Bronchiolitis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bronchiolitis is inflammation of the small airways also known as the
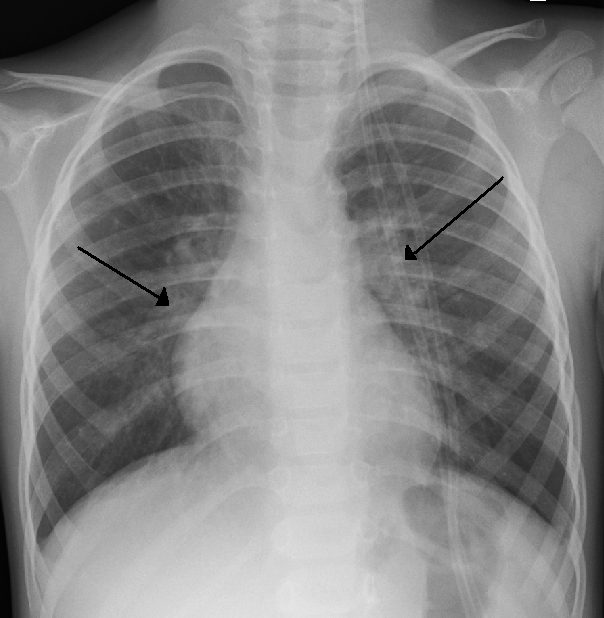 Testing for the specific viral cause can be done but has little effect on management and thus is not routinely recommended. The COVID pandemic has led to more viral testing to exclude COVID as a cause of the infection. At that point providers often also add on a flu and RSV test for completeness. RSV testing by direct immunofluorescence testing of a swab of the nose had a sensitivity of 61% and specificity of 89%, so it is not alway accurate. Identification of those who are RSV-positive can help providers recommend isolation precautions in the hospital or at home to avoid the infection spreading to others. Identification of the virus may help reduce the use of antibiotics because antibiotics are not recommended for viral illnesses such as bronchiolitis.
It is extremely rare for infants to be co-infected with a bacterial illness while having bronchiolitis. Infants with bronchiolitis between the age of two and three months have a second infection by bacteria (usually a
Testing for the specific viral cause can be done but has little effect on management and thus is not routinely recommended. The COVID pandemic has led to more viral testing to exclude COVID as a cause of the infection. At that point providers often also add on a flu and RSV test for completeness. RSV testing by direct immunofluorescence testing of a swab of the nose had a sensitivity of 61% and specificity of 89%, so it is not alway accurate. Identification of those who are RSV-positive can help providers recommend isolation precautions in the hospital or at home to avoid the infection spreading to others. Identification of the virus may help reduce the use of antibiotics because antibiotics are not recommended for viral illnesses such as bronchiolitis.
It is extremely rare for infants to be co-infected with a bacterial illness while having bronchiolitis. Infants with bronchiolitis between the age of two and three months have a second infection by bacteria (usually a
 One way to improve the
One way to improve the
 If children are having trouble maintaining their oxygen saturations on room air, clinicians may choose to give additional oxygen to children with bronchiolitis if their oxygen saturation is below 90%. Additionally, clinicians may choose to use continuous pulse oximetry in these people to monitor them.
The use of humidified, heated, high-flow
If children are having trouble maintaining their oxygen saturations on room air, clinicians may choose to give additional oxygen to children with bronchiolitis if their oxygen saturation is below 90%. Additionally, clinicians may choose to use continuous pulse oximetry in these people to monitor them.
The use of humidified, heated, high-flow
Bronchiolitis
Patient information from NHS Choices * from the
bronchioles
The bronchioles ( ) are the smaller branches of the bronchial airways in the lower respiratory tract. They include the terminal bronchioles, and finally the respiratory bronchioles that mark the start of the respiratory zone delivering air to t ...
in the lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s. Acute bronchiolitis is caused by a viral infection
A viral disease (or viral infection) occurs when an organism's body is invaded by pathogenic viruses, and infectious virus particles (virions) attach to and enter susceptible cells.
Examples include the common cold, gastroenteritis, COVID-19, t ...
, usually affecting children younger than two years of age. Symptoms may include fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, cough, runny nose or rhinorrhea
Rhinorrhea (American English), also spelled rhinorrhoea or rhinorrhœa (British English), or informally runny nose is the free discharge of a thin mucus fluid from the nose; it is an extremely common condition. It is a common symptom of allergie ...
, and wheezing
A wheeze is a clinical symptom of a continuous, coarse, whistling sound produced in the respiratory airways during breathing. For wheezes to occur, part of the respiratory tree must be narrowed or obstructed (for example narrowing of the lower ...
. More severe cases may be associated with nasal flaring, grunting, or respiratory distress. If the child has not been able to feed properly due to the illness, signs of dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild deh ...
may be present.
Chronic bronchiolitis is more common in adults and has various causes, one of which is bronchiolitis obliterans. Often when people refer to bronchiolitis, they are referring to acute bronchiolitis in children.
Acute bronchiolitis is usually the result of viral infection by respiratory syncytial virus
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), also called human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) and human orthopneumovirus, is a virus that causes infections of the respiratory tract. It is a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus. Its name is derive ...
(RSV) (59.2% of cases) or human rhinovirus (19.3% of cases). Diagnosis is generally based on symptoms. Tests such as a chest X-ray
A chest radiograph, chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film is a Projectional radiography, projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common fi ...
or viral testing are not routinely needed, but may be used to rule out other diseases.
There is no specific medicine that is used to treat bronchiolitis. Symptomatic treatment
Symptomatic treatment, supportive care, supportive therapy, or palliative treatment is any medical therapy of a disease that only affects its symptoms, not the underlying cause. It is usually aimed at reducing the signs and symptoms for the com ...
at home is generally effective and most children do not require hospitalization. This can include antipyretic
An antipyretic (, from ''anti-'' 'against' and ' 'feverish') is a substance that reduces fever. Antipyretics cause the hypothalamus to override a prostaglandin-induced increase in temperature. The body then works to lower the temperature, which r ...
s such as acetaminophen for fever and nasal suction for nasal congestion, both of which can be purchased over the counter. Occasionally, hospital admission for oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
, particularly high flow nasal cannula, or intravenous fluids
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
is needed in more severe cases of disease.
About 10% to 30% of children under the age of two years are affected by bronchiolitis at some point in time. It commonly occurs in the winter
Winter is the coldest and darkest season of the year in temperate and polar climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Dif ...
season in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
. It is the leading cause of hospitalizations in those less than one year of age in the United States. The risk of death among those who are admitted to hospital is extremely low at about 1%. Outbreaks of the condition were first described in the 1940s.
Signs and symptoms
Bronchiolitis typically presents in children under two years old and is characterized by symptoms of a respiratory illness.Signs of the disease include: * fever *rhinorrhea
Rhinorrhea (American English), also spelled rhinorrhoea or rhinorrhœa (British English), or informally runny nose is the free discharge of a thin mucus fluid from the nose; it is an extremely common condition. It is a common symptom of allergie ...
* cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and Microorganism, microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex fol ...
* wheeze
* mild tachypnea
Tachypnea, also spelt tachypnoea, is a respiratory rate greater than normal, resulting in abnormally rapid and shallow breathing.
In adult humans at rest, any respiratory rate of 1220 per minute is considered clinically normal, with tachypnea b ...
or increased breathing
Some signs of severe disease include:
* increased work of breathing (such as use of accessory muscles of respiration, rib & sternal retraction, tracheal tug)
* severe chest wall recession ( Hoover's sign)
* presence of nasal flaring and/or grunting
* severe tachypnea or increased breathing
* hypoxia (low oxygen levels)
* cyanosis
Cyanosis is the change of Tissue (biology), tissue color to a bluish-purple hue, as a result of decrease in the amount of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Cyanosis is apparent usually in the Tissue (bi ...
(bluish skin)
* lethargy and decreased activity
* poor feeding (less than half of usual fluid intake in preceding 24 hours)
These symptoms can develop over one to three days. Crackles
Crackles are the clicking, rattling, or crackling noises that may be made by one or both lungs of a human or animal with a respiratory disease during inhalation, and occasionally during exhalation. They are usually heard only with a stethosco ...
or wheeze are typical findings on listening to the chest with a stethoscope. Wheezes can occasionally be heard without a stethoscope. The child may also experience apnea
Apnea (also spelled apnoea in British English) is the temporary cessation of breathing. During apnea, there is no movement of the muscles of inhalation, and the volume of the lungs initially remains unchanged. Depending on how blocked the ...
, or brief pauses in breathing, but this can occur due to many conditions that are not just bronchiolitis. After the acute illness, it is common for the airways to remain sensitive for several weeks, leading to recurrent cough and wheeze.
Causes
Bronchiolitis is most commonly caused byrespiratory syncytial virus
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), also called human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) and human orthopneumovirus, is a virus that causes infections of the respiratory tract. It is a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus. Its name is derive ...
(RSV, also known as human pneumovirus). Other agents that cause this illness include, but are not limited to, human metapneumovirus
''Metapneumovirus'' is a genus of viruses in the family ''Pneumoviridae''.
Taxonomy
The genus contains the following two species, listed by scientific name and followed by the exemplar virus of the species:
* ''Metapneumovirus avis'', Avian metap ...
, influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
, parainfluenza, coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the comm ...
, adenovirus
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from t ...
, rhinovirus
The rhinovirus (from the "nose", , romanized: "of the nose", and the ) is a Positive-sense single stranded RNA virus, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus belonging to the genus ''Enterovirus'' in the family ''Picornaviridae''. Rhinoviru ...
and mycoplasma
''Mycoplasma'' is a genus of bacteria that, like the other members of the class ''Mollicutes'', lack a cell wall, and its peptidoglycan, around their cell membrane. The absence of peptidoglycan makes them naturally resistant to antibiotics ...
.
Risk factors
Children are at an increased risk for progression to severe respiratory disease if they have any of the following additional risk factors: * Preterm infant ( gestational age less than 37 weeks) * Younger age at onset of illness (less than 3 months of age) *Congenital heart disease
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly, congenital cardiovascular malformation, and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital he ...
* Immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromise, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that aff ...
* Chronic lung disease
* Neurological disorders
* Tobacco smoke exposure
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is typically made by a provider through clinical history and physical exam.Chest X-ray
A chest radiograph, chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film is a Projectional radiography, projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common fi ...
is sometimes useful to exclude bacterial pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
, but not indicated in routine cases. Chest x-ray may also be useful in people with impending respiratory failure. Additional testing such as blood cultures, complete blood count, and electrolyte analyses are not recommended for routine use although may be useful in children with multiple comorbidities or signs of sepsis or pneumonia. Electrolyte analyses may be performed if there is concern for dehydration.
urinary tract infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects a part of the urinary tract. Lower urinary tract infections may involve the bladder (cystitis) or urethra (urethritis) while upper urinary tract infections affect the kidney (pyel ...
) less than 6% of the time. When further evaluated with a urinalysis, infants with bronchiolitis had an accompanying UTI 0.8% of the time.
Differential diagnosis
There are many childhood illnesses that can present with respiratory symptoms, particularly persistent cough, runny nose, and wheezing. Bronchiolitis may be differentiated from some of these by the characteristic pattern of preceding febrile upper respiratory tract symptoms lasting for 1 to 3 days with associated persistent cough, increased work of breathing, and wheezing. However, some infants may present without fever (30% of cases) or may present withapnea
Apnea (also spelled apnoea in British English) is the temporary cessation of breathing. During apnea, there is no movement of the muscles of inhalation, and the volume of the lungs initially remains unchanged. Depending on how blocked the ...
without other signs or with poor weight gain prior to onset of symptoms. In such cases, additional laboratory testing and radiographic imaging may be useful. The following are some other diagnoses to consider in an infant presenting with signs of bronchiolitis:
* Upper Respiratory Infection
* Asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
and reactive airway disease
* Bacterial pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia is a type of pneumonia caused by bacterial infection.
Types
Gram-positive
'' Streptococcus pneumoniae'' () is the most common bacterial cause of pneumonia in all age groups except newborn infants. ''Streptococcus pneumoniae ...
* Whooping cough
Whooping cough ( or ), also known as pertussis or the 100-day cough, is a highly contagious, Vaccine-preventable diseases, vaccine-preventable Pathogenic bacteria, bacterial disease. Initial symptoms are usually similar to those of the common c ...
* Foreign body aspiration
* Congenital heart disease
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly, congenital cardiovascular malformation, and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital he ...
* Allergic reaction
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include Allergic rhinitis, hay fever, Food allergy, food al ...
* Vascular ring
* Heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to Cardiac cycle, fill with and pump blood.
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF ...
* Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive manner that impairs the normal clearance of Sputum, mucus from the lungs, which facilitates the colonization and infection of the lungs by bacteria, notably ''Staphy ...
* Chronic pulmonary disease
Prevention
Prevention of bronchiolitis relies strongly on measures to reduce the spread of the viruses that cause respiratory infections (that is, handwashing, and avoiding exposure to those symptomatic with respiratory infections). Guidelines are mixed on the use of gloves, aprons, orpersonal protective equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is protective clothing, helmets, goggles, or other garments or equipment designed to protect the wearer's body from injury or infection. The hazards addressed by protective equipment include physical, elect ...
.
 One way to improve the
One way to improve the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
is to feed the infant with breast milk, especially during the first month of life. Respiratory infections were shown to be significantly less common among breastfed infants and fully breastfed RSV-positive hospitalized infants had shorter hospital stays than non or partially breastfed infants. Guidelines recommend exclusive breastfeeding for infants for the first 6 months of life to avoid infection with bronchiolitis.
The US Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
(FDA) has currently approved two RSV vaccines for adults ages 60 and older, Arexvy (GSK plc
GSK plc (an acronym from its former name GlaxoSmithKline plc) is a British Multinational corporation, multinational Pharmaceutics, pharmaceutical and biotechnology company with headquarters in London. It was established in 2000 by a Mergers an ...
) and Abrysvo (Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered at The Spiral (New York City), The Spiral in Manhattan, New York City. Founded in 184 ...
). Abrysvo is also approved for "immunization
Immunization, or immunisation, is the process by which an individual's immune system becomes fortified against an infectious agent (known as the antigen, immunogen). When this system is exposed to molecules that are foreign to the body, called ' ...
of pregnant individuals at 32 through 36 weeks gestational age for the prevention of lower respiratory tract disease (LRTD) and severe LRTD caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in infants from birth through 6 months of age." It is unclear how effective these vaccines will be in preventing infection with bronchiolitis since they are new, although the FDA has approved them due to the clear benefit that they have shown in clinical trials.
Nirsevimab, a monoclonal antibody
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.
Monoclonal antibodie ...
against RSV, is approved by the FDA for all children younger than 8 months in their first RSV season. Additionally, children aged 8 to 19 months who are at increased risk may be recommended to receive Nirsevimab as they enter their second RSV season if they have increased risk factors for infection with RSV.
A second monoclonal antibody, Palivizumab, can be administered to prevent bronchiolitis to infants less than one year of age that were born prematurely and that have underlying heart disease or chronic lung disease of prematurity. Otherwise healthy premature infants that were born after a gestational age of 29 weeks should not be administered Palivizumab, as the harms outweigh the benefits.
Tobacco smoke exposure has been shown to increase both the rates of lower respiratory disease in infants, as well as the risk and severity of bronchiolitis. Tobacco smoke lingers in the environment for prolonged periods and on clothing even when smoking outside the home. Guidelines recommend that parents be fully educated on the risks of tobacco smoke exposure on children with bronchiolitis.
Management
Treatment of bronchiolitis is usually focused on the hydration and symptoms instead of the infection itself since the infection will run its course. Complications of bronchiolitis are typically from the symptoms themselves. Without active treatment, cases resolved in approximately eight to fifteen days. Children with severe symptoms, especially poor feeding or dehydration, may be considered for hospital admission.Oxygen saturation
Oxygen saturation (symbol SO2) is a relative measure of the concentration of oxygen that is Dissolution (chemistry), dissolved or carried in a given medium as a proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in that medium at the g ...
under 90%-92% as measured with pulse oximetry
Pulse oximetry is a noninvasive method for monitoring blood oxygen saturation. Peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) readings are typically within 2% accuracy (within 4% accuracy in 95% of cases) of the more accurate (and invasive) reading of art ...
is also frequently used as an indicator of need for hospitalization. High-risk infants, apnea
Apnea (also spelled apnoea in British English) is the temporary cessation of breathing. During apnea, there is no movement of the muscles of inhalation, and the volume of the lungs initially remains unchanged. Depending on how blocked the ...
, cyanosis
Cyanosis is the change of Tissue (biology), tissue color to a bluish-purple hue, as a result of decrease in the amount of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Cyanosis is apparent usually in the Tissue (bi ...
, malnutrition, and diagnostic uncertainty are additional indications for hospitalization.
Most guidelines recommend sufficient fluids and nutritional support for affected children along with frequent nasal suctioning. Measures for which the recommendations were mixed include nebulized hypertonic saline, nebulized epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
, and chest physiotherapy. Treatments which the evidence does not support include salbutamol
Salbutamol, also known as albuterol and sold under the brand name Ventolin among others, is a medication that opens up the medium and large airways in the lungs. It is a short-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist that causes relaxation of ...
, steroids
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter mem ...
, antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
, antivirals
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials ...
, and heliox.
Outpatient Management
Nutrition
Maintaining hydration is an important part of management of bronchiolitis. Infants with mild pulmonary symptoms may require only observation if feeding is unaffected. However, oral intake may be affected by nasal secretions and increased work of breathing. Poor feeding or dehydration, defined as less than 50% of usual intake, is often cited as an indication for hospital admission.Breathing/ Oxygen
Children must be closely monitored for changes in ability to breathe. Nasal suction can be used at home in order to decrease nasal congestion and open the airways. Inadequate oxygen supply to the tissue is one of the main concerns during severe bronchiolitis andoxygen saturation
Oxygen saturation (symbol SO2) is a relative measure of the concentration of oxygen that is Dissolution (chemistry), dissolved or carried in a given medium as a proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in that medium at the g ...
is often closely associated with both the need for hospitalization and continued length of hospital stay in children with bronchiolitis. However, oxygen saturation is a poor predictor of respiratory distress. Accuracy of pulse oximetry
Pulse oximetry is a noninvasive method for monitoring blood oxygen saturation. Peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) readings are typically within 2% accuracy (within 4% accuracy in 95% of cases) of the more accurate (and invasive) reading of art ...
is limited in the 76% to 90% range and there is weak correlation between oxygen saturation and respiratory distress as brief hypoxemia
Hypoxemia (also spelled hypoxaemia) is an abnormally low level of oxygen in the blood. More specifically, it is oxygen deficiency in arterial blood. Hypoxemia is usually caused by pulmonary disease. Sometimes the concentration of oxygen in the ...
is common in healthy infants. Additionally, pulse oximetry is associated with frequent false alarms and parental stress and fatigue.
Nasal Suction
Infants are nose breathers and bronchiolitis causes congestion of the airways with secretions that can make it difficult to feed and breathe. Nasal suctioning is a very common supportive measure used at home to decrease nasal congestion. It has not been extensively studied in the literature, but can be used to decrease secretions in the nose and has been proven mildly effective in one experimental trial. A nasal suction bulb can be purchased over the counter and directions for its use can be explained by a provider or on the back of the box. Clinical guidelines state that routine suctioning is safe and can provide relief for infants which allows them to eat and sleep more comfortably. In those same clinical guidelines, it is stated that deep suctioning, which is often performed in the hospital is not recommended as it may lead to increased length of hospital stay in children with bronchiolitis.Inpatient/ Hospital Management
Nutrition/ Fluid Therapy
When children are experiencing poor feeding or dehydration, the child may be admitted to the hospital. Approximately 50% of infants who are hospitalized due to bronchiolitis require fluid therapy. There are two main approaches to fluid therapy:intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
(IV) fluid therapy and enteral tube fluid therapy ( nasogastric or orogastric). Both approaches to fluid therapy are associated with a similar length of hospital stay. Enteral tube fluid therapy may reduce the risk of local complications, but the evidence for or against each approach is not clear. The risk of health care caused hyponatremia
Hyponatremia or hyponatraemia is a low concentration of sodium in the Serum (blood), blood. It is generally defined as a sodium concentration of less than 135 mmol/L (135 mEq/L), with severe hyponatremia being below 120 mEq/L. Symp ...
and fluid retention are minimal with the use of isotonic fluids such as normal saline
Saline (also known as saline solution) is a mixture of sodium chloride (salt) and water. It has a number of uses in medicine including cleaning wounds, removal and storage of contact lenses, and help with dry eyes. By intravenous therapy, inje ...
.
Oxygen
 If children are having trouble maintaining their oxygen saturations on room air, clinicians may choose to give additional oxygen to children with bronchiolitis if their oxygen saturation is below 90%. Additionally, clinicians may choose to use continuous pulse oximetry in these people to monitor them.
The use of humidified, heated, high-flow
If children are having trouble maintaining their oxygen saturations on room air, clinicians may choose to give additional oxygen to children with bronchiolitis if their oxygen saturation is below 90%. Additionally, clinicians may choose to use continuous pulse oximetry in these people to monitor them.
The use of humidified, heated, high-flow nasal cannula
The nasal cannula (NC) is a device used to deliver supplemental oxygen or increased airflow to a patient or person in need of respiratory help. This device consists of a lightweight tube which on one end splits into two prongs which are place ...
may be a safe initial therapy to decrease work of breathing and need for intubation
Intubation (sometimes entubation) is a medical procedure involving the insertion of a tube into the body. Most commonly, intubation refers to tracheal intubation, a procedure during which an endotracheal tube is inserted into the trachea to supp ...
. High flow nasal cannula may still be used in severe cases prior to intubation. The use of CPAP has very limited evidence for improving breathing (a decreased respiratory rate) and does not reduce the need for mechanical ventilation.
Blood gas testing is not routinely recommended for people hospitalized with the disease. However, people with severe worsening respiratory distress or impending respiratory failure may be considered for capillary blood gas testing.
Contradicting Evidence
Hypertonic saline
Guidelines recommend against the use of nebulized hypertonic saline in the emergency department for children with bronchiolitis but it may be given to children who are hospitalized. Nebulized hypertonic saline (3%) has limited evidence of benefit and previous studies lack consistency and standardization. It does not reduce the rate of hospitalization when therapy is given in the emergency department or outpatient setting. A 2017 review found tentative evidence that it reduces the risk of hospitalization, duration of hospital stay, and improved the severity of symptoms. Side effects were mild and resolved spontaneously.Bronchodilators
Guidelines recommend against the use of bronchodilators in children with bronchiolitis as evidence does not support a change in outcomes with such use. Additionally, there are adverse effects to the use of bronchodilators in children such astachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal ...
and tremor
A tremor is an involuntary, somewhat rhythmic muscle contraction and relaxation involving neural oscillations, oscillations or twitching movements of one or more body parts. It is the most common of all involuntary movements and can affect the h ...
s, as well as adding increased cost to the medical visit.
Several studies have shown that bronchodilation with β-adrenergic agents such as salbutamol
Salbutamol, also known as albuterol and sold under the brand name Ventolin among others, is a medication that opens up the medium and large airways in the lungs. It is a short-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist that causes relaxation of ...
may improve symptoms briefly but do not affect the overall course of the illness or reduce the need for hospitalization.
However, there are conflicting recommendations about the use of a trial of a bronchodilator, especially in those with history of previous wheezing. Bronchiolitis-associated wheezing is likely not effectively alleviated by bronchodilators anyway as it is caused by airway obstruction and plugging of the small airway diameters by luminal debris, not bronchospasm as in asthma-associated wheezing that bronchodilators usually treat well. If a clinician is concerned that reactive airway disease or asthma may be a component of the illness, a bronchodilator may be administered.
Anticholinergic
Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter at synapses in the central nervous system, central and peripheral nervous system.
These agents inhibit the parasympatheti ...
inhalers, such as ipratropium bromide, have a modest short-term effect at best and are not recommended for treatment.
Epinephrine
The current state of evidence suggests that nebulizedepinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
is not indicated for children with bronchiolitis except as a trial of rescue therapy for severe cases.
Epinephrine is an α and β adrenergic agonist that is used to treat other upper respiratory tract illnesses, such as croup
Croup ( ), also known as croupy cough, is a type of respiratory infection that is usually caused by a virus. The infection leads to swelling inside the trachea, which interferes with normal breathing and produces the classic symptoms of "bar ...
, as a nebulized solution. Current guidelines do not support the outpatient use of epinephrine in bronchiolitis given the lack of substantial sustained benefit.
A 2017 review found inhaled epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
with corticosteroids did not change the need for hospitalization or the time spent in hospital. Other studies suggest a synergistic effect of epinephrine with corticosteroids but have not consistently demonstrated benefits in clinical trials. Guidelines recommend against its use currently.
Non-effective Treatments
* Ribavirin is an antiviral drug which does not appear to be effective for bronchiolitis. *Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s are often given in case of a bacterial infection complicating bronchiolitis, but have no effect on the underlying viral infection and their benefit is not clear. The risks of bronchiolitis with a concomitant serious bacterial infection among hospitalized febrile infants is minimal and work-up and antibiotics are not justified. Azithromycin
Azithromycin, sold under the brand names Zithromax (in oral form) and Azasite (as an eye drop), is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of several bacterial infections. This includes otitis media, middle ear infections, strep throa ...
adjuvant therapy
Adjuvant therapy, also known as adjunct therapy, adjuvant care, or augmentation therapy, is a therapy that is given in addition to the primary or initial therapy to maximize its effectiveness. The surgeries and complex treatment regimens used in ...
may reduce the duration of wheezing and coughing in children with bronchiolitis but has not effect on length of hospital stay or duration of oxygen therapy.
* Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invol ...
, although useful in other respiratory disease such as asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
and croup
Croup ( ), also known as croupy cough, is a type of respiratory infection that is usually caused by a virus. The infection leads to swelling inside the trachea, which interferes with normal breathing and produces the classic symptoms of "bar ...
, have no proven benefit in bronchiolitis treatment and are not advised. Additionally, corticosteroid therapy in children with bronchiolitis may prolong viral shedding and transmissibility. The overall safety of corticosteroids is questionable.
* Leukotriene inhibitors, such as montelukast
Montelukast, sold under the brand name Singulair among others, is a medication used in the maintenance treatment of asthma. It is generally less preferred for this use than inhaled corticosteroids. It is not useful for acute asthma attacks. ...
, have not been found to be beneficial and may increase adverse effects.
* Immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses, includin ...
s are of unclear benefit.
Experimental Trials
Currently other medications do not yet have evidence to support their use, although they have been studied for use in bronchiolitis. Experimental trials with novel antiviral medications in adults are promising but it remains unclear if the same benefit will be present. *Surfactant
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension or interfacial tension between two liquids, a liquid and a gas, or a liquid and a solid. The word ''surfactant'' is a Blend word, blend of "surface-active agent",
coined in ...
had favorable effects for severely critical infants on duration of mechanical ventilation and ICU stay however studies were few and small.
* Chest physiotherapy, such as vibration or percussion, to promote airway clearance may slightly reduce duration of oxygen therapy but there is a lack of evidence that demonstrates any other benefits. People with difficulty clearing secretions due to underlying disorders such as spinal muscle atrophy or severe tracheomalacia may be considered for chest physiotherapy.
* Heliox, a mixture of oxygen and the inert gas helium, may be beneficial in infants with severe acute RSV bronchiolitis who require CPAP but overall evidence is lacking.
* DNAse
Deoxyribonuclease (DNase, for short) refers to a group of glycoprotein endonucleases which are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolytic cleavage of phosphodiester linkages in the DNA backbone, thus degrading DNA. The role of the DNase enzyme in cells ...
has not been found to be effective but might play a role in severe bronchiolitis complicated by atelectasis
Atelectasis is the partial collapse or closure of a lung resulting in reduced or absence in gas exchange. It is usually unilateral, affecting part or all of one lung. It is a condition where the Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli are deflated down to l ...
.
* There are no systematic reviews or controlled trials on the effectiveness of nasal decongestants, such as xylometazoline, for the treatment of bronchiolitits.
* Overall evidence is insufficient to support the use of alternative medicine. There is tentative evidence for Chinese herbal medicine, vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
, N-acetylcysteine, and magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
but this is insufficient to recommend their use.
Epidemiology
Bronchiolitis typically affects infants and children younger than two years, principally during the autumn and winter. It is the leading cause of hospital admission for respiratory disease among infants in the United States and accounts for one out of every 13 primary care visits. Bronchiolitis accounts for 3% of emergency department visits for children under 2 years old. Bronchiolitis is the most frequent lower respiratory tract infection and hospitalization in infants worldwide.COVID-19 Pandemic
TheCOVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
pandemic rapidly changed the transmission and presentation starting in late 2019. During the pandemic, there was a sharp decrease in cases of bronchiolitis and other respiratory illness, which is likely due to social distancing
In public health, social distancing, also called physical distancing, (NB. Regula Venske is president of the PEN Centre Germany.) is a set of non-pharmaceutical interventions or measures intended to prevent the spread of a contagious dise ...
and other precautions. After social distancing and other precautions were lifted, there was increases in the cases of RSV and bronchiolitis worldwide to varying degrees. There is unclear evidence on how COVID-19 will affect bronchiolitis moving forward. Recent evidence suggests that bronchiolitis still poses a large disease burden to both primary care providers and emergency departments.
References
External links
Bronchiolitis
Patient information from NHS Choices * from the
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network
Healthcare Improvement Scotland (HIS) () is the national healthcare improvement organisation for Scotland. It is a Scottish public body, public body which is part of the Scottish National Health Service, created in April 2011.
History
NHS Quali ...
*
{{Common Cold
Animal viral diseases
Inflammations
Pediatrics
Acute lower respiratory infections
Coronavirus-associated diseases
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate