cpr on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an
 In 2010, the
In 2010, the
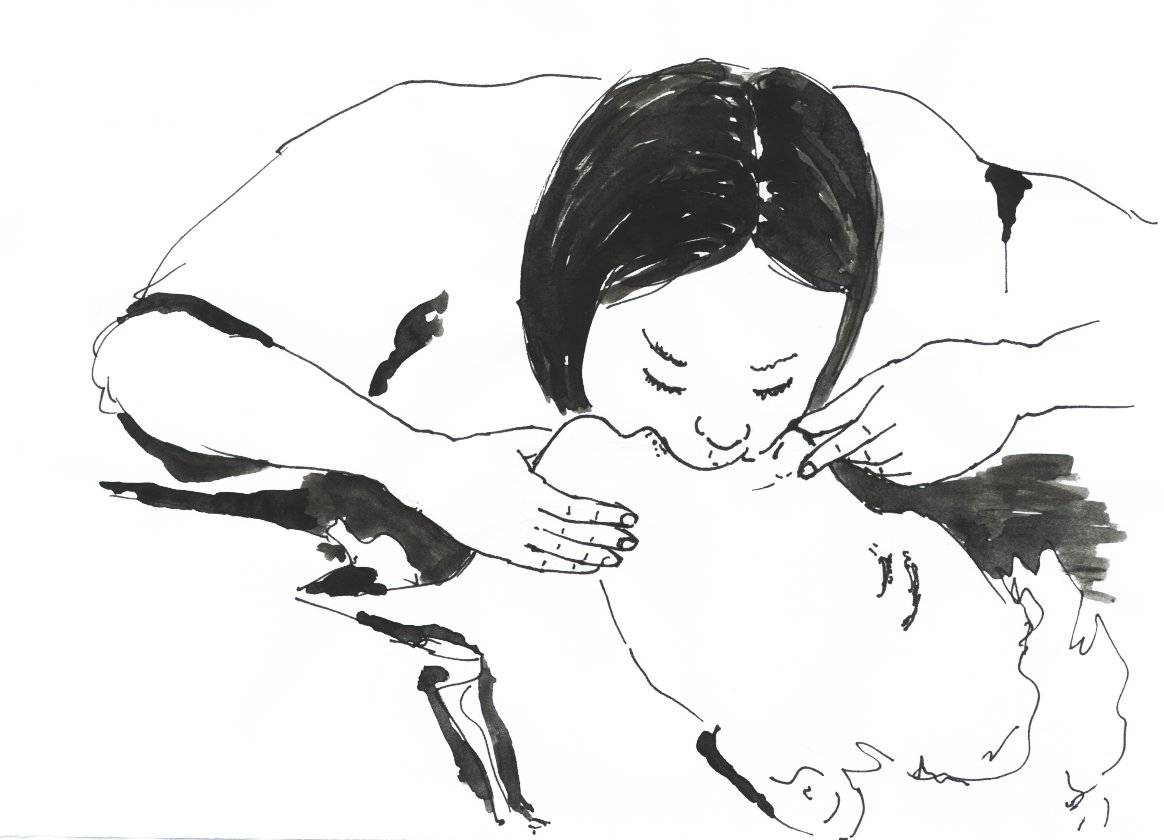
 A normal CPR procedure uses chest compressions and ventilations. The compressions push on the bone that is in the middle of the chest (
A normal CPR procedure uses chest compressions and ventilations. The compressions push on the bone that is in the middle of the chest ( In some cases, the patient has experienced one of the failures in the rhythm of the heart (ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia) that can be corrected with the electric shock of a
In some cases, the patient has experienced one of the failures in the rhythm of the heart (ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia) that can be corrected with the electric shock of a
 Compression-only CPR is not as good for children who are more likely to have cardiac arrest from respiratory causes. Two reviews have found that compression-only CPR had no more success than no CPR whatsoever. Rescue breaths for children and especially for babies should be relatively gentle. Either a ratio of compressions to breaths of 30:2 or 15:2 was found to have better results for children. Both children and adults should receive a hundred chest compressions per minute. Other exceptions besides children include cases of
Compression-only CPR is not as good for children who are more likely to have cardiac arrest from respiratory causes. Two reviews have found that compression-only CPR had no more success than no CPR whatsoever. Rescue breaths for children and especially for babies should be relatively gentle. Either a ratio of compressions to breaths of 30:2 or 15:2 was found to have better results for children. Both children and adults should receive a hundred chest compressions per minute. Other exceptions besides children include cases of
 Standard CPR is performed with the victim in
Standard CPR is performed with the victim in
For more help.

 Defibrillators produce a defibrillation (electric shocks) that can restore the normal heart function of the victim.
Nevertheless, they are only indicated for some
Defibrillators produce a defibrillation (electric shocks) that can restore the normal heart function of the victim.
Nevertheless, they are only indicated for some
instructions of defibrillators
that explain it step-by-step. There are several devices for improving CPR but, only defibrillators (as of 2010) have been found better than standard CPR for an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
emergency procedure An emergency procedure is a plan of actions to be conducted in a certain order or manner, in response to a specific class of reasonably foreseeable emergency, a situation that poses an immediate risk to health, life, property, or the environment. W ...
consisting of chest compressions often combined with artificial ventilation in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function until further measures are taken to restore spontaneous blood circulation and breathing in a person who is in cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. It is a medical emergency that, without immediate medical intervention, will result in sudden cardiac death within minutes. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and possib ...
. It is recommended in those who are unresponsive with no breathing or abnormal breathing, for example, agonal respirations.
CPR involves chest compressions for adults between and deep and at a rate of at least 100 to 120 per minute. The rescuer may also provide artificial ventilation by either exhaling air into the subject's mouth or nose ( mouth-to-mouth resuscitation) or using a device that pushes air into the subject's lungs (mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move ai ...
). Current recommendations place emphasis on early and high-quality chest compressions over artificial ventilation; a simplified CPR method involving only chest compressions is recommended for untrained rescuers. With children, however, 2015 American Heart Association
The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability and death ...
guidelines indicate that doing only compressions may actually result in worse outcomes, because such problems in children normally arise from respiratory issues rather than from cardiac ones, given their young age. Chest compression to breathing ratios is set at 30 to 2 in adults.
CPR alone is unlikely to restart the heart. Its main purpose is to restore partial flow of oxygenated blood to the brain
The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head ( cephalization), usually near organs for special ...
and heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon diox ...
. The objective is to delay tissue death
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated dige ...
and to extend the brief window of opportunity for a successful resuscitation without permanent brain damage
Neurotrauma, brain damage or brain injury (BI) is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating t ...
. Administration of an electric shock to the subject's heart, termed defibrillation
Defibrillation is a treatment for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, specifically ventricular fibrillation (V-Fib) and non-perfusing ventricular tachycardia (V-Tach). A defibrillator delivers a dose of electric current (often called a ''coun ...
, is usually needed in order to restore a viable, or "perfusing", heart rhythm. Defibrillation is effective only for certain heart rhythms, namely ventricular fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the Ventricle (heart), ventricles of the heart Fibrillation, quiver. It is due to disorganized electrical conduction system of the heart, electrical activity. Ventricular ...
or pulseless ventricular tachycardia, rather than asystole or pulseless electrical activity, which usually require the treatment of underlying conditions to restore cardiac function. Early shock, when appropriate, is recommended. CPR may succeed in inducing a heart rhythm that may be shockable. In general, CPR is continued until the person has a return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) or is declared dead.
Medical uses
CPR is indicated for any person unresponsive with no breathing or breathing only in occasional agonal gasps, as it is most likely that they are incardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. It is a medical emergency that, without immediate medical intervention, will result in sudden cardiac death within minutes. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and possib ...
. If a person still has a pulse
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the ...
but is not breathing ( respiratory arrest) artificial ventilations may be more appropriate, but, due to the difficulty people have in accurately assessing the presence or absence of a pulse, CPR guidelines recommend that lay persons should not be instructed to check the pulse, while giving healthcare professionals the option to check a pulse. In those with cardiac arrest due to trauma, CPR is considered futile but still recommended. Correcting the underlying cause such as a tension pneumothorax or pericardial tamponade
Cardiac tamponade, also known as pericardial tamponade (), is the buildup of fluid in the pericardium (the sac around the heart), resulting in compression of the heart. Onset may be rapid or gradual. Symptoms typically include those of obstruc ...
may help.
Pathophysiology
CPR is used on people in cardiac arrest in order to oxygenate the blood and maintain acardiac output
In cardiac physiology, cardiac output (CO), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols Q, \dot Q, or \dot Q_ , edited by Catherine E. Williamson, Phillip Bennett is the volumetric flow rate of the heart's pumping output: th ...
to keep vital organs alive. Blood circulation and oxygenation are required to transport oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
to the tissues. The physiology of CPR involves generating a pressure gradient between the arterial and venous vascular beds; CPR achieves this via multiple mechanisms The brain
The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head ( cephalization), usually near organs for special ...
may sustain damage after blood flow has been stopped for about four minutes and irreversible damage after about seven minutes. Typically if blood flow ceases for one to two hours, then body cells die. Therefore, in general CPR is effective only if performed within seven minutes of the stoppage of blood flow. The heart also rapidly loses the ability to maintain a normal rhythm. Low body temperatures, as sometimes seen in near-drownings, prolong the time the brain survives. Following cardiac arrest, effective CPR enables enough oxygen to reach the brain to delay brain stem death, and allows the heart to remain responsive to defibrillation
Defibrillation is a treatment for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, specifically ventricular fibrillation (V-Fib) and non-perfusing ventricular tachycardia (V-Tach). A defibrillator delivers a dose of electric current (often called a ''coun ...
attempts.
Methods
 In 2010, the
In 2010, the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability and death ...
and International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation updated their CPR guidelines. The importance of high quality CPR (sufficient rate and depth without excessively ventilating) was emphasized. The order of interventions was changed for all age groups except newborns from airway, breathing, chest compressions (ABC) to chest compressions, airway, breathing (CAB). An exception to this recommendation is for those believed to be in a respiratory arrest (airway obstruction, drug overdose, etc.). The most important aspect of CPR are: few interruptions of chest compressions, a sufficient speed and depth of compressions, completely relaxing pressure between compressions, and not ventilating too much. It is unclear if a few minutes of CPR before defibrillation results in different outcomes than immediate defibrillation.
Compressions with rescue breaths

 A normal CPR procedure uses chest compressions and ventilations. The compressions push on the bone that is in the middle of the chest (
A normal CPR procedure uses chest compressions and ventilations. The compressions push on the bone that is in the middle of the chest (sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. ...
) and the ventilations are made pinching the victim's nose and blowing air mouth-to-mouth. If the victim is a baby, the rescuer would make the ventilations covering the baby's mouth and nose at the same time. It is recommended for all victims of any age a general compression-to-ventilation ratio of 30:2 (30 rhythmic compressions before each 2 ventilations).
As an exception for the normal compression-to-ventilation ratio of 30:2, if at least two trained rescuers are present, and the victim is a child, a ratio of 15:2 is preferred. And, according to the AHA 2015 Guidelines, the ratio in newborns is 30:2 if one rescuer is present and 15:2 if two rescuers are present. In an advanced airway treatment, such as an endotracheal tube or laryngeal mask airway, the artificial ventilation should occur without pauses in compressions, at a rate of 1 breath every 6 to 8 seconds (8–10 ventilations per minute).
In all the victims, the compression speed is of at least 100 compressions per minute. Recommended compression depth in adults and children is of 5 cm (2 inches), and in infants it is 4 cm (1.6 inches). In adults, rescuers should use two hands for the chest compressions (one on the top of the other), while in children one hand can be enough, and with babies the rescuer must use only two fingers.
There exist some plastic shields and respirators that can be used in the rescue breaths between the mouths of the rescuer and the victim, with the purposes of sealing a better vacuum and avoiding infections.
 In some cases, the patient has experienced one of the failures in the rhythm of the heart (ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia) that can be corrected with the electric shock of a
In some cases, the patient has experienced one of the failures in the rhythm of the heart (ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia) that can be corrected with the electric shock of a defibrillator
Defibrillation is a treatment for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, specifically ventricular fibrillation (V-Fib) and non-perfusing ventricular tachycardia (V-Tach). A defibrillator delivers a dose of electric current (often called a ''coun ...
. It is important then that someone asks for the defibrillator and to use it, which would be easy, because the common models of defibrillator (the AEDs) are automatic portable machines that guide to the user with recorded voice instructions along the process, and analyze the victim, and apply the correct shocks if they are needed. Besides, there exist written instructions of defibrillators that explain how to use them step-by-step.
The recommended order of normal cardiopulmonary resuscitation is the 'CAB': first 'Chest' (chest compressions), followed by 'Airway' (attempt to open the airway by performing a head tilt and a chin lift), and 'Breathing' (rescue breaths). Anyway, as of 2010, the Resuscitation Council (UK) was still recommending an 'ABC' order if the victim is a child. It can be difficult to determine the presence or absence of a pulse, so the pulse check has been removed for common providers and should not be performed for more than 10 seconds by healthcare providers.
Compression only
For adults with cardiac arrest, compression-only (hands-only or cardiocerebral resuscitation) CPR which involves chest compressions without artificial ventilation is recommended as the method of choice for the untrained rescuer or those who are not proficient as it is easier to perform and instructions are easier to give over a phone. In adults with out-of-hospitalcardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. It is a medical emergency that, without immediate medical intervention, will result in sudden cardiac death within minutes. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and possib ...
, compression-only CPR by the lay public has an equal or higher success rate than standard CPR. Acknowledgements include: Mary Fran Hazinski, RN, MSN; Michael Shuster, MD; Michael W. Donnino, MD; et al., 2015. "The ''2015 AHA Guidelines Update for CPR and ECC'' is based on an international evidence evaluation process that involved 250 evidence reviewers from 39 countries." It is hoped that the use of compression-only delivery will increase the chances of the lay public delivering CPR. Compression-only CPR is not as good for children who are more likely to have cardiac arrest from respiratory causes. Two reviews have found that compression-only CPR had no more success than no CPR whatsoever. Rescue breaths for children and especially for babies should be relatively gentle. Either a ratio of compressions to breaths of 30:2 or 15:2 was found to have better results for children. Both children and adults should receive a hundred chest compressions per minute. Other exceptions besides children include cases of
Compression-only CPR is not as good for children who are more likely to have cardiac arrest from respiratory causes. Two reviews have found that compression-only CPR had no more success than no CPR whatsoever. Rescue breaths for children and especially for babies should be relatively gentle. Either a ratio of compressions to breaths of 30:2 or 15:2 was found to have better results for children. Both children and adults should receive a hundred chest compressions per minute. Other exceptions besides children include cases of drowning
Drowning is a type of suffocation induced by the submersion of the mouth and nose in a liquid. Most instances of fatal drowning occur alone or in situations where others present are either unaware of the victim's situation or unable to offer a ...
s and drug overdose
A drug overdose (overdose or OD) is the ingestion or application of a drug or other substance in quantities much greater than are recommended.
. In both these cases, compressions and rescue breaths are recommended if the bystander is trained and is willing to do so.
As per the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability and death ...
, the beat of the Bee Gees
The Bee Gees
were a musical group formed in 1958 by brothers Barry, Robin, and Maurice Gibb. The trio were especially successful in popular music in the late 1960s and early 1970s, and later as prominent performers in the disco music era i ...
song "Stayin' Alive
"Stayin' Alive" is a song written and performed by the Bee Gees from the ''Saturday Night Fever'' motion picture soundtrack. The song was released in 1977 as the second single from the '' Saturday Night Fever'' soundtrack. The band co-produce ...
" provides an ideal rhythm in terms of beats per minute to use for hands-only CPR, which is 104 beats-per-minute. One can also hum Queen
Queen or QUEEN may refer to:
Monarchy
* Queen regnant, a female monarch of a Kingdom
** List of queens regnant
* Queen consort, the wife of a reigning king
* Queen dowager, the widow of a king
* Queen mother, a queen dowager who is the mother ...
's " Another One Bites The Dust", which is 110 beats-per-minute and contains a memorable repeating drum pattern. For those in cardiac arrest due to non heart related causes and in people less than 20 years of age, standard CPR is superior to compression-only CPR.
Prone CPR
supine position
The supine position ( or ) means lying horizontally with the face and torso facing up, as opposed to the prone position, which is face down. When used in surgical procedures, it grants access to the peritoneal, thoracic and pericardial region ...
. Prone CPR, or reverse CPR, is performed on a victim in prone position
Prone position () is a body position in which the person lies flat with the chest down and the back up. In anatomical terms of location, the dorsal side is up, and the ventral side is down. The supine position is the 180° contrast.
Etymolog ...
, lying on the chest. This is achieved by turning the head to the side and compressing the back. Due to the head being turned, the risk of vomiting and complications caused by aspiration pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia is a type of lung infection that is due to a relatively large amount of material from the stomach or mouth entering the lungs. Signs and symptoms often include fever and cough of relatively rapid onset. Complications may in ...
may be reduced.
The American Heart Association's current guideline recommends performing CPR in the supine position
The supine position ( or ) means lying horizontally with the face and torso facing up, as opposed to the prone position, which is face down. When used in surgical procedures, it grants access to the peritoneal, thoracic and pericardial region ...
, and limits prone CPR to situations where the patient cannot be turned.
Pregnancy
Duringpregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
when a woman is lying on her back, the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ...
may compress the inferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of th ...
and thus decrease venous return. It is therefore recommended that the uterus be pushed to the woman's left. This can be done by placing a pillow or towel under her right hip so that she is on an angle of 15-30 degrees, and making sure their shoulders are flat to the ground. If this is not effective healthcare professionals should consider emergency resuscitative hysterotomy.
Family presence
Evidence generally supports family being present during CPR. This includes in CPR for children.Other
Interposed abdominal compressions may be beneficial in the hospital environment. There is no evidence of benefit pre-hospital or in children. Cooling during CPR is being studied as currently results are unclear whether or not it improves outcomes. Internal cardiac massage is manual squeezing of the exposed heart itself carried out through a surgical incision into thechest cavity
The thoracic cavity (or chest cavity) is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall ( rib cage and associated skin, muscle, and fascia). The central compartment of the thoracic cavity is the mediastinum. Ther ...
, usually when the chest is already open for cardiac surgery.
Active compression-decompression methods using mechanical decompression of the chest have not been shown to improve outcome in cardiac arrest.
CPR for Heart Attack: Airway:
If you’ve been trained in CPR after you’ve done the 30 compressions to your chest, you can open the airway for your child by performing the head-tilted chin-lift technique.
* Place your fingers on the forehead of the child and gently tilt the child’s head to the side.
* On the other hand, use the other hand to gently lift the cheeks forward to open the airwayFor more help.
Use of devices

Defibrillators
 Defibrillators produce a defibrillation (electric shocks) that can restore the normal heart function of the victim.
Nevertheless, they are only indicated for some
Defibrillators produce a defibrillation (electric shocks) that can restore the normal heart function of the victim.
Nevertheless, they are only indicated for some arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults ...
s (abnormal heart beatings), specifically ventricular fibrillation (VF) and pulseless ventricular tachycardia. Defibrillation is not indicated if the patient is conscious or has a normal pulse. Defibrillation is also not indicated if the heart has completely stopped, as in asystole or pulseless electrical activity (PEA), in those cases a normal CPR would be used to oxygenate the brain until the heart function can be restored. Improperly given electrical shocks can cause dangerous arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults ...
s, such as the ventricular fibrillation (VF).
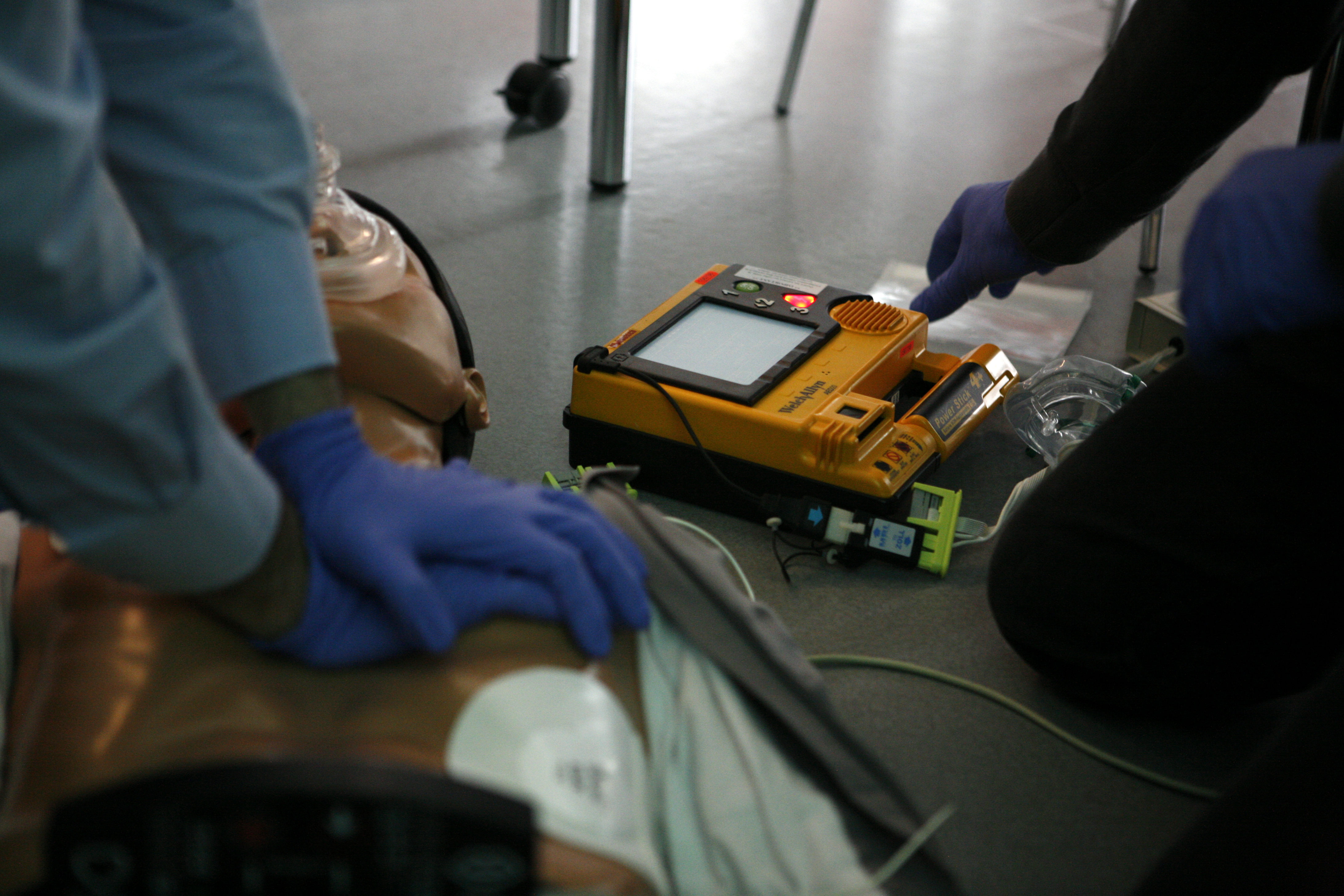
The standard defibrillation device, prepared for a fast use out of the medical centres, is the automated external defibrillator (AED), a portable machine of small size (similar to a briefcase) that can be used by any user with no previous training. That machine produces recorded voice instructions that guide to the user along the defibrillation process. It also checks the victim's condition to apply automatically electric shocks at a correct level, if they are needed. Other models are semi-automatic and need that the user push a button before producing an electric shock.
The defibrillation process is simple, but there exist writteinstructions of defibrillators
that explain it step-by-step. There are several devices for improving CPR but, only defibrillators (as of 2010) have been found better than standard CPR for an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
Devices for timing CPR
Timing devices can feature ametronome
A metronome, from ancient Greek μέτρον (''métron'', "measure") and νομός (nomós, "custom", "melody") is a device that produces an audible click or other sound at a regular interval that can be set by the user, typically in beats pe ...
(an item carried by many ambulance crews) in order to assist the rescuer in achieving the correct rate. Some units can also give timing reminders for performing compressions, ventilating and changing operators.
Devices for assisting in manual CPR
Mechanical chest compression devices have not been found to be better than standard manual compressions. Their use is reasonable in situations where manual compressions are not safe to perform such as a moving vehicle. Audible and visual prompting may improve the quality of CPR and prevent the decrease of compression rate and depth that naturally occurs with fatigue, and to address this potential improvement, a number of devices have been developed to help improve CPR technique. These items can be devices to be placed on top of the chest, with the rescuer's hands going over the device, and a display or audio feedback giving information on depth, force or rate, or in a wearable format such as a glove. Several published evaluations show that these devices can improve the performance of chest compressions. As well as its use during actual CPR on a cardiac arrest victim, which relies on the rescuer carrying the device with them, these devices can also be used as part of training programs to improve basic skills in performing correct chest compressions.Devices for providing automatic CPR
Mechanical CPR has not seen as much use asmechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move ai ...
; however, use in the prehospital setting is increasing. Devices on the market include the LUCAS device, developed at the University Hospital of Lund, and AutoPulse
The AutoPulse is an automated, portable, battery-powered cardiopulmonary resuscitation device created by Revivant and subsequently purchased and currently manufactured by ZOLL Medical Corporation. It is a chest compression device composed of a co ...
. Both use straps around the chest to secure the patient. The first generation of the LUCAS uses a gas-driven piston and motor-driven constricting band, while later version are battery operated.
There are several advantages to automated devices: they allow rescuers to focus on performing other interventions; they do not fatigue and begin to perform less effective compressions, as humans do; they are able to perform effective compressions in limited-space environments such as air ambulance
Air medical services is a comprehensive term covering the use of air transportation, aeroplane or helicopter, to move patients to and from healthcare facilities and accident scenes. Personnel provide comprehensive prehospital and emergency and cri ...
s, where manual compressions are difficult, and they allow ambulance workers to be strapped in safely rather than standing over a patient in a speeding vehicle. However the disadvantages are cost to purchase, time to train emergency personnel to use them, interruption to CPR to implement, potential for incorrect application and the need for multiple device sizes.
Several studies have shown little or no improvement in survival rates but acknowledge the need for more study.
Mobile apps for providing CPR instructions
To support training and incident management, mobile apps have been published on the largest app markets. An evaluation of 61 available apps has revealed that a large number do not follow international guidelines for basic life support and many apps are not designed in a user-friendly way. As a result, the Red Cross updated and endorsed its emergency preparedness application, which uses pictures, text and videos to assist the user. The UK Resuscitation Council, has an app, called Lifesaver, which shows how to perform CPR.Effectivity rate
CPR oxygenates the body and brain, which favours making a laterdefibrillation
Defibrillation is a treatment for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, specifically ventricular fibrillation (V-Fib) and non-perfusing ventricular tachycardia (V-Tach). A defibrillator delivers a dose of electric current (often called a ''coun ...
and the advanced life support
Advanced Life Support (ALS) is a set of life saving protocols and skills that extend basic life support to further support the circulation and provide an open airway and adequate ventilation (breathing).
Components
These include:
* Tracheal i ...
. Even in the case of a "non-shockable" rhythm, such as pulseless electrical activity (PEA) where defibrillation is not indicated, effective CPR is no less important. Used alone, CPR will result in few complete recoveries, though the outcome without CPR is almost uniformly fatal.
Studies have shown that immediate CPR followed by defibrillation within 3–5 minutes of sudden VF cardiac arrest dramatically improves survival. In cities such as Seattle where CPR training is widespread and defibrillation by EMS personnel follows quickly, the survival rate is about 20 percent for all causes and as high as 57 percent if a witnessed "shockable" arrest. In cities such as New York, without those advantages, the survival rate is only 5 percent for witnessed shockable arrest. Similarly in-hospital CPR is more successful when arrests are witnessed or are in the ICU or in patients wearing heart monitors, where the arrests are noticed immediately, as shown in the table and graph later in this article.
\* AED data here exclude health facilities and nursing homes, where patients are sicker than average.
In adults compression-only CPR by bystanders appears to be better than chest compressions with rescue breathing. Compression-only CPR may be less effective in children than in adults, as cardiac arrest in children is more likely to have a non-cardiac cause. In a 2010 prospective study of cardiac arrest in children (age 1–17) for arrests with a non-cardiac cause, provision by bystanders of conventional CPR with rescue breathing yielded a favorable neurological outcome at one month more often than did compression-only CPR ( OR 5.54). For arrests with a cardiac cause in this cohort, there was no difference between the two techniques (OR 1.20). This is consistent with American Heart Association guidelines for parents.
When done by trained responders, 30 compressions interrupted by two breaths appears to have a slightly better result than continuous chest compressions with breaths being delivered while compressions are ongoing.
Measurement of end-tidal carbon dioxide during CPR reflects cardiac output and can predict chances of ROSC.
In a study of in-hospital CPR from 2000 to 2008, 59% of CPR survivors lived over a year after hospital discharge and 44% lived over 3 years.
Consequences
Performing CPR is advised as an urgent intervention, for when a person is not breathing and therefore would certainly die without it. Survival rates: In US hospit