CFC-113 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
1,1,2-Trichloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane, also called trichlorotrifluoroethane (often abbreviated as TCTFE) or CFC-113, is a
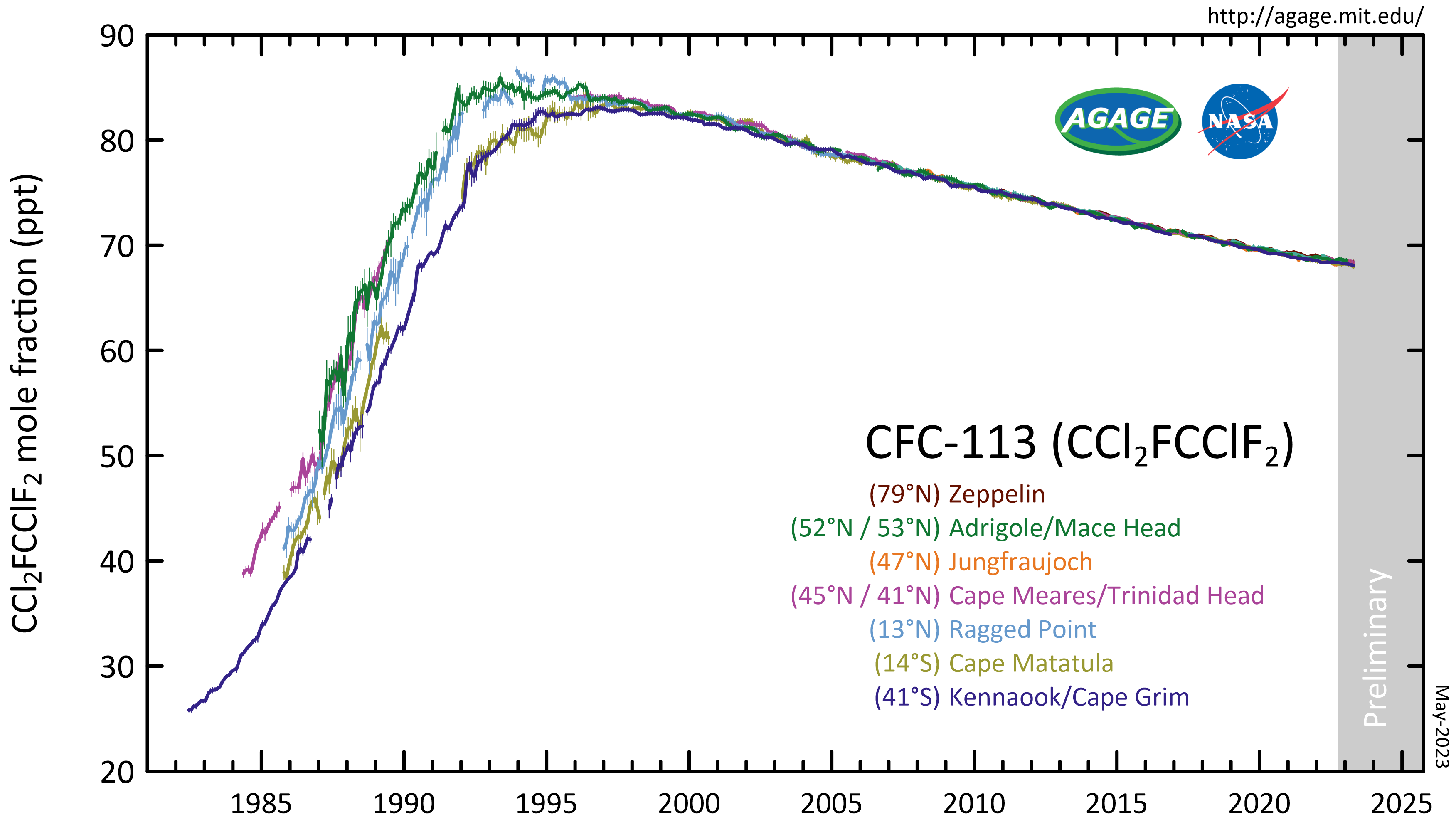 CFC-113 is a very unreactive chlorofluorocarbon. It may remain in the
CFC-113 is a very unreactive chlorofluorocarbon. It may remain in the
chlorofluorocarbon
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly Halogenation, halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F). They are produced as volatility (chemistry), volat ...
. It has the formula . This colorless, volatile liquid is a versatile solvent.
Production
CFC-113 can be prepared fromhexachloroethane
Hexachloroethane (perchloroethane) is an organochlorine compound with the chemical formula . Its structure is . It is a white or colorless solid at room temperature with a camphor-like odor. It has been used by the military in smoke compositions, ...
and hydrofluoric acid
Hydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride (HF) in water. Solutions of HF are colorless, acidic and highly corrosive. A common concentration is 49% (48–52%) but there are also stronger solutions (e.g. 70%) and pure HF has a boiling p ...
:
:
This reaction may require catalysts such as antimony
Antimony is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Sb () and atomic number 51. A lustrous grey metal or metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient t ...
, chromium
Chromium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6 element, group 6. It is a steely-grey, Luster (mineralogy), lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium ...
, iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
and alumina
Aluminium oxide (or aluminium(III) oxide) is a chemical compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula . It is the most commonly occurring of several aluminium oxides, and specifically identified as aluminium oxide. It is commonly ...
at high temperatures.
Another synthesis method uses HF on tetrachloroethylene
Tetrachloroethylene, also known as perchloroethylene or under the systematic name tetrachloroethene, and abbreviations such as perc (or PERC), and PCE, is a chlorocarbon with the formula . It is a non-flammable, stable, colorless and heavy liqu ...
instead.
Atmospheric reactions
 CFC-113 is a very unreactive chlorofluorocarbon. It may remain in the
CFC-113 is a very unreactive chlorofluorocarbon. It may remain in the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
up to 90 years, sufficiently long that it will cycle out of the troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the ...
and into the stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second-lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is composed of stratified temperature zones, with the warmer layers of air located higher ...
. In the stratosphere, CFC-113 can be broken up by ultraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of t ...
(UV, sunlight in the 190-225 nm range), generating chlorine radicals (Cl•), which initiate degradation of ozone requiring only a few minutes:
:
:
This reaction is followed by:
:
The process regenerates Cl• to destroy more . The Cl• will destroy an average of 100,000 molecules during its atmospheric lifetime of 1–2 years.
Uses
CFC-113 was one of the most heavily produced CFCs. In 1989, an estimated 250,000 tons were produced. It has been used as a cleaning agent for electrical and electronic components. CFC-113’s low flammability and low toxicity made it ideal for use as a cleaner for delicate electrical equipment, fabrics, and metals. It would not harm the product it was cleaning, ignite with a spark or react with other chemicals. It was used as a dry-cleaning solvent, as an alternative to perchloroethylene, introduced by Du Pont in March 1961 as "Valclene" and was also marketed as the "solvent of the future" byImperial Chemical Industries
Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) was a British Chemical industry, chemical company. It was, for much of its history, the largest manufacturer in Britain. Its headquarters were at Millbank in London. ICI was listed on the London Stock Exchange ...
in the 1970s under the tradename "Arklone". Others from this series were ''Perklone'' (Tetrachloroethylene
Tetrachloroethylene, also known as perchloroethylene or under the systematic name tetrachloroethene, and abbreviations such as perc (or PERC), and PCE, is a chlorocarbon with the formula . It is a non-flammable, stable, colorless and heavy liqu ...
), ''Triklone'' (Trichloroethylene
Trichloroethylene (TCE) is an organochloride with the formula C2HCl3, commonly used as an industrial metal-degreasing solvent. It is a clear, colourless, non-flammable, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like pleasant mild smell and sweet taste.
), ''Methoklone'' (Dichloromethane
Dichloromethane (DCM, methylene chloride, or methylene bichloride) is an organochlorine compound with the formula . This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like, sweet odor is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with ...
) and ''Genklene'' (1,1,1-Trichloroethane
1,1,1-Trichloroethane, also known as methyl chloroform and chlorothene, is a chloroalkane with the chemical formula CH3CCl3. It is an isomer of 1,1,2-trichloroethane. A colourless and sweet-smelling liquid, it was once produced industrially i ...
).
CFC-113 is one of the three most popular CFCs, along with CFC-11 and CFC-12.
CFC-113 in laboratory analytics has been replaced by other solvents.
Reduction of CFC-113 with zinc gives chlorotrifluoroethylene
Chlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE) is a chlorofluorocarbon with chemical formula CFCl=CF2. It is commonly used as a refrigerant in cryogenic applications. CTFE has a carbon-carbon double bond and so can be polymerized to form polychlorotrifluoroethy ...
:
:
Dangers
Aside from its immense environmental impacts, Freon 113, like most chlorofluoroalkanes, formsphosgene
Phosgene is an organic chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic, colorless gas; in low concentrations, its musty odor resembles that of freshly cut hay or grass. It can be thought of chemically as the double acyl chloride analog of ...
gas when exposed to a naked flame.
See also
*1,1,1-Trichloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethane
1,1,1-Trichloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethane, also called Asymmetrical trichlorotrifluoroethane or CFC-113a, is a chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) with the formula .
Ozone depletion
A team of researchers at the University of East Anglia analysed unpolluted ai ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Trichloro-1, 2, 2-trifluoroethane, 1, 1, 2- Dry cleaning Halogenated solvents Chlorofluoroalkanes Chlorofluorocarbons Greenhouse gases Ozone-depleting chemical substances