassonne is a French defensive wall, fortified city in the Departments of France, department of Aude, Regions of France, region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania. It is the prefectures in France, prefecture of the department.
...
*
Water features on the Canal du Midi
*
Louis XIV Victory Monument
*
List of Word Heritage Sites in France
Notes
Comments
Citations
References
* Michel Adgé, ''The Canal du Midi - Vol. 2: three centuries of inland water shipping and travels'', coll. "Canal du Midi", Ed. Jean-Denis Bergasse, 1984,
* Arnaud d'Antin de Vaillac, ''Understanding the Canal du Midi'', Éditions France Empire, 1997,
*
* Bernard Blancotte, ''The canal du midi, work of a titan'', Éditions Lacour
* Michel Cotte, ''The Canal du Midi, marvel of Europe'', Éditions Belin, 2003,
* René Gast, ''The Canal du Midi and the navigable waterways from the Atlantic to the Mediterranean'', éditions Ouest-France, 2000,
* Corinne Labat, Robert Fuggetta, Guy Jungblut, Marvin Holdt, and Gilles Bernard, ''The Canal du Midi from the 17th to the 21st century'', Éditions Empreinte, 2006,
*
Further reading
* (in English) L.T.C. Rolt, ''From Sea to Sea'', 2nd edition, Euromapping, 1994,
* Michel Adgé, ''The Canal du Midi - Vol. 1: Pierre-Paul Riquet and the Canal du Midi in arts and literature'', coll. "Canal du Midi", Ed. Jean-Denis Bergasse, 1984
* Michel Adgé, ''The Canal du Midi - Vol. 3: centuries of human adventure'', coll. "Canal du Midi", Ed. Jean-Denis Bergasse, 1984
* Michel Adgé, ''The Canal du Midi - Vol. 4: great moments and great sites. The Canals of Briare and Lez-Roissy'', coll. "Canal du Midi", Ed. Jean-Denis Bergasse, 1984
* Collective work of the Association for promotion of archeology in Midi-Pyrénées, ''Guide for the traveller to the canal du midi'', réédition 1853,
* Jean Broutin, ''The calm waters on the King's canal'', Éditions Belcastel,
* Philippe Calas, ''The Canal du Midi by bicycle'', Éditions EDISUD,
* Philippe Calas, ''Memoire in images: The Canal du Midi'', Éditions Alan Sutton,
* Philippe Calas, ''All knowledge on the Canal du Midi'', Éditions Grand Sud,
* Philippe Calas, ''The Canal du Midi: archives and photograph of the most beautiful canal in the world'', Éditions Grand Sud,
* Philippe Calas, ''The Canal du Midi seen from the air'', Éditions Sud Ouest,
* Gérard Crouzy et Philippe Cucurou, ''Supply System of the Montagne Noire'', Éditions Bares, 1993,
* Clément Debeir et Sophie Binder, ''Canal du Midi'', Privat, 2010,
* Pierre-Paul Riquet Bonrepos (Baron de
''History of the canal of Languedoc'' Impr. de Crapelet, 1805, 398 pages, OCLC 38684880
* Louis Destreme and Alain Félix, ''The Canal du Midi and the Lateral Canal of the Garonne'', Éditions du Chêne, 1996
* Jean-Yves Grégoire, ''On foot, on bicycle, the Canal du Midi and the lateral canal'', Rando-Éditions,
* Lionel Hignard, Françoise Lemonnier, Jean-Claude Pertuzé, ''Julot on the canal du Midi'', Toulouse, Éditions Loubatières
* André Maistre, ''The Canal des Deux-Mers, the Royal canal of Languedoc 1666-1810'', Éditions Privat, 1979,
* Jacques Morand, ''The Canal du Midi and Pierre-Paul Riquet'', Éditions EDISUD, 1993,
* Hélène Vérin, ''The Glory of the Engineers, the technical intelligence of the 16th to the 18th centuries'', Paris 1993, 455 p.
* Michel Adgé, Philippe Delvit, Robert Marconis, Jean-Loup Marfaing, Samuel Vanier, ''Canal royal de Languedoc: Le partage des eaux'', Toulouse, Éditions Loubatières, 2009,
* (English) Claudine Roland, Claudine (1997). The Canal du Midi (English Translation ed.). MSM. .
External links
English:
Canal du Midian
La Nouvelle branch with maps and details of places, ports and moorings, by the author of ''Inland Waterways of France'', Imray
Navigation details for 80 French rivers and canals(French waterways website section)
Aude Pays Cathare History and Heritage websiteExplore the Canal du Midi in the UNESCO collection on Google Arts and Culture
French:
Old Maps drawn by François Garipuy
Association of the ''Canal du midi en Languedoc''
History of the Canal du Midi
a personal website in French
Canal-du-Midi.org
Inter-regional Directorate VNF (South-West)
Inter-communal Tourism for the canal du Midi website
Actions taken by VNF to save the heritage of trees of the canal
Canal du Midi
Carcassonne
Intermunicipal tourist office of the Canal du Midi
{{Authority control
Midi
Musical Instrument Digital Interface (; MIDI) is an American-Japanese technical standard that describes a communication protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, ...
Landmarks in France
World Heritage Sites in France
Tourist attractions in Toulouse
Canals opened in the 17th century
Buildings and structures completed in 1681
Transport infrastructure completed in the 1680s
1681 establishments in France
Historic Civil Engineering Landmarks
 The Canal du Midi is located in the south of France, in the departments of
The Canal du Midi is located in the south of France, in the departments of  The building of a
The building of a  English translation:
English translation:
 Compared to canals, managing rivers is difficult but only one canal is required between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. Unlike a river, it is easier to manage the flow of a canal to ensure a constant flow of traffic throughout the year.
The Canal du Midi is a summit-level canal because it must pass over a height between two valleys. The construction of this canal required passage through the Seuil de Naurouze or the Seuil de Graissens.
Thirty years passed from the start of planning to the commencement of work: a similar project was also studied by a committee of which Riquet's father was a member.
Compared to canals, managing rivers is difficult but only one canal is required between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. Unlike a river, it is easier to manage the flow of a canal to ensure a constant flow of traffic throughout the year.
The Canal du Midi is a summit-level canal because it must pass over a height between two valleys. The construction of this canal required passage through the Seuil de Naurouze or the Seuil de Graissens.
Thirty years passed from the start of planning to the commencement of work: a similar project was also studied by a committee of which Riquet's father was a member.
 For this, he planned to recover the mountain waters in dams and reservoirs and then forward them to the Seuil de Naurouze through channels crossing the Seuil de Graissens. The water from the Sor passing near Revel was the main supply envisaged by Riquet. Other rivers from the Montagne Noire were also part of the system such as the Alzeau, the Laudot, the Rieutort, the Bernassonne, and the . The Montagne Noire is a region with twice the rainfall of the plain of Lauragais with 1400 millimetres per year at around above sea level. To store the river water he planned to create three basins: the Reservoir of Lampy-Vieux, a hexagonal harbour basin at Naurouze, and the Bassin de Saint-Ferréol with a large earth dam across the mouth of the valley of the Laudot stream.
In 1664, during the study of the project, the Estates of Languedoc asked Riquet to put into practice his idea experimentally. He then built a test channel diverting water from the Sor to the Seuil de Naurouze. It was the Rigole de la plaine which he completed in 1665 and used to prove that it is possible to bring water to the highest points of the course of the canal.Michel Cotte, ''Canal du Midi, marvel of Europe'', Paris: Belin, 2003, 191 pages, , p. 26. This was the event that reassured the Committee of Experts that the king had set up on site to inspect the choices and plans prepared by Riquet. From that moment
For this, he planned to recover the mountain waters in dams and reservoirs and then forward them to the Seuil de Naurouze through channels crossing the Seuil de Graissens. The water from the Sor passing near Revel was the main supply envisaged by Riquet. Other rivers from the Montagne Noire were also part of the system such as the Alzeau, the Laudot, the Rieutort, the Bernassonne, and the . The Montagne Noire is a region with twice the rainfall of the plain of Lauragais with 1400 millimetres per year at around above sea level. To store the river water he planned to create three basins: the Reservoir of Lampy-Vieux, a hexagonal harbour basin at Naurouze, and the Bassin de Saint-Ferréol with a large earth dam across the mouth of the valley of the Laudot stream.
In 1664, during the study of the project, the Estates of Languedoc asked Riquet to put into practice his idea experimentally. He then built a test channel diverting water from the Sor to the Seuil de Naurouze. It was the Rigole de la plaine which he completed in 1665 and used to prove that it is possible to bring water to the highest points of the course of the canal.Michel Cotte, ''Canal du Midi, marvel of Europe'', Paris: Belin, 2003, 191 pages, , p. 26. This was the event that reassured the Committee of Experts that the king had set up on site to inspect the choices and plans prepared by Riquet. From that moment  Riquet studied in depth the supply of water to the canal at the Seuil de Naurouze. His study appeared rigorous and included a pilot phase with the construction of the Rigole de la plaine to substantiate his claim. The project still remained unclear in many respects especially the route of the canal. This route was not final and was not precise as it would be today for a highway project or high-speed railway. Only the directions of the route were known and plotted on a map. Changes in the route could be made by the Contractor depending on the difficulties he encountered on the ground.
On the Atlantic side, he proposed several layouts: one to pass by
Riquet studied in depth the supply of water to the canal at the Seuil de Naurouze. His study appeared rigorous and included a pilot phase with the construction of the Rigole de la plaine to substantiate his claim. The project still remained unclear in many respects especially the route of the canal. This route was not final and was not precise as it would be today for a highway project or high-speed railway. Only the directions of the route were known and plotted on a map. Changes in the route could be made by the Contractor depending on the difficulties he encountered on the ground.
On the Atlantic side, he proposed several layouts: one to pass by  At the age of 63, Riquet started his great enterprise, sending his personal engineer, François Andreossy, and a local water expert, Pierre Roux, to the Montagne Noire to work on the water supply. This supply system successfully fed the canal with water where it crossed the continental divide, replacing water that drained toward the two seas. The system was a masterpiece of both hydraulic and
At the age of 63, Riquet started his great enterprise, sending his personal engineer, François Andreossy, and a local water expert, Pierre Roux, to the Montagne Noire to work on the water supply. This supply system successfully fed the canal with water where it crossed the continental divide, replacing water that drained toward the two seas. The system was a masterpiece of both hydraulic and  In November 1667 an official ceremony laid the foundation stone of the Garonne lock in Toulouse in the presence of representatives of the
In November 1667 an official ceremony laid the foundation stone of the Garonne lock in Toulouse in the presence of representatives of the  Channel management was ensured primarily by the descendants of Riquet. This was through the elder son Jean-Mathias who took control of the fief until 1714, then Victor-Pierre-François until 1760, then Victor-Maurice, and finally Jean-Gabriel. The Riquet family quickly put up a pyramidal organisation structure with a "Director-General of the Canal" who governs a board of directors responsible for specific geographic areas of the channel. Seven zones were defined in the west and the east: Toulouse, Naurouze, Castelnaudary, Trèbes Le Somail, Beziers, and Agde. Each Director is responsible for maintenance of his zone and is supported by a receiver and a controller. Hundreds of lock-keepers are responsible for the locks. This organization facilitates the control and hiring of employees.
In Toulouse, a group of three people form a steering committee: the director general of works, the Receiver General who sets the fees, and the Comptroller General in charge of accounting. Canal management ensures the supply of money to pay for various works and staff hired for the canal. In the 1770s a tax report showed an income of 640,000 livres, half of which went to maintenance and salaries, and half the profits and funds were exceptional works. In 1785 this benefit increased to 950,000 livres which was a very large sum for the time.
Channel management was ensured primarily by the descendants of Riquet. This was through the elder son Jean-Mathias who took control of the fief until 1714, then Victor-Pierre-François until 1760, then Victor-Maurice, and finally Jean-Gabriel. The Riquet family quickly put up a pyramidal organisation structure with a "Director-General of the Canal" who governs a board of directors responsible for specific geographic areas of the channel. Seven zones were defined in the west and the east: Toulouse, Naurouze, Castelnaudary, Trèbes Le Somail, Beziers, and Agde. Each Director is responsible for maintenance of his zone and is supported by a receiver and a controller. Hundreds of lock-keepers are responsible for the locks. This organization facilitates the control and hiring of employees.
In Toulouse, a group of three people form a steering committee: the director general of works, the Receiver General who sets the fees, and the Comptroller General in charge of accounting. Canal management ensures the supply of money to pay for various works and staff hired for the canal. In the 1770s a tax report showed an income of 640,000 livres, half of which went to maintenance and salaries, and half the profits and funds were exceptional works. In 1785 this benefit increased to 950,000 livres which was a very large sum for the time.
 Curiously, the canal did not really serve its purpose. The economic and political context hindered the economic development that had been expected. After two hundred years of operation, the canal began to suffer from competition from rail and road. It reached its peak in the middle of the 19th century. In 1858
Curiously, the canal did not really serve its purpose. The economic and political context hindered the economic development that had been expected. After two hundred years of operation, the canal began to suffer from competition from rail and road. It reached its peak in the middle of the 19th century. In 1858  The government tried to revive the renovation of the canal by enacting a legal program to lift the channel to the standards of the Freycinet gauge. The canals of northern France were already at this level and had traffic well above the Canal du Midi. However, the law remained unimplemented due to lack of funds.
At the end of the
The government tried to revive the renovation of the canal by enacting a legal program to lift the channel to the standards of the Freycinet gauge. The canals of northern France were already at this level and had traffic well above the Canal du Midi. However, the law remained unimplemented due to lack of funds.
At the end of the  The Canal du Midi is now used primarily by tourists, recreation, and housing.
It attracts more and more river tourism, including sailing on chartered boats, restaurant-boats, or hotel barges such as the Anjodi. Tourism has grown from the 1960s, most significantly from Britain, and then exploded in the 1980s. The canal was featured prominently in the
The Canal du Midi is now used primarily by tourists, recreation, and housing.
It attracts more and more river tourism, including sailing on chartered boats, restaurant-boats, or hotel barges such as the Anjodi. Tourism has grown from the 1960s, most significantly from Britain, and then exploded in the 1980s. The canal was featured prominently in the  During the dry season, the canal serves as a reservoir for
During the dry season, the canal serves as a reservoir for  While the canal was once seen as a tool of production, trade, and commerce it is now considered to be architectural and technical heritage as evidenced by the refusal of the mayor of Toulouse, Pierre Baudis, to allow space on the Canal du Midi to be used for an urban expressway. It has not been downgraded and remains open for navigation. On 7 December 1996 the channel and a buffer zone of 2,000 km were included in the list of
While the canal was once seen as a tool of production, trade, and commerce it is now considered to be architectural and technical heritage as evidenced by the refusal of the mayor of Toulouse, Pierre Baudis, to allow space on the Canal du Midi to be used for an urban expressway. It has not been downgraded and remains open for navigation. On 7 December 1996 the channel and a buffer zone of 2,000 km were included in the list of 
 It takes 90 million cubic metres of water to feed the canal for one year. To do this, Riquet set up a complex system of water supply to the canal. The idea was to capture the waters of the Montagne Noire located several tens of kilometres away and bring it to the Seuil de Naurouze, the highest point of the future canal, through channels.
These channels, called " Rigole de la montagne" (Channel of the Mountain) and " Rigole de la plaine" (Channel of the Plain) connected the upper three reservoirs (Lampy, Cammazes, and Saint-Ferréol) at the seuil de Naurouze. The Rigole de la Montagne measured long and has 22 structures between the outlet at Alzeau and the falls of Cammazes. The Rigole de la Plaine measured long at altitude and included 68 structures between the Crouzet bridge and the seuil de Naurouze.
Initially, two
It takes 90 million cubic metres of water to feed the canal for one year. To do this, Riquet set up a complex system of water supply to the canal. The idea was to capture the waters of the Montagne Noire located several tens of kilometres away and bring it to the Seuil de Naurouze, the highest point of the future canal, through channels.
These channels, called " Rigole de la montagne" (Channel of the Mountain) and " Rigole de la plaine" (Channel of the Plain) connected the upper three reservoirs (Lampy, Cammazes, and Saint-Ferréol) at the seuil de Naurouze. The Rigole de la Montagne measured long and has 22 structures between the outlet at Alzeau and the falls of Cammazes. The Rigole de la Plaine measured long at altitude and included 68 structures between the Crouzet bridge and the seuil de Naurouze.
Initially, two  Several ports were built at regular intervals along the route of the canal in order to load and unload goods and also to provide stopping-places for travellers. Toulouse has two ports: the port de l'Embouchure is located at the junction of the Canal du Midi, the Canal de Brienne, and the Lateral canal of the Garonne while Port Saint-Sauveur is located in the centre of town near the ''Hall of Grains''. There were two other ports in Toulouse but they were destroyed for urban development. So the ''Port des Minimes'' and the ''Port Saint-Etienne'' were replaced by towpaths.
Castelnaudary has a port of called ''Grand Basin'' built between 1666 and 1671. It served as a stopover halfway between Toulouse and Sète. Cybelle island in the middle of the basin was used to protect the barges from the wind. Carcassonne is today a major tourist stop on the canal and has a port built in 1810 at the time when the city was connected to the canal. The port of Trèbes is a major port which has numerous moorings for boats. There are also the ports of Homps which was one of the most important on the canal and Le Somail which was a popular place for rest and recreation. Finally, just before its arrival at the Mediterranean Sea, the canal has two ports: the port of Agde where there is the old hotel of the "Administration of the Canal", and the port of Onglous at Marseillan which is the last port before Sète and its royal canal giving access to the sea.
Newer ports were built such as Ramonville-Saint-Agne, called Port-Sud, which has many residential barges and is set directly overlooking the harbour, and Port-Lauragais located near Avignonet-Lauragais on a service area of the A61 autoroute.
Several ports were built at regular intervals along the route of the canal in order to load and unload goods and also to provide stopping-places for travellers. Toulouse has two ports: the port de l'Embouchure is located at the junction of the Canal du Midi, the Canal de Brienne, and the Lateral canal of the Garonne while Port Saint-Sauveur is located in the centre of town near the ''Hall of Grains''. There were two other ports in Toulouse but they were destroyed for urban development. So the ''Port des Minimes'' and the ''Port Saint-Etienne'' were replaced by towpaths.
Castelnaudary has a port of called ''Grand Basin'' built between 1666 and 1671. It served as a stopover halfway between Toulouse and Sète. Cybelle island in the middle of the basin was used to protect the barges from the wind. Carcassonne is today a major tourist stop on the canal and has a port built in 1810 at the time when the city was connected to the canal. The port of Trèbes is a major port which has numerous moorings for boats. There are also the ports of Homps which was one of the most important on the canal and Le Somail which was a popular place for rest and recreation. Finally, just before its arrival at the Mediterranean Sea, the canal has two ports: the port of Agde where there is the old hotel of the "Administration of the Canal", and the port of Onglous at Marseillan which is the last port before Sète and its royal canal giving access to the sea.
Newer ports were built such as Ramonville-Saint-Agne, called Port-Sud, which has many residential barges and is set directly overlooking the harbour, and Port-Lauragais located near Avignonet-Lauragais on a service area of the A61 autoroute.
 *the Malpas Tunnel long southeast of the Oppidum d'Ensérune which passes through a hill above sea level and was a technical challenge for the time
*the Argent-Double spillway located in La Redorte near the Argent-Double Aqueduct: this work incorporates eleven successive stone arches contemporary to Vauban, its designer; it was built by Antoine de Niquet and allows for the overflow water from the canal to be discharged into the stream
*the Fonserannes water slope, which bypasses the 6-lock staircase at Fonserannes, was built at the time when the canal was to be upgraded to Freycinet gauge to save time and allow larger vessels to work on. It has a unique machinery whose maintenance is expensive, but for several years, VNF has attempted to rehabilitate it to reduce waiting times at the Fonséranes locks
*the Ouvrages du Libron (the works of Libron), a unique achievement of its kind which allows the canal to cross the course of the Libron near Agde
*the
*the Malpas Tunnel long southeast of the Oppidum d'Ensérune which passes through a hill above sea level and was a technical challenge for the time
*the Argent-Double spillway located in La Redorte near the Argent-Double Aqueduct: this work incorporates eleven successive stone arches contemporary to Vauban, its designer; it was built by Antoine de Niquet and allows for the overflow water from the canal to be discharged into the stream
*the Fonserannes water slope, which bypasses the 6-lock staircase at Fonserannes, was built at the time when the canal was to be upgraded to Freycinet gauge to save time and allow larger vessels to work on. It has a unique machinery whose maintenance is expensive, but for several years, VNF has attempted to rehabilitate it to reduce waiting times at the Fonséranes locks
*the Ouvrages du Libron (the works of Libron), a unique achievement of its kind which allows the canal to cross the course of the Libron near Agde
*the  The canal is a long ribbon of water stretching through the landscape and attracts many animal species. Several species of fish such as bream breed in the canal, and others reproduce in its feeding rivers and spend part of their life in the canal.
The canal is a long ribbon of water stretching through the landscape and attracts many animal species. Several species of fish such as bream breed in the canal, and others reproduce in its feeding rivers and spend part of their life in the canal.  The Canal du Midi was one of the great achievements of the late 17th century. Riquet understood the hydraulic system of the Montagne Noire and had controlled it to serve the Canal du Midi. King
The Canal du Midi was one of the great achievements of the late 17th century. Riquet understood the hydraulic system of the Montagne Noire and had controlled it to serve the Canal du Midi. King