Buccal Space on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The buccal space (also termed the buccinator space) is a fascial space of the head and neck (sometimes also termed
 A
A
 Sometimes the buccal space is reported to be the most commonly involved fascial space by
Sometimes the buccal space is reported to be the most commonly involved fascial space by
fascia
A fascia (; : fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; ) is a generic term for macroscopic membranous bodily structures. Fasciae are classified as superficial, visceral or deep, and further designated according to their anatomical location.
...
l tissue spaces or tissue spaces). It is a potential space
In anatomy, a potential space is a space between two adjacent structures that are normally pressed together (directly apposed). Many anatomic spaces are potential spaces, which means that they are potential rather than realized (with their realiz ...
in the cheek
The cheeks () constitute the area of the face below the eyes and between the nose and the left or right ear. ''Buccal'' means relating to the cheek. In humans, the region is innervated by the buccal nerve. The area between the inside of th ...
, and is paired on each side. The buccal space is superficial to the buccinator muscle
The bucinator () is a thin quadrilateral muscle occupying the interval between the maxilla and the Human mandible, mandible at the side of the face. It forms the anterior part of the cheek or the lateral wall of the oral cavity.Illustrated Anatom ...
and deep to the platysma muscle
The platysma muscle or platysma is a superficial muscle of the human neck that overlaps the sternocleidomastoid. It covers the anterior surface of the neck superficially. When it contracts, it produces a slight wrinkling of the neck, and a "bowst ...
and the skin. The buccal space is part of the subcutaneous space, which is continuous from head to toe.
Structure
Boundaries
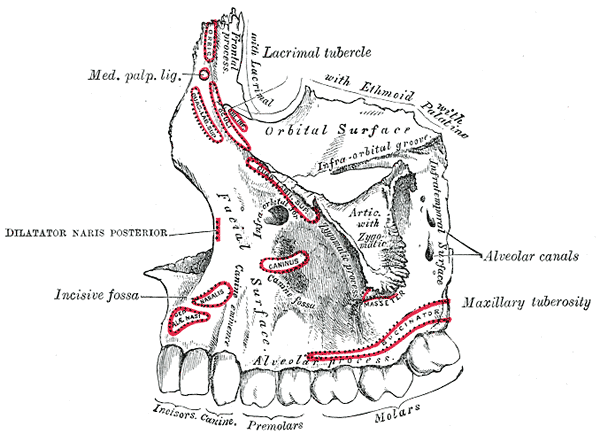
The boundaries of each buccal space are: * the angle of the mouth anteriorly, * the masseter muscle posteriorly, * the zygomatic process of the maxilla and the zygomaticus muscles superiorly, * thedepressor anguli oris muscle
The depressor anguli oris muscle (triangularis muscle) is a facial muscle. It originates from the mandible and inserts into the angle of the mouth. It is associated with frowning, as it depresses the corner of the mouth.
Structure
The depres ...
and the attachment of the deep fascia to the mandible inferiorly,
* the buccinator muscle medially (the buccal space is superficial to the buccinator),
* the platysma muscle, subcutaneous tissue and skin laterally (the space is deep to platysma).
Communications
* to thepterygomandibular space
The pterygomandibular space is a fascial space of the head and neck (sometimes also termed fascial spaces or tissue spaces). It is a potential space in the head and is paired on each side. It is located between the medial pterygoid muscle and th ...
, infratemporal space
The infratemporal space (also termed the infra-temporal space or the infra-temporal portion of the deep temporal space) is a fascial space of the head and neck (sometimes also termed fascial spaces or tissue spaces). It is a potential space in the ...
, submasseteric space or even to the lateral pharyngeal space posteriorly,
* to the infraorbital (canine) space superiorly.
Function
Contents
In health, the space contains: * the buccal fat pad, * the parotid duct ( Stensen duct), * the anterior facial artery and vein, * the transverse facial artery and vein.Clinical significance
 A
A hematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is ...
may create the buccal space, e.g. due to hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, ...
following wisdom teeth
The third molar, commonly called wisdom tooth, is the most posterior of the three molars in each quadrant of the human dentition. The age at which wisdom teeth come through ( erupt) is variable, but this generally occurs between late teens a ...
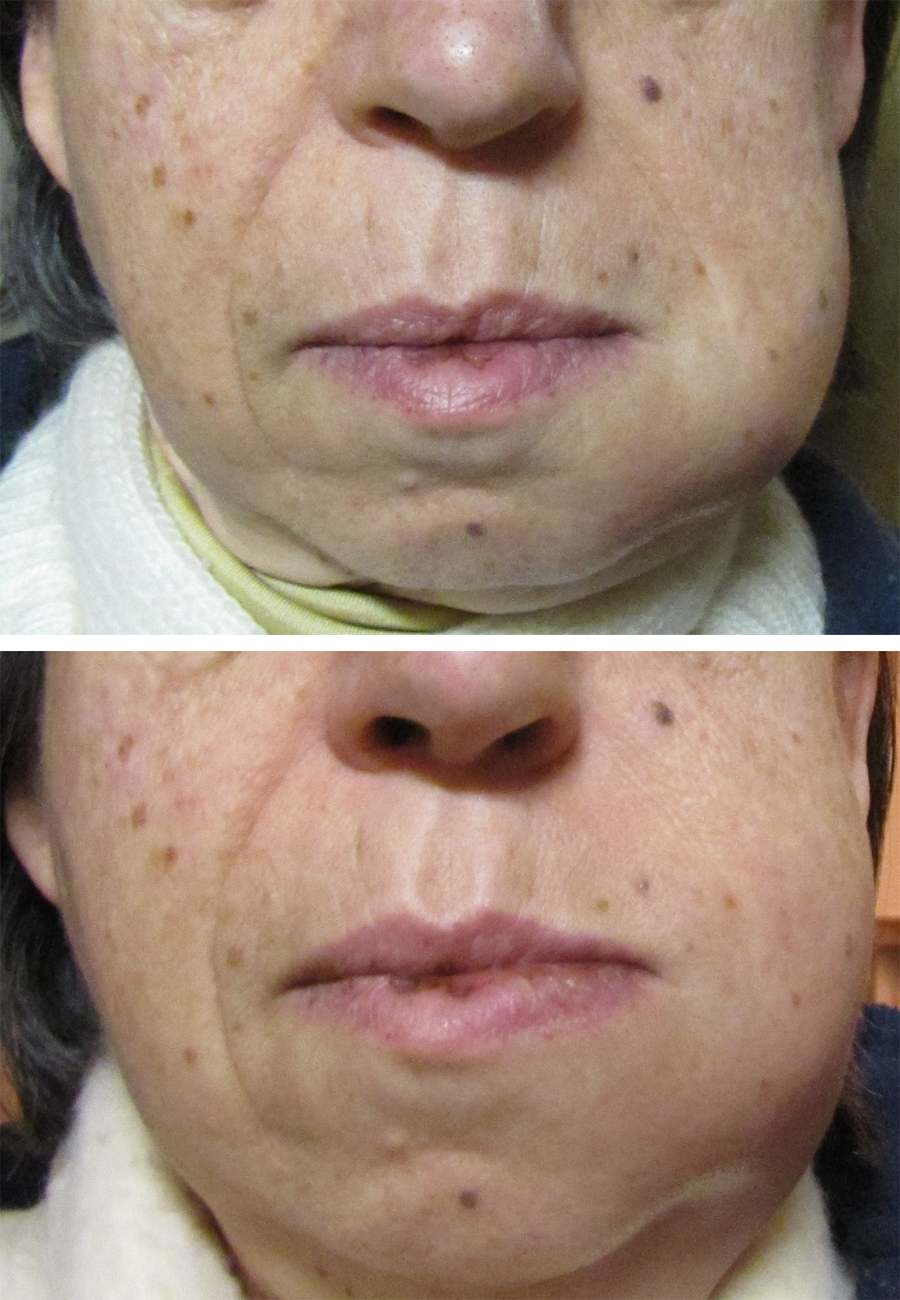
surgery. Buccal space abscesses typically cause a facial swelling over the cheek that may extend from the zygomatic arch above to the inferior border of the mandible below, and from the anterior border the masseter muscle posteriorly to the angle of the mouth anteriorly. Unless another space is also involved, the tissues around the eye are not swollen. It is usually treated by surgical incision and drainage
Incision and drainage (I&D), also known as clinical lancing, are minor surgical procedures to release pus or pressure built up under the skin, such as from an abscess, boil, or infected paranasal sinus. It is performed by treating the area wit ...
, and the incision is located inside the mouth to avoid a scar on the face. The incision are placed below the parotid papilla
The parotid duct or Stensen duct is a salivary duct. It is the route that saliva takes from the major salivary gland, the parotid gland, into the mouth.
Structure
The parotid duct is formed when several interlobular ducts, the largest ducts insid ...
to avoid damage to the duct, and forceps are used to divide buccinator and insert a surgical drain into the buccal space. The drain is kept in place for a variable period of time following the procedure.
Long standing buccal abscesses tend to spontaneously drain via a cutaneous sinus at the inferior of the space, near the inferior border of the mandible and the angle of the mouth. An untreated cutaneous sinus can cause disfiguring soft tissue fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is the development of fibrous connective tissue in response to an injury. Fibrosis can be a normal connective tissue deposition or excessive tissue deposition caused by a disease.
Repeated injuries, ch ...
, and the tract can become epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
lined.
Odontogenic infections
 Sometimes the buccal space is reported to be the most commonly involved fascial space by
Sometimes the buccal space is reported to be the most commonly involved fascial space by dental abscess
A dental abscess is a localized collection of pus associated with a tooth. The most common type of dental abscess is a periapical abscess, and the second most common is a periodontal abscess. In a periapical abscess, usually the origin is ...
es, although other sources report it is the submandibular space. Infections originating in either maxillary or mandibular teeth can spread into the buccal space, usually maxillary molars (most commonly) and premolars or mandibular premolars. Odontogenic infections which erode through the buccal cortical plate of the mandible or maxilla will either spread into the buccal vestibule (sulcus) and drain intra-orally, or into the buccal space, depending upon the level of the perforation in relation to the attachment of buccinator to the maxilla above and the mandible below (see diagrams). Frequently infection spreads in both directions as the buccinator is only a partial barrier. Infections associated with mandibular teeth with apices at a level inferior to the attachment, and maxillary teeth with apices at a level superior to the attachment are more likely to drain into the buccal space.
References
{{mouth anatomy Human head and neck Mouth Otorhinolaryngology Oral and maxillofacial surgery